Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Natural occurrence and production of tenuazonic acid in wine grapes in Argentina
- Pages: 523-531
- First Published: 23 February 2018
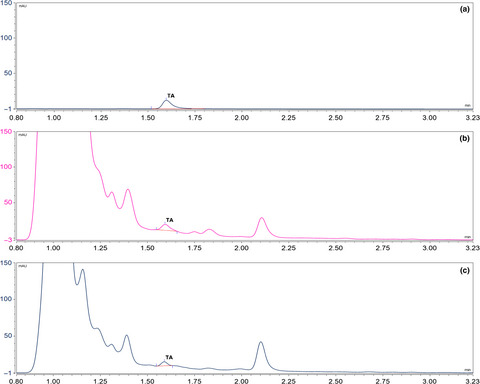
The 16.2% of wine grape samples collected during 2016 vintage in the region of DOC San Rafael (Argentina) showed TA contamination, with 4% of incidence in healthy samples (77 µg·kg−1) and 42% in rotten samples (10–778 µg·kg−1). Two of three Alternaria alternata strains were able to produce TA during inoculation experiments in wine grapes; they showed an optimum of production at 15°C and 25°C after 24 days of incubation. Nutritional composition of grapes results appropriate for A. alternata infection and TA production and, together with the adequate field conditions, favors TA natural occurrence in wine grapes.
Physical, chemical, and sensory properties of biscuits prepared from flour blends of unripe cooking banana, pigeon pea, and sweet potato
- Pages: 532-540
- First Published: 30 January 2018
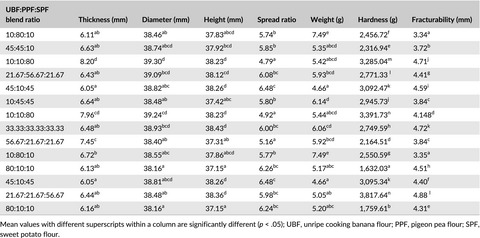
The quality attributes of biscuits prepared from flour blends of cooking banana (UBF), pigeon pea (PPF), and sweet potato (SPF) were investigated. Biscuits were significantly (p < .05) different in their nutrient composition, with the crude protein, crude fiber, ash, and dietary fiber contents increasing as the PPF level increased. Biscuit prepared from flour blend of 21.67% unripe cooking banana, 21.67% pigeon pea, and 56.67% sweet potato was the most preferred in terms of shape, mouthfeel, taste, crunchiness, and overall acceptability.
Mold infestation and aflatoxins production in traditionally processed spices and aromatic herbs powder mostly used in West Africa
- Pages: 541-548
- First Published: 02 February 2018
The study documented the first information about the occurrence of aflatoxins in the common spices used in West Africa. Around of 50% of samples investigated were contaminated by total aflatoxins with values higher than 10 µg/kg. So, there is a potential for sporadic aflatoxin poisoning related to the consumption of SAH powder as commercialized in Benin and other countries of West Africa region.
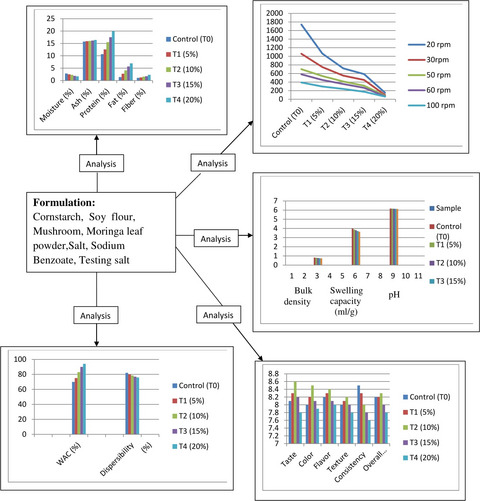
Effect of incorporation of soy flour on functional, nutritional, and sensory properties of mushroom–moringa-supplemented healthy soup
- Pages: 549-556
- First Published: 02 February 2018
Determination of geographical origin Turkish hazelnuts according to fatty acid composition
- Pages: 557-562
- First Published: 02 February 2018
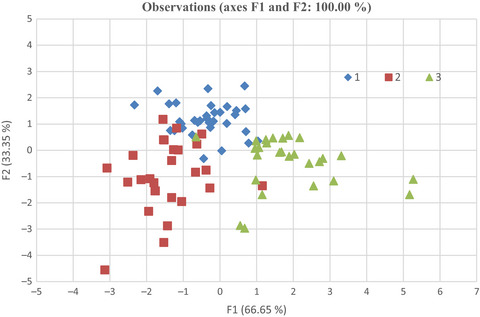
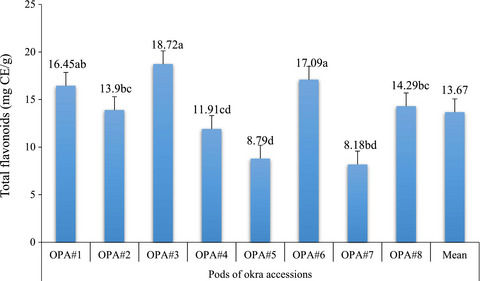
Indigenous Ethiopian okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) mucilage: A novel ingredient with functional and antioxidant properties
- Pages: 563-571
- First Published: 02 February 2018
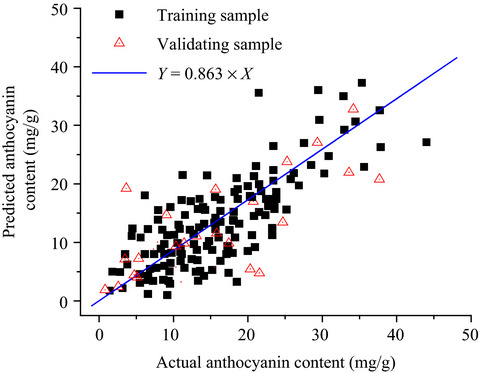
Estimating foliar anthocyanin content of purple corn via hyperspectral model
- Pages: 572-578
- First Published: 04 February 2018
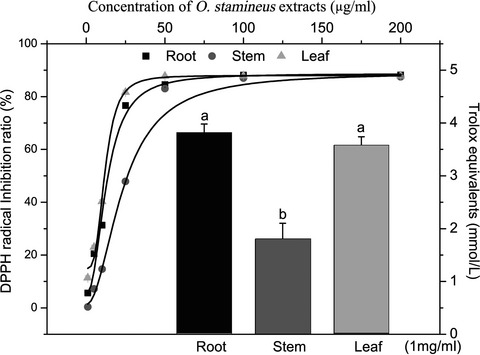
A comparative study of the antioxidant and intestinal protective effects of extracts from different parts of Java tea (Orthosiphon stamineus)
- Pages: 579-584
- First Published: 06 February 2018
Moisture sorption isotherm and changes in physico-mechanical properties of films produced from waste flour and their application on preservation quality of fresh strawberry
- Pages: 585-593
- First Published: 06 February 2018
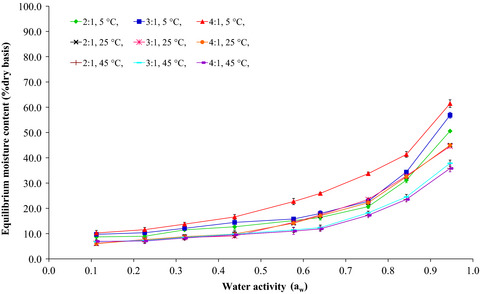
Waste flour from noodle production could be used to produce flour-based films. The moisture sorption isotherms of the films showed the correlation between the equilibrium moisture content and the water activities was well fitted by Henderson's equation. The flour film with plasticizers (glycerol and sorbitol) and potassium sorbate could be a promising alternative natural packaging material to reduce the use of nonbiodegradable synthetic polymer films in food applications.
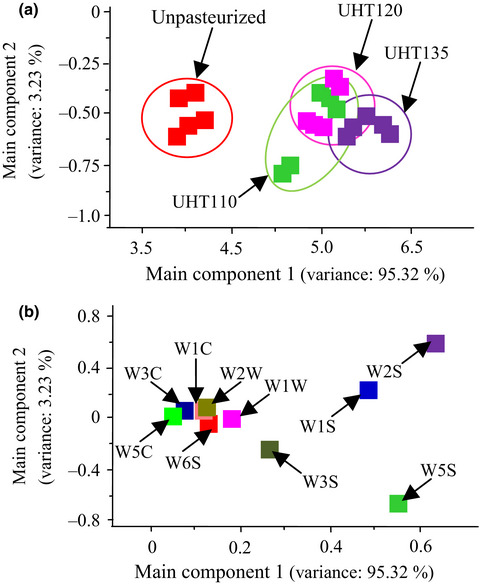
Effect of ultrahigh temperature treatment on qualities of watermelon juice
- Pages: 594-601
- First Published: 06 February 2018
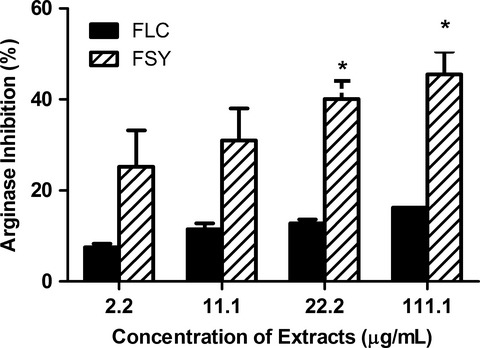
Local condiments from fermented tropical legume seeds modulate activities of critical enzymes relevant to cardiovascular diseases and endothelial function
- Pages: 602-608
- First Published: 08 February 2018
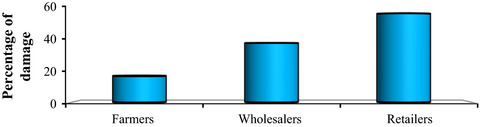
Assessment of banana fruit handling practices and associated fungal pathogens in Jimma town market, southwest Ethiopia
- Pages: 609-616
- First Published: 08 February 2018
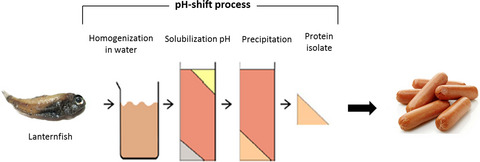
Physicochemical evaluation of sausages prepared by lantern fish (Benthosema pterotum) protein isolate
- Pages: 617-626
- First Published: 15 February 2018
A heating method for producing frozen pizza ingredients with increased total polyphenol content and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging activity
- Pages: 627-637
- First Published: 20 February 2018
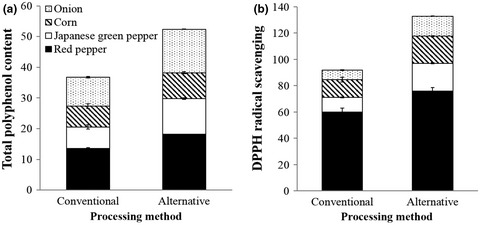
Frozen vegetable topping and par-baked pizza bases were processed by hot plate heating and heating at 500°C for 50 s, respectively, and compared to their conventional counterparts (i.e., steam-blanched vegetable toppings and commercially available par-baked pizza base, respectively) in terms of total polyphenol content (TPC) and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging activity (DPPH RSA). Replacing conventional with alternatively heat-treated vegetable toppings was estimated to increase TPC and DPPH RSA by 1.2-fold to 1.6-fold and 1.3-fold to 2.1-fold, respectively. Therefore, alternative heat treatment of selected frozen pizza ingredients may be a viable method for increasing the potential healthfulness of frozen pizza.
Physicochemical and nutritional properties of rice as affected by parboiling steaming time at atmospheric pressure and variety
- Pages: 638-652
- First Published: 20 February 2018

The interactive effect of rice parboiling steaming time and variety allows for rice to be produced with desired physicochemical and nutritional benefits. This method facilitated the identification of NERICA7 steamed at 35 min having lower total starch, higher protein, phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium content compared to other treatments.This is significant because this is the first time this work is being done especially using upland rice varieties and paves the way for using this method to screen varieties and produce rice for people with special needs.
Nutrient, phytochemical, and antinutrient composition of Citrus maxima fruit juice and peel extract
- Pages: 653-658
- First Published: 20 February 2018
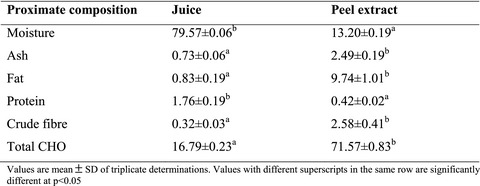
Citrus maxima peel extract contains significantly (p < .05) higher crude fiber (2.58%), fat (9.74%), ash (2.49%), and carbohydrate (71.57%) compared with Citrus maxima juice. Citrus maxima peel is highly nutritive and rich in phytochemicals; further research is recommended to investigate its therapeutic effect.
Evaluation of physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of kombucha “Tea Fungus” during extended periods of fermentation
- Pages: 659-665
- First Published: 20 February 2018
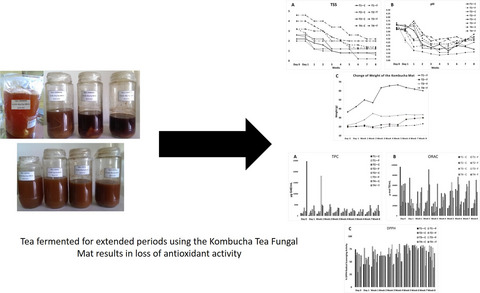
In this study, four Kombucha beverages were prepared by placing the tea fungal mats in sugared Sri Lankan black tea at varying concentrations for a period of 8 weeks. The antioxidant activities, physio-chemical and qualitative properties were monitored prior to the commencement of the fermentation process, one day after the inoculation with the microorganisms and subsequently, on a weekly basis. All samples displayed a statistically significant decrease (p < .05) in the antioxidant activity at the end 8 weeks, which was indicative of the decreasing functional properties of the beverage, while the physico-chemical properties indicated increased acidity and turbidity, which might decrease consumer appeal of the fermented beverage.
Galactomannan from Trigonella foenum-graecum L. seed: Prebiotic application and its fermentation by the probiotic Bacillus coagulans strain MTCC 5856
- Pages: 666-673
- First Published: 20 February 2018
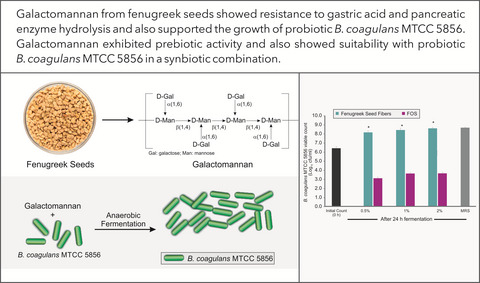
Galactomannan from fenugreek seeds showed resistance to gastric acid and pancreatic enzyme hydrolysis and also supported the growth of probiotic Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856. Galactomannan exhibited prebiotic activity and also showed suitability with probiotic B. coagulans MTCC 5856 in a synbiotic combination.
Intermittent energy restriction for weight loss: Spontaneous reduction of energy intake on unrestricted days
- Pages: 674-680
- First Published: 21 February 2018
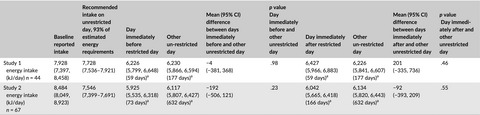
There is increasing interest in the potential for intermittent energy restriction (IER) to be used in weight management. However, there are concerns that IER could result in ‘rebound’ overconsumption of energy on unrestricted days. We studied self -reported food records from participants in two trials of IER versus continuous energy restriction. IER is associated with a spontaneous reduction in energy intake during all unrestricted days including the days immediately before and after the two day period of energy restriction. Consistency of restricted days was not associated with weight loss success.
Enhancing the fatty acid profile of milk through forage-based rations, with nutrition modeling of diet outcomes
- Pages: 681-700
- First Published: 28 February 2018
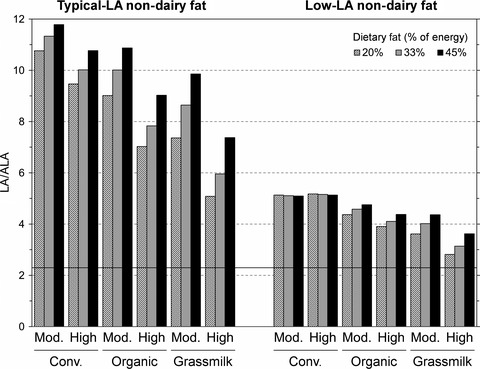
From a 3-year, U.S.-wide study, we report the fatty acid profile from 1,163 samples of milk from nearly 100% forage-fed cows (grass milk) and compare it to profiles from a similar study of conventional and organic milk. We find increases in omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid and a decrease in omega-6 fatty acids. In model human diets, these changes are sufficient to substantially reduce historically high omega-6/omega-3 ratios in modern diets.