Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Fate of chlorpyrifos, omethoate, cypermethrin, and deltamethrin during wheat milling and Chinese steamed bread processing
- Pages: 2791-2800
- First Published: 01 May 2021

Milling process decreased chlorpyrifos, omethoate, cypermethrin, and deltamethrin levels in flour. Cypermethrin and deltamethrin levels showed various degrees of increases during Chinese steamed bread processing. Changes of chlorpyrifos, omethoate, cypermethrin, and deltamethrin during Chinese steamed bread making process were firstly detailed reported.
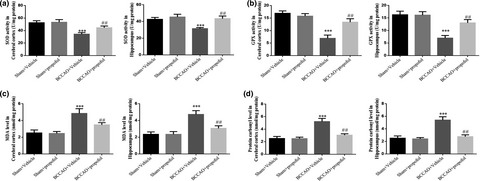
Propofol improves brain injury induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats
- Pages: 2801-2809
- First Published: 05 May 2021
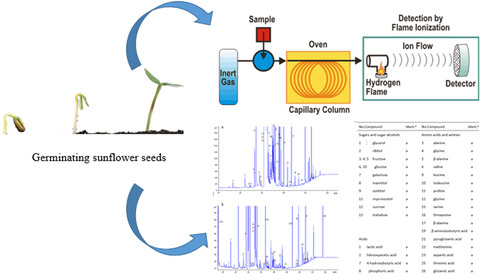
Effects of germinating temperature and time on metabolite profiles of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) seed
- Pages: 2810-2822
- First Published: 05 May 2021
Accumulating evidence to support the safe and efficacious use of a proprietary blend of capsaicinoids in mediating risk factors for obesity
- Pages: 2823-2835
- First Published: 04 May 2021
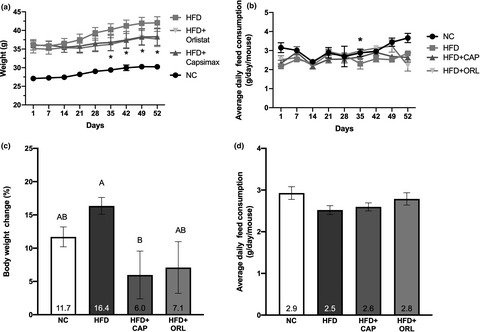
The present study found that mice fed a high-fat diet showed significantly lower weight gain upon CAP administration than their control counterparts. In addition, CAP decreased the high-fat diet-induced increases in fat mass and increased the circulating leptin levels. In support of these in vivo observations, CAP extracts decreased triacylglycerol content and affected gene expression consistent with increased thermogenesis and decreased lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and adipocytes.
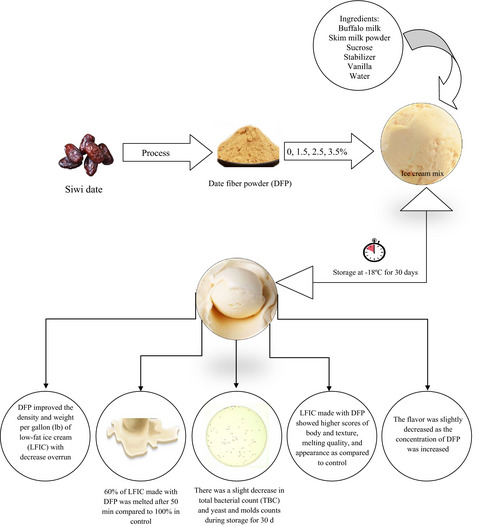
A novel process to improve the characteristics of low-fat ice cream using date fiber powder
- Pages: 2836-2842
- First Published: 01 May 2021
Thermally induced isomerization of linoleic acid and α-linolenic acid in Rosa roxburghii Tratt seed oil
- Pages: 2843-2852
- First Published: 04 May 2021
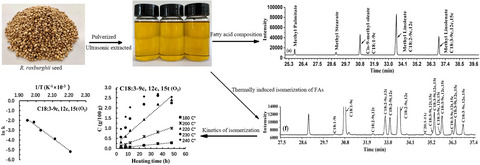
Rosa roxburghii seed oil was of high quality in terms of its high amount of unsaturated fatty acids. Heat treatment of R. roxburghii seed oil showed an increase in the relative percentage of linoleic acid and linolenic acid isomers with increasing temperature and time. The formation of linoleic acid and linolenic acid isomers followed a zero order reaction.
Effects of different harvesting times and processing methods on the quality of cultivated Fritillaria cirrhosa D. Don
- Pages: 2853-2861
- First Published: 15 March 2021
Characterization of volatile compounds of Pixian Douban fermented in closed system of gradient steady-state temperature field
- Pages: 2862-2876
- First Published: 29 March 2021
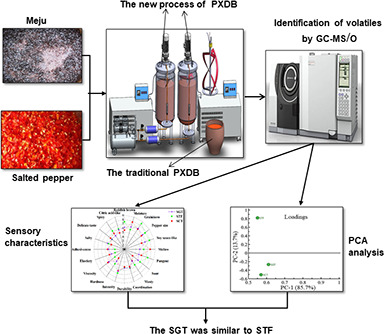
The results showed that flavor characteristics of SGT were similar to those of the STF. This study indicated that the closed system of GSTF could be applied in PXDB fermentation to obtain higher quality products, which brought a bright prospect of replacing the traditional fermentation process to realize the controllable industrialized production of PXDB.
Oral supplementation with fish cartilage hydrolysate accelerates joint function recovery in rat model of traumatic knee osteoarthritis
- Pages: 2877-2885
- First Published: 10 April 2021
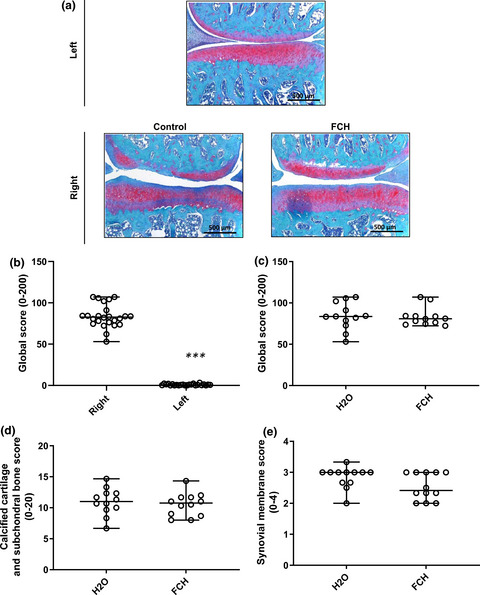
Oral skate fish cartilage hydrolysate tends to attenuate postsurgically nociceptive behavior such as mechanical allodynia and weight-bearing distribution, in an experimental rat OA model. These findings may have opened the way for further investigations of skate fish cartilage hydrolysate as a potential solution to reduce joint discomfort associated with OA.
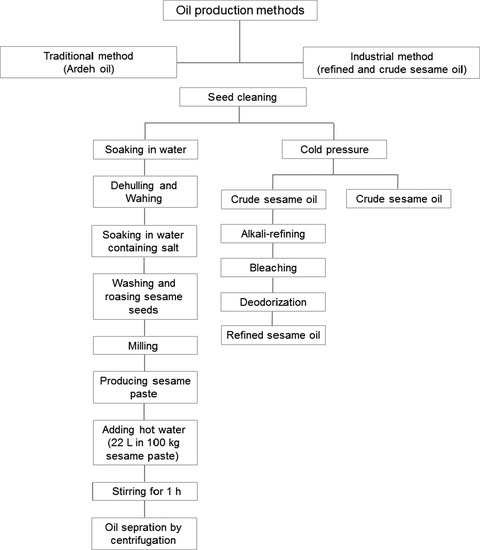
The chemical composition and heavy metal content of sesame oil produced by different methods: A risk assessment study
- Pages: 2886-2893
- First Published: 17 March 2021
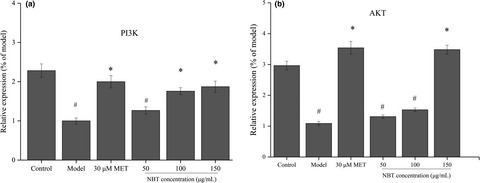
Maca extracts regulate glucose and lipid metabolism in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway
- Pages: 2894-2907
- First Published: 29 March 2021
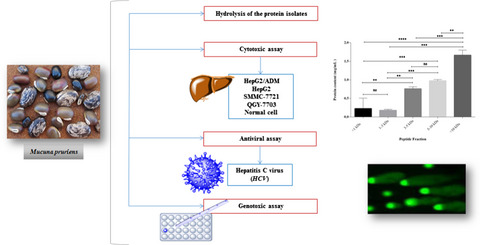
Therapeutic peptides of Mucuna pruriens L.: Anti-genotoxic molecules against human hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis C virus
- Pages: 2908-2914
- First Published: 25 March 2021
Knowledge and practices of dietary iron and anemia among early adolescents in a rural district in Ghana
- Pages: 2915-2924
- First Published: 02 April 2021
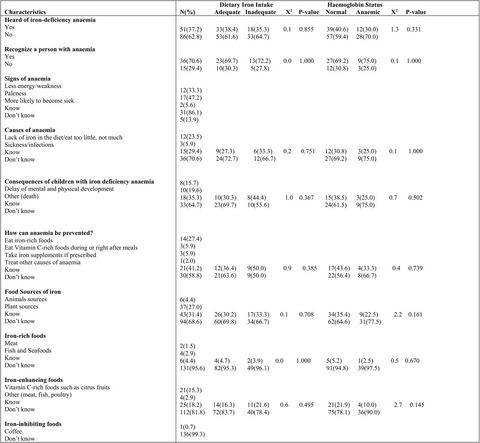
Anaemia, a type of micronutrient deficiency, is known to affect the physical and cognitive abilities of adolescents. The study assessed knowledge and practices of dietary iron intake and anaemia. Results show that majority of adolescents had little knowledge of iron, causes of anaemia and sources of iron-rich foods.
Assessment of (-) epicatechin as natural additive for improving safety and functionality in fresh “Piel de Sapo” melon juice
- Pages: 2925-2935
- First Published: 30 March 2021
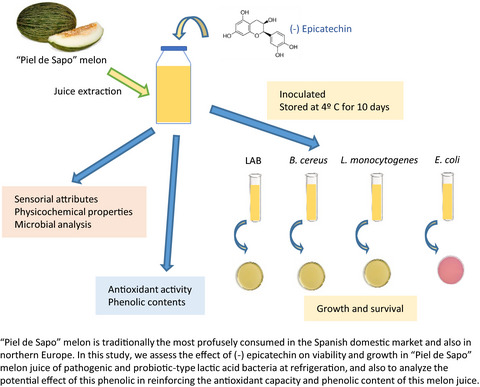
- (-) Epicatechin is a very abundant flavonoid in vegetable tissues that presents high antioxidant activity in living systems.
- (-) Epicathechin would be a promising ingredient for increasing the functional properties of “Piel de Sapo” MJ (phenolic compounds and antioxidant ability) whilst contributing to improving the safety of this type of juice during prolonged refrigerated storage at 4 ºC.
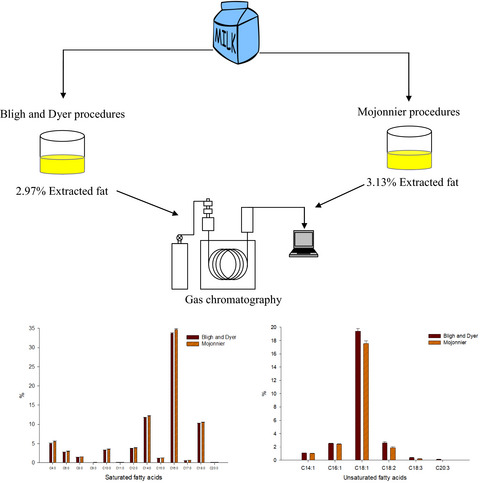
Effect of fat extraction methods on the fatty acids composition of bovine milk using gas chromatography
- Pages: 2936-2942
- First Published: 04 May 2021
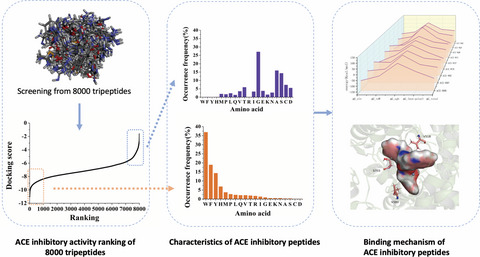
Investigation on the characteristics and mechanisms of ACE inhibitory peptides by a thorough analysis of all 8000 tripeptides via binding free energy calculation
- Pages: 2943-2953
- First Published: 03 May 2021
Effects of several tea extracts on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice fed with a high-fat diet
- Pages: 2954-2967
- First Published: 09 April 2021
Ribes himalense as potential source of natural bioactive compounds: Nutritional, phytochemical, and antioxidant properties
- Pages: 2968-2984
- First Published: 03 May 2021
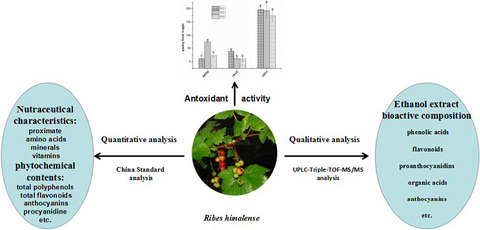
(1) Unambiguously recognized by comparing with reference standard compounds, such as analysis of nutrients content (including minerals, amino acids, vitamins); (2) characterized by cleavage pathways and typical fragment ions according to the relevant references; (3) preliminarily identified by searching Scifinder and Reaxy databases, like phenolic acids, flavonoids, proanthocyanidins, anthocyanins, and organic acids. These results suggested that this fruit has great potential in protecting human health, with the focus on the development of functional products.
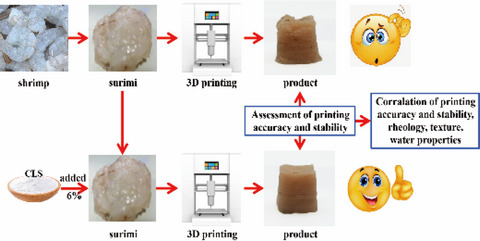
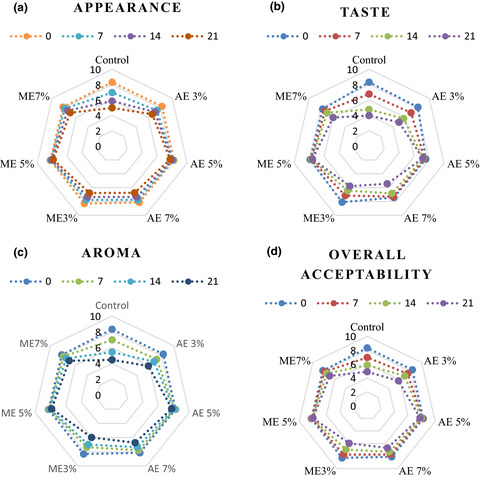
The relationship between rheological and textural properties of shrimp surimi adding starch and 3D printability based on principal component analysis
- Pages: 2985-2999
- First Published: 25 March 2021
The link between plant-based diet indices with biochemical markers of bone turn over, inflammation, and insulin in Iranian older adults
- Pages: 3000-3014
- First Published: 29 March 2021
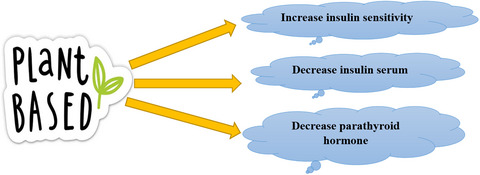
Plant-based dietary pattern may have influence on several chronic diseases; however, there is no study that investigates the beneficial effect of plant-based dietary pattern on biochemical markers of bone turn over, inflammation, and insulin on Iranian older adults. We found that adherence to plant-based dietary pattern and healthful plant-based dietary pattern have lucrative consequences on bone turn over, inflammation, and insulin biomarkers.
Effect of Zataria multiflora essential oil and potassium sorbate on inoculated Listeria monocytogenes, microbial and chemical quality of raw trout fillet during refrigerator storage
- Pages: 3015-3025
- First Published: 26 March 2021
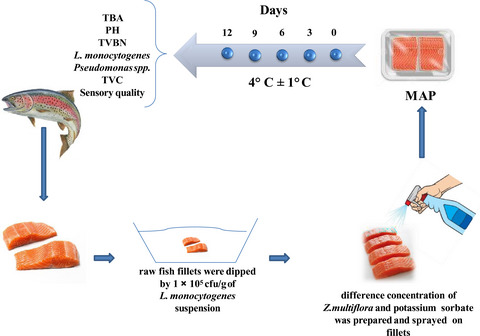
In this study, the antibacterial effect of Zataria multiflora essential oil and potassium sorbate on Listeria monocytogenes in Rainbow trout fillet was investigated. Based on the results of chemical, microbial, and sensory evaluation tests, 1.5% Zataria multiflora essential oil preserved Rainbow Trout fillet with the best quality for 12 days.
Detection of fraud in lime juice using pattern recognition techniques and FT-IR spectroscopy
- Pages: 3026-3038
- First Published: 24 March 2021
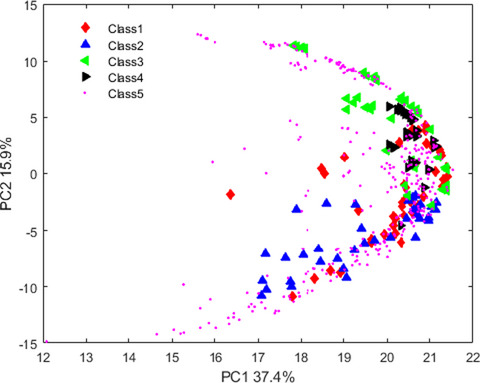
In this work, the authenticity of commercial lime juice was detected and quantified using FT-IR spectroscopy coupled with the VIP variable selection and CPANN models. The main advantage of the present contribution is the diversity of the calibrating samples which include broad ranges of natural, synthetic, and adulterated lime juice samples. Therefore, applicability domain of the developed discriminative model in this work would be broad and wide which is a needed property in fraud detection in lime juice industry.
Association of serum selenium with anemia-related indicators and risk of anemia
- Pages: 3039-3047
- First Published: 27 March 2021
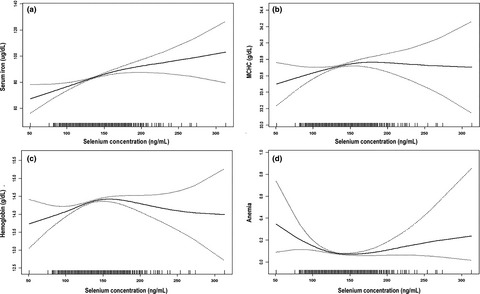
Higher serum selenium is associated with an increased serum iron level, MCHC, and hemoglobin level and a decreased risk of anemia. Due to the narrow physiological range of selenium, the relationships between selenium- and anemia-related indicators and risk of anemia were nonlinear. Our findings would provide new insights on selenium nutrition that implicate anemia and human health.
Stabilization and attributive amelioration of sugarcane juice by naturally derived preservatives using aonla and moringa extract
- Pages: 3048-3058
- First Published: 27 March 2021
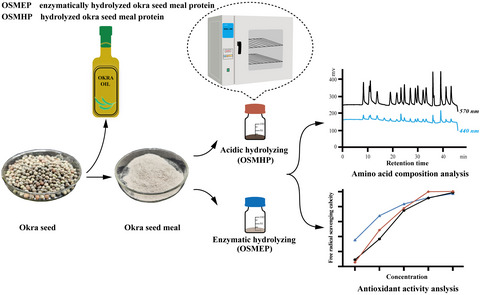
Preparation, amino acid composition, and in Vitro antioxidant activity of okra seed meal protein hydrolysates
- Pages: 3059-3070
- First Published: 02 April 2021
Mechanical and physical properties of polyethylene/sour cherry shell powder bio-composite as potential food packaging
- Pages: 3071-3077
- First Published: 29 March 2021
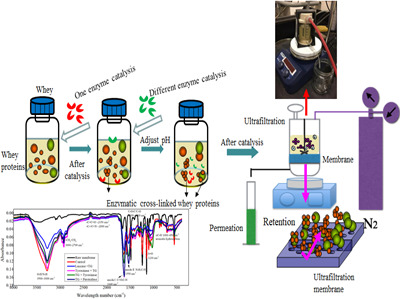
The effect of composite enzyme catalysis whey protein cross-linking on filtration performance
- Pages: 3078-3090
- First Published: 30 March 2021
Synergistic effects of black ginseng and aged garlic extracts for the amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mice
- Pages: 3091-3099
- First Published: 04 May 2021
Phytochemical profiles of lemon verbena (Lippia citriodora H.B.K.) and its potential application to cookie enrichment
- Pages: 3100-3113
- First Published: 29 March 2021
Role of Semisulcospira gottschei extract as medicinal food on reflux esophagitis in rats
- Pages: 3114-3122
- First Published: 06 May 2021
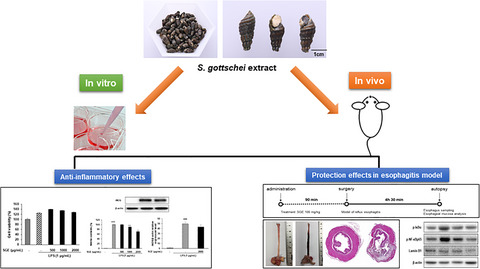
Semisulcospira gottschei extract demonstrates a protective effect on reflux esophagitis in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a globally prevalent disease. Treatment of reflux esophagitis rats markedly ameliorates mucosal lesion ratio indicated through histological changes, by suppressing inflammation-related gene expression. Notably, S. gottschei extract can elevate the expression of tight junction protein, Claudin-5, indicating an augmentation of the epithelium and endothelium to improve reflux esophagitis and present S. gottschei extract as a medicinal food source for the treatment of GERD.
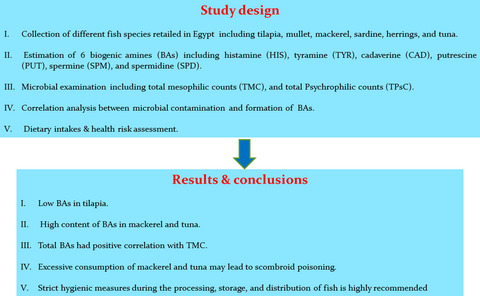
Formation of biogenic amines in fish: Dietary intakes and health risk assessment
- Pages: 3123-3129
- First Published: 06 April 2021
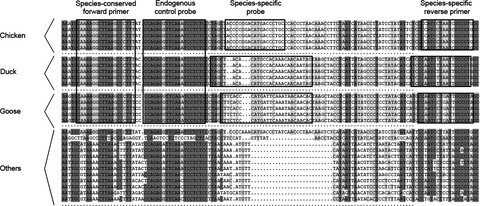
Improved triplex real-time PCR with endogenous control for synchronous identification of DNA from chicken, duck, and goose meat
- Pages: 3130-3141
- First Published: 02 April 2021
Toward the identification of molecular markers associated with phytochemical traits in the Iranian sumac (Rhus coriaria L.) population
- Pages: 3142-3154
- First Published: 03 May 2021
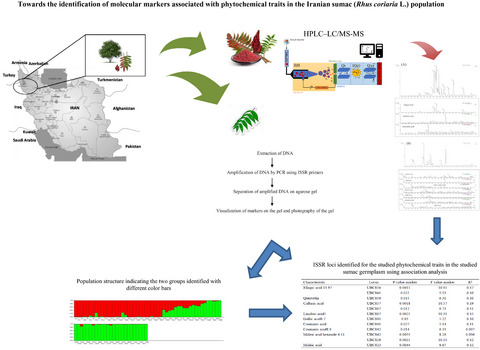
Present work was conducted to investigate population structure in a collection of Iranian sumac germplasm and identify the association of ISSR markers with phytochemical traits in the plant. A total 12 ISSR markers associated with studied traits was identified using an association mapping approach. These ISSR markers provide primary molecular information for marker-assisted selection in sumac.
Evaluation of bacterial diversity of traditional cheese in Tarbagatay Prefecture, China, and its correlation with cheese quality
- Pages: 3155-3164
- First Published: 09 April 2021
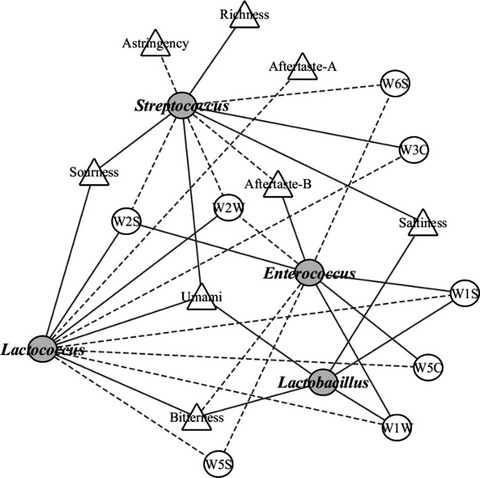
Traditional cheese of Xinjiang, China, has a long history and the consumption demand is also increasing. In recent years, people pay more and more attention to the quality and microbial diversity of Xinjiang traditional cheese, which also contains a variety of microbial resources. The results showed that the bacteria in Xinjiang traditional cheese were rich and diverse, and the core dominant genera were Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Lactococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, and Acetobacters. This study provides a basis for the industrialization of traditional fermented dairy products.
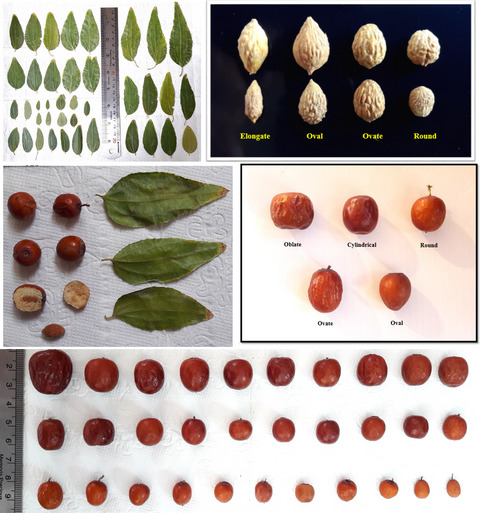
Identification of superior jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) genotypes based on morphological and fruit characterizations
- Pages: 3165-3176
- First Published: 05 April 2021
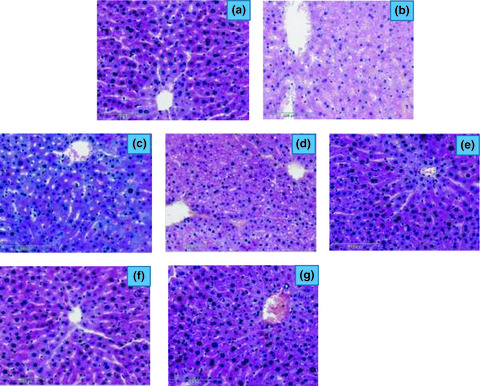
Inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis by camel milk mitigates cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity: Targeting Nrf2/HO-1 and AKT/eNOS/NO pathways
- Pages: 3177-3190
- First Published: 05 April 2021
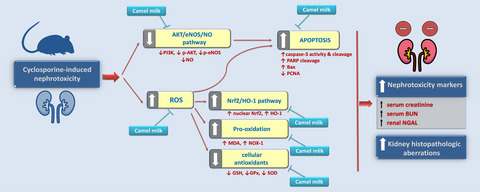
Camel milk lowers creatinine, BUN, and NGAL nephrotoxicity markers. It suppresses oxidative stress, NOX-1 expression, and lipid peroxides and activates Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, and boosts GSH, GPx, and SOD antioxidant moieties. It curtails renal apoptosis markers (Bax, PARP, and caspase-3) and upregulates PCNA, and activates the renal PI3K/Akt/eNOS/NO pathway.
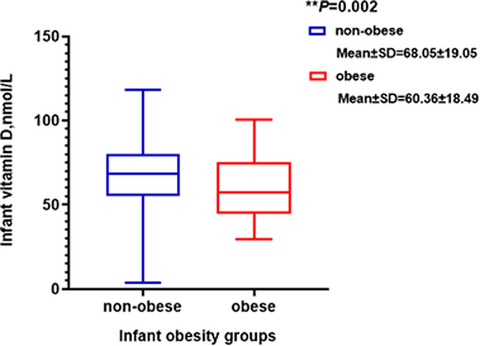
Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and obesity in one-year-old Chinese infants
- Pages: 3191-3199
- First Published: 03 May 2021
Brazilian green propolis promotes TNFR2 expression on regulatory T cells
- Pages: 3200-3208
- First Published: 07 April 2021
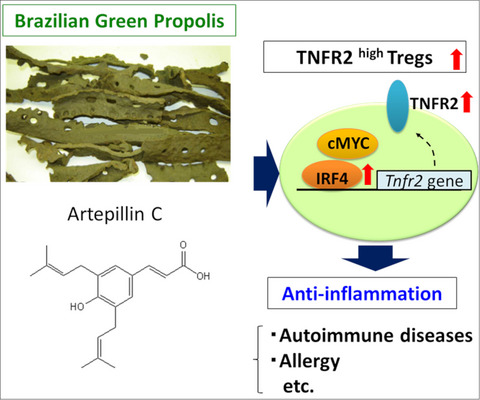
Bee product of propolis is a famous functional food that has an anti-inflammatory effect. We showed Brazilian green propolis increases TNFR2 expression through the IRF4/cMyc axis in Tregs, and artepillin C was a major effective component of propolis on Tregs. These results indicate that propolis and artepillin C have the potential as a Treg activator via TNFR2 expression and may be useful for the prevention and/or therapy of autoimmune or inflammatory diseases.
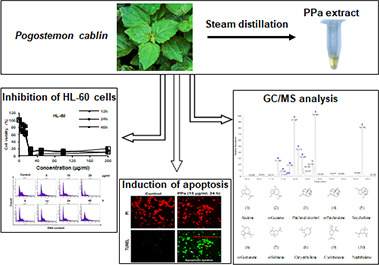
Pogostemon cablin extract as an anticancer agent on human acute myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 3209-3218
- First Published: 02 May 2021
Impact of different cooking methods on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rabbit meat
- Pages: 3219-3227
- First Published: 03 May 2021
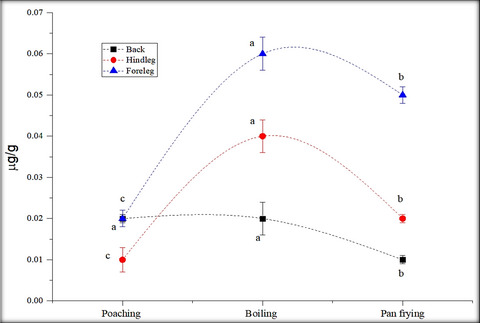
It was difficult to compare our results with the previous studies because there is no such type of literature in rabbit meat by using a variety of processing treatments. The effect of diversified cooking techniques, a variety of oils, and temperature are important factors for controlling PAHs concentration in meat.
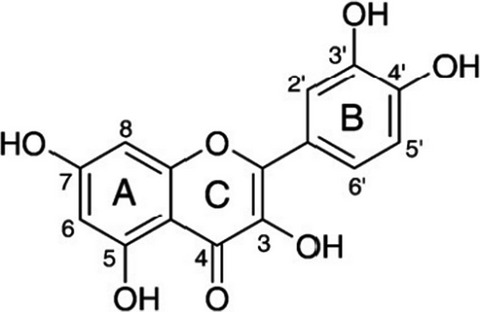
Validated HPTLC and antioxidant activities for quality control of catechin in a fermented tea (Camellia sinensis var. assamica)
- Pages: 3228-3239
- First Published: 04 May 2021
Inositol hexaphosphate modulates the behavior of macrophages through alteration of gene expression involved in pathways of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses, and resolution of inflammation pathways
- Pages: 3240-3249
- First Published: 10 April 2021
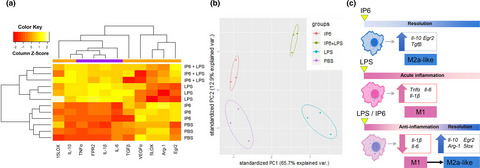
IP6 facilitates macrophage polarization toward the M2a-like subtype. IP6 can also accelerate the transition process from the pro-inflammatory phase toward resolving inflammation in LPS-treated BMDM by altering the expression of genes associated with anti-inflammatories and resolution of inflammation pathways.
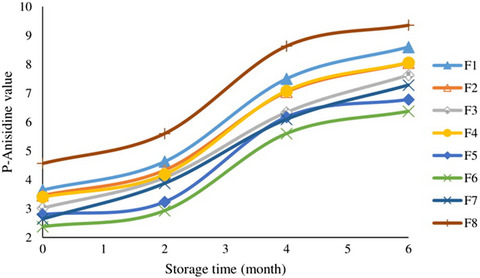
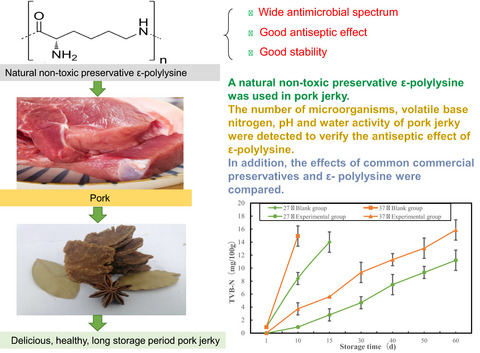
Application of ε-polylysine in extending the storage period of pork jerky
- Pages: 3250-3257
- First Published: 04 May 2021
Comparison of the composition and function of the gut microbiome in herdsmen from two pasture regions, Hongyuan and Xilingol
- Pages: 3258-3268
- First Published: 04 May 2021
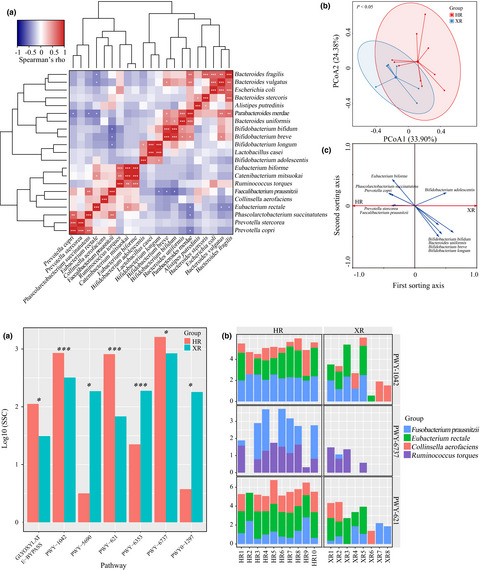
There is a close relationship between the gut microbiome and health in humans including regulation of immunity and energy metabolism. This study investigated differences in the gut microbiome of herdsmen from two regions: Hong Yuan pasture in Sichuan and Xilingol pasture in Inner Mongolia. We found significant differences in the gut microbiome between the two groups. In addition, a higher energy demands in the gut microbiome of Hong Yuan herdsmen. Significantly more genes encoding pathways associated with glycolysis, starch degradation, and sucrose degradation were also found in the gut microbiome of Hong Yuan herdsmen compared with Xilingol herdsmen. These results support the hypothesis that the composition of the host gut microbiome is shaped by dietary intake.
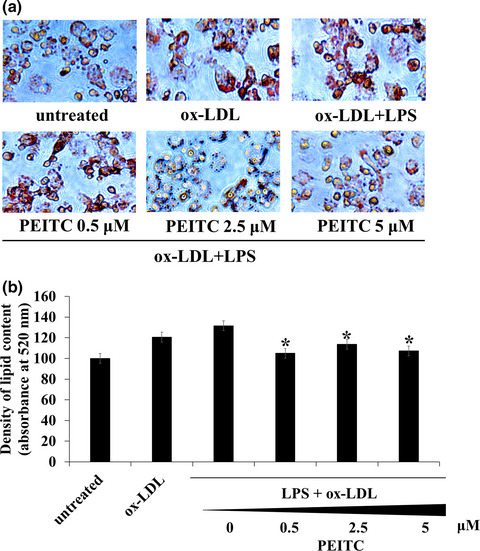
Protective effects of phenethyl isothiocyanate on foam cell formation by combined treatment of oxidized low-density lipoprotein and lipopolysaccharide in THP-1 macrophage
- Pages: 3269-3279
- First Published: 04 May 2021
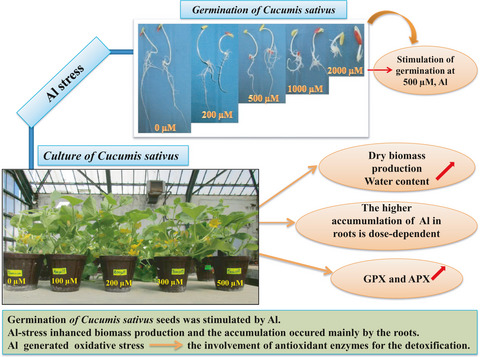
Behavior of Cucumis sativus L. in presence of aluminum stress: Germination, plant growth, and antioxidant enzymes
- Pages: 3280-3288
- First Published: 05 May 2021
Evaluation of the bioaccessibility of a carotenoid beadlet blend using an in vitro system mimicking the upper gastrointestinal tract
- Pages: 3289-3296
- First Published: 04 May 2021
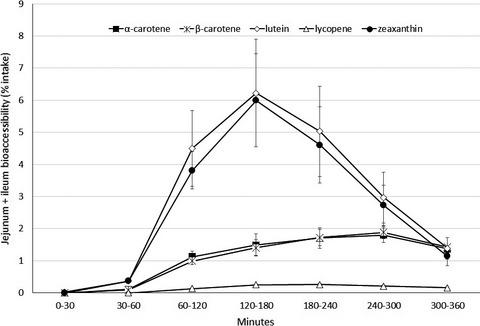
The release characteristics of a unique blend of carotenoid beadlets designed for increased bioavailability were tested using the dynamic gastrointestinal model TIM-1. Peak bioaccessibility measurements separated over approximately 3–4 hr in the order of lutein and zeaxanthin first, followed by lycopene, and then finally alpha and beta carotene; both when tested as a beadlet blend alone and when tested as compressed tablets.
The potential of Quercetin to protect against loperamide-induced constipation in rats
- Pages: 3297-3307
- First Published: 04 May 2021
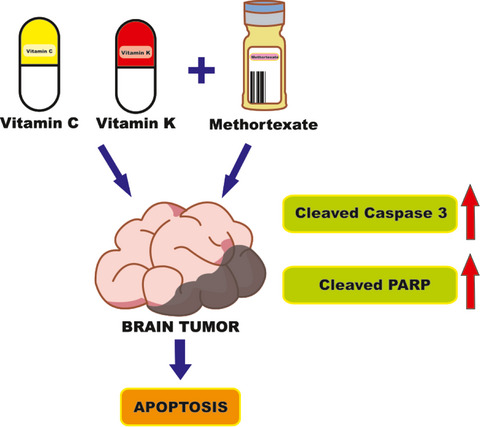
Antioxidant vitamins promote anticancer effects on low-concentration methotrexate-treated glioblastoma cells via enhancing the caspase-3 death pathway
- Pages: 3308-3316
- First Published: 01 May 2021
Optimization of gamma-aminobutyric acid production by Lactobacillus brevis PML1 in dairy sludge-based culture medium through response surface methodology
- Pages: 3317-3326
- First Published: 02 May 2021
Mechanical, sensory, and consumer evaluation of ketogenic, gluten-free breads
- Pages: 3327-3335
- First Published: 04 May 2021
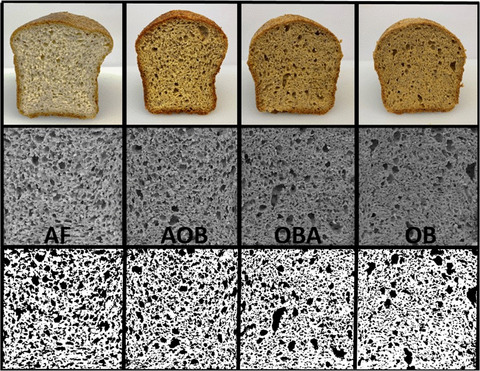
Textural properties, sensory attributes, and consumer acceptance were analyzed for ketogenic, gluten-free breads comprised of almond flour, oat bran fiber, or combinations of both. Higher ratios of almond flour to oat bran fiber resulted in a bread with better structure, flavor and texture which was preferred by trained panelist and consumers.
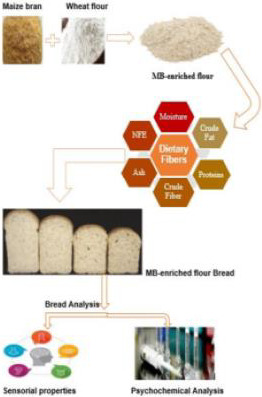
Biochemical and nutritional profile of maize bran-enriched flour in relation to its end-use quality
- Pages: 3336-3345
- First Published: 04 May 2021
Effects of different drying methods and ascorbic acid pretreatment on carotenoids and polyphenols of papaya fruit in Ethiopia
- Pages: 3346-3353
- First Published: 04 May 2021
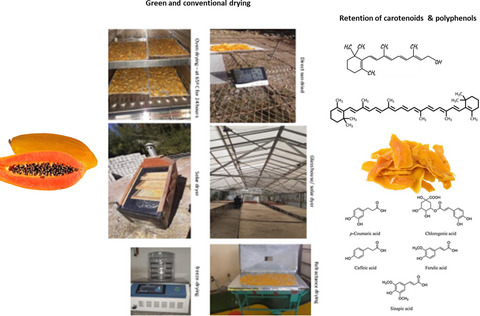
This study evaluated the retention of total polyphenols, flavonoids, ß-carotene contents of papaya fruit with ascorbic acid pretreatment and dried under different techniques of solar, refractance window, and oven drying. Refractance window and solar glass house drying can constitute a promising food systems to increase year-round availability of vitamin A-rich fruits like papaya.
REVIEWS
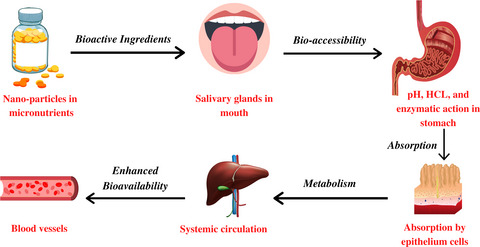
Nanotechnology: A novel tool to enhance the bioavailability of micronutrients
- Pages: 3354-3361
- First Published: 04 May 2021
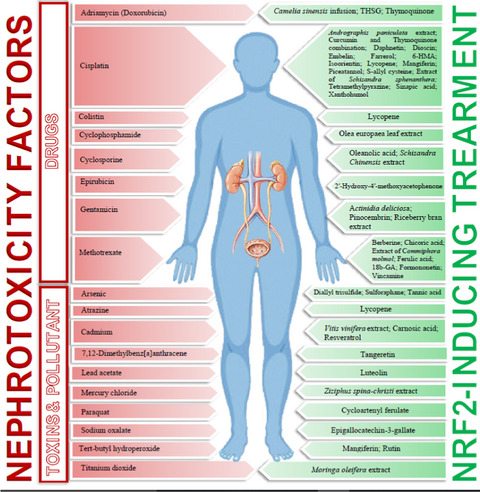
Nephroprotective activity of natural products against chemical toxicants: The role of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway
- Pages: 3362-3384
- First Published: 01 May 2021