Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
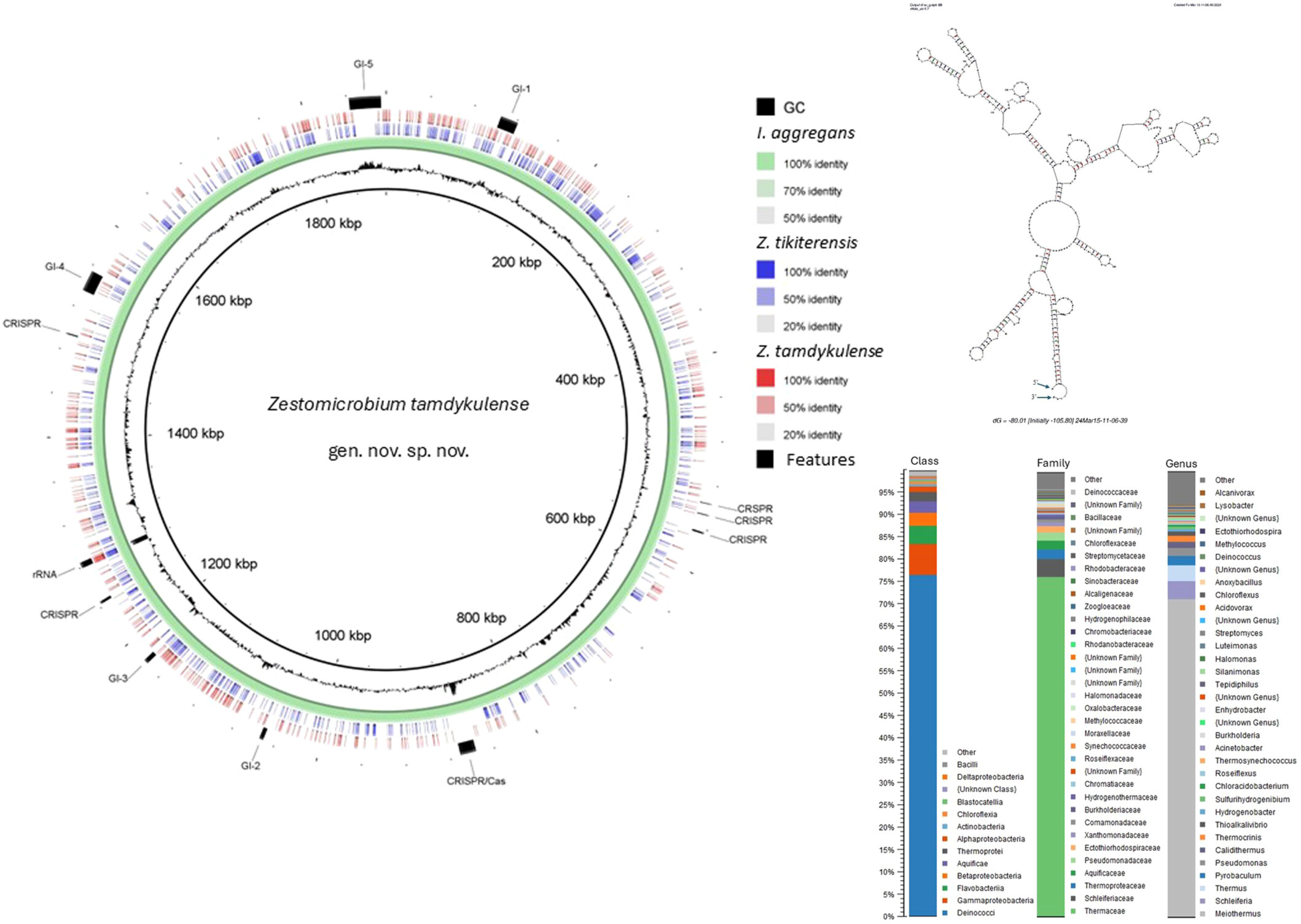
The metagenomic landscape of a high-altitude geothermal spring in Tajikistan reveals a novel Desulfurococcaceae member, Zestomicrobium tamdykulense gen. nov., sp. nov
- First Published: 10 October 2024
High-quality genome of a novel Thermosynechococcaceae species from Namibia and characterization of its protein expression patterns at elevated temperatures
- First Published: 04 October 2024
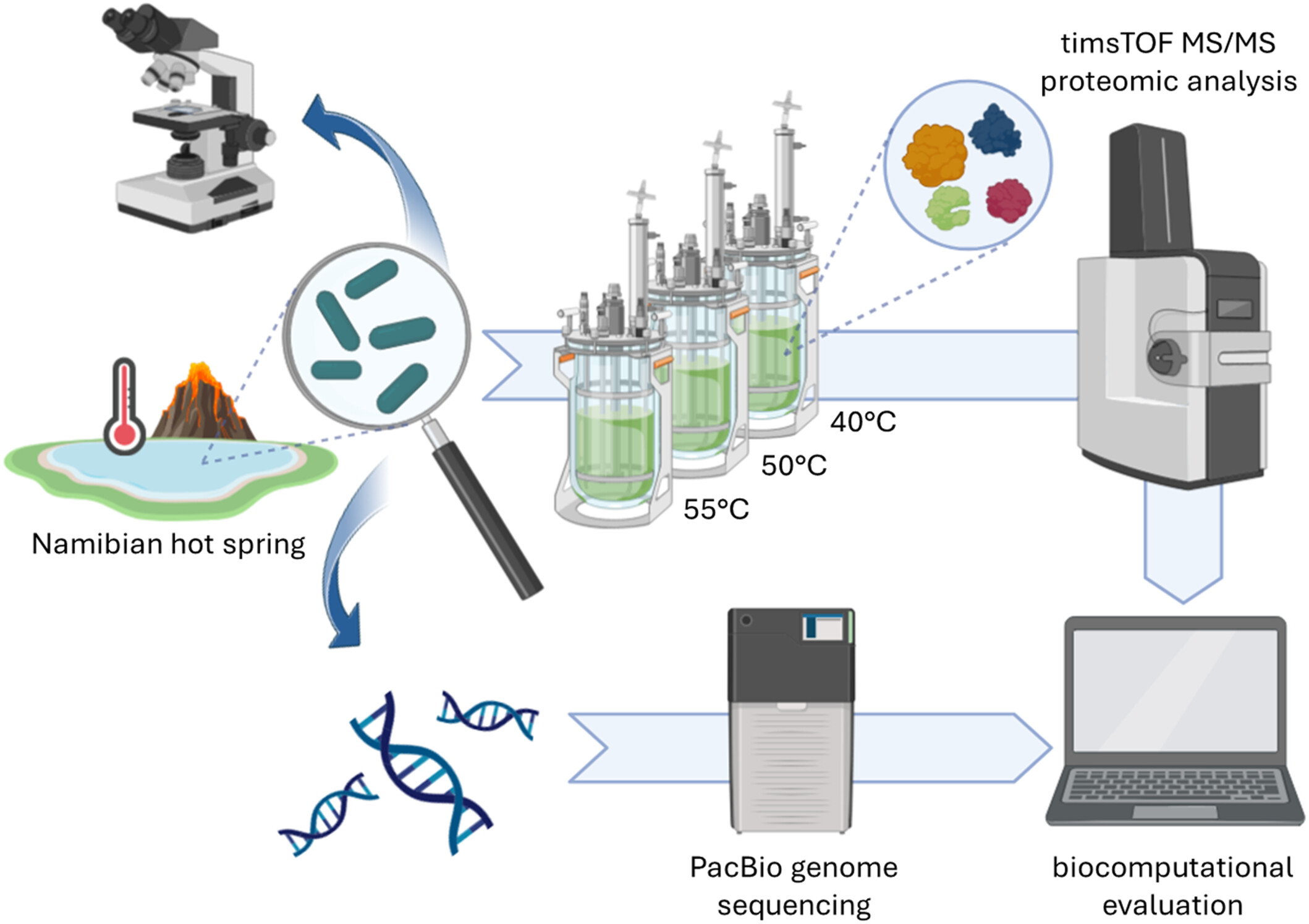
In this study, the genome of a new thermophilic cyanobacterium, Thermosynechococcaceae cyanobacterium sp. Okahandja, isolated from a hot spring near Okahandja in Namibia, was sequenced. Additionally, cultivations were conducted at elevated temperatures of 40, 50, and 55°C, followed by analyses of the respective adapted proteomes based on the annotated genome.
Influence of microbiota on the growth and gene expression of Clostridioides difficile in an in vitro coculture model
- First Published: 15 October 2024
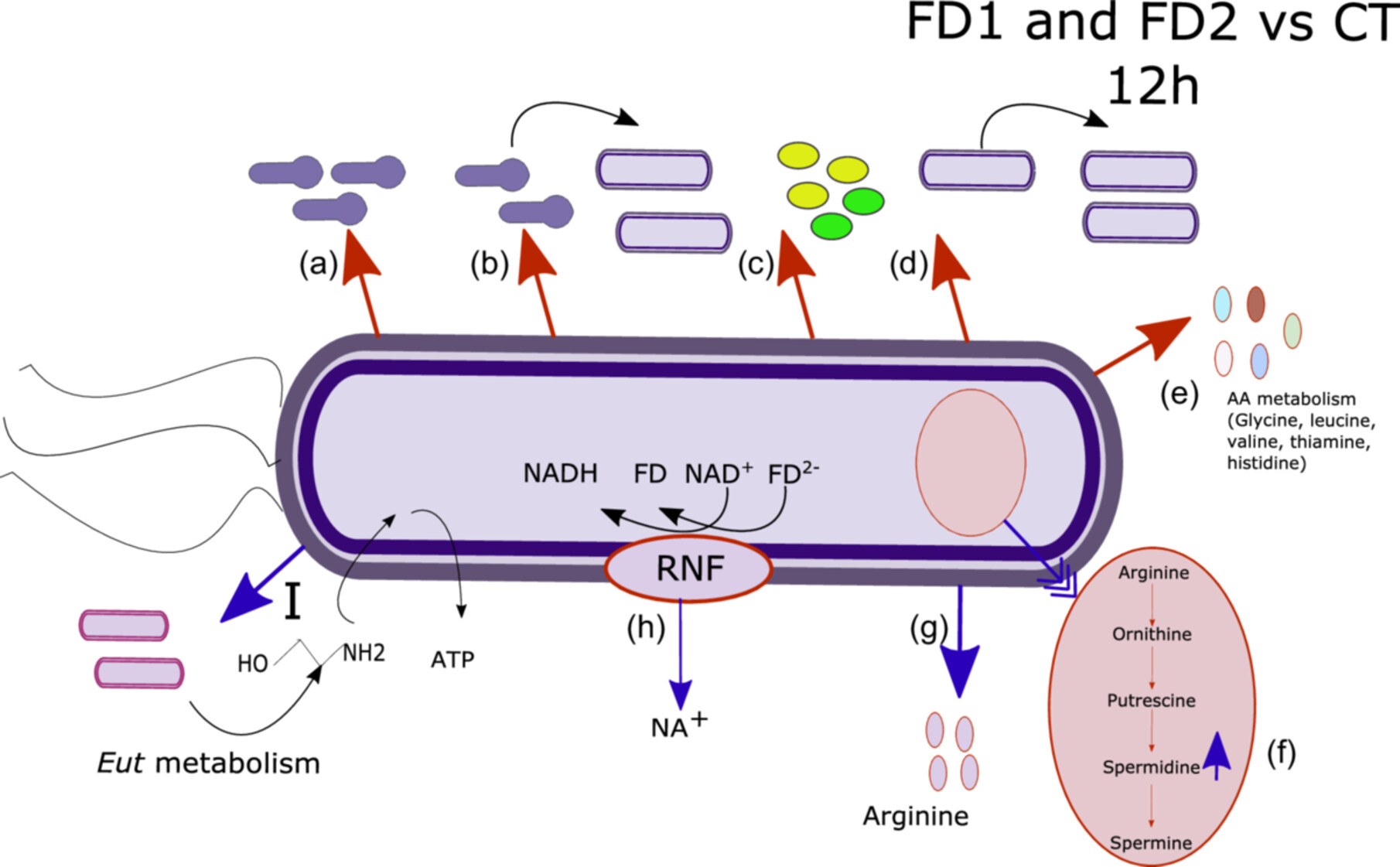
The presence of microbiota did not affect the growth of Clostridioides difficile in this study. However, it did influence the expression of C. difficile genes related to sporulation, germination, and virulence, which are crucial for the transmission of the pathogen. In the presence of microbiota, C. difficile activates defence mechanisms to survive competition, such as adapting to an iron-limited environment and utilizing ethanolamine metabolism.
REVIEW
Listeria monocytogenes in the seafood industry: Exploring contamination sources, outbreaks, antibiotic susceptibility and genetic diversity
- First Published: 17 October 2024
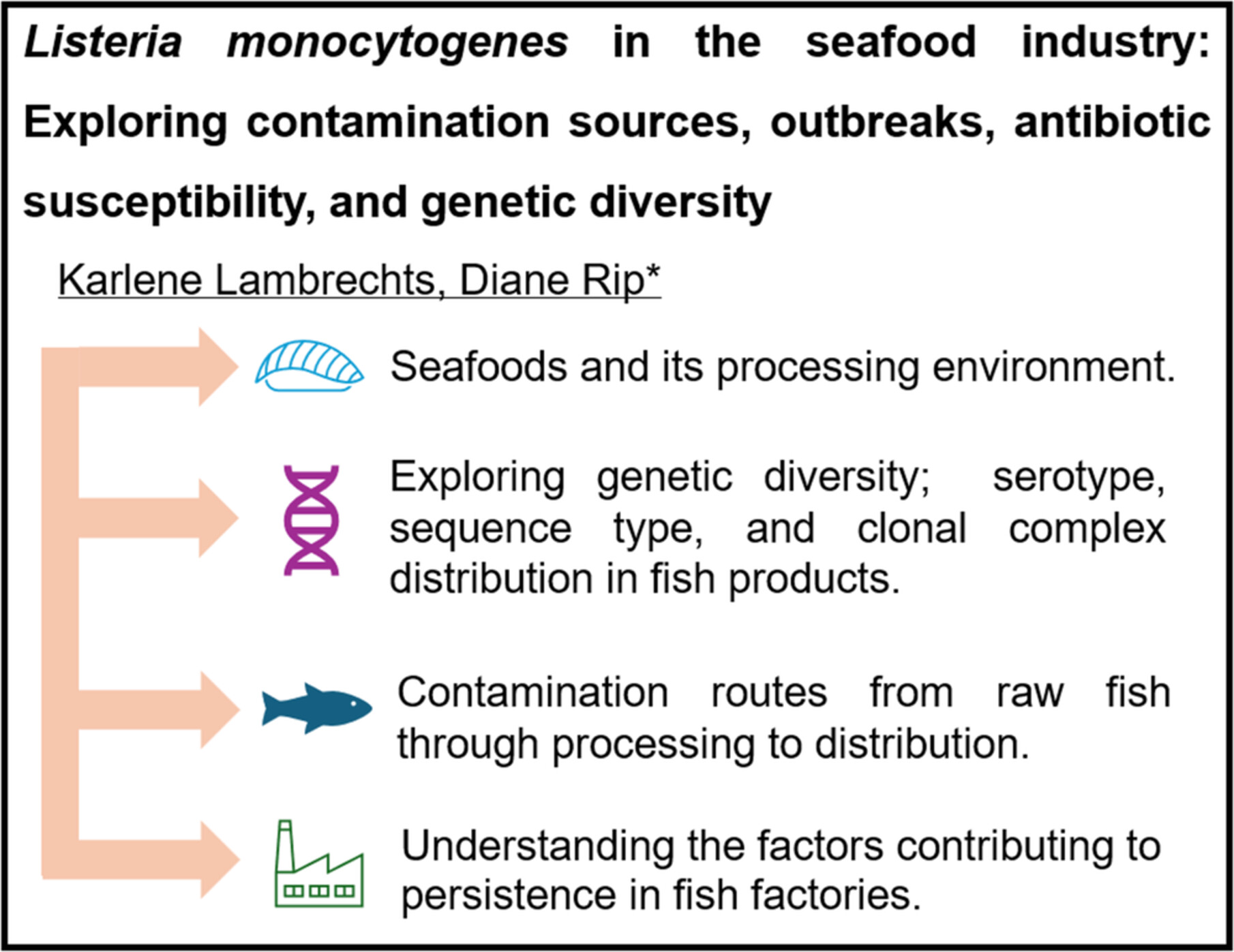
Listeria monocytogenes presents a significant concern in fish and its processing environments. This literature review aimed to gather global insights on fish and its processing settings, exploring genetic diversity and contamination pathways from raw fish through processing to distribution. Additionally, understanding the factors contributing to the persistence of Listeria in fish factories was a key objective.
The effects of stress on gut virome: Implications on infectious disease and systemic disorders
- First Published: 23 September 2024
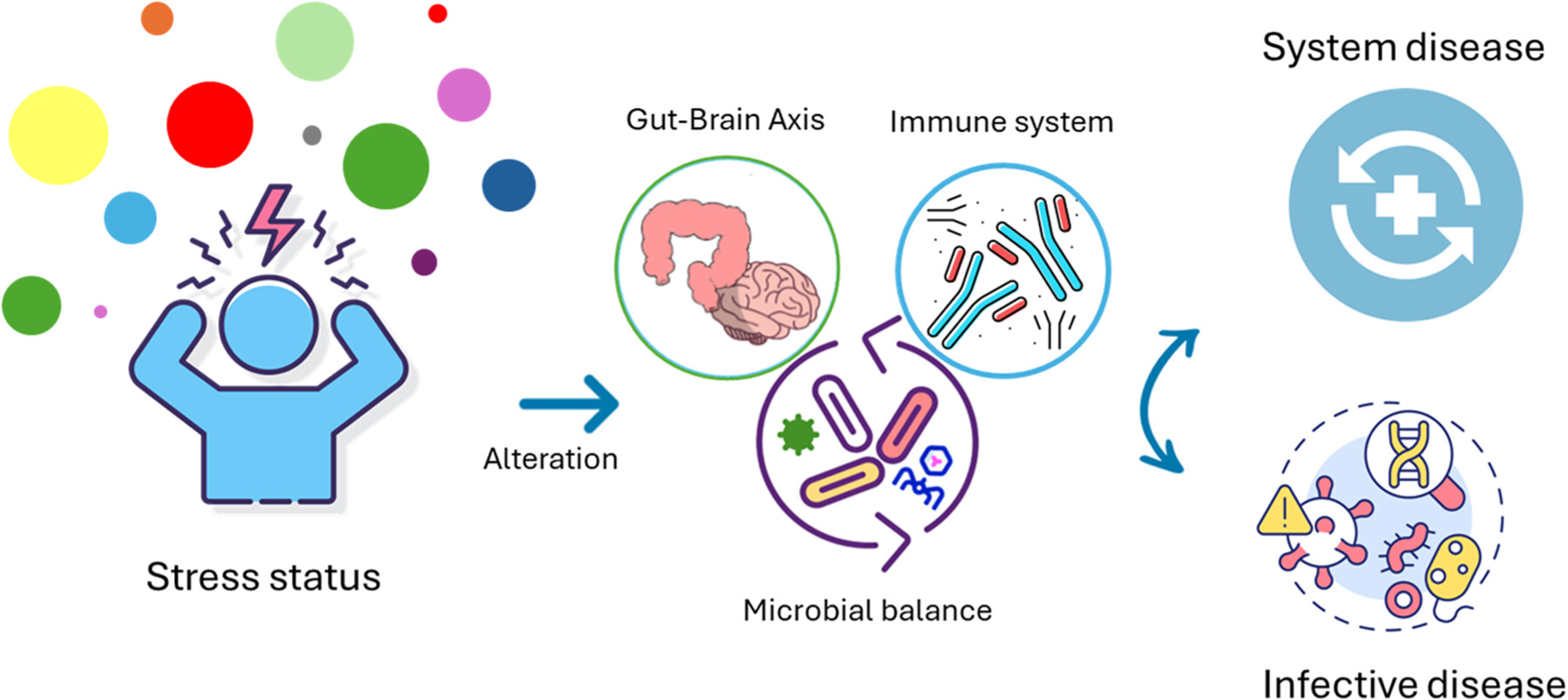
Stress conditions can weaken the host's immune system, affecting the entire gut–brain axis. Concurrently, disruptions in the composition of the gut microbiota are associated with exacerbations of diseases. This review explores the complex interplay between stress, gut virome, and the host immune system. It highlights how stress-induced immune system alterations and gut virome dysbiosis contribute to both infectious and noninfectious diseases. The article further discusses the need for more research to fully understand the underlying molecular mechanisms and microbial correlations.