Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine
Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover
- First Published: 07 February 2020

The cover image is based on the Original Article Lessons learned from expanded reproductive carrier screening in self-reported Ashkenazi, Sephardi, and Mizrahi Jewish patients by Gidon Akler et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.1053.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
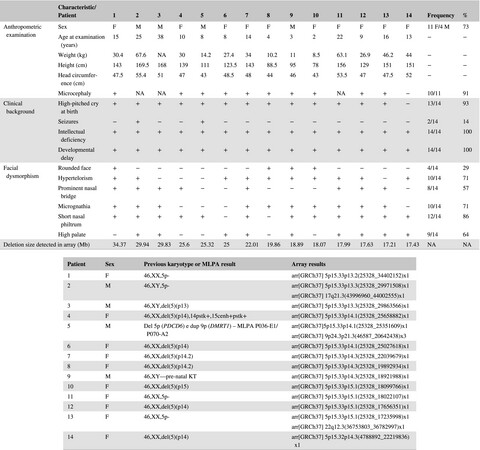
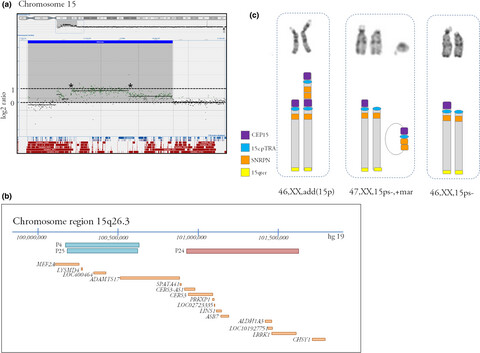
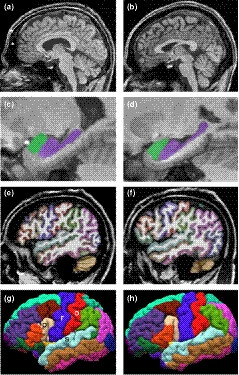
Breakpoint delineation in 5p- patients leads to new insights about microcephaly and the typical high-pitched cry
- First Published: 30 September 2019
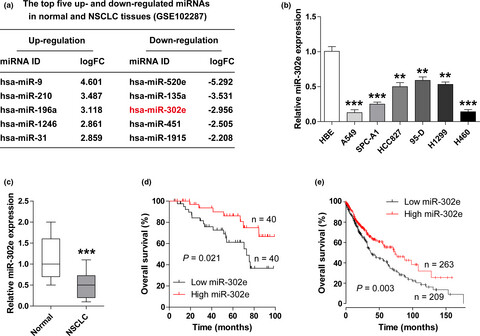
Circular RNA circ-CMPK1 contributes to cell proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer by elevating cyclin D1 via sponging miR-302e
- First Published: 21 December 2019
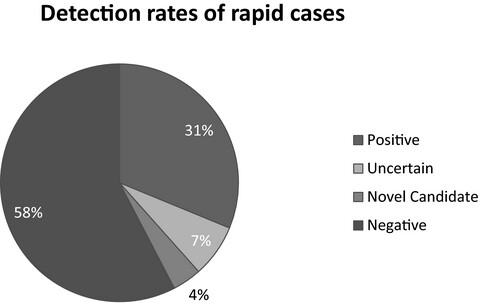
When moments matter: Finding answers with rapid exome sequencing
- First Published: 24 December 2019
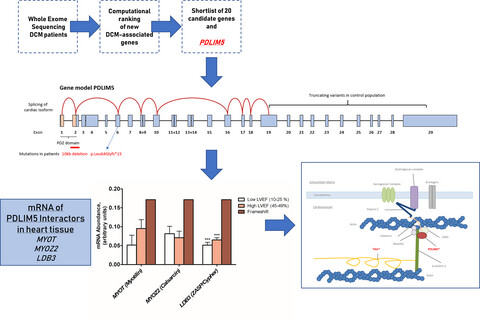
Mutations in PDLIM5 are rare in dilated cardiomyopathy but are emerging as potential disease modifiers
- First Published: 27 December 2019
Lessons learned from expanded reproductive carrier screening in self-reported Ashkenazi, Sephardi, and Mizrahi Jewish patients
- First Published: 27 December 2019
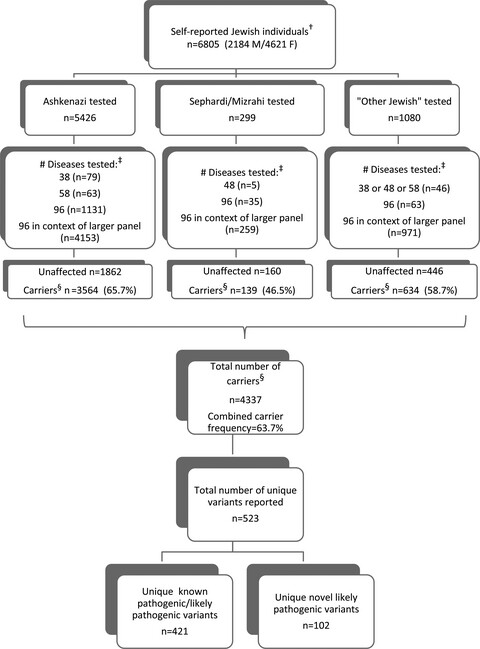
This retrospective study examines a specific cohort of 6,805 self-reported Jewish (Ashkenazi/Sephardi/Mizrahi) patients who underwent carrier screening using NGS-based expanded panels. Results are presented from an extracted set of 96 genes initially classified as “Jewish-relevant,” albeit that a majority of the patients (79% of cohort) opted for much larger panels that contained this set of 96. The findings highlight the value of large, universal sequence-based panels, given that (a) self-reported ethnic information is often unreliable/complex, and (b) many patients want maximal information for their reproductive decision making.
Identification of a novel protein truncating mutation p.Asp98* in XPC associated with xeroderma pigmentosum in a consanguineous Pakistani family
- First Published: 10 January 2020
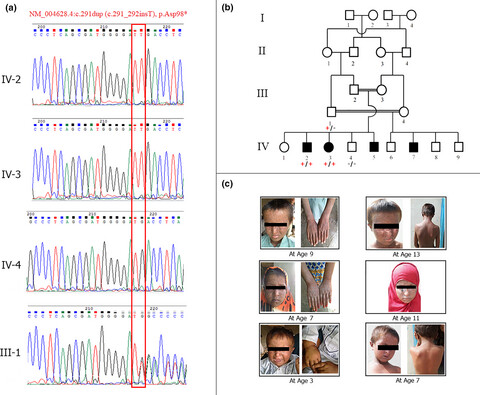
In this study, we report a novel protein truncating mutation (p.Asp98*) in XPC of xeroderma pigmentosum patient. The identified mutation presumably truncates all functional domains of the XPC protein, which likely results in the loss of protein function. The study expands the knowledge of the mutational spectrum of XPC and would be valuable for genetic counseling of affected individuals and their families.
Evidence of positively selected G6PD A- allele reduces risk of Plasmodium falciparum infection in African population on Bioko Island
- First Published: 24 December 2019
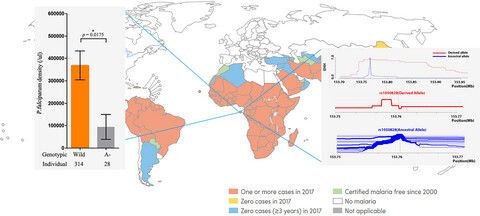
In this work, we firstly analysed a large case–control study of 342 malaria cases and 1,287 health controls on Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea. Our findings demonstrate G6PD A- allele could reduce the risk of Plasmodium falciparum infection in African population and indicate malaria has recent positive selection on G6PD A- allele.
A report of 2 cases of Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) and an analysis of clinical and genetic characteristics in a Chinese CdLS cohort
- First Published: 24 December 2019
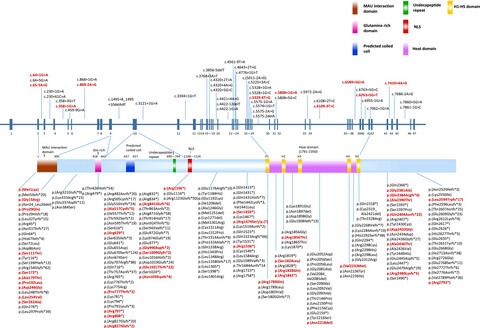
We found two patients presented with typical phenotypes, characteristic complications of CdLS and mutations in the NIPBL gene. By investigating 26 Chinese cases of CdLS, we observed that the clinical data and gene variants in the Chinese cohort of CdLS patients were generally in accordance with those of other populations. To date, the NIPBL-LOVD database (Leiden open variation database) describes 266 unique DNA variants, reported in 352 individuals (last accessed July 2017) which include substitutions (65.1%, 229/352), deletions (23.9%, 84/352), duplications (8.8%, 31/352), insertions/deletions (1.4%, 5/352) and insertions (0.9%, 3/352) (Figure 4).
A dominant RAD51C pathogenic splicing variant predisposes to breast and ovarian cancer in the Newfoundland population due to founder effect
- First Published: 28 November 2019
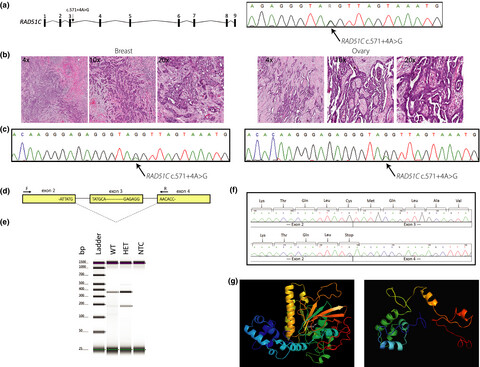
RAD51C is important in DNA repair and carriers of pathogenic RAD51C variants have increased risk of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC), an autosomal dominant genetic predisposition to early onset breast and/or ovarian cancer. This study identified five female HBOC probands that shared a recurrent variant of uncertain significance in RAD51C (NM_058216.3: c.571 + 4A > G). Our analyses demonstrated that the RAD51C c.571 + 4A > G variant affects mRNA splicing and should be re-classified as pathogenic according to American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics guidelines.
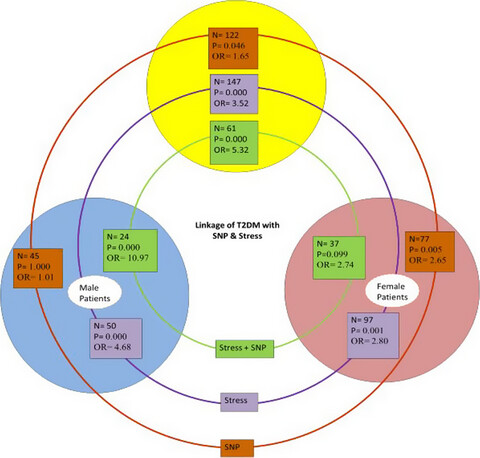
Association of polymorphism in heat shock protein 70 genes with type 2 diabetes in Bangladeshi population
- First Published: 09 December 2019
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: An innovative panel containing a set of insertion/deletion loci for individual identification and its forensic efficiency evaluations in Chinese Hui ethnic minority
- First Published: 22 December 2019
We previously constructed a panel of 35 InDel loci with relative high polymorphisms in Chinese three populations for individual identifications. In present study, the forensic statistical analyses also revealed these loci showed relatively high genetic polymorphisms in studied Chinese Hui group and could be served as a tool in the aspect of individual identifications in Chinese Hui group. Population genetic evaluations indicated that Chinese Hui group had close genetic relationships with East Asian populations.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
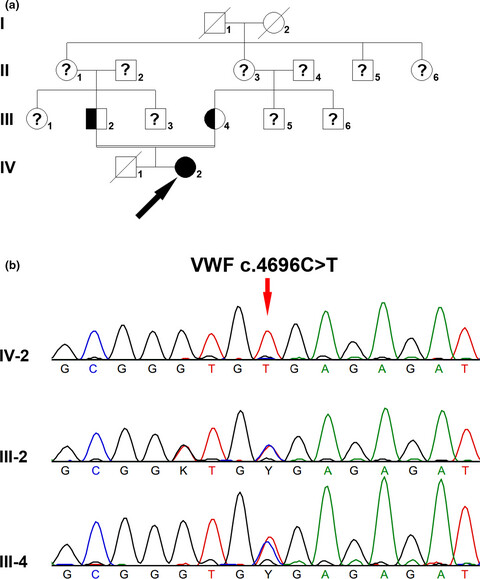
Two cases of von Willebrand disease type 3 in consanguineous Chinese families
- First Published: 02 December 2019
Targeted regions sequencing identified four novel PNPLA1 mutations in two Chinese families with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis
- First Published: 13 December 2019
Genetic analyses in the present study revealed four novel PNPLA1 variants that are predicted to be probably to lead to ARCI in three patients of two families. In addition, these variants co segregate in the two pedigrees and are all within highly conserved regions of the PNPLA1 protein, which indicate that the four mutations are likely pathogenic.
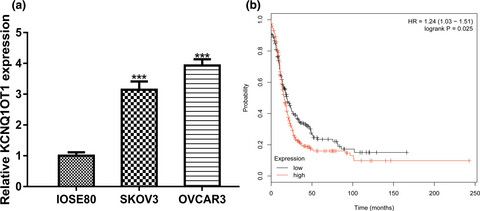
KCNQ1OT1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via modulating MIR-142-5p/CAPN10 axis
- First Published: 07 January 2020
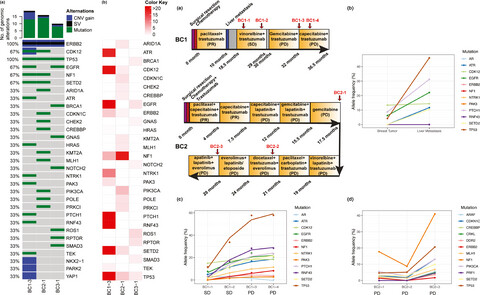
Monitoring treatment efficacy and resistance in breast cancer patients via circulating tumor DNA genomic profiling
- First Published: 23 December 2019
Superoxide imbalance triggered by Val16Ala-SOD2 polymorphism increases the risk of depression and self-reported psychological stress in free-living elderly people
- First Published: 31 December 2019
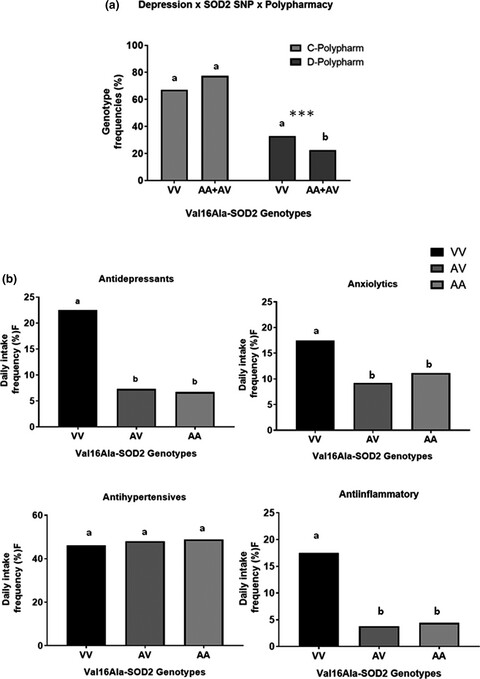
Our results showed that the VV-SOD2 genotype significantly increased the risk for depression and psychological stress in the elderly subjects. VV-subjects also had a higher daily intake of antidepressants, anxiolytics, and anti-inflammatory drugs. The findings support the hypothesis that genetically induced oxidative superoxide-hydrogen peroxide imbalance may be involved in an increased risk for developing depression and psychological stress in free-living elderly people.
Prevalence of mutations in inherited retinal diseases: A comparison between the United States and India
- First Published: 09 December 2019
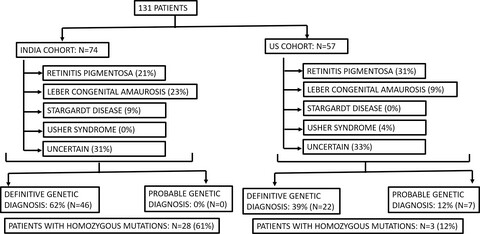
Hispanic/non-White patients had a lower diagnostic rate for retinal disorders on NGS testing and the Indian cohort had a higher rate of homozygous variants. Heterogeneity in racial background may lead to different diagnostic rates within individual populations, which may be important for patient counseling.
Novel FSHR variants causing female resistant ovary syndrome
- First Published: 12 December 2019
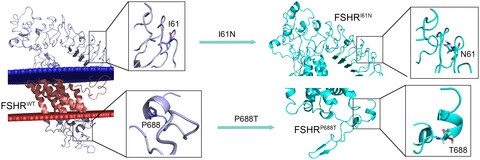
We identified a novel inactivating compound heterozygous FSHR mutation (I61N, P688T) in a pair of siblings affected by ROS. This study expands the genotypic spectrum of FSHR mutations and our knowledge of phenotype–genotype correlations, including anti-Müllerian hormone level and primordial follicle in the ovary.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Genetic polymorphism and phylogenetic analyses of 21 non-CODIS STR loci in a Chinese Han population from Shanghai
- First Published: 08 December 2019
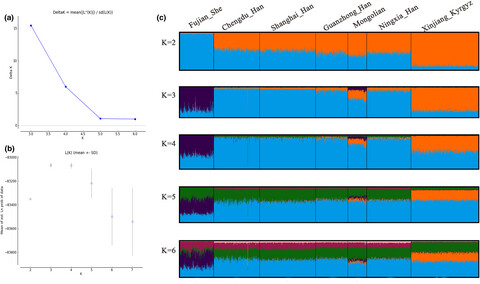
Twenty-one autosomal noncombined DNA index system (non-CODIS) STR loci were detected in a Chinese Han population from Shanghai. Forensic potential was estimated by calculating forensic parameters, such as CPD and CPE. Genetic relationships of the studied population and other reported reference populations in Chinese mainland were analyzed.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Pathogenic copy number variants are detected in a subset of patients with gastrointestinal malformations
- First Published: 14 December 2019
A data and text mining pipeline to annotate human mitochondrial variants with functional and clinical information
- First Published: 10 December 2019
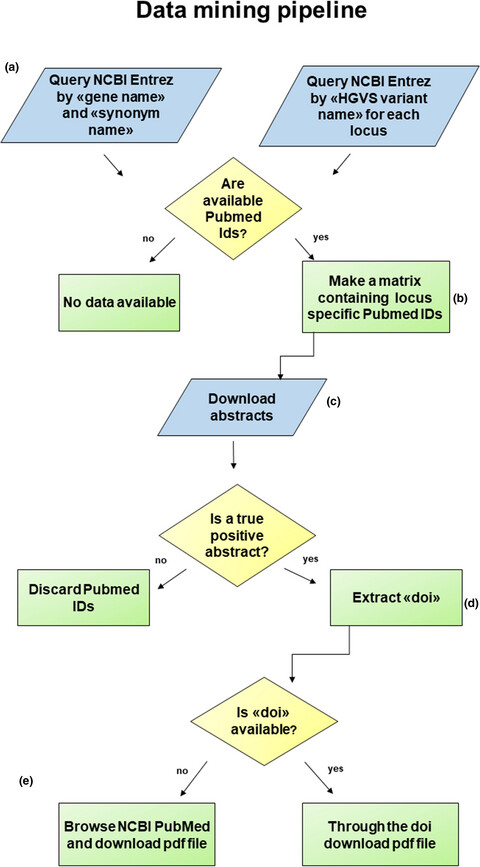
The “data and text mining” pipeline, developed using the programming language R, is capable of extracting information from the literature regarding mtDNA functional studies and related clinical assessments. The application of the pipeline will contribute in supporting the interpretation of pathogenicity of human mitochondrial variants by facilitating diagnosis to clinicians and researchers that approach to this task.
Multi-institutional experience of genetic diagnosis in Ecuador: National registry of chromosome alterations and polymorphisms
- First Published: 12 December 2019
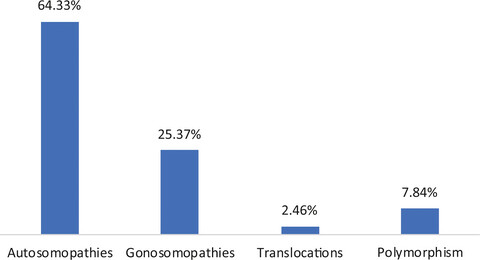
Of 28,806 karyotypes analyzed in Ecuador, 6,008 (20.9%) exhibited alterations. Down syndrome was the most frequent autosome alteration (88.28%), followed by Turner syndrome (60.50%). Translocations (2.46%) and polymorphisms (7.84%) were not as numerous as autosomopathies (64.33%) and gonosomopathies (25.37%).
MiR-338 regulates NFATc1 expression and inhibits the proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- First Published: 11 December 2019
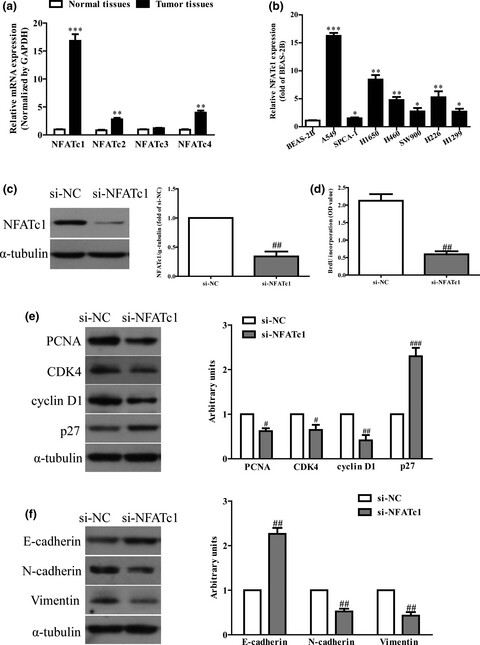
Overexpression of miR-338 significantly inhibited the proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell. Moreover introduction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1) reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-338 overexpression. Therefore, our outcomes showed critical roles for miR-338/ NFATc1 axis in the pathogenesis of NSCLC and suggested its possible application in tumor treatment.
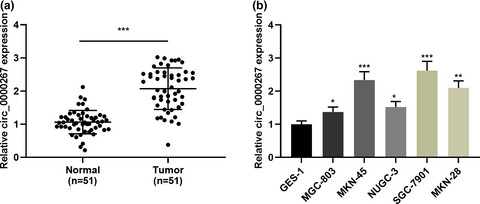
Circ_0000267 promotes gastric cancer progression via sponging MiR-503-5p and regulating HMGA2 expression
- First Published: 17 December 2019
Development of a new methylation-based fetal fraction estimation assay using multiplex ddPCR
- First Published: 10 December 2019
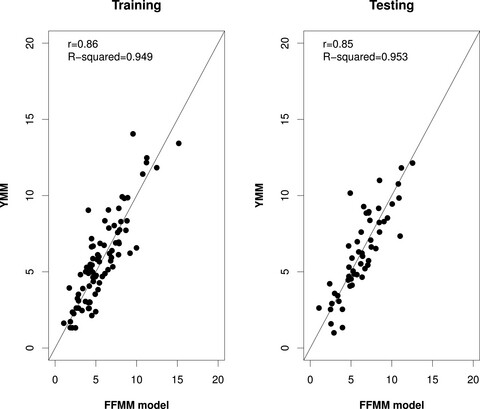
We have developed a multiplex droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) assay for accurate fetal fraction estimation using methylation sensitive restriction enzymes (MSREs) and a robust set of novel fetal-specific differentially methylated regions (DMRs). Clinical implementation of our assay as a first-tier fetal fraction estimation in NIPT can minimize the possibility of incorrect calls due to low fetal fraction estimation.
A de novo MAPRE2 variant in a patient with congenital symmetric circumferential skin creases type 2
- First Published: 05 January 2020
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Forensic characteristics and genetic affinity analyses of Xinjiang Mongolian group using a novel six fluorescent dye-labeled typing system including 41 Y-STRs and 3 Y-InDels
- First Published: 26 December 2019
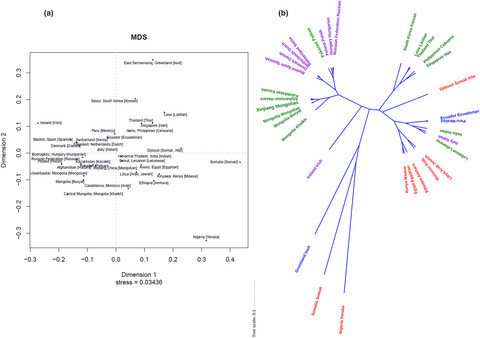
Investigating genetic characteristics of the Mongolian group using 41 Y-chromosomal short tandem repeat and 3 insertion/deletion molecular genetic markers. Exploring the genetic relationships between the Mongolian group and 23 comparison populations from China, as well as between the Mongolian group and 33 comparison populations from worldwide nations.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
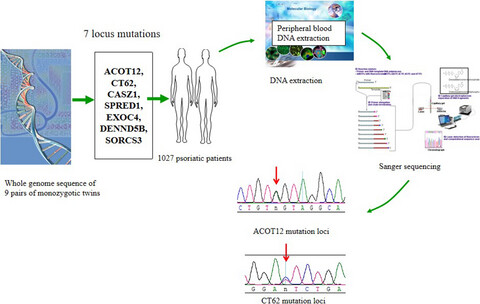
Variation at ACOT12 and CT62 locus represents susceptibility to psoriasis in Han population
- First Published: 20 December 2019
The role of race and ethnicity in views toward and participation in genetic studies and precision medicine research in the United States: A systematic review of qualitative and quantitative studies
- First Published: 23 December 2019
This systematic review details the general public's knowledge of genetics, engagement and participation in genetic research, facilitators and barriers to participation in research, and cultural considerations for conducting genetic research with minority populations. We conclude that the majority of participants of all racial and ethnic backgrounds are willing to participate in precision medicine research studies. However, there are many different facilitators and barriers to participation that may not be as simple as previously outlined in the literature and which must be collectively addressed in order to create more inclusive research practices.
A novel de novo nonsense mutation in ZC4H2 causes Wieacker-Wolff Syndrome
- First Published: 30 December 2019
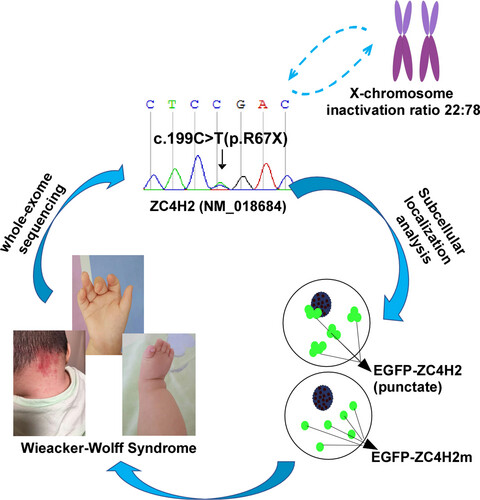
A novel nonsense heterozygous mutation (p.R67X; c.199C>T) in ZC4H2 (Zinc Finger C4H2-Type Containing) gene was discovered in a patient with Wieacker-Wolff syndrome. The mutation resulted in a 66 amino-acid truncated ZC4H2 protein. The results demonstrated that female heterozygous carriers with nonsense mutation with a truncated ZC4H2 protein could lead to the pathogenesis of Wieacker-Wolff syndrome and our study provides a potential new target for the disease treatment.
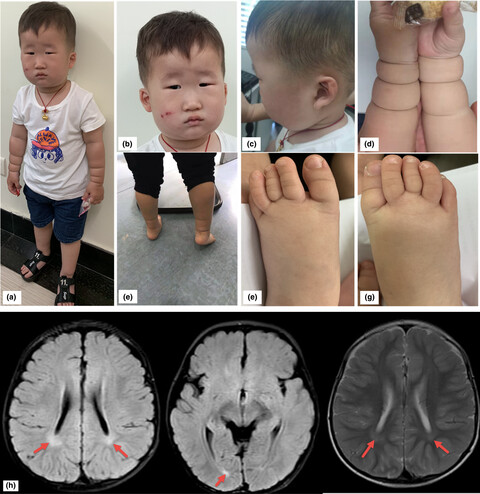
Novel VAC14 variants identified in two Chinese siblings with childhood-onset striatonigral degeneration
- First Published: 26 December 2019
REVIEW ARTICLE
Diagnostic accuracy of midkine for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- First Published: 27 November 2019
CLINICAL REPORTS
Developmental aspects of FXAND in a man with the FMR1 premutation
- First Published: 03 January 2020
MeCP2_e2 partially compensates for lack of MeCP2_e1: A male case of Rett syndrome
- First Published: 09 December 2019
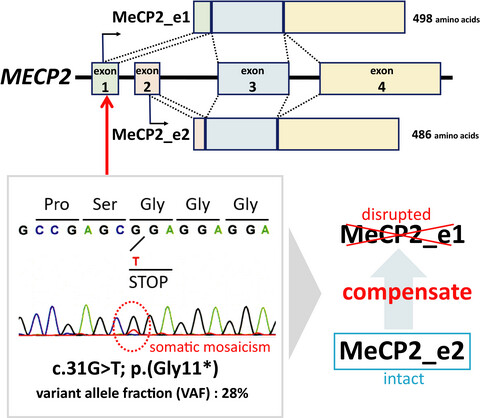
A male case with a novel nonsense and mosaic variant in exon 1 of methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) manifested Rett syndrome symptoms that were milder in severity compared to those in other male cases with mosaic variants in MECP2 exon 3 or 4. This is probably because the variants in MECP2 exon 3 or 4 disrupt both isoforms of MeCP2, whereas the variant in exon 1 disrupts only MeCP2_e1 but not MeCP2_e2. Therefore, our findings indicate that MeCP2_e2 may partially compensates for a deficiency in MeCP2_e1.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
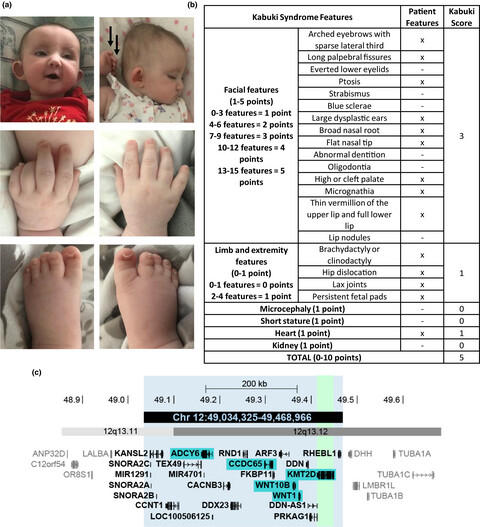
Haploinsufficiency of KMT2D is sufficient to cause Kabuki syndrome and is compatible with life
- First Published: 08 December 2019