Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARY
The Effects of Carbonate on Candida albicans Filamentation, Biofilm Formation, and Antifungal Resistance
- First Published: 13 November 2024
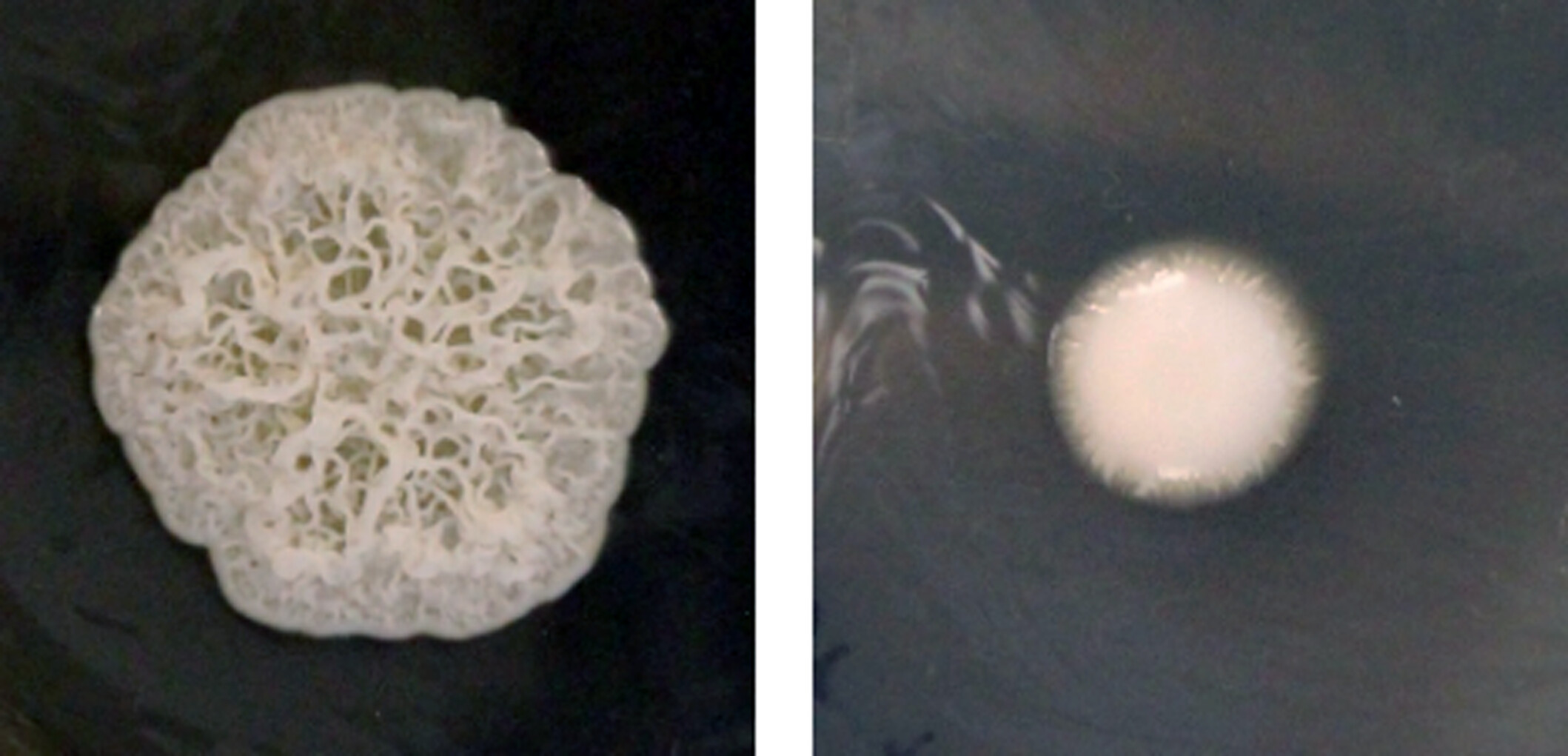
Bacillus xiamenensis Inhibits the Growth of Moraxella osloensis by Producing Indole-3-Carboxaldehyde
- First Published: 13 November 2024
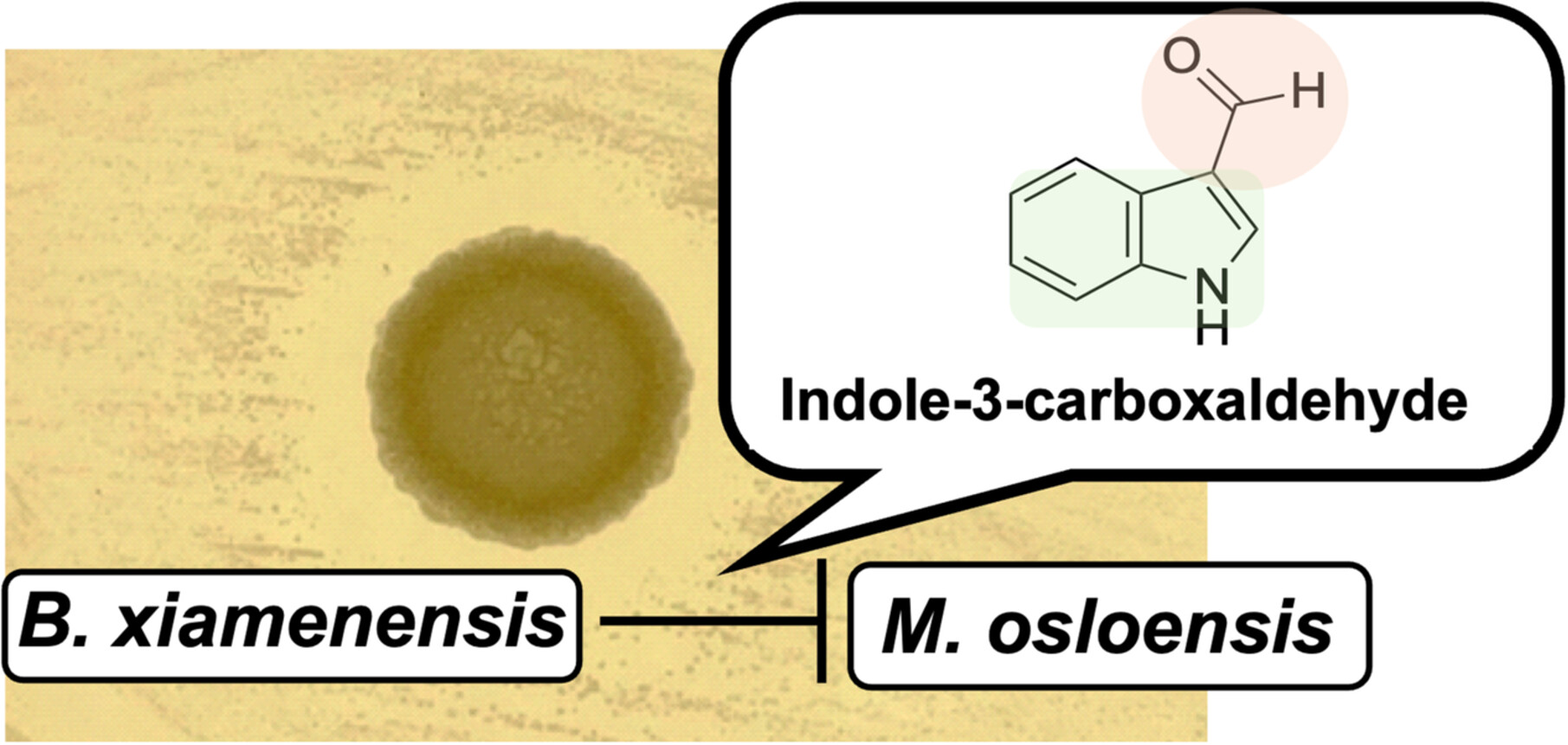
Bacillus xiamenensis interacts with Moraxella osloensis, and the indole-3-carboxaldehyde produced by B. xiamenensis is a promising agent with specific bactericidal activity against M. osloensis. structure–activity relationship analysis indicates that the indole ring and aldehyde moiety of indole-3-carboxaldehyde are vital for its anti-M. osloensis activity.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Evaluation of DNA Extraction Methods for Microbial Community Profiling in Deadwood Decomposition
- First Published: 13 November 2024
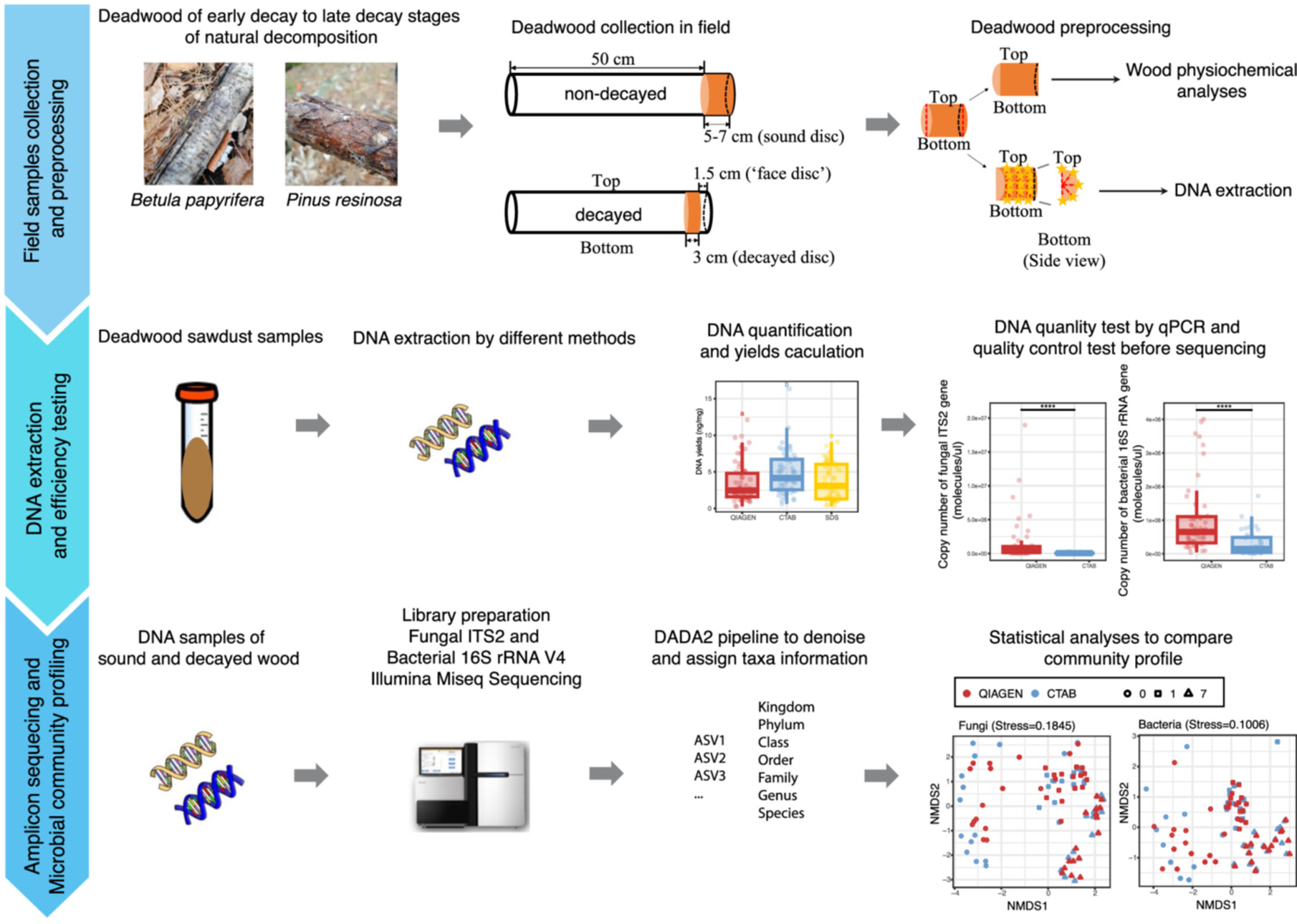
By extracting DNA from sound and decayed wood samples at various stages of natural decomposition in both conifer (gymnosperm) and angiosperm wood substrates, we found that DNA quality significantly impacted the ability to amplify and sequence the samples. Despite variability in extraction efficiency, extraction bias (the types of microbes identified) among the methods tested was negligible, lending confidence to comparisons of previously published amplicon data sets. This study provides a cost-benefit table for making protocol decisions and offers novel guidance on fungal DNA extractions from complex organic substrates, which will benefit future metagenomic efforts currently challenging for fungi.
COMMENTARY
Diclofenac Degradation by Immobilized Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Scenedesmus obliquus
- First Published: 17 December 2024
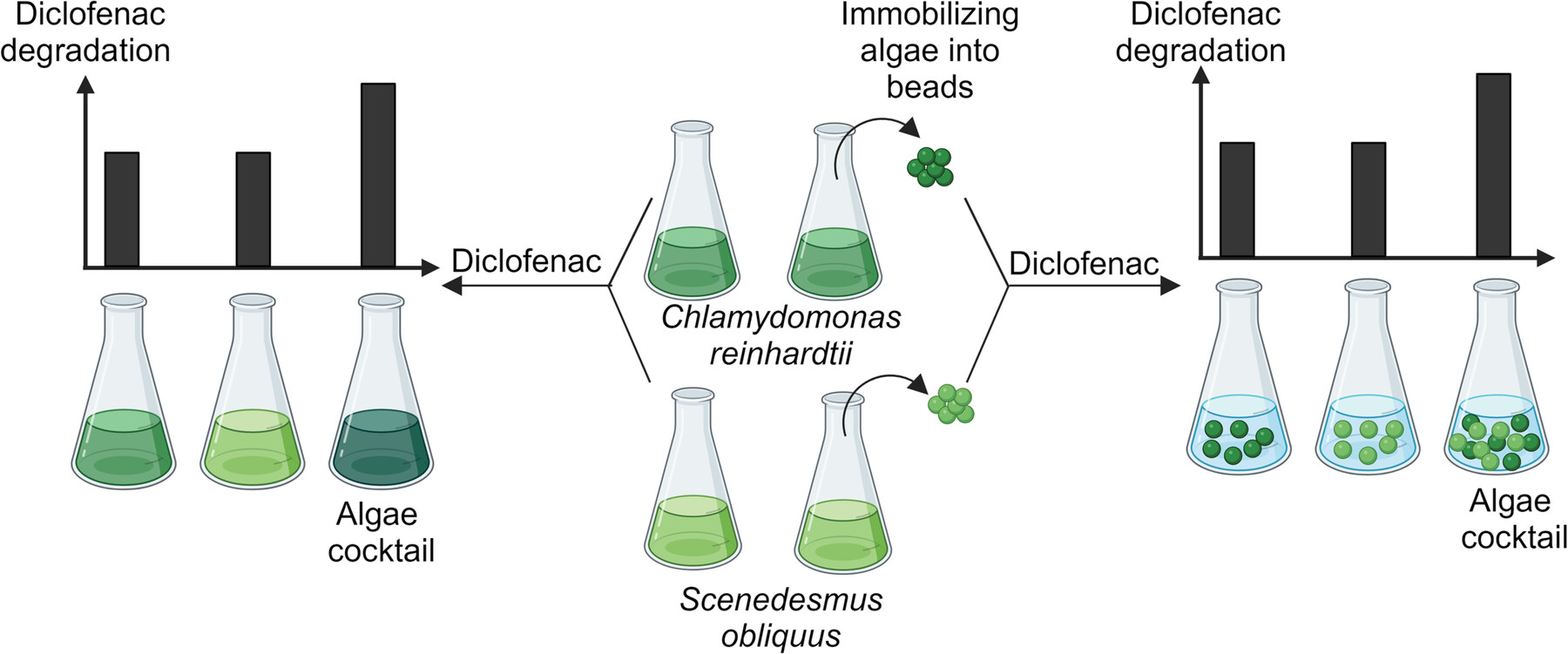
Immobilized freshwater microalgae, specifically a combination of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Scenedesmus obliquus, exhibit superior efficiency in the removal of diclofenac from water compared to their free-floating counterparts. This research validates the concept of employing immobilized algal cocktails to effectively degrade diclofenac in wastewater treatment processes. “Created with BioRender.com”.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Prophylactic phage administration reduces Salmonella Enteritidis infection in newly hatched chicks
- First Published: 16 December 2024
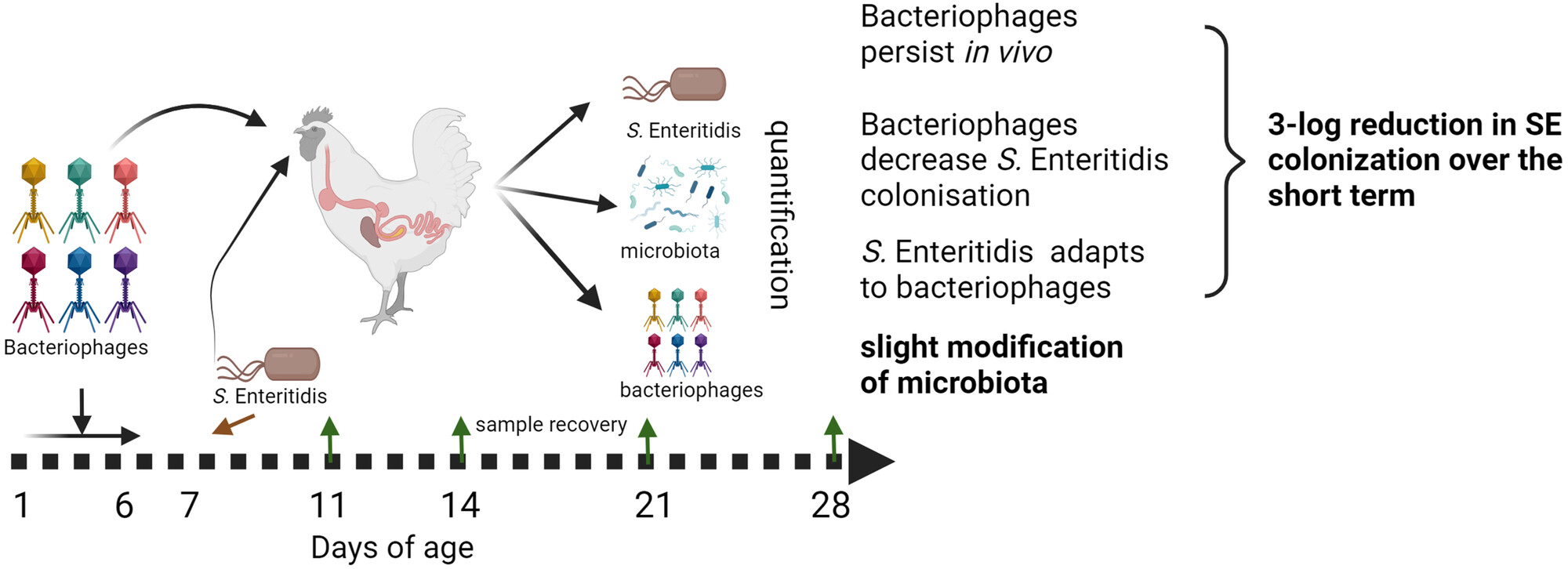
This study evaluated the effectiveness of prophylactic phage treatment in reducing Salmonella Enteritidis levels in chickens and its impact on their overall gut microbiome. Additionally, we examined the persistence of phages in vivo, both in the presence and absence of Salmonella, and investigated the emergence of bacterial resistance to the 6-phage cocktail used.
Physiological Effects of TolC-Dependent Multidrug Efflux Pumps in Escherichia coli: Impact on Motility and Growth Under Stress Conditions
- First Published: 11 November 2024
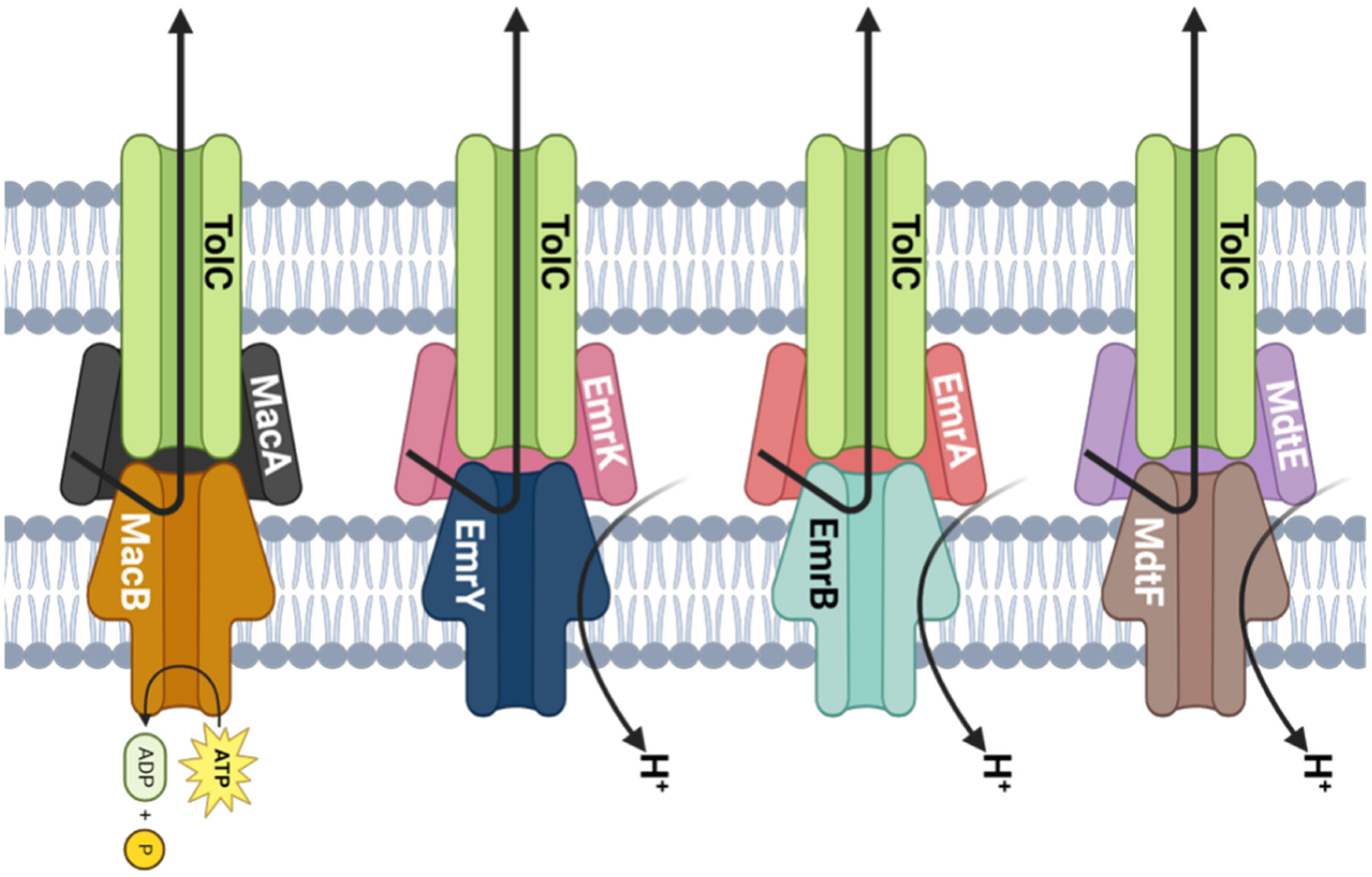
The eight TolC-dependent multidrug efflux pumps of Escherichia coli confer resistance to antibiotics. We report that while individual TolC-dependent pumps are dispensable for growth under many stress conditions in the absence of antimicrobials, possibly due to their partially overlapping substrate profiles, TolC-dependent efflux is required for maximal growth under most conditions.
COMMENTARY
Compounds Containing 2,3-Bis(phenylamino) Quinoxaline Exhibit Activity Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, and Their Biofilms
- First Published: 12 December 2024
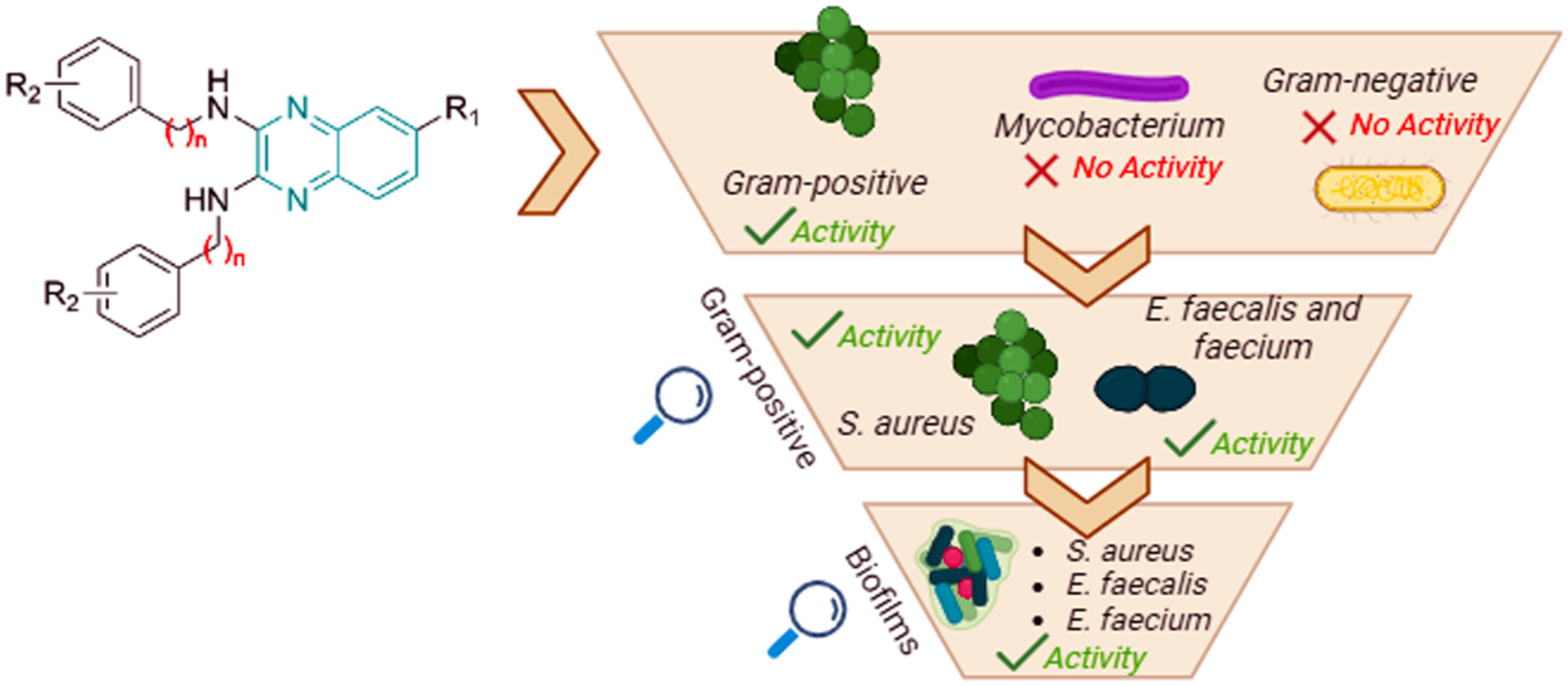
This study investigated the antimicrobial activity of 2,3-N,N-diphenyl quinoxaline derivatives against representative bacteria and mycobacteria species. The findings indicated selective activity against Gram-positive clinical isolates, including Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecium, and Enterococcus faecalis, particularly antibiotic-resistant isolates. Additionally, two derivatives showed efficacy against bacterial biofilms.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Monitoring the Persistence of Pseudomonas sivasensis Strain CF10PS3 in Cereal Fields
- First Published: 18 November 2024
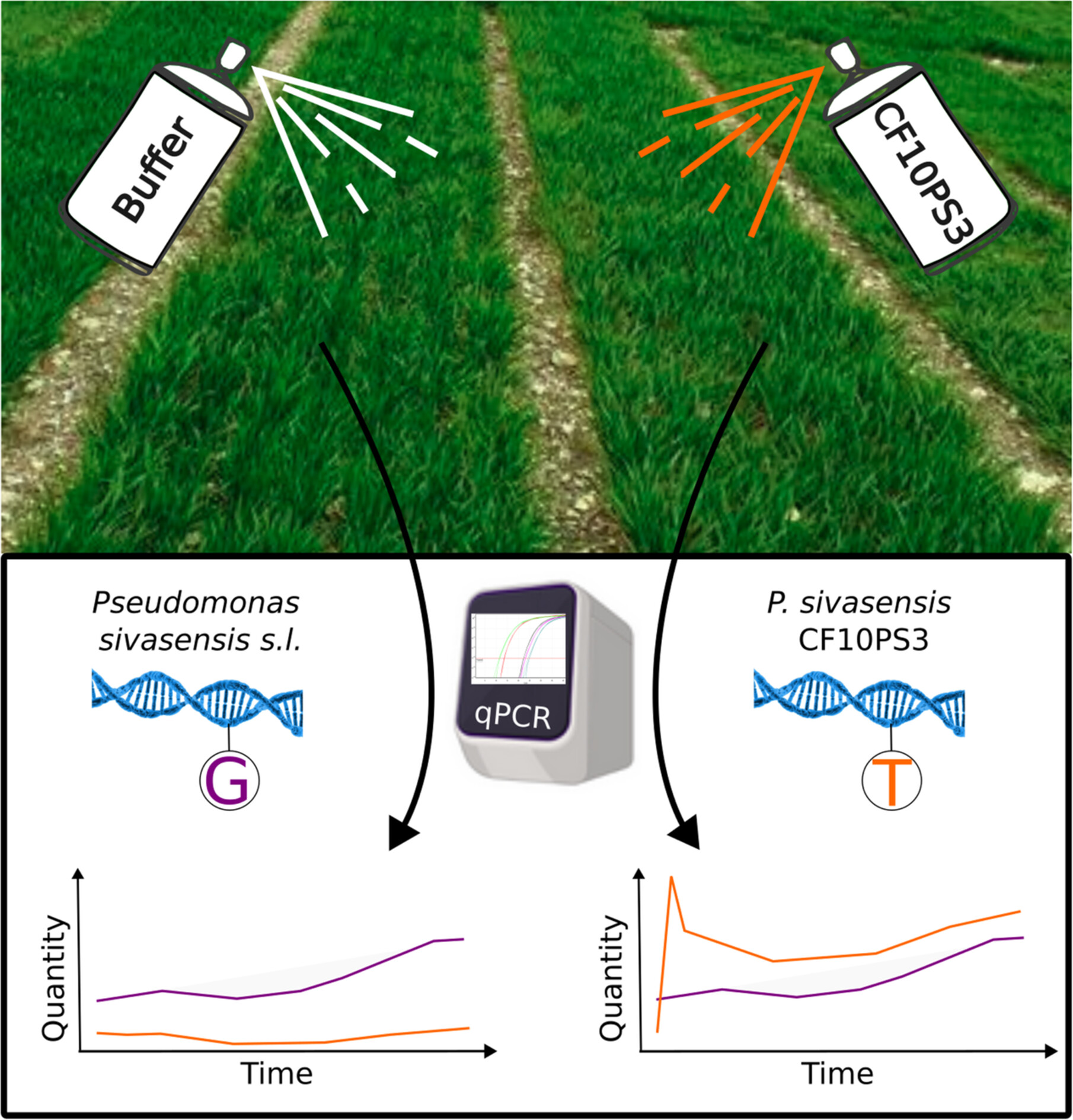
This study developed qPCR probes that specifically distinguish Pseudomonas sivasensis CF10PS3 from other strains within the species. These probes enabled precise monitoring of CF10PS3 persistence in the wheat phyllosphere under field conditions, providing insights into microbial population dynamics.
Temporal Changes in Tick-Borne Pathogen Prevalence in Questing Ixodes ricinus Across Different Habitats in the North-Eastern Italian Alps
- First Published: 10 December 2024
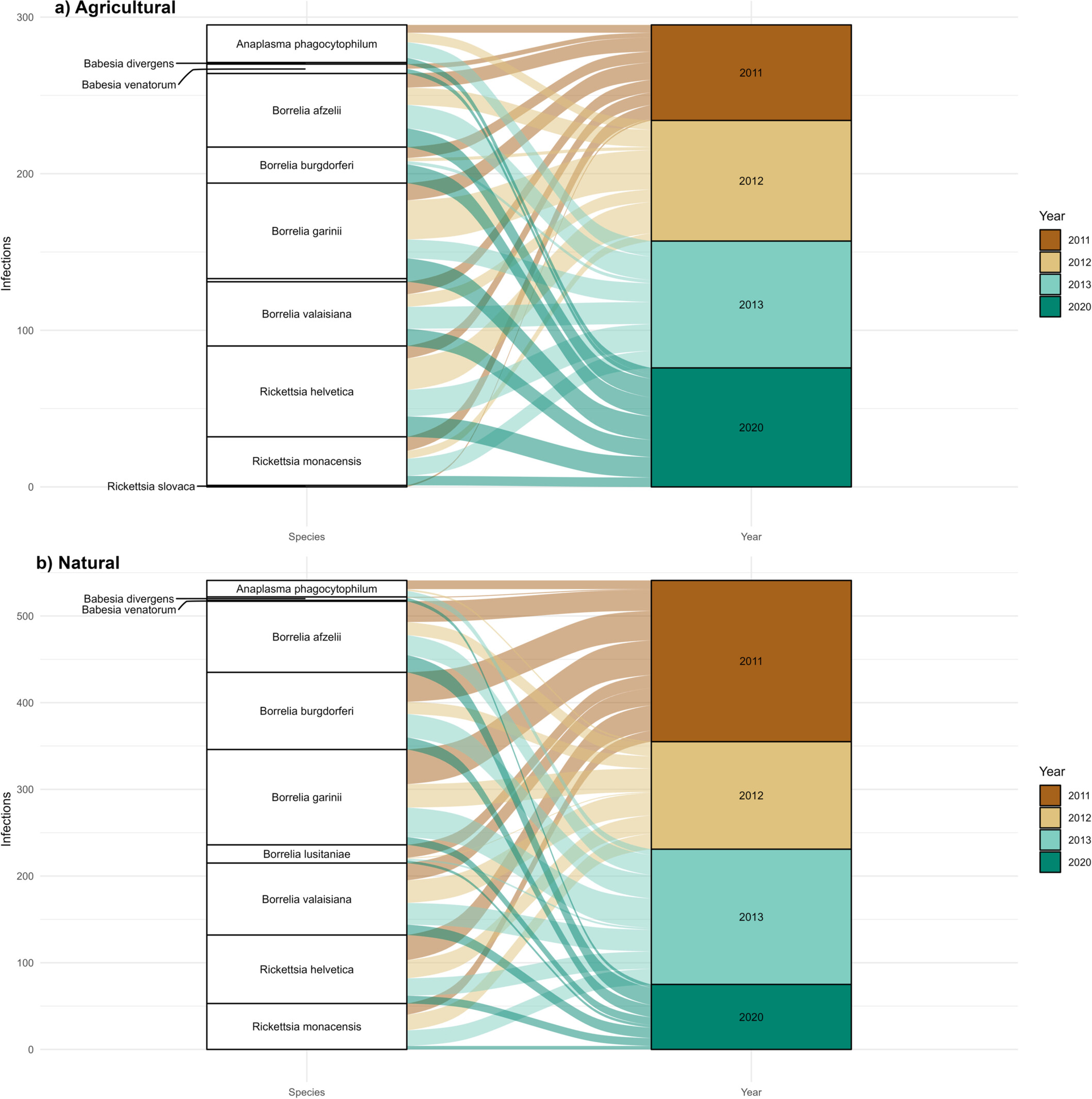
This study examines the prevalence of tick-borne pathogens in Ixodes ricinus ticks in the north-eastern Italian Alps. It found an average infection rate of 27.1%, with 11 zoonotic pathogens identified, showing varying infection rates across different years and habitats. Notably, co-infections were present in 8% of positive ticks, highlighting the dynamic risk of tick-borne diseases in this region.
CerM and Its Antagonist CerN Are New Components of the Quorum Sensing System in Cereibacter sphaeroides, Signaling to the CckA/ChpT/CtrA System
- First Published: 18 December 2024
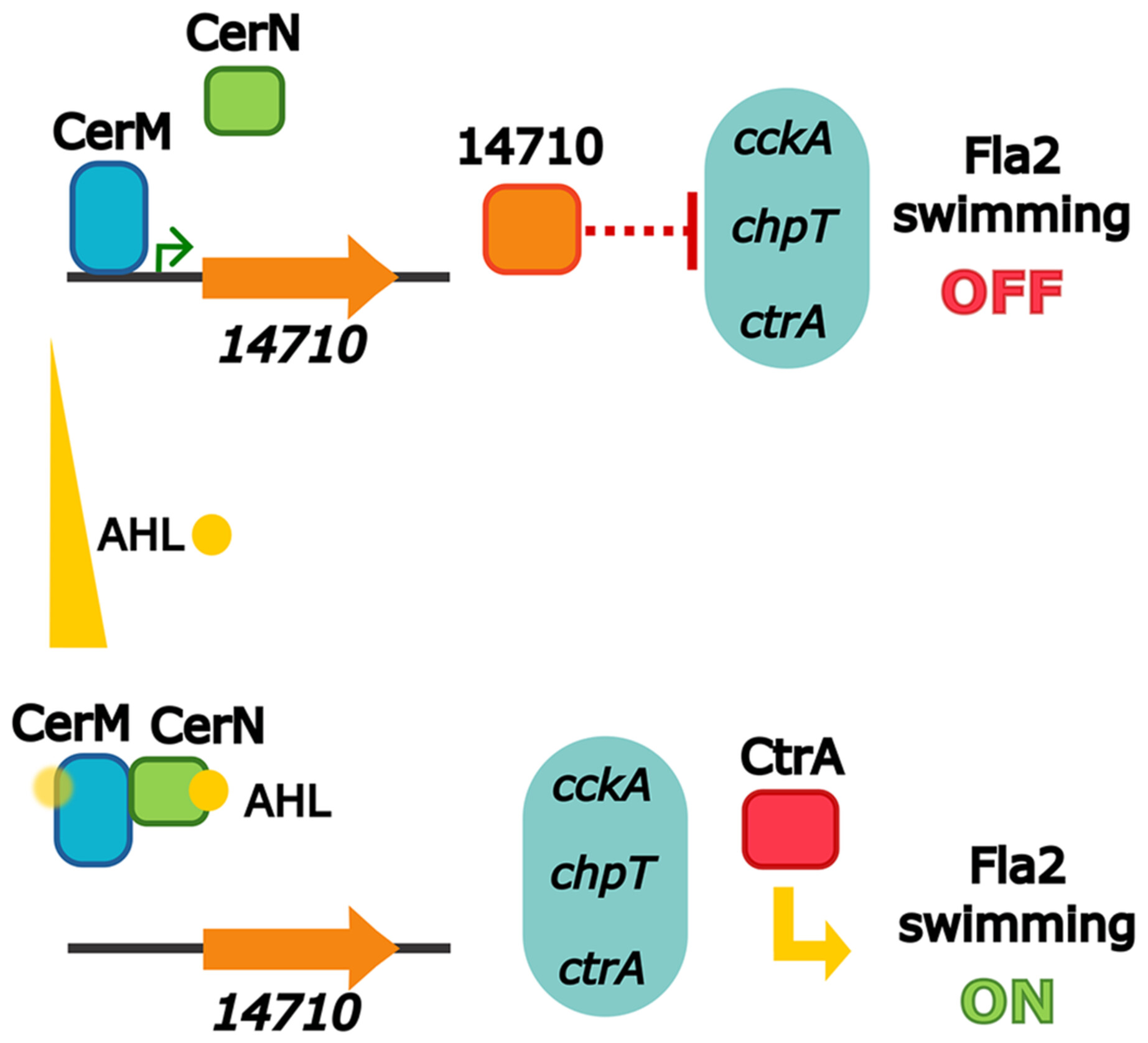
The quorum sensing (QS) system of Cereibacter sphaeroides includes six LuxR homologs and one acylhomoserine lactone synthase homolog. Two LuxR homologs, CerM and CerN, are involved in regulating the expression of ctrA, which is part of the CckA/ChpT/CtrA two-component system that controls flagellar motility. This study indicates that CerN-AHL counteracts CerM's repression of ctrA, thereby connecting the QS system with the regulation by the two-component system.