Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Effects of immunological processes and mild ambient atmosphere alterations on the brain in health and disease
- Pages: 179-181
- First Published: 11 September 2024
REVIEW
Microglial senescence in neurodegeneration: Insights, implications, and therapeutic opportunities
- Pages: 182-195
- First Published: 15 September 2024
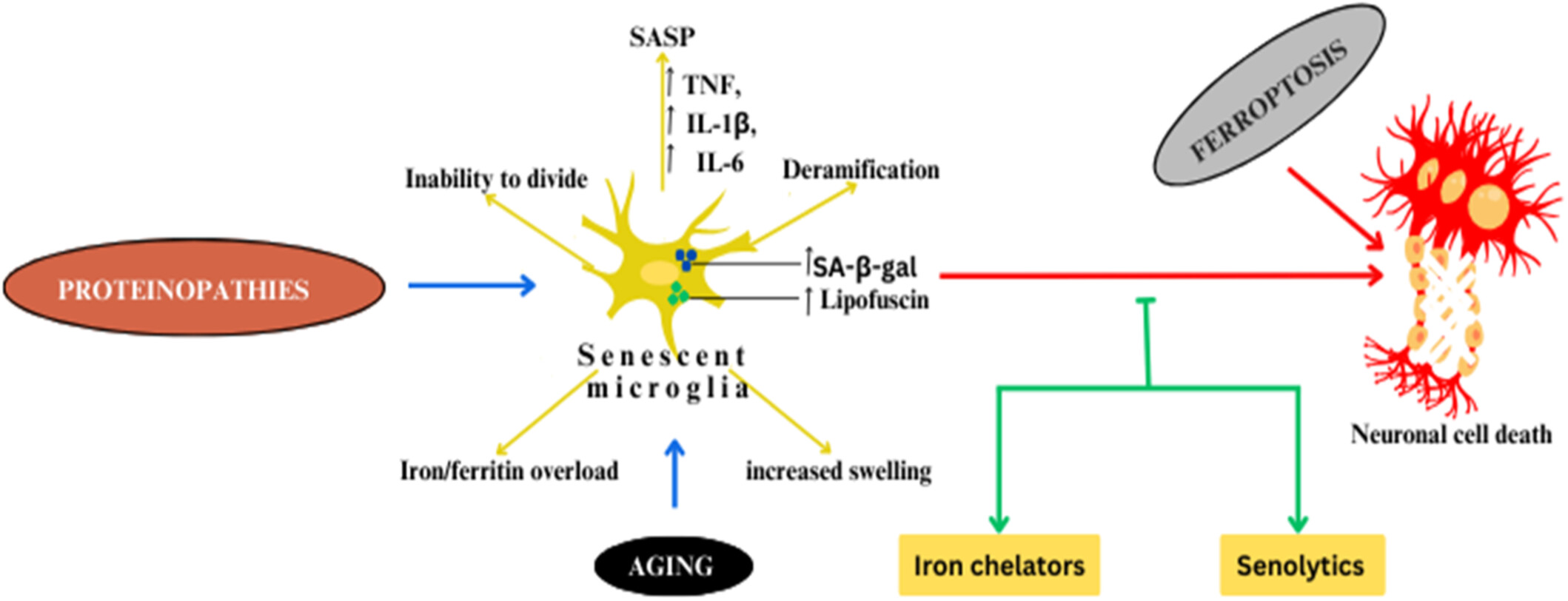
Microglial senescence plays a critical role in increasing susceptibility to neuronal degeneration. This study highlights that aging and the proteinopathies characteristic of various neurodegenerative diseases contribute to the induction of microglia senescence. Therapeutic strategies involving iron chelators and senolytics may hold promise for managing age-related neurodegenerative diseases. IL, interleukin; SA-β-gal, senescence-associated β-galactosidase; SASP, senescence-associated secretory phenotype; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on the effect of hyperglycemia at admission on clinical outcomes after endovascular thrombectomy
- Pages: 196-202
- First Published: 04 September 2024
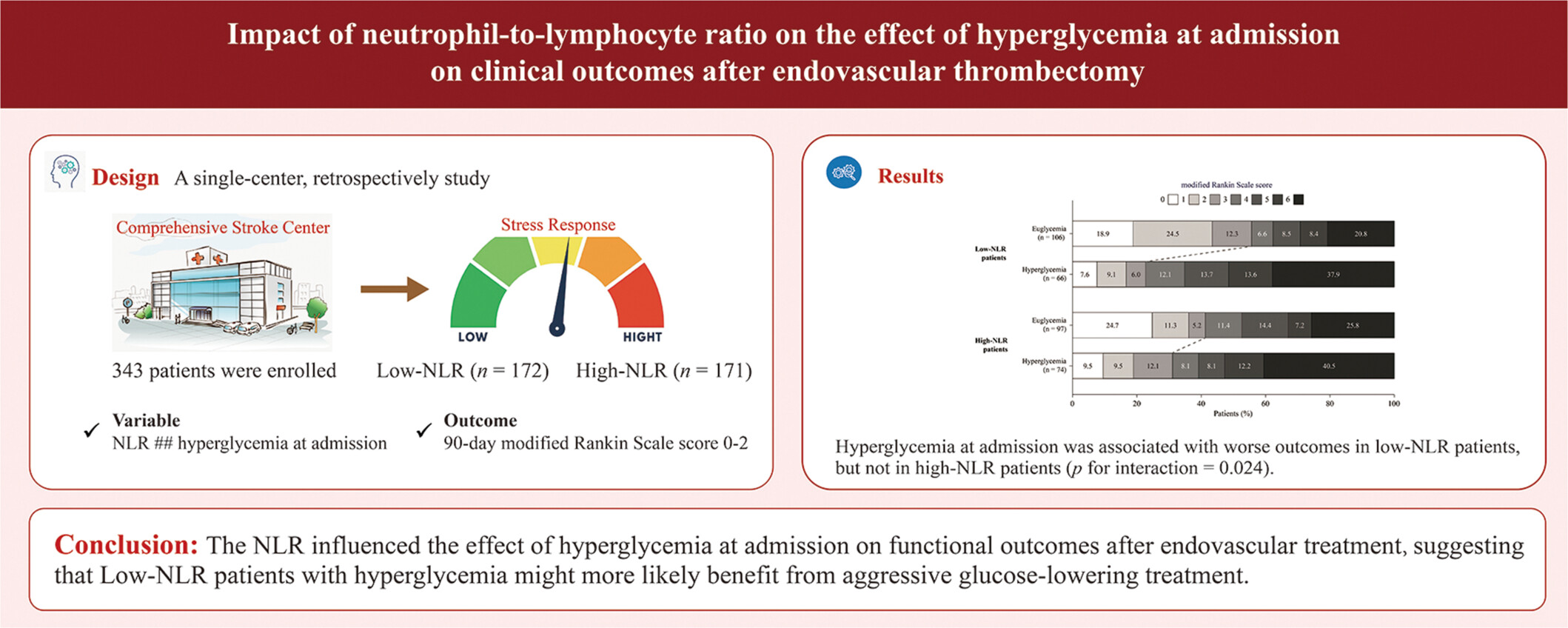
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte (NLR) ratio influenced the effect of hyperglycemia at admission on functional outcome in patients undergoing endovascular thrombectomy. This result sheds light on blood glucose management in the thrombectomy setting, that is, hyperglycemic patients with low NLR might more likely benefit from aggressive glucose-lowering treatment.
Interleukin-6 induces cognitive impairment via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in mice with chronic kidney disease
- Pages: 203-215
- First Published: 09 September 2024
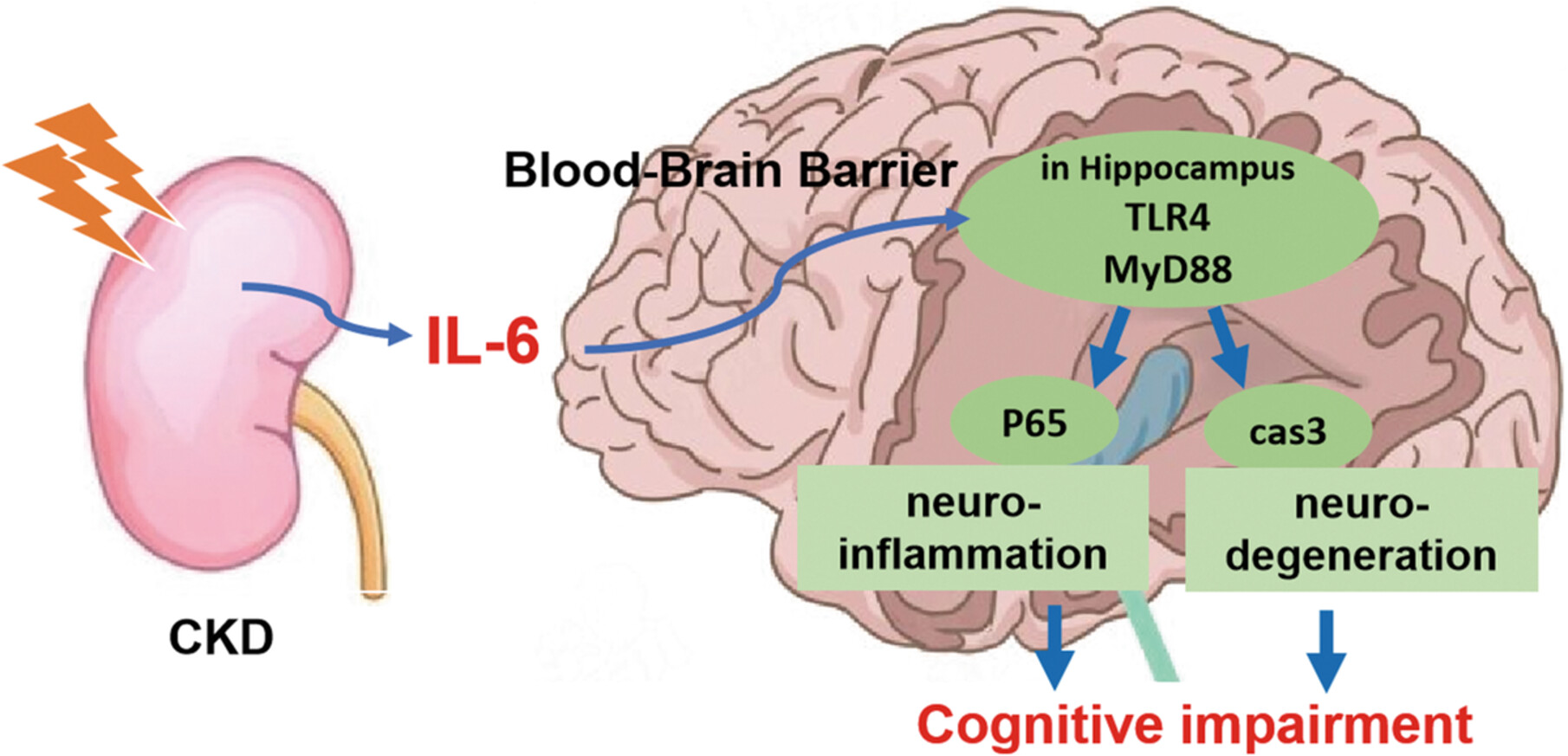
Diagrammatic representation of the role of IL-6/TLR4 between CKD and cognitive impairment. CKD patients suffer fromimpaired renal function, accompanied by inflammatory reactions in the body, and simultaneous increased levels of inflammatory factors in the brain, especially IL-6. This triggers overactivation of the TLR4/MyD88 pathway, increasing the expression of p65 and CL-Casp3, and thus promoting neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration leading to cognitive dysfunction. CKD, chronic kidney disease; IL, interleukin; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4.
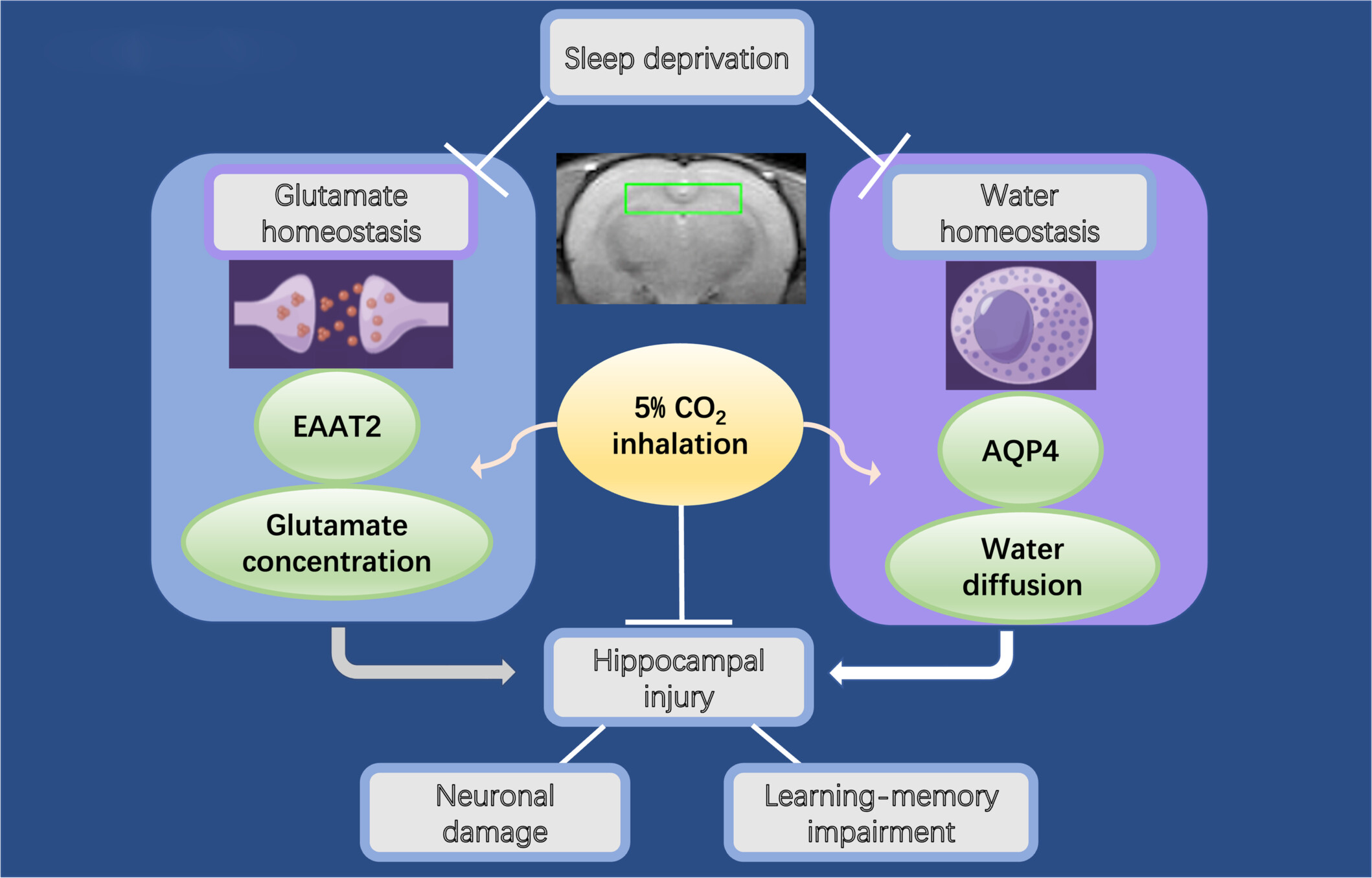
Five percent CO2 inhalation alleviates hippocampal glutamate and water homeostasis disturbance, neuronal damage, and learning-memory impairment in sleep-deprived rats
- Pages: 216-227
- First Published: 30 August 2024
RAPID REPORT
Tolerability and first hints for potential efficacy of motor-cognitive training under inspiratory hypoxia in health and neuropsychiatric disorders: A translational viewpoint
- Pages: 228-242
- First Published: 04 June 2024