Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Evolutionary Insight and Expression Pattern of WUSCHEL-Related Homebox Genes of Dendrobium huoshanense
- First Published: 23 February 2025
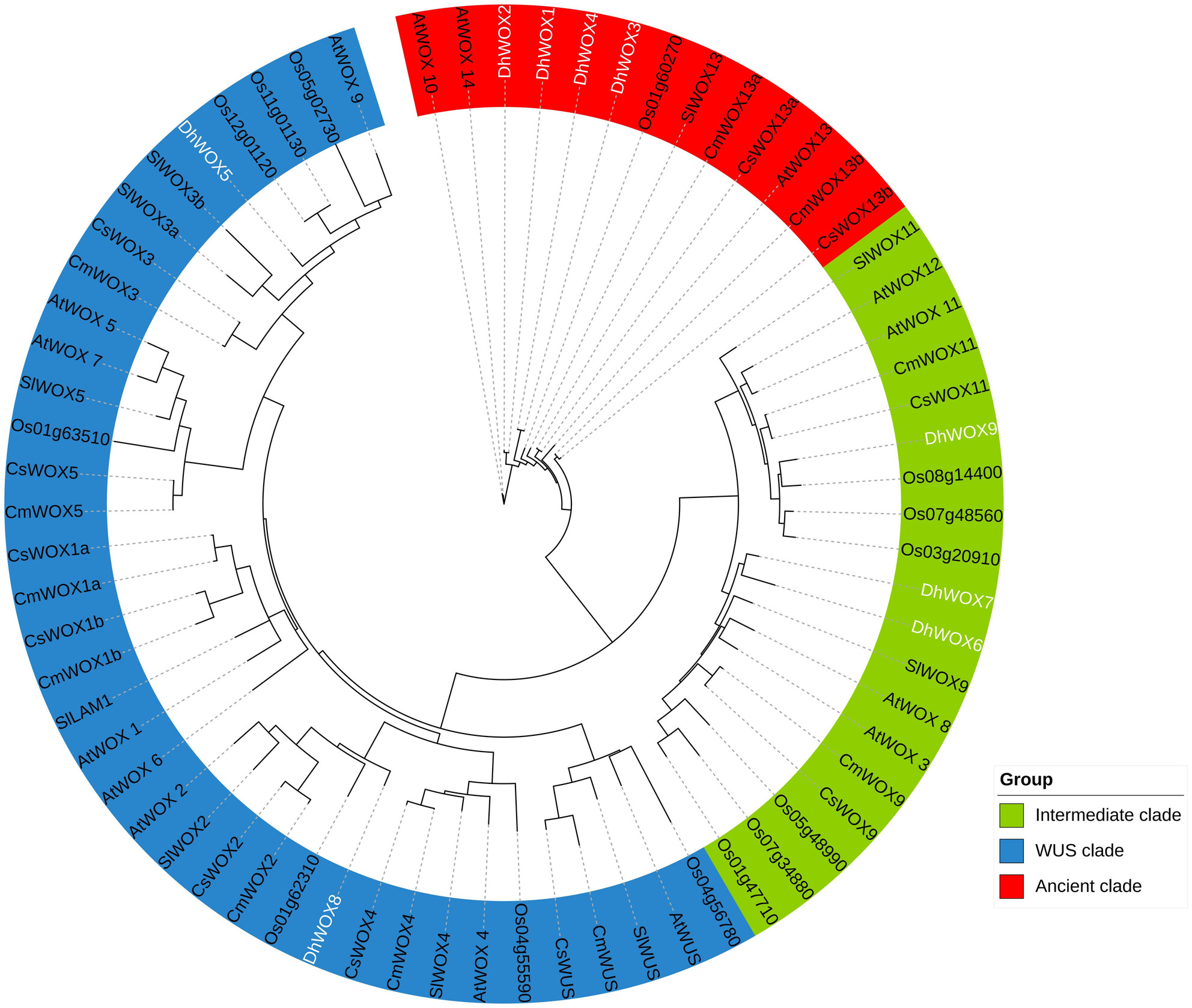
Nine WOX genes were identified in D. huoshanense. The phylogenetic tree suggests they belong to three classical clades. All DhWOX genes are subject to purifying selection, with replication times dating back as early as 363 MYA. D. huoshanense has more gene pairs with its relative species, consistent with their genetic relationship. The cis-regulatory elements in promoter regions are mainly associated with hormone signaling, vegetation development stages, and stress responses.
Detection of Quality Deterioration of Packaged Raw Beef Based on Hyperspectral Technology
- First Published: 19 March 2025
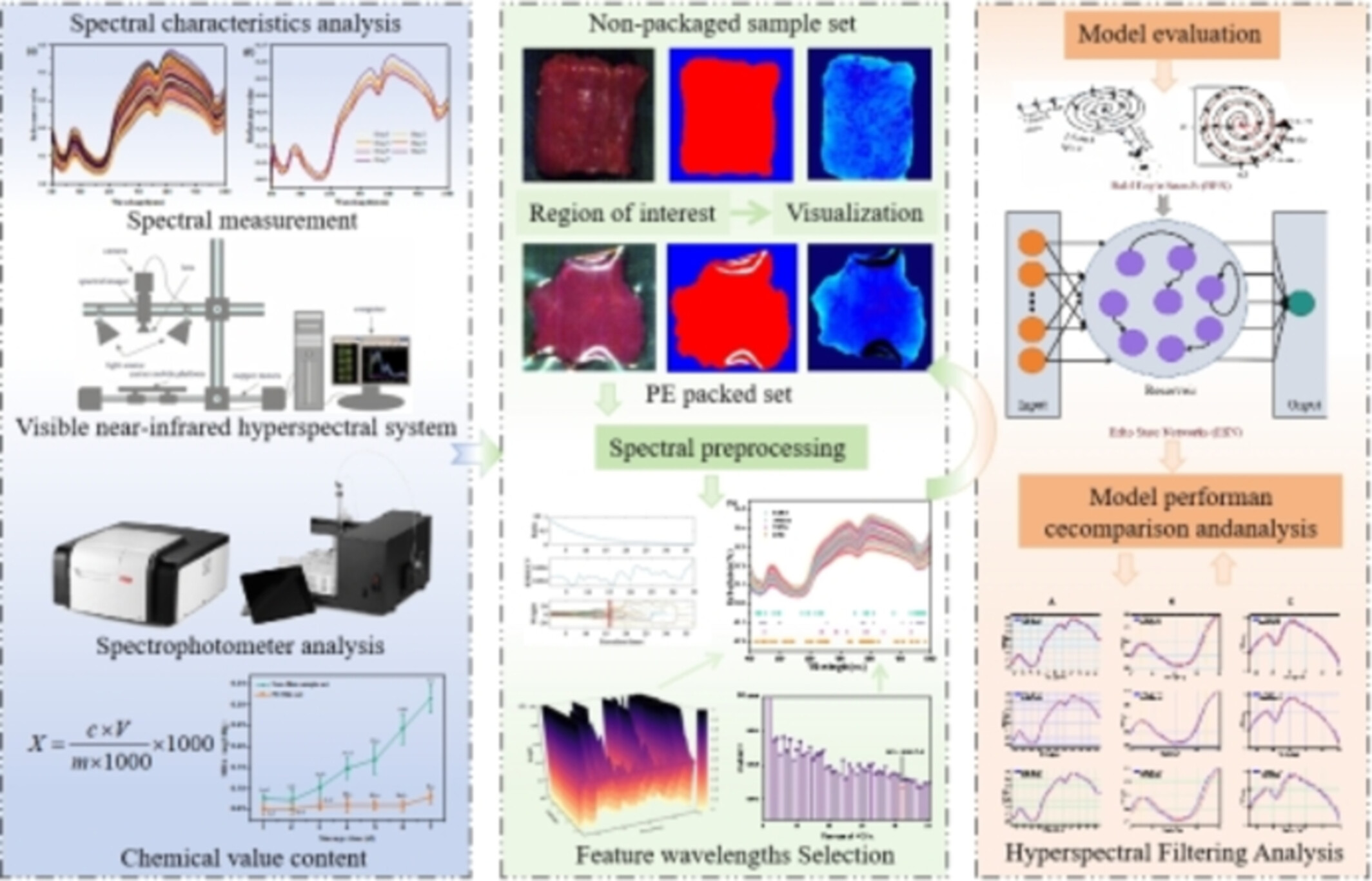
A rapid nondestructive detection of fresh meat after packaging based on hyperspectral imaging was proposed. Gaussian filtering was applied to reduce the interference effect caused by the packaging film. Multivariate combinatorial modeling based on echo-neural networks optimized by vulture optimization algorithms.
REVIEW
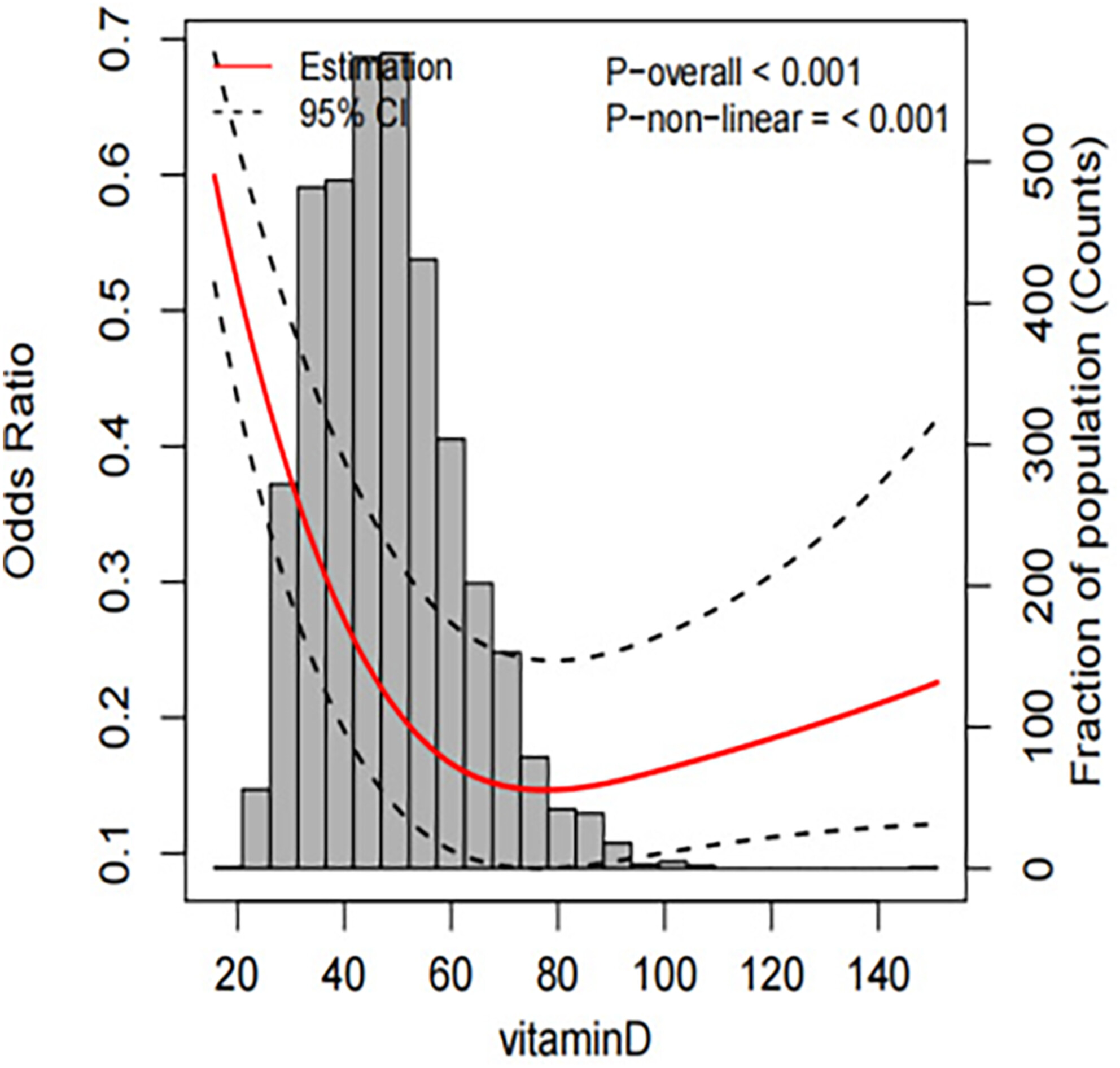
Serum Vitamin D Levels and Risk of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study and Mendelian Randomization Analysis
- First Published: 24 February 2025
A Systematic Review of the Phytochemical Profile and Potential Medicinal Functions of Codonopsis pilosula in Cancer
- First Published: 24 February 2025
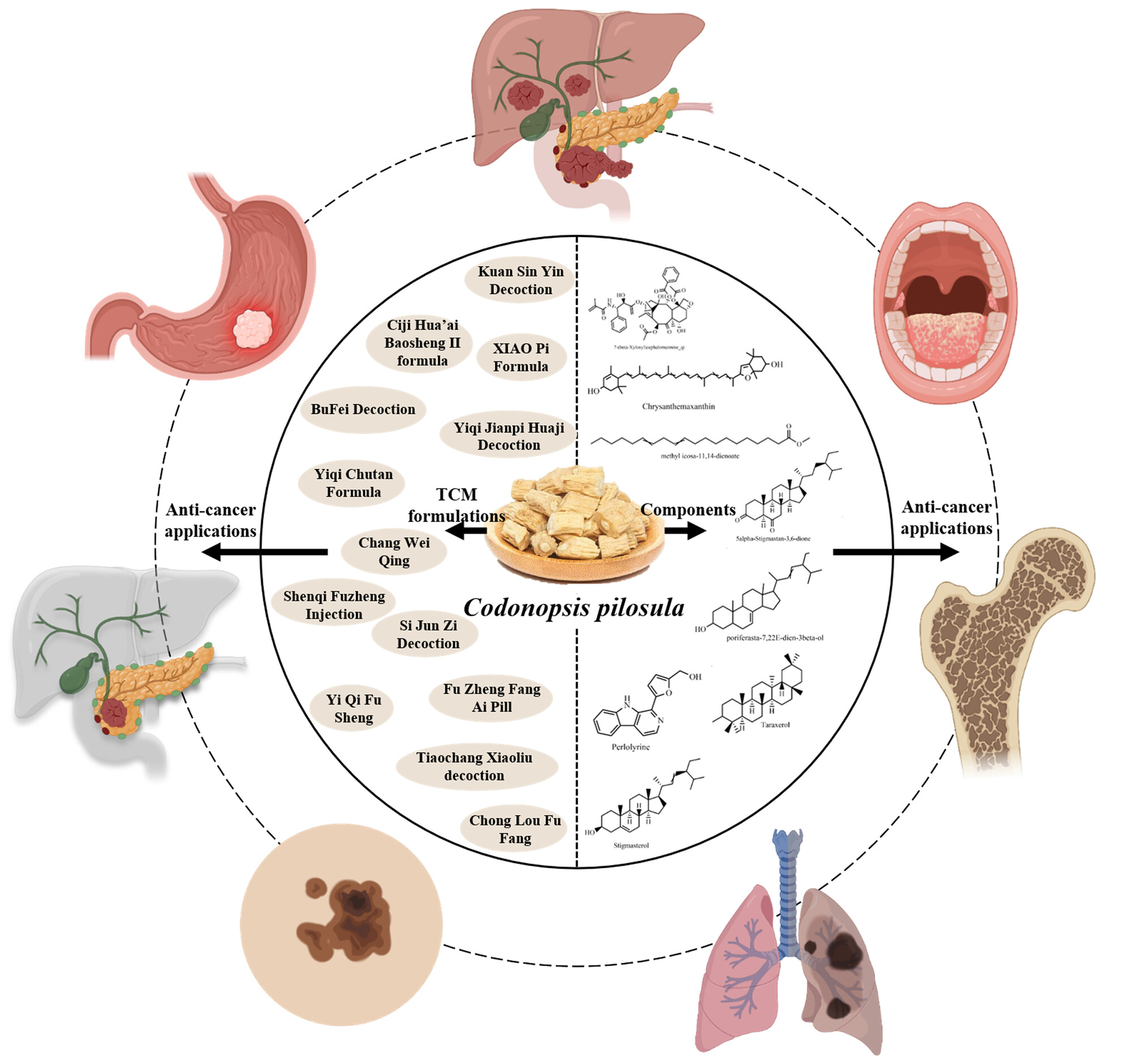
Codonopsis pilosula may serve as a potential treasure trove for pharmaceuticals, functional foods, and cosmetic additives in the future. The available evidence warrants further research into the possible role of C. pilosula in preventing human carcinogenesis. This review provides theoretical research and references for profound systematic testing and development in the use of C. pilosula in the fields of food and medicine.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The Prebiotic Effect of Kaempferol in Regulating Bile Acid Metabolism
- First Published: 24 February 2025
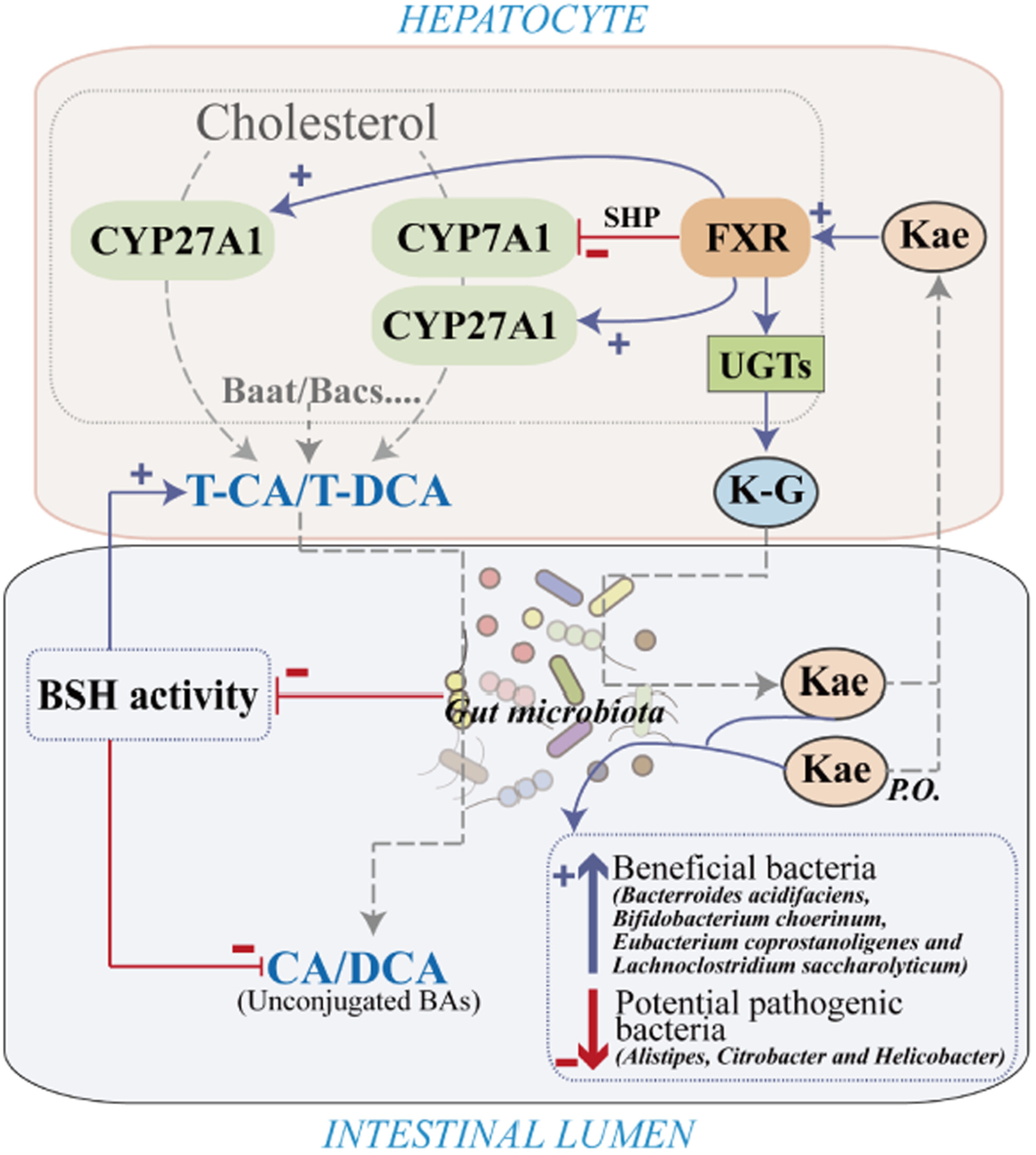
Kaempferol (Kae) can suppress the expression of CYP7A1, while increasing the CYP27A1 and UGTs expression by activating the liver FXR. Kae modulates the BA profile by decreasing the BSH activities. Kae markedly increases the abundance of beneficial bacteria and inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
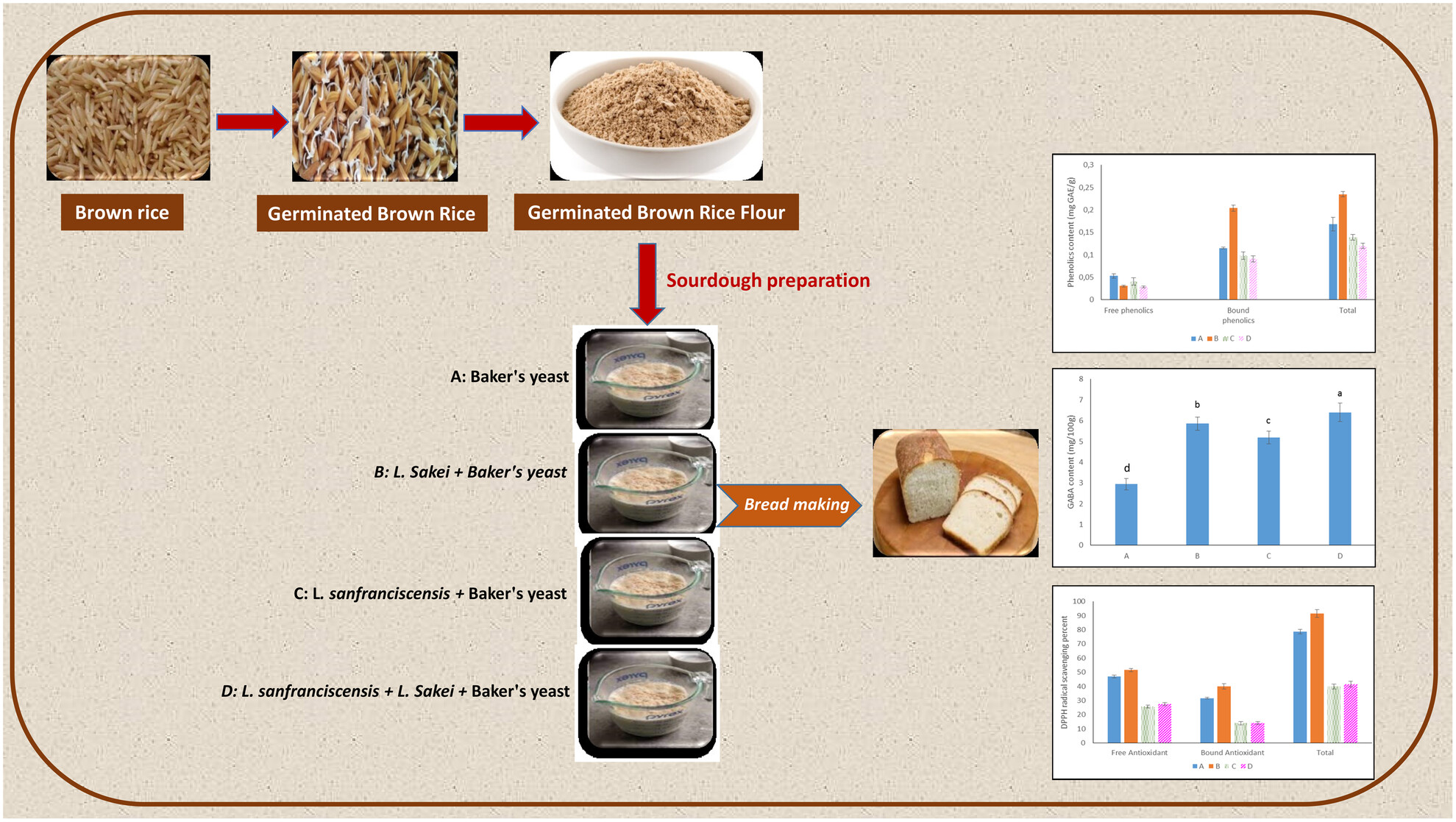
Development of Functional Sourdough Bread Using Lactobacillus sakei and Germinated Brown Rice: Evaluation of Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Capacity, Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid (GABA) Content, and Sensory Characteristics
- First Published: 24 February 2025
EGCG Alleviates H2O2-Induced Inflammatory Injury and Apoptosis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells Through Nrf2 Pathway Activation and p38MAPK Pathway Inhibition
- First Published: 25 February 2025
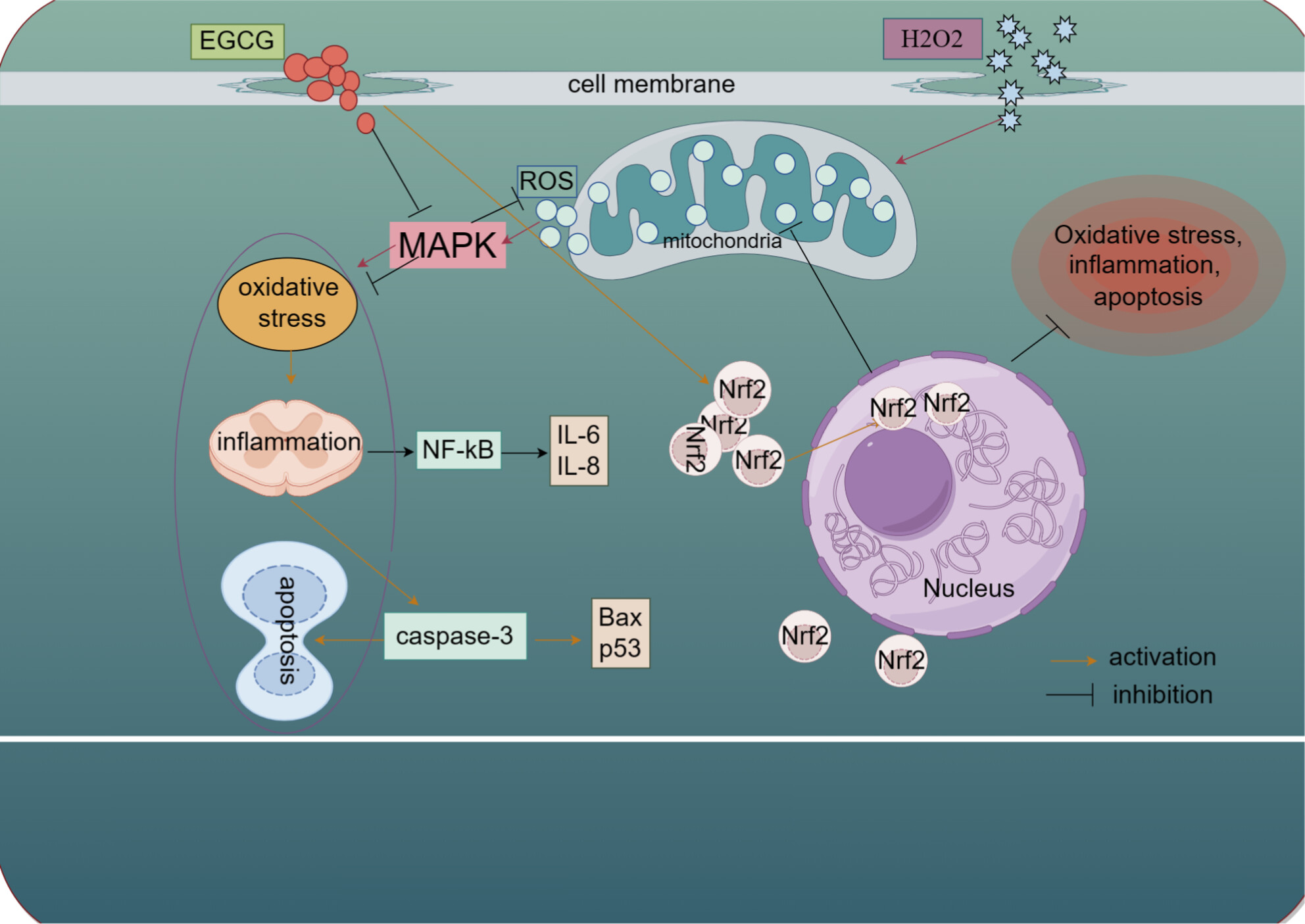
The present study sought to investigate the protective effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, and related mechanisms. The test showed that EGCG could improve the antioxidant function of bovine mammary epithelial cells by activating the Nrf2 and inhibiting the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways, reducing inflammation and mitochondrial damage. This study provides a theoretical basis for further study of exogenous EGCG to prevent mastitis in dairy cows.
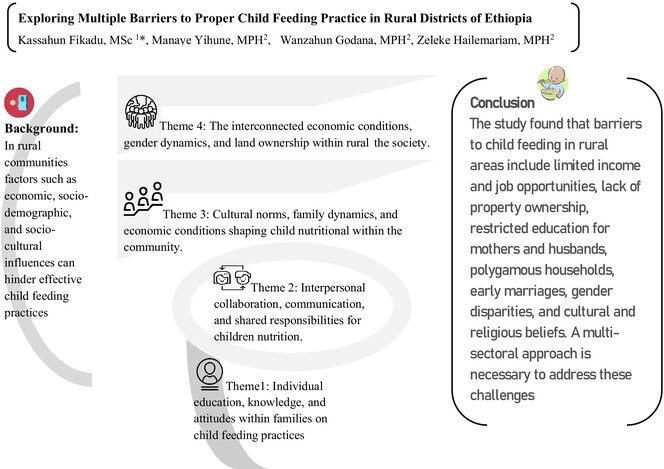
Exploring Multiple Barriers to Proper Child Feeding Practices in Rural Districts of Ethiopia
- First Published: 25 February 2025
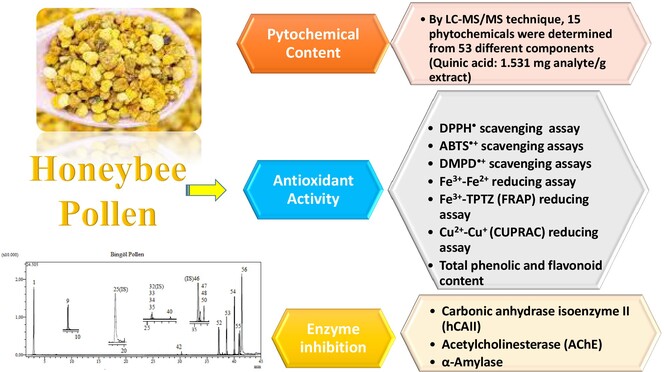
Determination of Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, Anticholinergic, Antiglaucoma Properties and Comprehensive Phytochemical Content by LC-MS/MS of Bingöl Honeybee Pollen
- First Published: 03 March 2025
Effect of Fermentation Time on the Physicochemical Properties and Phenolic Composition of Malted Finger Millet Beverages
- First Published: 10 March 2025
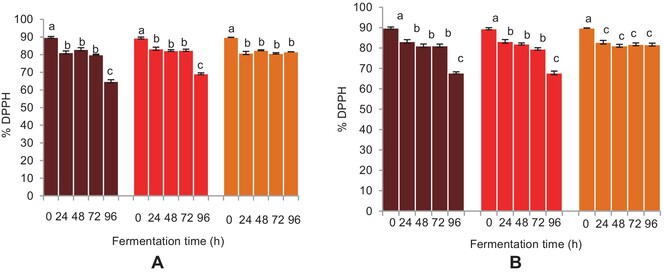
The study investigated the effect of fermentation time on the physicochemical properties and phenolic composition of two cultivars of finger millet (FM) malt beverages, compared to sorghum. The 24-h fermented FM malt beverages retained a higher amount of total phenolics and had higher antioxidant activity. The study shows that FM could be used as a functional grain in the production of nonalcoholic beverages with health benefits.
Edible Films Based on Plant and Animal Origin Proteins: Comparison of Some Mechanical and Physicochemical Characteristics
- First Published: 17 March 2025
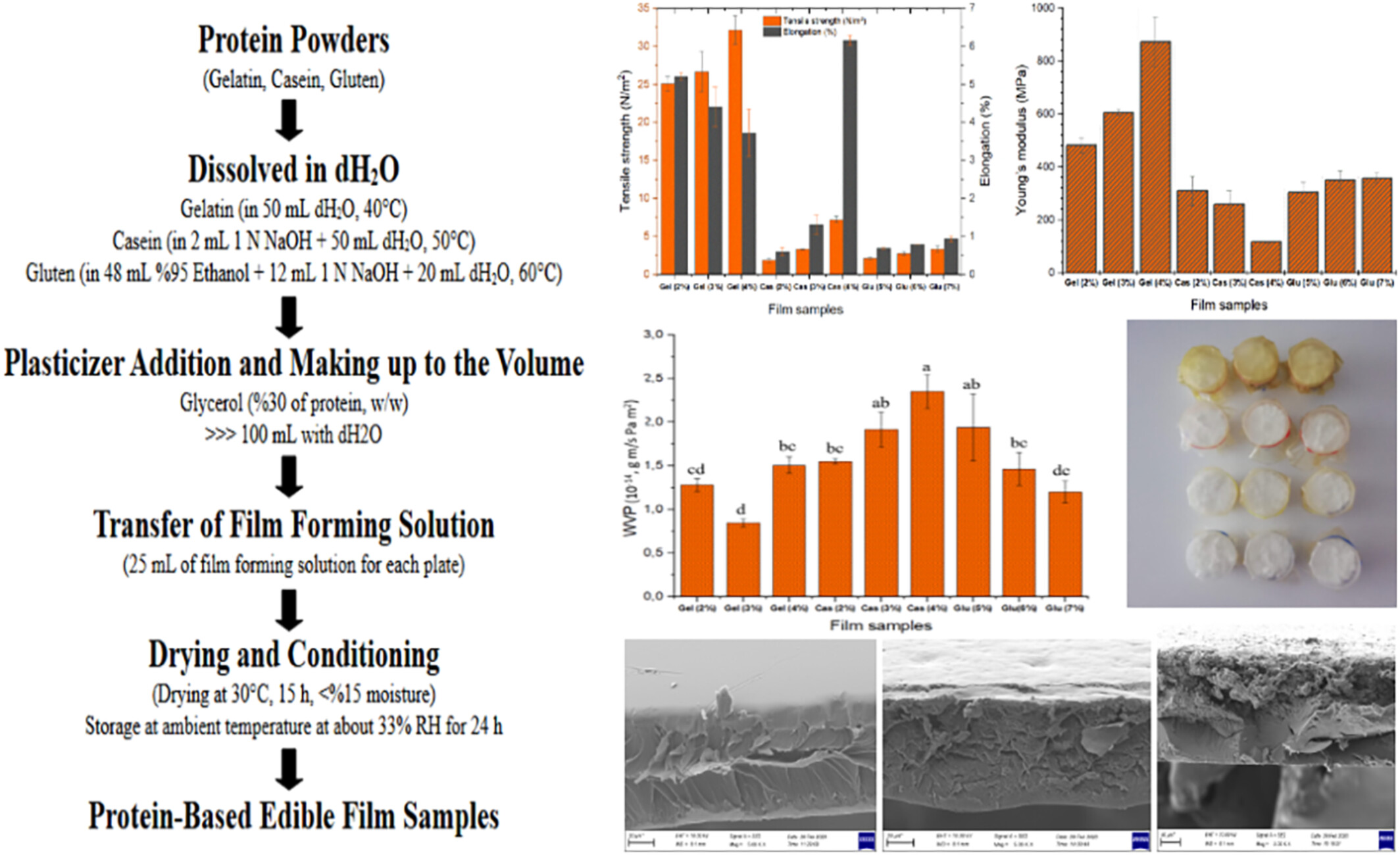
This manuscript presents valuable data on comparison of mechanical strength and some other physicochemical features of edible films obtained by three different proteins. Gelatin leads to an extendable film with highly elastic structure while gluten and casein films are more rigid but strong. Visual look of the films is also comparable, and gelatin films are transparent and light in color while casein and gluten films are more like yellowish and turbid to some extent. Gelatin is concluded to be a better carrier protein compared to casein and gluten for production of edible films due to its superior mechanical and visual features along with its ease of use, high solubility, and homogeneous film structure achieved.
Perceptions of In-Home Usage Experience and Price: Results of Consumer Research on Nutritional Innovations for Improving Maternal and Child Nutrition in Ethiopia
- First Published: 28 February 2025
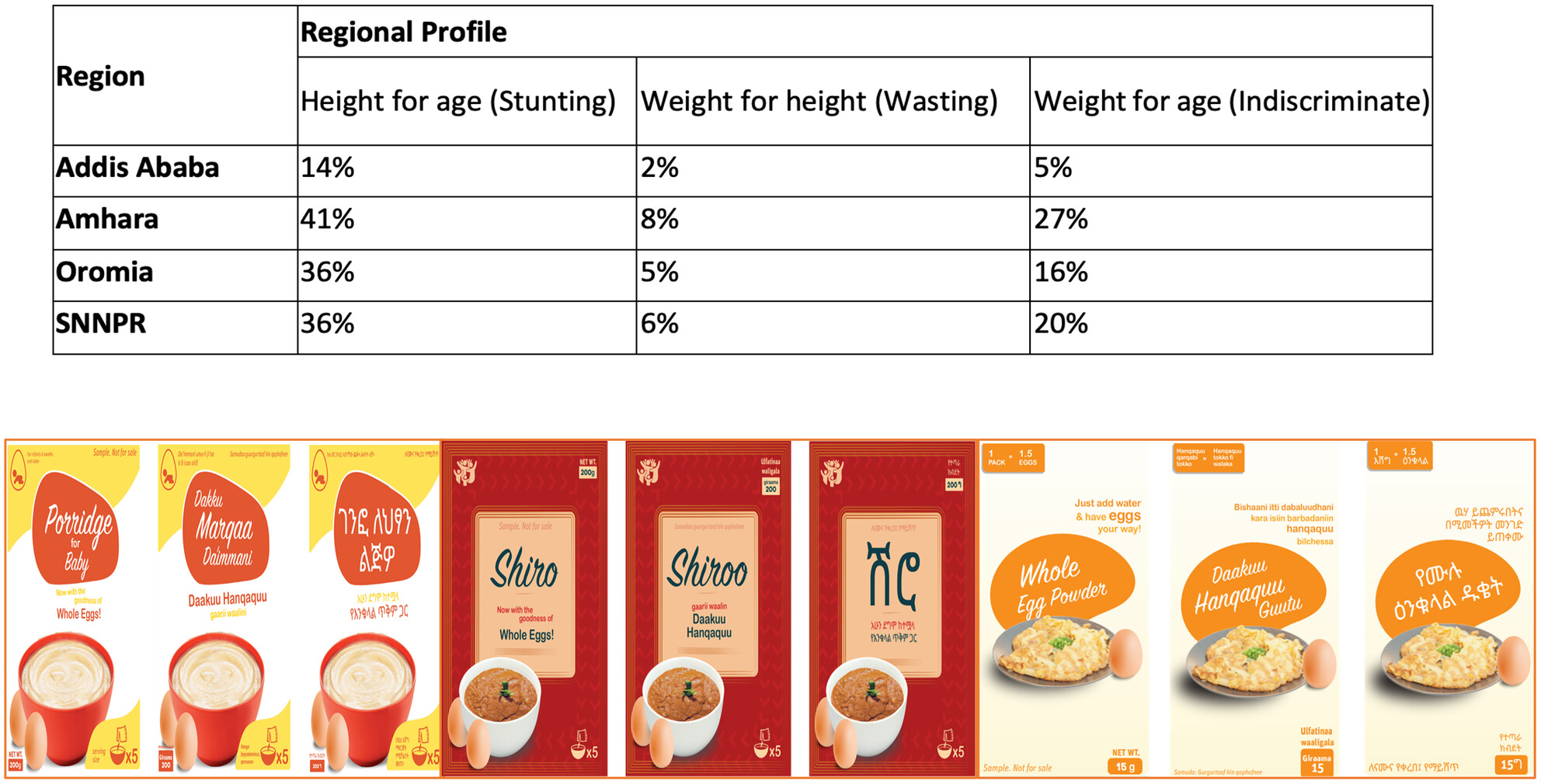
Egg powder is a promising solution to address malnutrition that offers several benefits over whole eggs such as reduced transport/storage costs, increased shelf-life, and offers a wide range of uses. A consumer research study was conducted by Sight and Life (SAL) in collaboration with the Ethiopian Public Health Institute (EPHI) to understand and frame opportunities-for-entry for a powdered egg product targeting pregnant and lactating women (PLW) and children 6–60 months old in Ethiopia. The study found that the egg powder prototypes were met with positive reactions, with clear areas of improvement indicated.
Remodeling of Gut Microbiome of Pakistani Expats in China After Ramadan Fasting
- First Published: 26 February 2025
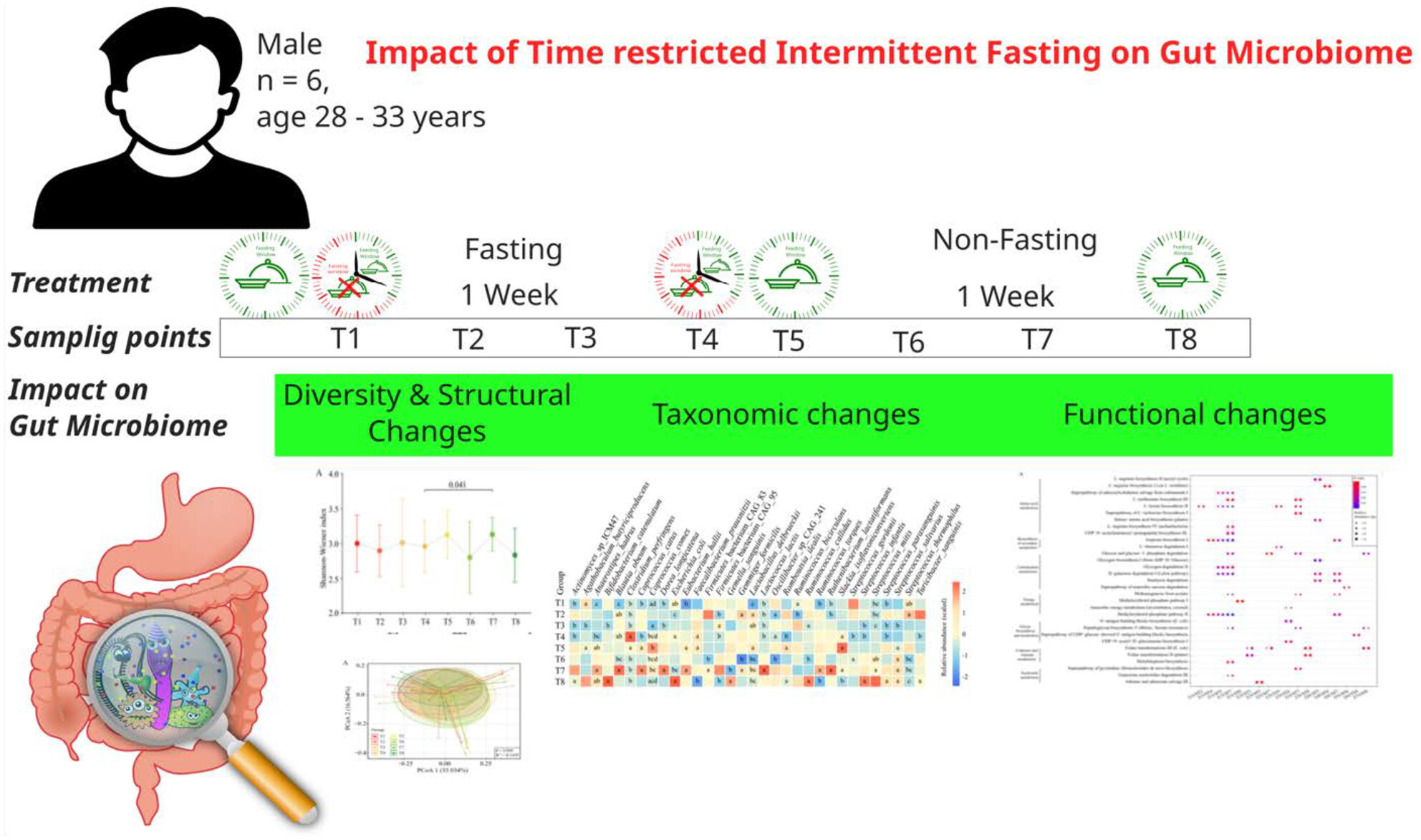
Time-restricted intermittent fasting (TRIF) significantly changed the microbial structure and compositions of Pakistani Expats living in China. TRIF mainly affected the gut microbial pathways of amino acid, carbohydrate, and energy metabolism and glycan biosynthesis metabolism of cofactors and vitamins.
Identification of High-Yielding and Drought-Tolerant Melon Genotypes Based on Yield–Trait Combinations: A Comparison of Pcor Index and GYT Biplot Approaches
- First Published: 28 February 2025
Investigating Infrared Radiation on Peeling and Roasting Chestnut Seeds (Castanea sativa Mill.) and Its Effect on the Physical, Chemical, and Sensory Characteristics of the Product
- First Published: 27 February 2025
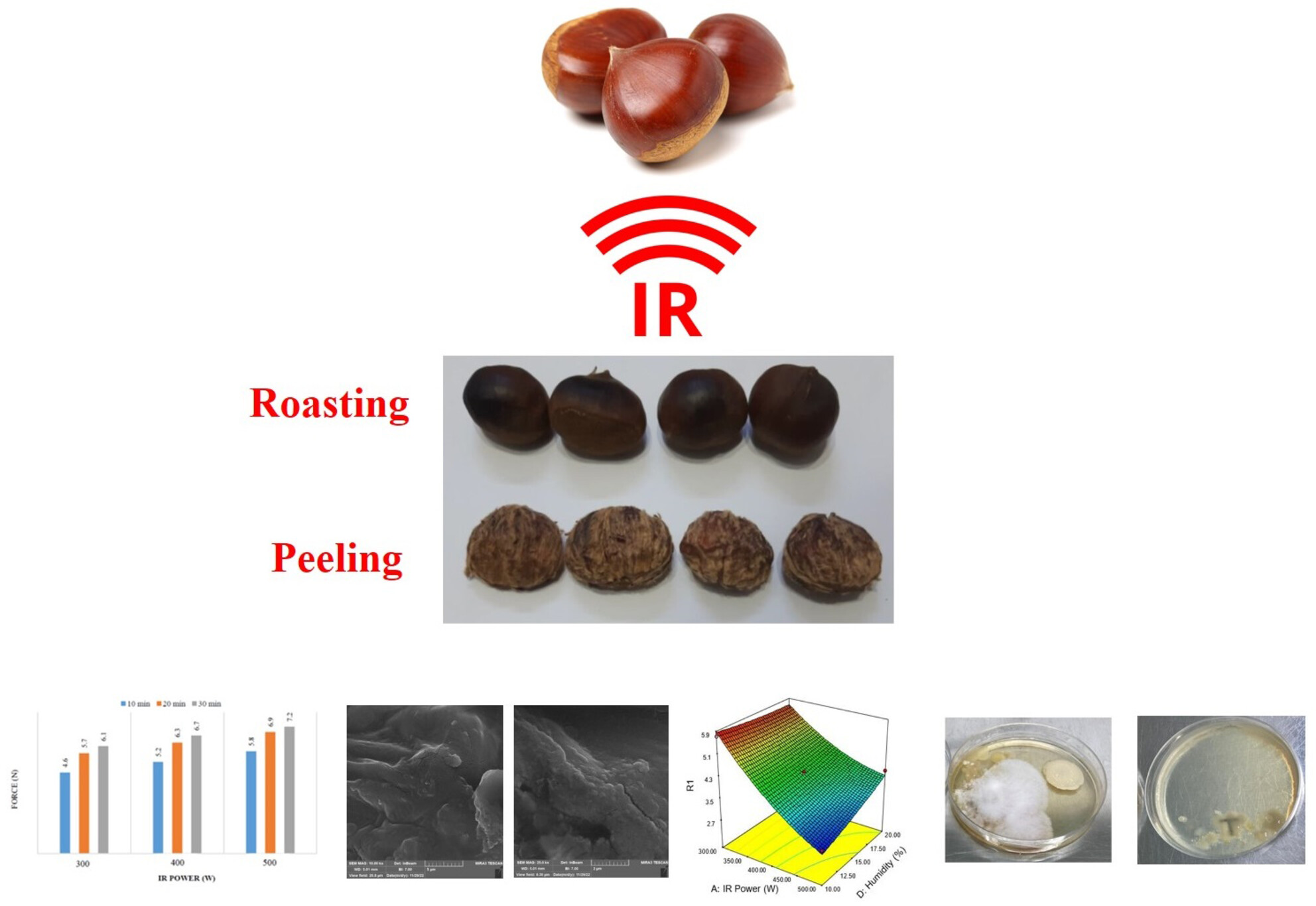
This study investigates the application of infrared radiation (IR) for processing chestnuts, focusing on optimizing roasting and peeling conditions using response surface methodology. The optimized IR-treated chestnuts displayed improved physicochemical properties, enhanced antioxidant content, and superior sensory attributes over 60 days of storage. The findings suggest that IR technology significantly enhances the quality and storage stability of chestnuts, offering promising industrial applications.
REVIEW
Exploring Punicalagin Potential Against Cancers: A Comprehensive Review
- First Published: 27 February 2025
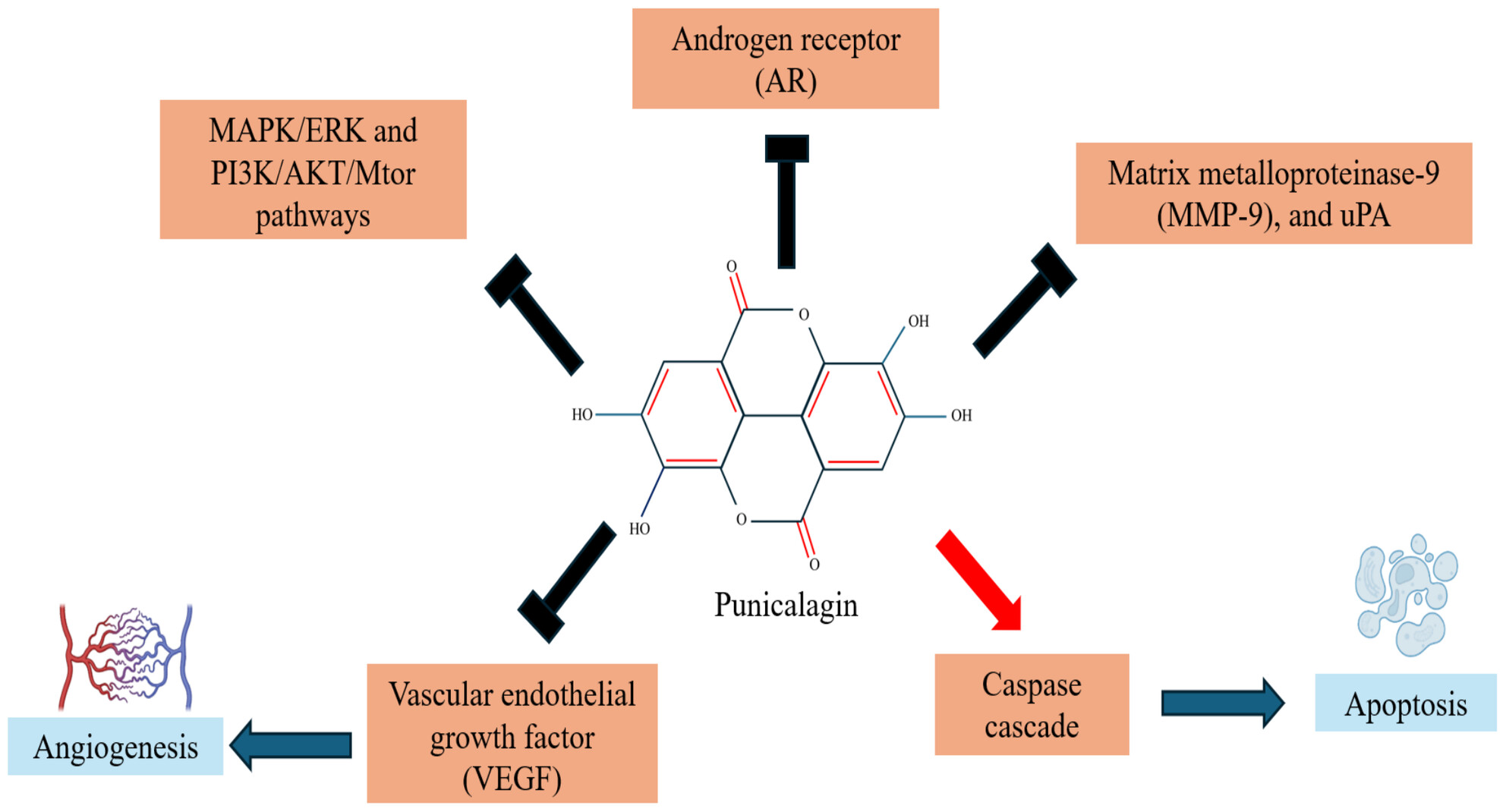
This paper focuses on highlighting the therapeutic potential of punicalagin against tumors and cancers. Punicalagin inhibits tumor growth within the body through various cellular pathway interactions. This compound has efficacy in eliminating tumor cells from the liver, stomach, prostate, and lungs. Different animal model studies have demonstrated the potential of punicalagin in blocking the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways, fighting against cancer. Through the inhibition of cell division, punicalagin may be capable of eradicating breast cancer cells. Punicalagin strongly inhibits the activities of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and uPA. Punicalagin effectively inhibits androgen receptor (AR), a protein essential for the development and metastasis of prostate cancer.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
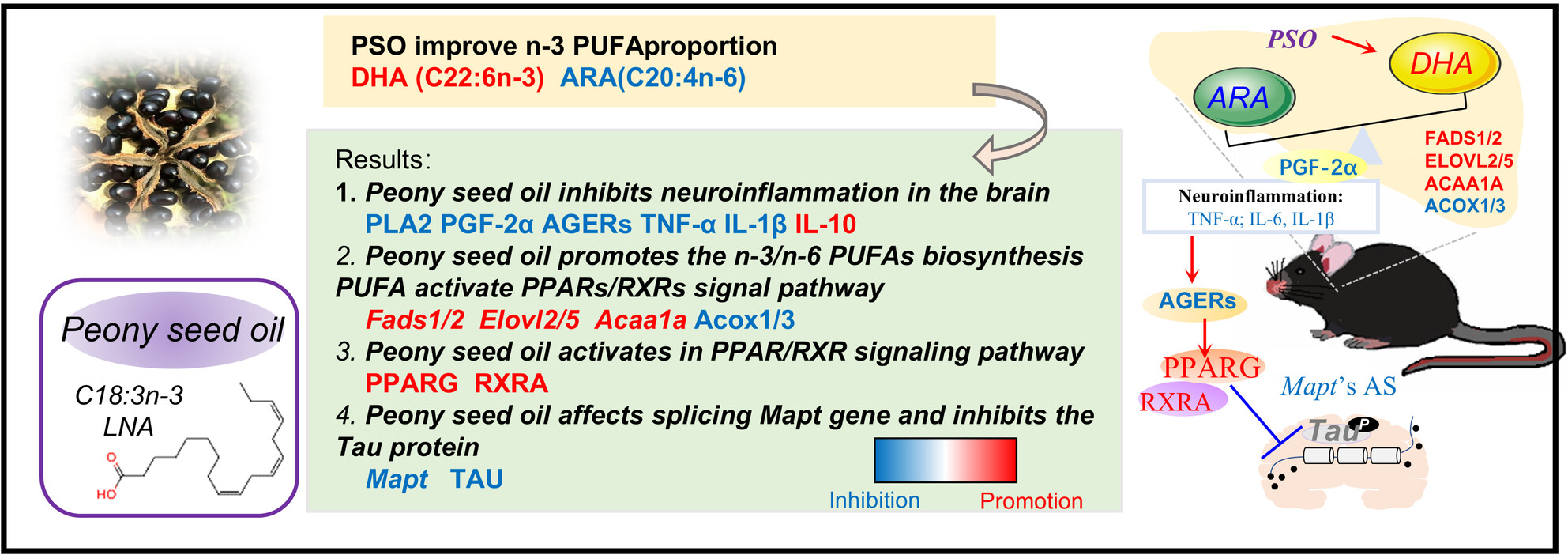
Peony Seed Oil Inhibited Neuroinflammation by PPAR/RXR Signaling Pathway in D-Gal Induced Mice
- First Published: 27 February 2025
Resveratrol Relieves Hepatic Steatosis and Enhances the Effects of Atorvastatin in a Mouse Model of NAFLD by Regulating the Renin-Angiotensin System, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation
- First Published: 04 March 2025
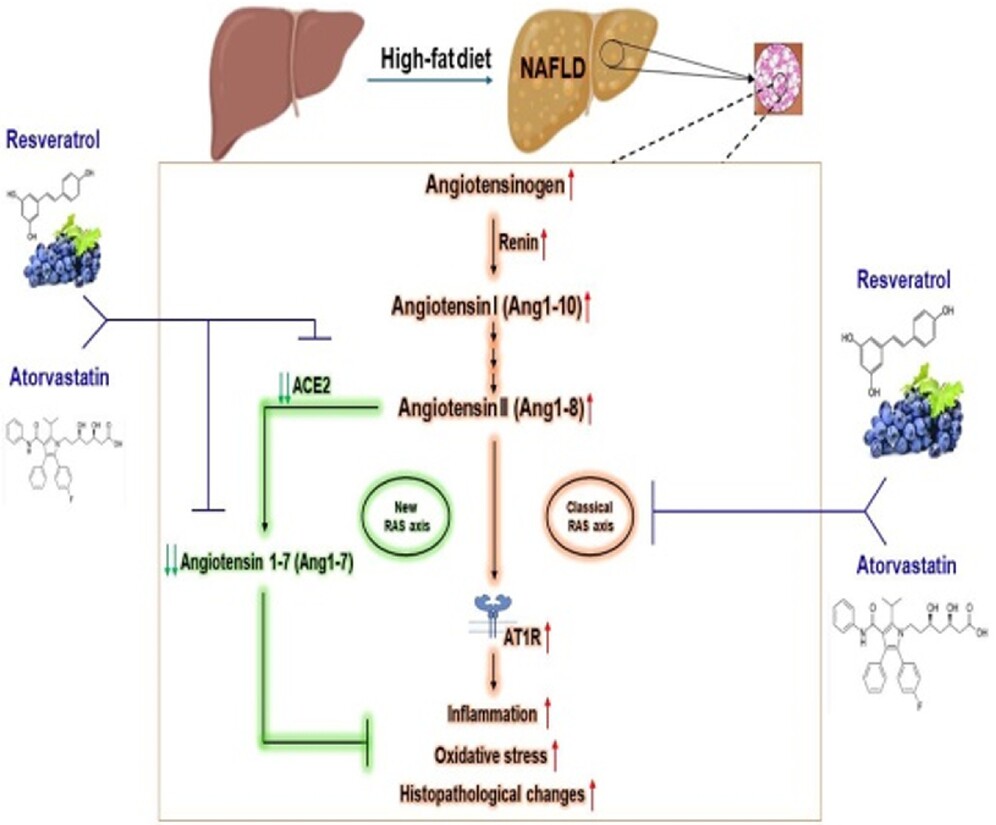
In mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), the classical renin-angiotensin (RAS) axis was activated, leading to oxidative stress, inflammation, and histopathological changes in the liver. In contrast, the new RAS axis was inactivated, as manifested by the downregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and angiotensin 1-7 (Ang1-7). Administration of resveratrol and atorvastatin considerably ameliorated NAFLD in mice by modulating new and classical RAS axes.
Assessing Traditional Chinese Medicines for Anti-Dengue Using a National Health Insurance Research Database and Bioassays
- First Published: 28 February 2025
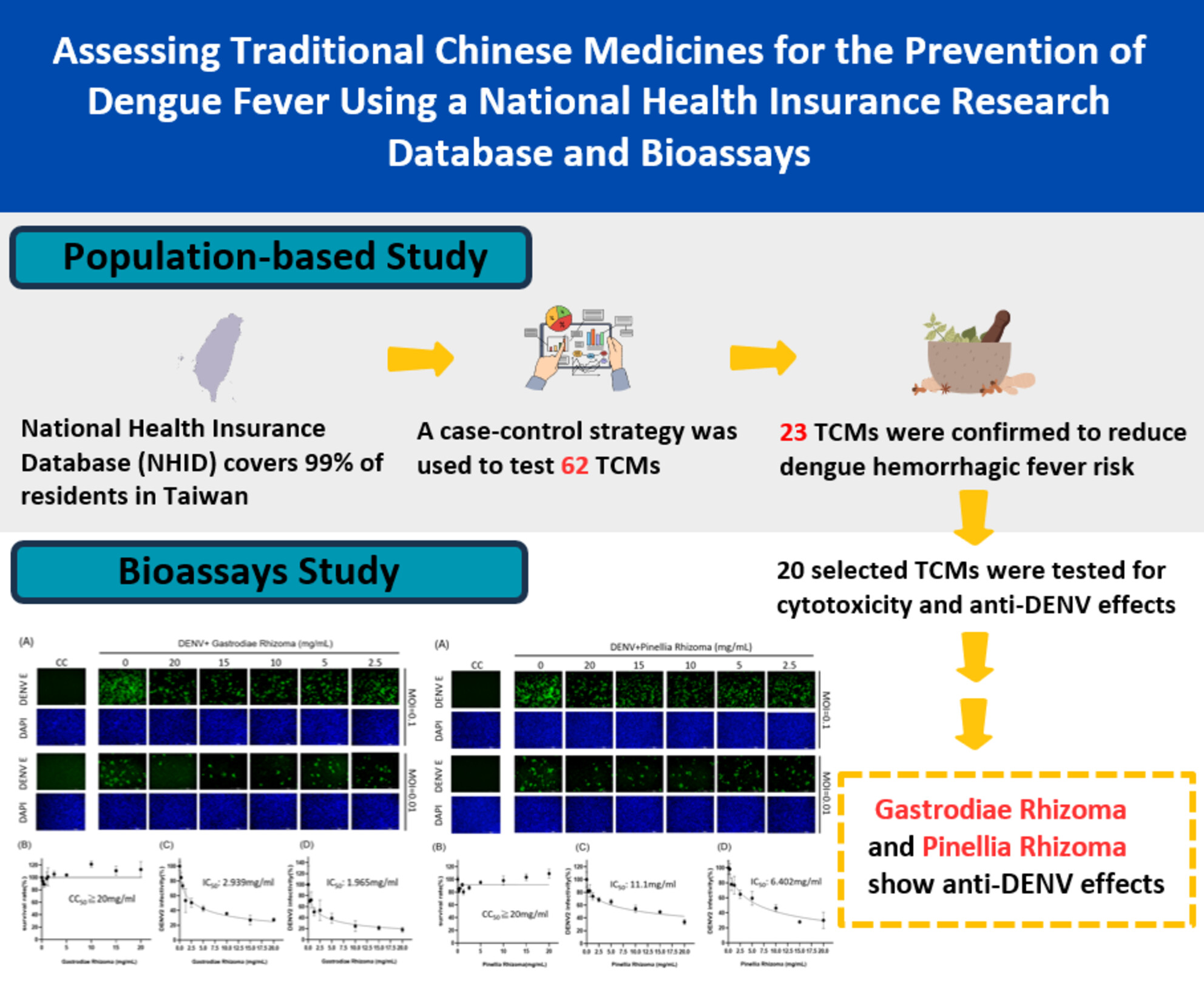
Our study leverages Taiwan's NHI Database to identify and verify the antiviral properties of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) against dengue fever, discovering that Gastrodia elata and Pinellia ternate exhibit significant anti-DENV activity, positioning them as promising candidates for future antiviral drug development.
Allium Macrostemon Bge. Attenuates the Cognitive Decline of Aging Mice by Enhancing BDNF/TrkB Pathway
- First Published: 28 February 2025
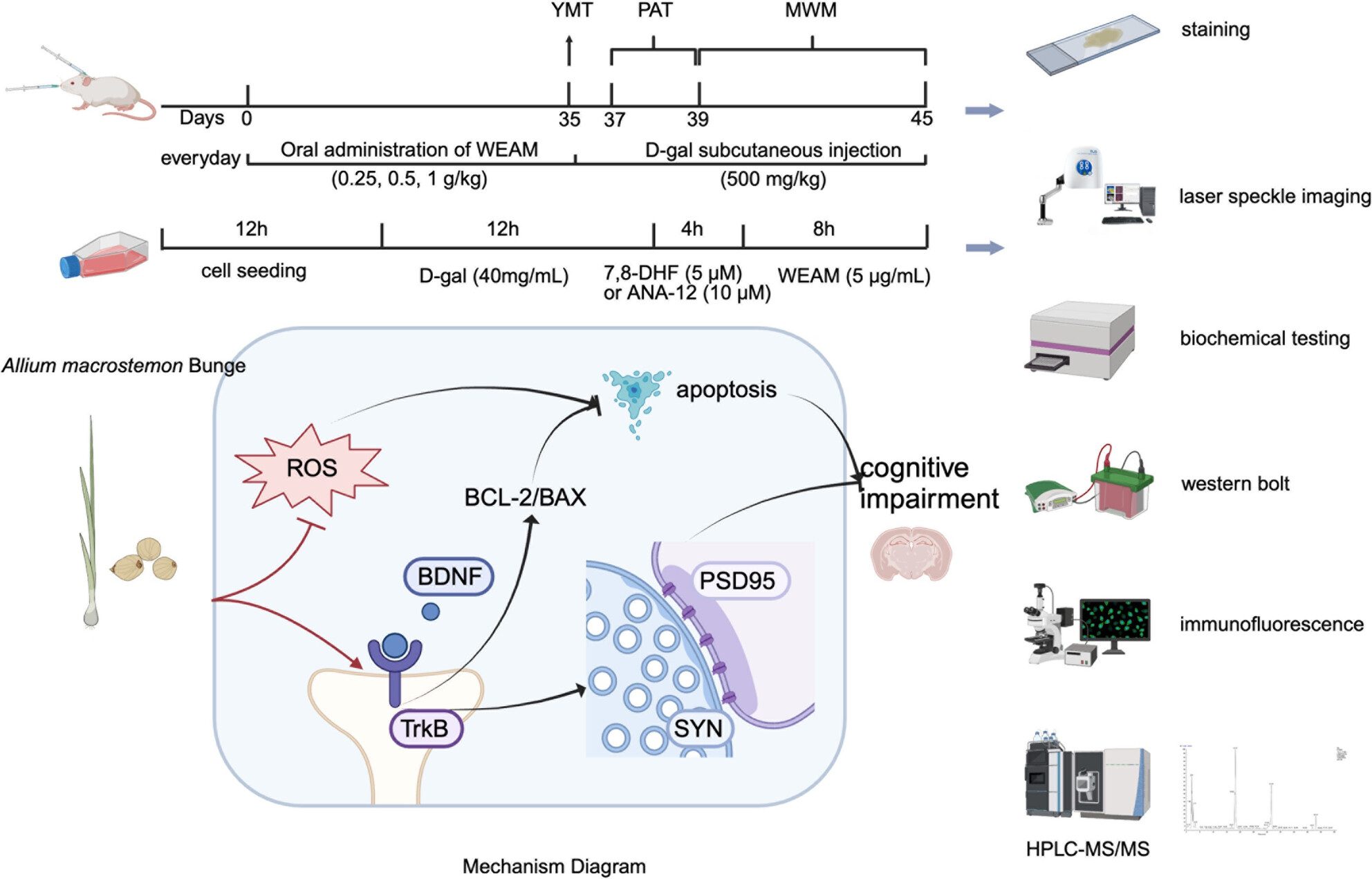
In conclusion, the work first established that WEAM ameliorated ARCI, with its mechanisms primarily involving the attenuation of oxidative stress and synaptic damage through activating the BDNF/TrkB pathway. These results hint that Allium macrostemon Bge. may serve as a potential culinary spice for improving aging and ARCI.
Integrative Profiling of Phytohormones, Metabolomics, and Transcriptomics Reveals Key Regulators of Cold Tolerance in Cucumber Leaves
- First Published: 02 March 2025
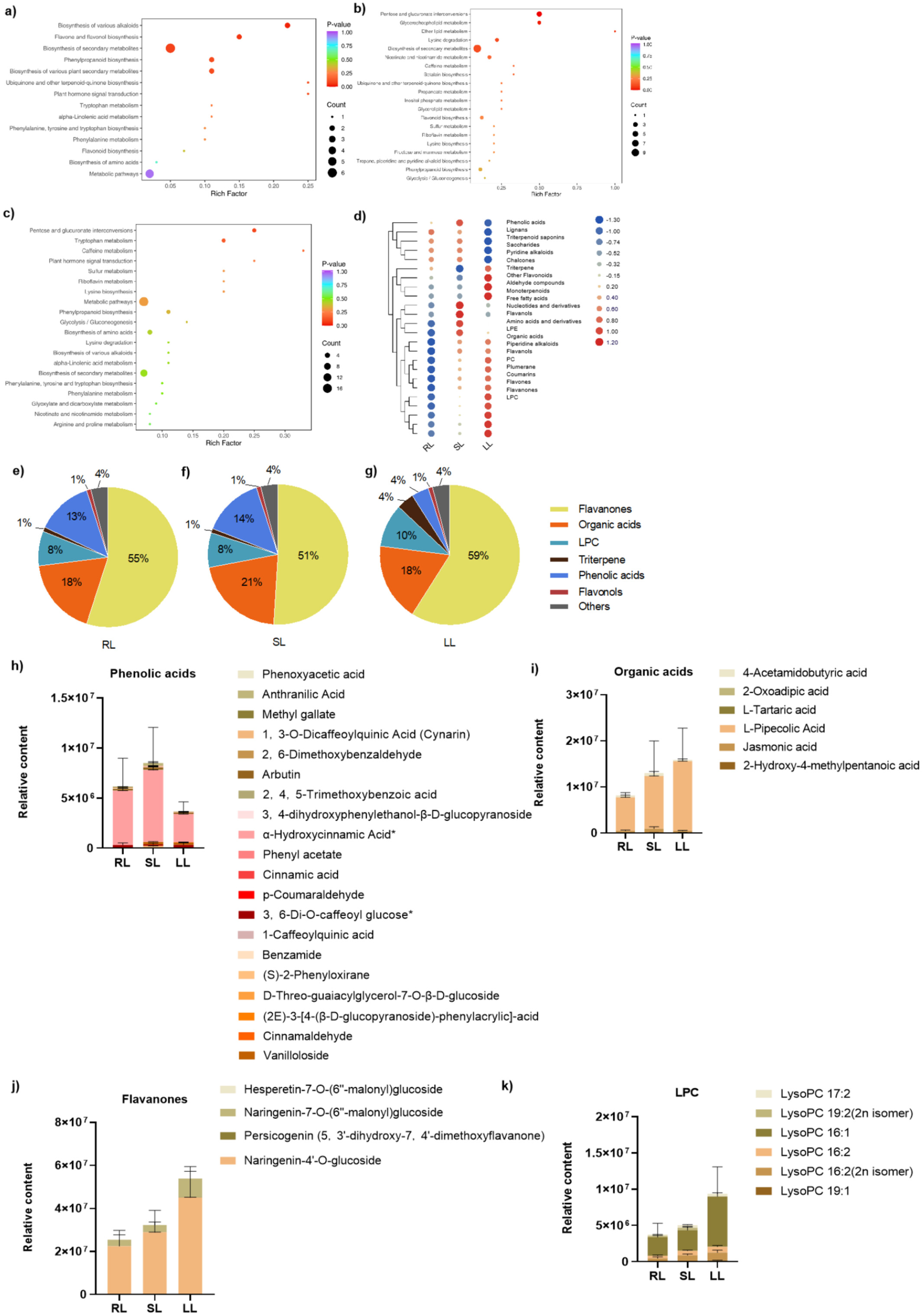
Through integrative physiological and biochemical analysis, auxin emerges as the most significant accumulated hormone, accounting for 88% in room temperature-treated leaves (RL), 99% in suboptimal temperature-treated leaves (SL), and 94% in low-temperature-treated leaves (LL). Under chilling stress, flavanones were the most abundant metabolite in cucumber leaves, constituting over 50% of total metabolites, while phenolic acids showed a marked decrease. Several differentially expressed transcription factors (DETFs), such as LOB (CsaV3_3G020650), MYB (CsaV3_3G043510), and bHLH (CsaV3_2G005070 and CsaV3_4G029740), were upregulated in SL and LL, potentially enhancing cucumber's defense against chilling injury.
Association Between Atherogenic, Thrombogenic, and Lipophilic Indices and the Odds of Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Case–Control Study
- First Published: 04 March 2025
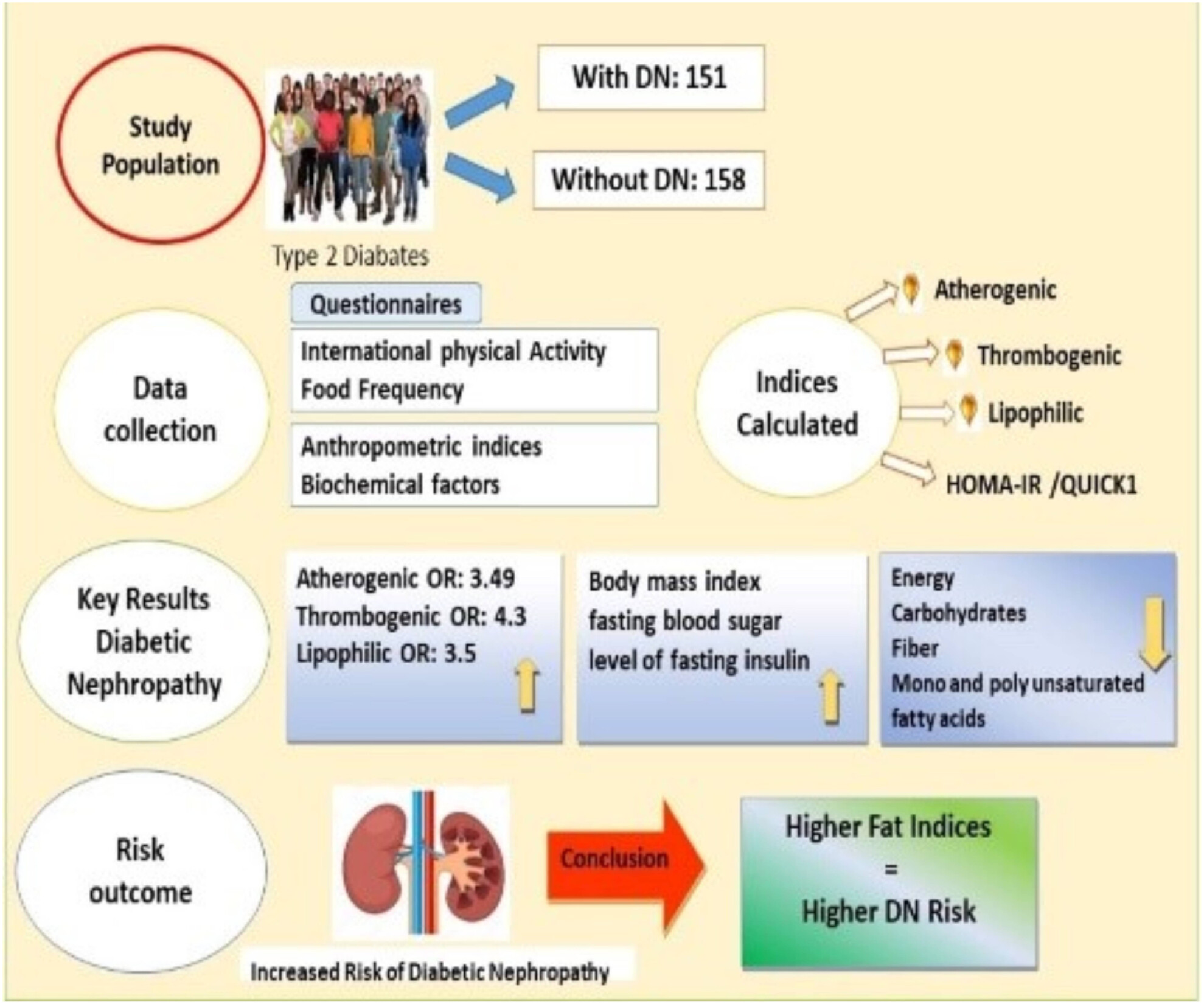
This is the first investigation that examined the association between atherogenic (IA), thrombogenic (IT), and lipophilic (LT) indices -as fat intake indicators- and diabetic nephropathy (DN). This study found Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients in the highest quartile of atherogenic, thrombogenic, and lipophilic indices had a greater likelihood of developing DN. Also, higher values of IA, IT, and LT were associated with a higher probability of DN in T2DM patients.
A Traditional Gum Exudate From Pistacia atlantica Ameliorates Etha-Nol-Mediated Gastric Ulcer in Rats: Possible Molecular Mechanisms
- First Published: 02 March 2025
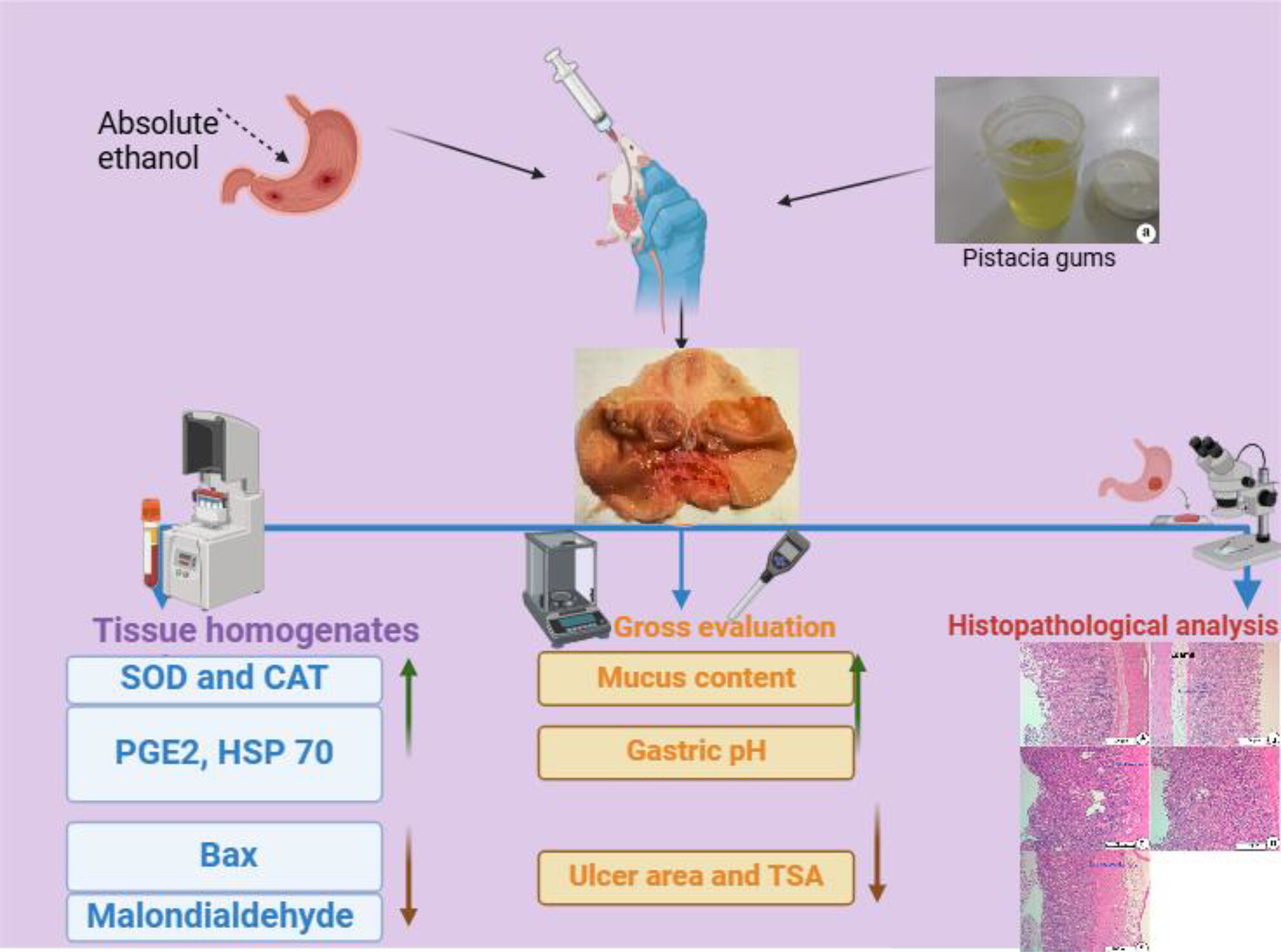
Pistacia atlantica gum (PAG) is a native Mediterranean plant that exudates a resinous therapeutic oleoresin gum used for many inflammatory-related diseases—PAG has shown significant anti-ulcer potential against ethanol-mediated ulcers in rats. PAG supplementation restored gastric defense barriers (mucopolysaccharides), mucus secretion, and significantly increased gastric pH, up-regulated SOD, CAT, PGE2, and IL-10, while reducing inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6). PAG gastroprotection could be linked to its phytochemical potential in modulating antioxidants, Bax, and HSP 70 proteins.
Chitosan-Orange (Citrus sinensis) Essential Oil Coatings With Combined Treatment of KMnO4 to Enhance the Shelf-Life and Storage Quality of Ercolini Pears
- First Published: 10 March 2025

The study evaluated the effects of chitosan coating combined with Orange (Citrus sinensis) essential oil (OEO) and potassium permanganate (KMnO4) sachets as ethylene inhibitors on maintaining quality and extending the shelf-life of Ercolini pears. The group of fruits treated with the chitosan-OEO coating and KMnO4 exhibited the lowest weight reduction and lowest incidence of superficial scald compared to the control. The highest levels of TPC, TFC, and antioxidant activity were observed in the chitosan-OEO-coated fruit group at the end of the storage period.
Enrichment of Oil Cake With Cinnamon Extract Positively Effects Antioxidant Activity and Textural Profile
- First Published: 04 March 2025
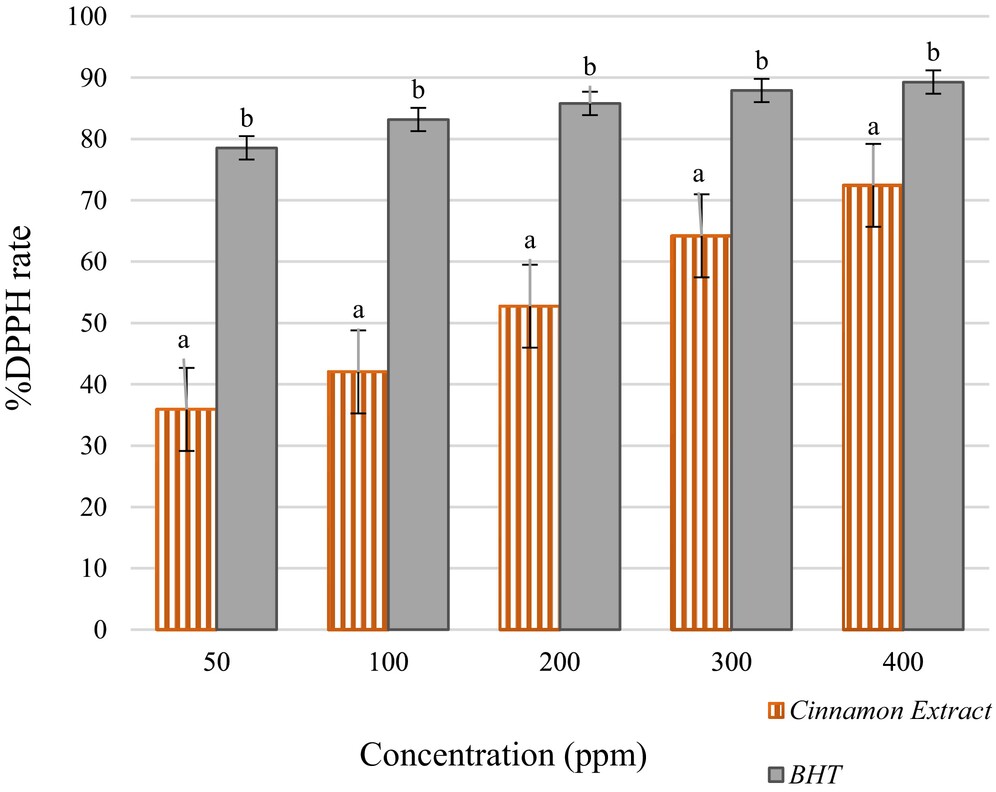
This study shows that incorporating aqueous cinnamon extract into oil cakes improves antioxidant activity, texture, and consumer acceptability. Concentrations of 0.20% and 0.25% significantly boosted total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity while enhancing texture and lowering fat and carbohydrate levels. Cinnamaldehyde, the main compound in the extract, contributed to these improvements, indicating that cinnamon extract is a valuable natural additive for enhancing the nutritional and sensory quality of oil cakes.
REVIEW
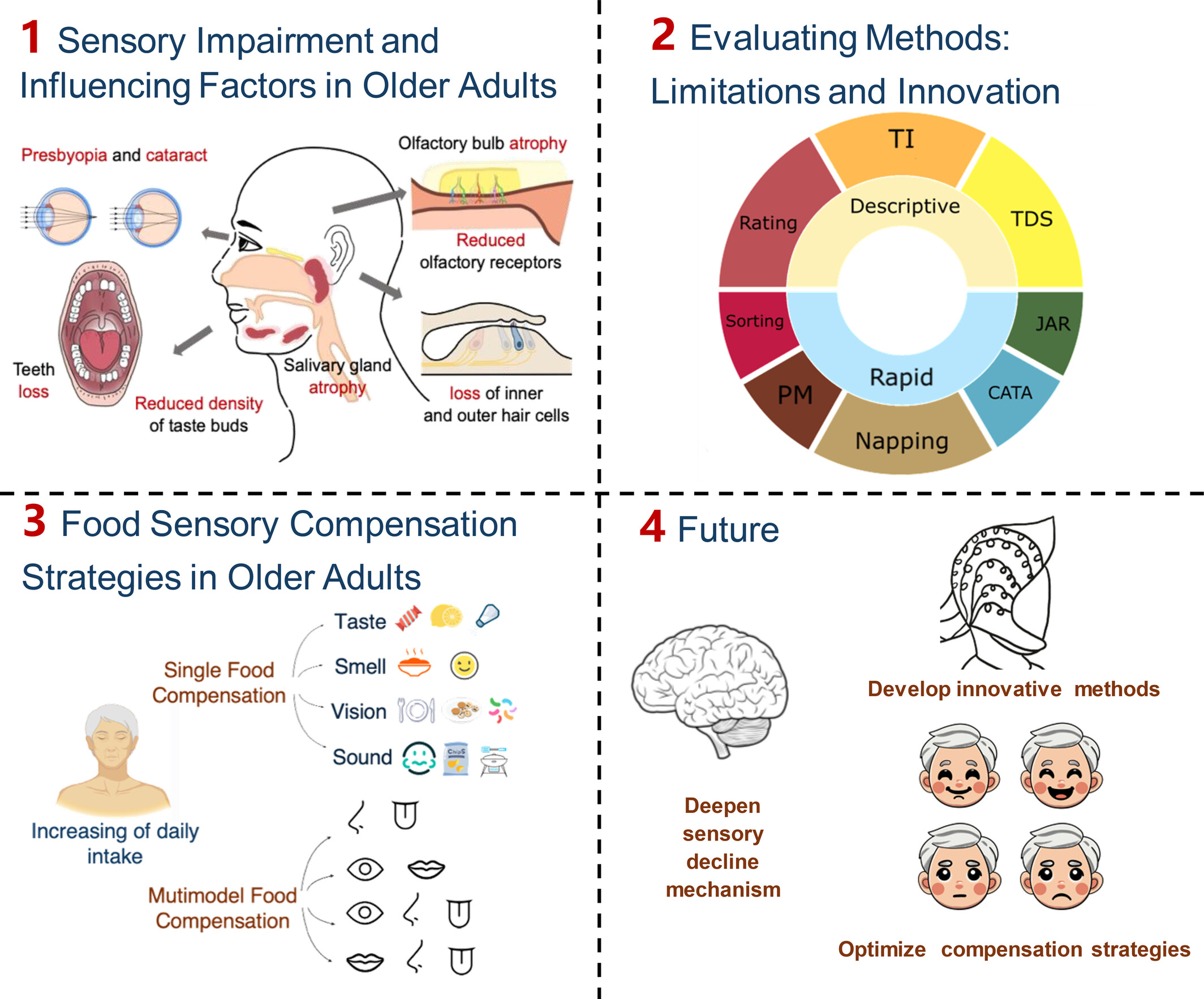
Sensory Insights in Aging: Exploring the Impact on Improving Dietary Through Sensory Enhancement
- First Published: 03 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Potentially Functional Apple Snacks Infused in the Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract Obtained by Convective and Infrared Drying: Kinetics of Drying and Phytochemical Analysis
- First Published: 04 March 2025
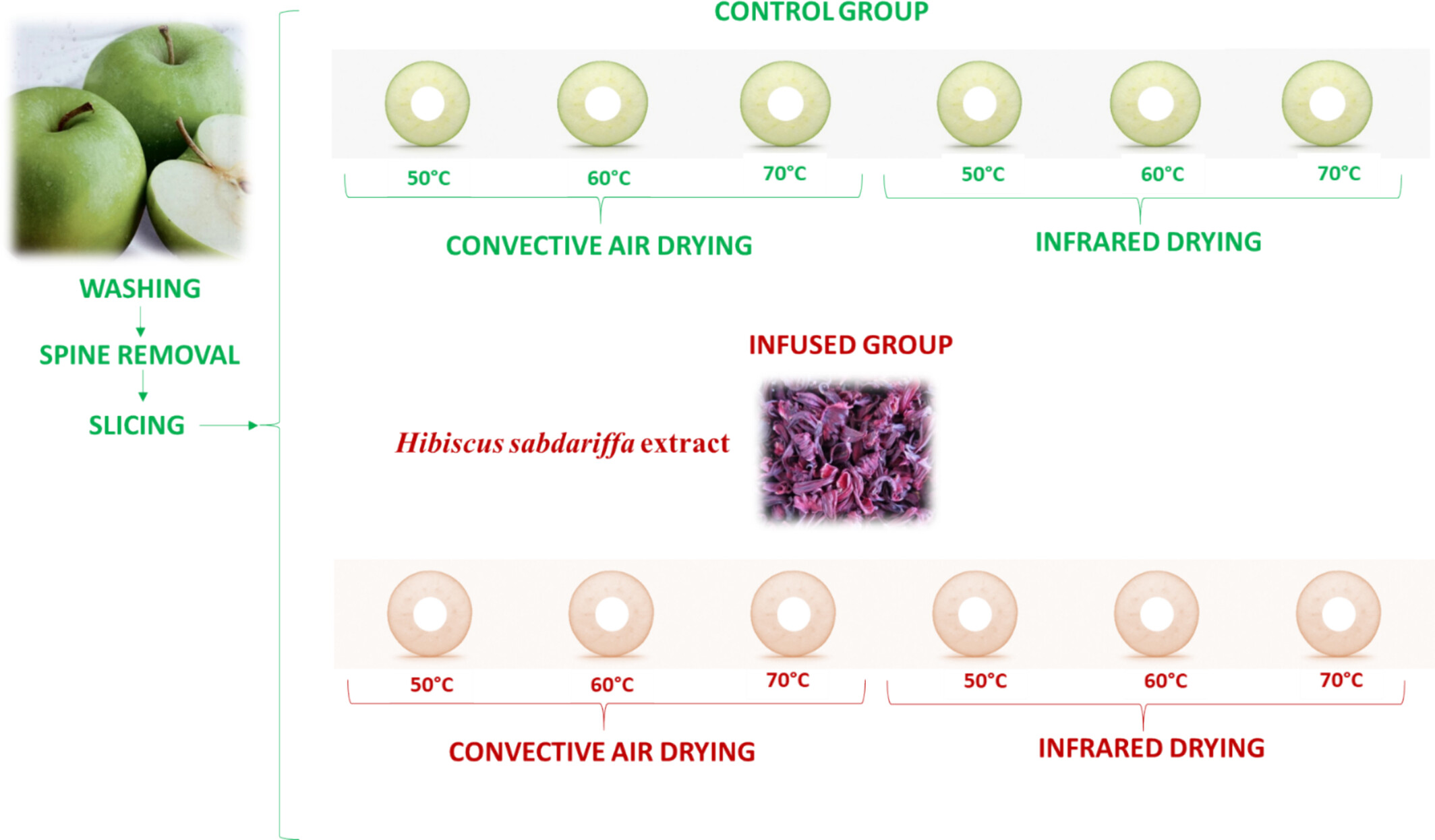
Apple snacks were obtained by using convective air (CD) and infrared drying (IR). The apple slices were immersed in the Hibiscus sabdariffa aqueous extract for 30 min, followed by drying at temperatures varying between 50°C and 70°C. The potentially functional properties of the infused apple snacks were appreciated based on the phytochemical profile, antioxidant activity, color, and textural properties.
CORRECTION
Correction to “Comparative Study on the Hypoglycemic Effects of Different Parts of Musa balbisiana”
- First Published: 04 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
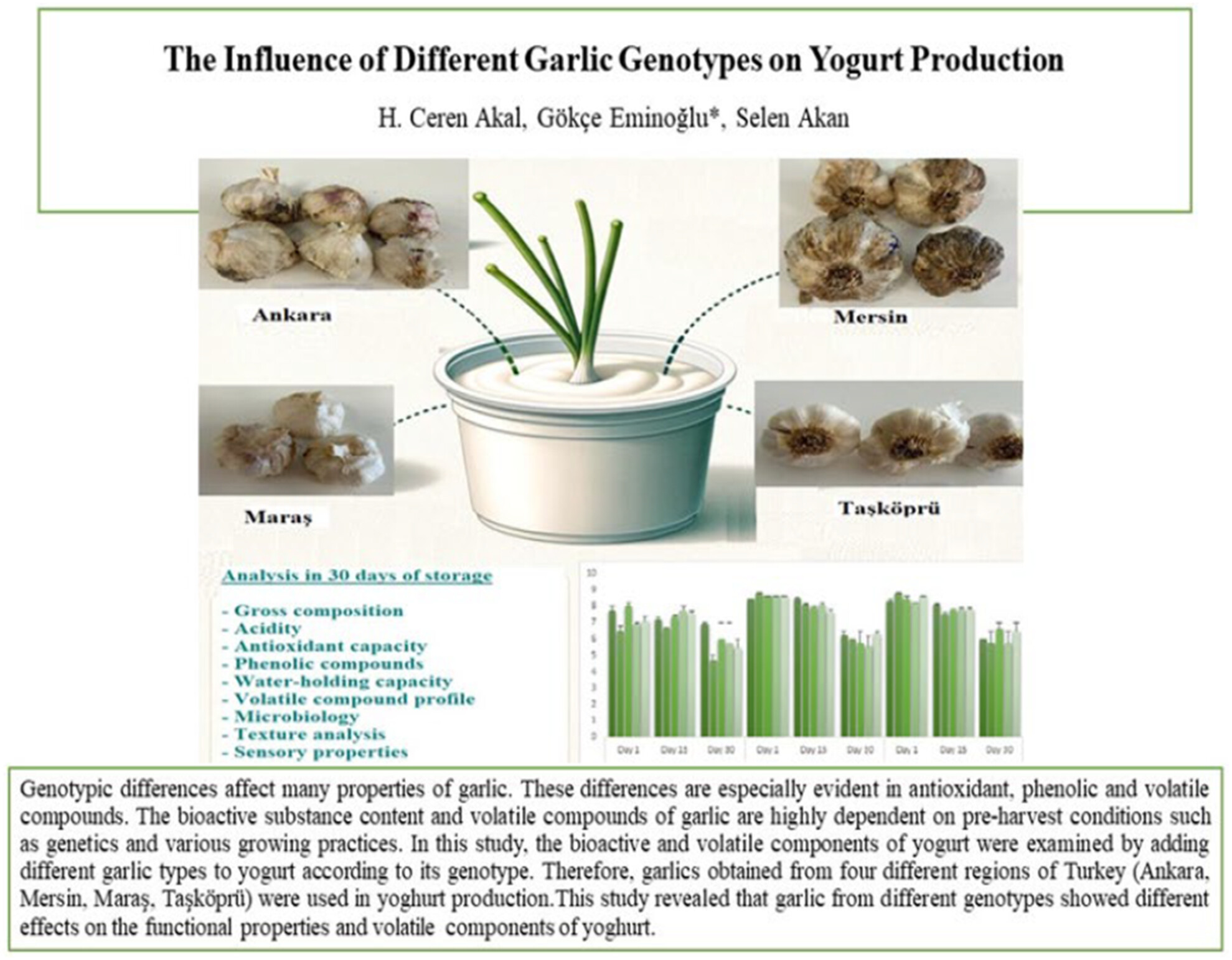
The Influence of Different Garlic Genotypes on Yogurt Production
- First Published: 04 March 2025
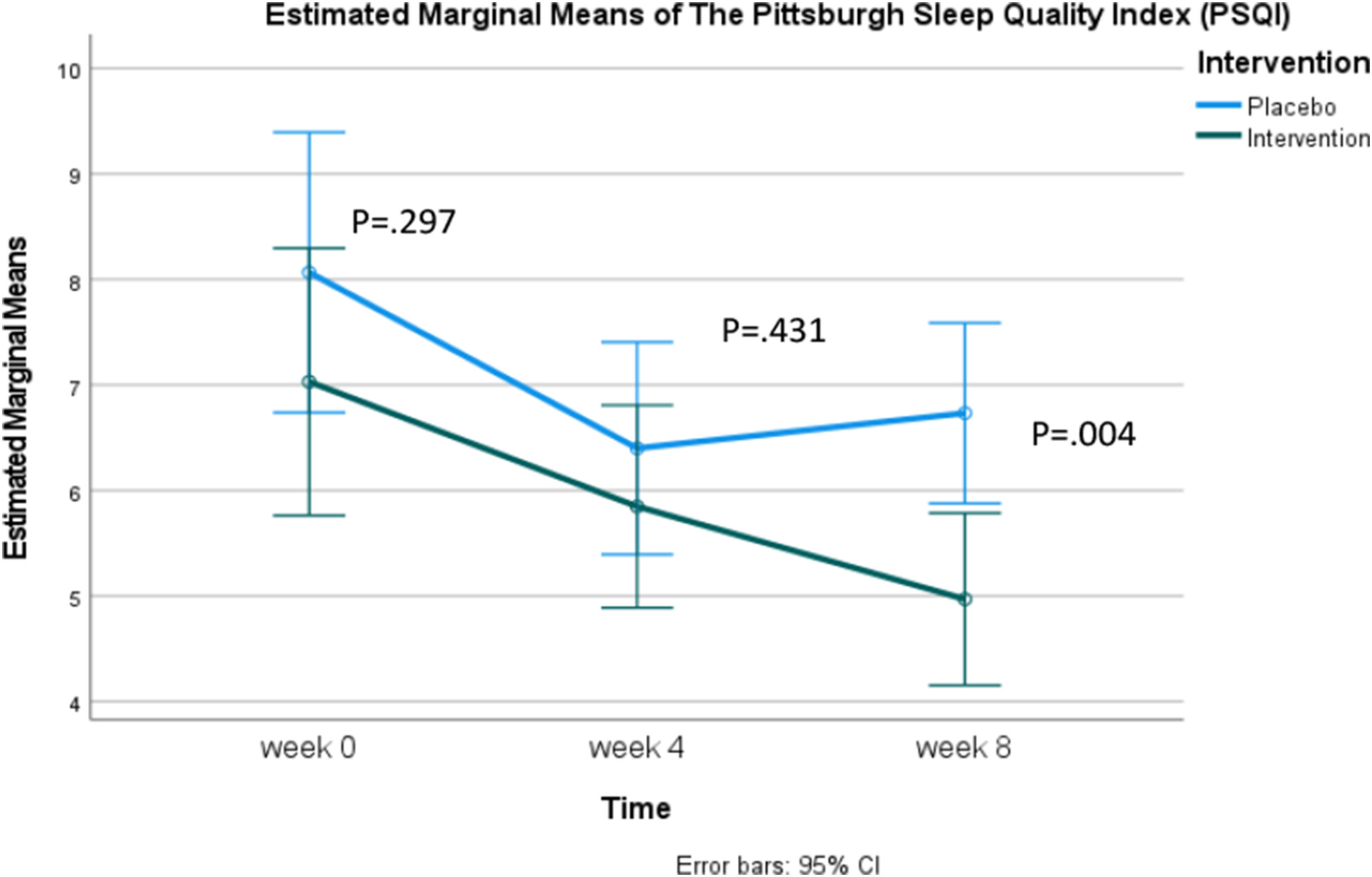
Effectiveness of an Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) Softgel Supplementation on Sleep Quality, Mental Health Status, and Body Mass Index in Mild to Moderately Severe Depression Adults: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- First Published: 05 March 2025
Evaluation of In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacological Activity of Elatostema sessile With In Silico Approaches
- First Published: 06 March 2025
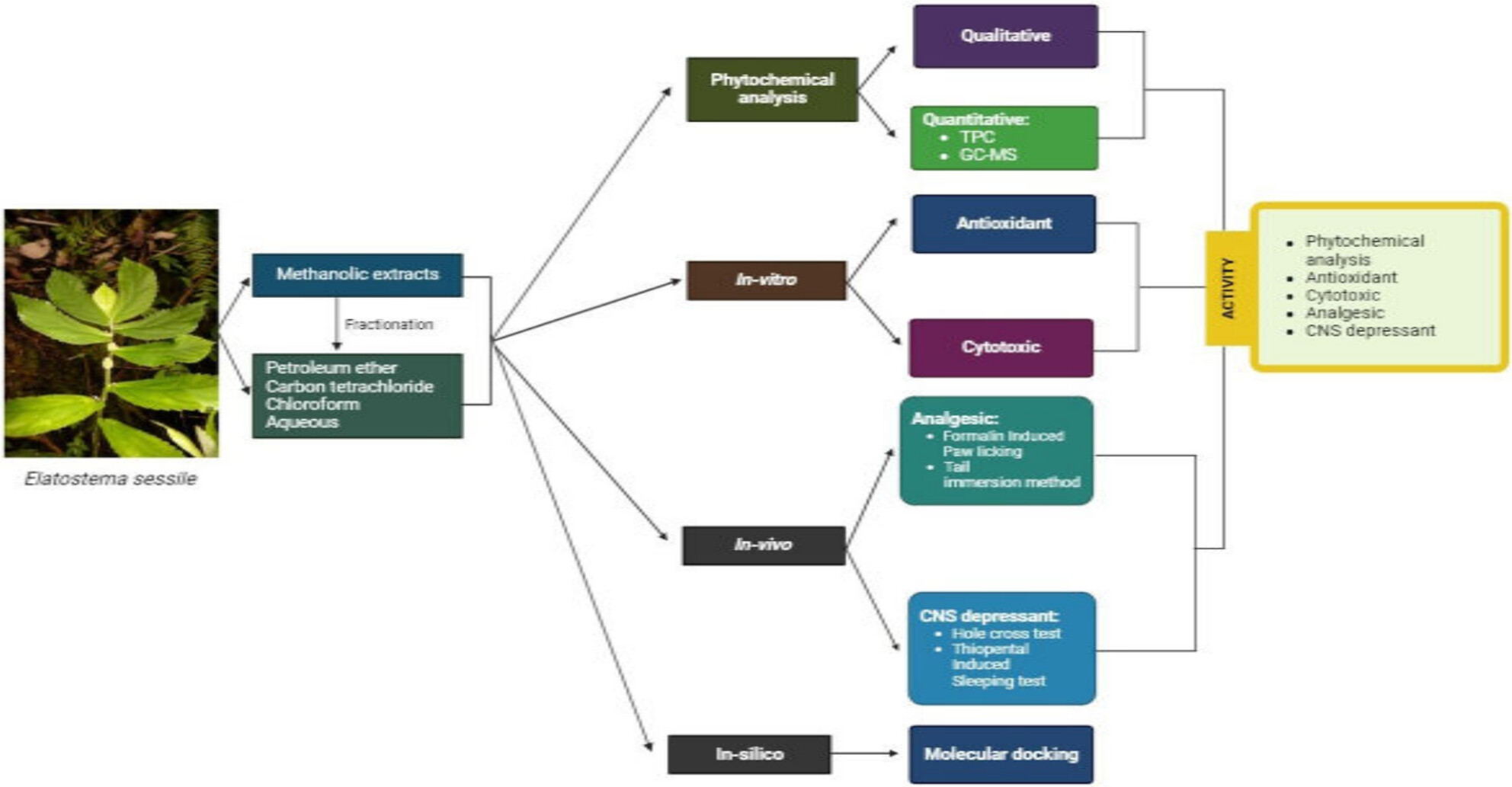
Elatostema sessile exhibits remarkable antioxidant properties, effectively scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, crucial in preventing various diseases. Additionally, its cytotoxic potential suggests promising anticancer applications, while its analgesic effects help in pain management by modulating nociceptive pathways. Furthermore, the plant demonstrates sedative activity, contributing to CNS depression and relaxation, making it a valuable candidate for developing natural therapeutic agents in pharmacology and traditional medicine.
Delivery of Sumac (Rhus coriaria L.) Extract in a Chewing Gum System and Its Functional, Textural, and Sensory Characterization
- First Published: 05 March 2025
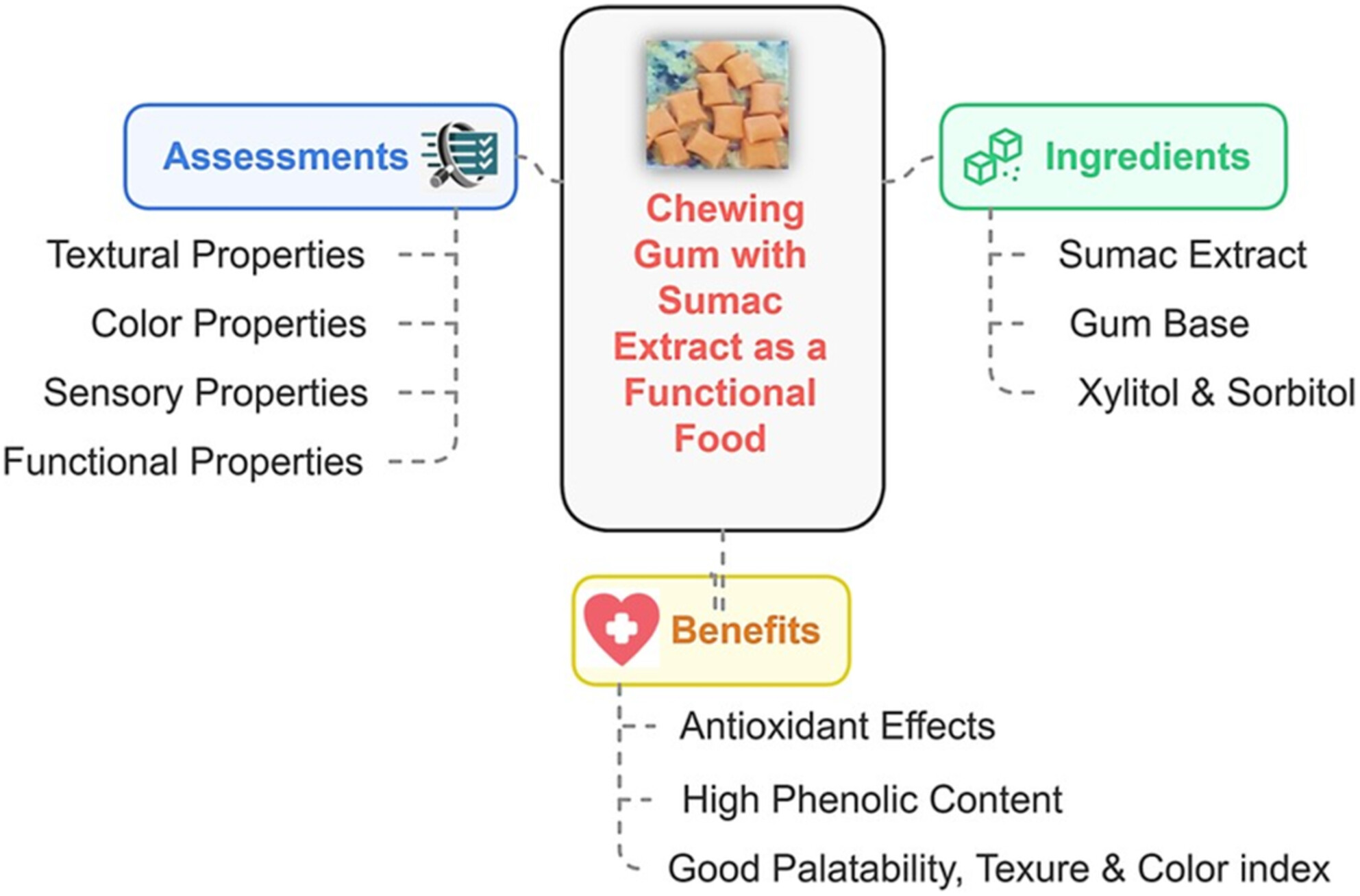
Sumac is a rich source of polyphenols and anthocyanins with potential antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant characteristics. According to our findings, the antioxidant and phenolic content of sumac chewing gum significantly increased in a dose-dependent manner by increasing the sumac extract amount, and all samples had favorable sensory scores, which show the suitability of sumac usage.
Evaluation of Psyllium (Plantago ovata L.) Husk Powder as a Stabilizer in Coconut Milk-Based Probiotic Yogurt Production
- First Published: 05 March 2025
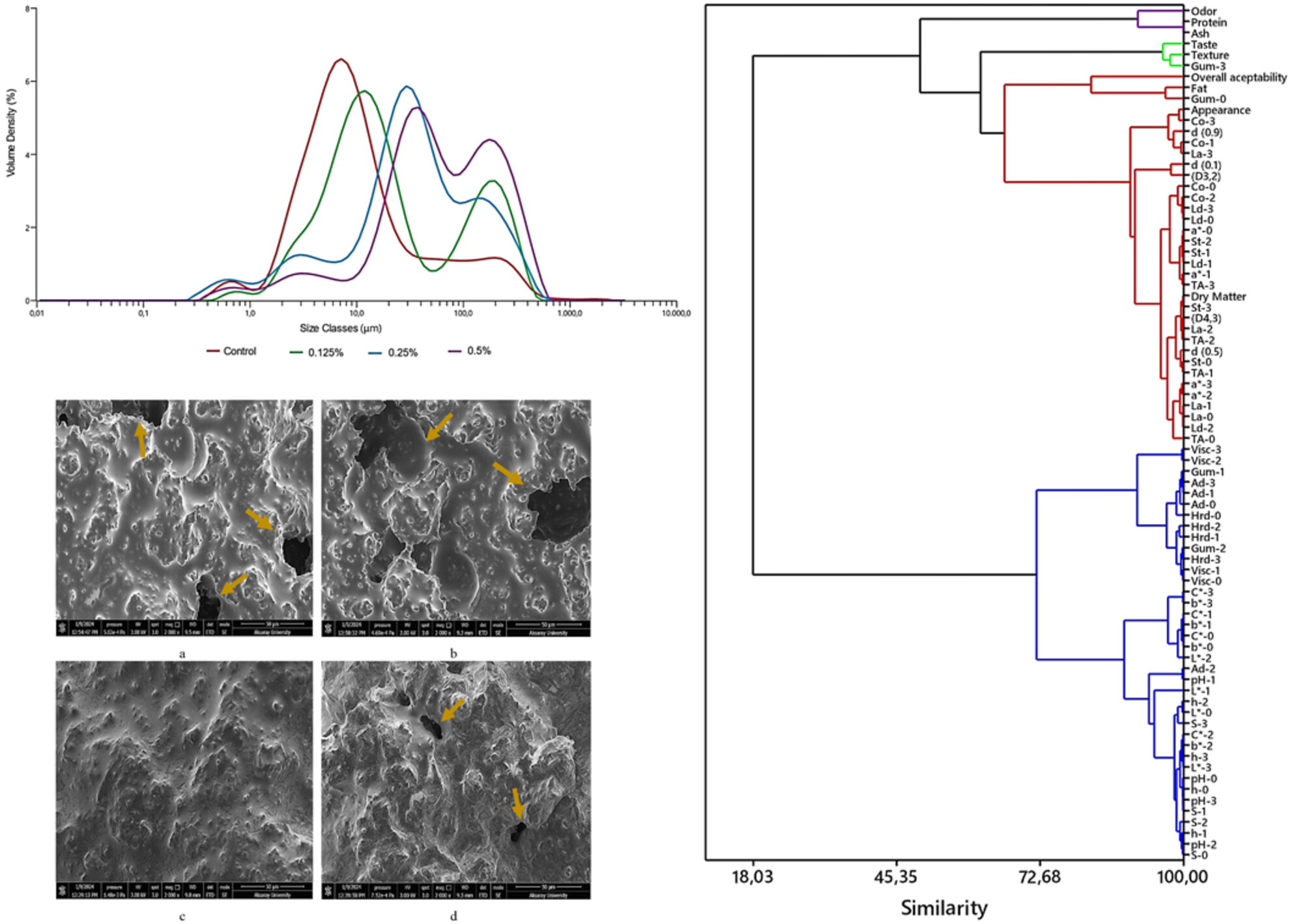
Psyllium husk powder (PHP) was used as a stabilizer in the production of coconut milk-based yogurt. PHP improved the textural, rheological, and microstructural properties of plant-based yogurt. PHP contributed greatly to bacterial growth during fermentation. Adding 0.25% PHP was found to be appropriate in the production of coconut milk-based yogurt.
Alisol B 23-Acetate Down-Regulated GRP94 to Restore Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasis on Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
- First Published: 05 March 2025
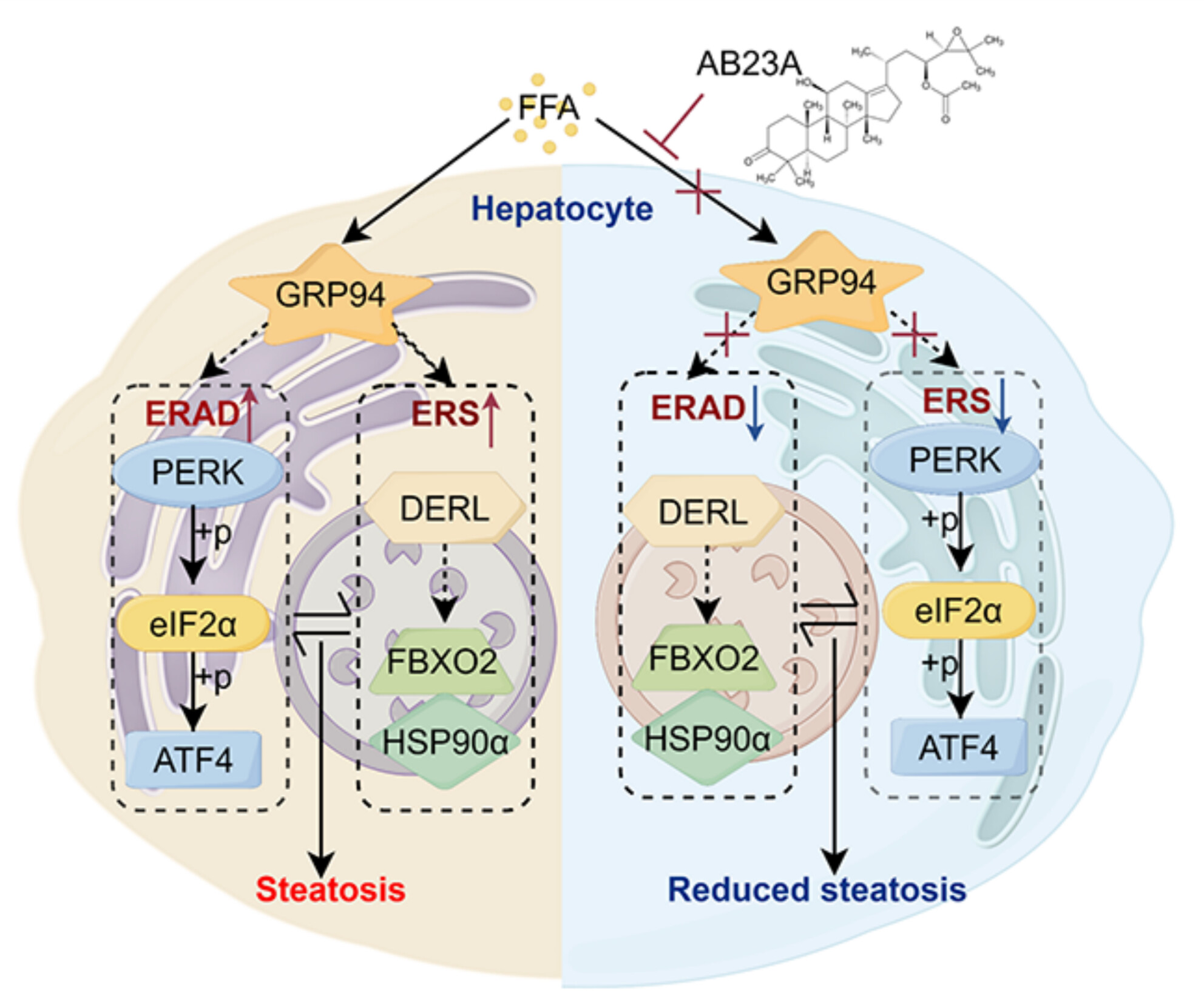
Alisol B 23-Acetate (AB23A) alleviated hepatic injury and lipid deposition in MCD diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) mice. Alisol B 23-Acetate reduced liver cell damage by restoring endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis. AB23A down-regulated GRP94, suppressing ER stress and ER-associated degradation (ERAD).
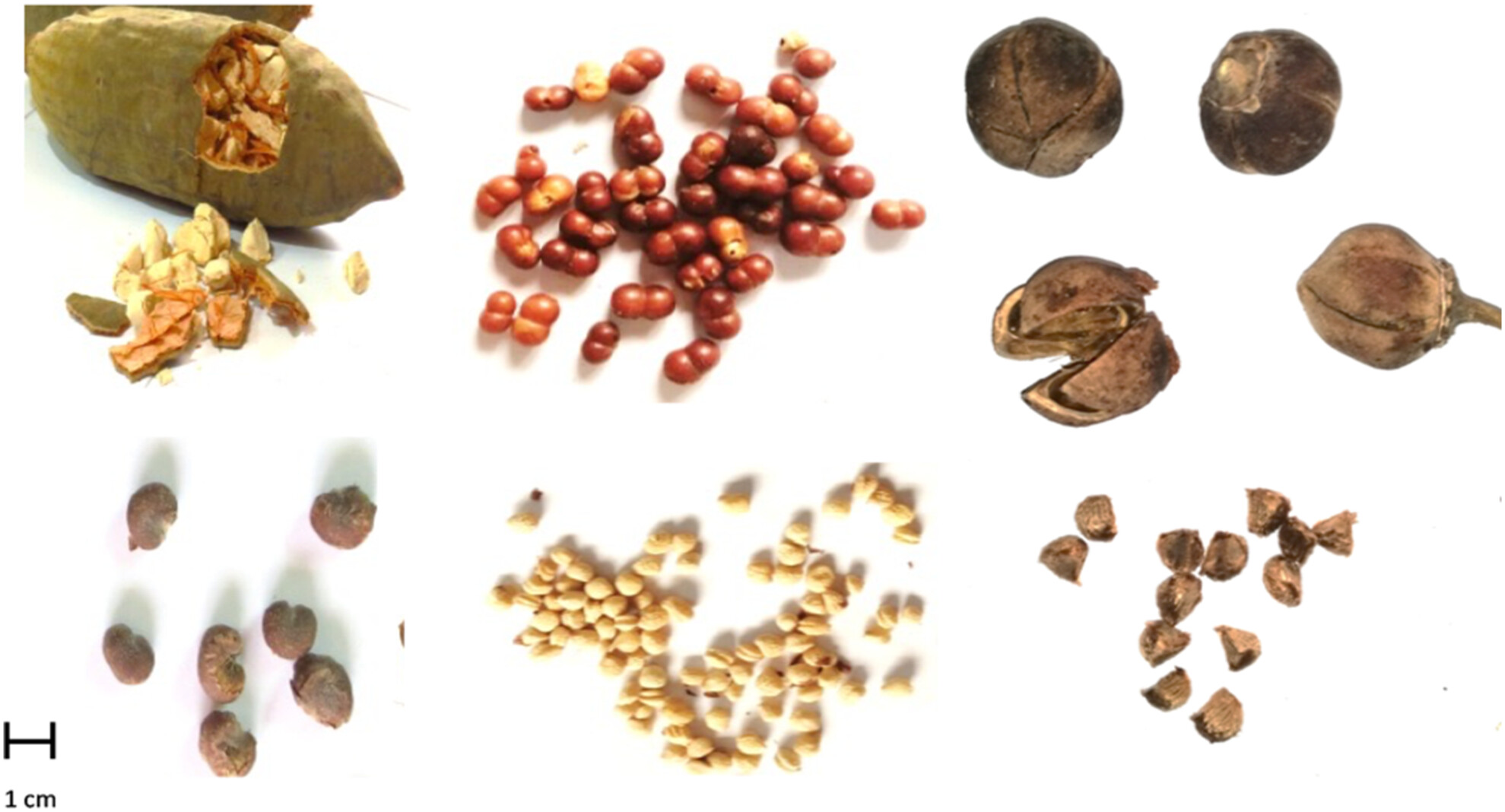
Nutraceutical Potential of Oilseeds and By-Products (Cakes) of Three Underutilized Malvaceae Trees Grown in Sudan
- First Published: 05 March 2025
Silicon Dioxide Nanoparticles Affect the In Vitro Digestion of Sodium Caseinate but Not the Formation and Functionality of Bioactive Peptides
- First Published: 06 March 2025
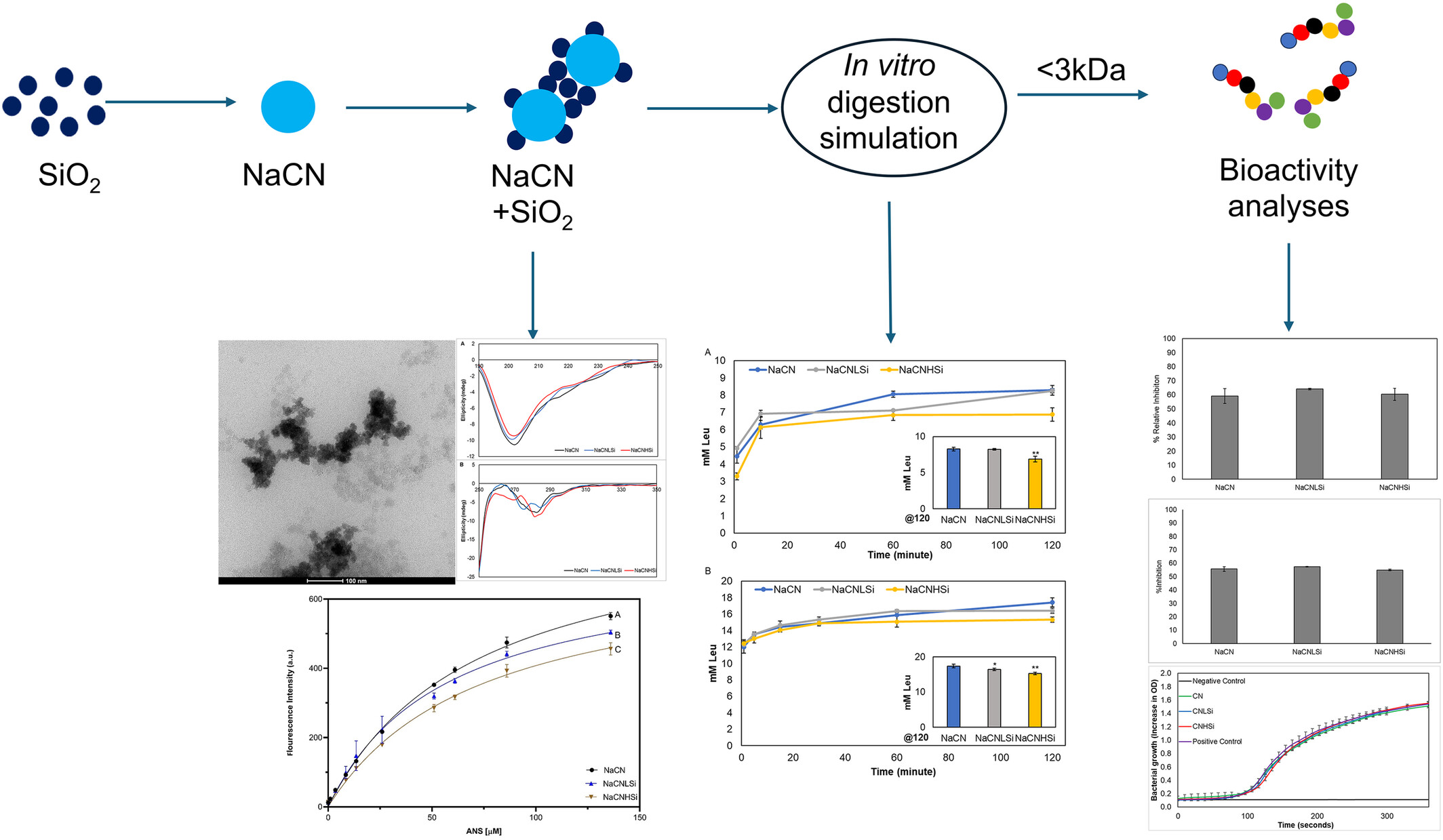
This study aimed to investigate the effect of SiO2 nanoparticles on sodium caseinate structure and digestibility. SiO2 nanoparticles change the secondary and tertiary structures of NaCN. Also, SiO2 nanoparticles influence in vitro digestibility of NaCN. However, it does not affect the bioactivity of the < 3-kDa peptide fraction.
Social Determinants of Food Literacy in Iranian Adult Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 07 March 2025
Promoting informed eating practices across diverse demographic groups may be useful to achieve healthier communities in Iran. Understanding sociodemographic factors such as gender, age, marital status, education using social media and attitude toward it is crucial for developing targeted interventions aimed at improving Iranian food literacy. Performing future investigations within specific contexts could help determine effective strategies for enhancing nutritional knowledge.
The Impact of Carbonic Maceration Pretreatment on the Convective Drying of Seedless Grapes: RSM Optimization, Drying Characteristics and Microstructure
- First Published: 08 March 2025
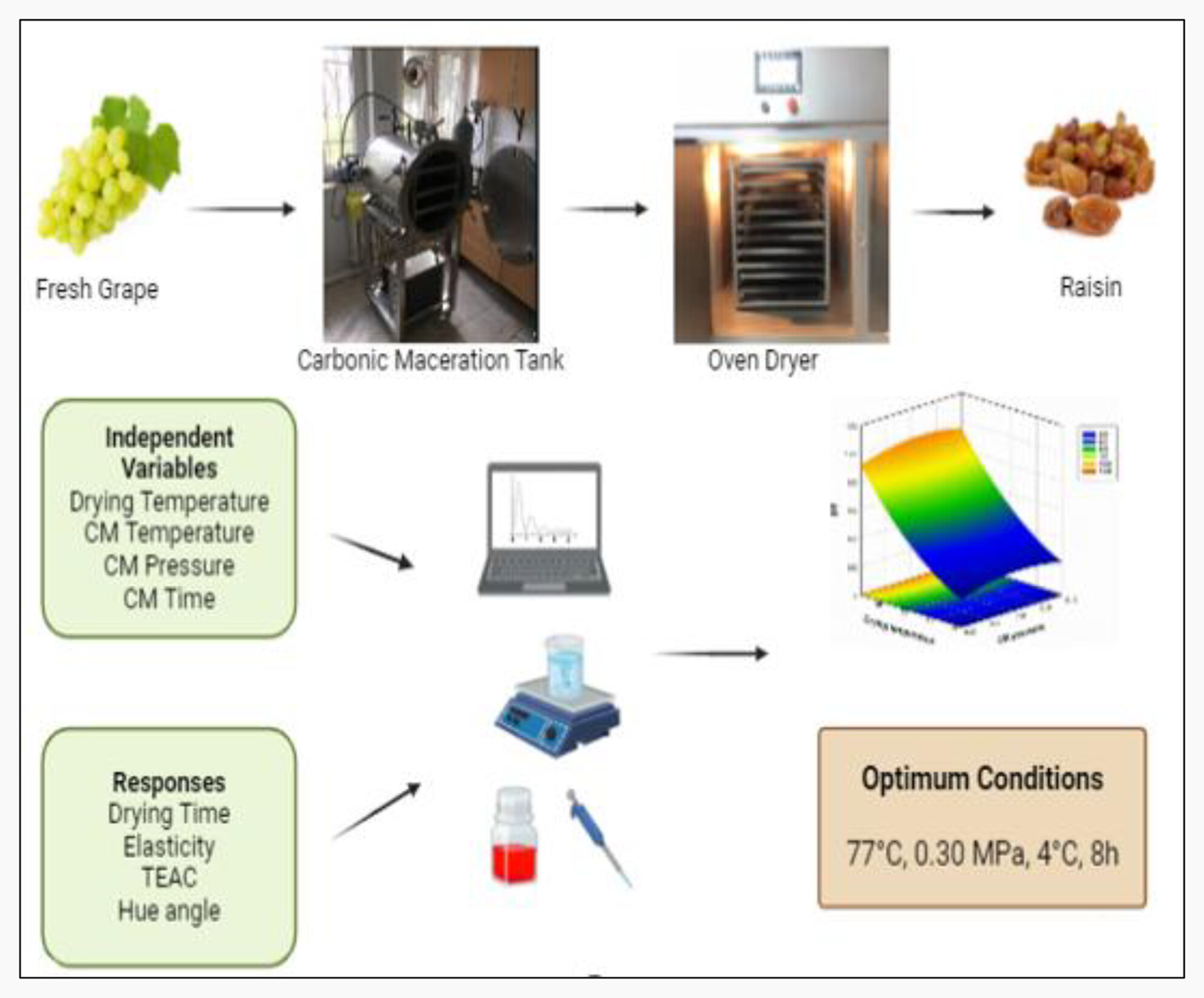
Carbonic maceration (CM) is an effective technique as a pretreatment of the drying process. In particular, the CM treatment accelerated the drying process of grapes by more than 24% compared with the control. For drying operations, CM's significant advantages should be considered in terms of enhancing the process and the product. Additionally, antioxidant activity, surface color, and texture were better preserved in dried grapes treated with CM.
Unlocking the Potential of Freeze-Dried Broccoli Powder: A Novel Approach to Enhancing Cognitive Resilience in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
- First Published: 08 March 2025
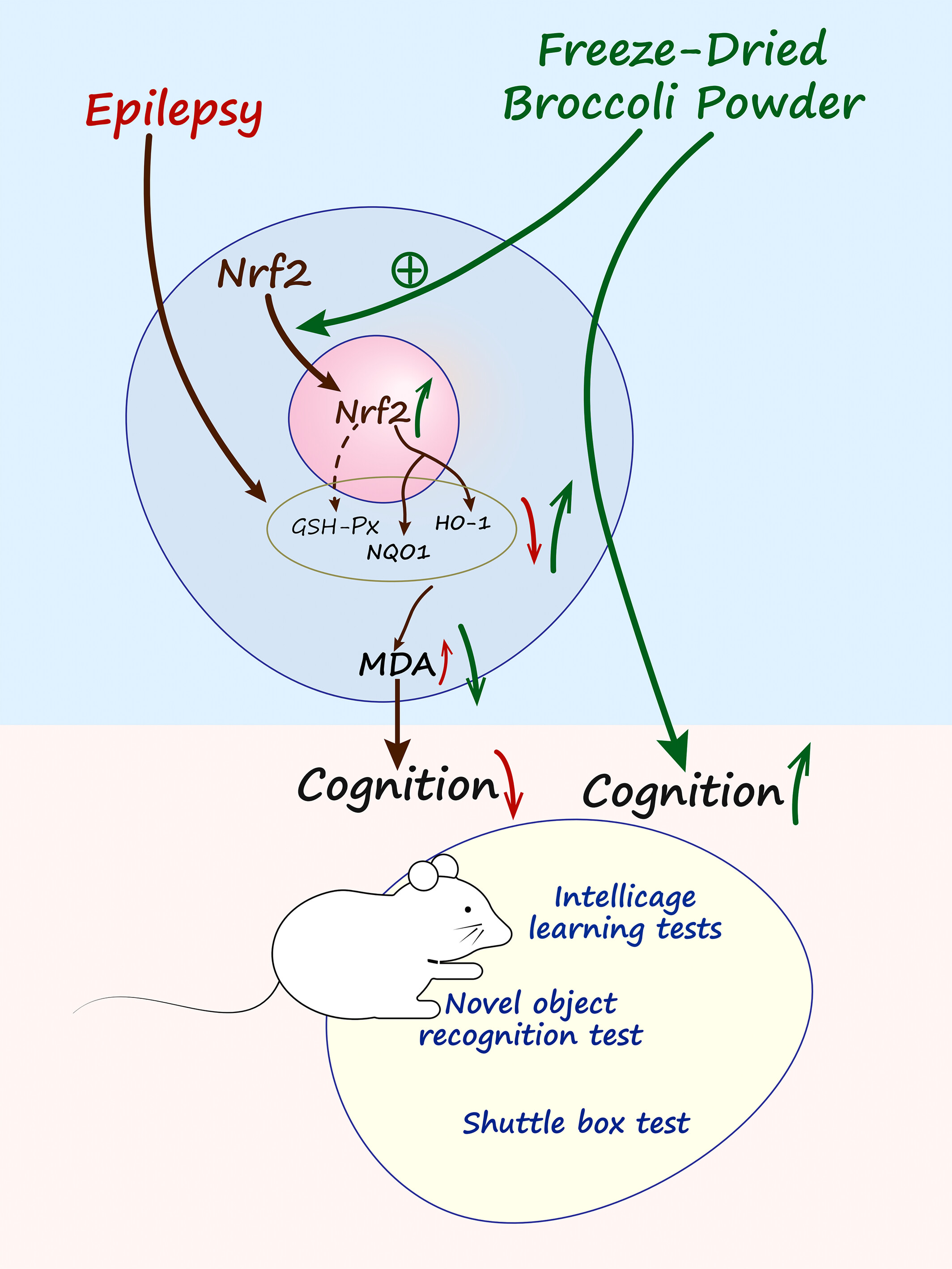
The graphic abstract presents a focused study on the neuroprotective role of freeze-dried broccoli powder in epilepsy, centering on the activation of the Nrf2 pathway. This activation leads to enhanced antioxidative enzyme expression (GSH-Px, HO-1, NQO1) and decreased OS markers (MDA), suggesting a mechanistic pathway for cognitive function improvement in epilepsy models. The investigation highlights the therapeutic efficacy of broccoli-derived compounds in addressing cognitive impairments, offering a novel, adjunctive approach to epilepsy management.
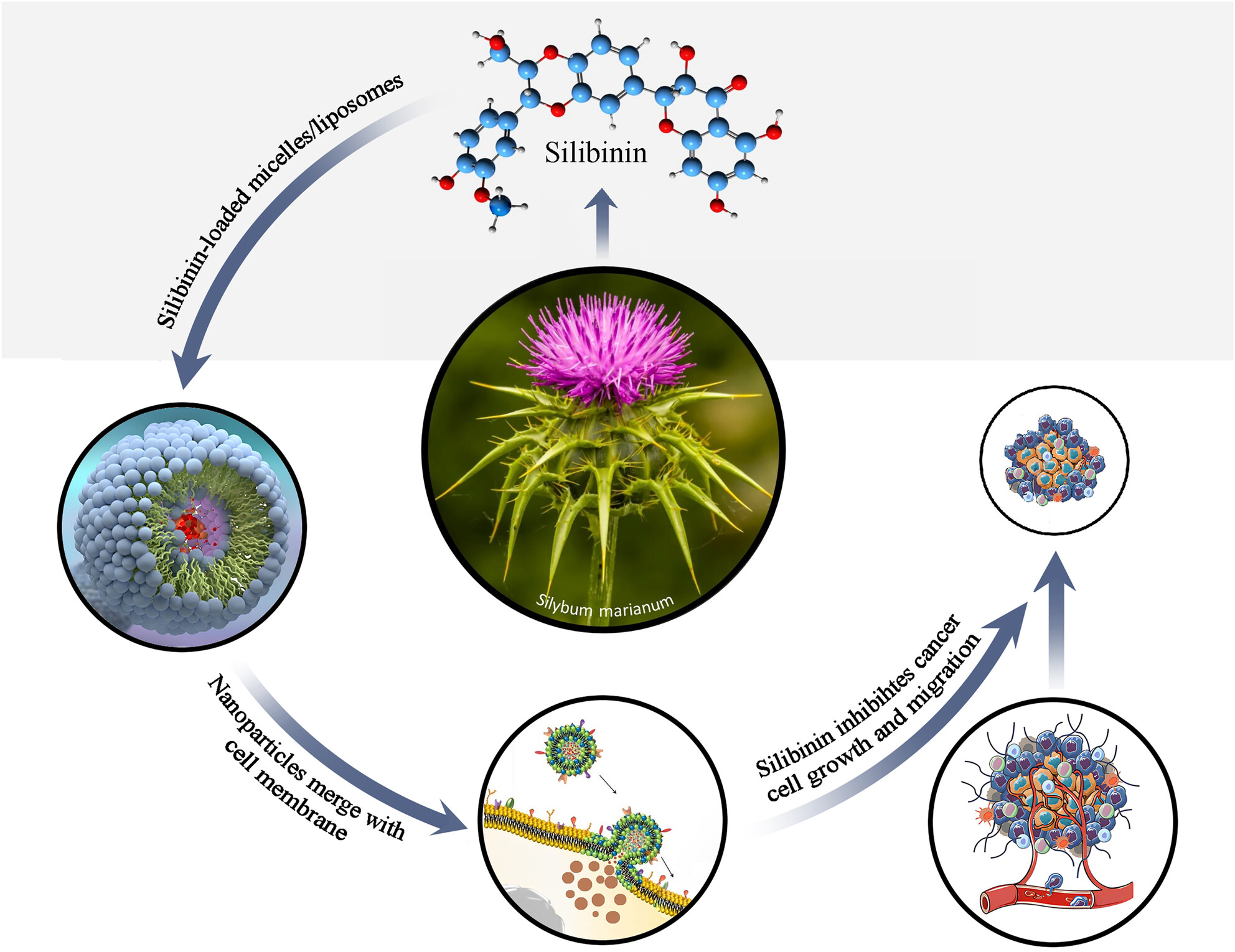
Silibinin-Loaded Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery in Gastric Cancer: In Vitro Modulating miR-181a and miR-34a to Inhibit Cancer Cell Growth and Migration
- First Published: 11 March 2025
REVIEW
Carotenoids Improve Obesity and Fatty Liver Disease via Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review
- First Published: 10 March 2025

Carotenoids are natural micronutrients that are found in plants and microorganisms, but are not synthesized by animals. Our findings showed that dietary supplementation of lycopene, zeaxanthin, fucoxanthin, capsanthin, astaxanthin, and lutein can positively affect obesity and FLD by regulating GM and intestinal barrier integrity.
Isoflavones: Promising Natural Agent for Cancer Prevention and Treatment
- First Published: 11 March 2025
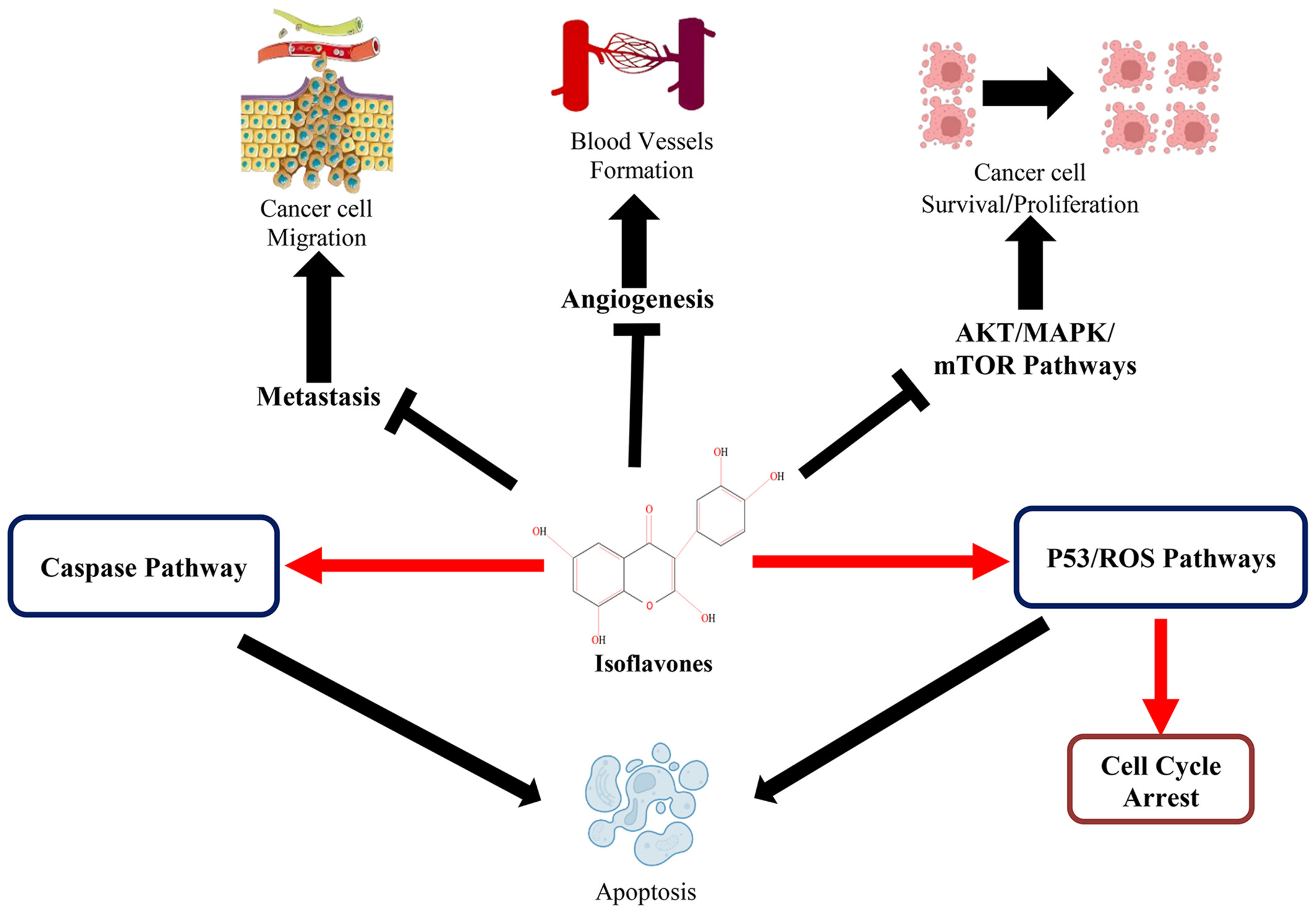
Isoflavones are currently being investigated by researchers in order to demonstrate their ability to prevent the proliferation of cancer cells. The current review aimed to demonstrate the potential of isoflavones to eliminate cancerous cells in the stomach, liver, lung, breast, and prostate, as their anticancer properties are due to the ability to block the signaling pathways of the extracellular signal-controlled kinase (MAPK/ERK) and proteasome (PI3K/AKT/mTOR). Isoflavones can inhibit the cell division of various cancer cells. Isoflavones can block the androgen receptor (AR), a protein that is required for the growth and dissemination of prostate cancer.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Integration of Destructive and Non-Destructive Analytical Determinations for Evaluating Quality of Fresh and Roasted Hazelnuts Subjected to Different Processing Temperatures
- First Published: 12 March 2025
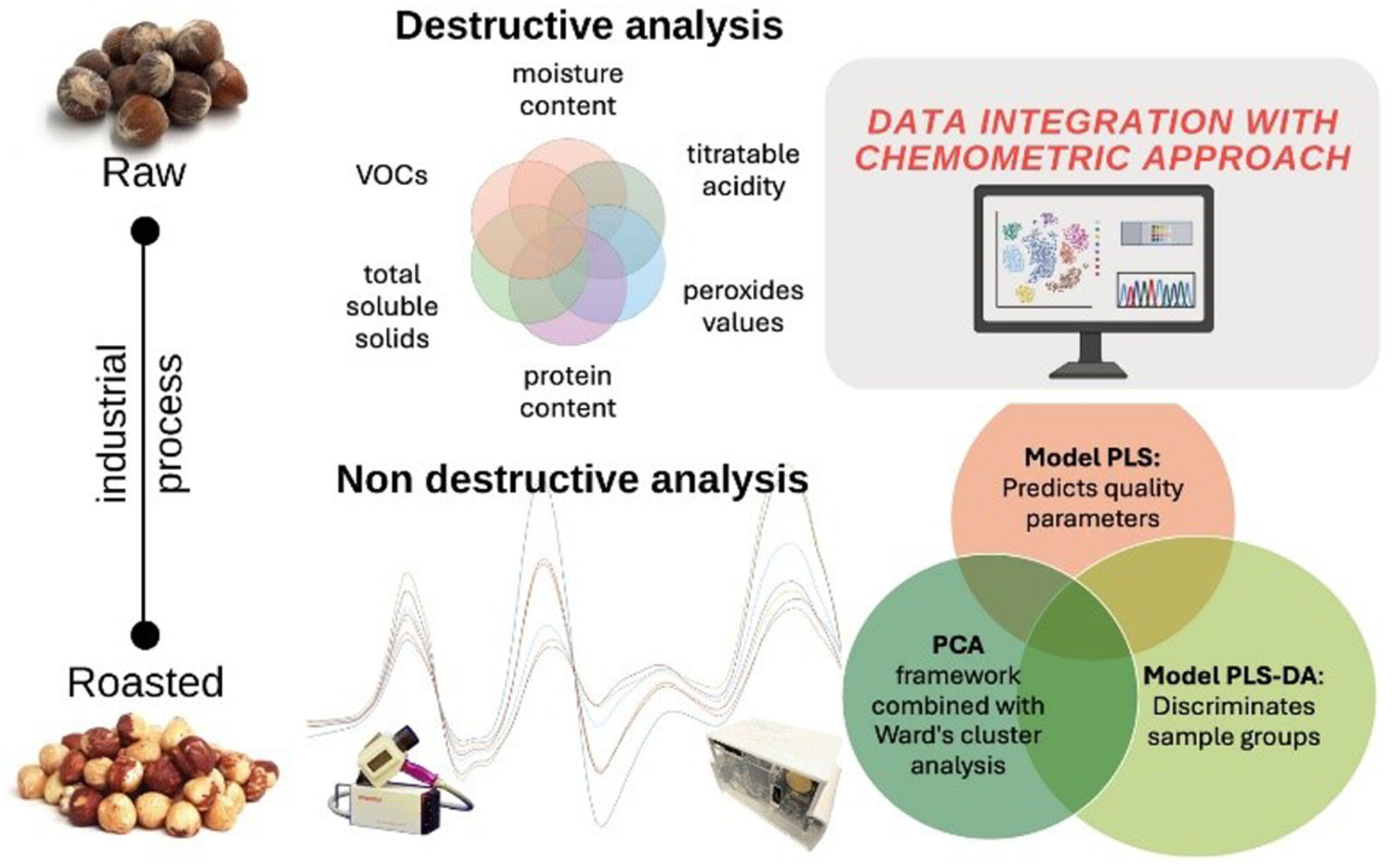
Non-destructive techniques including FT-NIR spectroscopy and E-nose detection, combined with chemometric approaches, demonstrated strong potential for real-time hazelnut quality assessment. FT-NIR spectroscopy accurately predicted moisture content, while E-nose differentiated roasting intensities. Their feasibility in process monitoring highlights a significant advantage over traditional, labor-intensive methods, offering a rapid and efficient solution for quality control in the hazelnut industry.
Optimization and Modeling of Ultrasound- and Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Turmeric to Efficiently Recover Curcumin and Phenolic Antioxidants Followed by Food Enrichment to Enhance Health-Promoting Effects
- First Published: 20 March 2025

Antioxidants are biologically important molecules playing a crucial role in combating reactive species under oxidative stress conditions. In this study, microwave-assisted extraction and ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) processes are used for the extraction of antioxidants from turmeric using an ethanol-water mixture. As a model food system, the red lentil soup was enriched with extracts obtained by the UAE process, and the effects of extract addition to a protein-rich food matrix and spontaneous protein–curcumin interaction were investigated in association with simulated gastrointestinal digestion.
Fortification of Sunflower Oil by Nanoemulsions Containing Vitamin-D3: Formation, Stability, and Release
- First Published: 14 March 2025
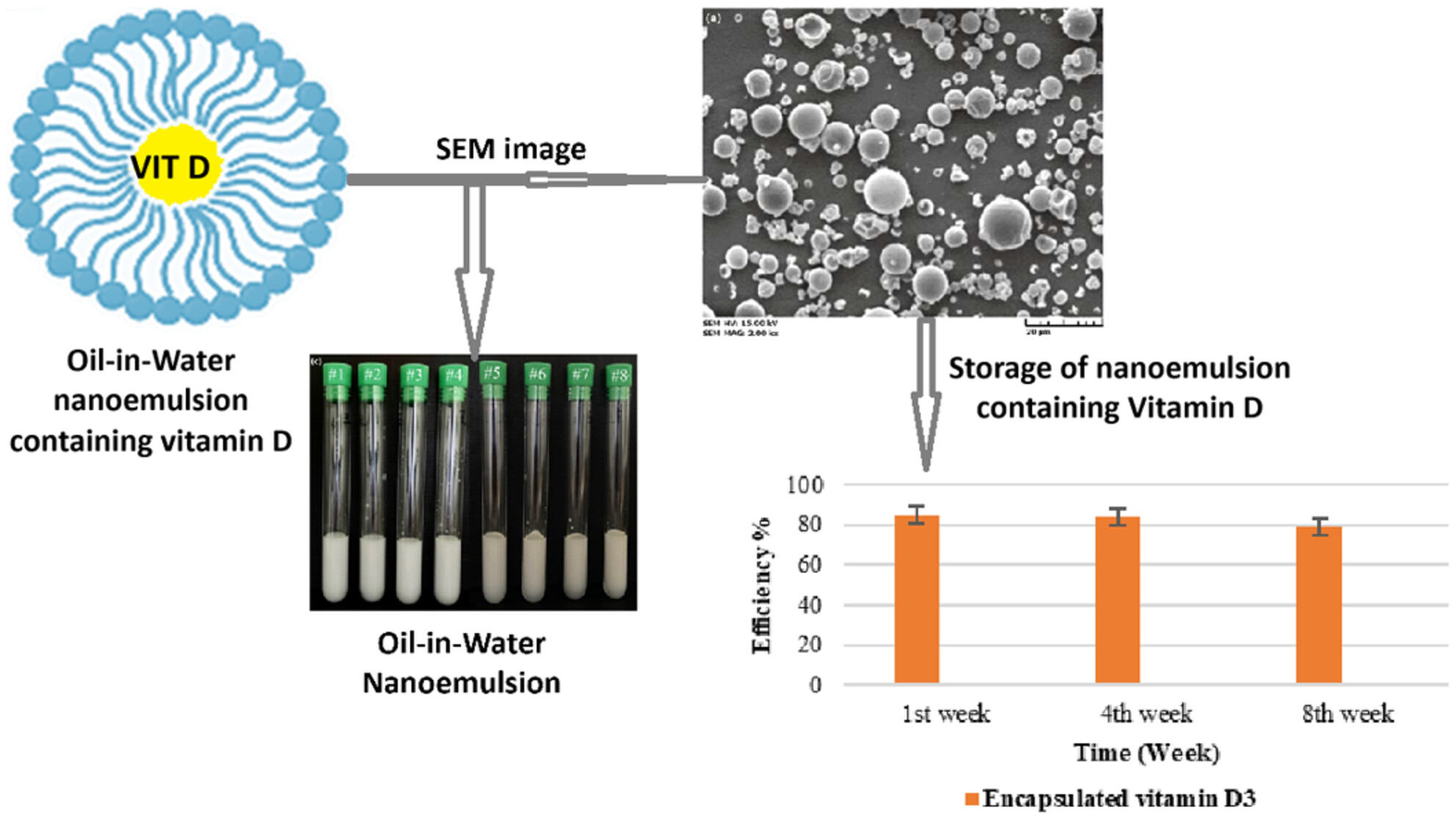
Vitamin D3 (VIT D) was encapsulated in oil-in-water (Q/W) nanoemulsion. Optimal encapsulation was obtained at 27.5% oil, 2.5% surfactant, 1% WPC, and 2% pectin. The nanoemulsion stability was over 60 days of storage with a z-average particle size of 98.2 nm. HPLC analysis indicated a 90% recovery of encapsulated VIT D in sunflower oil.
The Impacts of Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Lactobacillus rhamnosus to Promote In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Profile of RA-Macrophages
- First Published: 16 March 2025
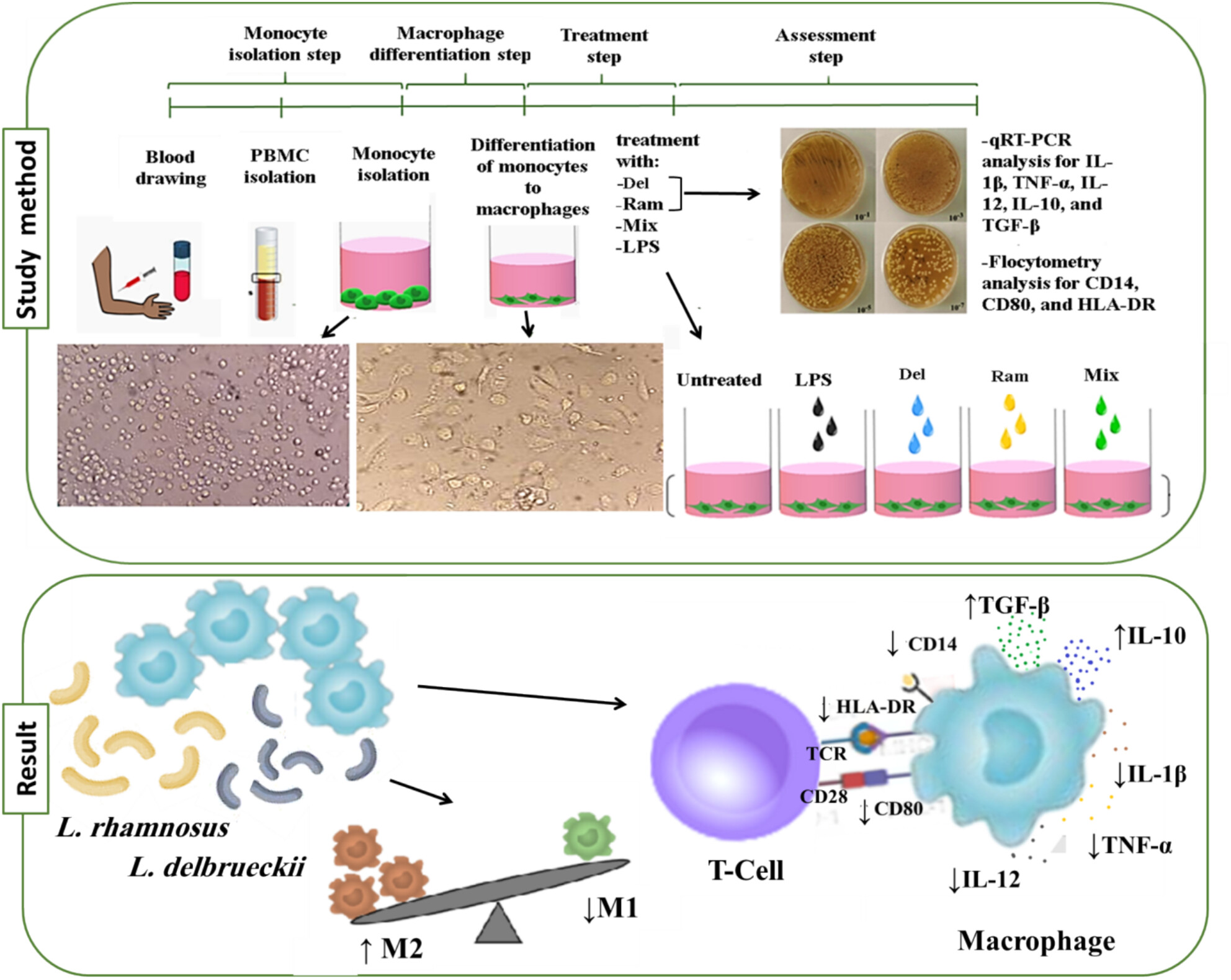
PBMCs were first separated from blood using the Ficoll method. Then, monocytes were isolated from PBMC using the plastic adherence method to differentiate them into macrophages within 5 days. Subsequently, they were treated with LPS, Lactobacillus delbrueckii (Del), Lactobacillus rhamnosus (Ram), and a mix of them. The probiotic effects on macrophages were assessed using qRT-PCR and flow cytometry. Treating macrophages with L. delbrueckii and L. rhamnosus significantly alters their capability to stimulate CD4+ T cells. Probiotic bacteria not only reduce the expression of HLA-DR, which is essential for T cell receptor (TCR) signaling (the first stimulatory signal for T cells) but also decrease the CD80 co-stimulatory marker on macrophages, which interacts with CD28 on T cells (the second stimulatory signal for T cells). Additionally, these probiotic bacteria lower the expression of CD14 on macrophages, a receptor involved in receptor-mediated phagocytosis. Significantly, treatment with these probiotics enhances the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-10 and TGF-β, while simultaneously diminishing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-12, IL-1β, and TNF-α in macrophages. These findings suggest a polarization of macrophages toward the M2 phenotype in both RA patients and healthy individuals. LPS-treated groups, treatment with probiotic bacteria (Del, Ram, and Mix).
Luteolin Inhibits Dexamethasone-Induced Osteoporosis by Autophagy Activation Through miR-125b-5p/SIRT3/AMPK/mTOR Axis, an In Vitro and In Vivo Study
- First Published: 17 March 2025
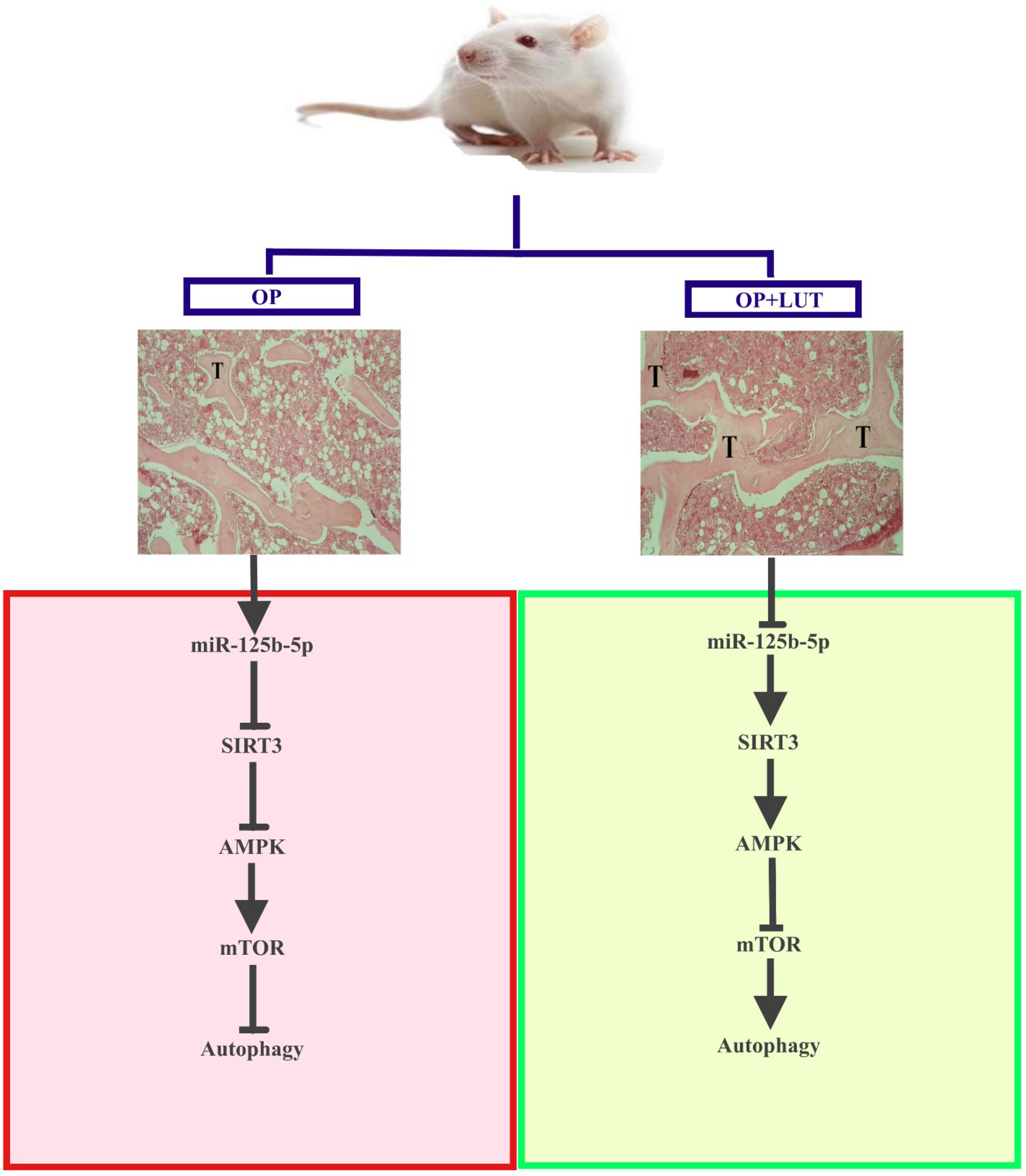
The present findings revealed that osteoporosis is associated with the overexpression of miR-125b-5p and alteration in the SIRT3/AMPK/mTOR axis, which is followed by the suppression of autophagy in BMSCs and bone tissue. Meanwhile, the administration of luteolin was able to improve the bone tissue of animals treated with DEX according to histological, biochemical, and molecular analyses. The change in the expression of miR-125b-5p and the SIRT3/AMPK/mTOR axis, which was accompanied by the induction of autophagy, could be considered the underlying mechanism of the therapeutic properties of luteolin in confronting osteoporosis. Nonetheless, the current findings cannot be assumed as evidence for the application of luteolin as a therapeutic strategy in patients with osteoporosis, since further studies, especially clinical trials, are necessary.
RETRACTION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Rosa roxburghii Fermentation Broths Attenuate Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 Signaling Pathway and Modulating Gut Microbiota
- First Published: 19 March 2025
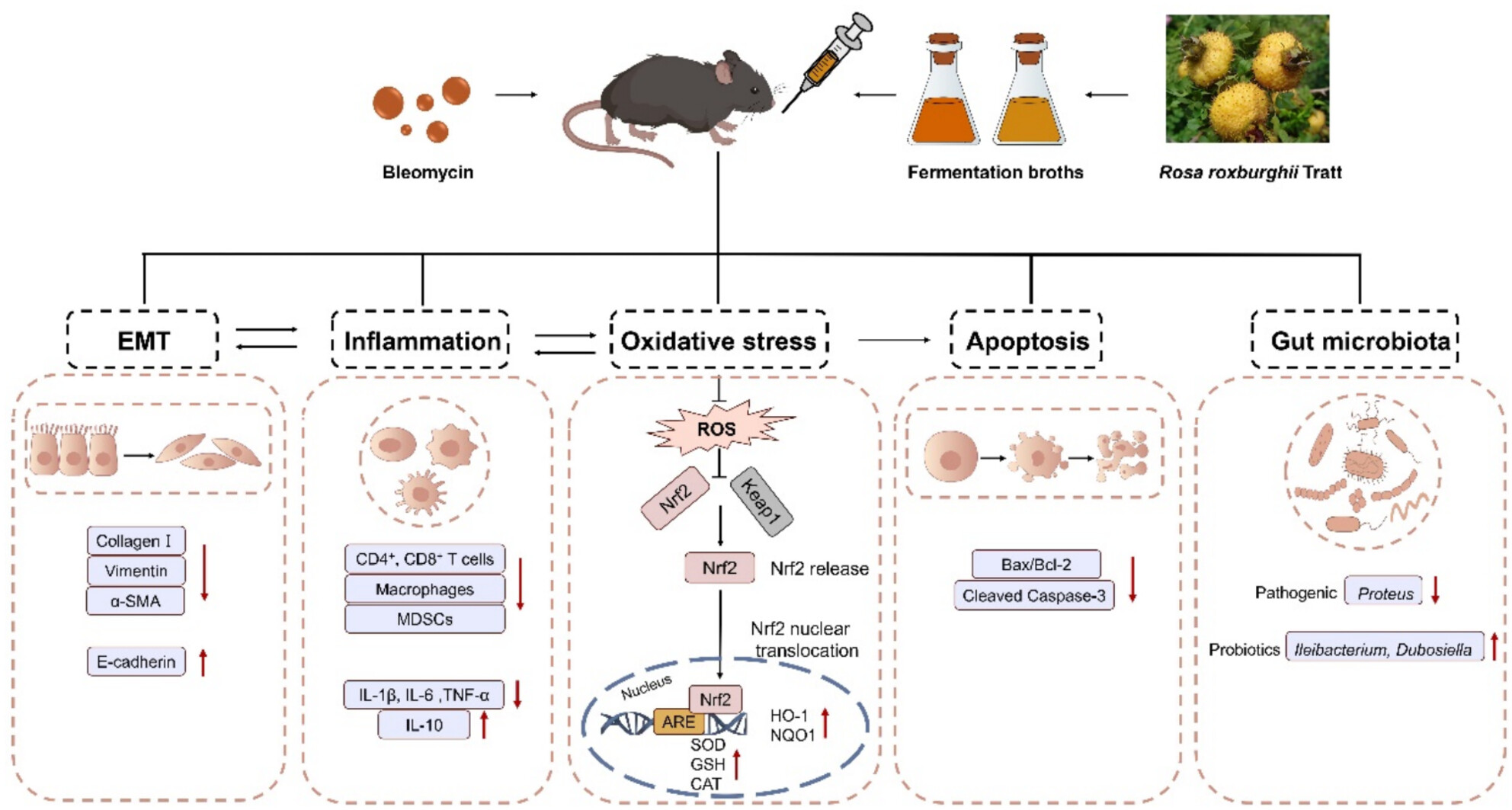
RRFBs exert a lung-protective effect by inhibiting oxidative stress and alleviating intestinal disturbances. Our results revealed that RRFBs attenuated BLM-induced PF in mice. With respect to the underlying mechanisms, RRFBs ameliorated inflammatory responses, EMT, oxidative stress, and apoptosis by activating the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway. They also attenuated alterations in the gut microbiota in PF; in particular, RRFBs decreased the relative abundance of the pathogenic bacterium Proteus while increasing the relative abundance of the probiotics Ileibacterium and Dubosiella.
CORRECTION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Investigating Coriander Leaf Phenolics With HPLC-UV and Their Role in Modulating Nitrogen Metabolism
- First Published: 17 March 2025
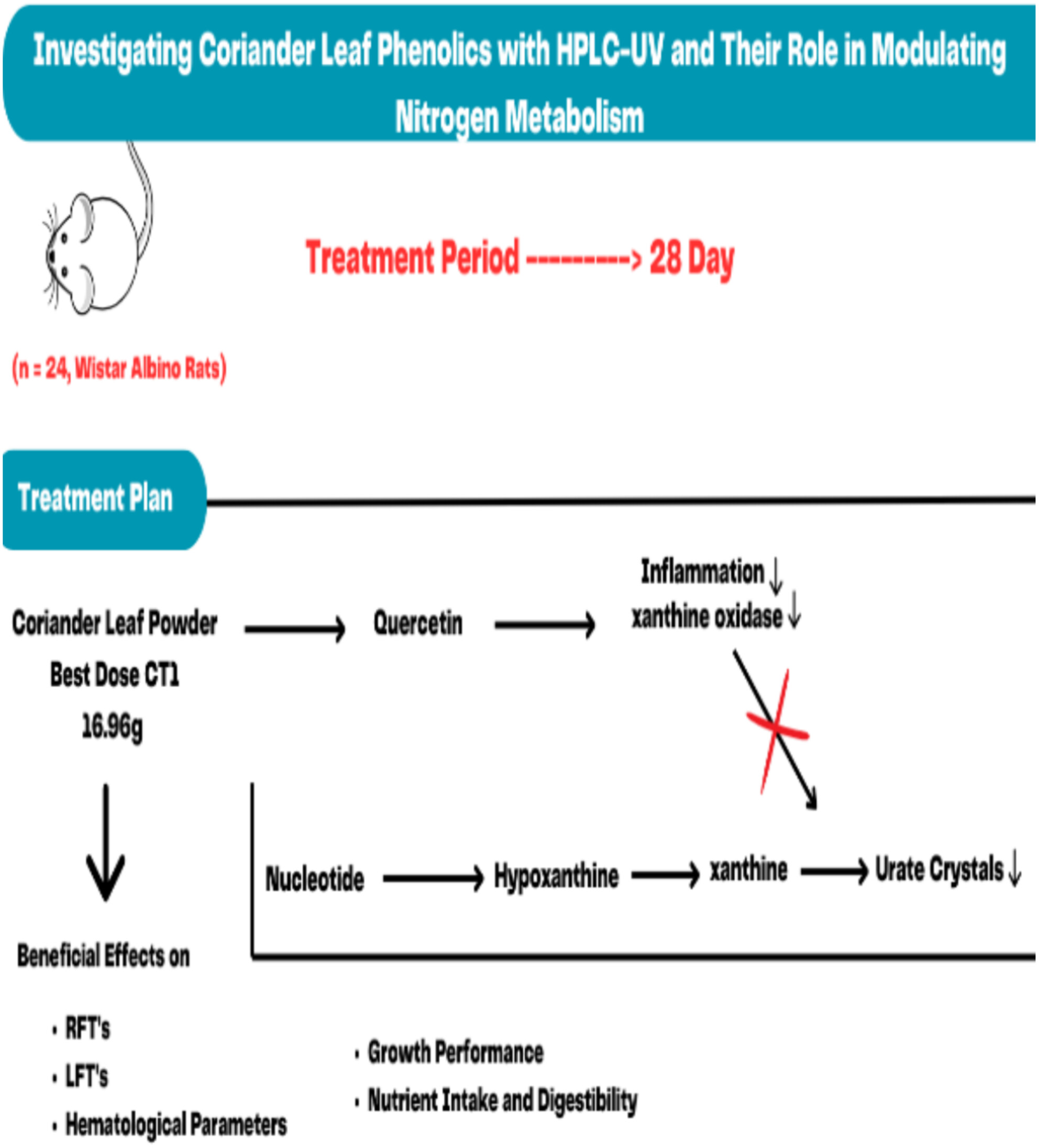
Coriander has the antibacterial, immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory, free radical scavenging, antilipidemic, and antiaging it significantly lower the prevalence of hyperuricemia. Coriander inhibits the xanthine oxidase enzyme because of the variable amount of quercetin that has the capacity to reduce uric acid in the body. Therefore, in this research study, Coriander leaf powder is used to prevent the formation of uric acid crystals, which proved to be much more effective and have no side effects.
Antioxidant, Phenolic, Flavonoid, and Mineral Content of L. officinalis and Its Cytotoxic Effect on Human Embryonic Kidney (Hek-293) Cells
- First Published: 19 March 2025
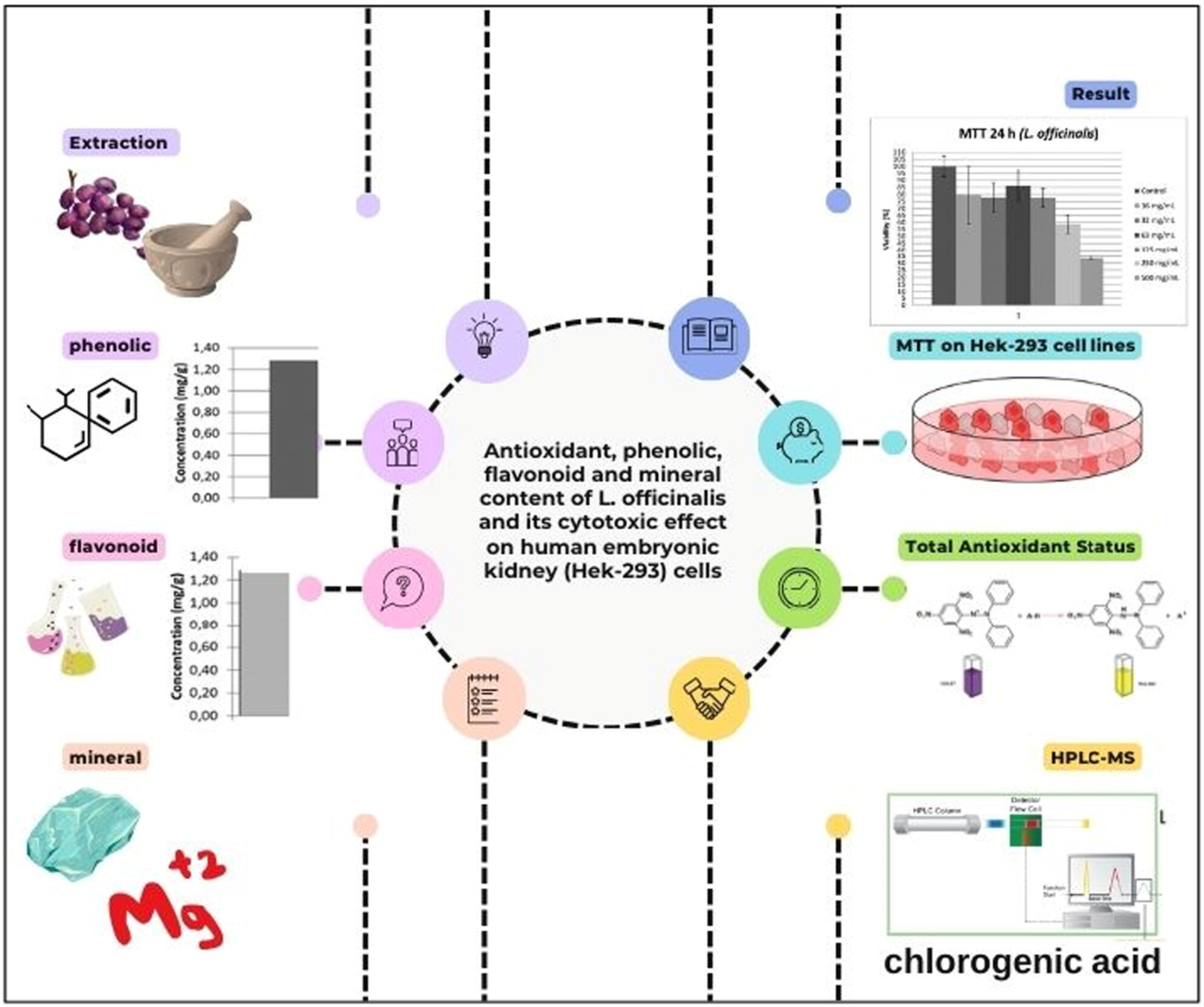
L. officinalis is mostly known as a hypoglycemic summer fruit and is used as a folk medicine in Turkey between diabetic patients. Its phenolic, flavonoid, mineral content (mostly Mg), antioxidant capacity is high, and the phenolic compound found in cherry laurel due to HPLC analysis is mostly chlorogenic acid. These contents are good sources for preventing chronic diseases, but in this case, even in healthy cells, natural products have shown cytotoxic effects in a dose-dependent manner.
REVIEW
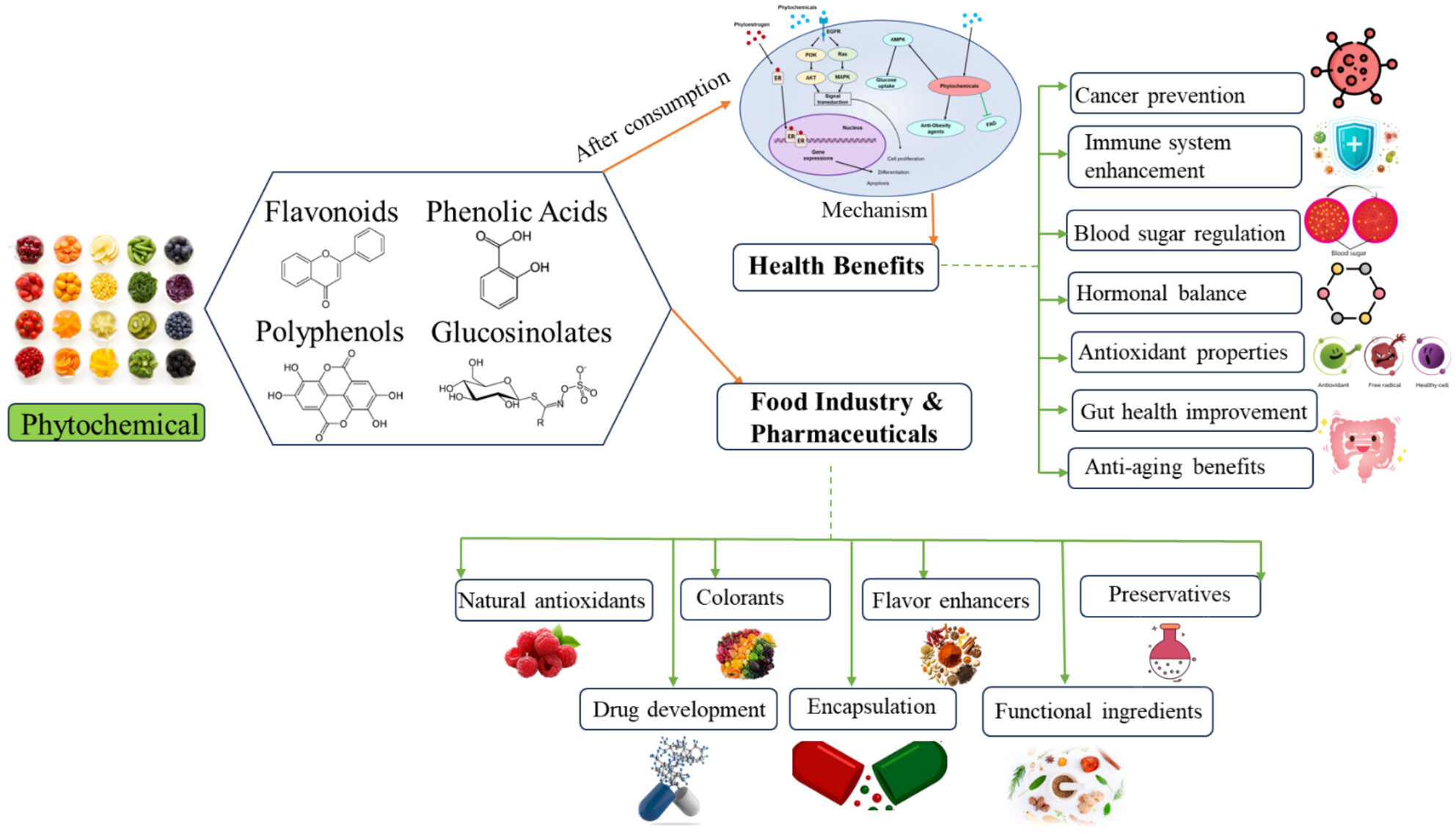
Dietary Phytochemicals in Health and Disease: Mechanisms, Clinical Evidence, and Applications—A Comprehensive Review
- First Published: 19 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Effect of Lyophilised Sweet Potato on the Quality and Nutritional Characteristics of Set Yogurt
- First Published: 19 March 2025
Sugar-Sweetened Beverages, Artificially Sweetened Beverages and Sugar Forms With Long-Term Risk of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Large-Scale Prospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 19 March 2025
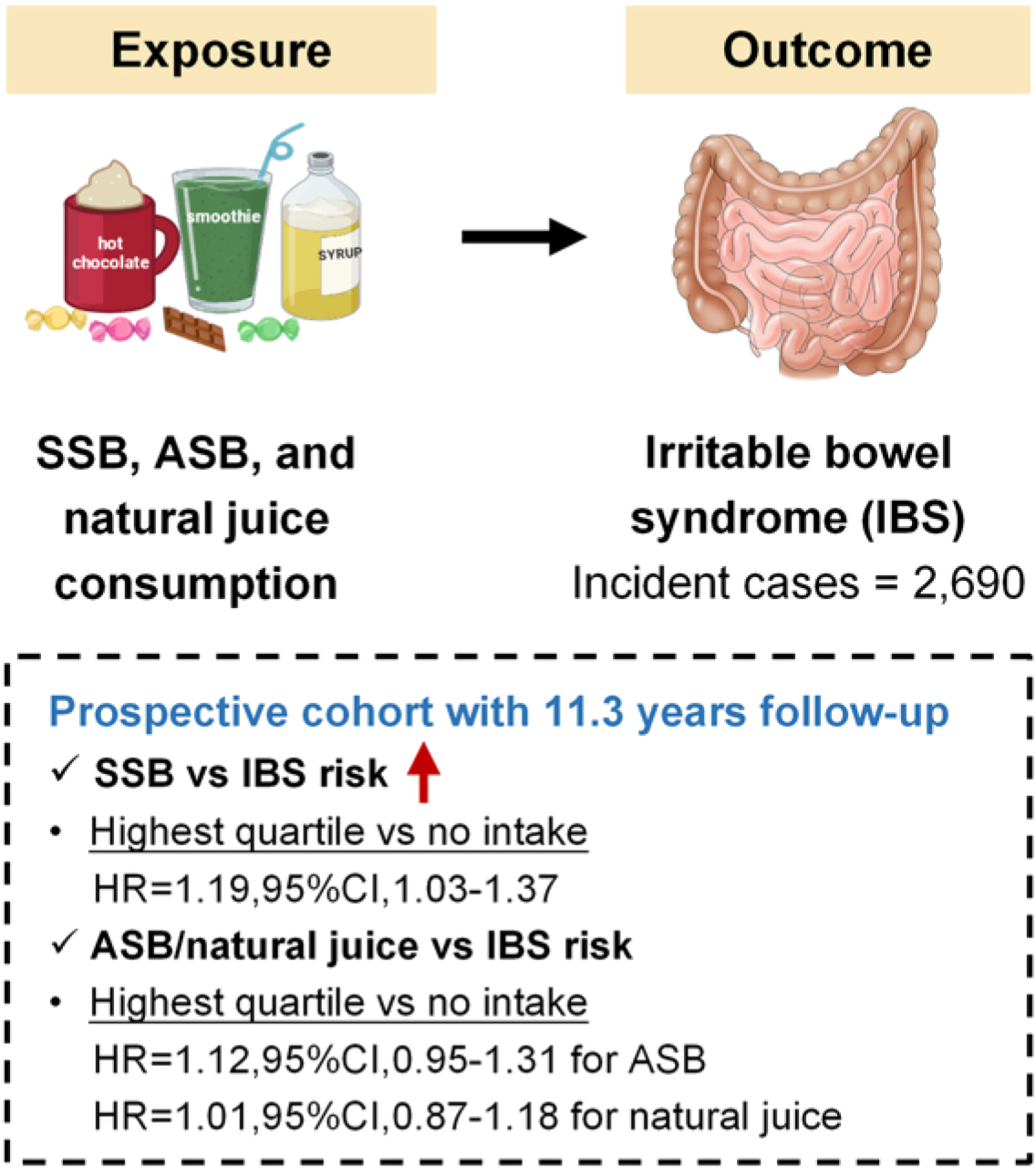
In this large-scale prospective cohort, higher intake of sugar-sweetened beverages is associated with a higher risk of incident IBS, rather than the null association for artificially sweetened beverages or natural juice intake. Higher consumption of added sugar, instead of naturally occurring sugar, is associated with an increased risk of IBS development, suggesting the potential role of sugar forms rather than simply the amount.
REVIEW
The Inflammation-Initiating and Resolving Mechanisms and Oxidation: Could Periodontal Therapy and Nutritional Strategy Improve the Systemic Health? A Narrative Review
- First Published: 20 March 2025
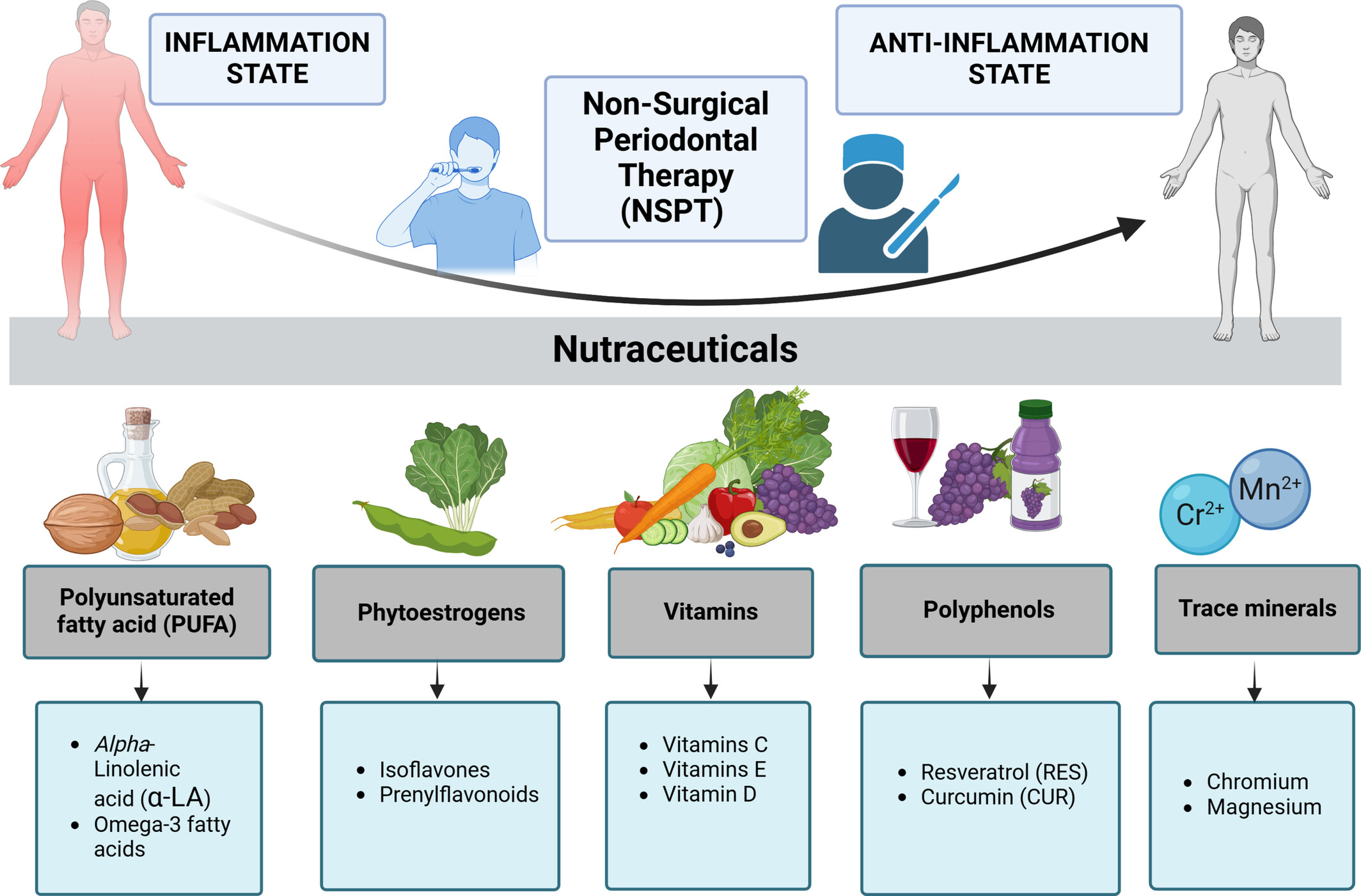
This review examines the role of nonsurgical periodontal therapy (NSPT) and nutrition in managing periodontitis and associated systemic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and rheumatoid arthritis. Findings suggest that combining NSPT with dietary interventions can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, but long-term success requires integrating these strategies into a sustainable lifestyle.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
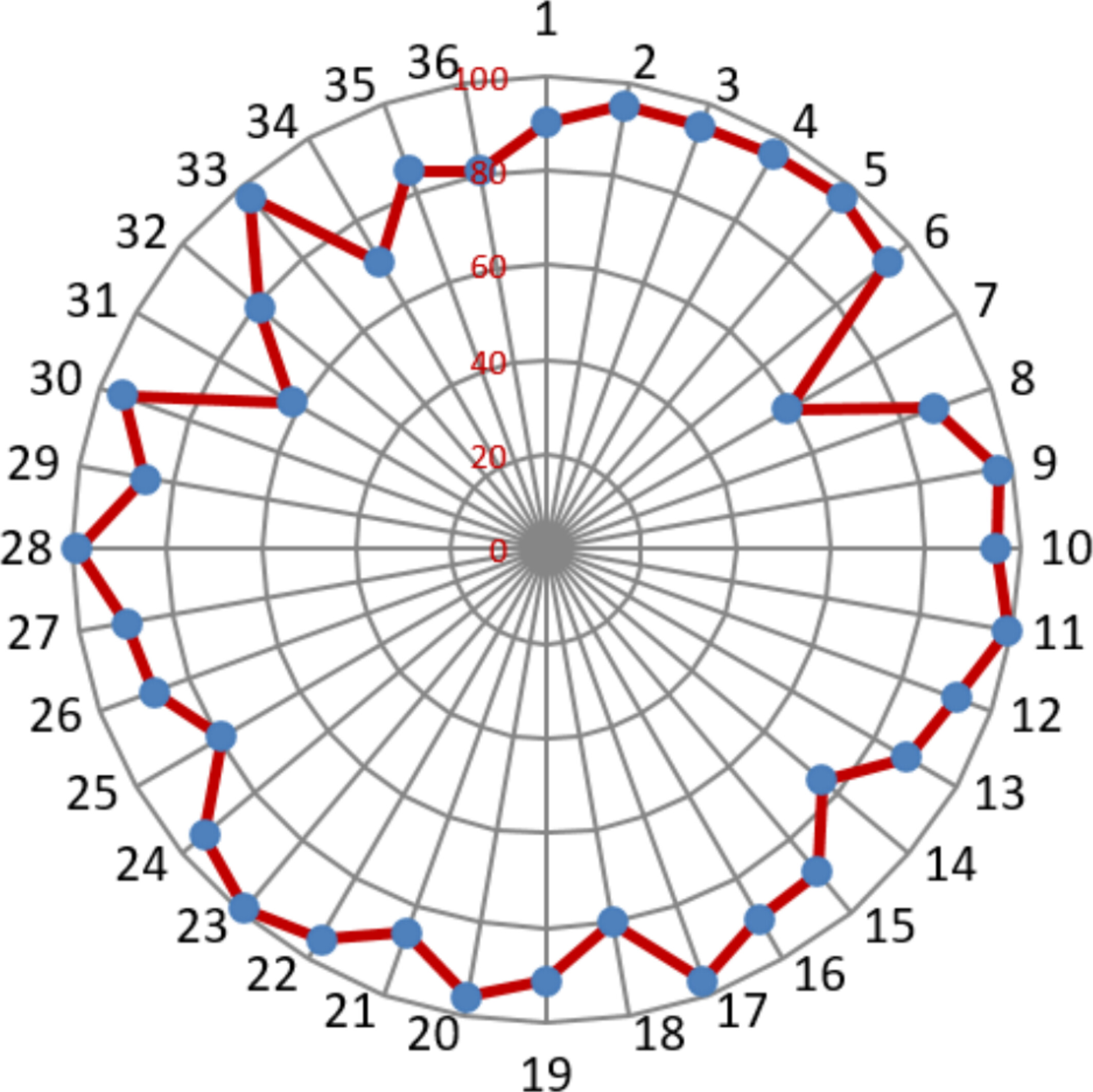
Genome-Wide Identification, Molecular Evolution, and Expression Divergence of CLC, ALMT, VDAC, and MSL Gene Family in Barley
- First Published: 22 March 2025
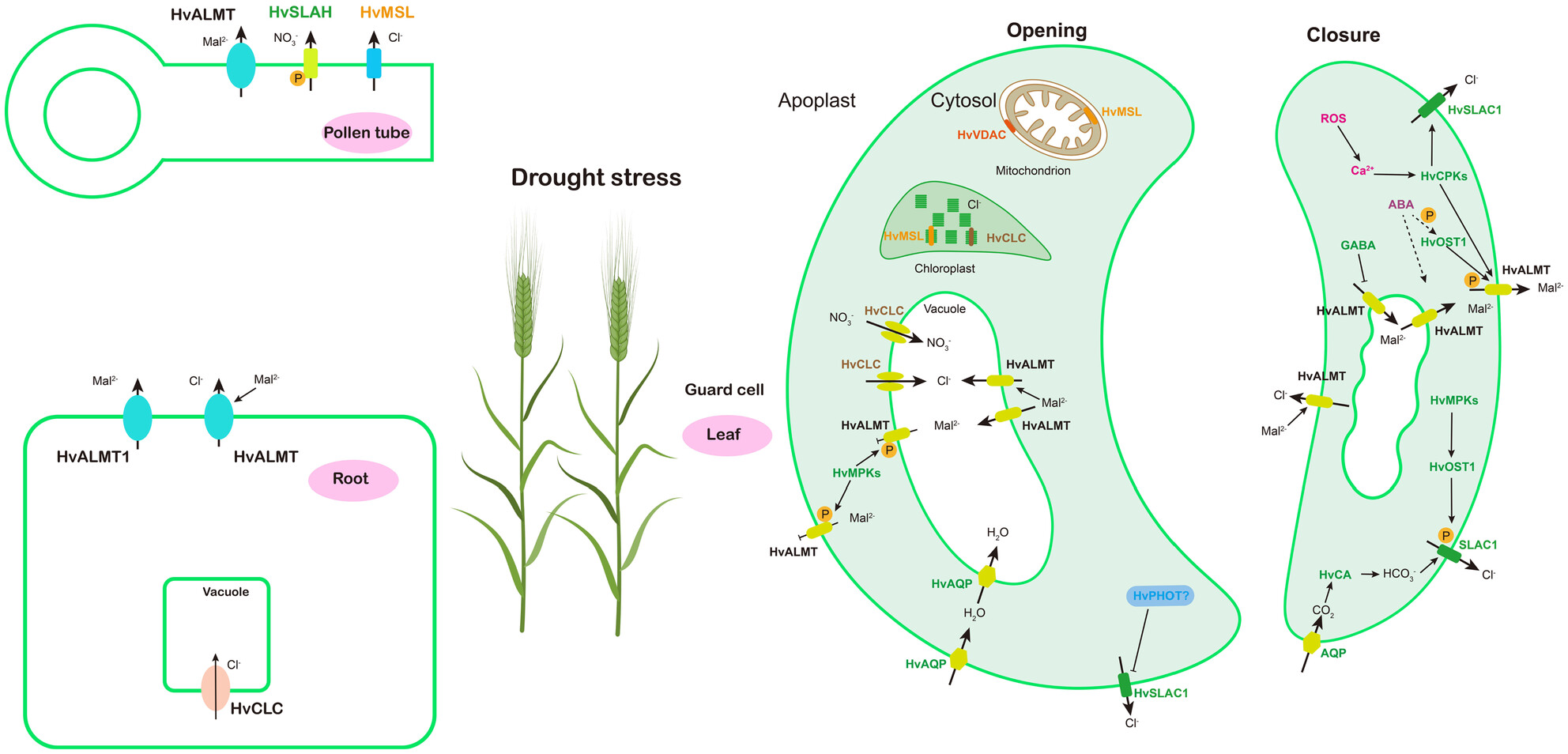
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the CLC, ALMT, VDAC, and MSL anion channel gene families in barley. We identifies 43 anion channel proteins and examines their expression patterns in multiple tissues and drought stress. The results show that these genes play crucial roles in drought tolerance and ion homeostasis, with different cultivars exhibiting diverse responses. The findings offer insights into the molecular mechanisms of anion channels in stress adaptation and provide a foundation for developing drought-resistant barley varieties.
Effect of Zein-Persian Gum Water-in-Oleogels on Quality Characteristics of Unsaturated Fatty Acid-Rich and Low-Fat Croissant
- First Published: 12 March 2025
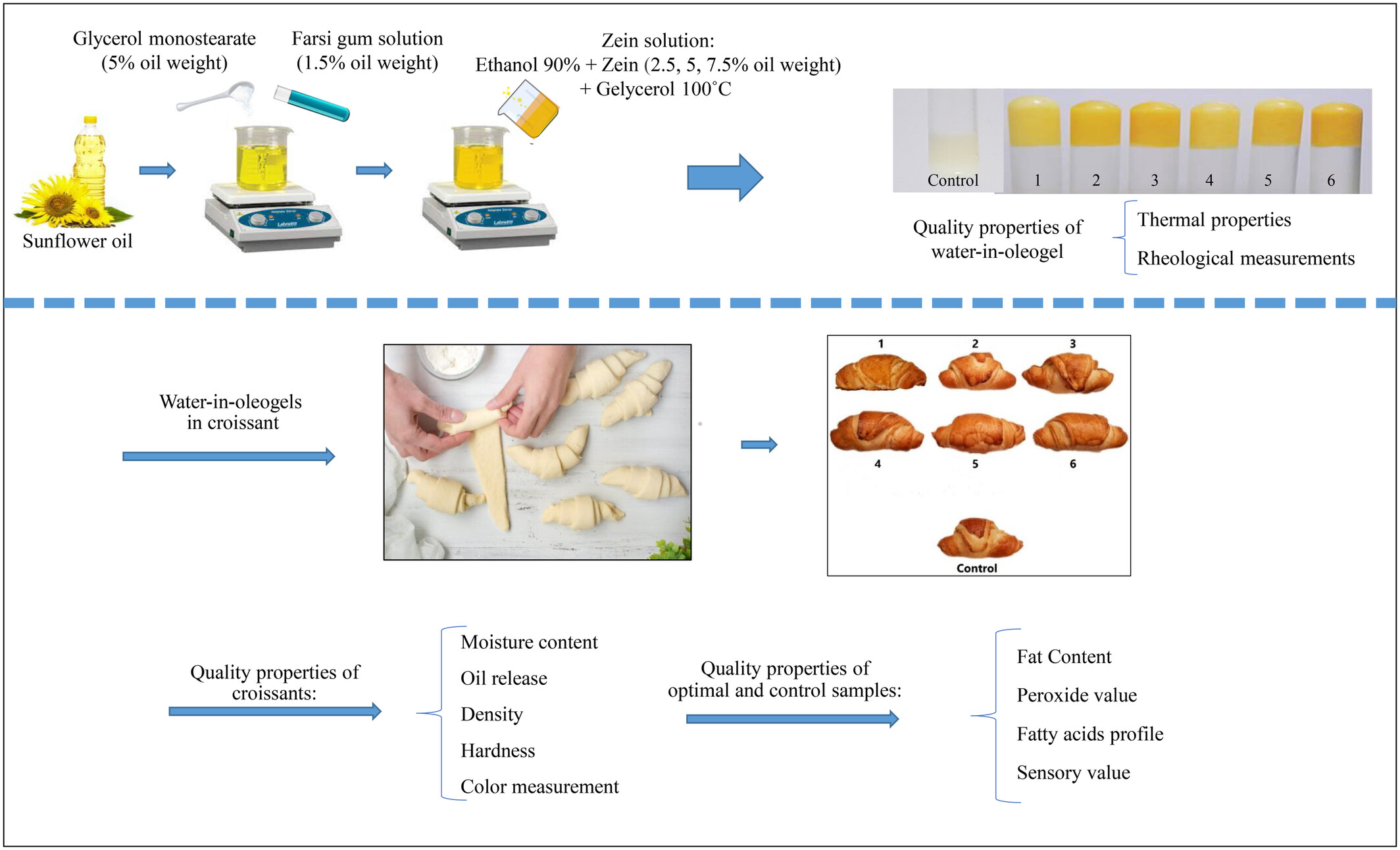
The moisture content and hardness of croissants produced with water-in-oleogels were higher and lower, respectively, than those in the control. Using hydrocolloid next to increasing the Zein concentration decreased the oil release of the product. The water-in-oleogel prepared with 2.5% Zein was useful in the production of croissants with favorable quality properties and 15% lower fat compared to the control without significant difference in terms of peroxide value. The total volume of the saturated and essential unsaturated fatty acids in the developed product decreased by 47% and increased by 65%, respectively, next to maintaining the aroma, taste, color, and most of the organoleptic properties.