Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Dynamic interactions between Candida albicans and different streptococcal species in a multispecies oral biofilm
- First Published: 03 October 2023
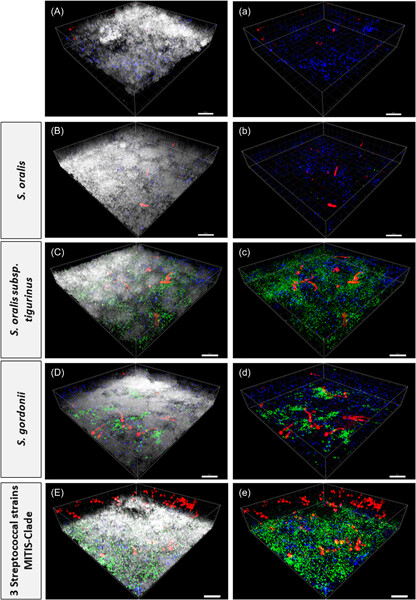
There is evidence that multispecies biofilms containing oral streptococci and the yeast Candida albicans may negatively affect the host and even promote infections. The results of this study show the presence of Streptococcus mutans in a four-species biofilm with Streptococcus oralis or S. oralis subsp. tigurinus did not differ significantly in C. albicans colony-forming unit (CFU) counts compared to biofilms without S. mutans. However, compared to other mitis species, Streptococcus gordonii combined with S. mutans resulted in the lowest CFUs of C. albicans.
A loophole in soap dispensers mediates contamination with Gram-negative bacteria
- First Published: 29 September 2023
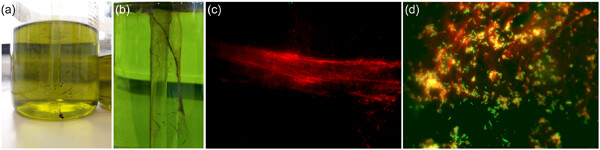
Liquid soap dispensers are widely used in domestic and clinical settings. In previous studies, the risk of bacterial contamination of refillable systems was pointed out and a bacterial contamination rate of 25%, with values of up to 108 colony-forming units/mL was reported. We contaminated different dispensing systems with Pseudomonas aeruginosa /Pluralibacter gergoviae biofilm, to reveal the route of contamination and identified the pressure release of standard pump dispensers as the loophole for microbial contamination.
Relationship between the Rod complex and peptidoglycan structure in Escherichia coli
- First Published: 09 October 2023
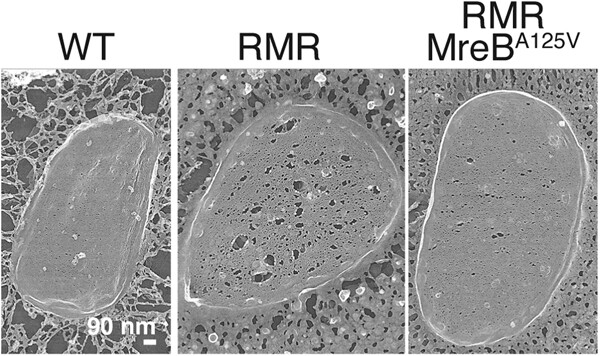
The structures of the peptidoglycan of the wild-type strain, the mutant strain of the Rod complex, and its suppressor mutant strains were observed. The peptidoglycan purified from the Rod complex mutant had many large holes, whereas the number and size of holes were reduced in the suppressor mutants. We visualized the relationship between the Rod complex activity and the peptidoglycan structure.
COMMENTARY
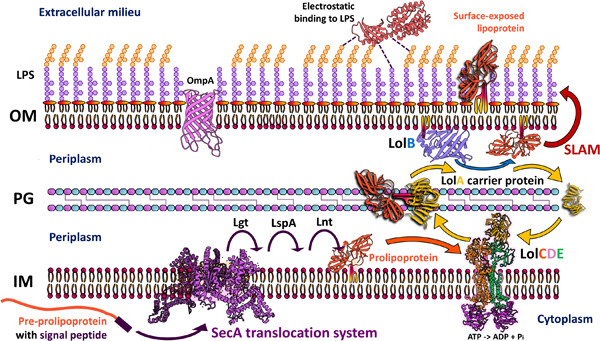
Bacterial surface-exposed lipoproteins and sortase-mediated anchored cell surface proteins in plant infection
- First Published: 14 September 2023
Similarity in milk microbiota in replicates
- First Published: 30 September 2023
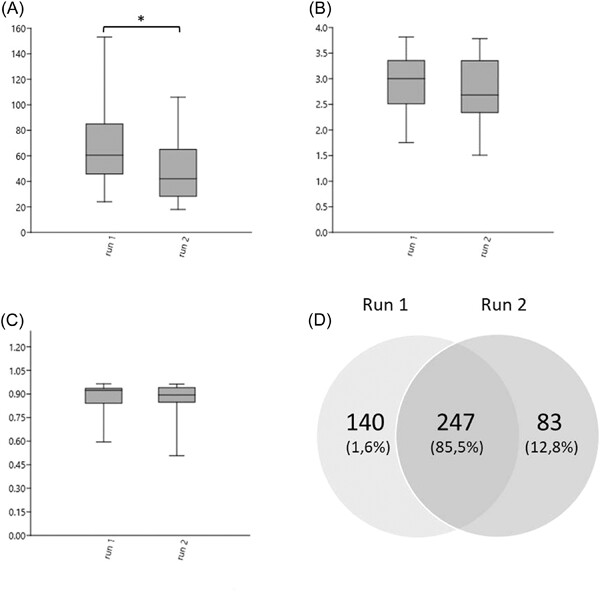
For this study, bacterial DNA from 44 milk samples was extracted twice, and the V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was sequenced in two separate runs. After submitting the sequence data to the same bioinformatic pipeline, results from the two runs are compared. We show that repeated DNA extraction and sequencing can significantly affect the results of a low microbial biomass microbiota study.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
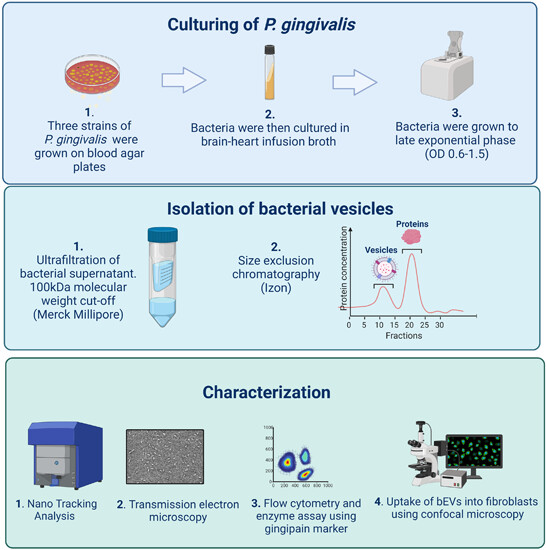
Isolation, characterization, and fibroblast uptake of bacterial extracellular vesicles from Porphyromonas gingivalis strains
- First Published: 16 October 2023
Biosynthetic gene cluster synteny: Orthologous polyketide synthases in Hypogymnia physodes, Hypogymnia tubulosa, and Parmelia sulcata
- First Published: 17 October 2023
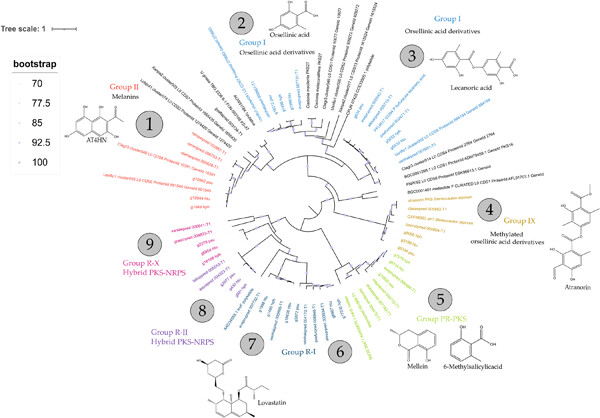
The new Parmelia sulcata genome from the metagenomic sample was evaluated with Hypogymnia physodes and Hypogymnia tubulosa to identify orthologous polyketide synthase (PKS)-related biosynthetic gene clusters (BGC). The phylogenetic tree highlights the relation of investigated sequences. Evaluation of orthologous PKS-related BGCs emphasizes the high homology of biosynthetic core genes.
Influence of light conditions on the production of chrysolaminarin using Phaeodactylum tricornutum in artificially illuminated photobioreactors
- First Published: 18 September 2023
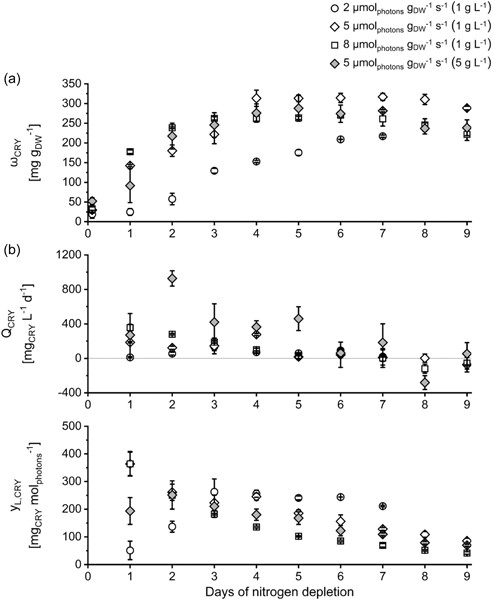
Here we examine the influence of the amount of light per gram biomass (specific light availability) and the influence of two different biomass densities (at the same amount of light per gram biomass) on the accumulation of the storage product chrysolaminarin and potential co-products: fucoxanthin, eicosapentaenoic acid, and fatty acids used for energy storage (C16 fatty acids), during nitrogen depletion in artificially illuminated flat panel airlift photobioreactors. Our results show that the time course of C-allocation between chrysolaminarin and fatty acids as storage compounds depends on specific light availability and cell concentration.
Transcriptomics-guided identification of an algicidal protease of the marine bacterium Kordia algicida OT-1
- First Published: 10 October 2023
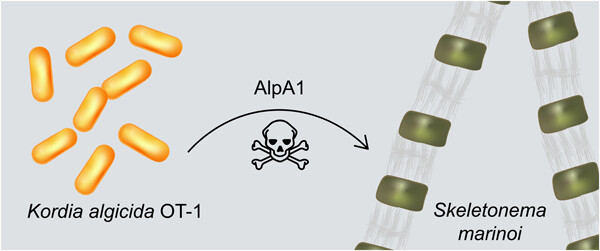
Algicidal bacteria shape the plankton communities of the oceans by lysing microalgae and consuming the released nutrients. Kordia algicida is an environmentally relevant marine bacterium whose algicidal activity is mediated by secreted proteases. In this study, we utilize a transcriptomics-guided approach to identify the secreted serine protease AlpA1 as a key factor in the algicidal process. This discovery offers new approaches for the real-time monitoring and manipulation of algicidal bacteria in algal blooms.
COMMENTARY
Orientia tsutsugamushi: A life between escapes
- First Published: 10 September 2023
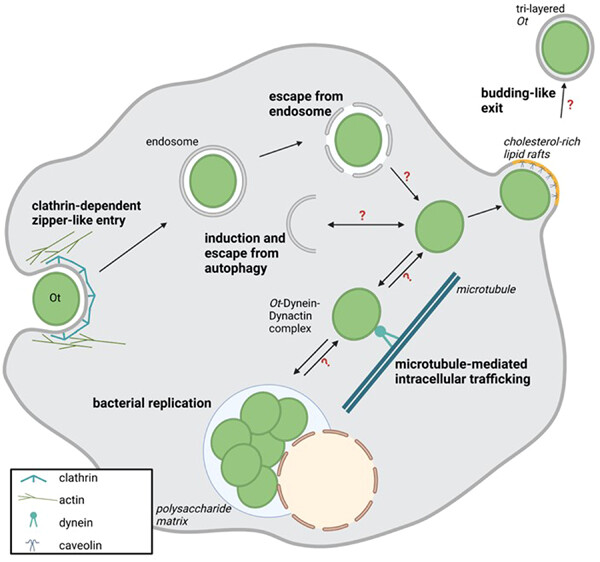
The life cycle of the mite-borne, obligate intracellular pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi (Ot), the causative agent of human scrub typhus, differs in many aspects from that of other members of the Rickettsiales order. Particularly, the nonlytic cellular exit of individual Ot bacteria at the plasma membrane closely resembles the budding of enveloped viruses but has only been rudimentarily studied at the molecular level. This brief article is focused on the current state of knowledge of escape events in the life cycle of Ot and highlights differences in strategies of other rickettsiae.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
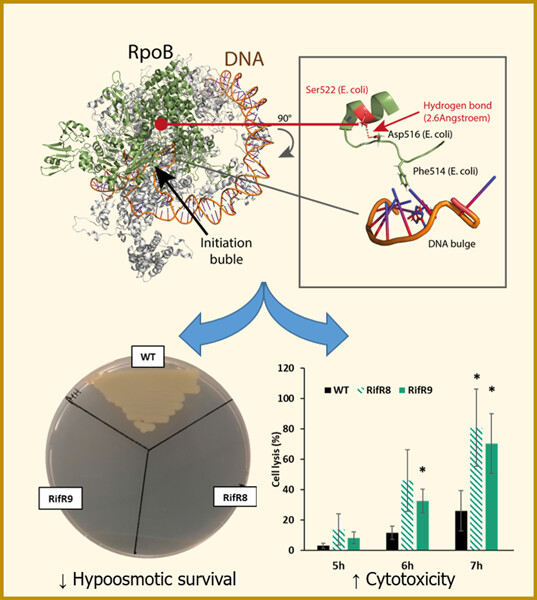
Rifampicin-resistant RpoB S522L Vibrio vulnificus exhibits disturbed stress response and hypervirulence traits
- First Published: 10 September 2023