Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
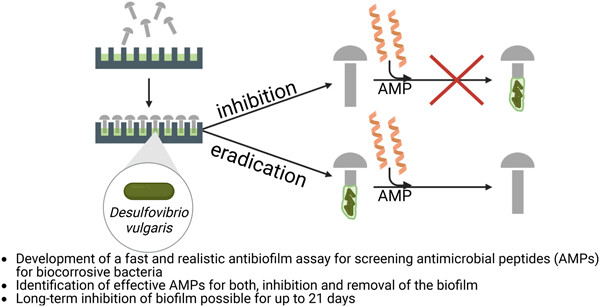
Antibiofilm assay for antimicrobial peptides combating the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio vulgaris
- First Published: 21 August 2023
COMMENTARY
Cattle–compost–soil: The transfer of antibiotic resistance in livestock agriculture
- First Published: 18 August 2023
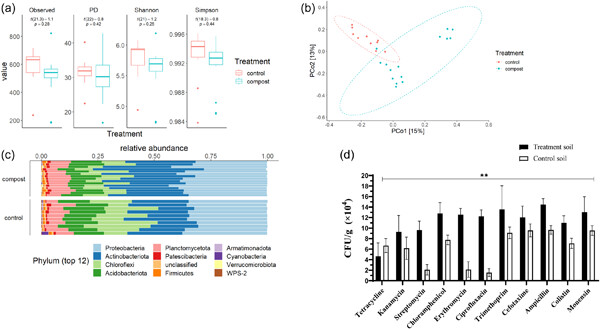
The study describes the analysis of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) abundance and the overall bacterial diversity of cattle farm soils that have been treated with animal manure compost. Our results showed that ARB abundance was greatest in fresh manure and significantly lower in composted manure. However, the application of composted manure on paddock soil led to a significant increase in soil ARB abundance. The paper discusses this apparent conflict and raises hypotheses for future studies to explain it.
REVIEWS
Evaluating models and assessment techniques for understanding oral biofilm complexity
- First Published: 29 August 2023
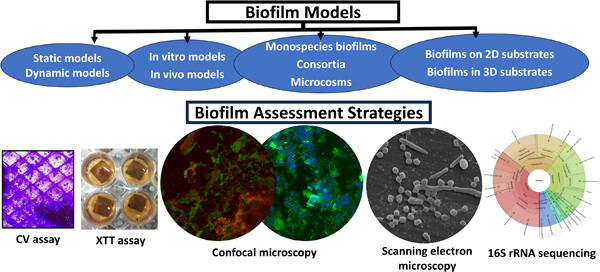
This review focuses on diverse biofilm models and assessment strategies, highlighting the transition in the field from two-dimensional models to the recently explored novel three-dimensional models that aim to mimic biofilm development in the microenvironment of biological structures. The review further explores culture-dependent biofilm assessment strategies such as colony-forming unit assay, crystal violet assay, 2,3-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide inner salt (XTT) assay, and imaging techniques, as well as the culture-independent approach of next-generation sequencing.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Isolation, biochemical characterization, and genome sequencing of two high-quality genomes of a novel chitinolytic Jeongeupia species
- First Published: 06 August 2023
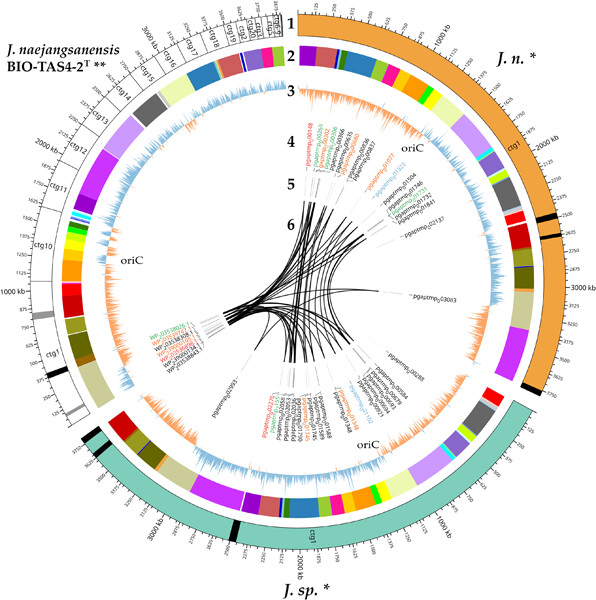
In this study, a novel chitinolytic Jeongeupia species “wiesaeckerbachi” was isolated from soil samples, characterized biochemically, and sequenced with the long-read platform PacBio Sequel IIe. In silico analysis unraveled genomic differences to the closest related type strain Jeongeupia naejangsanensis TAS4-2 in addition to an usually extensive chitinolytic machinery.
Transforming the untransformable with knockout minicircles: High-efficiency transformation and vector-free allelic exchange knockout in the fish pathogen Photobacterium damselae
- First Published: 21 August 2023
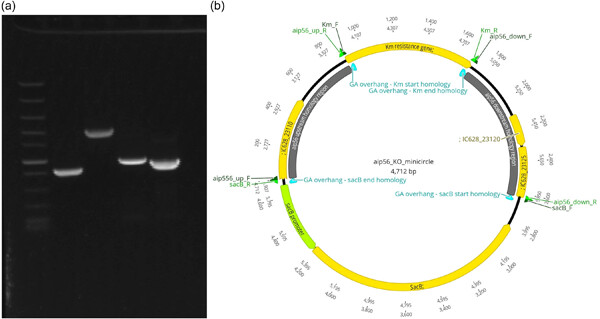
We describe efficient vector-free allelic exchange mutagenesis in Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida, potentially adaptable to any other bacterial species. It involves electroporation of minimalistic constructs containing only homology arms and selection markers, knockout minicircles, into cells rendered competent using concentrated sucrose solution. This approach is appropriate for genetic targets located on small plasmids and does not induce off-target mutations, as demonstrated by knockout inactivation of aip56 gene and sequencing of multiple mutagenesis clones, respectively.
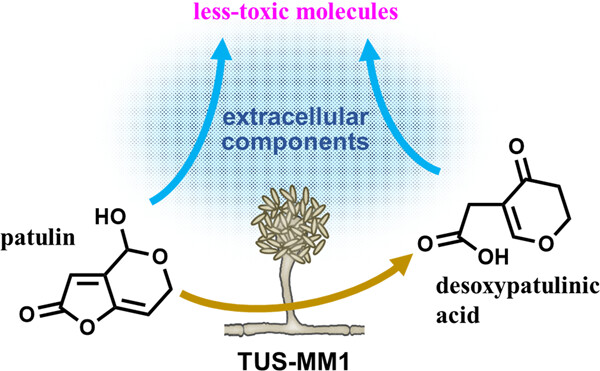
Isolation and characterization of filamentous fungi capable of degrading the mycotoxin patulin
- First Published: 11 August 2023
Clay-associated microbial communities and their relevance for a nuclear waste repository in the Opalinus Clay rock formation
- First Published: 10 July 2023
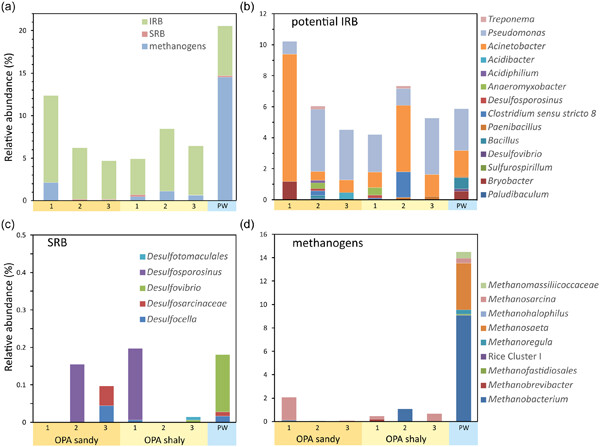
Biocorrosion and microbial mineral transformation can affect the safety of deep geological repositories for high-level nuclear waste storage. We analyzed the composition and evaluated the importance of mineral-associated microbial communities in Opalinus Clay for safety purposes. Rock-attached communities were dominated by phyla capable of corrosive biofilm formation. Based on the abundance of potential iron-reducing bacteria and available electron acceptors, iron reduction appeared to be the most important process. Site-specific mineralogy and geochemistry have selected for subcommunities and specific metabolic functions.
Co-localization of clinically relevant antibiotic- and heavy metal resistance genes on plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae from marine bivalves
- First Published: 19 July 2023
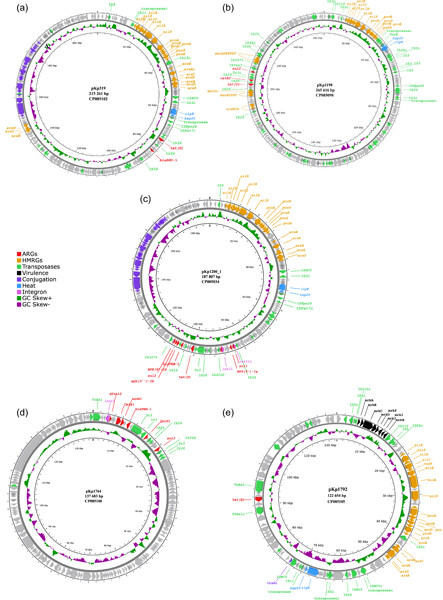
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen frequently associated with antibiotic resistance and present in a wide range of environments. In this study, five antibiotic-resistant K. pneumoniae isolates recovered from bivalves, of which four also carried heavy metal resistance genes, were selected for complete genome sequencing. This study shows the co-occurrence of antibiotic- and heavy metal resistance genes on a transferable IncFIB plasmid from K. pneumoniae from marine bivalves and further highlights the importance of the marine environment and seafood as a possible dissemination route for antimicrobial resistance.
Isolation and functional analysis of phage-displayed antibody fragments targeting the staphylococcal superantigen-like proteins
- First Published: 16 July 2023
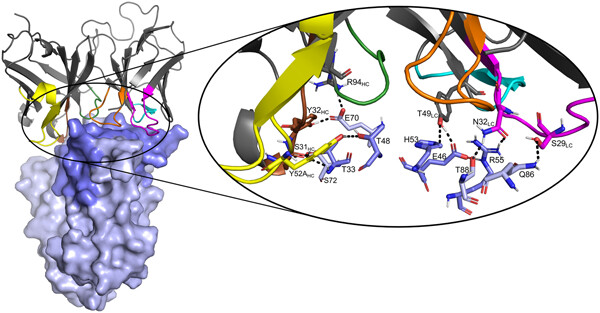
In this study, we report the identification of phage-displayed scFv-antibodies able to recognize the staphylococcal superantigen-like proteins SS1, SSL5, and SSL10. All three SSLs bind to and inhibit host immune components and contribute to Staphylococcus aureus immune evasion. We were able to show in vitro that one scFv was able to inhibit SSL1 and maintain matrix metallopeptidase (MMP9) activity in a concentration-dependent manner.