Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Hepatitis B virus genotype is an independent prognostic factor of telbivudine and tenofovir treatment in hepatitis B surface antigen-positive pregnant women
- Pages: 3-11
- First Published: 29 November 2021
REVIEWS
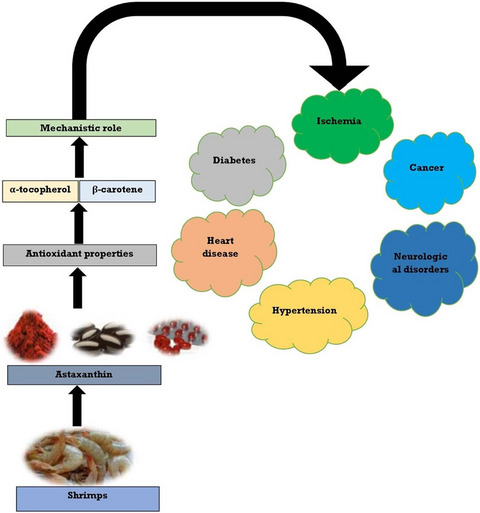
Mechanistic role of astaxanthin derived from shrimp against certain metabolic disorders
- Pages: 12-20
- First Published: 30 November 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
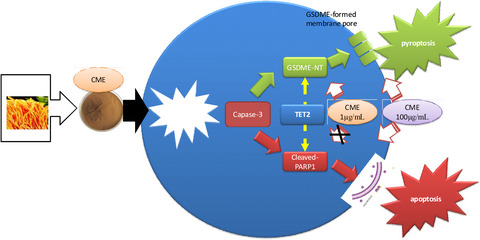
Cordyceps militaris extract induces apoptosis and pyroptosis via caspase-3/PARP/GSDME pathways in A549 cell line
- Pages: 21-38
- First Published: 30 October 2021
Changes in fast food intake in Iranian households during the lockdown period caused by COVID-19 virus emergency, National Food and Nutrition Surveillance
- Pages: 39-48
- First Published: 01 November 2021
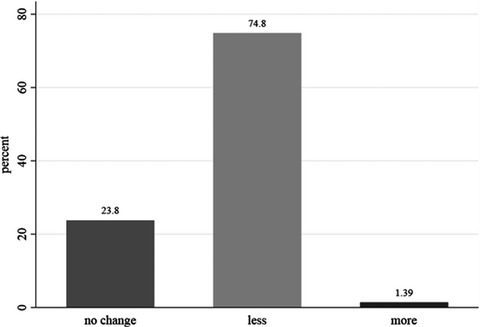
The result of this study showed that fast food consumption has dramatically decreased during the lock-down period in Iranian households. Fear of contamination of fast foods by coronavirus and increase in the number of people at home were the most and the less frequent reasons for decreasing fast food consumption, respectively.
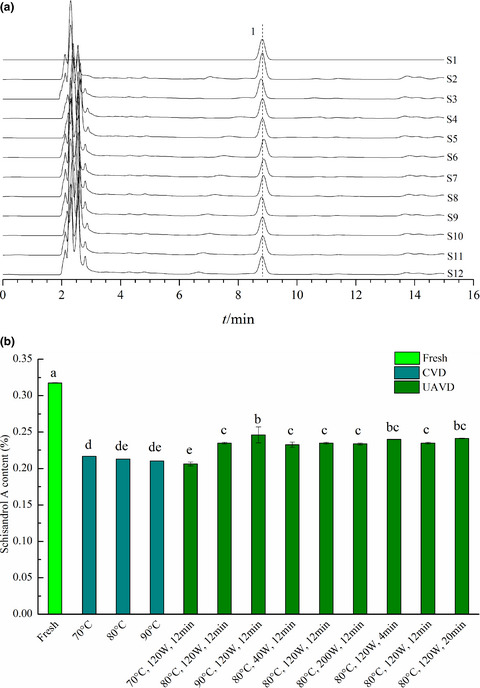
A novel ultrasound-assisted vacuum drying technique for improving drying efficiency and physicochemical properties of Schisandra chinensis extract powder
- Pages: 49-59
- First Published: 03 November 2021
Epidemiological analysis of wild mushroom poisoning in Zhejiang province, China, 2016–2018
- Pages: 60-66
- First Published: 29 October 2021
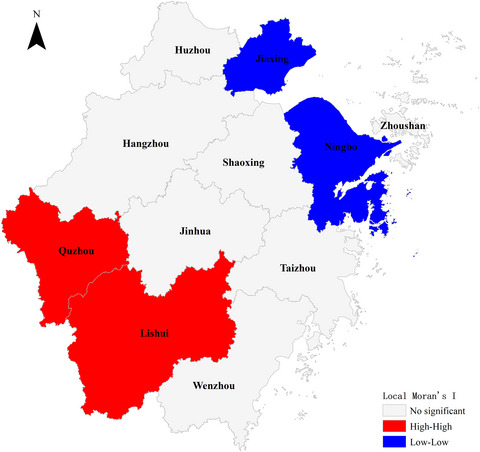
- There were seasonal, high-incidence areas and high-risk groups in wild mushroom poisoning.
- The incidence of mushroom poisoning in Zhejiang province was high in households (91.6%), mainly in rural households.
- Local spatial autocorrelation showed that the “hot spots” of wild mushroom poisoning in Zhejiang province from 2016 to 2018 were Quzhou and Lishui.
Safety evaluation of Lactococcus lactis IDCC 2301 isolated from homemade cheese
- Pages: 67-74
- First Published: 17 November 2021
Preparation of blueberry anthocyanin liposomes and changes of vesicle properties, physicochemical properties, in vitro release, and antioxidant activity before and after chitosan modification
- Pages: 75-87
- First Published: 02 December 2021
Blueberry anthocyanins with high entrapment efficiency were successfully prepared in this paper. Blueberry anthocyanin liposomes were modified with biopolymer chitosan, and the stability was improved after modification. It provides a basis for further research and identification of blueberry anthocyanins.
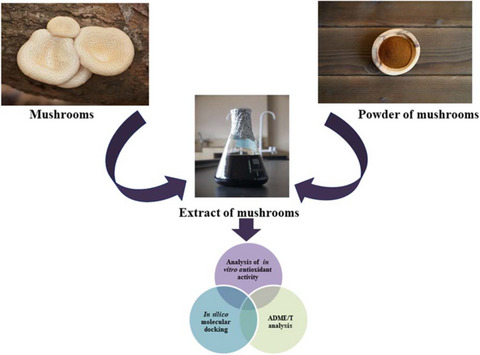
Profiling of phytochemical and antioxidant activity of wild mushrooms: Evidence from the in vitro study and phytoconstituent's binding affinity to the human erythrocyte catalase and human glutathione reductase
- Pages: 88-102
- First Published: 02 November 2021
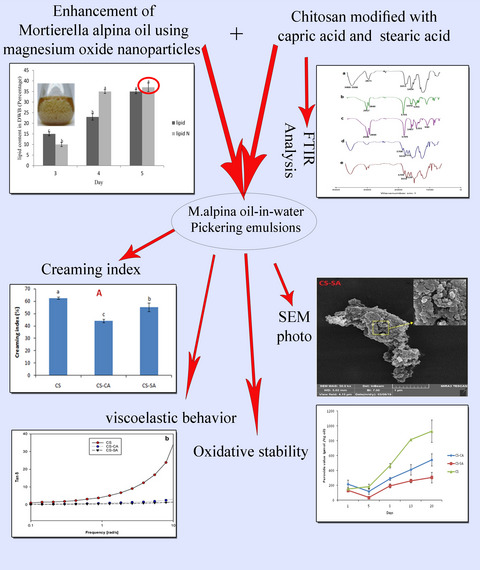
Enhancement of oil productivity of Mortierella alpine and investigation into the potential of Pickering oil-in-water emulsions to improve its oxidative stability
- Pages: 103-114
- First Published: 02 November 2021
Erucic acid exposure during the first year of life—Scenarios with precise food-based dietary guidelines
- Pages: 115-121
- First Published: 07 November 2021

In infancy, the diet requires both, an especially high nutritional quality and toxicological safety. In view of the recent TDI for erucic acid issued by EFSA, our scenarios show that the nutritionally safe food-based dietary guidelines for infancy in Germany may no longer be safe with regard to potential exposure to erucic acid that originates mainly from rapeseed oil. In addition to the strong data base on erucic acid in rapeseed oil in Germany, timely data bases for human milk and formula are needed to definitely decide on the toxicological safety of infant nutrition.
Impact of the magnetic field-assisted freezing on the moisture content, water migration degree, microstructure, fractal dimension, and the quality of the frozen tilapia
- Pages: 122-132
- First Published: 07 November 2021
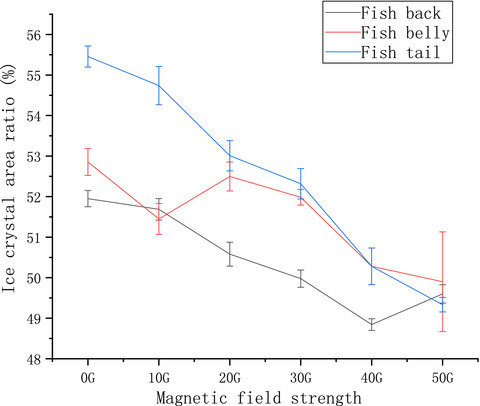
The application of alternating magnetic field-assisted freezing in tilapia can be helpful in tilapia storage. The effect of alternating magnetic fields on different parts of frozen tilapia can provide a theoretical basis for tilapia quality research. The experimental results of alternating magnetic field-assisted freezing in tilapia can provide a theoretical basis for the application of the magnetic field.
Phytochemical profile and anti-oxidation activity changes during ginger (Zingiber officinale) harvest: Baby ginger attenuates lipid accumulation and ameliorates glucose uptake in HepG2 cells
- Pages: 133-144
- First Published: 14 November 2021
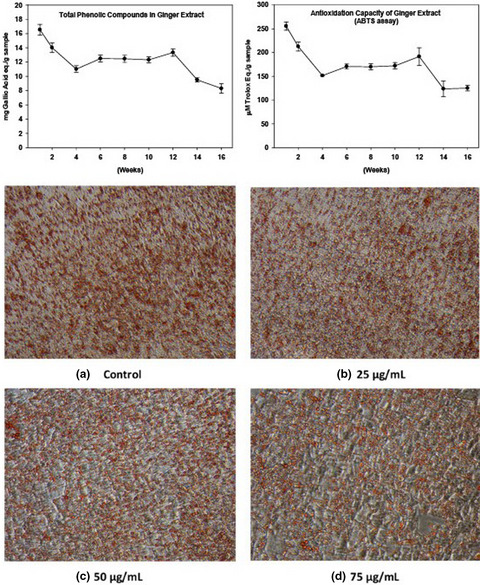
6-gingerol is the primary component in ginger; it is about 15-fold and 53-fold higher than 6-paradol and 6-shogaol, respectively. Consistent with TPC and antioxidant activity, the highest amount of these major phytochemicals was obtained when harvested at the first week; however, these phenolic compounds were gradually reduced to 50% of originals as ginger matured.
REVIEWS
Effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid on bone health: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Pages: 145-154
- First Published: 29 November 2021
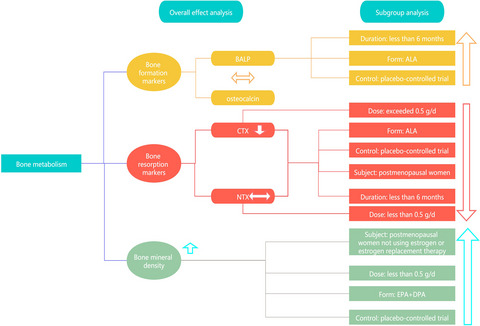
N-3 PUFAs may play a beneficial role on bone health by inhibiting bone resorption, as well as promoting bone formation and enhancing BMD, especially for ALA intervention form or for postmenopausal women. In addition, n-3 PUFAs supplementations might have short-term effects for bone turnover markers and long-term effects for BMD.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial interactions between resveratrol and eugenol in carboxymethyl cellulose biodegradable film
- Pages: 155-168
- First Published: 15 November 2021
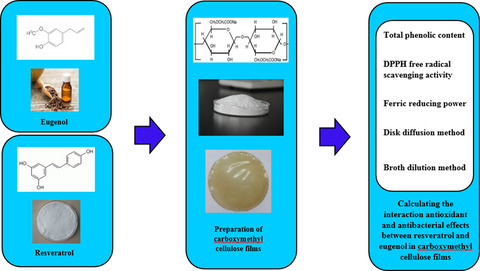
The aim of present study was to compare the in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial properties of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) films containing resveratrol (RES) and eugenol (EUG), alone and in combination, and to calculate the dose interactions between them. The combined use of RES and EUG in CMC films had synergistic antioxidant and antagonistic antibacterial effects.
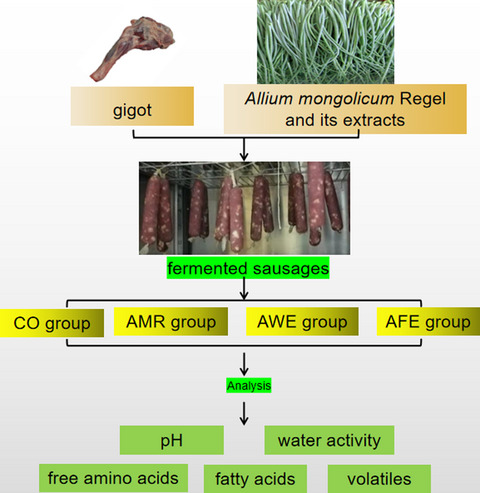
Effects of Allium mongolicum Regel and its extracts on the quality of fermented mutton sausages
- Pages: 169-178
- First Published: 01 December 2021
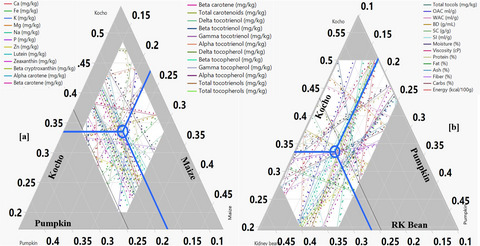
Effect of two postharvest technologies on the micronutrient profile of cashew kernels from Mozambique
- Pages: 179-190
- First Published: 23 November 2021

Impact of nut drying technologies on carotenoids, tocopherols, tocotrienols, minerals, fatty acids and amino acids in cashew kernels was investigated. Higher concentrations of the carotenoids lutein and β-carotene in the testa-containing kernels were confirmed. Higher concentrations of minerals, fatty acids and some amino acids were found in baby butts than in whole white and split grades, underlining the nutritional value and possible better market value of the baby butt grades.
Microencapsulation of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) anthocyanins: Effects of drying conditions on some physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of spray-dried powder
- Pages: 191-203
- First Published: 08 December 2021
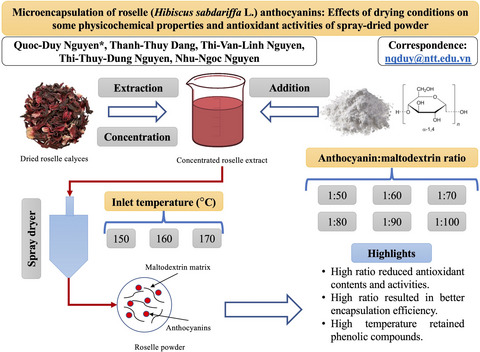
Increasing the carrier ratio reduced antioxidant contents and activities. High inlet temperature effectively retained phenolic compounds. High encapsulation efficiency of anthocyanin (above 85%) was obtained at an ACN:MD ratio of 1:100 (w/w). Increasing carrier ratio and inlet temperature resulted in decrease in moisture content, and the solubility of all samples exceeded 93.71%.
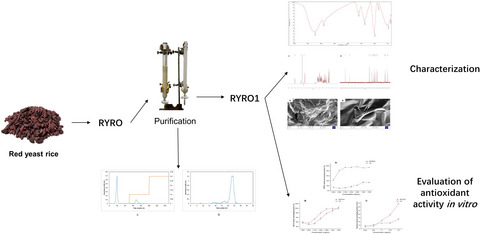
Ultrasonic extraction, structural characterization, and antioxidant activity of oligosaccharides from red yeast rice
- Pages: 204-217
- First Published: 24 November 2021
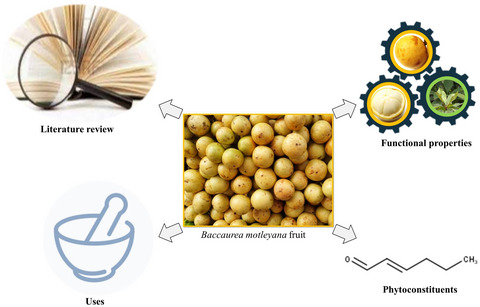
Bioactive compounds and functional properties of Rambai (Baccaurea motleyana Müll. Arg.) fruit: A comprehensive review
- Pages: 218-226
- First Published: 23 November 2021
METHOD
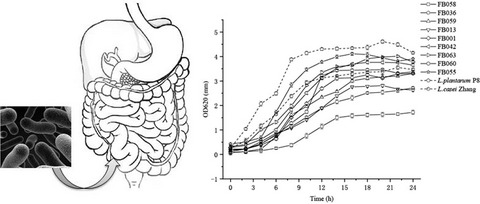
Evaluation of tolerance to artificial gastroenteric juice and fermentation characteristics of Lactobacillus strains isolated from human
- Pages: 227-238
- First Published: 10 December 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Optimization of nutritional and functional qualities of local complementary foods of southern Ethiopia using a customized mixture design
- Pages: 239-252
- First Published: 22 November 2021
Effect of clover sprouts protein hydrolysates as an egg substitute on physicochemical and sensory properties of mayonnaise
- Pages: 253-263
- First Published: 06 December 2021
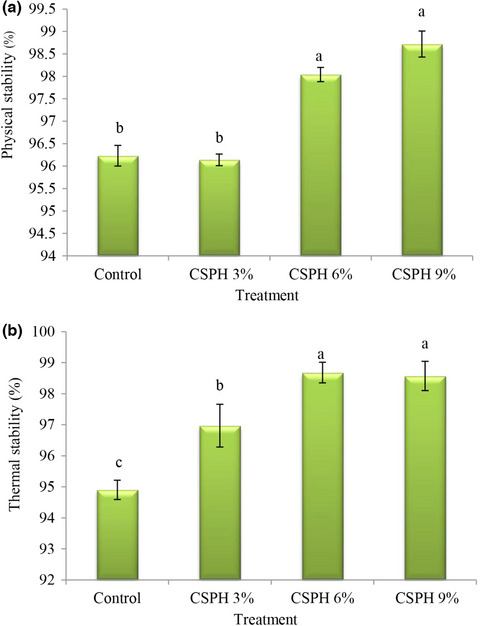
Mayonnaise is an oil-in-water emulsion that in addition to eggs other stabilizers and thickeners are used as emulsifiers for better stability. Although eggs are an important ingredient in the production of mayonnaise, the health problems associated with the use of eggs is increasing due to their high cholesterol content. The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of clover sprout protein to replace eggs for the production mayonnaise. The results indicate that using clover protein up to 6% can satisfactorily remove most of the mayonnaise egg and produce low-egg mayonnaise, thus producing a functional product and preventing the side effects of egg yolk consumption.
The effect of lactic acid bacteria and co-culture on structural, rheological, and textural profile of corn dough
- Pages: 264-271
- First Published: 30 November 2021
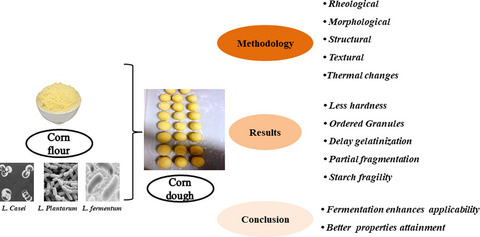
Assessing the effect of L. casei, L. plantarum and L. fermentum on corn flour using dynamic characterization methods including RVA, TPA, Rheometer, SEM, DSC along with co-culture technique in order to enhance its applicability by evaluating the variations in rheological, textural, morphological, thermal and structural properties.
REVIEWS
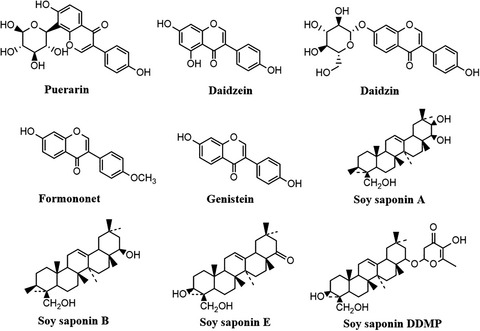
Protective effect of isoflavones and triterpenoid saponins from pueraria lobata on liver diseases: A review
- Pages: 272-285
- First Published: 10 December 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Effect of iron-fortified infant cereal on nutritional status of infants in Ghana
- Pages: 286-294
- First Published: 26 November 2021
Egg consumption improves vascular and gut microbiota function without increasing inflammatory, metabolic, and oxidative stress markers
- Pages: 295-304
- First Published: 30 November 2021