Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Comprehensive diagnostic model of metastasis in prostate cancer: Individual and combined bioscore model of ADC value, Gleason score, and PSA
- Pages: 140-147
- First Published: 29 June 2024
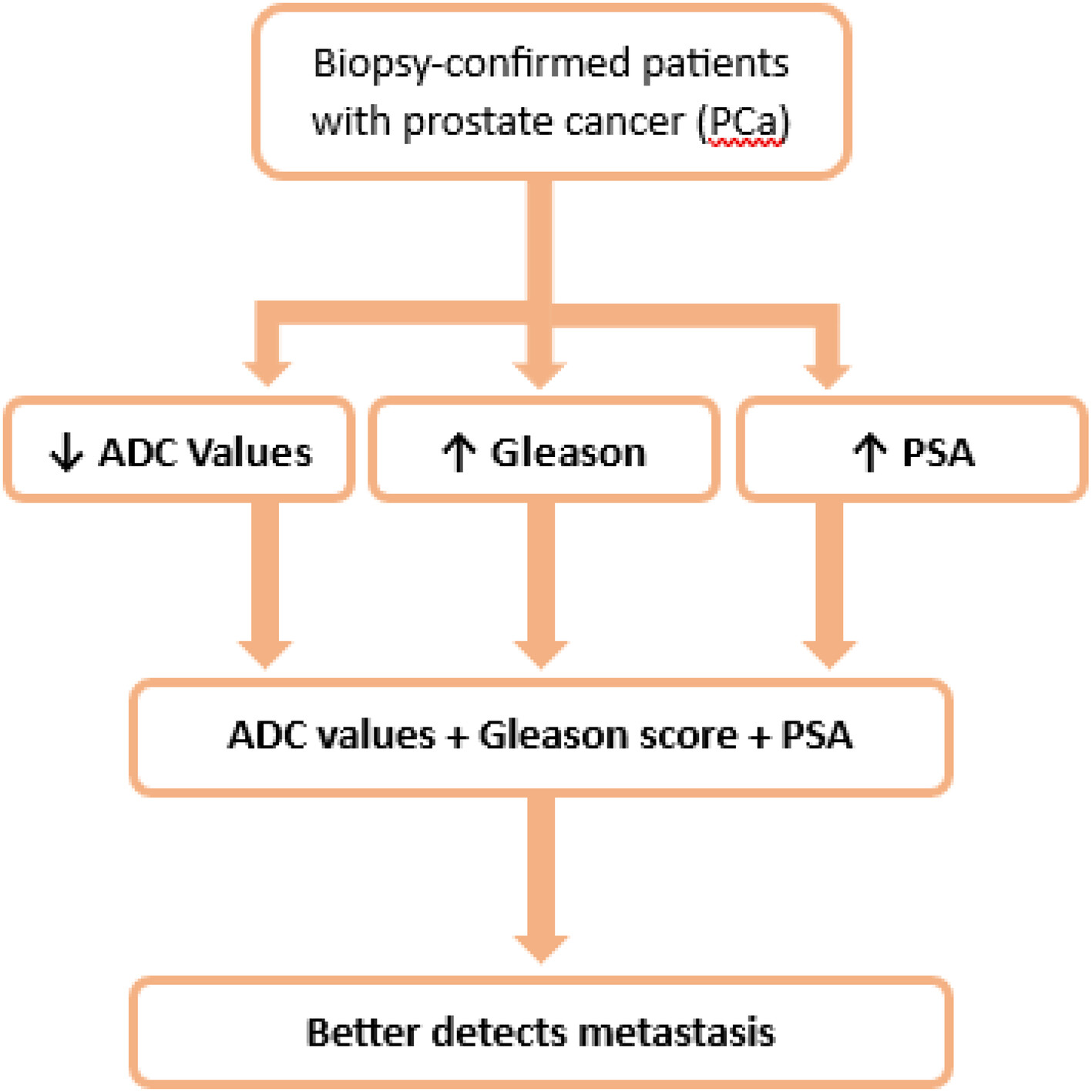
This study evaluates the diagnostic efficacy of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), Gleason score, and PSA for prostate cancer (PCa) metastasis in 120 patients. Results indicate ADC as a significant individual marker, with combined ADC, PSA, and Gleason score significantly improving metastasis detection. This suggests potential for improved diagnosis and treatment strategies in PCa management.
Identification and verification of KEAP1-related genes and targets regulated by potential ingredients in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer
- Pages: 148-166
- First Published: 16 July 2024
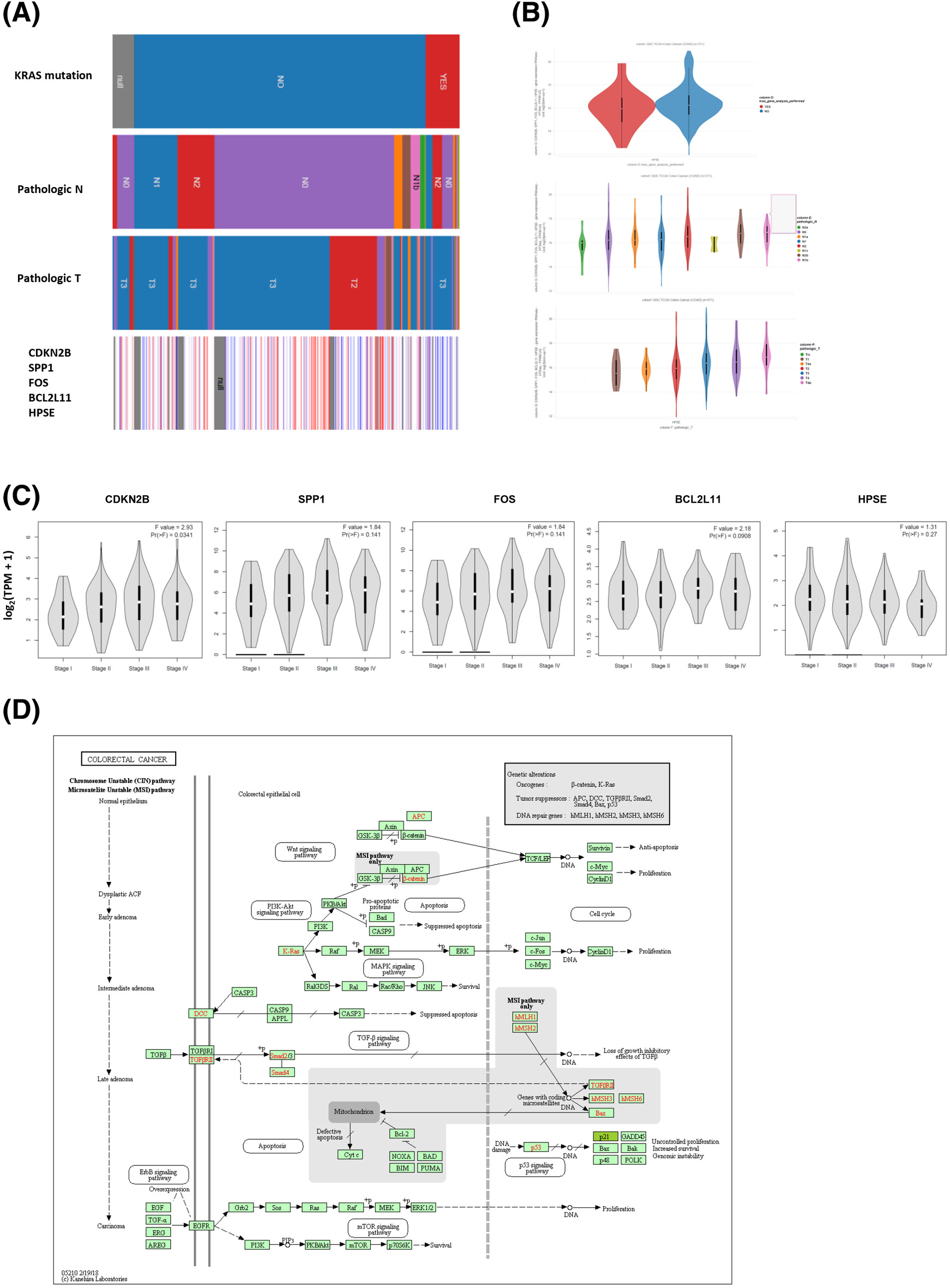
This study aimed to explore and identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the crosstalk among KEAP1 oncogenic signatures of KRAS mutation that were linked with development, metastasis, and poor prognosis in CRC. We further investigated the correlations between the clinical characteristics and expressions of prognostic genes among the KRAS and KEAP1-related key hub genes in CRC, which as predicted targets and demonstrated the anticancer activities of potential drugs in HERB database. We identified the roles of KEAP1-related oncogenes of KRAS mutant subtypes in CRC, which may provide new targets for CRC treatments by performing comprehensive bioinformatic analysis. The KEAP1-related prognostic genes could effectively predict the OS of KRAS mutant CRC patients. Also, key genes (such as FOS and SPP1) were identified as potential biomarkers for predicting the prognosis of CRC. Therefore, cyclopamine, identified as a potential anti-CRC agent, may contribute to the clinical treatments of CRC. Furthermore, this study proved the importance of KEAP1-related signaling pathway in CRC, which may be potential drug targets in KRAS mutant CRC.
The CT and pathological features of intestinal inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
- Pages: 167-171
- First Published: 15 September 2024
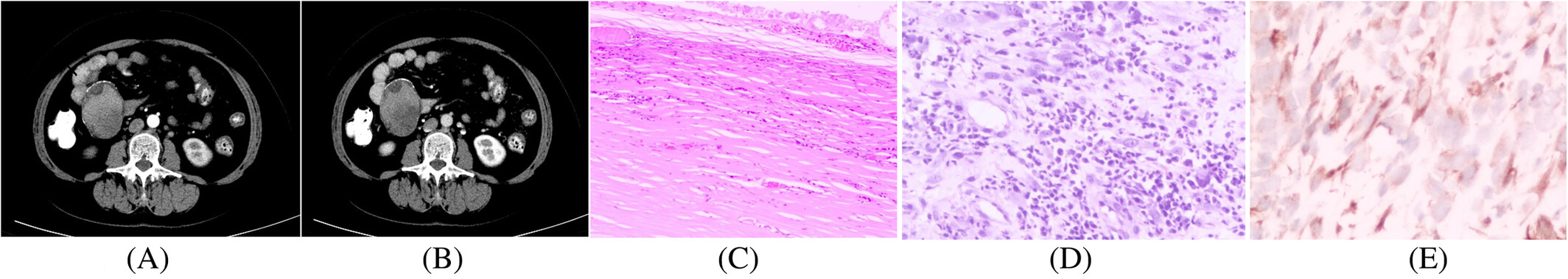
CT imaging and pathological findings of typical case 1 (patient, female, 56 years old, IMT). A: CT enhanced arterial phase; B: venous stage; C: Postoperative pathological map (H&E, ×100); D: Postoperative pathology (H&E, ×200); E: Immunohistochemistry (×400). CT showed the intestinal tube. Exocystic solid mass with flaky low-density cystic necrosis and marginal linear calcification. The enhanced scan was moderately progressive. The postoperative pathology showed that the tumor cells were fusiform, with abundant cytoplasm, eosinophilic, fasciculate distribution, a small number of giant tumor cells, mesenchymal myxoid transformation, and more lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration. Proliferating fusiform cells were found in the wall of the capsule, with bundle distribution, hyalinosis in most areas, more lymphocyte infiltration, and smooth muscle actin (SMA) positive.
Gambogic acid and chloroquine synergistically induce cell death via increasing mitochondria damage in human NSCLC cells
- Pages: 172-180
- First Published: 02 October 2024
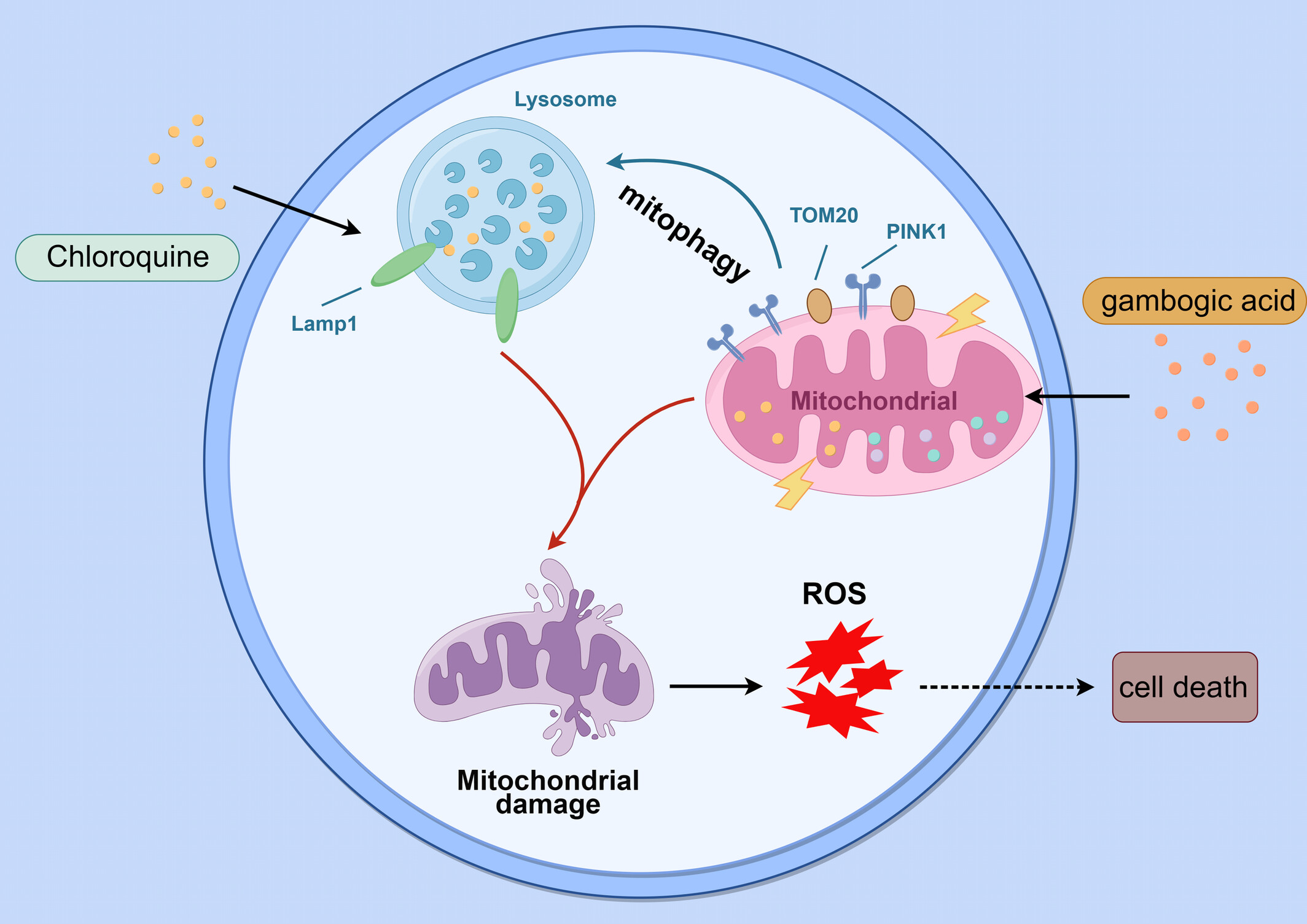
This study aims to investigate whether the combination of gambogic and chloroquine, one of inhibitor of autophagy, could increase cell death in human NSCLC cells. As a result, the combination of gambogic acid and chloroquine significantly promotes apoptosis than that either alone does. Mechanistically, gambogic acid activated mitophagy, however, treatment of chloroquine could inhibit lysosomal function, therefore disrupting the clearance of damaged mitochondria. Therefore, co-treatment of gambogic acid and chloroquine results in an elevated level of ROS, which facilitates to cell death. Taken together, our finding highlights that the synergistically inhibitory effect of gambogic acid and chloroquine on NSCLC cells is associated with the accumulation of mitochondrial damage.
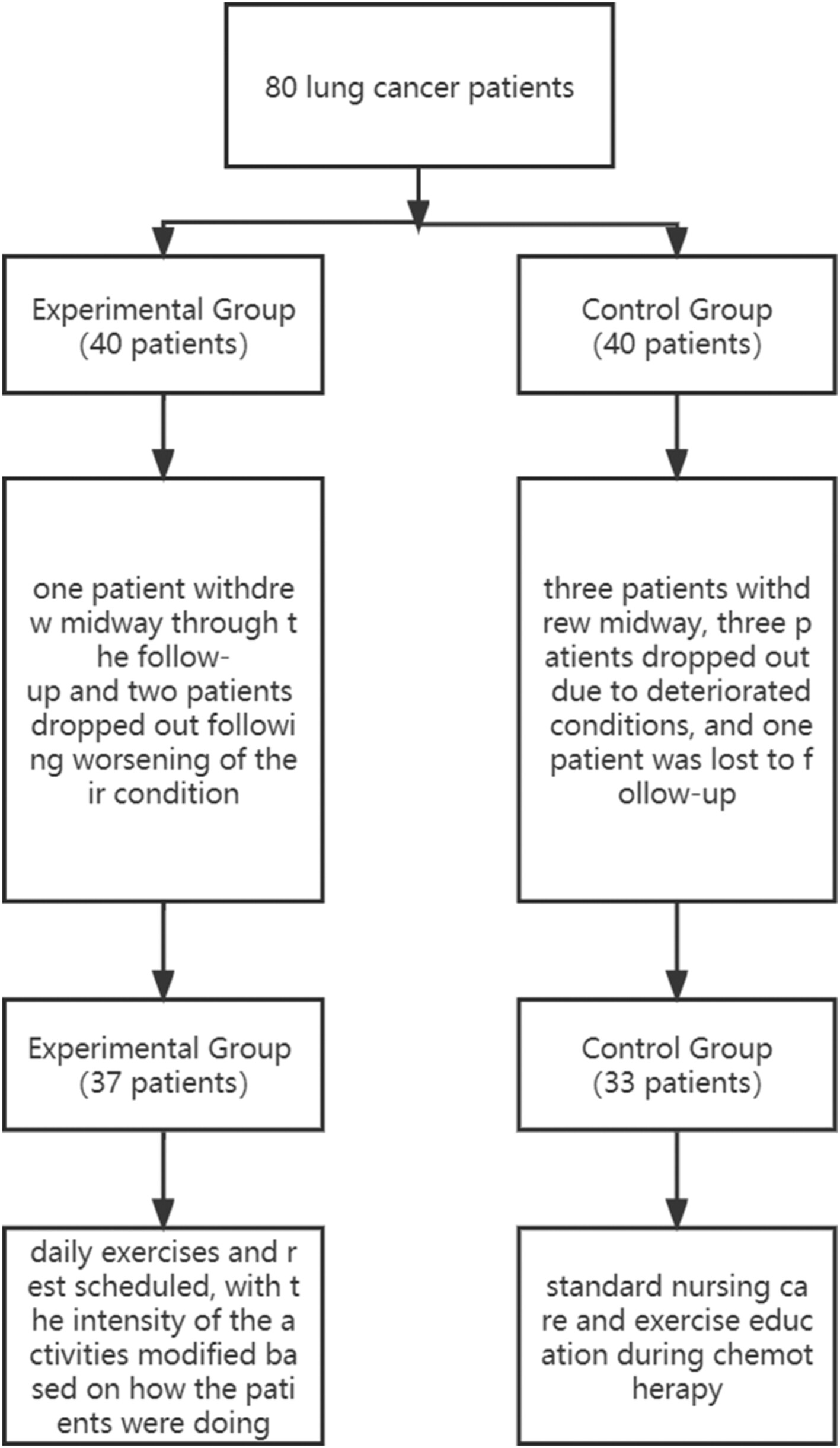
The effects of a positive emotional exercise intervention on the quality of life and psychological well-being in cancer chemotherapy patients
- Pages: 181-188
- First Published: 03 September 2024