Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
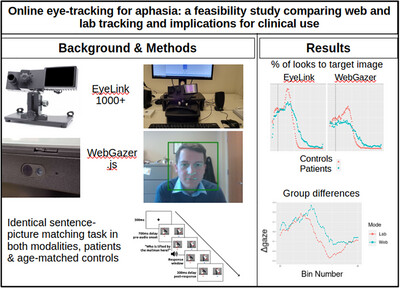
Online Eye Tracking for Aphasia: A Feasibility Study Comparing Web and Lab Tracking and Implications for Clinical Use
- First Published: 29 October 2024
The Role of Hearing Aids in Improving Dual-Task Gait Performance in Older Adults With Presbycusis: A Cognitive and Motor Analysis
- First Published: 31 October 2024
Correlation Between Regulation of Intestinal Flora by Danggui-Shaoyao-San and Improvement of Cognitive Impairment in Mice With Alzheimer's Disease
- First Published: 31 October 2024
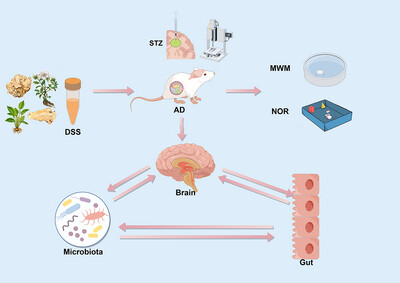
DSS regulated the gut microbiota of AD mice, improved the cognition of AD mice, reduced the deposition of pathological products of AD in the brain and colon, regulated the expression of proteins related to glucose metabolism, and improved the brain–colon barrier structure and neural ultrastructure of AD mice.
REVIEW
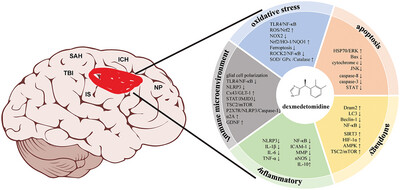
Progress on the Mechanisms and Neuroprotective Benefits of Dexmedetomidine in Brain Diseases
- First Published: 31 October 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Exploring the Association Between Cognitive Decline and Triglyceride-Glucose Index: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 31 October 2024

The role of insulin resistance and triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) has been investigated in cognitive decline and dementia. Based on 17 included studies, patients with cognitive decline had significantly higher levels of TyG index compared to controls. TyG, as a surrogate marker of insulin resistance, could be a potentially useful biomarker in dementia and cognitive decline.
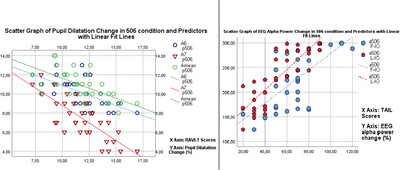
Investigating Sensitivity to Auditory Cognition in Listening Effort Assessments: A Simultaneous EEG and Pupillometry Study
- First Published: 31 October 2024
REVIEW
The Basis of Cognitive and Behavioral Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- First Published: 05 November 2024
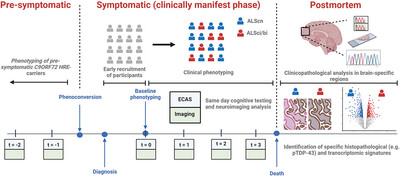
This review examines the clinical, pathological, and imaging associations of cognitive and behavioral dysfunction in ALS, with a critique of recent longitudinal studies. It advocates for more robust protocols for assessing clinicopathological correlates of neuropsychological abnormalities in the future, particularly using pre-symptomatic C9orf72 repeat expansion-carrying cohorts.
BRIEF REPORT
Cannabidiol Treatment for Adult Patients with Drug-Resistant Epilepsies: A Real-World Study in a Tertiary Center
- First Published: 05 November 2024
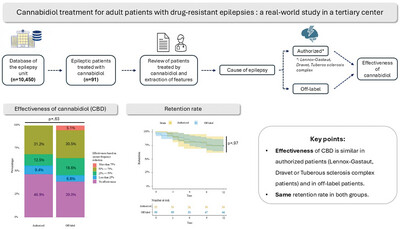
We extracted all adult patients treated at our tertiary center with cannabidiol for pharmacoresistant epilepsy, with a follow-up of at least 1 year, and evaluated the efficacy and retention based on the indication. We found similar efficacy and retention rates in patients with Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, Dravet syndrome, and tuberous sclerosis complex compared to other forms of pharmacoresistant epilepsy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Association Between Dietary Fiber Intake and Sleep Disorders: Based on the NHANES Database
- First Published: 05 November 2024
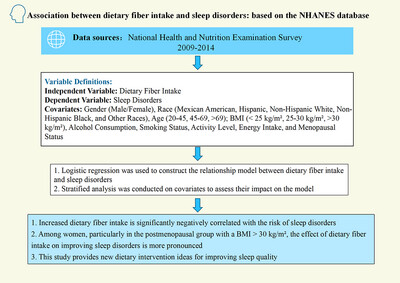
This study utilizes data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) conducted between 2009 and 2014 to explore the association between dietary fiber intake and sleep disorders. The independent variable is dietary fiber intake, while the dependent variable is sleep disorders. Logistic regression analysis was employed to construct a relationship model between dietary fiber intake and sleep disorders, and stratified analysis was conducted on covariates to assess their impact on the model. The results indicate that increased dietary fiber intake is significantly negatively correlated with the risk of sleep disorders. Among women, particularly in the postmenopausal group with a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2, the effect of dietary fiber intake on improving sleep disorders is more pronounced. This study provides new dietary intervention ideas for improving sleep quality.
Levels and Predictors of Suicide Literacy and Suicide Stigma in Spanish-Speaking Individuals
- First Published: 05 November 2024

Lower levels of suicide literacy were significantly correlated with higher suicide stigma, particularly among individuals with stronger religious or spiritual beliefs. Factors such as older age, stronger religious or spiritual beliefs, and being male were associated with lower suicide literacy and higher suicide stigma. The research highlights that Latin Americans reported higher levels of suicide glorification, emphasizing the need for culturally sensitive interventions to address suicide stigma and improve suicide literacy.
REVIEW
A Remedy for Crime? A Systematic Review on the Effects of Pharmacological ADHD Treatment on Criminal Recidivism and Rehabilitation in Inmates With ADHD
- First Published: 07 November 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
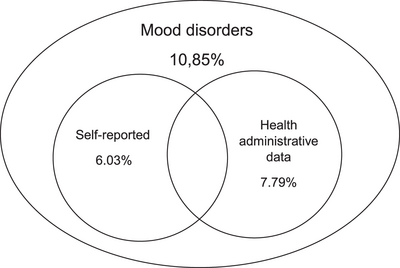
Identification of Mood Disorders in Self-Reported Versus Health Administrative Data
- First Published: 07 November 2024
Associations of Dietary Intake of Vitamin B6 and Plasma Pyridoxal 5′-Phosphate Level With Depression in US Adults: Findings From NHANES 2005–2010
- First Published: 07 November 2024

The intake of vitamin B6 in the diet seems to be related to the occurrence of depression. This relationship is not simply linear, but reveals different effects of intake at certain levels through restrictive splines (RCS). Specifically, a negative linear coefficient (−0.9954) indicates that as vitamin B6 intake increases, the risk of depression decreases within a certain range, but this decrease is not a linear decline. The nonlinear coefficient (0.9200) indicates that after a certain intake, the decrease in depression risk may tend to stabilize or reverse, that is, excessive intake of vitamin B6 may no longer continue to reduce depression risk, and may even increase. This result indicates that the relationship between plasma pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) levels and depression is nonlinear. Although an increase in PLP levels is slightly negatively correlated with the risk of depression, the effect is very small (linear coefficient of −0.02734), and at higher levels of PLP, the risk may slightly increase (nonlinear coefficient of 0.03954).
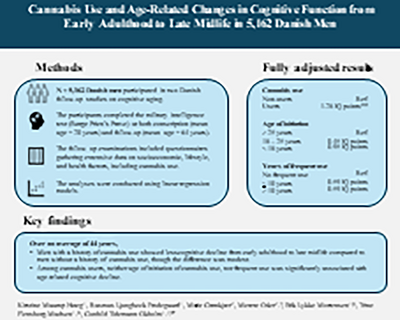
Cannabis Use and Age-Related Changes in Cognitive Function From Early Adulthood to Late Midlife in 5162 Danish Men
- First Published: 07 November 2024
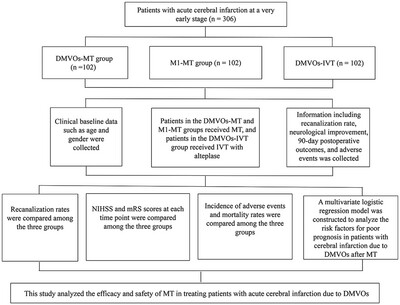
Mechanical Thrombectomy for Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction due to Distal Medium Vessel Occlusions: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 07 November 2024
REVIEW
Effect of Dual-Site Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation on Upper-Limb Function After Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 07 November 2024
This meta-analysis evaluates the efficacy of dual-site non-invasive brain stimulation (DS-NIBS) in improving upper extremity motor function after stroke. The analysis included 10 trials with 426 participants, indicating that DS-NIBS showed higher efficacy on post-stroke upper extremity motor function impairment compared to the sham and single-NIBS. Additionally, dual-site repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation was found to generate better improvement than dual-site transcranial direct current stimulation.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Association Between the Fetal-Type Posterior Cerebral Artery and Hypertensive Thalamic Hemorrhage
- First Published: 07 November 2024
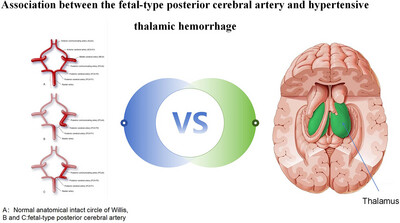
We found that the FTP (p = 0.003, odds ratio [[OR]: 2.712, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.407-5.225) and homocysteine levels (p = 0.007; OR: 1.051; 95% CI: 1.014-1.089) were significantly correlated with the occurrence of HTH. Early recognition and appropriate monitoring are warranted for cases of FTP.
Rhynchophylline Alleviates Hyperactivity and Cognitive Flexibility Impairment Associated With Inhibition of Inflammatory Responses in Mice That Partly Lack the Dopamine Transporter Protein
- First Published: 11 November 2024
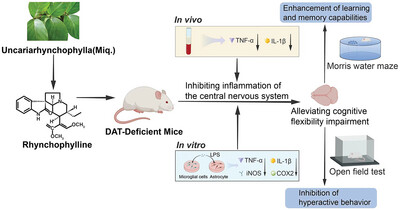
(1) RHY reduced hyperactivity and improved cognitive flexibility in DAT-deficient mice. (2) RHY inhibited inflammatory factor expression in vivo (TNF-α, IL-1β) and in vitro (TNF-α, IL-1β, iNOS, COX-2). (3) This study suggests RHY's therapeutic potential for neuropsychiatric disorders involving dopamine transporter deficiency through anti-inflammatory effects.
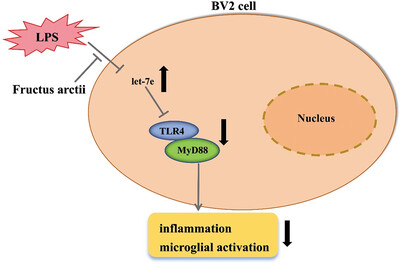
Fructus Arctii Mitigates Depressive Disorder via the Let-7e-Modulated Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 13 November 2024
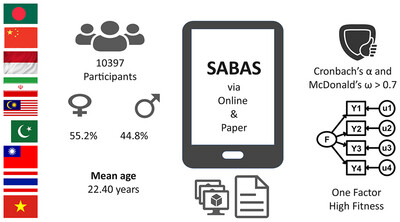
Smartphone Application-Based Addiction Scale: Psychometric Evidence Across Nine Asian Regions Using Advanced Analytic Methods
- First Published: 17 November 2024
Active and Passive Offline Breaks Differentially Impact the Consolidation of Procedural Motor Memories in Children and Adults
- First Published: 17 November 2024
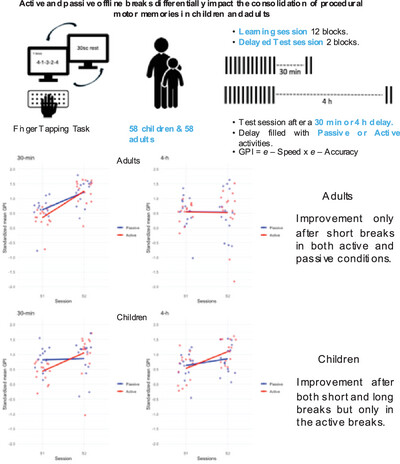
This study examined the impact of post-learning breaks on procedural motor memory in adults and children. Results revealed spontaneous post-learning motor performance improvements at both short and long delays in children, but only in the active post-training condition, unlike adults who showed improvements only at short delays, regardless of activity type. This suggests developmental differences in offline conditions (duration and activity) linked to plasticity mechanisms underlying procedural motor memory consolidation.
REVIEW
A Methodological Quality Assessment of Meta-Analyses on Sleep Disorder Treatments Using AMSTAR 2
- First Published: 17 November 2024
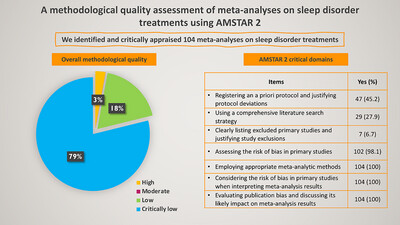
The methodological quality of recent meta-analyses on sleep disorder treatments is unsatisfactory, with the majority rated as critically low. Greater attention should be paid to providing a list of excluded studies with justifications for exclusions, using a comprehensive literature search strategy, registering a protocol prior to conducting reviews, and justifying any protocol deviations.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Transcranial Doppler as a Primary Screening Tool for Detecting Right-to-Left Shunt in Cryptogenic Stroke Patients?
- First Published: 17 November 2024
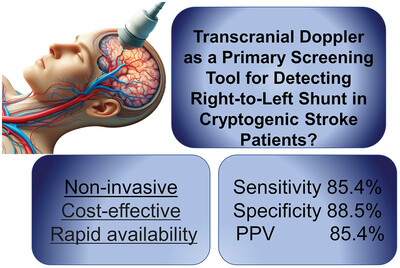
TCD exhibited high diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for detecting high-risk PFO in patients with CS when compared to the gold-standard TEE. As a noninvasive modality, TCD may serve as an effective screening tool to identify CS patients who could potentially benefit from confirmatory TEE and subsequent PFO closure intervention.
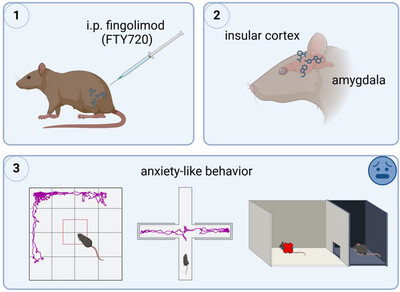
Behavioral Analyses in Dark Agouti Rats Following Repeated Systemic Treatment With Fingolimod (FTY720)
- First Published: 17 November 2024
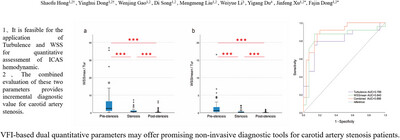
Evaluation of Carotid Stenosis in a High-Stroke-Risk Population by Hemodynamic Dual-Parameters Based on Ultrasound Vector Flow Imaging
- First Published: 17 November 2024
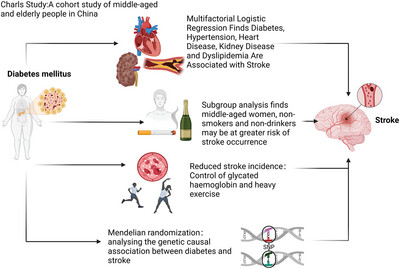
Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Future Stroke: Evidence From CHARLS and Mendelian Randomization Analyses
- First Published: 17 November 2024
Acceptability and Feasibility of Using Hair Samples for Chronic Stress Measurement Among Transgender Women in Brazil
- First Published: 17 November 2024
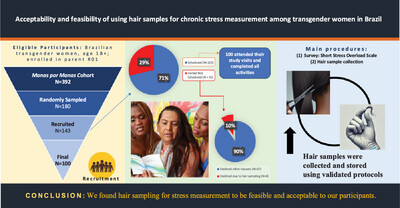
Hair has promising benefits as a chronic stress biometric, and research with this novel method is burgeoning, yet rarely involves transgender (“trans”) people, despite high levels of reported stress from experiences of stigma and discrimination. Since hair is a key part of gender presentation, trans women might be more hesitant than cisgender women to donate hair for research. To explore the feasibility and acceptability of hair collection with trans women, we nested a study into an ongoing clinical trial in São Paulo, Brazil, “Manas por Manas” (Sisters for Sisters). We randomly selected a subsample (n = 180) from the Manas cohort (n = 392. We invited 143 trans women to participate, of whom 100 attended their study visits and completed all activities. Of those who declined participation, only four individuals said it was because of the hair sample collection. Given these results, we found hair sampling for stress measurement to be feasible and acceptable.
The COVID-19 Pandemic and Its Influence on Patients With Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1: Lessons Learned
- First Published: 17 November 2024

The occurrence and effects of COVID-19 in a myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) population (n = 195) were studied. We found DM1 patients were more susceptible to complicated COVID-19 disease. However, patient-reported longitudinal data on physical functioning suggested that the COVID-19 pandemic did not influence the course of disease in DM1.
Accelerating Brain MR Imaging With Multisequence and Convolutional Neural Networks
- First Published: 17 November 2024
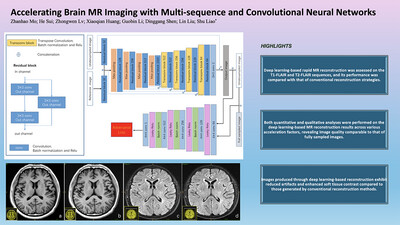
Deep learning-based rapid MR reconstruction was assessed on the T1-FLAIR and T2-FLAIR sequences, and its performance was compared with that of conventional reconstruction strategies. Both quantitative and qualitative analyses were performed on the deep learning-based MR reconstruction results across various acceleration factors, revealing image quality comparable to that of fully sampled images. Images produced through deep learning-based reconstruction exhibit reduced artifacts and enhanced soft tissue contrast compared to those generated by conventional reconstruction methods.
Neurofilament Light Chain Is Associated With Acute Mountain Sickness
- First Published: 17 November 2024
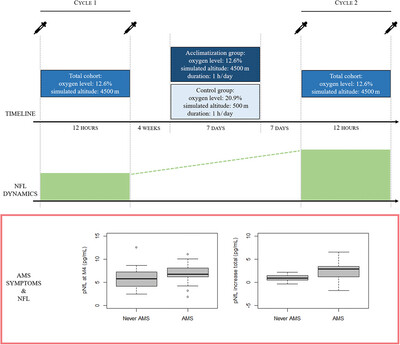
Healthy subjects were exposed to simulated high altitude (4500 m) two times, i.e., within Cycle 1 and Cycle 2, the latter with a random assignment to prior acclimatization or sham acclimatization. Before and after each cycle, pNfL was measured. pNfL levels increased over the total study period. Subjects suffering from AMS during the study procedures showed higher pNfL levels at M4 and a higher total pNfL increase.
REVIEW
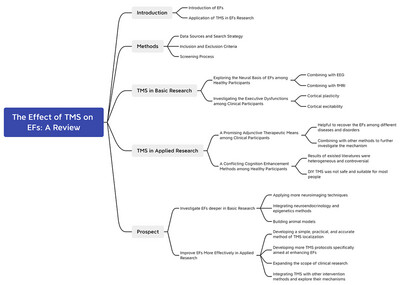
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Applications in the Study of Executive Functions: A Review
- First Published: 25 November 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Exploring the Relationship of Smartphone Addiction on Attention Deficit, Hyperactivity Symptoms, and Sleep Quality Among University Students: A Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 22 November 2024
EEG Spectral Power Changes in Patients With Dysexecutive Syndrome Following Cognitive Intervention
- First Published: 22 November 2024
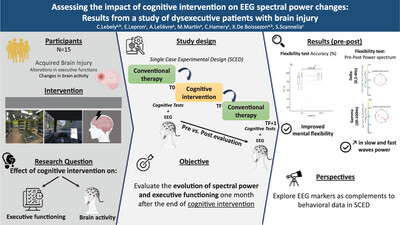
This study investigates the effects of cognitive rehabilitation on brain activity and executive functioning in patients with acquired brain injury (ABI). EEG recordings and performance on the Test of Attentional Performance (TAP) were analyzed before and one month after an ecological rehabilitation intervention. Results show significant improvements in executive functioning, particularly in mental flexibility (FL), as evidenced by faster reaction times and higher correct response rates. Additionally, EEG analysis revealed increased power in slow and fast frequency bands (delta, theta, gamma) during cognitive tasks, reflecting changes in brain activity associated with the intervention. These findings suggest cognitive rehabilitation may enhance compensatory mechanisms in brain function post-injury.
Disrupted White Matter Topology Organization in Preschool Children with Tetralogy of Fallot
- First Published: 22 November 2024
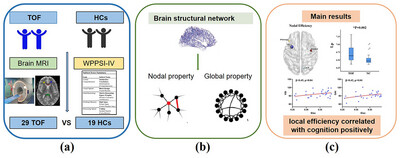
Schematic diagram of the study. Population enrollment and data collection (a). Construction and analysis of brain structure network (b). The main results of the study (c). TOF = Tetralogy of Fallot; HC = Health control; MRI = Magnetic resonance imaging; WPPSI-IV = the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence—fourth edition.
Clustering Electrophysiological Predisposition to Binge Drinking: An Unsupervised Machine Learning Analysis
- First Published: 22 November 2024
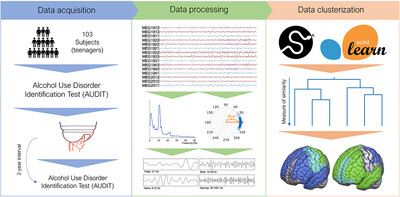
Electrophysiological activity in certain brain networks, characterized by unsupervised machine learning, predispose certain adolescents to develop heavy drinking patterns in later years. The clustering of these functional networks in the brain allows us to understand risk factors in society, as well as to program new forms of prevention.
REVIEW
Detailed Analysis of the Palmomental Reflex and Its Clinical Significance
- First Published: 22 November 2024
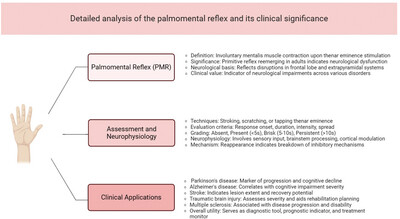
The palmomental reflex, a primitive reflex typically absent in adults, reemerges in various neurological disorders. Its presence and characteristics offer valuable insights for diagnosis, disease progression assessment, and treatment monitoring across conditions such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
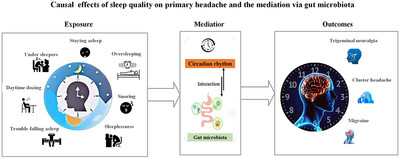
Causal Effects of Sleep Quality on Primary Headache and the Mediation via Gut Microbiota: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 28 November 2024
Patients' Characteristics Associated With Size of Ruptured and Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms
- First Published: 28 November 2024

In a large cohort study, multiple putative size risk factors (RF) for ruptured/unruptured intracranial aneurysms could be identified. To facilitate future reporting of research and treatment, we propose hereby a comparable risk chart system, which is here used for the identified RF ([i] stabilizing/protective factors (turquoise), [ii] destabilizing factors (potentially growth-promoting) (pink), and [iii] destabilizing factors (potentially rupture-promoting).
Resting-State Electroencephalogram Complexity Is Associated With Oral Ketamine Treatment Response: A Bayesian Analysis of Lempel–Ziv Complexity and Multiscale Entropy
- First Published: 28 November 2024
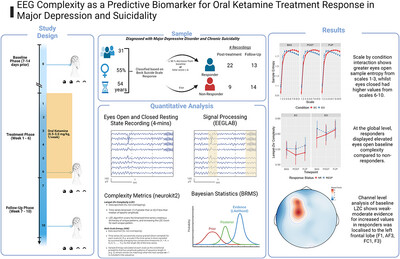
EEG-complexity metrics may be sensitive biomarkers for evaluating and predicting oral-ketamine treatment response. These findings underscore the value in evaluating both eyes open and closed conditions, and indicate elevated baseline eyes open complexity in the left pre-frontal cortex may predict a favourable oral-ketamine treatment response.
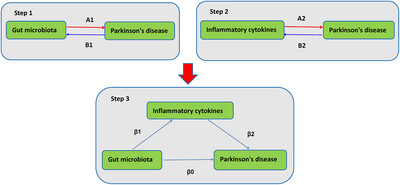
Dissecting Causal Links Between Gut Microbiota, Inflammatory Cytokines, and Parkinson's Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 28 November 2024
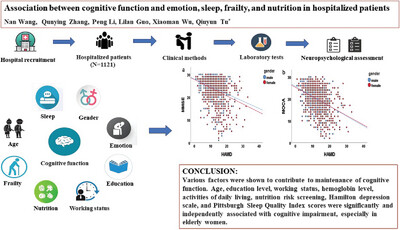
Association Between Cognitive Function and Emotion, Sleep, Frailty, and Nutrition in Hospitalized Patients
- First Published: 28 November 2024
Antidepressant- and Anxiolytic-Like Effect of the Froriepia subpinnata Extract in the Rat: Neurochemical Correlates
- First Published: 28 November 2024
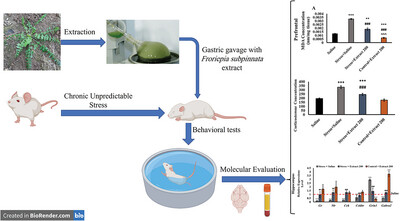
The potential antianxiety and antidepressant effects of Froriepia subpinnata were explored. Behavioral tests, including the elevated plus-maze, open field, sucrose preference, Morris water maze, and passive avoidance, were conducted. Real-time PCR was employed to examine changes in the expression of candidate genes associated with stress response and memory. Oxidative stress markers and corticosterone levels in serum were measured.