Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
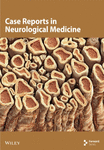
Assessment of swallowing performance in patients with neurodegenerative disease: A hierarchical cluster analysis
- First Published: 28 August 2024
This study uses hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) to examine the relationship between variables in major neurodegenerative diseases (MND) with swallowing disorders. Data were collected from 173 patients with neurological diagnoses, aging between 42 and 104. The results showed statistical significance in clusters around Edinburgh Feeding Evaluation Scale (EdFED), Eating Assessment Tool (EAT-10), and age in each MND. This study provides clinicians with a different perspective on determining and managing elderly swallowing problems, suggesting that variables should be examined concurrently in clinics for MND.
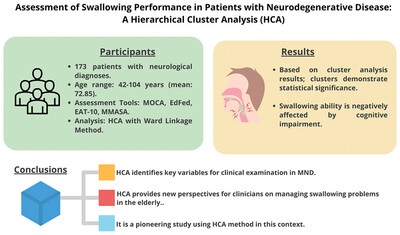
Risk of Parkinson's disease and depression severity in different populations: A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- First Published: 01 September 2024
The present study aimed to employ Mendelian randomization (MR) to investigate the causal relationship between Parkinson's disease (PD) and the risk of depression severity across different populations. Our findings indicate that the observed increased depression in PD patients is likely attributable to modifiable acquired factors rather than being genetically determined.
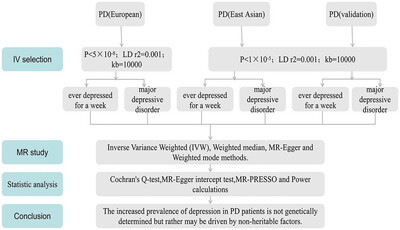
Conversion between the Rowland Universal Dementia Assessment Scale and Mini-Mental State Examination test scores in majority and minority populations
- First Published: 01 September 2024
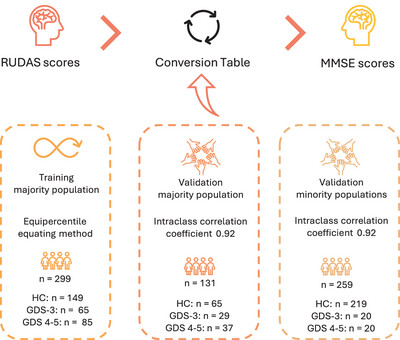
This study aimed to develop a conversion table to predict MMSE scores from observed RUDAS scores, allowing an easy-to-use method to compare both screening tests. The equipercentile equating method was used to develop the conversion table using a training sample consisting of cognitively intact participants and individuals with early-stage AD. The resulting conversion table was validated in two samples, comprising participants from majority and minority populations assessed in Spanish, showing excellent reliability.
The modulation of temporal predictability on attentional boost effect
- First Published: 01 September 2024
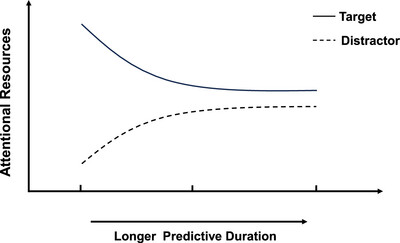
This study investigates the attentional boost effect (ABE) and its relationship with event predictability. Using encoding-recognition and remembering/knowing paradigms, it was found that short and medium predictive intervals enhance memory for target-paired words, while long intervals do not. Predictability alters task demands, allowing better allocation of attentional resources. Under short predictability, more attention is given to target stimuli, enhancing memory (ABE). Under long predictability, attention is distributed more broadly, reducing the ABE.
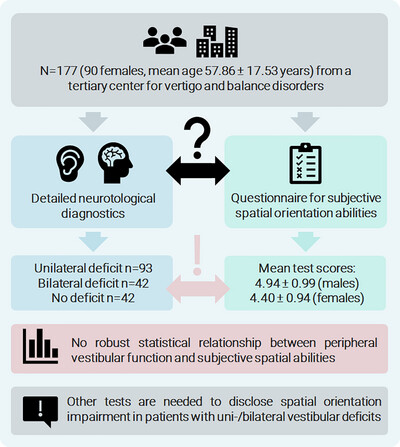
Unreliable association between self-reported sense of direction and peripheral vestibular function
- First Published: 08 September 2024
Lauric acid with or without levodopa ameliorates Parkinsonism in genetically modified model of Drosophila melanogaster via the oxidative–inflammatory–apoptotic pathway
- First Published: 08 September 2024
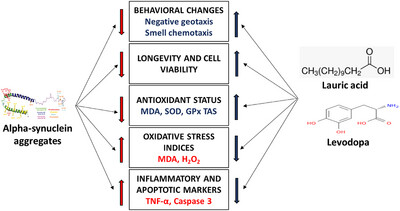
Lauric acid exhibits therapeutic potential in alpha-synuclein-mediated Parkinsonism by mitigating behavioral impairment, reducing oxidative stress, and curbing neuroinflammation. It also appears to counteract apoptosis and enhance neuronal longevity. These effects collectively suggest lauric acid could be a promising adjunctive treatment for Parkinson's disease.
Transforming text to music using artificial intelligence improves the frontal lobe function of normal older adults
- First Published: 05 September 2024
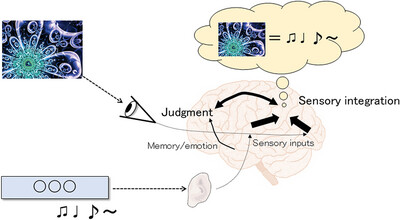
We investigated the effectiveness of an online meeting in which normal older adults (otokai) used a music-generative artificial intelligence (AI) that transforms text to music (Music Trinity Generative Algorithm-Human Refined [MusicTGA-HR]). Using MusicTGA-HR, the participants chose music that they thought was the most suitable to a given theme. Each class held an online meeting once a week for 6 months, and each participant presented the music they selected. As a result, the frontal lobe function and memory were improved.
Hypoperfusion of periaqueductal gray as an imaging biomarker in chronic migraine beyond diagnosis: A 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling MR imaging
- First Published: 05 September 2024
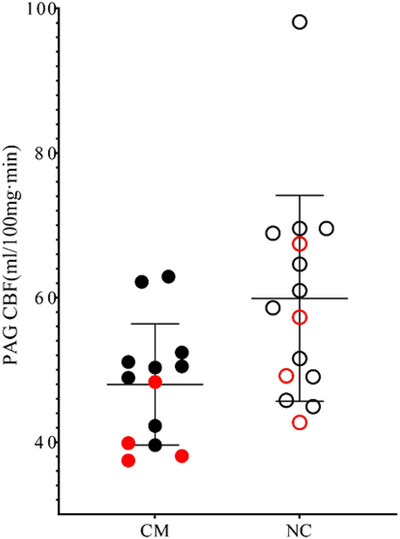
The cerebral blood flow (CBF) value of periaqueductal gray (PAG) in chronic migraine (CM) patients (47.98 ± 8.38 mL/100 mg min) was significantly lower than that of the control group (59.87 ± 14.24 mL/100 mg min). Red solid circle and empty circle, male CM and normal controls; Black solid circle and empty circle, female CM and normal controls.
Zuranolone therapy protects frontal cortex neurodevelopment and improves behavioral outcomes after preterm birth
- First Published: 05 September 2024
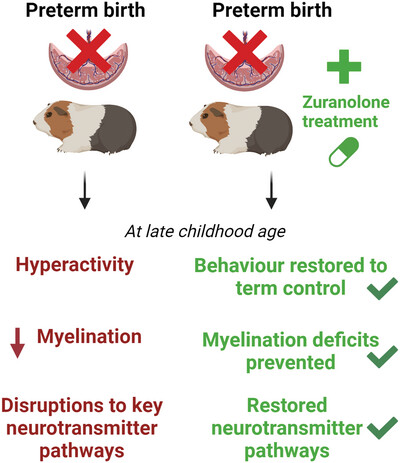
Preterm-born guinea pigs displayed hyperactive behavior, reduced myelin, and disrupted neurotransmitter pathway expression at late childhood equivalence. Treatment with zuranolone in the immediate postnatal period following preterm birth was able to prevent these deficits from occurring and restore behavioral abnormalities to a term-born phenotype.
A meta-analysis of the association between vasopressor use and intensive care unit-acquired weakness
- First Published: 05 September 2024
Relationships among tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels, beta-amyloid accumulation, and hippocampal atrophy in patients with late-life major depressive disorder
- First Published: 05 September 2024
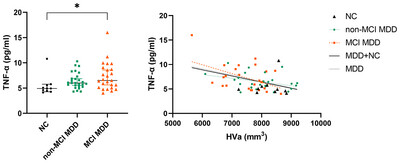
Patients with MDD and MCI exhibited higher TNF-α levels and reduced hippocampal volumes compared to controls. An inverse relationship was observed between TNF-α levels and hippocampal volume in the MCI MDD group, the overall MDD group, and across all subjects. No significant correlations were found between beta-amyloid deposition and TNF-α levels, hippocampal volume, or cognitive measures.
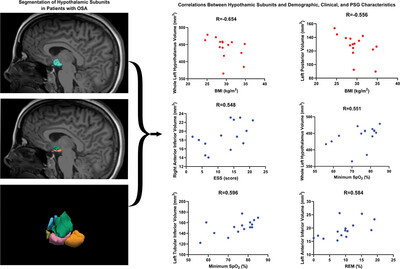
Volumetric analysis of the hypothalamic subunits in obstructive sleep apnea
- First Published: 05 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Effects of intracranial artery stenosis of anterior circulation on cognition—A CT perfusion-based study
- First Published: 05 September 2024
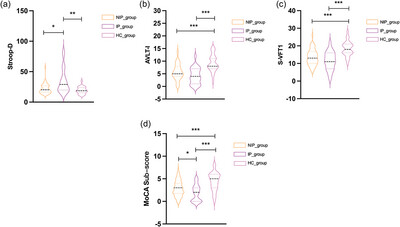
The results elucidate that executive, memory, and language function were better in ICAS patients without ischemic penumbra compared with the ischemic penumbra group. “b” and “c” show that there is no significant difference in memory and language function (p = .054; p = .06) between the non-ischemic penumbra group and the ischemic penumbra group. “a” and “d” show that there are statistical differences in Stroop-D and MoCA sub-items (memory + language) between the NIP and IP groups (p = .042; p = .046). Hence, this study suggests that controlling ICAS-induced hypoperfusion may be involved in the occurrence of VCI.
REVIEW
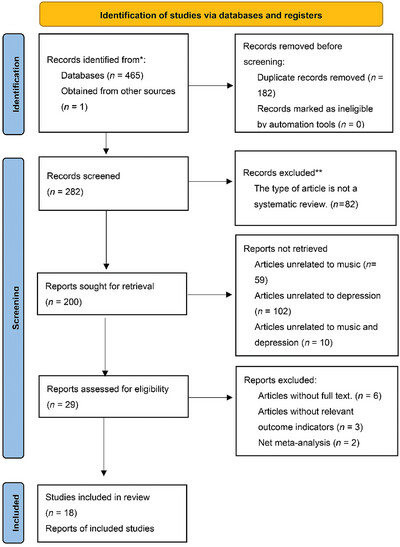
The safety and effectiveness of music medicine as an intervention for depression: A systematic evaluation and re-evaluation
- First Published: 11 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Simulated microgravity-induced dysregulation of cerebrospinal fluid immune homeostasis by disrupting the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier
- First Published: 11 September 2024
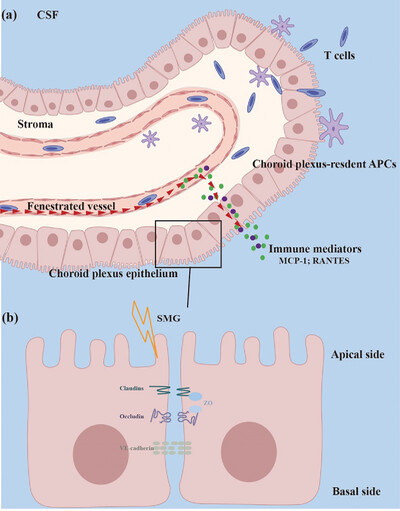
Disruption of blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier mediates altered cerebrospinal fluid immune homeostasis under simulated microgravity: a proposed model. Lymphocytes migrate from the choroid plexus microvasculature to the plexus stroma and then cross the choroid plexus epithelia, where they are locked by tight junctions and enter the cerebrospinal fluid. Simulated microgravity causes disruption of intercellular junctions, allowing more lymphocytes and cytokines to cross the choroid plexus epithelia and enter the cerebrospinal fluid.
Association of obesity indicators with cognitive function among US adults aged 60 years and older: Results from NHANES
- First Published: 11 September 2024
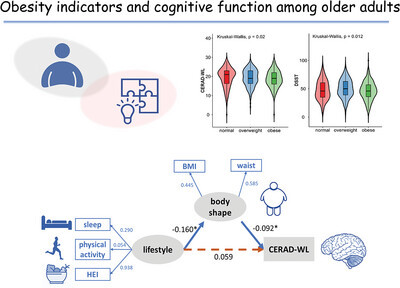
Obese subjects had lower scores in the CERAD word list learning tasks (CERAD-WL) and digit symbol substitution test (DSST). Body shape had a mediating effect on the path from lifestyle to cognition (CERAD-WL). Sleep, physical activity, and diet influenced the degree of obesity, which subsequently determined cognitive function.
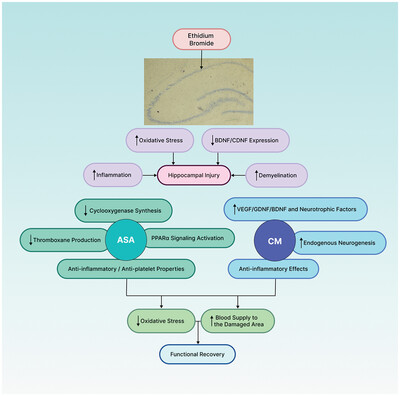
Exploring the impact of acetylsalicylic acid and conditioned medium obtained from mesenchymal cells, individually and in combination, on cognitive function, histological changes, and oxidant–antioxidant balance in male rats with hippocampal injury
- First Published: 11 September 2024
Pain neuroscience education and motor imagery-based exercise protocol for patients with fibromyalgia: A randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 11 September 2024
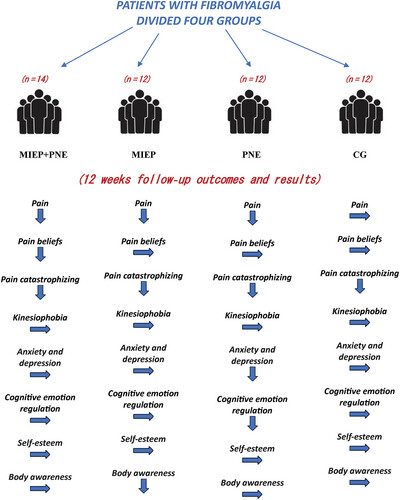
This study showed that the combined application of pain neuroscience education (PNE) and motor imagery-based exercise protocol (MIEP) had a reducing effect, although not superior, on pain, which is the primary outcome, compared to individual applications In particular, PNE was superior in reducing cognitive–emotion regulation, anxiety, and depression, and MIEP was superior in reducing body awareness. No intergroup superiority was found on pain catastrophizing, self-esteem, and kinesiophobia in the control and all intervention groups.
Association between geriatric nutritional risk index and cognitive function in older adults with/without chronic kidney disease
- First Published: 11 September 2024
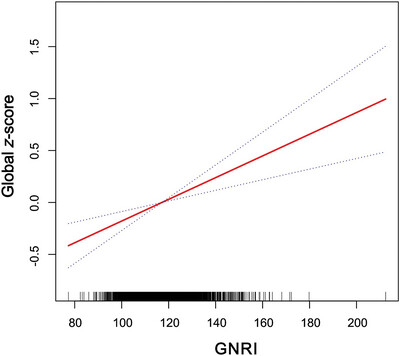
Lower levels of the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index (GNRI) are significantly associated with cognitive decline in the elderly population in the United States. GNRI may represent a new indicator for assessing cognitive health risks in the elderly. As a tool for evaluating the nutritional status of older adults, GNRI is cost-effective and easily obtainable in clinical practice.
C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a novel predictor for nutritional status of geriatric patients
- First Published: 11 September 2024
Acute treatment residual depression symptoms and functional impairment among depressive patients of different age groups and education levels in China: A prospective, multicenter, randomized study
- First Published: 11 September 2024
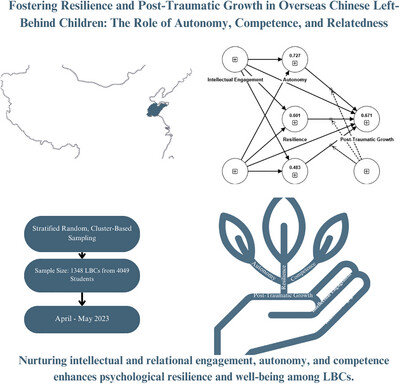
Fostering resilience and post-traumatic growth in overseas Chinese left-behind children: The role of autonomy, competence, and relatedness
- First Published: 11 September 2024
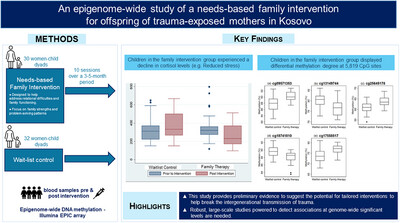
An epigenome-wide study of a needs-based family intervention for offspring of trauma-exposed mothers in Kosovo
- First Published: 11 September 2024
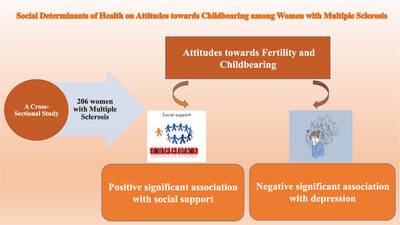
Social determinants of health on attitudes toward childbearing among women with multiple sclerosis: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 12 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Neurosarcoidosis: Clinical, biological, and MRI presentation of central nervous system disease in a national multicenter cohort
- First Published: 15 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
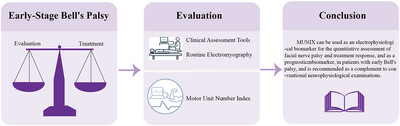
Motor unit number index in Bell's palsy: A potential electrophysiological biomarker for early evaluation
- First Published: 15 September 2024
Masking level differences under two different measurement conditions: A normative study of young adults
- First Published: 18 September 2024
Changes in the Firmicutes to Bacteriodetes ratio in the gut microbiome in individuals with anorexia nervosa following inpatient treatment: A systematic review and a case series
- First Published: 18 September 2024
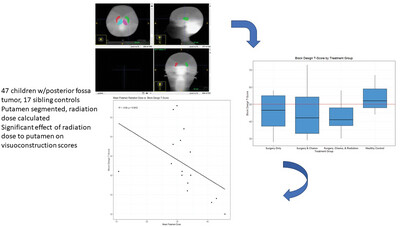
Dose-dependent cranial irradiation associations with brain structures and neuropsychological outcomes in children with posterior fossa brain tumors
- First Published: 18 September 2024
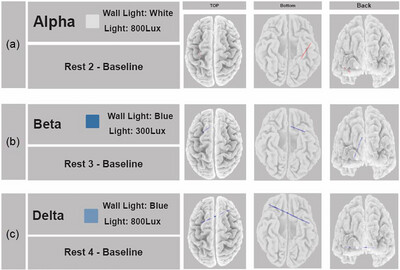
Color and brightness at work: Shedding some light on mind wandering
- First Published: 18 September 2024
Physical activity and frontoparietal network connectivity in traumatic brain injury
- First Published: 18 September 2024
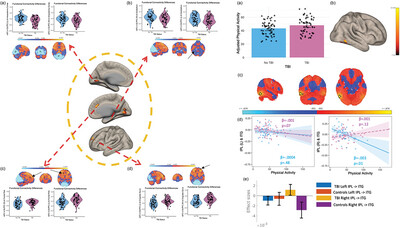
The objective of this study was to test if physical activity engagement was associated with functional connectivity of the cognitively relevant frontoparietal control network (FPCN) in adults with a traumatic brain injury (TBI) history. Individuals with a history of TBI show functional connectivity alterations of the FPCN. Moreover, engagement in physical activity is associated with functional network connectivity of the FPCN in those with a TBI. These findings are consistent with the evidence that physical activity affects FPCN connectivity in non-injured adults, however, this effect presents differently in those with a history of TBI.
Strategies to overcome mental health stigma: Insights and recommendations from young people with major depressive disorder (MDD)
- First Published: 18 September 2024
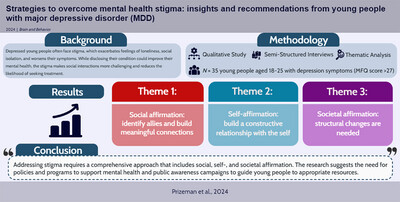
Stigma among depressed young people worsens loneliness, isolation, and symptoms, hindering social interactions and treatment. To break this cycle, 35 participant interviews recommended three forms of affirmation: social, self-, and societal affirmation. Public awareness campaigns, policies, and programs supporting mental health are crucial to guiding young people to appropriate resources.
Knowledge, attitude, and practice of depression among university students
- First Published: 18 September 2024
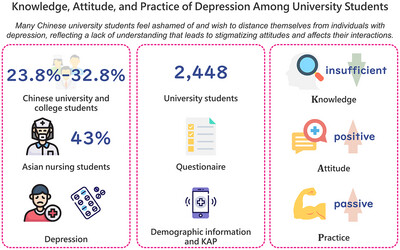
This research summarizes a survey of 2448 students from 14 universities in Shandong Province. The survey assessed knowledge, attitude, and practice toward depression. Results show insufficient knowledge, positive attitudes, and passive practices. Factors negatively affecting practice include being a junior or senior, having divorced parents, having relatives with depression, and lacking close friends. A positive attitude was strongly associated with better practices. The study highlights the need for targeted education and support to improve depression management among students.
Longitudinal DNA methylation in parent–infant pairs impacted by intergenerational social adversity: An RCT of the Michigan Model of Infant Mental Health Home Visiting
- First Published: 18 September 2024
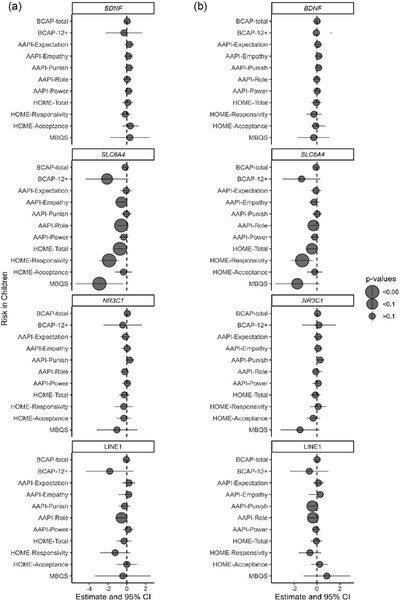
Families at greater risk for disruptions to the parent–child relationship received either weekly Infant Mental Health Home Visiting parent–infant psychotherapy or treatment as usual for 12 months. DNA methylation, which controls gene expression, was measured at stress responsive genes. Children's saliva DNA methylation at SLC6A4 and LINE1 was associated with parenting attitudes, and BDNF methylation also decreased in response to therapy.
Neuroprotective effects of salvianolic acids combined with Panax notoginseng saponins in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats concerning the neurovascular unit and trophic coupling
- First Published: 18 September 2024
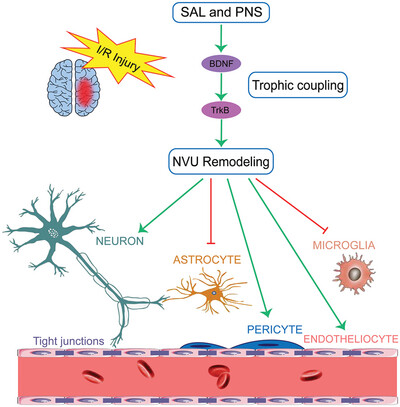
This study suggests that salvianolic acids and Panax notoginseng saponins can effectively repair cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Specifically, they improve trophic coupling damage and repair the structural and functional damage of neurons, microvascular endothelial cells, microglia, astrocytes, and pericytes in the neurovascular unit, promoting neurovascular unit remodeling. Compared with individual treatment, salvianolic acids combined with Panax notoginseng saponins treatment showed enhanced effects. This treatment method may be a potential strategy for repairing cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Subclinical hyperthyroidism and the risk of dementia: A meta-analysis
- First Published: 18 September 2024
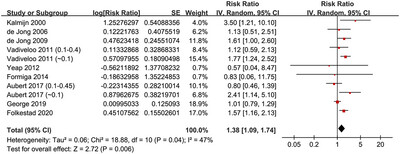
A meta-analysis incorporating nine cohort studies of 49218 community-derived participants showed that subjects with subclinical hyperthyroidism may have a higher risk of dementia compared to those with euthyroidism. These results highlight the importance of the evaluation of thyroid dysfunction in the risk stratification of dementia in the general population, even for those with subclinical hyperthyroidism.
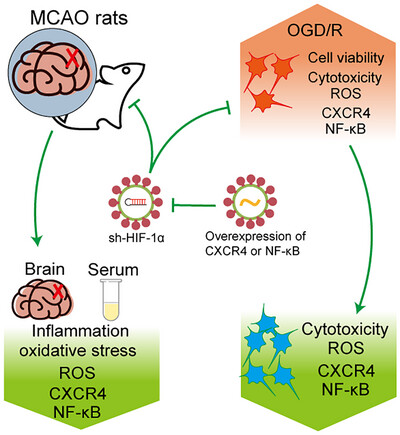
HIF-1α knockdown attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in ischemic stroke male rats via CXCR4/NF-κB pathway
- First Published: 18 September 2024
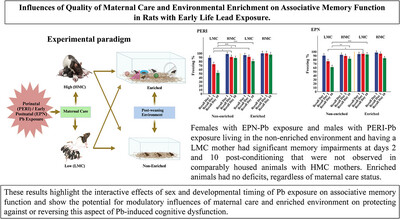
Influences of quality of maternal care and environmental enrichment on associative memory function in rats with early life lead exposure
- First Published: 18 September 2024
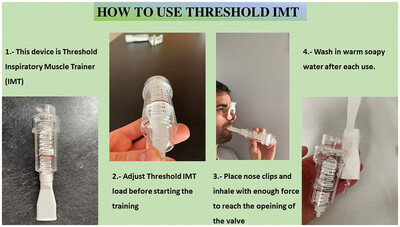
Benefits of inspiratory muscle training therapy in institutionalized adult people with cerebral palsy: A double-blind randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 18 September 2024
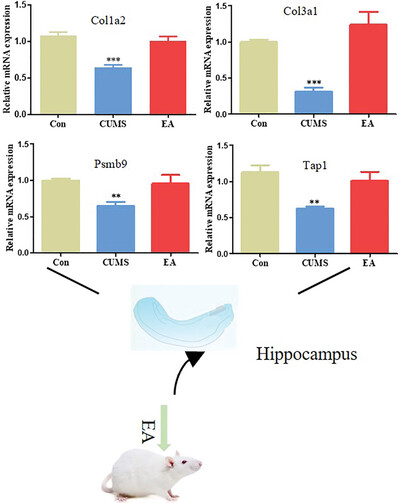
Transcriptome analysis of rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress treated with electroacupuncture
- First Published: 18 September 2024
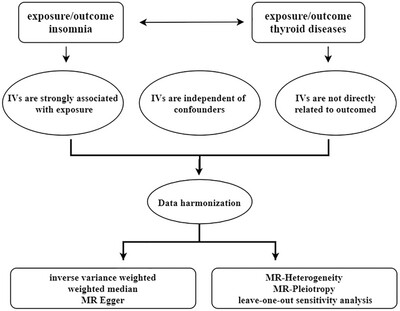
Causal relationship between insomnia and thyroid disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 18 September 2024
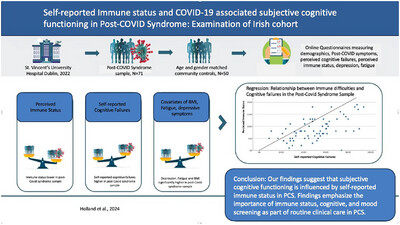
Self-reported immune status and COVID-19 associated subjective cognitive functioning in post-COVID-19 syndrome: Examination of an Irish cohort
- First Published: 24 September 2024
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Post-COVID dysphagia requires exclusion of SARS-CoV-2–associated brainstem encephalitis, vasculitis, polyneuritis cranialis, and myositis
- First Published: 24 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The relationship between menstrual cycle pattern and post-traumatic stress in women following the 2023 earthquake in Turkey
- First Published: 25 September 2024
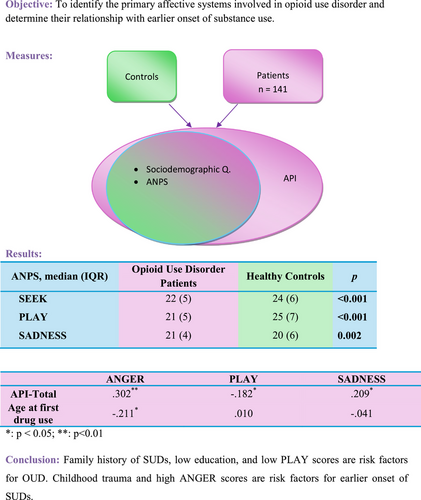
Affective neuroscience personality traits in opioid use disorder patients: The relationship with earlier onset of substance use, the severity of addiction, and motivational factors to quit opiate use
- First Published: 24 September 2024
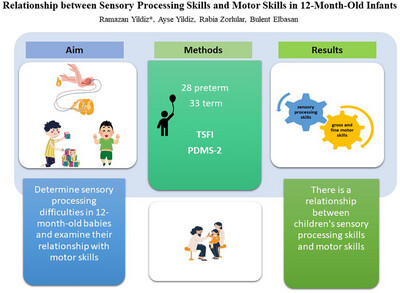
Relationship between sensory processing skills and motor skills in 12-month-old infants
- First Published: 24 September 2024
Effect of Motor Interference Therapy on Distress Related to Traumatic Memories: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Feasibility Trial
- First Published: 24 September 2024
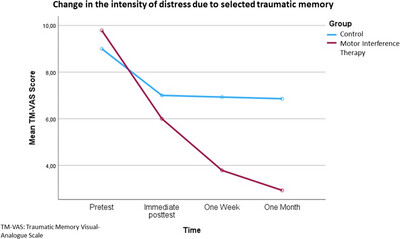
Decrease in perceived distress when recalling the traumatic memory (TM), measured through the visual analog scale for TM (TM-VAS). Participants who received motor interference therapy (red line) had a greater reduction in the distress generated by recalling the traumatic memory compared to the group that received progressive muscle relaxation (blue line).
Exploring the link between empathy, stress, altruism, and loneliness in university students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 25 September 2024
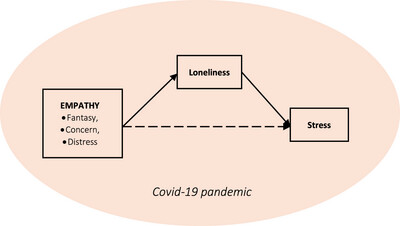
Our results support the idea that empathy is a multidimensional construct that may support and undermine individual mental health. Operationalizing empathy in terms of the Interpersonal Reactivity Index, we find that in times of social isolation different types of empathy increase the experience of individual loneliness and, by extension, stress.