Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
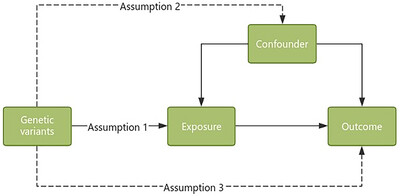
The causal association between epilepsy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 27 September 2024
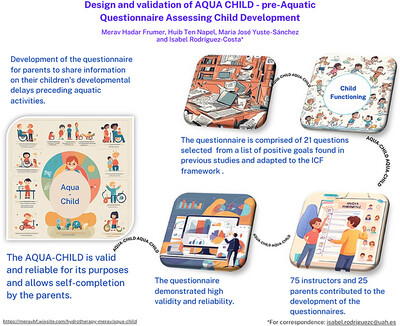
Design and validation of AQUA CHILD—Pre-aquatic questionnaire assessing child development
- First Published: 29 September 2024
Cortical activation during the verbal fluency task for obstructive sleep apnea patients with depressive symptoms: A multi-channel fNIRS study
- First Published: 29 September 2024
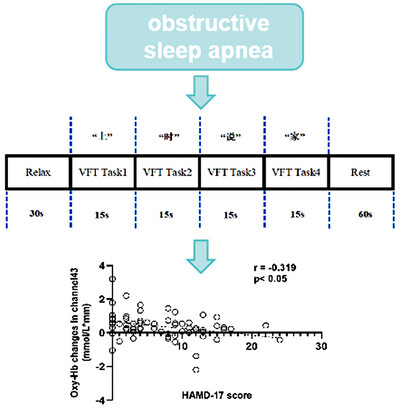
Our study investigated the relationship between brain function and depression in OSA patients. The functional near-infrared spectroscopy was used to monitor the concentration of Oxy-Hb in the brain, whereas the participants performed the verbal fluency task, and the degree of depression was scored using the 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression. The right frontal polar region may be significant in assessing depressive symptoms in patients with OSA.
Neuroticism and posttraumatic stress disorder: A Mendelian randomization analysis
- First Published: 30 September 2024
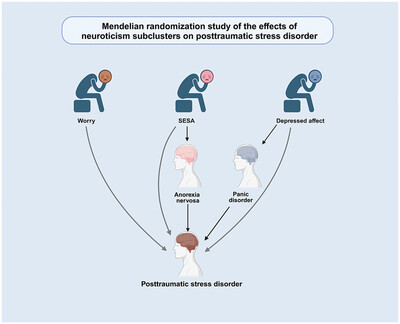
This study employs Mendelian randomization to demonstrate that neuroticism subclusters (worry, SESA, and depressed affect) influence the risk of developing posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The analysis identifies anorexia nervosa (AN) and panic disorder (PD) as mediating factors, illustrating the complex pathways through which neuroticism contributes to PTSD.
The volumes of amygdala subregions and peripheral programmed cell death protein-1 levels are associated with cognitive decline in individuals with knee osteoarthritis
- First Published: 30 September 2024
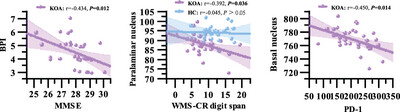
This study indicates that individuals with knee osteoarthritis (KOA) exhibit significantly cognitive impairment compared to healthy individuals, with a negative correlation between pain degree and cognitive performance and structural changes in certain amygdala subfields. Specifically, reduced volumes in these subregions were linked to immediate recall and PD-1 levels. These findings suggest that alterations in amygdala subregion volumes and serum PD-1 levels may contribute to the cognitive decline in KOA individuals.
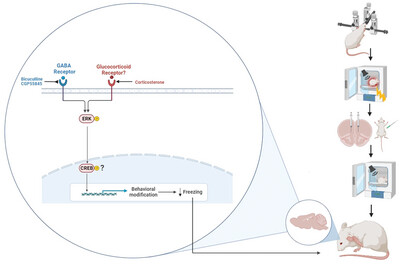
Systemic corticosterone enhances fear memory extinction in rats: Involvement of the infralimbic medial prefrontal cortex GABAA and GABAB receptors
- First Published: 30 September 2024
Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts short-term mortality in acute ischemic stroke with severe stenosis of internal carotid artery associated pneumonia
- First Published: 30 September 2024
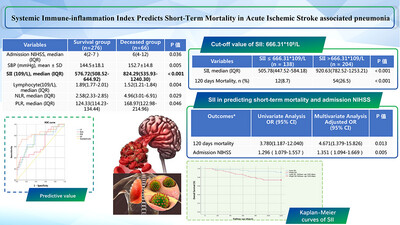
Among 342 patients with severe stenosis ICA-AIS and SAP, death occurred in 66 patients during 120 days follow-up. Multivariate regression analyses indicated that increased SII predicts higher mortality in 120 days follow-up, and the risk of short-term mortality in SII > 666.31 × 109/L group is increased 4.671-fold. Patients with SII > 666.31 × 109/L had higher proportion of male, hypertension, smoking, higher admission NIHSS score, higher systolic blood pressure, and higher proportion of 120 days mortality. Higher SII predicted a worse 120 days mortality was worked out by Kaplan-Meier methods.
Brain Functional Alterations in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Demonstrate the Visual–Vestibular Interaction and Integration
- First Published: 30 September 2024
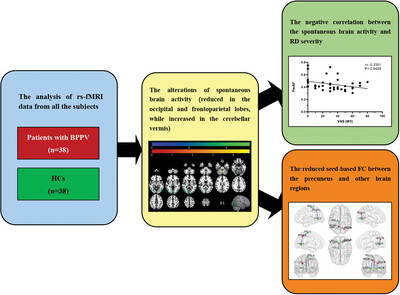
This study discovered brain functional alterations in patients with BPPV in the visual cortex, frontoparietal lobes and cerebellar vermis that conformed to the inhibitory interaction between the multisensory systems, notably between the visual-vestibular system. The study also emphasized the role of the precuneus for integration in BPPV. It also demonstrated the relevance of the observed brain functional alterations to severity of RD, and suggested that functional alterations in the visual cortex and precuneus were probably adaptive responses associated with RD.
Verbal Weight-Related Abuse and Binge Eating Behavior: The Mediating Role of Attentional Bias to Threat Cues and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation
- First Published: 30 September 2024

This study examined the relationship between verbal weight-related abuse (WRA) and binge eating behavior (BE) through attentional bias (AB) to threat cues and difficulties in emotion regulation. The parallel mediation model revealed that verbal WRA had a direct effect on BE. Although difficulties in emotion regulation could mediate the association between verbal WRA and BE, AB to threat cues could not mediate this relationship.
Danggui Shaoyao San Alleviates Early Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer's Disease Mice Through IRS1/GSK3β/Wnt3a-β-Catenin Pathway
- First Published: 30 September 2024

In vitro, HT22 cells were induced with streptozotocin to investigate the impact of GSK3β on pathway transduction. The active components in the DSS stock solution were validated using mass spectrometry. Subsequently, an AD model in C57BL/6J mice was established through streptozotocin injection into both ventricles. The success of the model was validated behaviorally and pathologically. The Morris Water Maze test, immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, quantitative reverse transcription-PCR, and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) were employed to evaluate the influence of DSS on memory and pathological changes in AD. DSS potentially confers cognitive protection by alleviating central hypoglycemia through the IRS1/GSK3β/Wnt3a-β-catenin pathway.
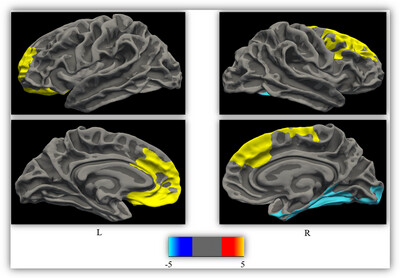
Surface-Based Morphometry Analysis of the Cerebral Cortex in Patients With Probable Idiopathic Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder
- First Published: 30 September 2024
The Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Was Associated With Intraplaque Neovascularization of the Carotid Artery on AngioPLUS
- First Published: 30 September 2024

The monocyte–lymphocyte ratio (MLR) is a hematological test parameter that reflects the status of both monocytes and lymphocytes as inflammatory cells. We found that elevated MLR is closely associated with the presence of high carotid intraplaque neovascularization (IPN) and may serve as a surrogate biomarker for carotid IPN.
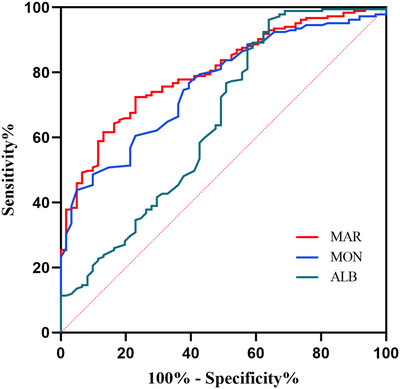
Monocyte-to-Albumin Ratio Is Associated With Hematoma Expansion in Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- First Published: 30 September 2024
Acute Augmented Effect of Virtual Reality (VR)–Integrated Relaxation and Mindfulness Exercising on Anxiety and Insomnia Symptoms: A Retrospective Analysis of 103 Anxiety Disorder Patients With Prominent Insomnia
- First Published: 30 September 2024
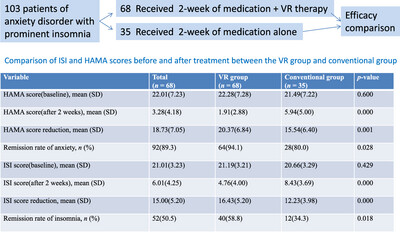
This explorative and retrospective study evaluated the effect of VR-integrated relaxation and mindfulness exercising in improving anxiety and insomnia symptoms in patients with anxiety disorders and prominent insomnia and indicated that 2-week augmented VR-integrated relaxation and mindfulness exercising is acutely beneficial for relieving both anxiety and insomnia.
Apathy and Impulsivity Co-Occur in Huntington's Disease
- First Published: 30 September 2024
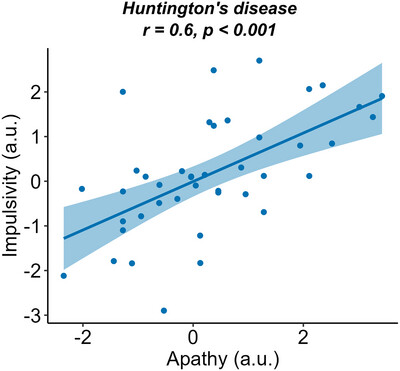
Morris et al. investigated the co-occurrence of apathy and impulsivity in Huntington's disease. These behavioral changes were significantly associated, and this association was not otherwise explained by cognition, mood, or motor disease severity. This suggests a common neurobiological mechanism underpinning these seemingly disparate behaviors—an important treatment target given their impact on wellbeing and life quality.
Diagnostic Value of Serum Apolipoprotein B100 Combined With Hippocampal Volume in Alzheimer's Disease
- First Published: 30 September 2024
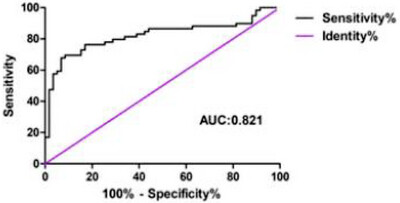
To explore the diagnostic value of serum apolipoprotein B100 (Apo B100) combined with hippocampal volume in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was plotted, and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated to compare the diagnostic efficacy of individual and combined detection of serum Apo B100 levels and hippocampal volume in AD. ROC curve analysis showed that the AUC of the combined serum Apo B100 level and hippocampal volume for AD was higher than that of either alone (AUC = 0.821, p < 0.01).
The Initial Clinical and Electrophysiological Characteristics of Different Subtypes of Guillain–Barré Syndrome Diagnosed Based on Serial Electrophysiological Examinations
- First Published: 30 September 2024
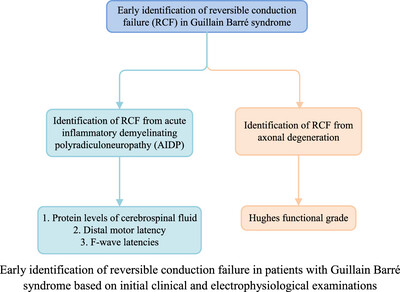
Our study aimed to identify reversible conduction failure (RCF) early in patients with Guillain–Barré syndrome based on initial clinical and electrophysiological examinations. The early identification of RCF from acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP) exhibits relatively distinct features, including protein levels in cerebrospinal fluid, distal motor latency, and F-wave latencies. However, differentiating RCF from axonal degeneration remains challenging, with the Hughes functional grade potentially serving as a distinguishing factor.
Causal Relationship Between Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Immune Cell Traits: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 30 September 2024
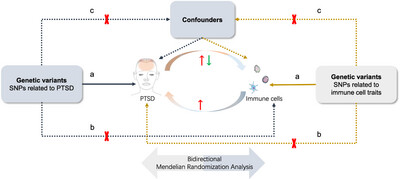
We explored the causal relationship between post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and immune cells using a Mendelian randomization study approach on the basis of publicly available genome-wide association studies (GWAS) data. The results revealed that PTSD affects some immune cell levels, whereas individual immune cells also increase the risk of developing PTSD. This demonstrates the complex relationship between PTSD and immune function.
REVIEW
Neurophysiological Basis of Electroacupuncture Stimulation in the Treatment of Cardiovascular-Related Diseases: Vagal Interoceptive Loops
- First Published: 30 September 2024
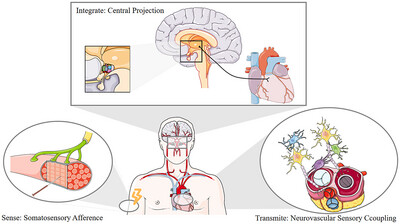
Mechanisms by which electroacupuncture (EA) drives vagal interoceptive to maintain cardiovascular activity. Vagal interoceptive can be a critical process for sensing, receiving, integrating, and down-transmitting information, which is crucial for sustaining physiological activities, including blood pressure homeostasis. EA can manage cardiovascular disease in multiple ways by stimulating sensory afferents, facilitating central integration, and modulating visceral efferents. The sensory nerve–muscle junction is postulated to play a pivotal role in mediating the component of EA stimulation that detects noxious information and initiates the subsequent signaling cascades. These signals are then synthesized by central nuclei, such as the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), before being relayed to cardiac tissue through the vagus nerve. The precise modulation of multimodal vagal endoreceptors is fundamental to the cardiovascular system's capacity to exhibit varied responses to the reception of EA stimuli, thereby facilitating a nuanced regulatory function in cardiovascular dynamics.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Mendelian Randomization Study Supports Genetic Liability to Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder Associated With the Risk of Alzheimer's Disease
- First Published: 30 September 2024
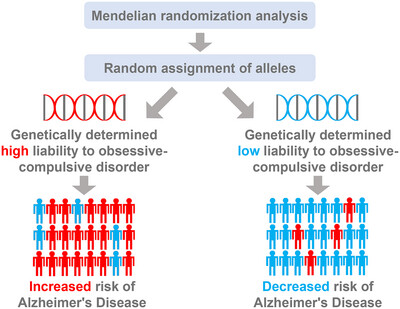
This study conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis based on genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics for obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). Using various MR methods and sensitivity tests, the study ultimately indicates that genetic liability to OCD is causally associated with an increased risk of AD.
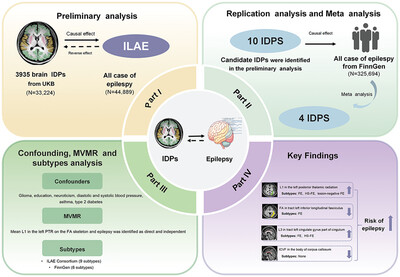
Brain imaging traits and epilepsy: Unraveling causal links via mendelian randomization
- First Published: 30 September 2024
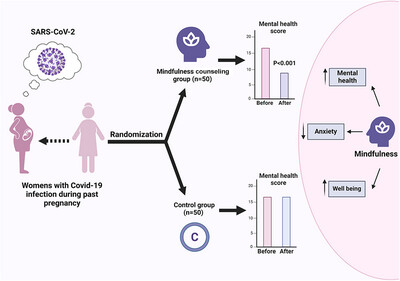
The Impact of Mindfulness-Based Counseling on the Mental Health of Women With a History of COVID-19 During Pregnancy: A Quasi-Experimental Study
- First Published: 30 September 2024
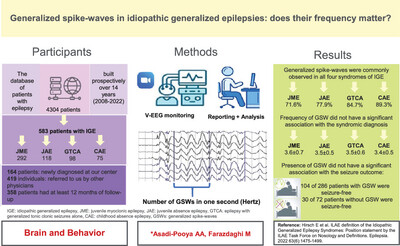
Generalized spike–waves in idiopathic generalized epilepsies: Does their frequency matter?
- First Published: 04 October 2024
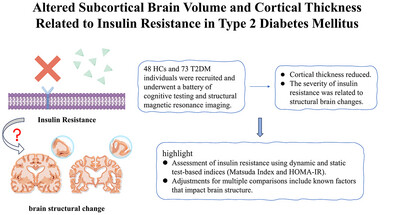
Altered Subcortical Brain Volume and Cortical Thickness Related to Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- First Published: 04 October 2024
Comparison of Clinical Effects and Physical Examination of Transforaminal and Caudal Steroid Injection With Targeted Catheter in Lumbar Radiculopathy: A Single-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
- First Published: 04 October 2024
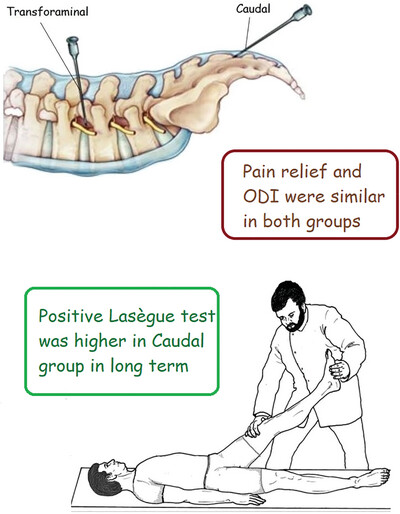
• Transforaminal and caudal steroid injection (with a targeted catheter) in lumbar radiculopathy had similar effects in controlling low back and radicular pain and improving functional disability in the short term. • The cases of positive Lasègue test recurrence in the long term in the caudal group may indicate the preference for the transforaminal approach.
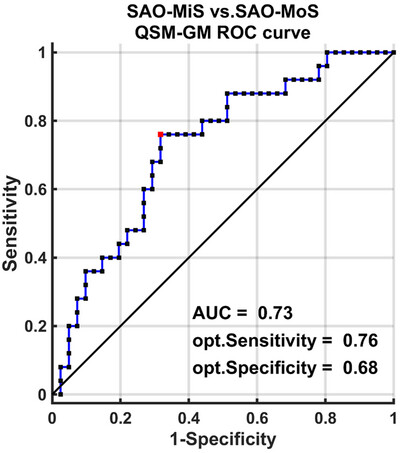
Combining Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping With the Gray Matter Volume to Predict Neurological Deficits in Patients With Small Artery Occlusion
- First Published: 04 October 2024
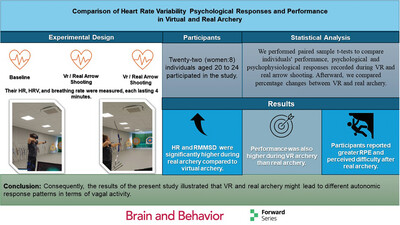
Comparison of Heart Rate Variability Psychological Responses and Performance in Virtual and Real Archery
- First Published: 08 October 2024
Characteristic Changes of Prefrontal and Motor Areas in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Major Depressive Disorder During a Motor Task of Tai Chi Chuan: A Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study
- First Published: 08 October 2024
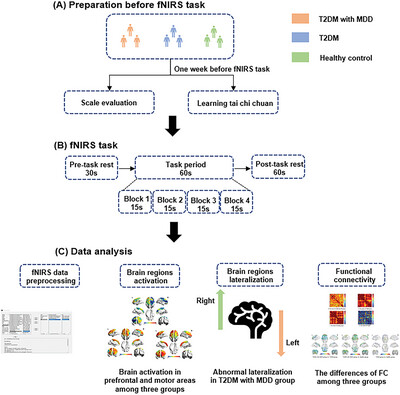
Schematic overview of the data analysis pipeline: (A) preparation before fNIRS task—including subject recruitment, scale evaluation, and learning tai chi chuan; (B) fNIRS task—subjects received fNIRS assessment when conducting tai chi chuan task; (C) data analysis—differences of activation, lateralization, and functional connectivity among three groups.
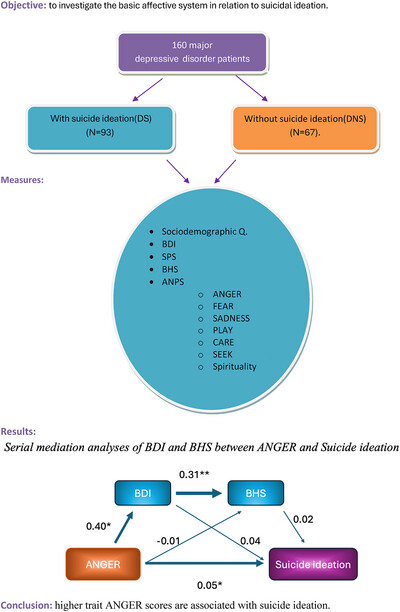
Why Do Some Depressive Patients Have Suicidal Ideation but Others Not? Suicidal Ideation From the Perspective of Affective Neuroscience Personality Traits
- First Published: 08 October 2024
The Relationship Between Attention and Suicidal Ideation Among Patients With Adult-Onset Chronic Schizophrenia
- First Published: 08 October 2024
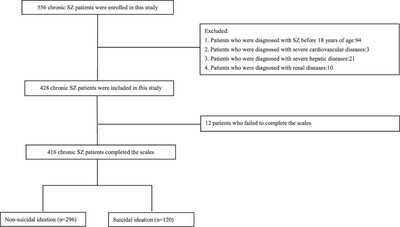
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to detect the relationship between distinct cognitive domains and suicidal ideation among patients with adult-onset chronic SZ. High attention scores of RBANS were a risk factor for suicidal ideation among patients with adult-onset chronic schizophrenia. It might help us clarify the underlying mechanism of suicidal ideation and provide a new proposal for reducing the occurrence of suicidal ideation.
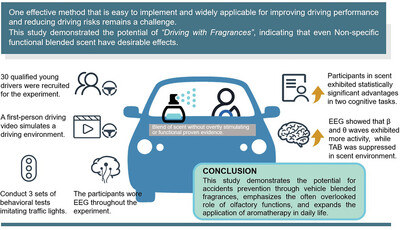
An Empirical Study on the Effect of Blended Scents in Driving Environments From a Neuro-Cognitive Perspective
- First Published: 08 October 2024
High Somatization Rates, Frequent Spontaneous Recovery, and a Lack of Organic Biomarkers in Post-Covid-19 Condition
- First Published: 08 October 2024
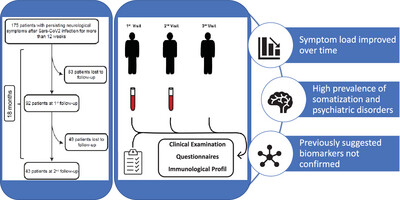
Numerous patients report neuropsychiatric symptoms following SARS-CoV-2 infection, with fatigue, stress intolerance, and cognitive deficits being predominant. In a cohort of 175 patients, 61% exhibited somatization, frequently accompanied by higher symptom load. Questionnaire assessments and self-reported symptom load showed a reduction in symptoms over time for the majority of patients. Biomarker testing did not support Epstein–Barr virus involvement, and cortisol levels remained within the normal range.
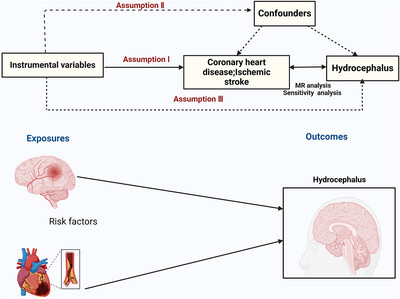
A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study of the Causal Association Between Ischemic Stroke, Coronary Heart Disease, and Hydrocephalus
- First Published: 08 October 2024
Loss of Control Eating in Adults With Impulsive and/or Inattentive Tendencies
- First Published: 08 October 2024
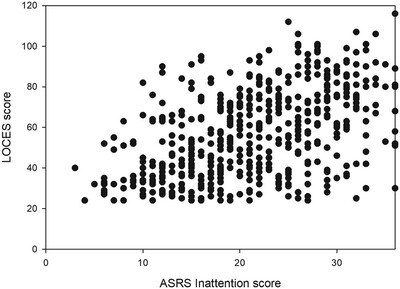
This study investigated the relationship between loss of control eating (LOC) and levels of inattentive and impulsive tendencies in adults. A sample of 516 adults was surveyed online about their inattentive and impulsive tendencies, LOC, and disordered eating (ED) behaviors. Findings revealed that levels of inattentive and, to a lesser extent, impulsive tendencies are significantly associated with LOC in adults, even after ED is accounted for. Inattentive tendencies were found to be more significantly associated with LOC than impulsive tendencies.
REVIEW
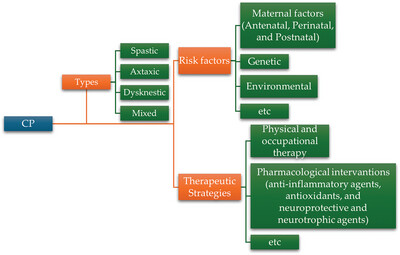
Neurobiological Insights Into Cerebral Palsy: A Review of the Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
- First Published: 08 October 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
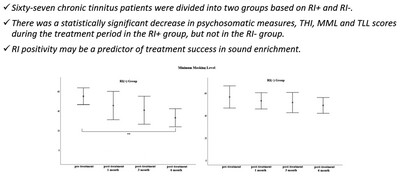
Can Residual Inhibition Predict the Success of Sound Enrichment Treatment for Tinnitus?
- First Published: 08 October 2024
REVIEW
Quantitative Electroencephalography Monitoring in Type A Aortic Dissection Surgery: A Clinical Case Review and Prospective Applications
- First Published: 08 October 2024
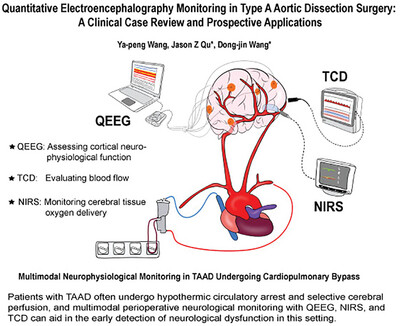
The crux of perioperative monitoring of TAAD lies in the continuous assessment of central nervous system function, which can be achieved through a multimodal approach encompassing NIRS for monitoring oxygen delivery, QEEG for evaluating neurological function, and TCD for assessing blood flow, with QEEG potentially aiding in the early detection of neurological abnormalities, though further research and development is warranted in this regard.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Evaluating the Effects of Different Cognitive Tasks on Autonomic Nervous System Responses: Implementation of a High-Precision, Low-Cost Complementary Method
- First Published: 08 October 2024
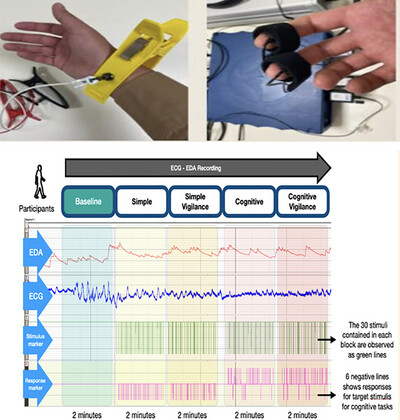
We developed a low-cost, user-friendly tool to evaluate autonomic nervous system (ANS) responses under varying cognitive workloads. Our study showed that this tool effectively induced cognitive load, significantly impacting skin conductance levels (SCL), reaction times (RTs), and heart rate variability (HRV). The findings validate the tool's effectiveness in assessing ANS responses, highlighting its potential for broader research applications.
The Role of Sex and Other Personal Characteristics in the Effects of Symptoms Severity on Self-Care Agency in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis
- First Published: 14 October 2024
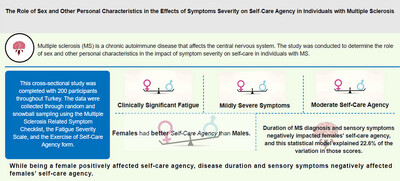
This study found that females with multiple sclerosis had better self-care agency compared to males, but disease duration and sensory symptoms negatively impacted their self-care. The findings emphasize the need for personalized care strategies considering sex differences in managing multiple sclerosis.
REVIEW
Effect of Acupuncture on Cognitive Function in Patients With Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 14 October 2024
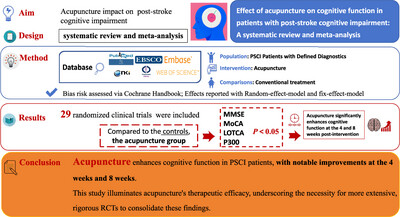
This study systematically reviewed and meta-analyzed randomized controlled trials to evaluate the impact of acupuncture on post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI). The analysis included 29 trials with 2477 participants, indicating that acupuncture could significantly improve cognitive function as measured by Mini-Mental State Examination and Montreal Cognitive Assessment scores, and enhance daily living abilities as shown by Barthel Index scores and P300 event-related potential. Subgroup analysis suggested that acupuncture was particularly effective at 4 weeks post-treatment. While promising, the study calls for future research with larger samples and longer treatment durations to solidify these findings.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
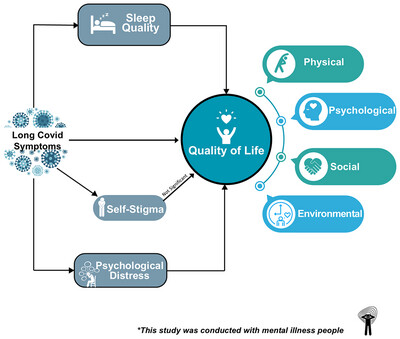
Parallel Mediating Effects of Sleep Quality, Psychological Distress, and Self-Stigma in the Associations Between Long COVID Symptoms and Quality of Life Among Taiwanese Individuals With Mental Health Illness
- First Published: 14 October 2024
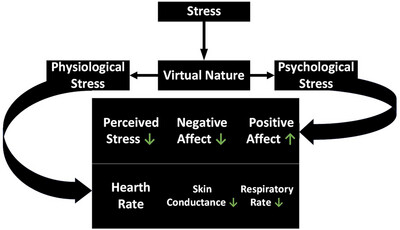
Effect of Relaxation-Based Virtual Reality on Psychological and Physiological Stress of Substance Abusers Under Detoxification: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- First Published: 14 October 2024
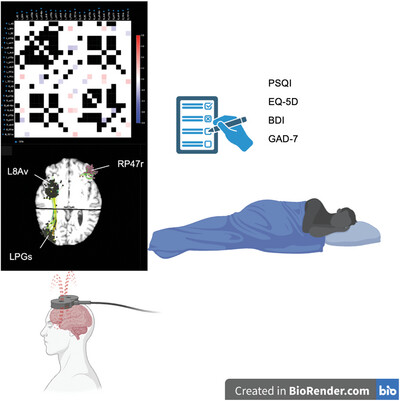
Improvements in Sleep Quality in Patients With Major Depressive and Generalized Anxiety Disorders Treated With Individualized, Parcel-Guided Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
- First Published: 17 October 2024
REVIEW
Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Values Quantification in Deep Gray Matter Structures for Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 17 October 2024
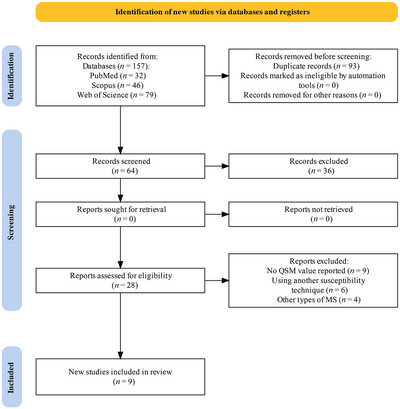
The study revealed that iron accumulation was significantly increased in the putamen, globus pallidus, and caudate nucleus of patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). However, quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) values did not show significant differences in the thalamus. Interestingly, younger RRMS patients (< 40 years) exhibited greater iron deposition in the putamen, globus pallidus, and caudate nucleus, while male populations (> 25%) showed higher iron deposition in the putamen and globus pallidus. Furthermore, QSM values were elevated in certain brain regions (putamen, globus pallidus, and caudate nucleus) during the early stages of RRMS but decreased in the thalamus during the later stages compared to healthy controls. These findings suggest that QSM could be a valuable biomarker for detecting neurodegeneration in RRMS.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Rehabilitation Response in Tremor- and Non-Tremor-Dominant Parkinson Disease: A Task-fMRI Study
- First Published: 17 October 2024
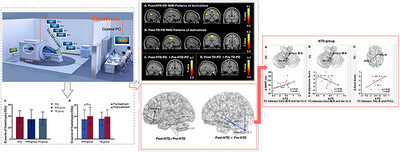
Changes of brain activation and functional connectivity were different in tremor-dominant and nontremor-dominant Parkinson's disease during foot tapping task after rehabilitation. TD-PD patients showed increased recruitments of the sensorimotor cortex and the bilateral thalamus after rehabilitation, and NTD-PD patients showed increased cerebellar activation and within-cerebellar connectivity that was associated with better motor performance.
Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio as an Indicator of Brain Activity Changes in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Resting-State fMRI Study
- First Published: 17 October 2024
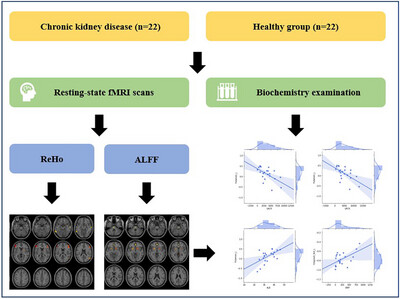
A cohort comprising 22 non–dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients and 22 healthy controls underwent resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans, coupled with biochemistry examinations. The amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFFs) and regional homogeneity (ReHo) were calculated. Notably, alterations within the bilateral putamen regions were identified through both ALFF and ReHo analyses. Furthermore, linear regression analyses revealed that urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR), as well as serum albumin levels were significantly associated with putamen activity.
Mental health and its consequences in people living with HIV: A network approach
- First Published: 20 October 2024
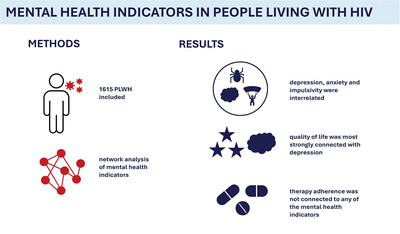
Psychiatric symptoms occur frequently in people living with HIV (PLWH). This study shows that in PLWH, depression, anxiety, and impulsivity are interrelated. Importantly, quality of life in PLWH is strongly connected to depression. However, we found no relation between any mental health indicator and the adherence to HIV treatment.
The Risk of Exacerbation of Myasthenia Gravis After COVID-19 Omicron Infection
- First Published: 20 October 2024
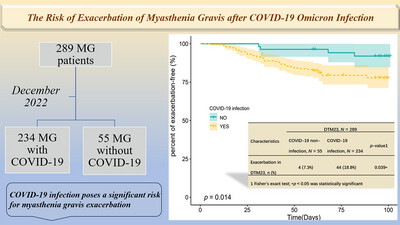
This retrospective cohort study employed questionnaires to investigate the COVID-19 infection status and exacerbation of myasthenia gravis (MG) patients after the relaxation of prevention and control measures in China. Statistical results demonstrate that COVID-19 infection poses a significant risk for MG exacerbation, compared to the MG group without COVID-19.
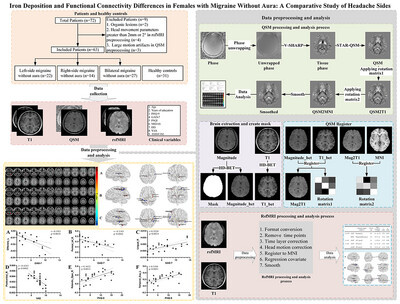
Iron Deposition and Functional Connectivity Differences in Females With Migraine Without Aura: A Comparative Study of Headache Sides
- First Published: 22 October 2024
Basilar Artery Tortuosity Increases the Risk of Persistent Dizziness and Unsteadiness After Posterior Circulation Infarction
- First Published: 22 October 2024
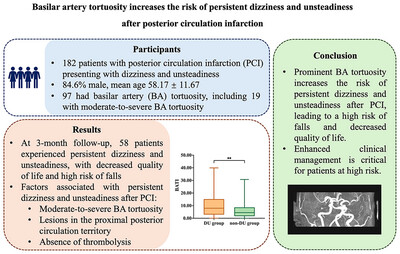
In this prospective study of 182 posterior circulation infarction (PCI) patients presenting with dizziness and unsteadiness, 31.9% reported persistent dizziness and unsteadiness at 3-month follow-up, associated with increased risk of fall and decreased quality of life. Prominent basilar artery tortuosity, proximal posterior circulation territory infarcts, and the absence of thrombolysis emerged as predictive factors. Targeted clinical management is essential for these high-risk patients after PCI.
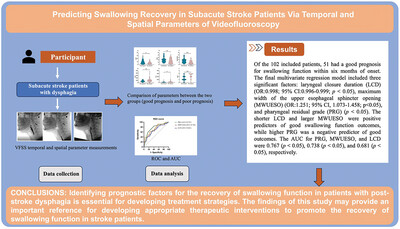
Predicting Swallowing Recovery in Subacute Stroke Patients via Temporal and Spatial Parameters of Videofluoroscopy
- First Published: 22 October 2024
REVIEW
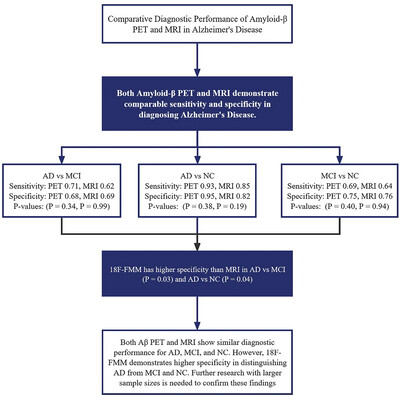
Comparative Diagnostic Performance of Amyloid-β Positron Emission Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Alzheimer's Disease: A Head-to-Head Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 22 October 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
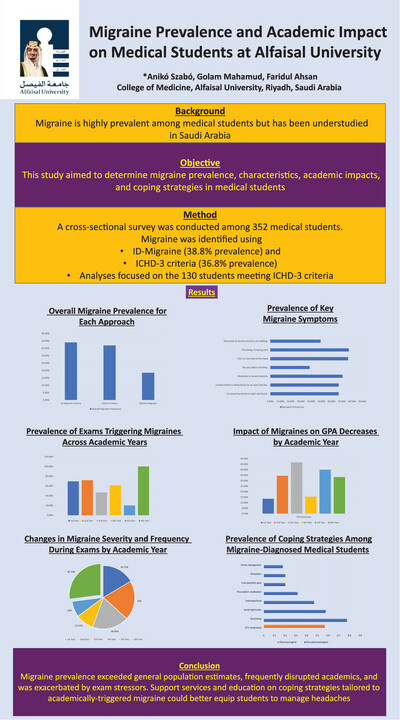
Migraine Prevalence and Academic Impact on Medical Students at Alfaisal University
- First Published: 23 October 2024
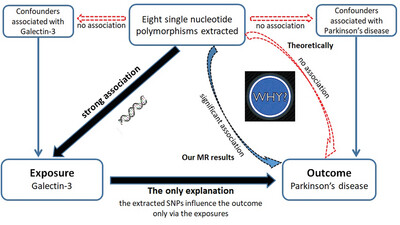
Association Between Serum Galectin-3 and Parkinson's Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 23 October 2024
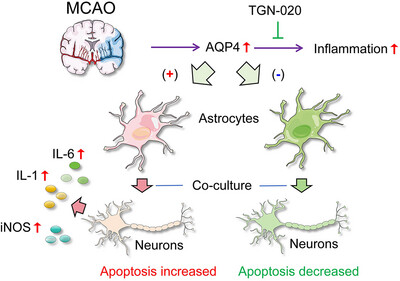
Neuroprotective Role of AQP4 Knockdown in Astrocytes After Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation
- First Published: 23 October 2024
The Activation of PKM2 Induces Pyroptosis in Hippocampal Neurons via the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD Pathway in Neonatal Rats With Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
- First Published: 23 October 2024
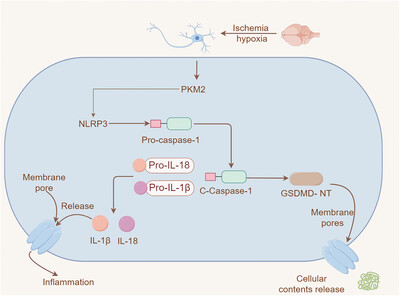
In this study, we observed an upregulation of PKM2 expression in the hippocampal tissues of the HIBD model. Inhibition of PKM2 resulted in a reduction of neuronal damage in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, alongside improvements in behavioral test outcomes and body weight gain in rats. Moreover, the inhibition of PKM2 mitigated neuronal pyroptosis possibly by downregulating the expression of NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD pathway (By Figdraw ID:TIAIPb2442) .
Altered Patterns of Maternal Behavior Transitions in Rats Exposed to Limited Bedding and Nesting Material Paradigm
- First Published: 23 October 2024
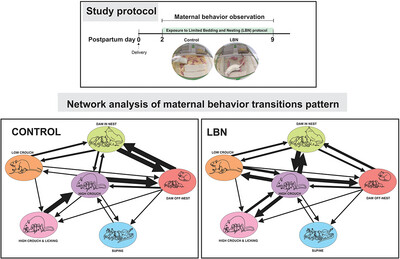
The limited bedding and nesting (LBN) protocol affects rat maternal behavior by increasing high crouch posture, reducing exits from the nest, and increasing behavioral transitions. Further network analysis shows that LBN primarily disrupts high crouch nursing (HG) posture and nest exits (OFF-nest) patterns of dams during early postpartum days.
Night Eating Syndrome Among University Students in Bangladesh: Investigation of Prevalence and Associated Factors
- First Published: 23 October 2024
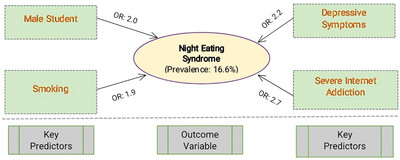
This cross-sectional study examined the prevalence and correlates of night eating syndrome (NES) among university students in Bangladesh (n = 500). The prevalence of NES among participants was 16.6%. Logistic regression revealed that male participants, smoking, depressive symptoms, and severe internet addiction were significantly associated with increased odds of experiencing NES. These findings underscore the need for heightened healthy eating awareness programs along with targeted mental health interventions for students attending Bangladeshi universities.
Effects of Goreisan in the Perioperative Period of Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson's Disease
- First Published: 28 October 2024
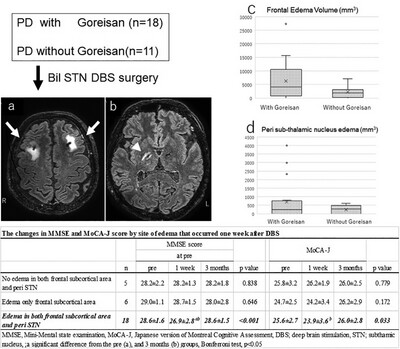
One week after deep brain stimulation surgery, edema occurred frequently around the leads. The frontal edema volume had significantly less edema in the group that used Goreisan. MMSE and MoCA-J scores at 1 week were significantly worse in the presence of edema in both frontal and peri-STN than preoperatively.
REVIEW
The Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Breast Cancer Patients and Survivors: A Systematic Review of Interventional Studies
- First Published: 28 October 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
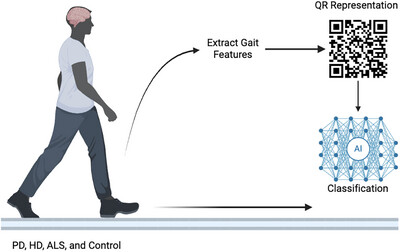
CNN-Based Neurodegenerative Disease Classification Using QR-Represented Gait Data
- First Published: 28 October 2024
Consensus-Based Guidelines for Communicating a Misdiagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis to Reduce Psychological Distress
- First Published: 28 October 2024
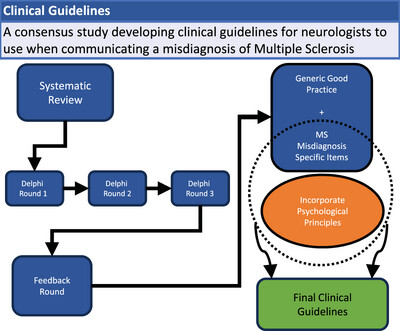
This consensus study used a modified Delphi technique to identify very important items to be considered for inclusion in clinical guidelines for communicating a misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS). Items identified as being specific to the MS misdiagnosis communication were embedded with psychological principles known to contribute to the therapeutic relationship between doctor and patient. The outcomes of this systematic process are seven recommendations for doctors to use when communicating a misdiagnosis to a patient in a psychologically-informed way that aims to reduce the distress for the patient and the doctor.