Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Identification of a stable immunosuppressive molecular subtype in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma based on inflammation-related genes
- Pages: 192-203
- First Published: 20 November 2024
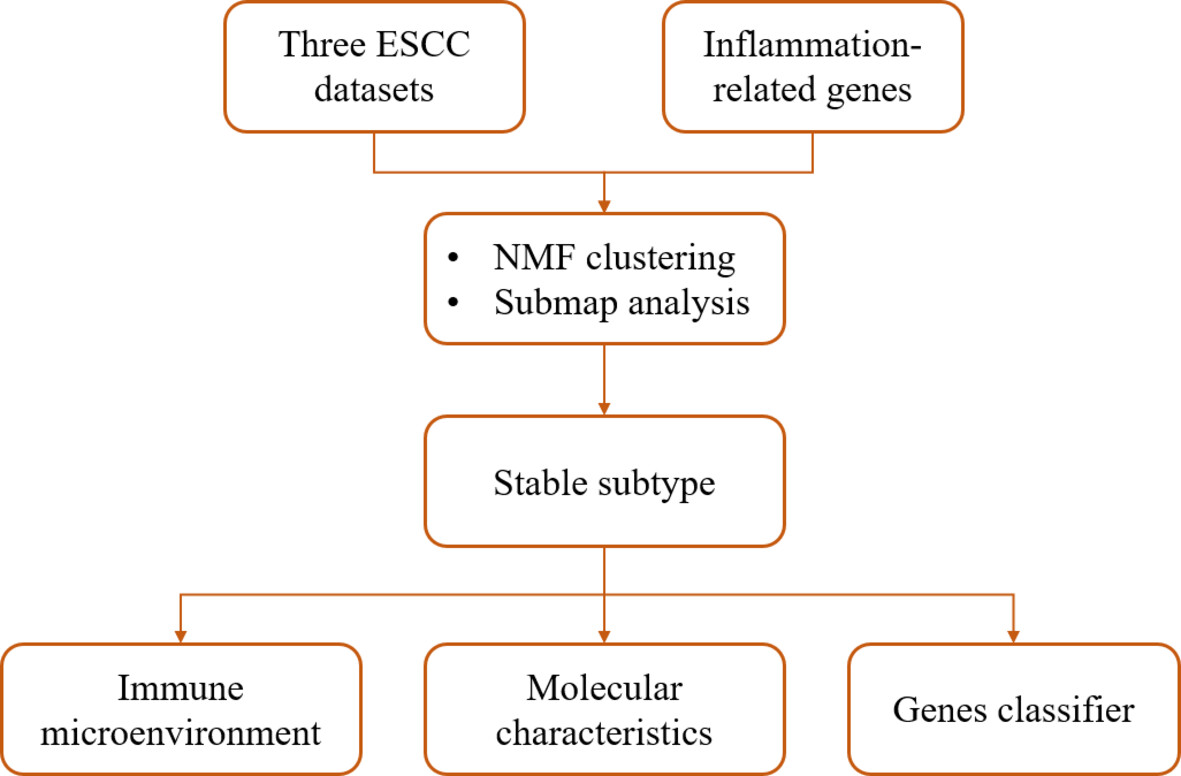
Flow diagram of this study. The expression profile of inflammation-related genes was extracted from three esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) datasets and clustered using the non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) method. Submap analysis was applied to identify stable subtype across the three datasets. Subsequently, the immune microenvironment and molecular characteristics of the stable subtype were analyzed, leading to the construction and validation of a gene classifier for the stable subtype.
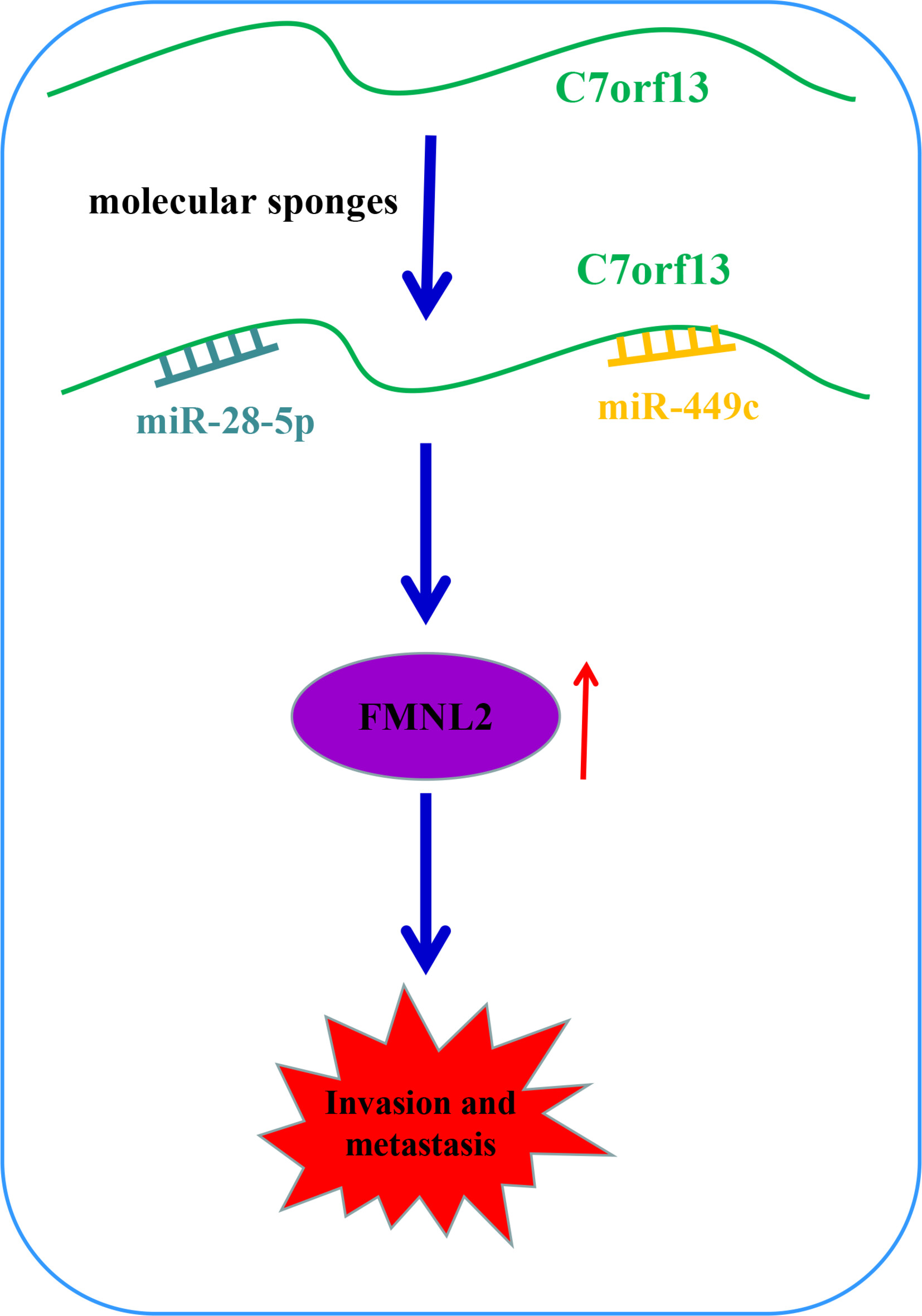
LncRNA C7orf13 facilitates cell proliferation and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via targeting miR-449c/miR-28-5p-FMNL2 axis
- Pages: 204-213
- First Published: 03 December 2024
The causal relationship between drinking water and gastrointestinal cancers: a two-sample mendelian randomization analysis
- Pages: 214-220
- First Published: 10 September 2024
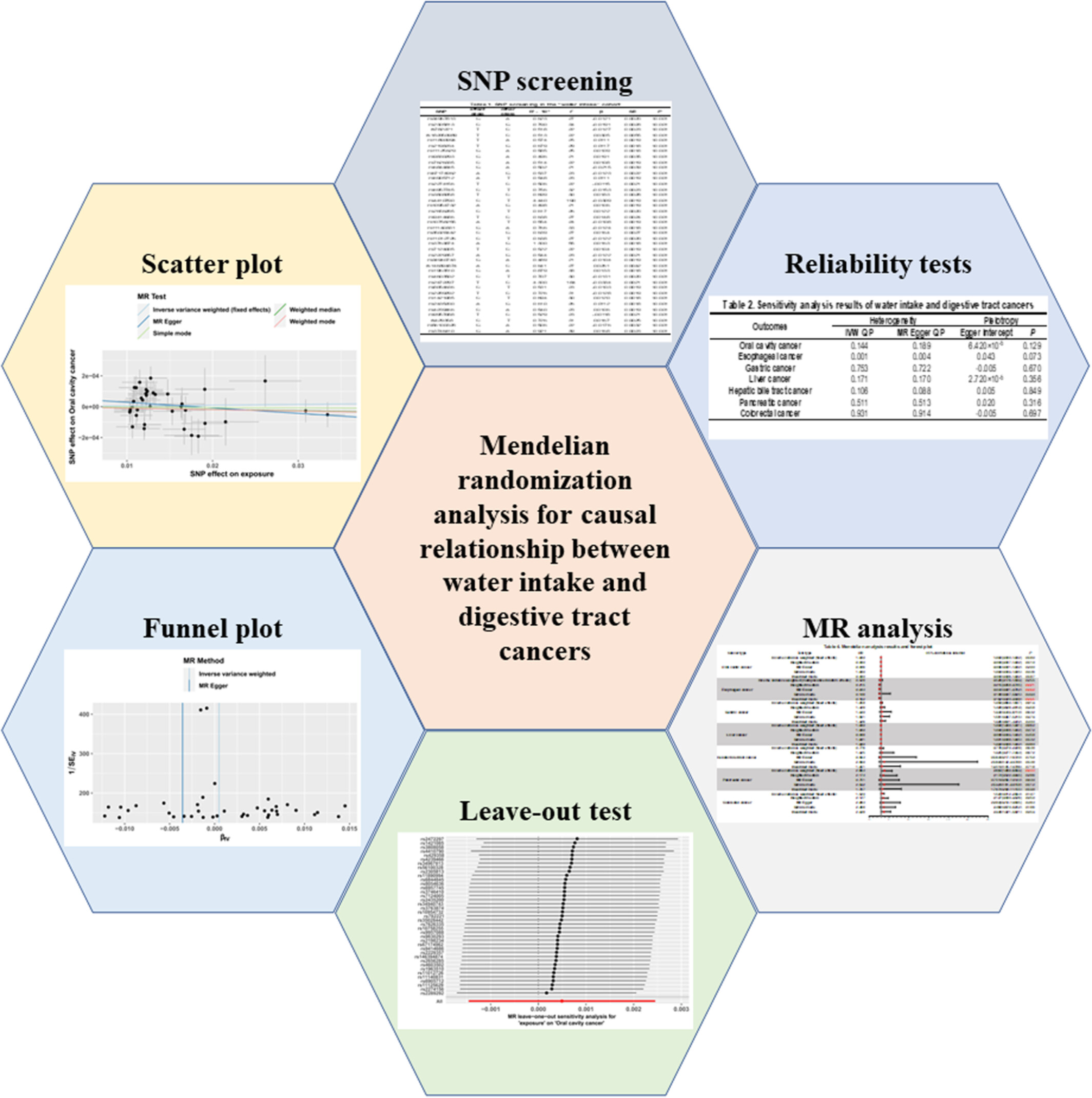
In the present study, we assessed the underlying correlations between daily water intake and digestive tract cancers. We discovered a negative association between water consumption and esophageal cancer, while positive relation between water intake and pancreatic cancer. In the meantime, water intake was also found to have potential effects on cancers including gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. These results possess great clinical feasibility due to the daily nature and importance of drinking water.
Identification of expression profiles and transcription factors during EGFR-TKI acquired resistance in LUAD
- Pages: 221-231
- First Published: 10 October 2024
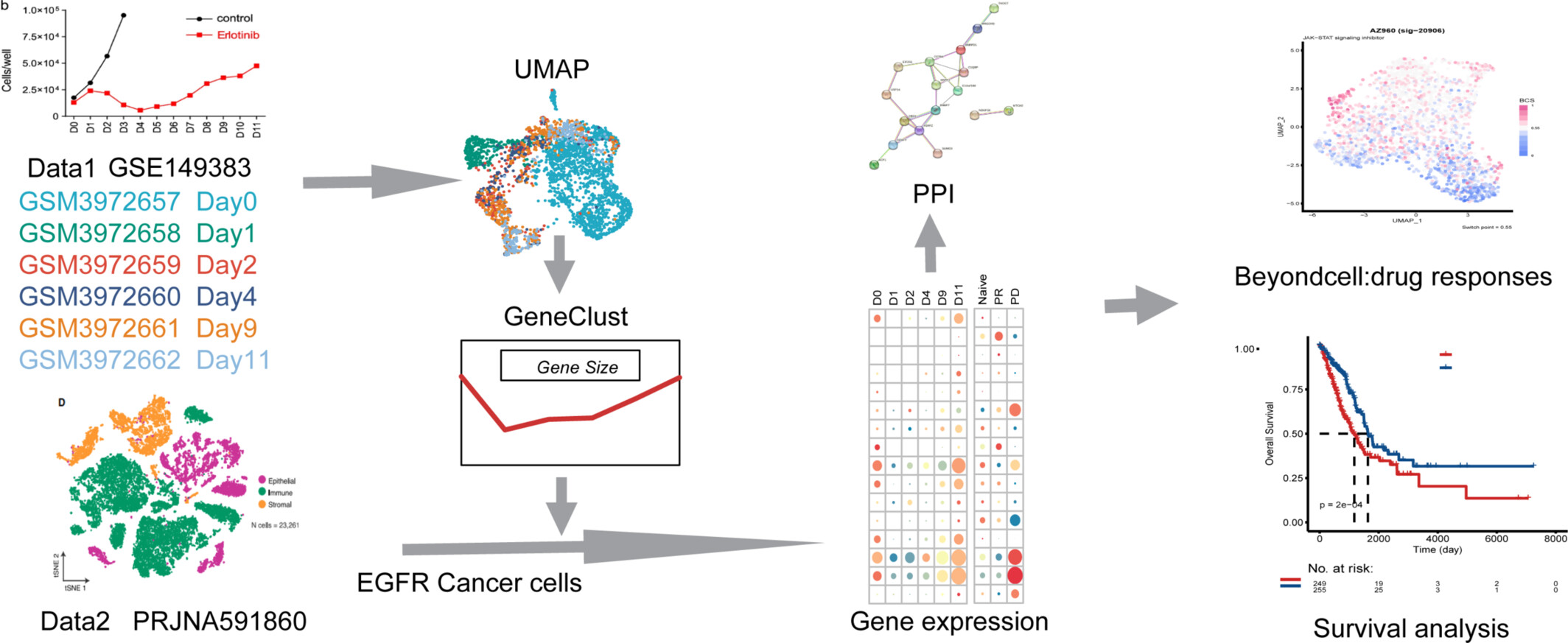
By GSE149383 and PRJNA591860 databases, we identified the typical tendency of “decrease early and raise later” during EGFR-TKI acquired resistance progression in LUAD while we recognized transcription factor-target gene pairs and interacting drugs with EGFR-TKI during EGFR-TKI acquired resistance, which could provide a novel insight for clinical treatments.
Application of nurse-led CINV management scheme based on risk assessment in breast cancer patients
- Pages: 232-241
- First Published: 27 May 2024
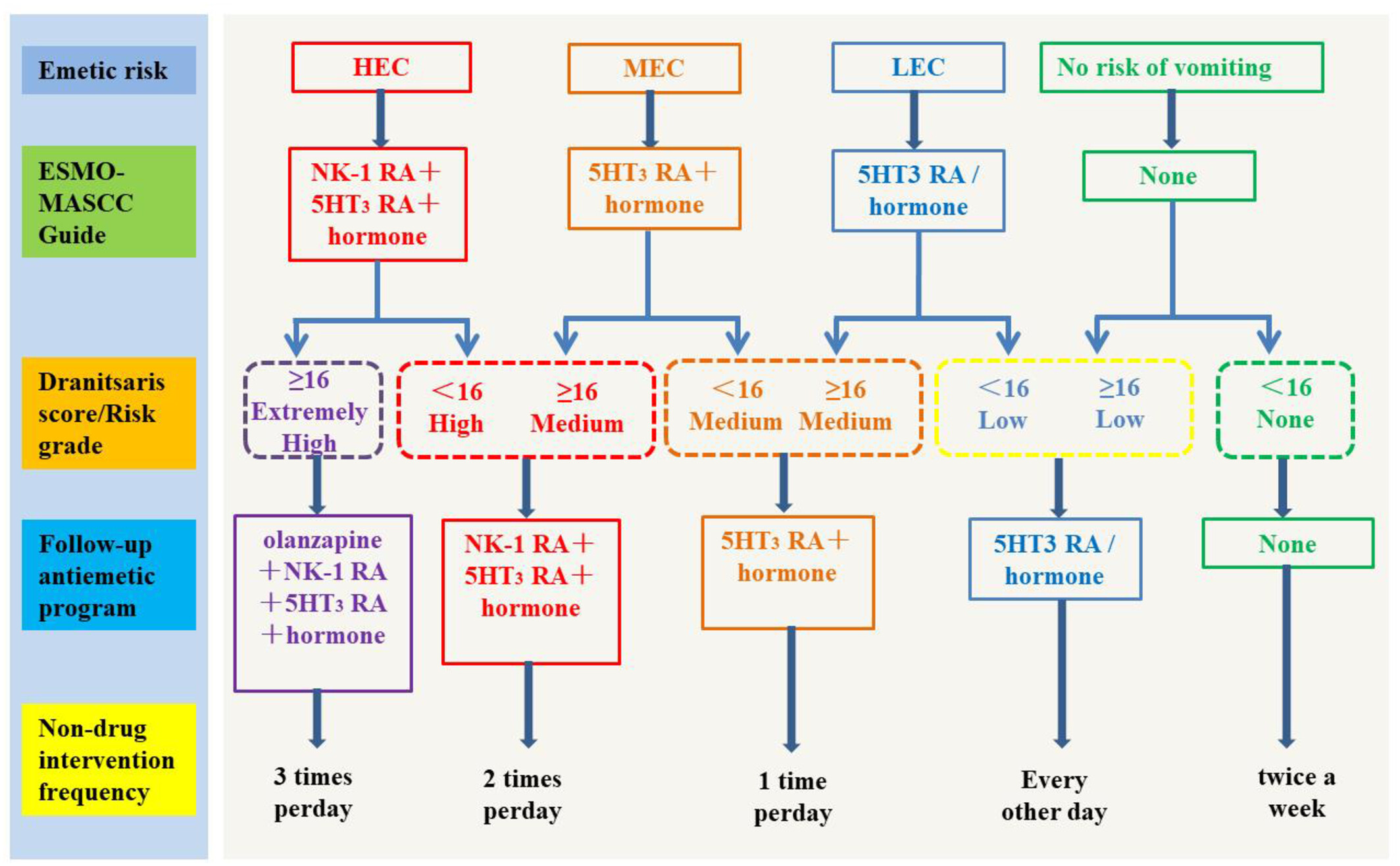
As one of the common adverse reactions after chemotherapy in breast cancer patients, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) seriously affects the quality of life of breast cancer patients. To explore the application effect of nurse-led CINV management scheme based on risk assessment in breast cancer patients. The researchers selected 90 breast cancer patients who received chemotherapy at Jiangsu Cancer Hospital from June 1, 2022, to June 1, 2023. They were divided into control and intervention group. The control group implemented the routine nursing mode, and the intervention group implemented the nurse-led intervention program based on risk assessment. On this basis, the intervention group applied the symptom management theory to the construction of intervention strategy to compare the CINV situation, quality of life, and psychological distress level between the two groups. The frequency of vomiting and the degree of nausea in the intervention group were lower than those in the control group (p<.05). The vital function index of nausea and vomiting in the intervention group was higher than that in the control group both at the acute and delayed stage (p<.05). The psychological pain scores in the intervention group were lower than those in the control group both at the acute and delayed stage (p<.05). Nurse-led CINV management scheme based on risk assessment could effectively reduce the frequency of vomiting, reduce the degree of nausea, improve the quality of life, and alleviate psychological pain in breast cancer patients.