Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Phenomapping approach to interpreting coronary dimensions in febrile children
- Pages: 233-240
- First Published: 15 December 2022
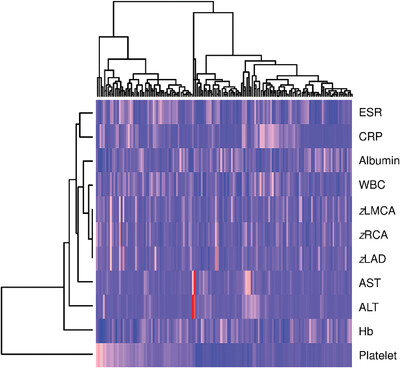
Unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis of phenotypic data including age, hemoglobin, white cell count, platelet count, C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, albumin, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and coronary artery z scores was performed in 239 febrile children with (n = 180) and with (n = 59) Kawasaki disease (KD). Three phenogroups that differed in a clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic parameters were identified. The phenomapping approach identified useful laboratory parameters that aid the diagnosis of KD in febrile children with relatively normal-sized coronary arteries.
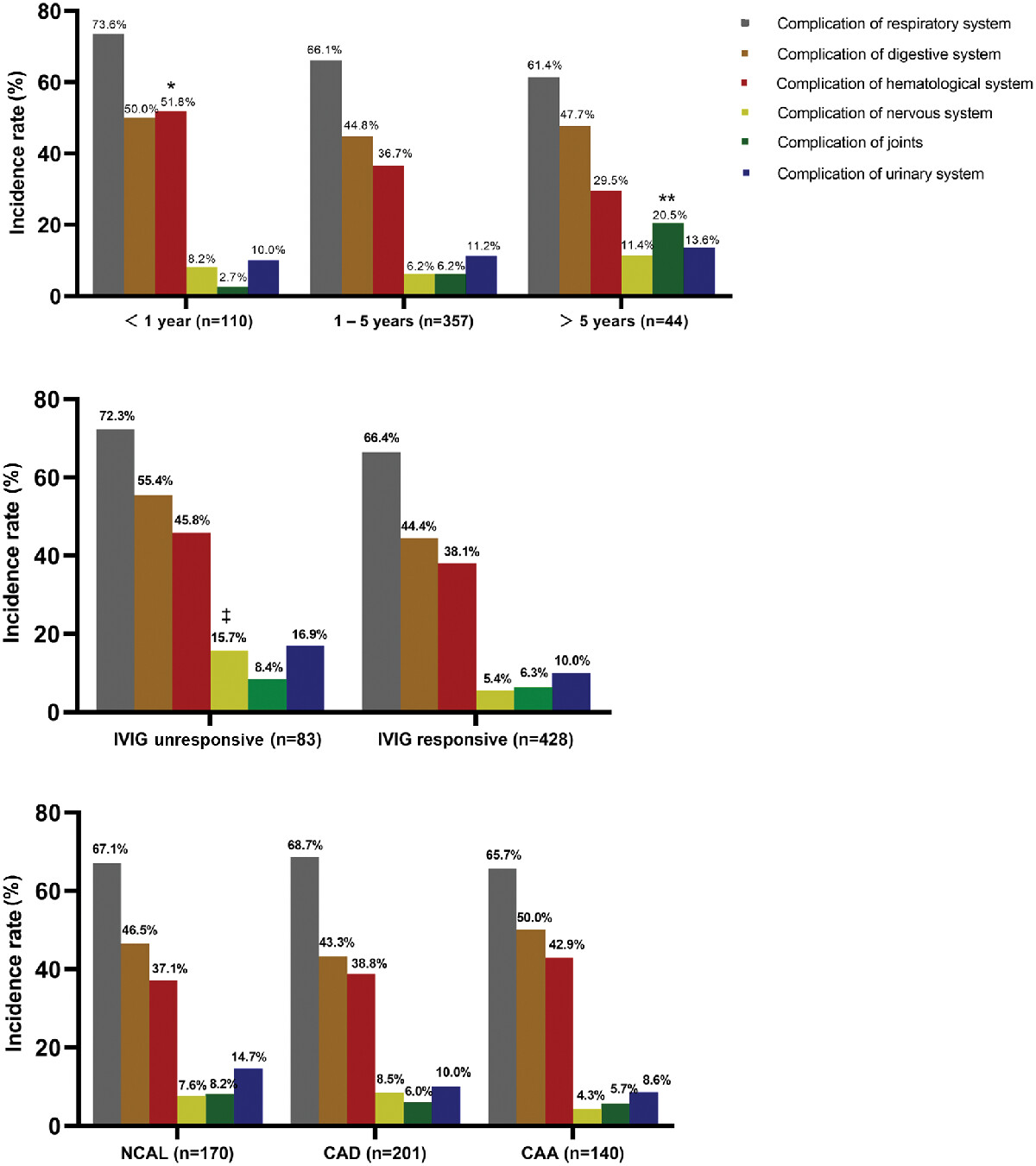
Extracardiovascular injury complications in Kawasaki disease
- Pages: 241-249
- First Published: 22 November 2022
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with the modified myeloablative conditioning regimen for children with chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection
- Pages: 250-259
- First Published: 15 November 2022
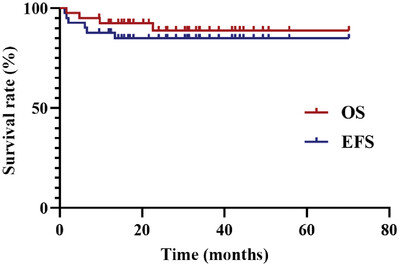
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) with the modified myeloablative conditioning (MAC) regimen is safe and effective for pediatric chronic active Epstein–Barr virus. The 3-year overall survival (OS) and 3-year event-free survival (EFS) rates were 88.8% ± 5.4% and 85.0% ± 5.7%, respectively. The 3-year OS and EFS did not significantly differ between the hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and non-HLH groups, or among the complete remission, partial remission, and activity disease groups. Patients with concomitant HLH and patients with the active disease before allo-HSCT also benefit from modified MAC-HSCT. Patients with grade III–IV acute graft-versus-host diseases (aGVHD) had lower 3-year OS and EFS rates than those without aGVHD or with grade I–II aGVHD.
RESEARCH LETTER
Outcomes of complete surgical repair versus palliative intervention in neonates with Tetralogy of Fallot
- Pages: 260-263
- First Published: 23 October 2022
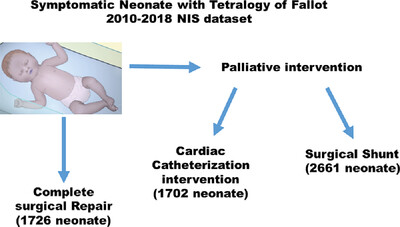
Using the US National Inpatient Sample dataset (2010 to 2018), we compared outcomes of neonates with Tetralogy of Fallot who had early primary surgical repair (1726 neonate) and those who had staged palliative intervention with transcatheter (1702 neonate) or surgical palliative shunt (2661 neonate).
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Optical coherence tomography of the pulmonary arteries in children with congenital heart diseases: A systematic review
- Pages: 264-270
- First Published: 30 November 2022
REVIEW
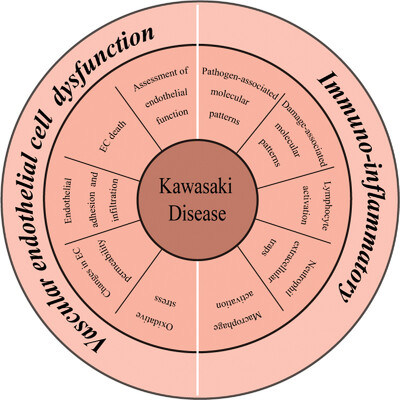
Advances in understanding Kawasaki disease-related immuno-inflammatory response and vascular endothelial dysfunction
- Pages: 271-279
- First Published: 01 August 2022
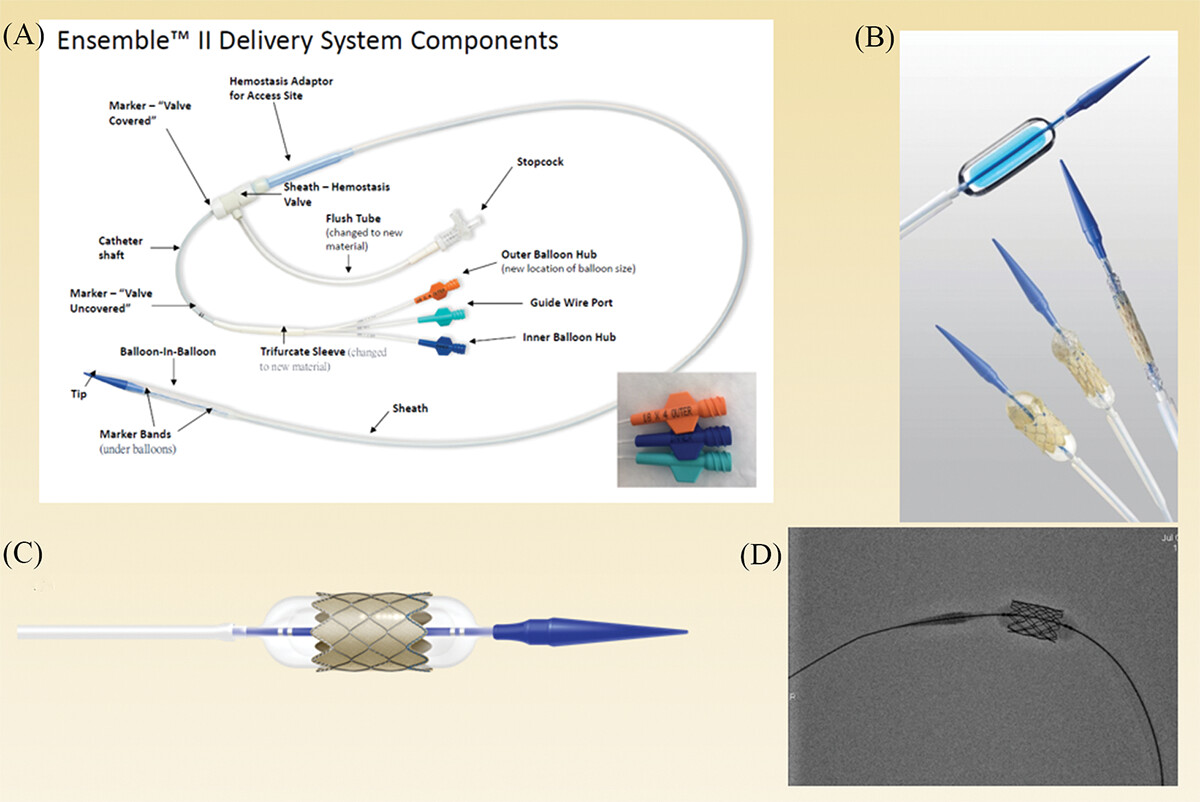
Transcatheter pulmonary valve replacement in congenital heart diseases
- Pages: 280-290
- First Published: 05 December 2022
Newborn screening for genetic disorders: Current status and prospects for the future
- Pages: 291-298
- First Published: 24 October 2022
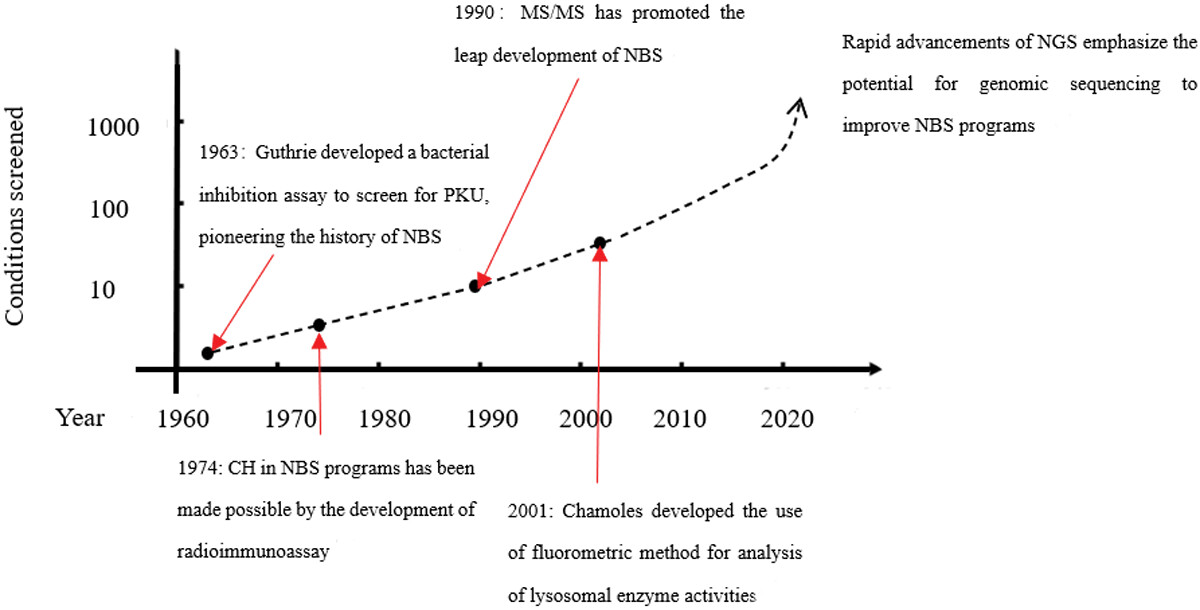
The history of NBS began with PKU screening in the 1960s, but it expanded slowly. A revolutionary turning point came in the 1990s with the introduction of MS/MS. Enzymatic assay provides a reliable screening method for some disorders. Recently, NGS has emerged as a robust tool, raising concerns regarding its application in population screening.
EDITORIAL
Sitting intolerance: A new disease entity in children and adolescents
- Pages: 299-301
- First Published: 05 November 2022
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Rett syndrome with atrial tachycardia in a girl
- Pages: 302-304
- First Published: 12 October 2022







.png)

