Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image
- First Published: 13 May 2025
The cover image is based on the article Detecting PI3K and TP53 Pathway Disruptions in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Among Hispanic/Latino Patients by Cecilia Monge et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.70791.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Role of SIRT7 in Prostate Cancer Progression: New Insight Into Potential Therapeutic Target
- First Published: 01 April 2025
Chemokines: Orchestration of the Tumor Microenvironment and Control of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression
- First Published: 27 March 2025
The Role of Cholesterol Metabolism and Its Regulation in Tumor Development
- First Published: 27 March 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
REVIEW
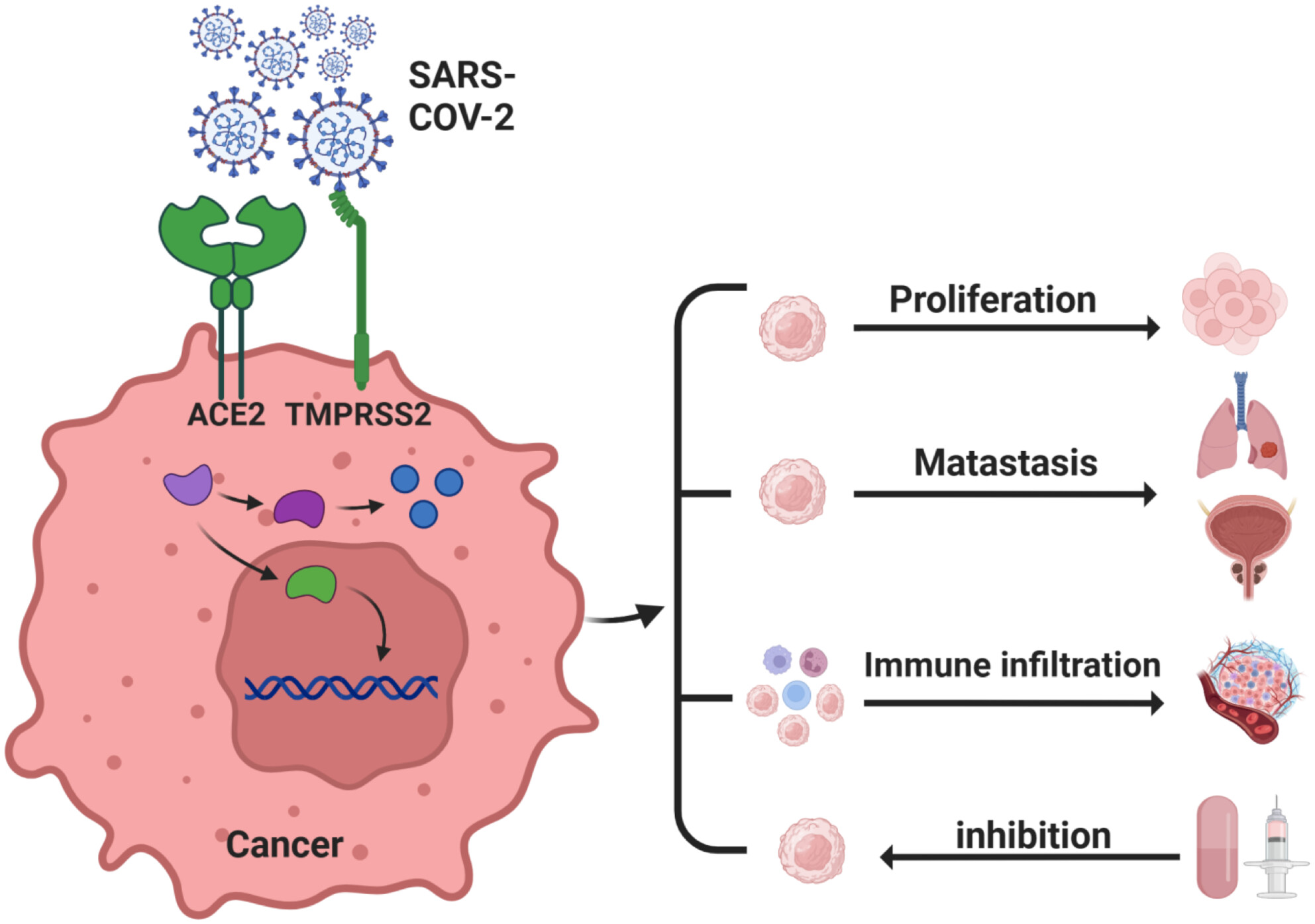
Bridging Cancer and COVID-19: The Complex Interplay of ACE2 and TMPRSS2
- First Published: 27 March 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Tumor-Associated Lactic Acidosis and Early Death in Patients With Lymphoma
- First Published: 28 March 2025
Decoding Genomic Diversity to Guide Tumor Lesion-Specific Treatment of Multifocal Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- First Published: 27 March 2025
“We Were Still Left in the Back Field, Not Knowing”: Pediatric Cancer Patients and Parents Describe Obstacles to Prognostic Communication
- First Published: 08 April 2025
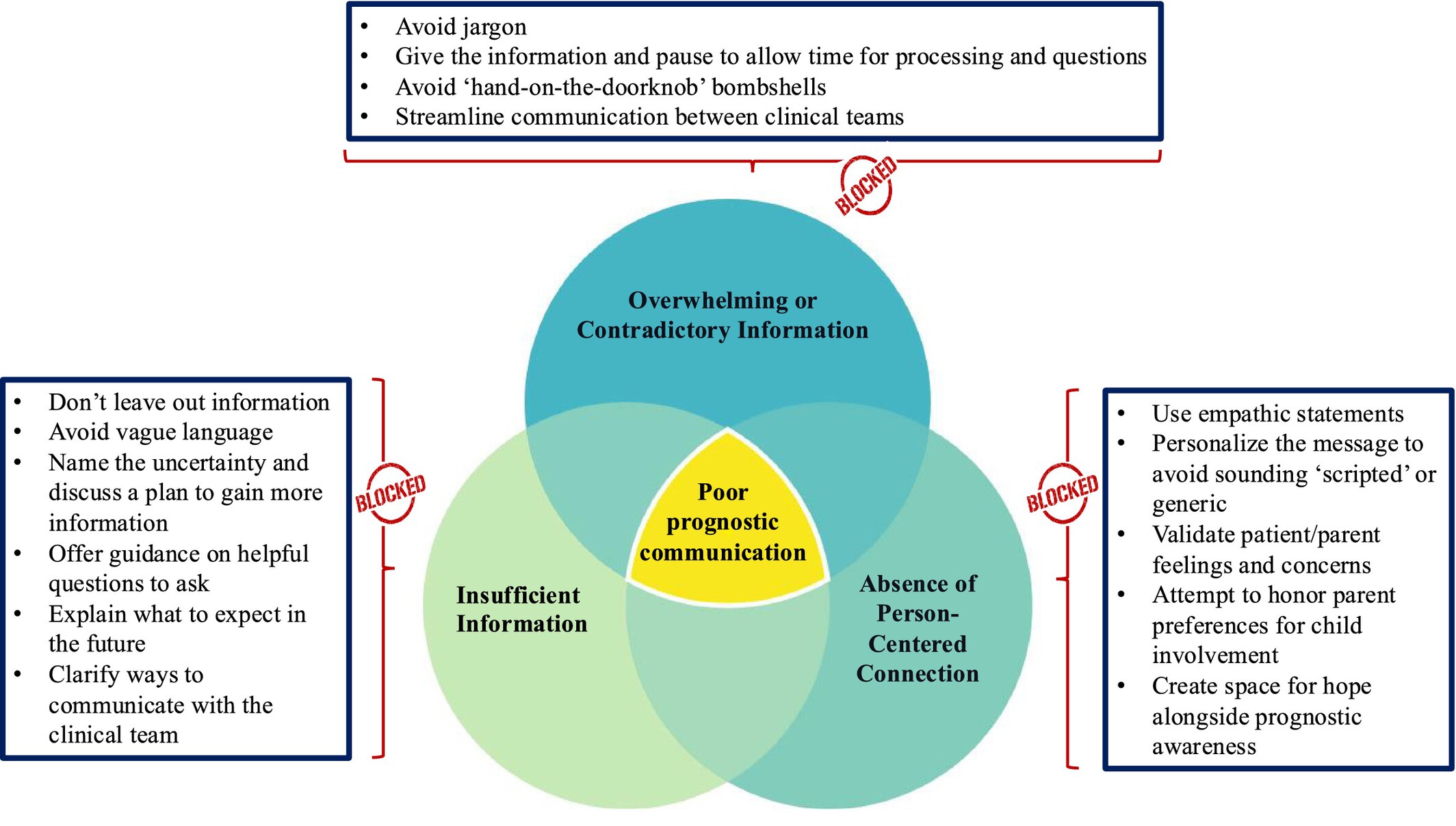
Patients with cancer and their families have important lessons to teach oncology clinicians about how to improve care. In this study, we asked pediatric patients and parents to reflect on how their doctors talked about prognosis to help us identify ways to improve this process. We learned that when patients and parents feel that the doctor did not discuss prognosis in a good way, it was usually due to (1) insufficient information, (2) overwhelming or contradictory information, and (3) absence of person-centered connection. These findings will help guide communication training and future research to improve communication.
Inequalities in Fertility-Impacting Cancer Incidence Among Young Populations in the United States
- First Published: 06 April 2025
REVIEW
Characterization of the Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasm Immune Microenvironment
- First Published: 27 March 2025
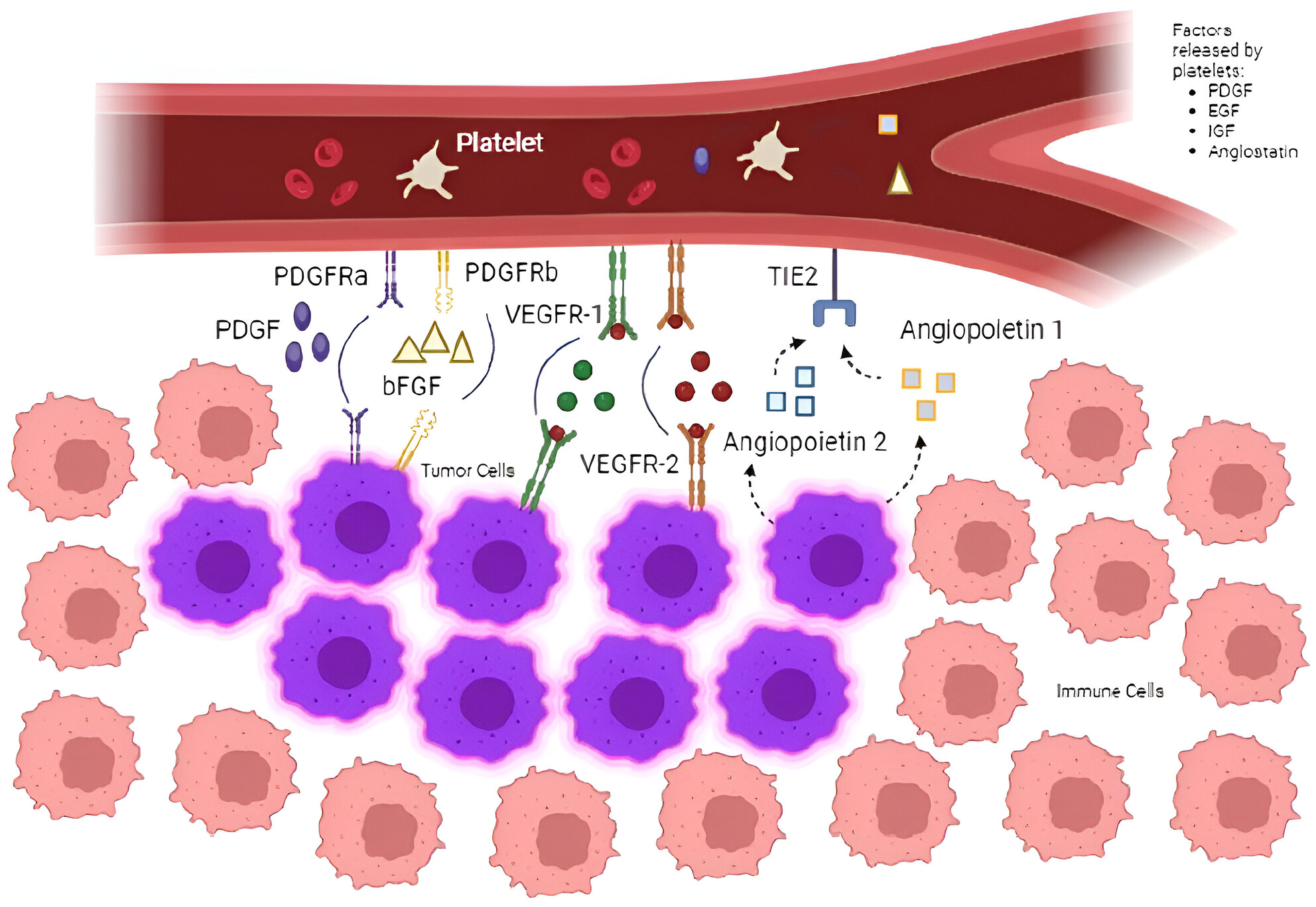
Enhancements in the creation of animal models that most accurately represent the aggressive types of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms are necessary to create therapeutic protocols that combine immunotherapies with other medication classes to help patients with metastatic disease recover or respond to treatment more durably. Tumor microenvironment is thought to be essential to immunotherapy's effectiveness; nonetheless, assessing the immune microenvironment and its clinical ramifications remains difficult, particularly in neuroendocrine neoplasms.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Phase I/IB, Open Label, Dose Finding Study to Evaluate Safety, Pharmacodynamics and Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Combination With Vorinostat in Patients With Advanced Prostate, Renal or Urothelial Carcinoma
- First Published: 27 March 2025
KPNA5 Suppresses Malignant Progression of Ovarian Cancer Through Importing the PTPN4 Into the Nucleus
- First Published: 27 March 2025
Overall Survival With Palbociclib and Aromatase Inhibitor Versus Aromatase Inhibitor Alone in Older Patients With HR+/HER2− Metastatic Breast Cancer
- First Published: 27 March 2025
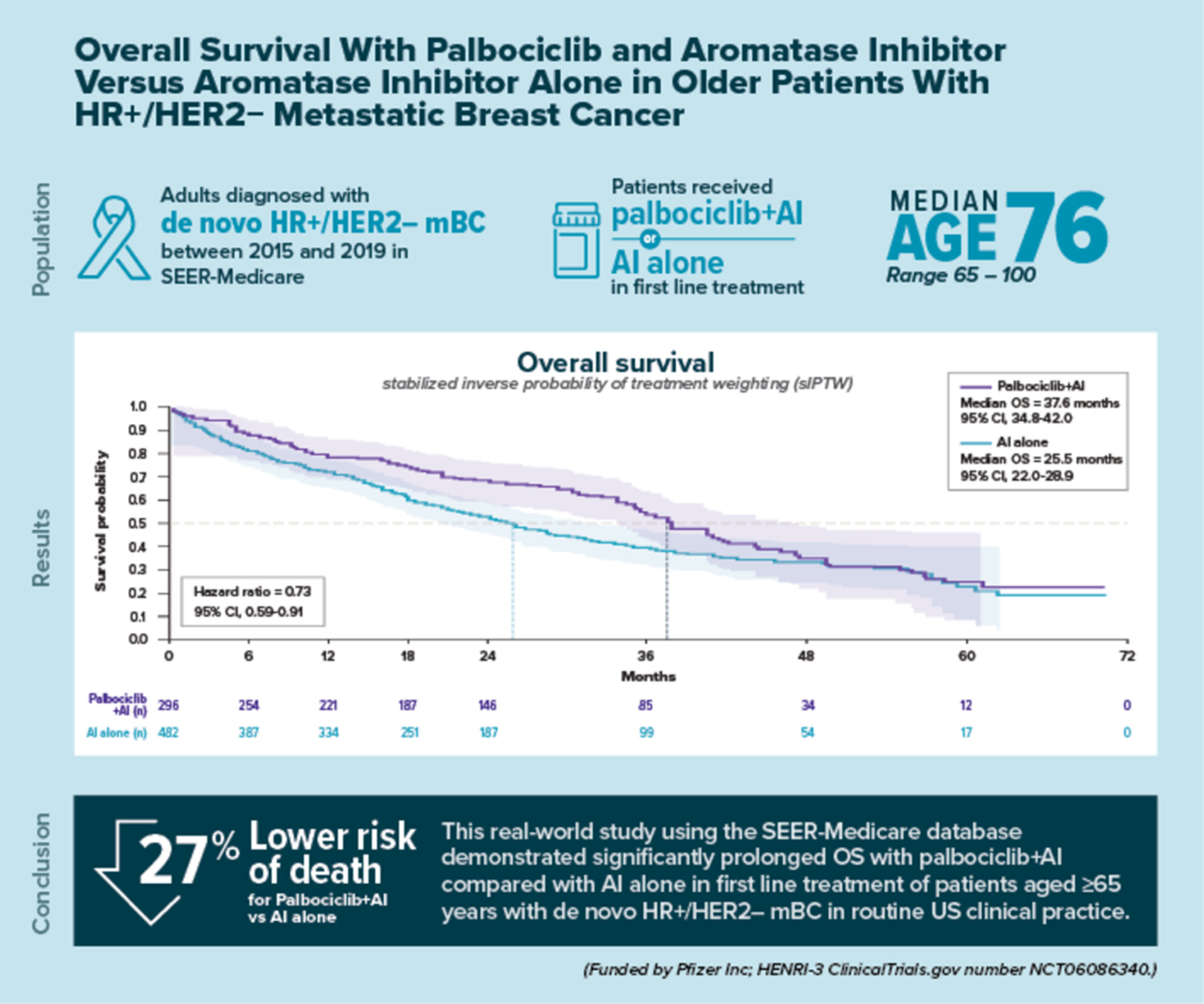
This real-world study conducted with SEER-Medicare data of patients aged 65 years or older with de novo HR+/HER2– metastatic breast cancer found that treatment with palbociclib in combination with an aromatase inhibitor (AI) was associated with significantly prolonged overall survival compared with AI alone.
Eligibility Criteria in Advanced Urothelial Cancer Clinical Trials: An Assessment of Modernization and Inclusion
- First Published: 27 March 2025
Exploring the Dynamics of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Eosinophilia in Advanced/Metastatic Melanoma: A Comprehensive Retrospective Analysis
- First Published: 27 March 2025
Patterns of Clinical Trial Enrollment for Pediatric Patients With Hepatoblastoma and Wilms Tumor: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group
- First Published: 27 March 2025
NEPA (Netupitant/Palonosetron) for the Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV) in Patients Receiving Highly or Moderately Emetogenic Chemotherapy Who Experienced Breakthrough CINV in Cycle 1 of Chemotherapy: A Phase II Clinical Trial
- First Published: 27 March 2025
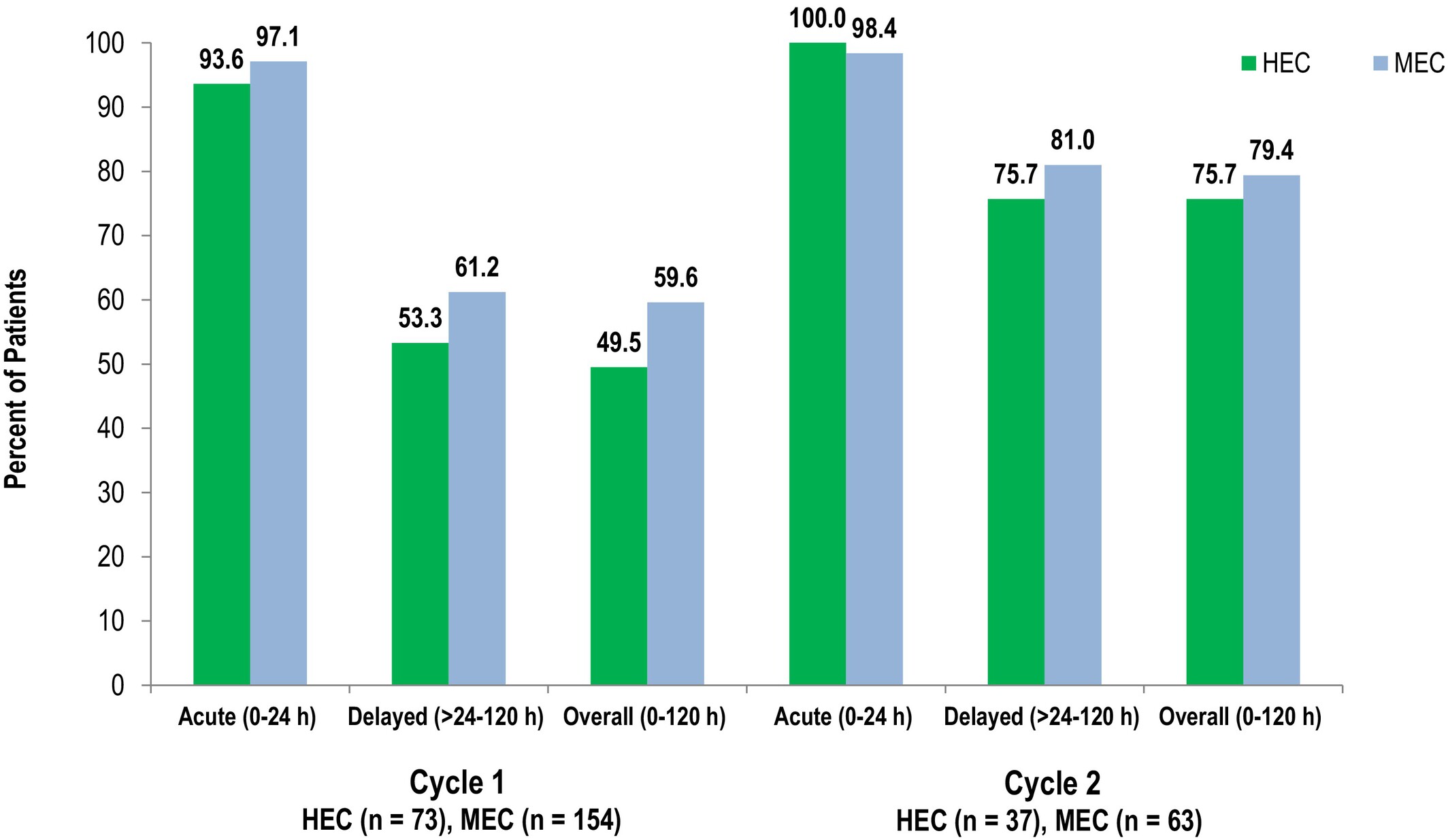
This study was designed to evaluate the use of NEPA (netupitant/palonosetron) plus dexamethasone with or without olanzapine for the prevention of CINV in the second cycle of chemotherapy for patients receiving highly (HEC) or moderately emetogenic chemotherapy (MEC) who developed breakthrough CINV in their first cycle despite guideline-directed prophylactic antiemetics. Of the 227 patients enrolled in Cycle 1, 100 patients (n = 37 HEC, 63 MEC) experienced breakthrough CINV and received the NEPA-based treatments in Cycle 2. The complete response (no emesis/no rescue use) rates during the overall (0–120 h) phase were 76% and 79% in the HEC and MEC groups, respectively, suggesting that NEPA with or without olanzapine is an effective approach for CINV prevention for patients receiving HEC or MEC who develop breakthrough CINV after their first course of chemotherapy.
Fear of Cancer Recurrence and Associated Factors in Lymphoma Survivors and Their Family Caregivers: A Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 29 March 2025
REVIEW
Advances in the Prevention of Cervical Cancer by Anti-Human Papillomavirus Agents
- First Published: 06 April 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Identification of Diagnostic Biomarkers for Colorectal Polyps Based on Noninvasive Urinary Metabolite Screening and Construction of a Nomogram
- First Published: 08 April 2025
Comparative Efficacy of Various Exercise Types on Cancer-Related Fatigue for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- First Published: 27 March 2025
The Impact of Carboplatin Dosing Design Using Adjusted Serum Creatinine on Carboplatin Plus Paclitaxel Therapy for Ovarian Cancer
- First Published: 27 March 2025
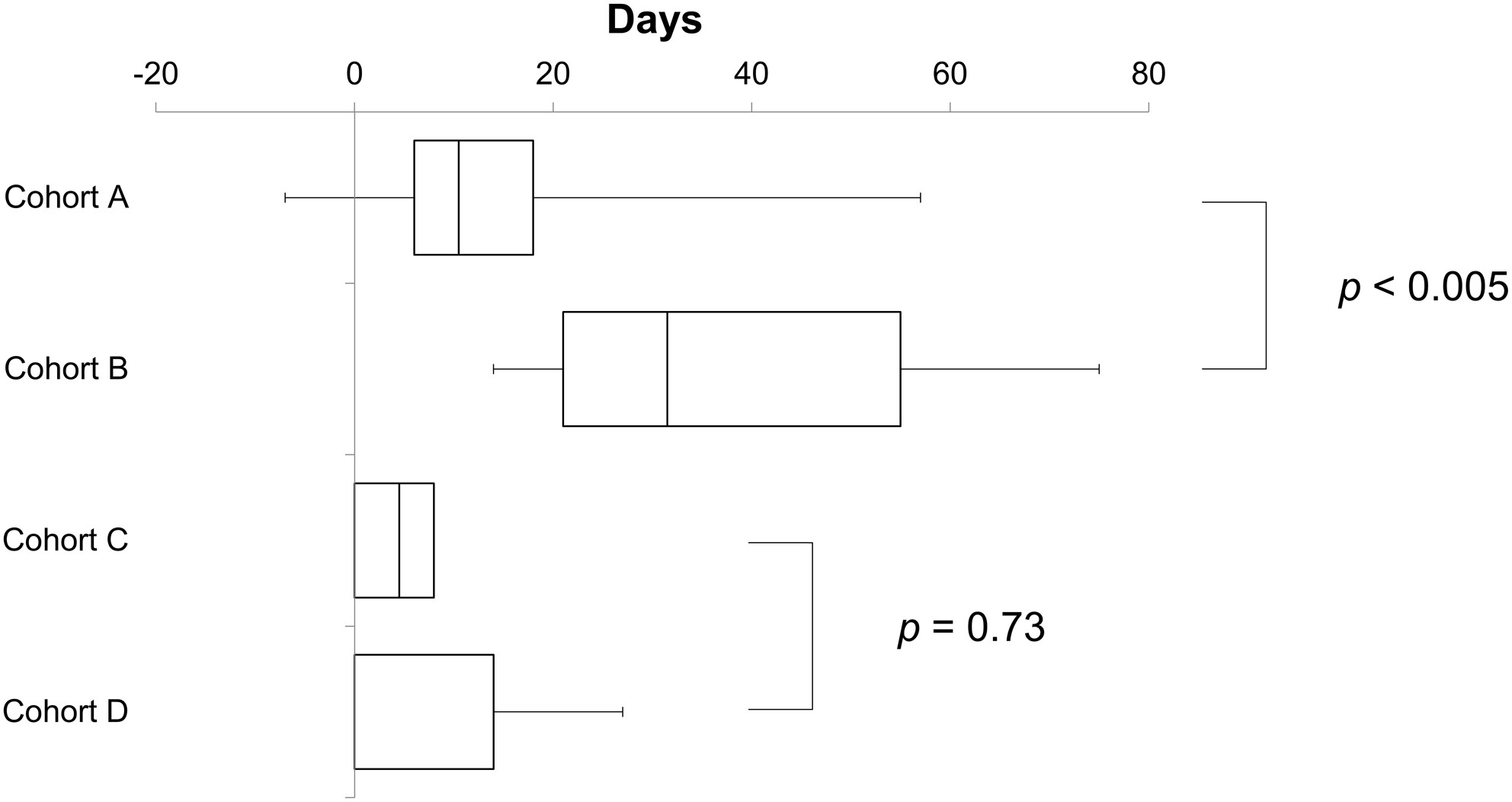
This retrospective study aimed to assess the impact of adjusting serum creatinine (SCr) values when determining carboplatin (CBDCA) doses in ovarian cancer chemotherapy. Patients treated with CBDCA + paclitaxel (TC) were categorized based on the regimen they received (dose-dense TC or tri-weekly TC) and whether or not their SCr levels were adjusted. Our findings suggest that in patients receiving dose-dense TC, but not in those receiving tri-weekly TC, adjusting SCr did not compromise the dose intensity of total CBDCA and may contribute to maintaining dose intensity, highlighting potential benefits in reducing treatment modification and adverse events.
Efficacy of Low-Dose Fluconazole for Primary Prophylaxis of Invasive Candida Infections in Patients With Acute Leukemia: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
- First Published: 28 March 2025
Developing the Short-Form of Lymphedema Needs Questionnaire for Iranian Breast Cancer Patients
- First Published: 28 March 2025
REVIEW
Culture Is Key: Engaging Culturally and Linguistically Diverse Populations in Breast Cancer Screening in High Income Contexts: A Scoping Review
- First Published: 28 March 2025
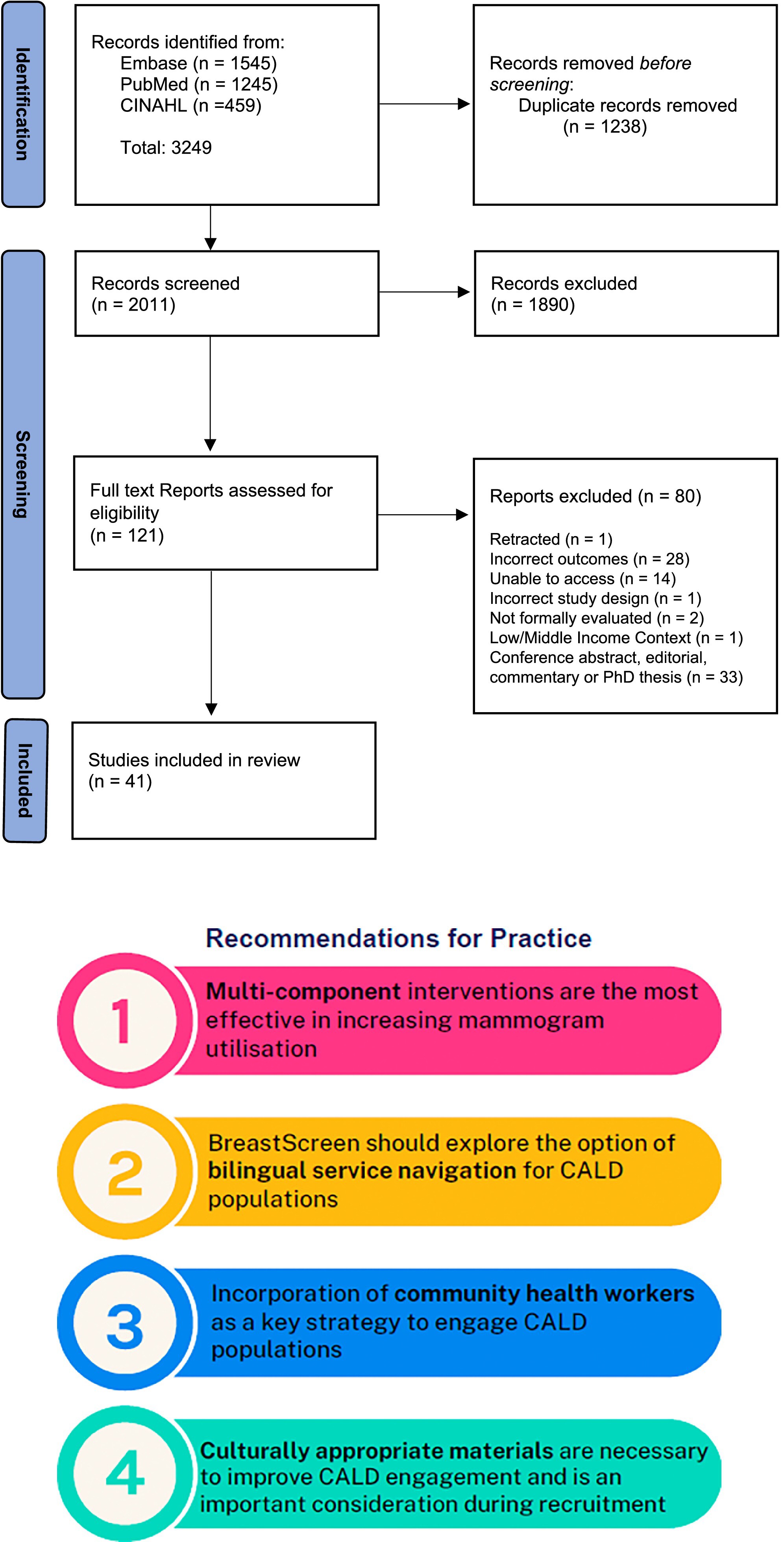
Culturally and linguistically diverse populations have lower engagement and experience multiple challenges accessing breast screening services. Specific culturally appropriate, tailored, multi-component strategies are necessary to improve engagement in breast screening services for these populations.
Dose–Volume Constraints for Thoracic, Abdominal, and Pelvic Carbon Ion Radiotherapy: A Literature Review
- First Published: 28 March 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Detecting PI3K and TP53 Pathway Disruptions in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Among Hispanic/Latino Patients
- First Published: 01 April 2025
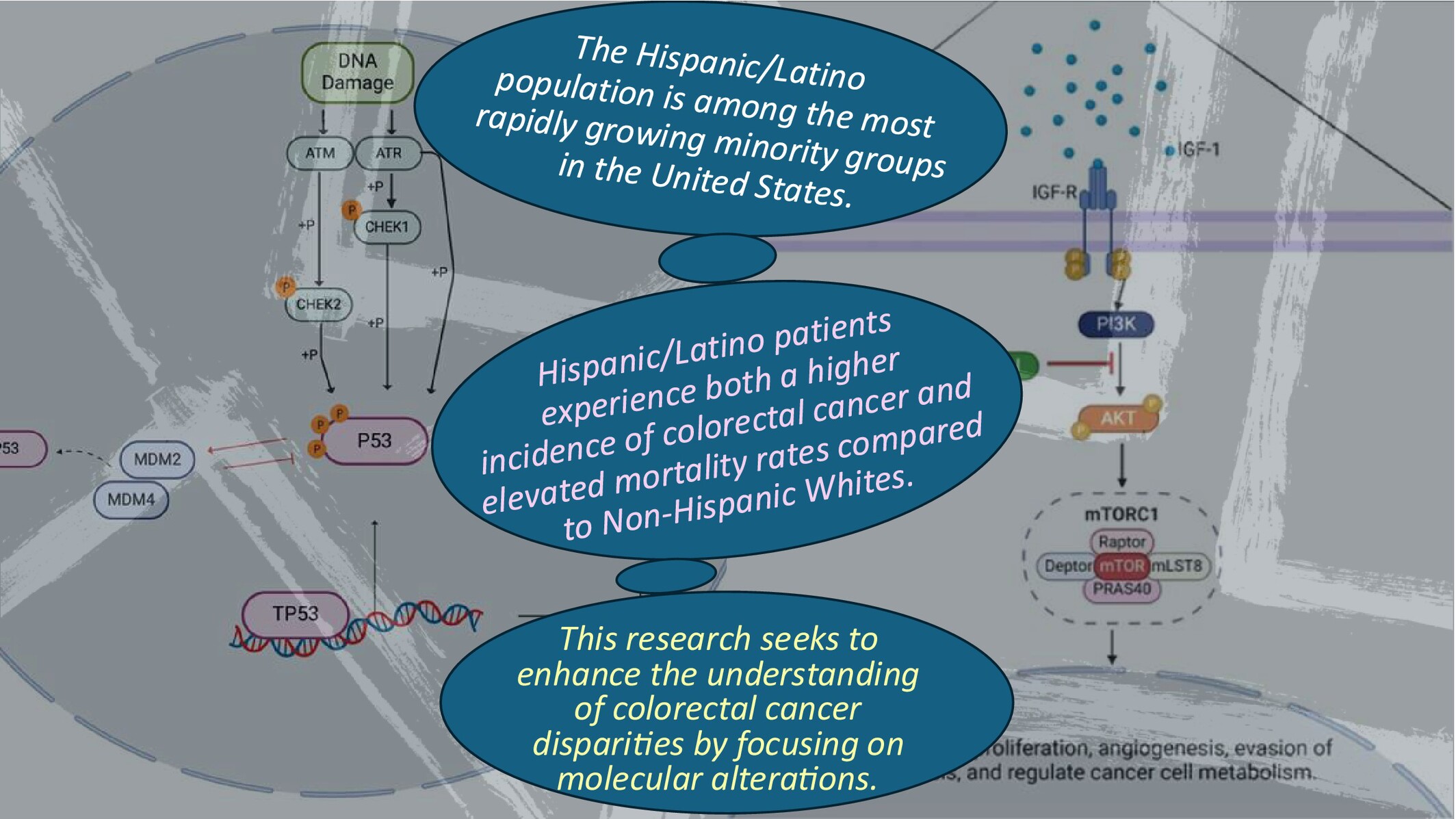
This study identifies distinct PI3K and TP53 pathway disruptions in early-onset colorectal cancer among Hispanic/Latino patients, with findings suggesting a higher prevalence of PI3K alterations and potential differences in outcomes associated with TP53 disruptions compared to non-Hispanic Whites. While these results provide valuable insights into potential molecular drivers of disparities, further research is needed to fully understand their clinical implications. These findings may suggest new directions for precision medicine approaches aimed at addressing cancer health disparities and improving equity in colorectal cancer care.
Prediction of Sleep Quality in Cancer Survivors Based on Arousal, Pain, and Worry: The Mediating Role of Dysfunctional Beliefs and Attitudes About Sleep
- First Published: 01 April 2025
Optimizing the Follow-Up Interval After Successful Cold Knife Conization of CIN3: A 10-Year Retrospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 29 March 2025
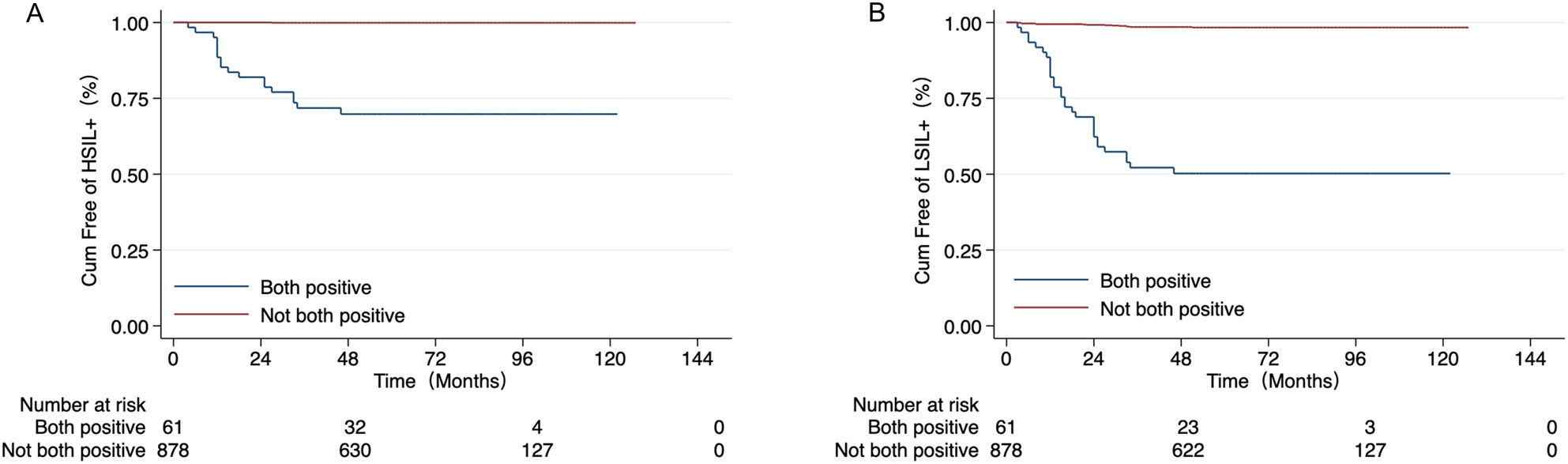
This retrospective cohort study followed up women who underwent CKC and had negative margins on conization for up to 10 years. The risk of residual or recurrent HSIL+ was higher in patients with HPV persistence for 12 months compared with HPV positive at 6 months after CKC. In patients with negative margins, extending the follow-up interval to 12 months may reduce the number of HPV tests and colposcopy referral rates while maintaining HSIL+ detection.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
A Prospective, Multicenter Analysis of Recurrence-Free Survival After Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Decisions Influenced by the 31-GEP
- First Published: 01 April 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Central Nervous System Prophylaxis Approach in High-Risk Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients: A Retrospectively Collected, Single-Center Cohort Analysis
- First Published: 01 April 2025
Bioinformatics Combined With Biological Experiments to Identify the Pathogenetic Link of Type 2 Diabetes for Breast Cancer
- First Published: 09 April 2025
Predictors of Transplant Regret: A Case–Control Study Nested Within a Prospective Cohort of HSCT Recipients
- First Published: 01 April 2025
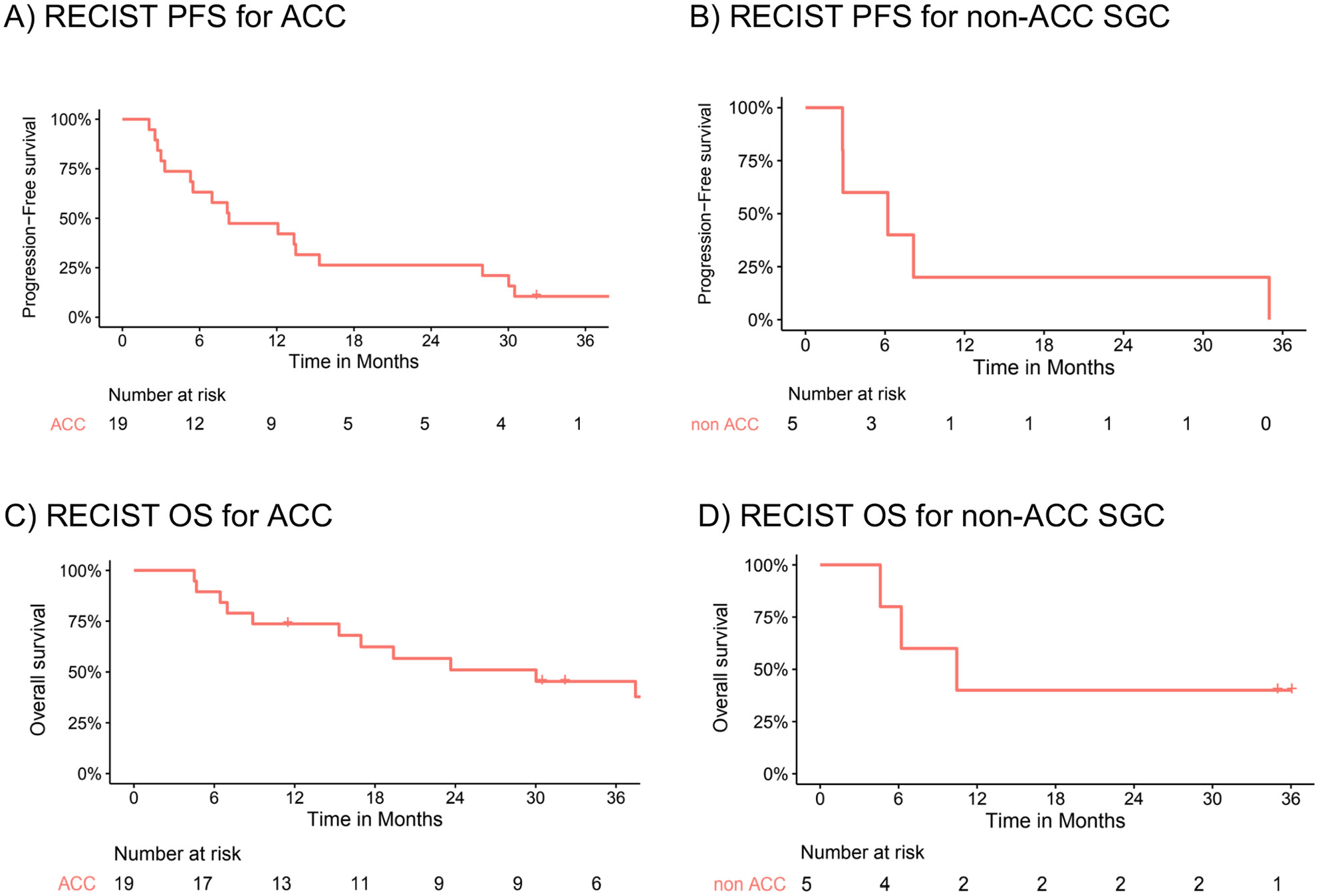
Phase II Study of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Treatment of Metastatic/Recurrent Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) of all Anatomic Sites of Origin and Other Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors
- First Published: 01 April 2025
A Population-Based Study of Infectious Diseases Mortality Risk in Patients With Hematologic Malignancies 2000–2020
- First Published: 01 April 2025
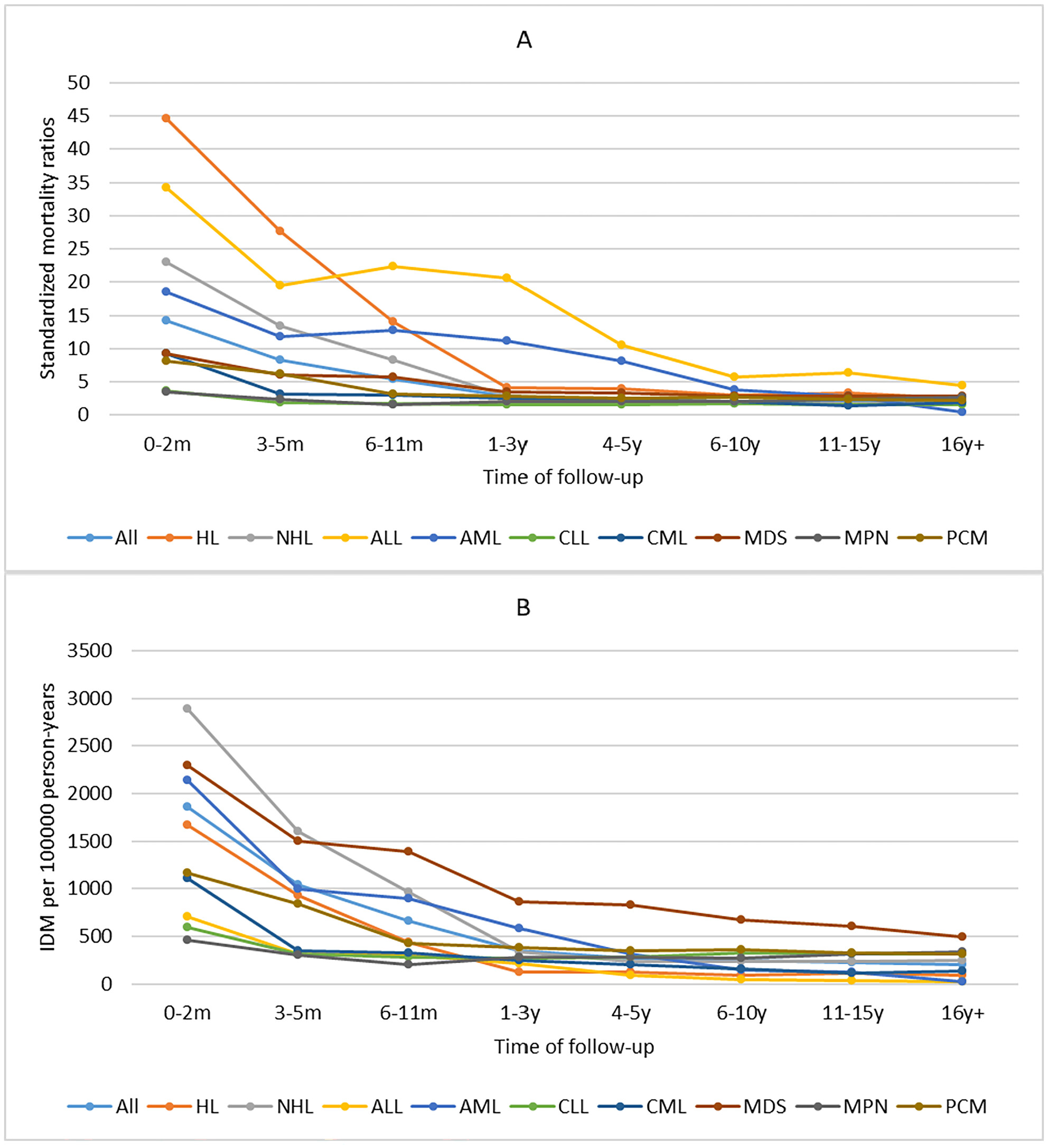
For hematologic malignancies, the infectious diseases mortality (IDM) rates were highest in the first 2 months after diagnosis and gradually declined thereafter. It is extremely important to identify patients at high risk of IDM and provide timely intervention to prevent early death from infections and improve prognosis.
REVIEW
Clinical Prediction Models for Contact X-Ray Brachytherapy in Managing Rectal Cancers: A Scoping Review
- First Published: 03 April 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Cancer Accumulation and Anticancer Activity of “CROX (Cluster Regulation of RUNX)” PIP in HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer Evaluated by Chicken Egg Cancer Model
- First Published: 02 April 2025
Influence Factors Analyses of PICC-Related Bloodstream Infection, PICC-Related Venous Thrombosis, and Infected Puncture Site and Their Influence on Cancer Patients' Death: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 02 April 2025
METTL3, an Independent Adverse Prognostic Factor for AML, Promotes the Development of AML by Modulating the PGC-1α–MAPK Pathway and PGC-1α–Antioxidant System Axis
- First Published: 02 April 2025
Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Longitudinal Analysis of 1,120,377 Individuals From the NHISS Cohort
- First Published: 06 April 2025
RETRACTION
RETRACTION: ING5-Mediated Antineuroblastoma Effects of Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid
- First Published: 04 April 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Establishment and Characterization of a Brain Parenchymal Metastatic Cell Line AlmoR1 Derived From an NSCLC Patient With EGFR-TKI Resistance
- First Published: 02 April 2025
REVIEW
Effects of FABP5 Expression on Clinicopathological and Survival Characteristics in Digestive System Malignancies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 03 April 2025
The Critical Role of Inhibitor of Differentiation 4 in Breast Cancer: From Mammary Gland Development to Tumor Progression
- First Published: 05 April 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
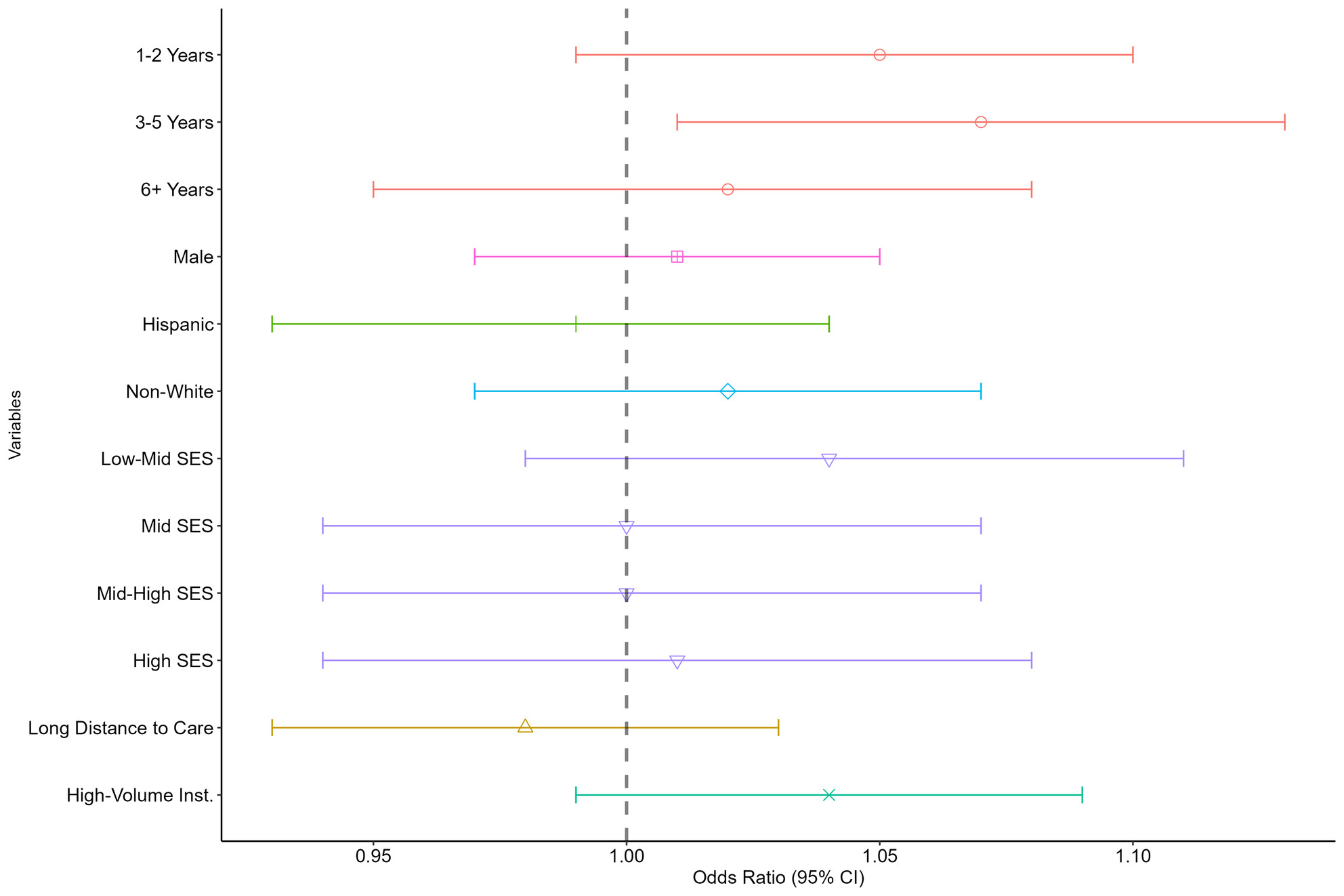
Area Deprivation and Clinical Biomarkers of Inflammation in Cancer Survivors of the National Institutes of Health All of Us Research Program
- First Published: 04 April 2025
Delta-He as a Novel Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Patients With NSCLC Treated With PD–1/PD-L1 Inhibitors
- First Published: 05 April 2025
Circulating Tumour DNA in Patients With EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Early Disease Progression After First-Line Osimertinib Treatment: The ELUCIDATOR Multicentre Prospective Observational Study
- First Published: 05 April 2025
Navigating Life With High-Grade Glioma: Experiences and Needs of Adolescents and Young Adults
- First Published: 08 April 2025
Adolescents and young adults (AYAs) with high-grade glioma (HGG) face unique challenges at critical life stages, including disruptions to education, careers, relationships, and independence due to cognitive and physical impairments. This mixed-methods study, combining surveys and interviews, identified three key themes: managing the impact of symptoms on life goals, addressing social and relational challenges, and coping with identity loss and dependency. Findings highlight the need for tailored interventions and support programs to address the specific needs of AYAs with HGG.
Whole Exome Sequencing Study Identifies Distinct Characteristics of Transformed Small Cell Lung Cancer With EGFR Mutation Compared to De Novo Small Cell and Primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers
- First Published: 08 April 2025
Expression of Cancer-Testis Antigens MAGE-A1, MAGE-A4, NY-ESO-1 and PRAME in Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcomas: The Experience From a Single Center in China
- First Published: 28 March 2025
Immunohistochemical-Based Molecular Typing of ACRG Combined With Immune-Associated PD-L1 Expression Can Predict the Prognosis of Gastric Cancer
- First Published: 09 April 2025