Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Featured Cover
- First Published: 20 March 2023

The cover image is based on the Original Article Contrasting seasonal dynamics of dormancy, respiratory metabolism and cell cycle state in grapevine buds of a subtropical and Mediterranean climate by Yazhini Velappan et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.431. Image Credit: Michael J. Considine.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
WHIRLY protein functions in plants
- First Published: 17 March 2022
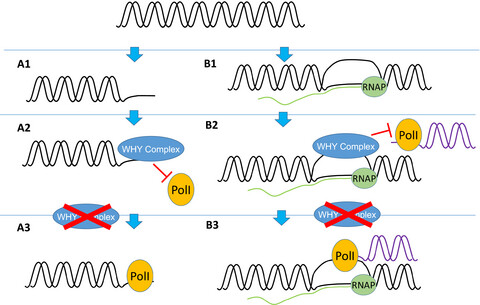
WHY proteins serve important roles in plant development and stress tolerance. They function as transcription factors in the nucleus, as well as fulfilling crucial roles in DNA and RNA metabolism in chloroplasts and mitochondria. They are excellent potential targets for plant breeding strategies aiming to improve sustainable agriculture.
Redox regulation in C3 and C4 plants during climate change and its implications on food security
- First Published: 15 May 2022

This review focus on the similarities and differences in redox regulation in C3 and C4 plants. Antioxidant defence response against abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity and high temperatures is reviewed. The redox mediated regulation of growth and development of C3 and C4 plants are also addressed.
Trends in rice research: 2030 and beyond
- First Published: 27 June 2022

We have analysed the trends in rice research in the past three decades in both Asian (Oryza sativa) and African (O. glaberrima) rice, with their impact on rice cultivation. We have also analysed the trends in population growth, rice cultivation, production, price, consumption and varietal release along with their projections for 2030 and beyond.
Biofortification of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) with iron and zinc: Achievements and challenges
- First Published: 30 June 2022
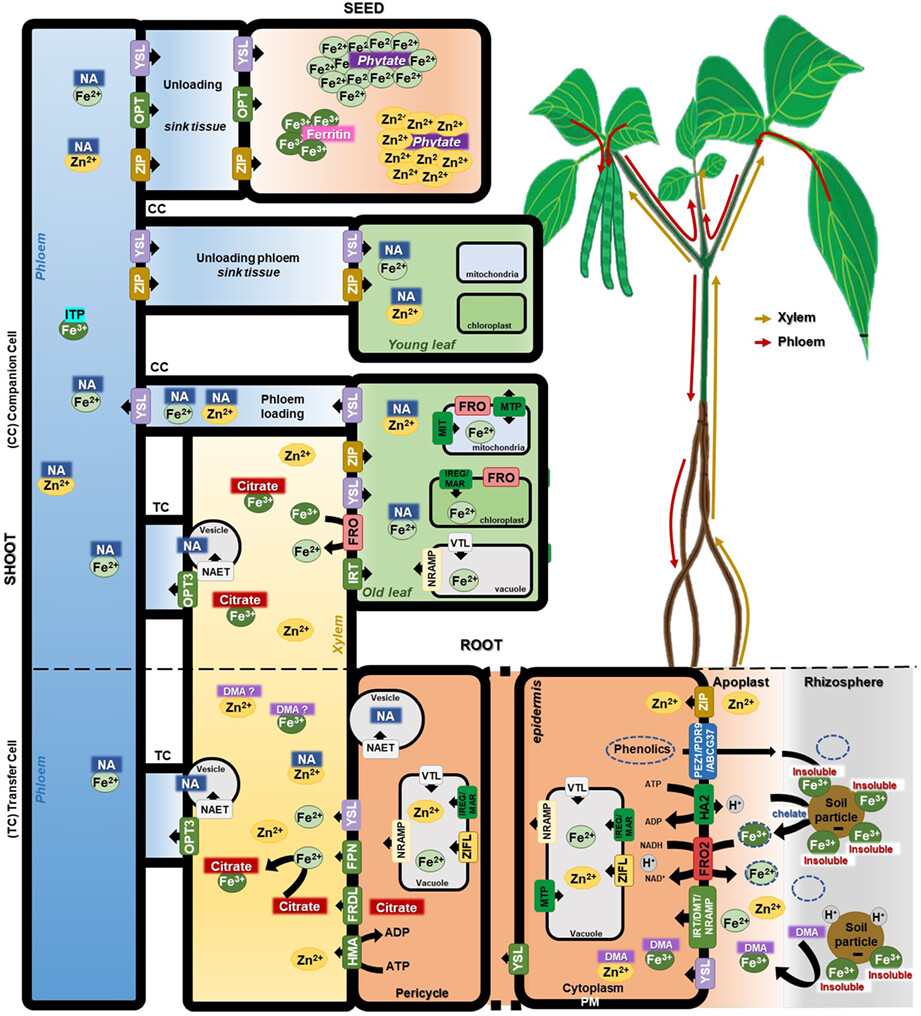
This review describes the genes and processes associated with Fe and Zn accumulation in common bean, a significant food source in Africa that plays an important role in nutritional security. We discuss the conventional plant breeding, transgenic and gene editing approaches that are being deployed to improve Fe and Zn accumulation in beans. We also consider the requirements of successful bean biofortification programmes, highlighting gaps in current knowledge, possible solutions and future perspectives.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Perspective on the present state and future usefulness of marama bean (Tylosema esculentum)
- First Published: 14 September 2022
REVIEW
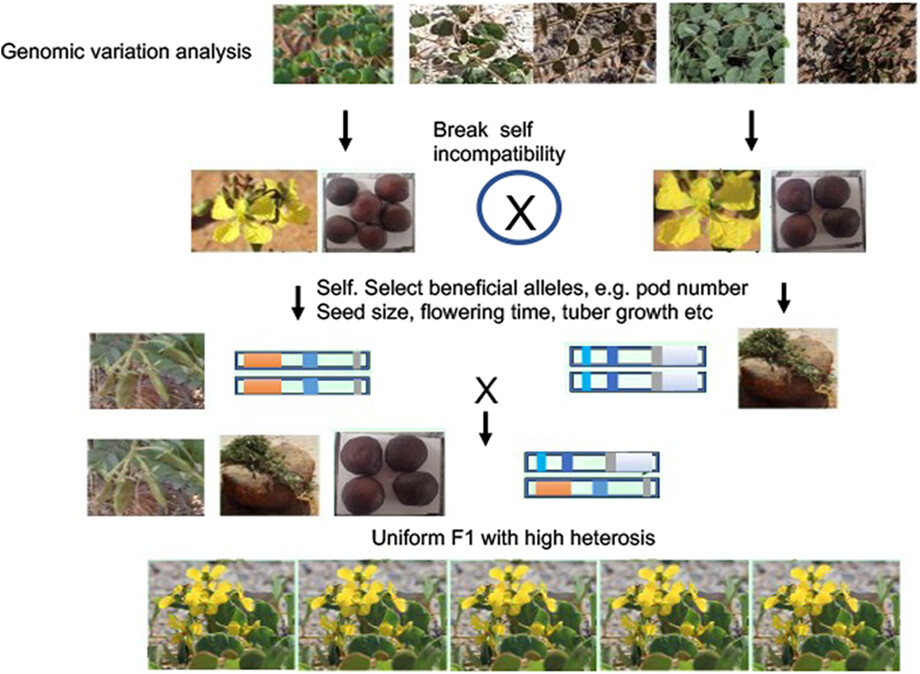
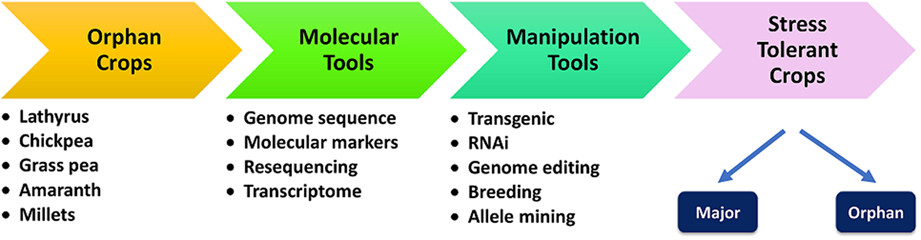
Orphan crops: A genetic treasure trove for hunting stress tolerance genes
- First Published: 13 December 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Does green vertical farming offer a sustainable alternative to conventional methods of production?: A case study from Scotland
- First Published: 07 December 2022
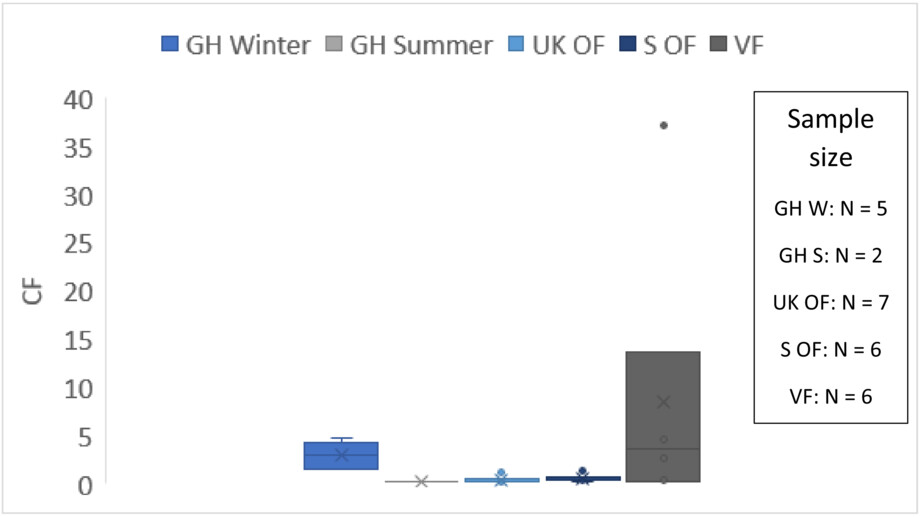
Life cycle analysis using lettuce as an example crop indicate that electricity consumption by VF account for 91% of the carbon footprint. Under the 2020 Scottish electricity mix, vertical farming was seen to be comparable with UK open-field agriculture in environmental impacts. This lowers further under a 100% renewable electricity generation scenario, offer a low carbon production method and a potential alternative for sustainable future produce.
The future of sustainable food consumption in China
- First Published: 21 June 2022
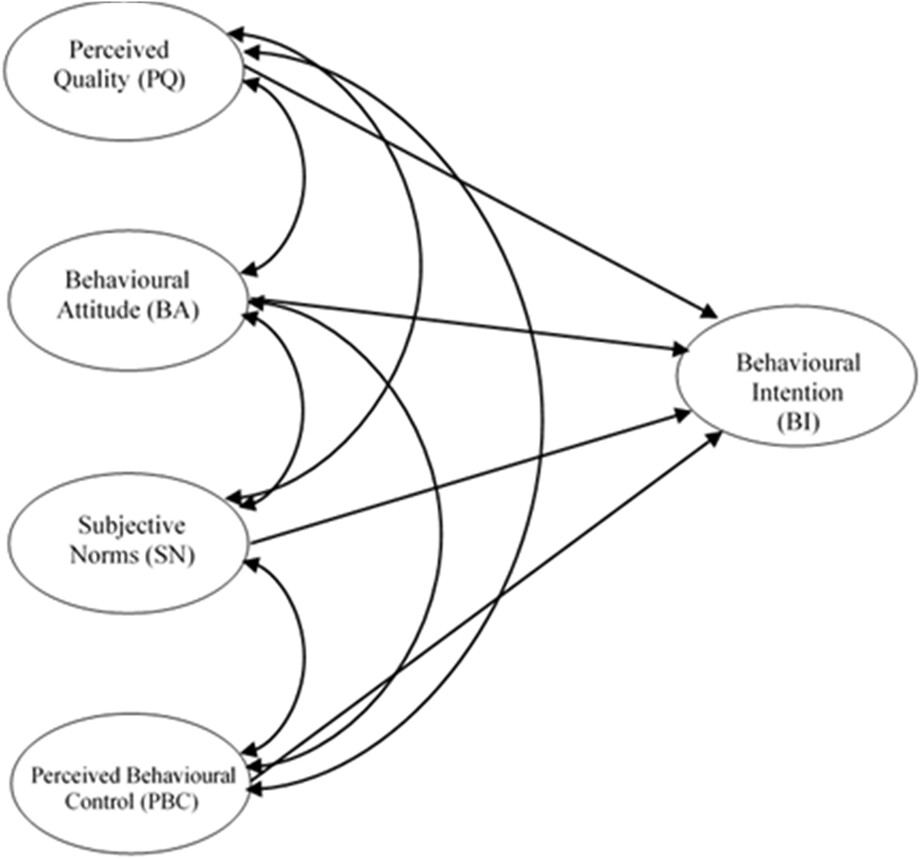
Food production is one of the main contributors to climate change. This paper investigated factors influencing Chinese consumers’ purchase intentions for sustainable food baskets using extensive survey data. The research tested whether public education through information provision effectively achieves sustainable diet transition in China.
A technological quality control system for rice supply chain
- First Published: 08 April 2022
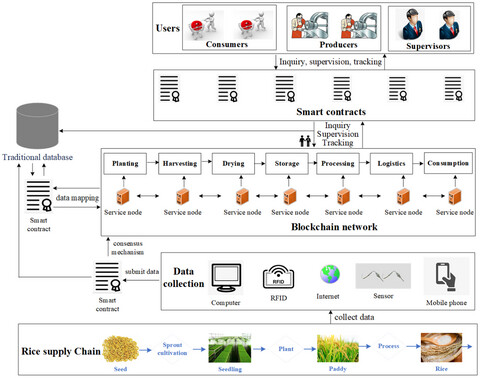
A risk assessment and traceability mechanism of hazardous factor is proposed to deal with the hazard factors in advance. We explored a shelf-life model of rice to predict the remaining shelf life of rice products, preventing the circulation of spoiled food from entering the market and reducing food waste. We constructed a rice supply chain traceability management system in rice supply chain to protect food quality and safety.
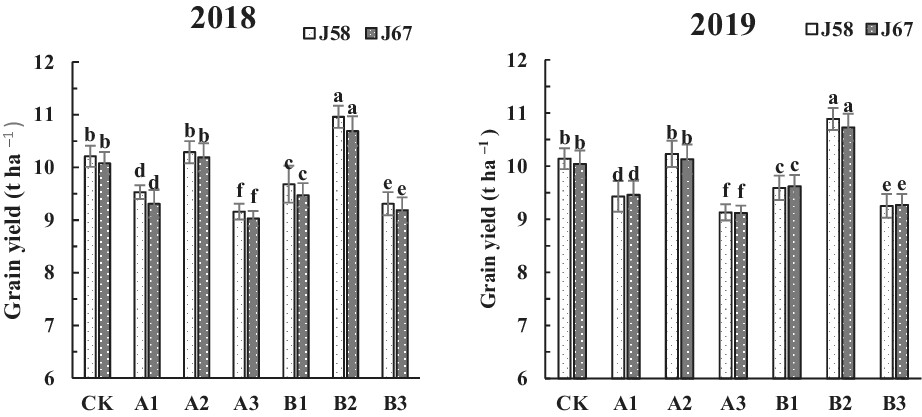
Effects of a one-time application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on quality and yield of rice
- First Published: 19 October 2022
Sustainable management of fall armyworm in smallholder farming: The role of a multi-channel information campaign in Rwanda
- First Published: 04 August 2022
REVIEW
Current status and prospects of rice canopy temperature research
- First Published: 21 October 2022
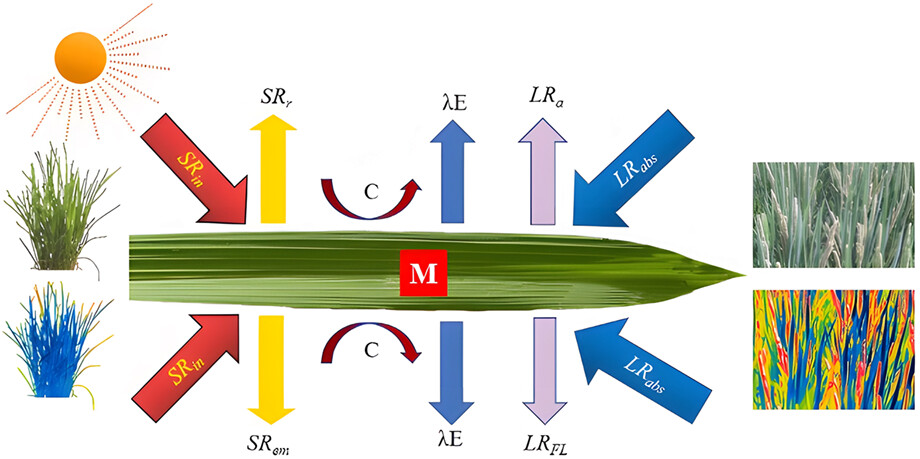
This paper reviews the formation process, influencing factors, variation patterns, practical applications, and measurement techniques of rice canopy temperature. Moreover, this study analyzes the drawbacks in current studies on rice canopy temperature, proposes to strengthen studies on the influencing mechanism of rice canopy temperature, improves the methods and techniques of rice canopy temperature measurement, and systematically assess the effect of canopy temperature on rice production, to construct a systemic analysis and auxiliary decision-making system for rice production with canopy temperature as the main marker.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Rhizosphere soil nitrification ability controls nitrogen-use efficiency in rice growth period
- First Published: 04 November 2022
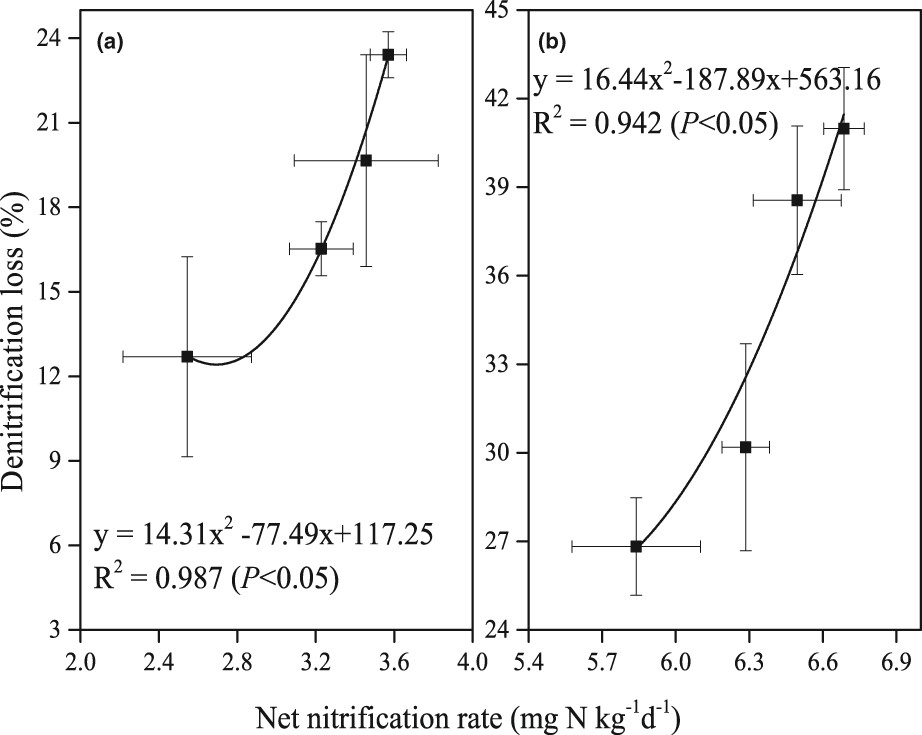
The impacts of the rhizosphere soil nitrification rate on NUE and denitrification losses at different rice growth stages in two paddy soils were investigated. Rhizosphere nitrification played a dominant role in increasing denitrification and decreasing NUE. Rhizosphere nitrification rate was affected by soil pH and nitrifying microbial community composition.
Contrasting seasonal dynamics of dormancy, respiratory metabolism and cell cycle state in grapevine buds of a subtropical and Mediterranean climate
- First Published: 16 November 2022
Impact assessment of Striga resistant maize varieties and fertilizer use in Ghana: A panel analysis
- First Published: 06 November 2022
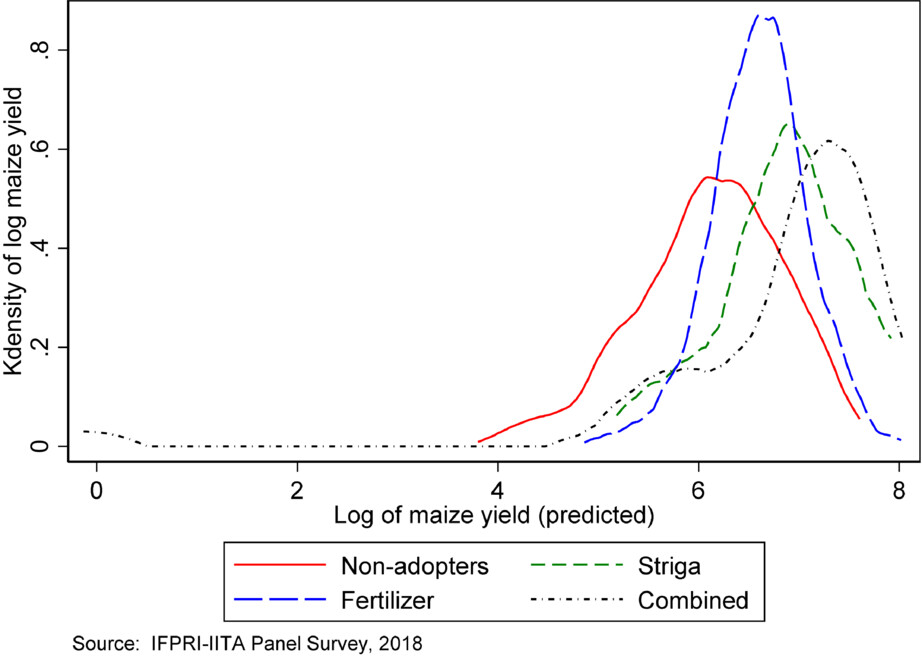
The study estimated the impact of a component of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) technology on yield and food security. The results show a positive effect of Striga-resistant maize (SRM) varieties and mineral fertilizers on yield and food security. The adoption of multiple agricultural technologies is key to the economic development of rural households.
Estimation of grain yield in wheat using source–sink datasets derived from RGB and thermal infrared imaging
- First Published: 13 December 2022
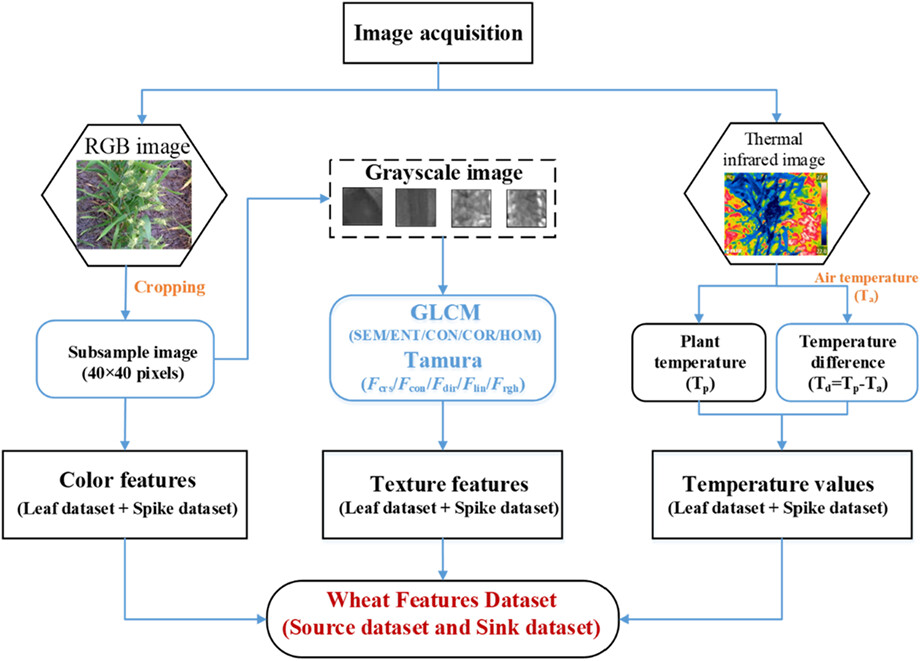
Selecting appropriate source-sink indicators is a method that can provide strategies to develop crop productivity. In this study, RGB and thermal infrared sensors were used to obtain multivariate eigenvalues of wheat source organs and sink organs, respectively. This study demonstrates that the multivariate eigenvalues of both source and sink organs have the potential to predict wheat yield, and that the combination of machine learning models and variable selection methods can significantly affect the accuracy of yield prediction models and achieve effective monitoring of crop growth at late reproductive stages.
A seven-year study on the effects of four tillage modes on soil physicochemical properties, microbial biomass, enzymatic activities, and grain yield in a rice–ratoon rice cropping system
- First Published: 11 January 2023
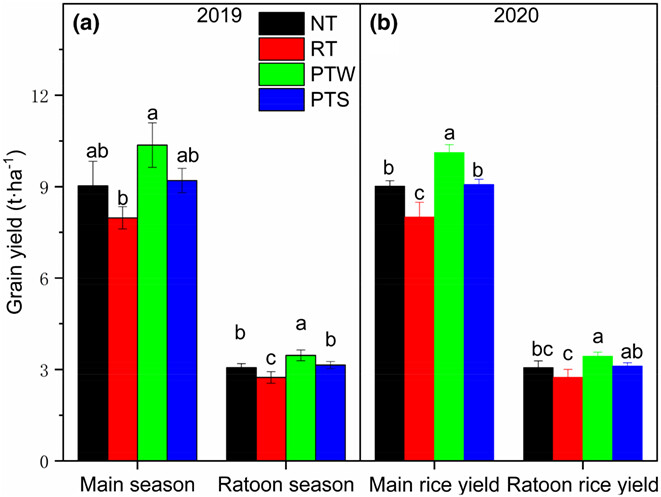
A long-term study on the effects of tillage on soil traits and yield in a rice–ratoon rice cropping system has been carried out. Plowing tillage in winter + rotatory tillage (PTW) maintains soil permeability at a depth of 0–40 cm. Independent of tillage methods and ratoon rice systems require increased SOM input to maintain C storage. PTW had the highest soil microbial biomass, soil enzyme activity, and grain yield.
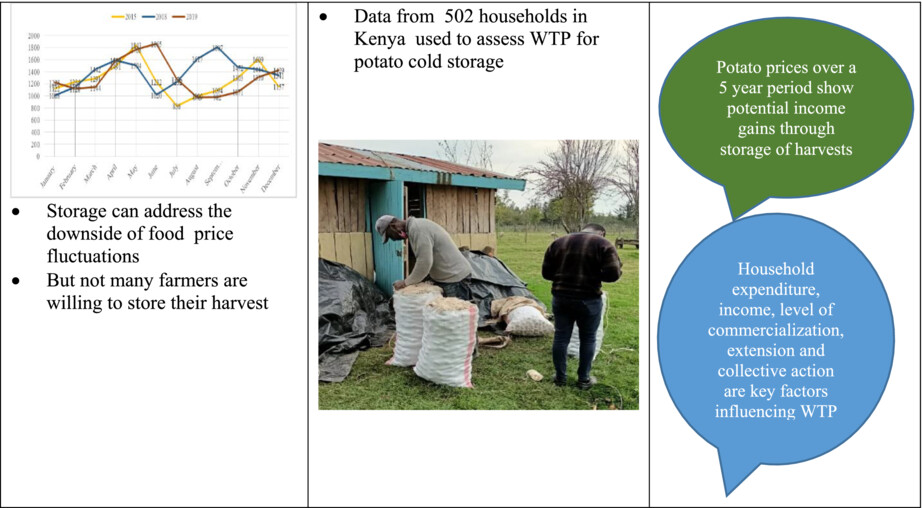
To sell or store? Assessing smallholder farmers' willingness to pay for potato cold storage in Kenya
- First Published: 07 December 2022
Elevated CO2 enhances rice root growth under alternate wetting and drying irrigation by involving ABA response: Evidence from the seedling stage
- First Published: 19 December 2022
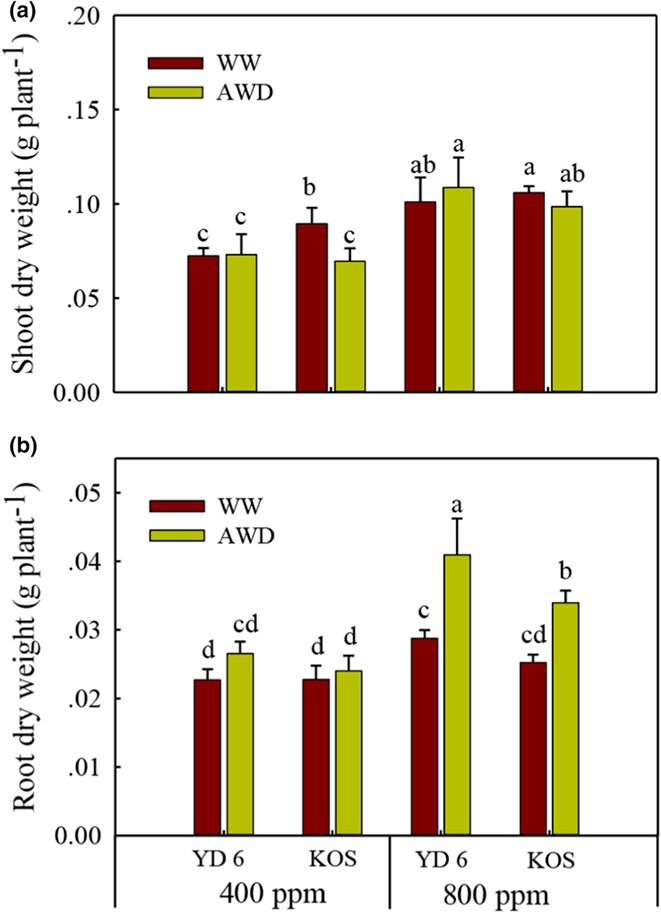
The atmospheric CO2 enrichment can seriously affect rice root growth. Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) irrigation, which can also increase root growth, is a widely promoted water-saving technology for future climate, yet how elevated CO2 (eCO2) influences rice root growth under AWD remains unclear. In the present study, we examined the root growth of Yangdao 6 (YD 6, a cultivar with strong response to eCO2) and Koshihikari (KOS, a cultivar with weak response to eCO2) cultured under different water irrigation regimes (well-watered and AWD) and CO2 concentration (400 and 800 ppm).