Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Morphological and physiological impacts of salinity on colonial strains of the cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa
- First Published: 28 June 2023
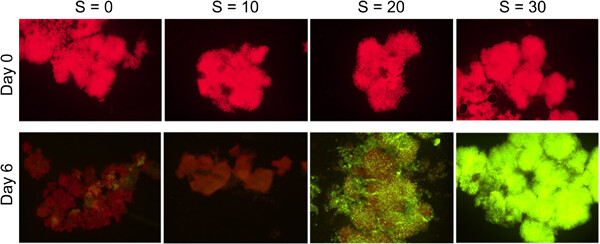
High salinity affects the morphology and viability of colonial strains of the cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa producing different amounts of mucilage. We demonstrate that the collective organization of colonies embedded in an extracellular polymeric substance improves their ability to cope with osmotic shock when compared to unicellular strains. These results suggest Microcystis survival and a potential proliferation in mesohaline estuaries after transfer from freshwater.
Genome comparison reveals that Halobacterium salinarum 63-R2 is the origin of the twin laboratory strains NRC-1 and R1
- First Published: 13 June 2023
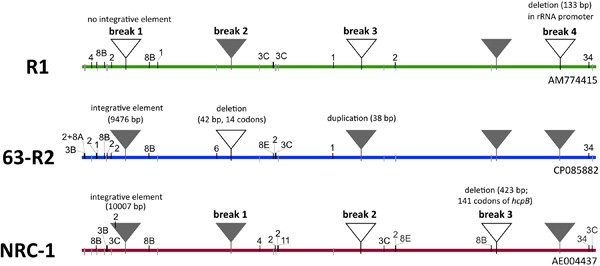
The complete genomes of four Halobacterium salinarum strains were compared in detail. Two strains (91-R6T and 63-R2) were isolated in 1934 by Lochhead from cow and buffalo hides. From the results of these comparisons, we conclude that strain 63-R2 is the immediate ancestor of the two, widely used laboratory strains NRC-1 and R1.
Aedes albopictus microbiome derives from environmental sources and partitions across distinct host tissues
- First Published: 12 June 2023
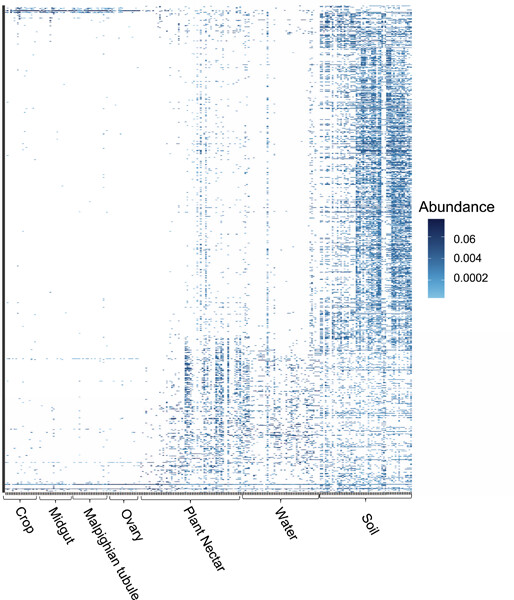
The processes that govern how environmental microbes assemble across the tissues within mosquitoes remain poorly resolved. We use ecological network analyses to examine how environmental bacteria assemble to form bacteriomes among Aedes albopictus host tissues. Broadly, these data demonstrate that mosquito tissue microbiomes are nested within environmental sources, and form specialized modules based on tissue type.
Potential impacts of environmental bacteria on the microbiota of loggerhead (Caretta caretta) and green (Chelonia mydas) sea turtle eggs and their hatching success
- First Published: 05 June 2023
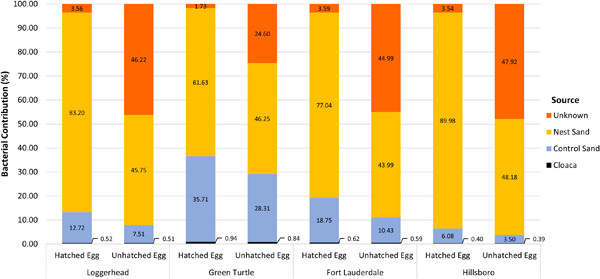
Here we used 16S rRNA gene sequencing to characterize and compare the bacterial communities of hatched and unhatched eggshells from loggerhead and green sea turtles to those in the cloaca of nesting sea turtles and sand within and surrounding the nests. Significant differences were identified between hatched and unhatched egg microbiota with the differences associated predominately with Pseudomonas spp., found in higher abundances in unhatched eggs than hatched eggs. Microbiota similarities indicate that the nest sand environment played a larger role than the nesting mother's cloaca in influencing egg microbiota. However, additional unknown sources may contribute to pathogenic bacteria introduction into unhatched eggs.
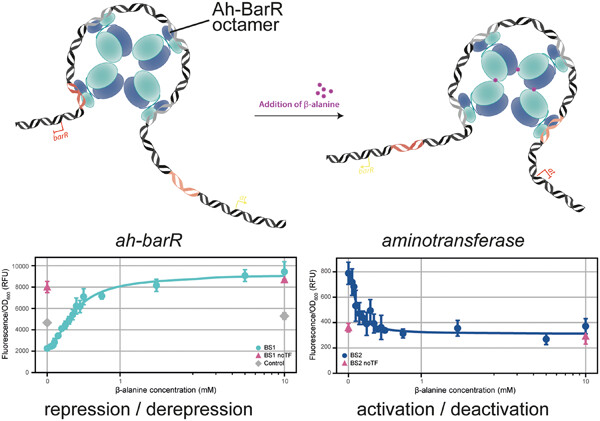
Molecular mechanisms of regulation by a β-alanine-responsive Lrp-type transcription factor from Acidianus hospitalis
- First Published: 22 May 2023
Responses of Anabaena sp. PCC7120 to lindane: Physiological effects and differential expression of potential lin genes
- First Published: 27 April 2023
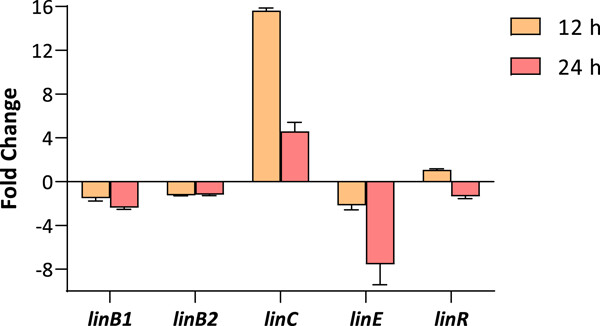
In this article, the tolerance of Anabaena sp. to lindane was studied as well as the expression of its potential lin genes. Our goal was to obtain information to create strategies for lindane bioremediation and also to find the induction of genes in the presence of lindane that can be used in the development of whole-cell biosensors.
Effects of sponge-to-sponge contact on the microbiomes of three spatially competing Caribbean coral reef species
- First Published: 27 April 2023

We conducted an investigation of microbiome impacts during spatial competition among coral reef sponges. Microbiome diversity and composition in zones of direct contact were indistinguishable from no-contact zones and control sponges. These findings indicate that allelopathic interactions and competitive outcomes in sponges are not mediated by microbiome damage or destabilization.
COMMENTARY
Development of a new multiplex quantitative PCR for the detection of Glaesserella parasuis, Mycoplasma hyorhinis, and Mycoplasma hyosynoviae
- First Published: 15 May 2023
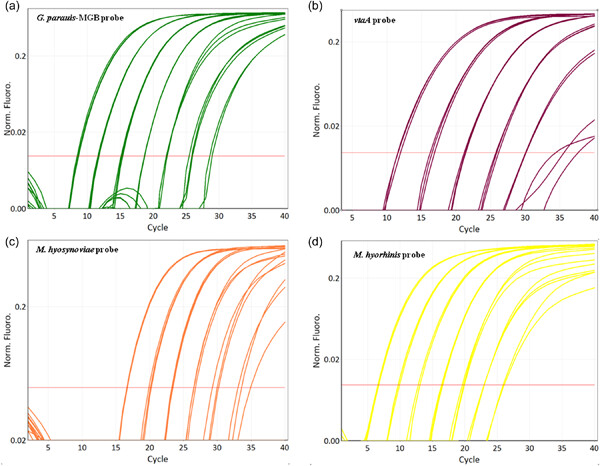
The aim of the study was to develop a multiplex PCR for identification of Glaesserella parasuis and its virulence marker vtaA distinguishing between highly virulent and non-virulent strains. Furthermore, Mycoplasma hyorhinis and Mycoplasma hyosynoviae can be identified targeting 16S rRNA. The developed multiplex PCR provides a simple one-tube assay, which can be performed rapidly and cost-efficiently allowing an efficient throughput of samples in veterinary diagnostic laboratories.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
An improved method for intracellular DNA (iDNA) recovery from terrestrial environments
- First Published: 25 June 2023
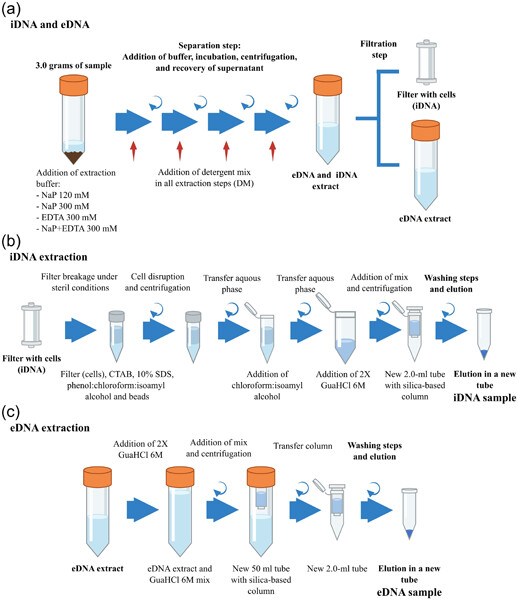
The simultaneous extraction of intracellular DNA (iDNA) and extracellular DNA (eDNA) can be improved by using a highly concentrated sodium phosphate buffer with a detergent mix or EDTA. This improved protocol allows for higher recovery of iDNA from various environmental samples, including low-biomass iron-bearing rock samples, while buffers based solely on sodium phosphate are recommended for studies focusing on eDNA. These modifications may contribute to a more accurate characterization of modern and past ecosystems in environmental studies