Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
CLINICAL GUIDELINE
Radiotherapy guidelines for rectal cancer in China (2020 Edition)
- Pages: 4-31
- First Published: 01 March 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Investigation of the systemic inflammatory index as a predictor of downstaging in locally advanced rectal cancer patients with preoperative chemoradiation
- Pages: 32-38
- First Published: 03 March 2022

Purpose: To find the correlations between blood systemic inflammatory biomarkers at three treatment time points and clinical effects of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (neo-CRT) through a retrospective study.
Methods: In total 101 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) were included in the current study. Patients were divided into two groups based on the T-downstaging, among which 54 patients had T-downstaging. We used non-parametric tests to compare the differences between the variables in two groups. We performed a logistic regression analysis to evaluate the predictive value of blood systemic inflammatory biomarkers.
Results: Pre/nadir/post-systemic immune-inflammation (SII), nadir-neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), nadir/post-platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and post-Lymphocyte (post-Lym) have differences between groups (P 0.05 for all). We included P 0.05 indicators and clinical related factors into the multivariate analysis, respectively, and we found that lower pre-SII, nadir-SII/NLR/PLR, and post-PLR were associated with better therapeutic effects (P 0.05).
Conclusions: The systemic inflammatory index was indicative in predicting the therapeutic effects of LARC patients after neo-CRT.
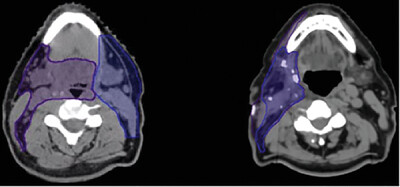
Patterns of care in the radiotherapeutic management of head and neck cancer of unknown primary origin: in search of a standard
- Pages: 39-45
- First Published: 09 February 2022
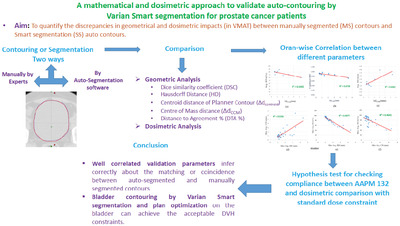
A mathematical and dosimetric approach to validate auto-contouring by Varian Smart segmentation for prostate cancer patients
- Pages: 46-58
- First Published: 06 March 2022
REVIEWS
Proton beam radiation therapy treatment for head and neck cancer
- Pages: 59-68
- First Published: 01 December 2021
Carbon ion radiotherapy in the management of non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 69-74
- First Published: 22 March 2022
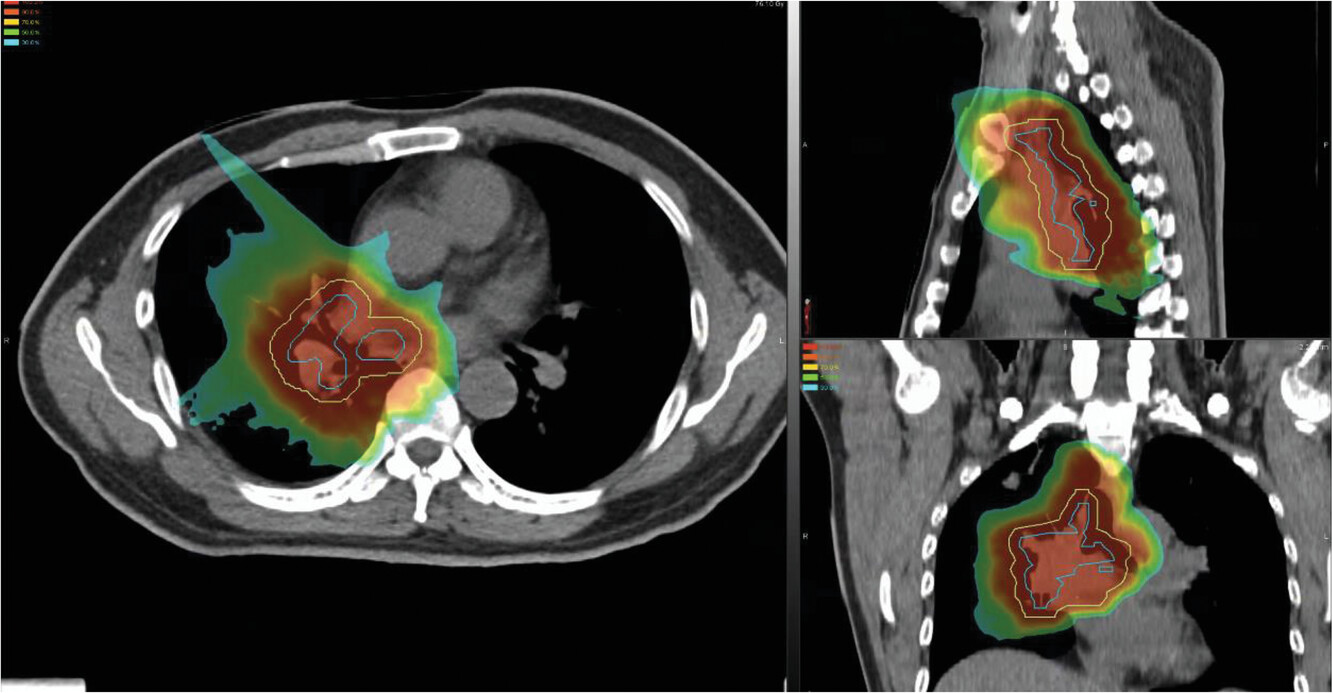
Carbon ion radiotherapy is a form of high-linear energy transfer radiation therapy that may have several theoretical advantages over traditional low-linear energy transfer therapies in the treatment of both early-stage and locally advanced non-small cell cancer. These potential advantages include the ability to achieve high intratumoral radiation doses while sparing adjacent critical structures of the mediastinum, delivering adequate radiation doses in fewer fractions, limiting/eliminating the use of concurrent cytotoxic chemotherapy, and increasing the response to immunotherapy, thereby reducing eventual metastatic spread.
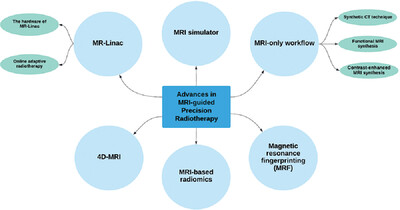
Advances in MRI-guided precision radiotherapy
- Pages: 75-84
- First Published: 22 January 2022
The role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in the management of pulmonary metastases: a systematic review
- Pages: 85-95
- First Published: 24 March 2022

Stereotactic body radiation therapy is a relatively novel treatment that can be used for the management of pulmonary metastases. On examination of various survival outcomes, SBRT showed promising benefits regarding overall survival and local control, with indications for future research comparing it directly with metastasectomy.