Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Fisetin: An anticancer perspective
- Pages: 3-16
- First Published: 25 November 2020
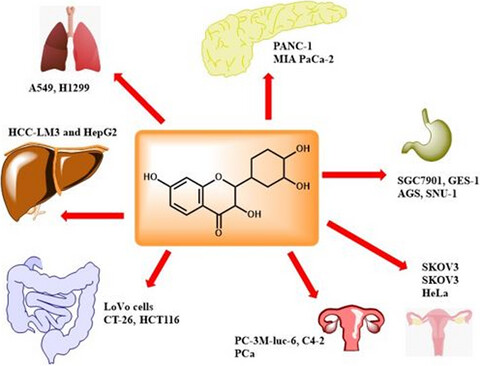
Many efforts have been made on researching potential anticancer agents in last decades. Natural products were among the popularly investigated agents. They are considered to have wider targeting pathways in comparison with synthetic drugs. Fisetin as a polyphenol with pleiotropic pharmacological properties showed promising anticancer activity in a wide range of cancers
Dietary intake of carbohydrates in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes—A narrative review
- Pages: 17-24
- First Published: 12 December 2020
Longitudinal changes in the bioactive proteins in human milk of the Chinese population: A systematic review
- Pages: 25-35
- First Published: 19 December 2020
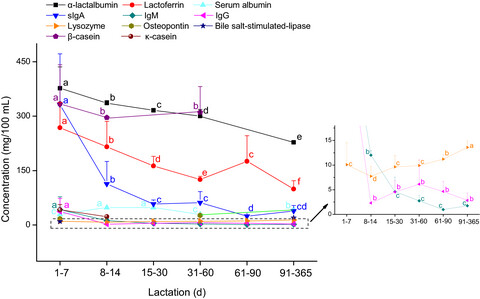
This systematic review aims at investigating the longitudinal changes in the bioactive proteins in the human milk of the Chinese population. The concentrations of α-lactalbumin, lactoferrin, β-casein, and three immunoglobulins (sIgA, IgM, and IgG) decrease during lactation. Lysozyme concentrations increase during lactation.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Effects of different food ingredients on the color and absorption spectrum of carminic acid and carminic aluminum lake
- Pages: 36-43
- First Published: 03 December 2020
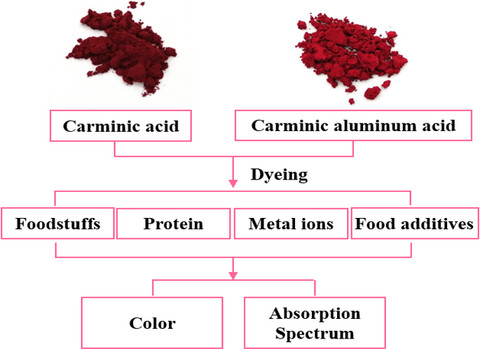
Three foodstuffs (surimi, minced meat and milk) were dyed by carminic acid and carminic aluminum lake. The effects of protein, metal ions and food additives on the color of carminic acid and carminic aluminum lake were investigated.This paper provides a reference for the application of carminic acid and carminic aluminum lake in food industry.
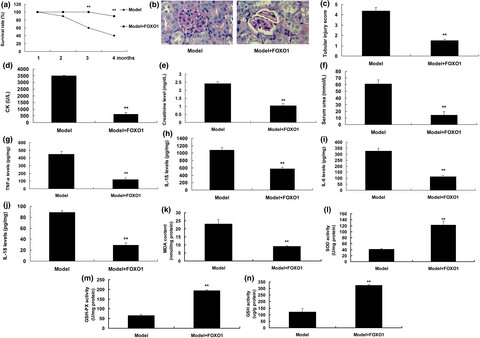
Forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) /SERPINB1 ameliorates ROS production in diabetic nephropathy
- Pages: 44-51
- First Published: 20 December 2020
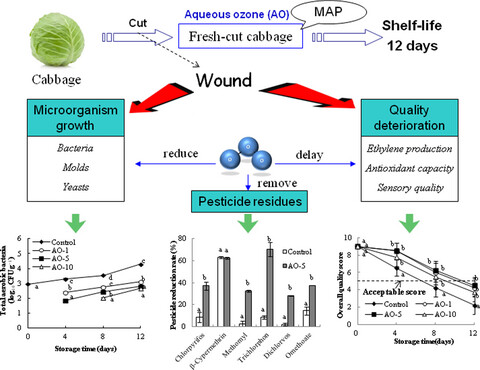
Effects of aqueous ozone treatment on microbial growth, quality, and pesticide residue of fresh-cut cabbage
- Pages: 52-61
- First Published: 16 December 2020
Enhancement of low-fat Feta cheese characteristics using probiotic bacteria
- Pages: 62-70
- First Published: 26 November 2020
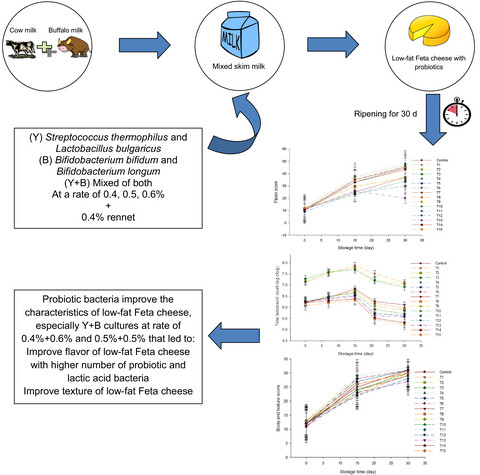
The objective of this study was to manufacture low-fat Feta cheese (LFC) using different types of starter cultures, such as yogurt (Y) cultures (Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus), bifidobacterium (B) cultures (Bifidobacterium bifidum and Bifidobacterium longum), and mixed of them (Y+B) at a different rate (0.4, 0.5, and 0.6%). The Y+B cultures improved the flavor and body and texture of LFC, especially at a ratio of 0.4+0.6% and 0.5+0.5%, which is similar to the typical full-fat Feta cheese (FC). Also, the LFC maintained a higher number of probiotics and lactic acid bacteria after 30 d of storage.
Effects of simultaneous and sequential cofermentation of Wickerhamomyces anomalus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on physicochemical and flavor properties of rice wine
- Pages: 71-86
- First Published: 26 November 2020
Nonvolatile taste compounds of Shanghai smoked fish: A novel three stages control techniques
- Pages: 87-98
- First Published: 24 November 2020
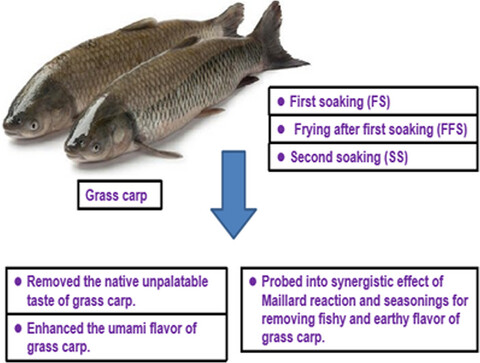
Removing the native unpalatable taste of grass carp is key for increasing its umami flavor and economic value. Therefore, the effect of processing stages including first soaking (FS), frying after first soaking (FFS), and second soaking (SS) on nonvolatile taste compounds of Shanghai smoked fish was investigated using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and automatic amino acid analyzer.
Diversity of the microbial community and antioxidant activity during fermentation of red raspberry Enzymes
- Pages: 99-110
- First Published: 22 December 2020
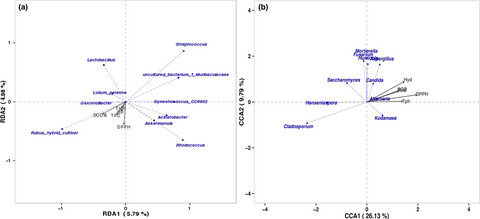
Red raspberry Enzymes inoculated with mixed fermentation had higher antioxidant activity than the sample without inoculated fermentation. The microbiota structures differed between the two samples. The results indicated that the fermentation by microorganisms significantly improves the oxidation resistance and helps to improve the quality of the Enzymes.
Lipid composition and antioxidant activities of some underused wild plants seeds from Burundi
- Pages: 111-122
- First Published: 01 November 2020

This study showed 14 species of wild plants that can provide oils with a wide variety of chemical compositions. They have been characterized by high contents of polyunsaturated fatty acids while they exhibit several positive health effects. These results suggest the important utility in various domain such as energy, cosmetics and especially the diversification of edible oils.
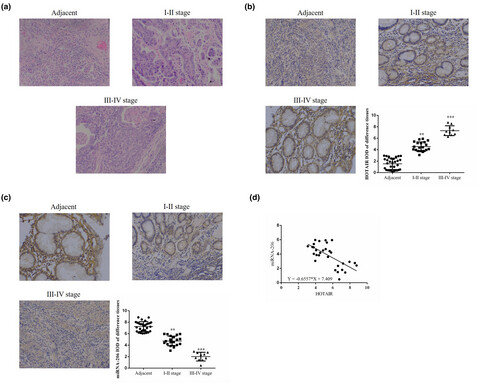
lncRNA HOTAIR knockdown suppresses gastric cancer cell biological activities
- Pages: 123-134
- First Published: 30 October 2020
Determining factors associated with breastfeeding and complementary feeding practices in rural Southern Benin
- Pages: 135-144
- First Published: 06 November 2020

In the present study, we evaluated breastfeeding and complementary feeding practices among children aged, respectively, 0–17 months and 6–17 months in a rural and food-insecure area in Southern-Benin, West Africa. We determined also socioeconomic and agricultural factors, which were associated to these practices in order to well design a nutrition education program. This graph presents the percentages of children who have achieved recommended breastfeeding and complementary feeding practices in the rural districts of Bopa and Houeyogbe (Southern Benin).
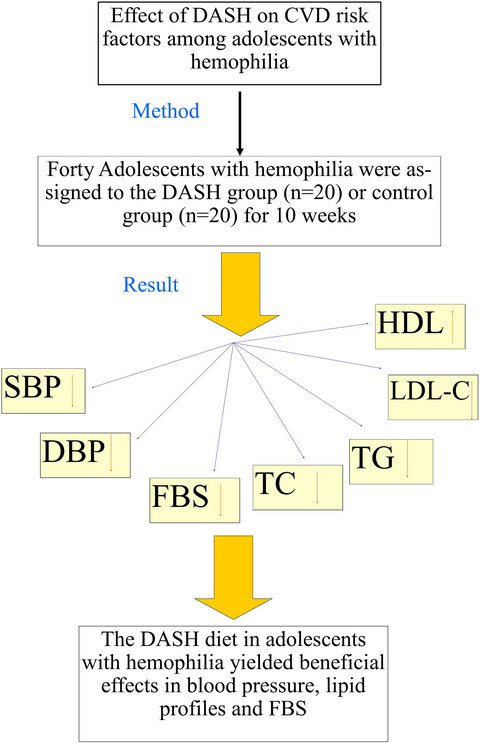
Effects of the dietary approach to stop hypertension (DASH) diet on blood pressure, blood glucose, and lipid profile in adolescents with hemophilia: A randomized clinical trial
- Pages: 145-153
- First Published: 29 October 2020
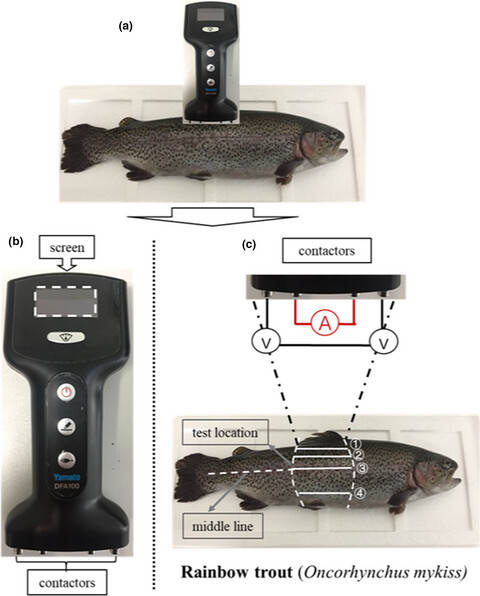
Estimating freshness of ice storage rainbow trout using bioelectrical impedance analysis
- Pages: 154-163
- First Published: 14 November 2020
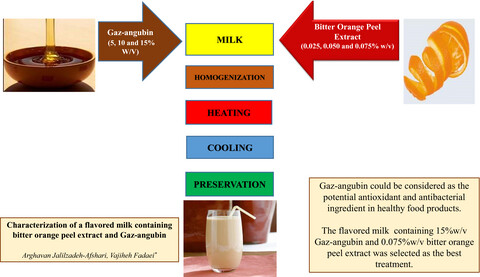
Characterization of flavored milk containing bitter orange peel extract and Gaz-angubin
- Pages: 164-171
- First Published: 29 October 2020
Nutritional composition and antinutrient content of Heteromorpha arborescens (Spreng.) Cham. & Schltdl. leaves: An underutilized wild vegetable
- Pages: 172-179
- First Published: 24 December 2020
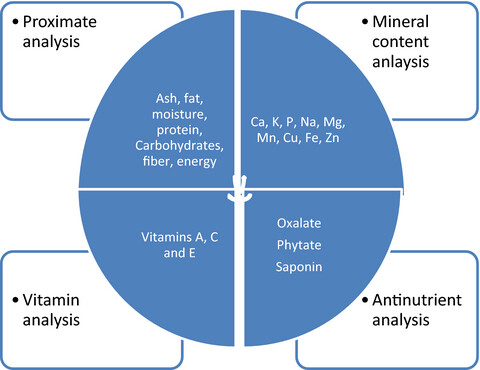
Proximate contents of H. arborescens leaves were present in significant amounts and very rich in K, Ca, and Fe with considerable amounts of Mg, Mn, Na, P, Cu, and Zn .Vitamins A, C, and E were observed in high amounts. Phytate, oxalate, saponin, and alkaloids were below toxic levels except for saponin which was in moderately high level. The results indicate that H. arborescens leaves are nutrient-rich and can contribute effectively to the daily nutrient requirements alongside its therapeutic properties.
Fraud detection and quality assessment of olive oil using ultrasound
- Pages: 180-189
- First Published: 04 November 2020
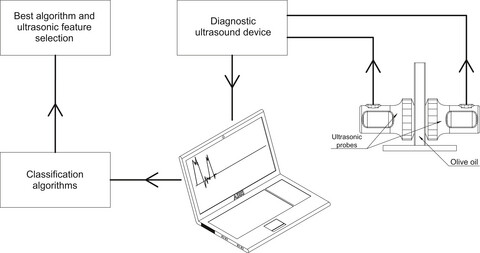
Due to the nutritional value and high price of EVOO, there is a lot of cheating in it. In this study, to fraud detection of EVOO four ultrasonic properties of oil in five levels of adulteration (5%, 10%, 20%, 35%, and 50%) were extracted. The results showed that among the seven different classification models, Naïve Bayes and support vector machine methods and gradient boosting classifier with 90.2%, 88.24%, and 88.24% were the most accurate classification algorithms, respectively.
Organic production of vinegar from mango and papaya
- Pages: 190-196
- First Published: 20 November 2020
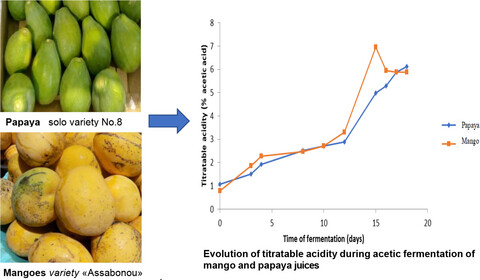
The production of vinegar from mango and papaya was realized through the process of directed alcoholic and acetic fermentation. The concentration of acetic acid is the highest of the organic acids for the four vinegars ranging from 37.46 ± 4.6 g/L to 55.85 ± 9.94 g/L. The acetic acid contents of mango and papaya vinegars are close to that of unpasteurized cider vinegar from France but higher than that of vinegar produced in Côte d'Ivoire.
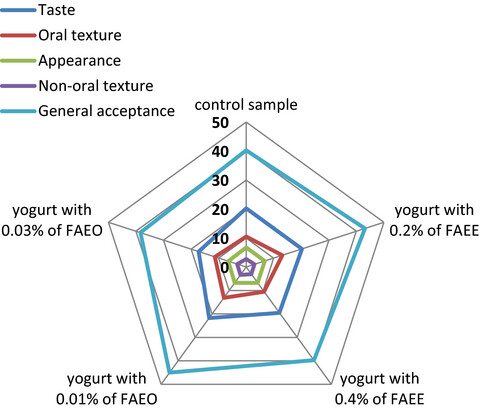
Effect of the ethanolic extract and essential oil of Ferulago angulata (Schlecht.) Boiss. on protein, physicochemical, sensory, and microbial characteristics of probiotic yogurt during storage time
- Pages: 197-208
- First Published: 04 November 2020
Curcumin inhibits the proteolytic process of SREBP-2 by first inhibiting the expression of S1P rather than directly inhibiting SREBP-2 expression
- Pages: 209-216
- First Published: 08 November 2020
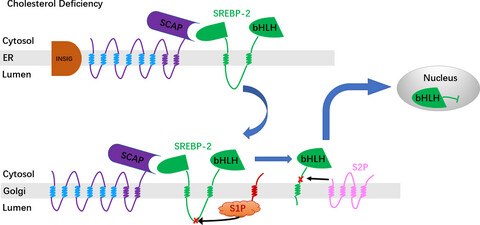
This study found for the first time that although curcumin could indeed downregulate the expression of SREBP-2 mRNA, it did not down-regulate the expression of SREBP-2 protein. This discovery is different from all previous studies on the relationship between curcumin and SREBP-2, which is a new discovery. In addition, this study also found that curcumin inhibited the process of SREBP-2 proteolysis, possibly by inhibiting the expression of S1P, which is also a new discovery and has not been reported.
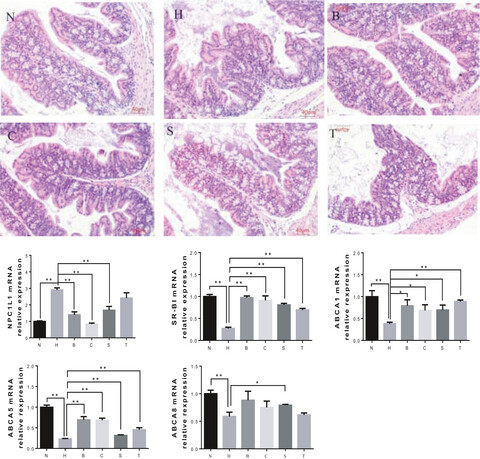
Effects of sorghum rice and black rice on genes associated with cholesterol metabolism in hypercholesterolemic mice liver and intestine
- Pages: 217-229
- First Published: 14 November 2020
Optimization of fermentation conditions for production of l-arabinose isomerase of Lactobacillus plantarum WU14
- Pages: 230-243
- First Published: 24 November 2020
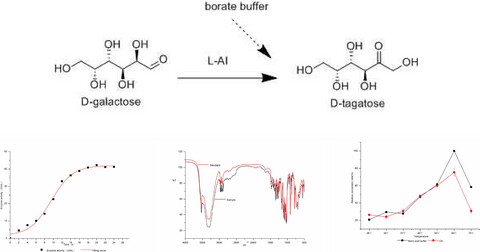
Lactobacillus plantarum WU14 was isolated from sauerkraut, and it has high ability to transform d-tagatose by l-arabinose isomerase. On the base of the fermentation medium optimization of l-AI produced by L. plantarum WU14, a mathematical model was established, and d-tagatose was separated from the fermentation broth. The Logistic equation and the Boltzmann model were used to nonlinearly fit the experimental data of L. plantarum WU14 biomass and l-AI activity. It was found that when the conversion temperature was 60°C, the reaction pH was 7.17, the volume ratio of the crude enzyme solution to the d-galactose was 5:1, and the volume ratio of borate to d-galactose was 2:1. After 24 hr of conversion, the conversion of d-tagatose was increased 12%.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Biochemical profile of milk thistle (Silybum Marianum L.) with special reference to silymarin content
- Pages: 244-250
- First Published: 09 November 2020
Milk thistle is safe, well tolerated in different preparation form and producing no any serious side effects. Milk thistle seeds can be used in raw form or made into a tea. Milk thistle seed tea has significant attention, both in scientific and consumer communities owing to its health benefits against variety of maladies. Furthermore, it is exposed that overall anti-oxidant level improves in humans by using milk thistle tea. The free radicals quenching ability of milk thistle tea is better than black tea.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Effects of screw configuration on chemical properties and ginsenosides content of extruded ginseng
- Pages: 251-260
- First Published: 21 November 2020
The twin-screw extruding function obviously improves the antioxidant ability of Ginseng extract. The content of total saponins in ginseng extract was increased by twin-screw extruder. The content of rare ginsenoside Rg3 increased significantly after extrusion. Extensive additional research is necessary prior to industrial implementation.
Screening of dominant strains in red sour soup from Miao nationality and the optimization of inoculating fermentation conditions
- Pages: 261-271
- First Published: 20 November 2020
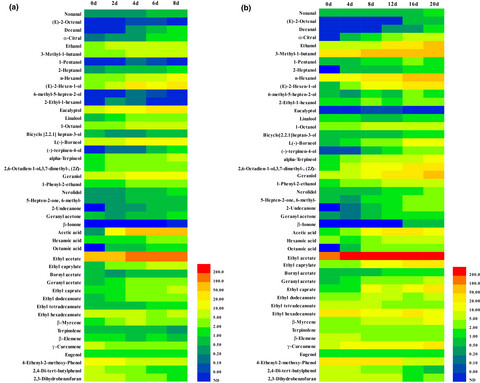
An acid-producing dominant strain H9 was screened from the red sour soup, and was identified as Lactobacillus buchneri. The inoculating fermentation conditions of red sour soup were optimized using L. bucheneri H9 as external starter. The article provide a feasibility for the rapid fermentation of red sour soup using L. bucheneri H9 as external starter, under the premise of flavor fidelity.
Mathematical modeling of weight loss and crust temperature of toast bread containing guar gum during baking process
- Pages: 272-281
- First Published: 04 December 2020
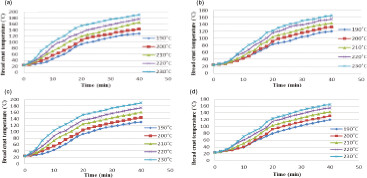
This research is following two goals: (a) studying the effect of the baking time, baking temperature, and guar gum on crust temperature and weight loss of toast bread during baking process, and (b) developing a mathematical model for predicting the crust temperature and weight loss of toast bread at different oven temperatures and baking times.
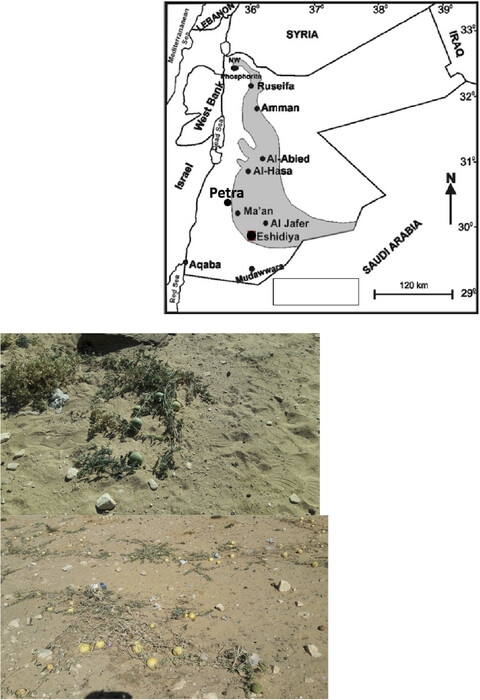
Evaluation of the anticancer activity and fatty acids composition of “Handal” (Citrullus colocynthis L.) seed oil, a desert plant from south Jordan
- Pages: 282-289
- First Published: 10 November 2020
Kinetics of α‑dicarbonyl compounds formation in glucose-glutamic acid model of Maillard reaction
- Pages: 290-302
- First Published: 08 November 2020
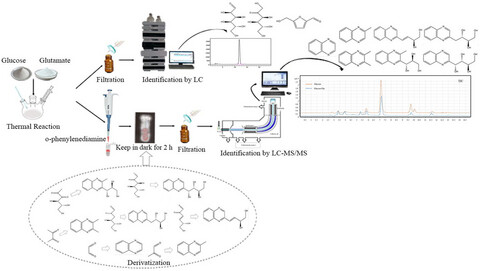
Kinetics of 7 α-dicarbonyl compounds formation in glucose-only and glucose-glutamic acid systems was investigated. The formation kinetics of each compound varies with the heating temperature. Shortening the heating time and reducing heating temperature (except glyoxal in glucose-only system) are effective method to reduce the content of α-dicarbonyl compounds in the two systems tested
The effect of yogurt co-fortified with probiotic and vitamin D on lipid profile, anthropometric indices and serum 25-hydroxi vitamin D in obese adult: A Double-Blind Randomized- Controlled Trial
- Pages: 303-312
- First Published: 10 November 2020
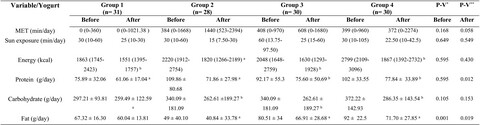
A 10-week parallel-group, double-blind, randomized and controlled trial was conducted on 140 obese men and women. The participants were randomly allocated to receive either 1) plain low-fat yogurt or 2) probiotic yogurt or 3) vitamin D-fortified yogurt or 4) probiotic and vitamin D co-fortified yogurt. All groups received low-calorie diet. vitamin D increased significantly in group 4 (p = 0.008), group 3 (p = 0.001) and group 1 (p = .012 with no difference between groups. Vitamin D-fortified yogurt had the most effect size and showed a significant difference vs. plain (p = 0.018) and probiotic yogurt (p = 0.002).
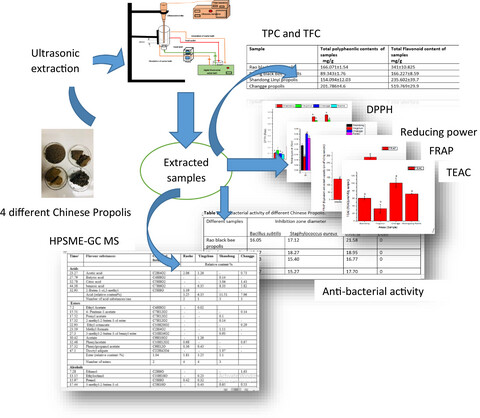
Chinese Propolis: Ultrasound-assisted enhanced ethanolic extraction, volatile components analysis, antioxidant and antibacterial activity comparison
- Pages: 313-330
- First Published: 20 November 2020
Incorporation of omega-3 fatty acid-rich grape seed oil in yoghurt: Response surface optimization of physicochemical, textural, and sensory attributes during refrigerated storage
- Pages: 331-344
- First Published: 07 November 2020
Evaluation of microbiological, chemical, and sensory properties of cooked probiotic sausages containing different concentrations of astaxanthin, thymol, and nitrite
- Pages: 345-356
- First Published: 12 November 2020
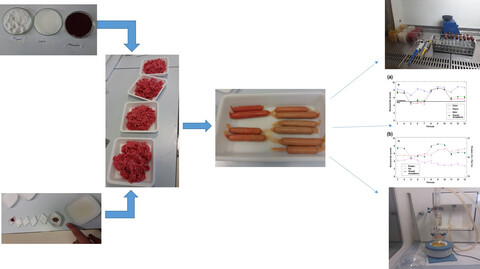
In heat-treated meat products such as cooked sausage, probiotics are generally not used because of adverse effect of thermal treatment on their viability and stability. One of the novel techniques to improve nutritional attributes of meat products is integration of Bacillus coagulans, a thermophilic probiotic microorganism. Using some natural derived additives and preservatives such as astaxanthin and thymol is a novel approach to decrease the use of nitrite and extend the shelf-life of cooked sausages and their safety.
Effects of energy supplements on the differentiation of skeletal muscle satellite cells
- Pages: 357-366
- First Published: 13 December 2020
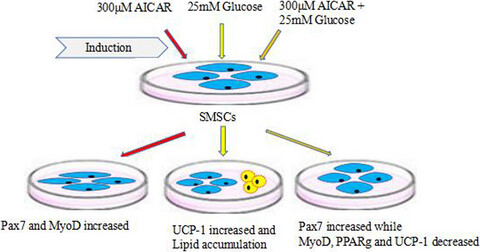
To investigate the effects of the activator of AMPK and high glucose on the differentiation of mouse SMSCs, primary SMSCs were isolated from mouse extensor digitorum longus muscle and grown to near confluence (80%). Postconfluent cells were cultured in a growth medium with different inductors: AICAR, glucose, and AICAR mixed with glucose. The present study indicated that the certain energy supplements influence the direction of SMSC differentiation which may contribution on the structure of muscle and meat quality, sequentially.
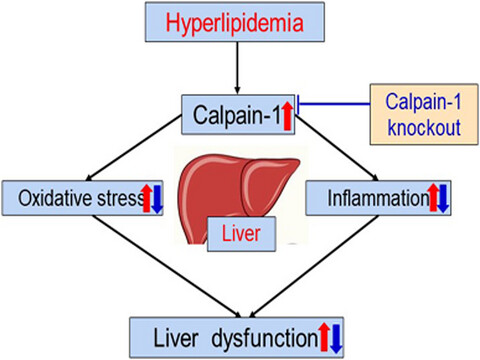
Knockout of calpain-1 protects against high-fat diet-induced liver dysfunction in mouse through inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation
- Pages: 367-374
- First Published: 22 December 2020
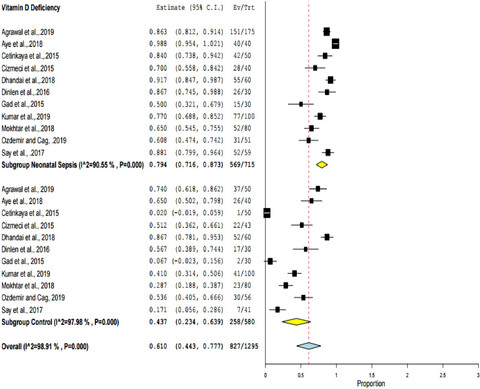
Effects of vitamin D on neonatal sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 375-388
- First Published: 10 November 2020
Tyrosinase inhibition by p-coumaric acid ethyl ester identified from camellia pollen
- Pages: 389-400
- First Published: 11 December 2020
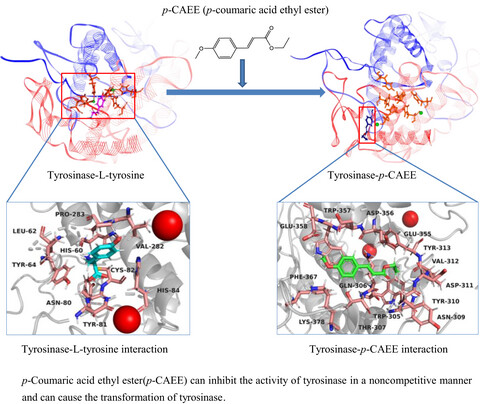
p-Coumaric acid ethyl ester was first found in camellia pollen. The inhibition is reversible and dose-dependent. p-Coumaric acid ethyl ester altered the structure of tyrosinase. p-Coumaric acid ethyl ester and pollen had potential applications for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and fruit preservation. p-Coumaric acid ethyl ester (p-CAEE) can inhibit the activity of tyrosinase in a noncompetitive manner and can cause the transformation of tyrosinase.
Influence of rootstocks on fruit physical and chemical properties of peach cv. UFSun
- Pages: 401-413
- First Published: 01 December 2020
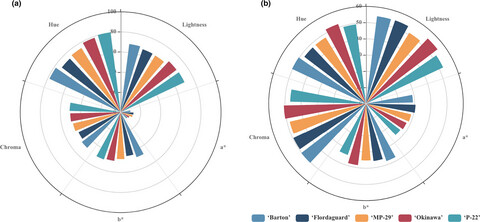
Significant differences in fruit weight and size, soluble solids content, titratable acidity, and firmness were found among some rootstocks. 'MP-29'rootstock seems to induce the highest fruit quality, showing higher contents of total soluble solids, total titratable acidity, total phenolic compounds, total antioxidant activity, and total anthocyanin content. Selecting the right combination of the rootstock and cultivar is important for optimizing fruit quality parameters.
Consumer acceptance among Dutch and German students of insects in feed and food
- Pages: 414-428
- First Published: 01 December 2020
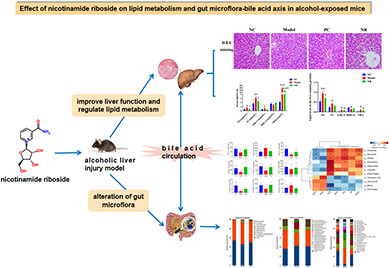
Effect of nicotinamide riboside on lipid metabolism and gut microflora-bile acid axis in alcohol-exposed mice
- Pages: 429-440
- First Published: 21 December 2020
Effect of herbal formulation intake on health indices in albino Wistar rat model
- Pages: 441-448
- First Published: 10 November 2020
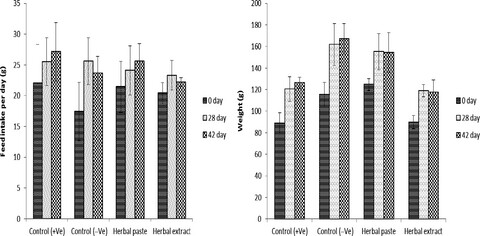
Herbal medicines are primitive and conventional therapeutics for around 80% of the world's population due to their wide acceptability, availability, and affordability while their safety claims are in the process of validation in line with the consumer safety standards of the recent era. Findings of this subchronic exposure study on evaluating the synergistic effect of garlic-, ginger-, onion-, apple cider vinegar-, and honey-based conventional herbal formulations against dyslipidemia validated existing therapeutic claims of the recipe.
The difference of regulatory effect of two Inonotus obliquus extracts on high-fat diet mice in relation to the fatty acid elongation function of gut microbiota
- Pages: 449-458
- First Published: 24 November 2020
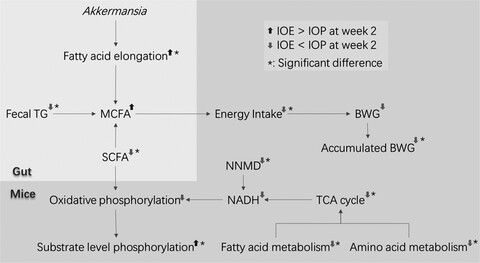
The fatty acid elongation function of bacteria (especially Akkermansia) increased MCFA and decreased SCFA. Increasing MCFA reduced energy intake and weight gain. Reducing SCFA reduced the level of oxidative phosphorylation, TCA cycle, and nutrient metabolism and increased the level of substrate phosphorylation.
Hypolipidemic properties of Chlorella pyrenoidosa organic acids via AMPK/HMGCR/SREBP-1c pathway in vivo
- Pages: 459-468
- First Published: 11 December 2020

The aim of this study was to investigate the effects and mechanism of 95% ethanol extract of Chlorella pyrenoidosa (CPE95) on lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-fed rats. Chemical compositions of CPE95 were determined by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS). The present results that Chlorella pyrenoidosa organic acids could improve lipid metabolism disorders by regulating AMPK/HMGCR/SREBP-1c gene expressions.
A weak post-acidification Lactobacillus helveticus UV mutant with improved textural properties
- Pages: 469-479
- First Published: 15 November 2020
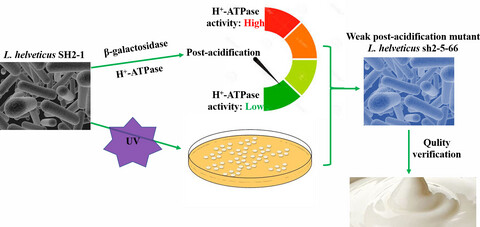
H+-ATPase activity was demonstrated to be highly related to the postacidification of L. helveticus SH2-1. By detecting H+-ATPase activity, the weak postacidify mutant renamed as L. helveticus sh2-5–66 was selected from 80 UV mutants. The milk fermented with L. helveticus sh2-5–66 showed improvement in textural and rheological properties and flavor during storage.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Effect of adding Aloe vera jell on the quality and sensory properties of yogurt
- Pages: 480-488
- First Published: 13 December 2020
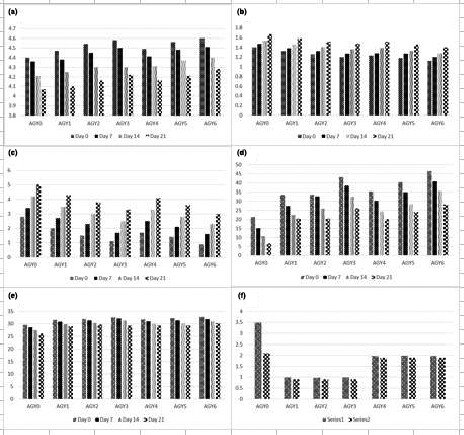
The current research is helpful in broaden the spectrum of aloe vera gel application for the development of fermented product. Aloe vera gel is useful to improve the physicochemical and organoleptic attributes of the yogurt. The experimental work is scientific basis for the stakeholders to utilize for product development at commercial level. The study has wide application for the development of various functional foods.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
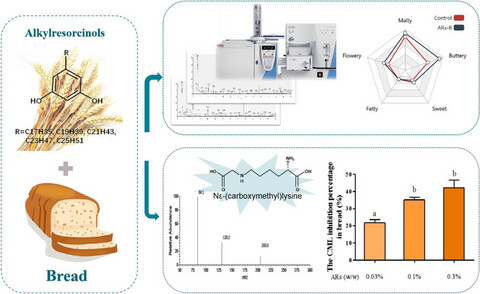
Effect of alkylresorcinols on the formation of Nε-(carboxymethyl)lysine and sensory profile of wheat bread
- Pages: 489-498
- First Published: 18 November 2020
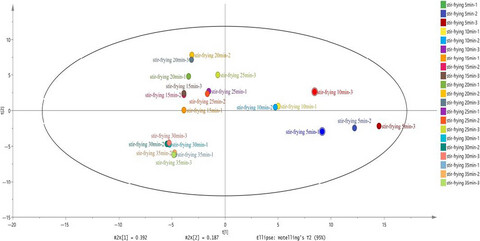
Characterization of flavor volatile compounds in industrial stir-frying mutton sao zi by GC-MS, E-nose, and physicochemical analysis
- Pages: 499-513
- First Published: 10 December 2020
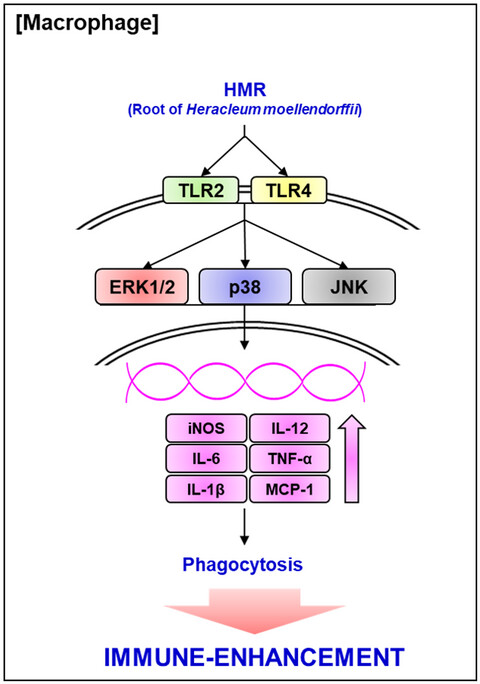
Heracleum moellendorffii root extracts exert immunostimulatory activity through TLR2/4-dependent MAPK activation in mouse macrophages, RAW264.7 cells
- Pages: 514-521
- First Published: 16 November 2020
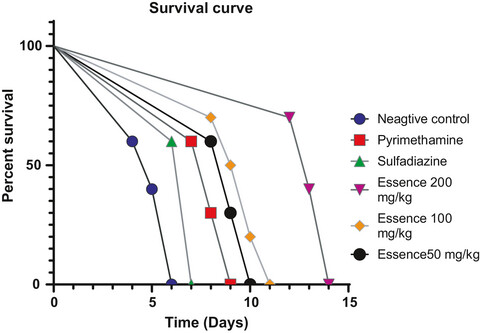
In vitro and in vivo Anti-Toxoplasma activity of Dracocephalum kotschyi essential oil
- Pages: 522-531
- First Published: 12 November 2020
Mathematical and intelligent modeling of stevia (Stevia Rebaudiana) leaves drying in an infrared-assisted continuous hybrid solar dryer
- Pages: 532-543
- First Published: 12 November 2020
A comparative study was performed among mathematical, artificial neural networks (ANNs), and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy System (ANFIS) models for predicting the experimental moisture ratio (MR) of stevia leaves during the drying in an infrared (IR)-assisted continuous-flow hybrid solar dryer. The drying time was decreased significantly by increasing the inlet air temperature and increasing IR lamp input power (p < .05). It was concluded that artificial intelligence modeling is an effective approach for accurate prediction of the drying kinetics of stevia leaves.
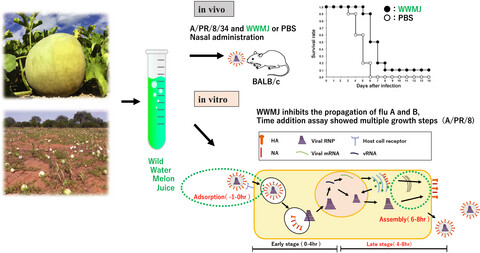
Juice of Citrullus lanatus var. citroides (wild watermelon) inhibits the entry and propagation of influenza viruses in vitro and in vivo
- Pages: 544-552
- First Published: 27 November 2020
Development of nanochitosan-based active packaging films containing free and nanoliposome caraway (Carum carvi. L) seed extract
- Pages: 553-563
- First Published: 18 November 2020
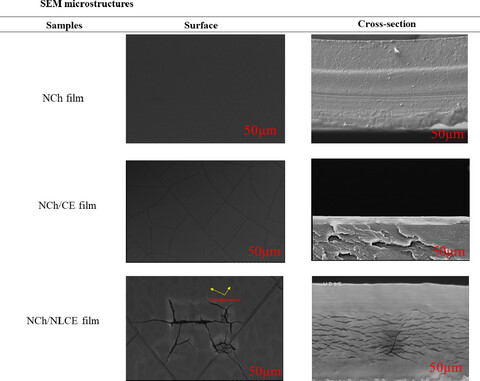
The article describes the development of eco-friendly nanostructured chitosan films that might be used as biodegradable packaging materials to replace plastics. In particular, it shows that the physical, mechanical, barrier, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties of nanocomposite films can be modulated by adding essential oil nanoliposomes into chitosan matric.
The effects of thermal treatment on the bacterial community and quality characteristics of meatballs during storage
- Pages: 564-573
- First Published: 02 December 2020
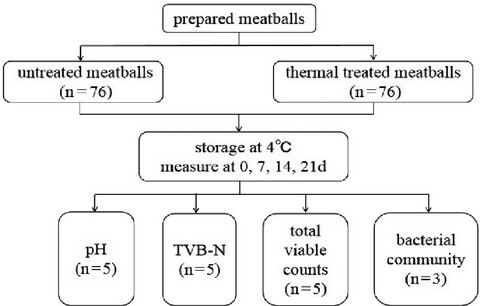
The findings of this study demonstrated that thermal treatment (121°C, 15 min) could significantly decrease bacterial community diversity and the growth of potential spoilage bacteria in meatballs. In particular, thermal treatment could largely decrease the relative abundance of bacterial metabolic pathways in meatballs, such as carbohydrate, amino acid, and lipid metabolism to maintain the freshness of meatballs during storage.
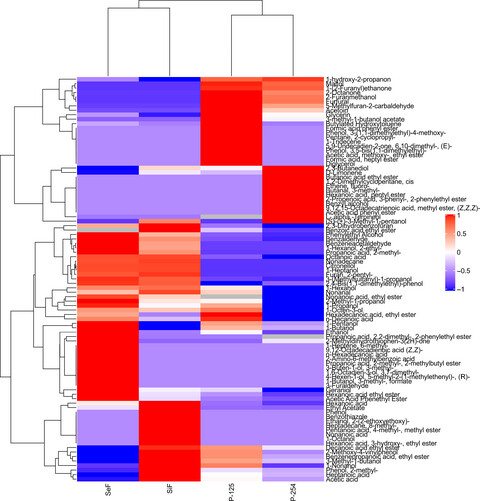
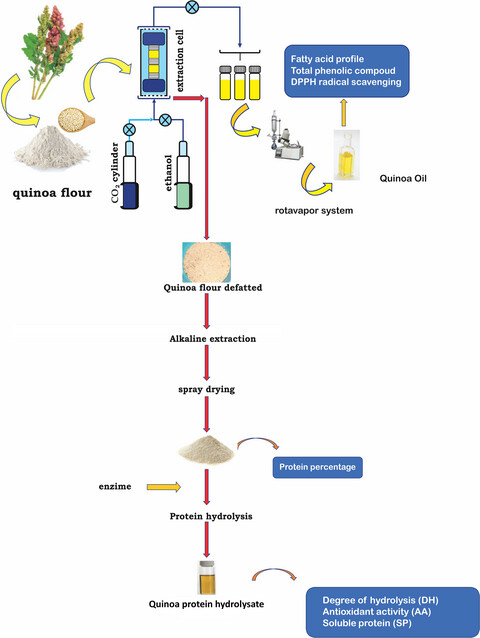
Effect of pretreatment by supercritical fluids on antioxidant activity of protein hydrolyzate from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.)
- Pages: 574-582
- First Published: 03 December 2020
COMMENTARY
Critique of the Chinese dietary guidelines on the consumption of cooking oils
- Pages: 583-585
- First Published: 05 November 2020