Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
Monitoring of gastrointestinal carcinoma via molecular residual disease with circulating tumor DNA using a tumor-informed assay
- Pages: 16687-16696
- First Published: 21 August 2023
The role of cytoreductive radical prostatectomy and lymph node dissection in bone-metastatic prostate cancer: A population-based study
- Pages: 16697-16706
- First Published: 27 June 2023
Concordance in detection of microsatellite instability by PCR and NGS in routinely processed tumor specimens of several cancer types
- Pages: 16707-16715
- First Published: 28 June 2023
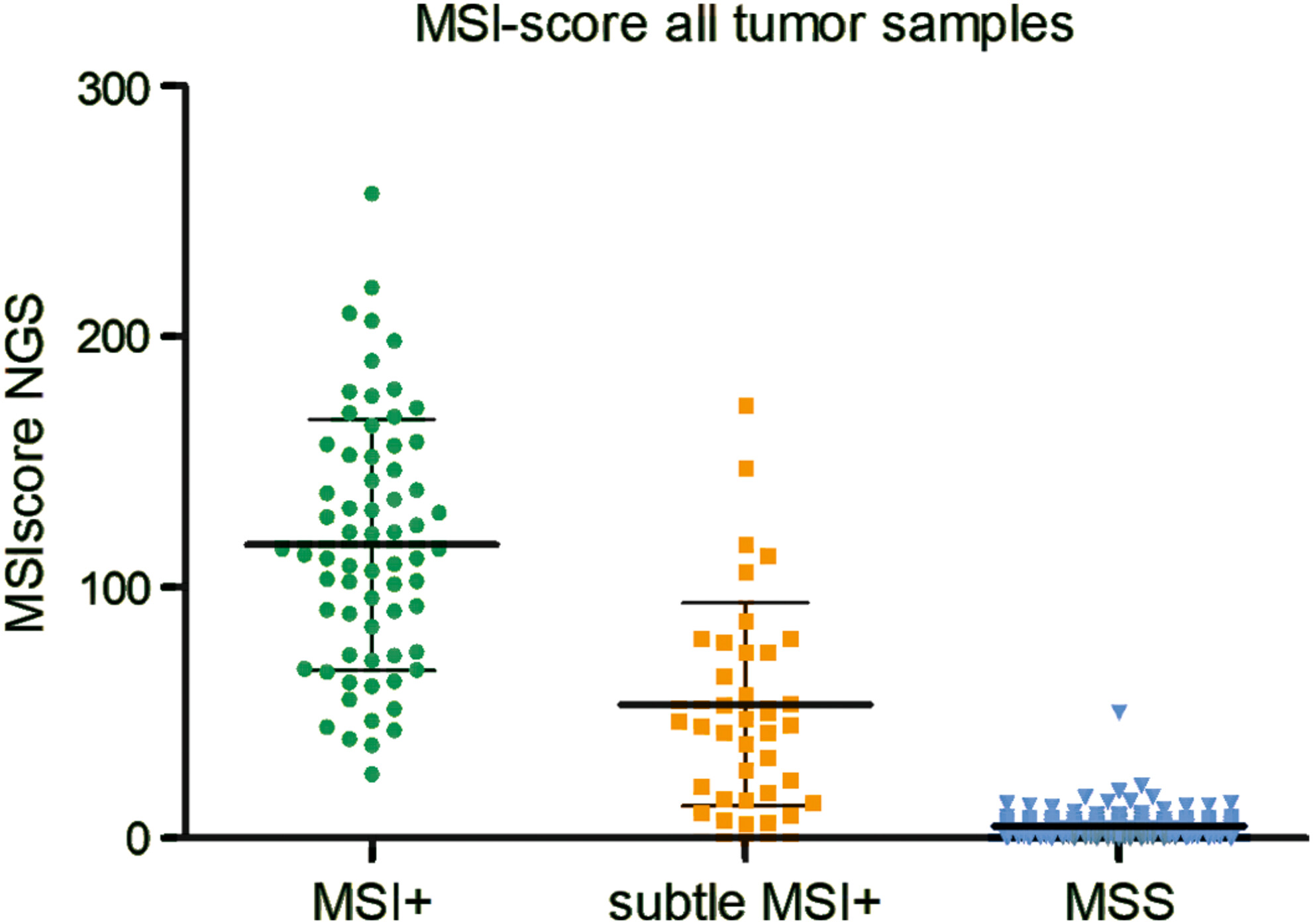
Microsatellite instability (MSI) analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) DNA by NGS is feasible and the results show a high concordance in comparison with the monomorphic marker MSI-PCR (overall sensitivity and specificity of the NGS assay in comparison with the MMR-IHC/MSI-PCR were 92.2% and 98.8%). However, cases with a subtle MSI+ phenotype, most frequently manifest in endometrial cancer (EC), have a risk of a false-negative result by NGS and should be preferentially analyzed by capillary electrophoresis.
Prognostic and immune infiltration significance of ARID1A in TCGA molecular subtypes of gastric adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 16716-16733
- First Published: 27 June 2023
A nomogram for predicting the rapid progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma established by combining baseline PET/CT total metabolic tumor volume, lesion diffusion, and TP53 mutations
- Pages: 16734-16743
- First Published: 27 June 2023
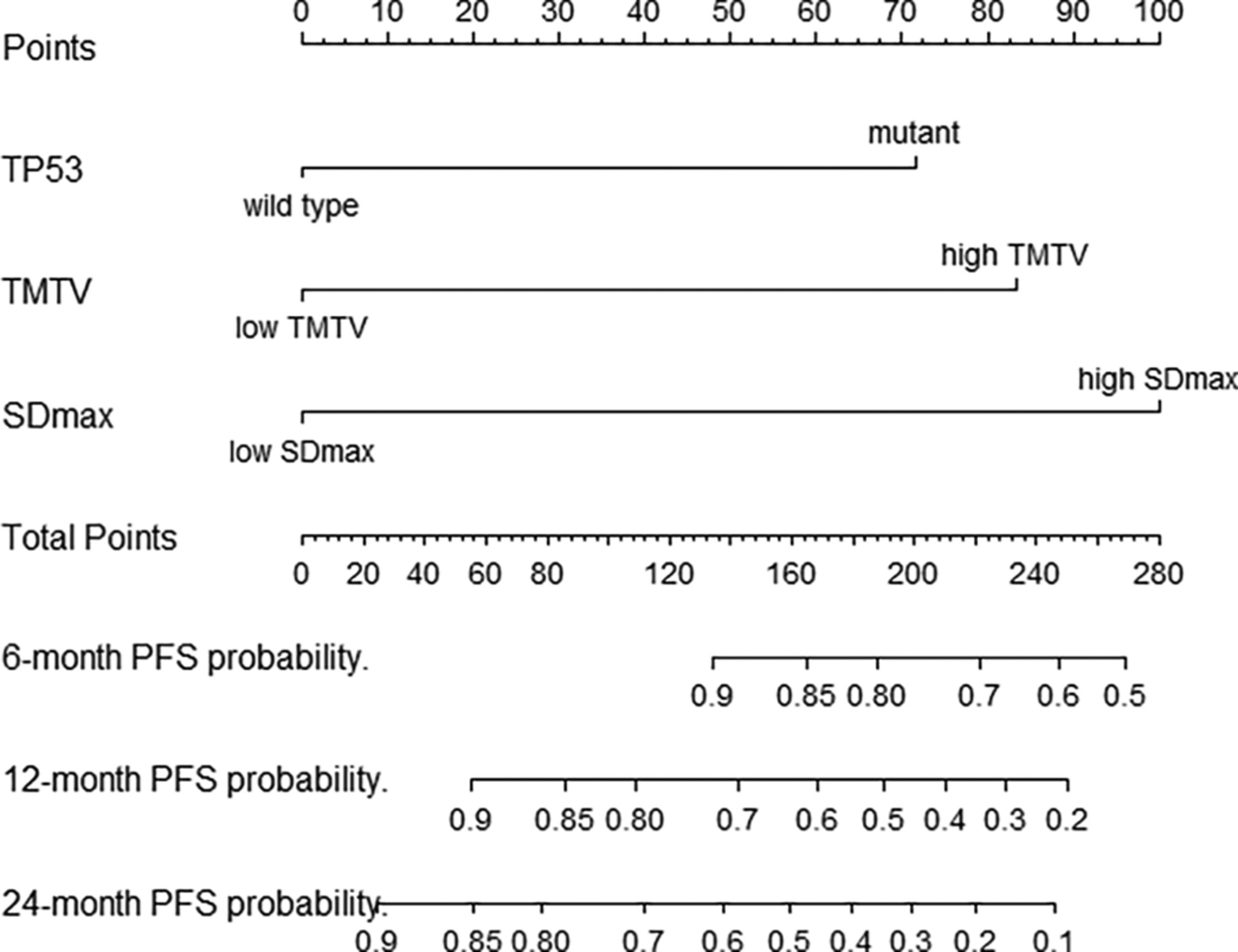
In the era of immunity and targeted therapy, the existing International Prognostic Index scoring system has failed to fully identify high-risk population for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). By analyzing the positron emission tomography/computed tomography parameters and next-generation sequencing of primary DLBCL patients in the training cohort and validation cohort, we found the nomogram based on imaging factors and TP53 status could lead to a more accurate selection of DLBCL patients with rapid progression, to increase tailor therapy.
Estimating the influencing factors for T1b/T2 gallbladder cancer on survival and surgical approaches selection
- Pages: 16744-16755
- First Published: 27 June 2023
REVIEW
Clinical Cancer Research
Potential role of intratumor bacteria outside the gastrointestinal tract: More than passengers
- Pages: 16756-16773
- First Published: 28 June 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
Overexpression of CD73 is associated with recurrence and poor prognosis of gingivobuccal oral cancer as revealed by transcriptome and deep immune profiling of paired tumor and margin tissues
- Pages: 16774-16787
- First Published: 01 July 2023
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
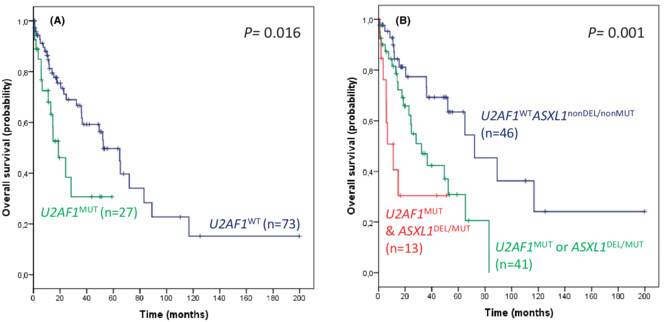
Incidence and prognostic impact of U2AF1 mutations and other gene alterations in myelodysplastic neoplasms with isolated 20q deletion
- Pages: 16788-16792
- First Published: 05 July 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
Effectiveness, safety, and impact on quality of life of eribulin-based therapy in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic breast cancer: A real-world analysis
- Pages: 16793-16804
- First Published: 05 July 2023
The present study suggests that eribulin-based therapy is an effective treatment option and well tolerated for heavily pre-treated patients with MBC. Eribulin combination therapy might improve PFS and HRQoL compared with eribulin monotherapy.
A multicenter prospective study of TACE combined with lenvatinib and camrelizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus
- Pages: 16805-16814
- First Published: 30 June 2023
Primary cardiac sarcomas: A clinicopathologic study in a single institution with 25 years of experience with an emphasis on MDM2 expression and adjuvant therapy for prognosis
- Pages: 16815-16828
- First Published: 03 July 2023
Misuse of tumor marker levels leads to an insufficient International Germ Cell Consensus Classification (IGCCCG) risk group assignment and impaired treatment
- Pages: 16829-16836
- First Published: 01 July 2023
Primary resistance to nivolumab plus ipilimumab therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 16837-16845
- First Published: 05 July 2023
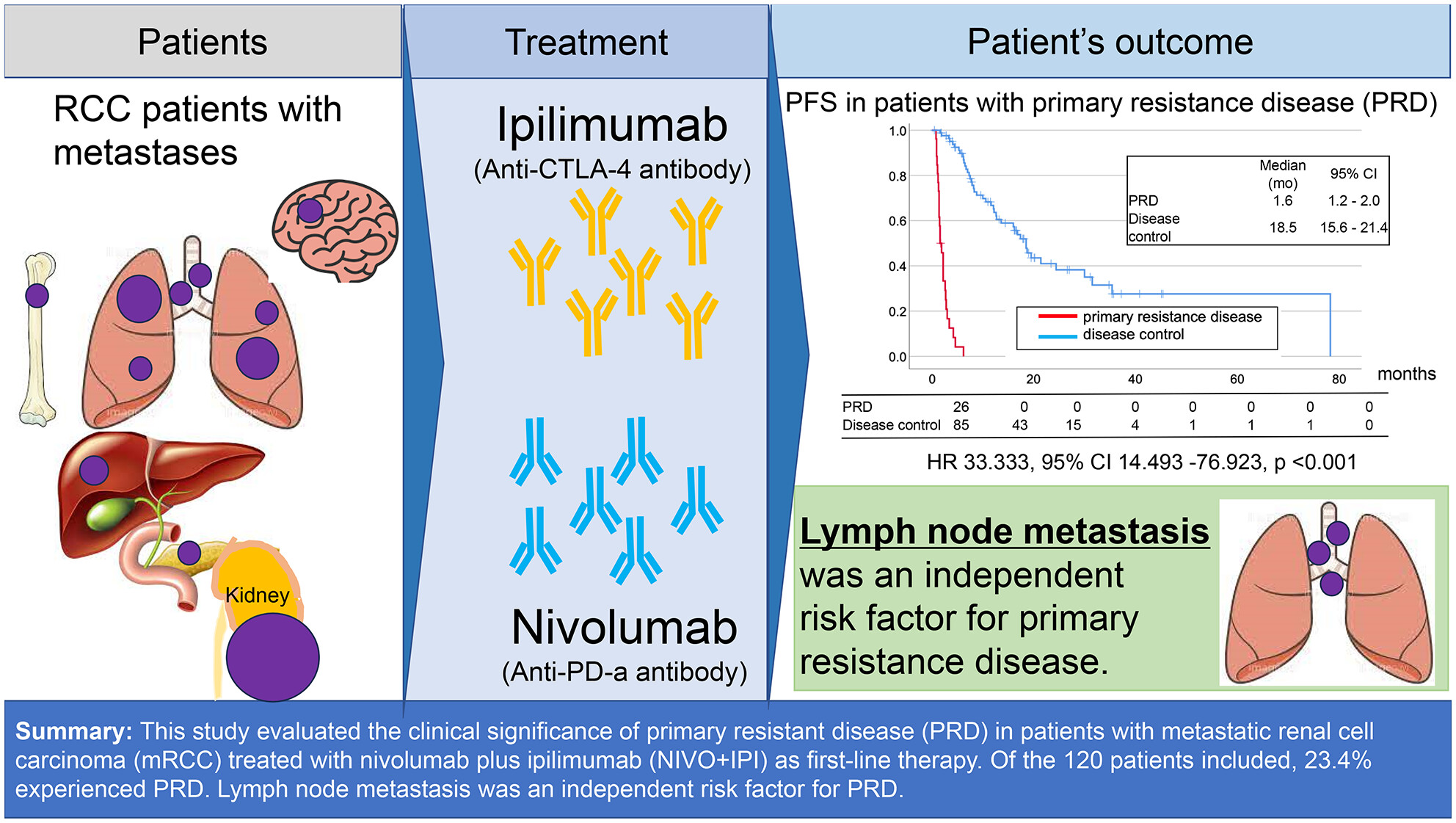
This study evaluated the clinical significance of primary resistant disease (PRD) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) treated with nivolumab plus ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) as first-line therapy. Of the 120 patients included, 23.4% experienced PRD, which was associated with worse overall survival (hazard ratio: 4.525). Lymph node metastasis (LNM) was an independent risk factor for PRD. This study suggests that LNM could be used to identify patients who may not benefit from NIVO+IPI as first-line therapy.
Learning curve of trans-areola single-site endoscopic thyroidectomy in a high-volume center: A CUSUM-based assessment
- Pages: 16846-16858
- First Published: 03 July 2023
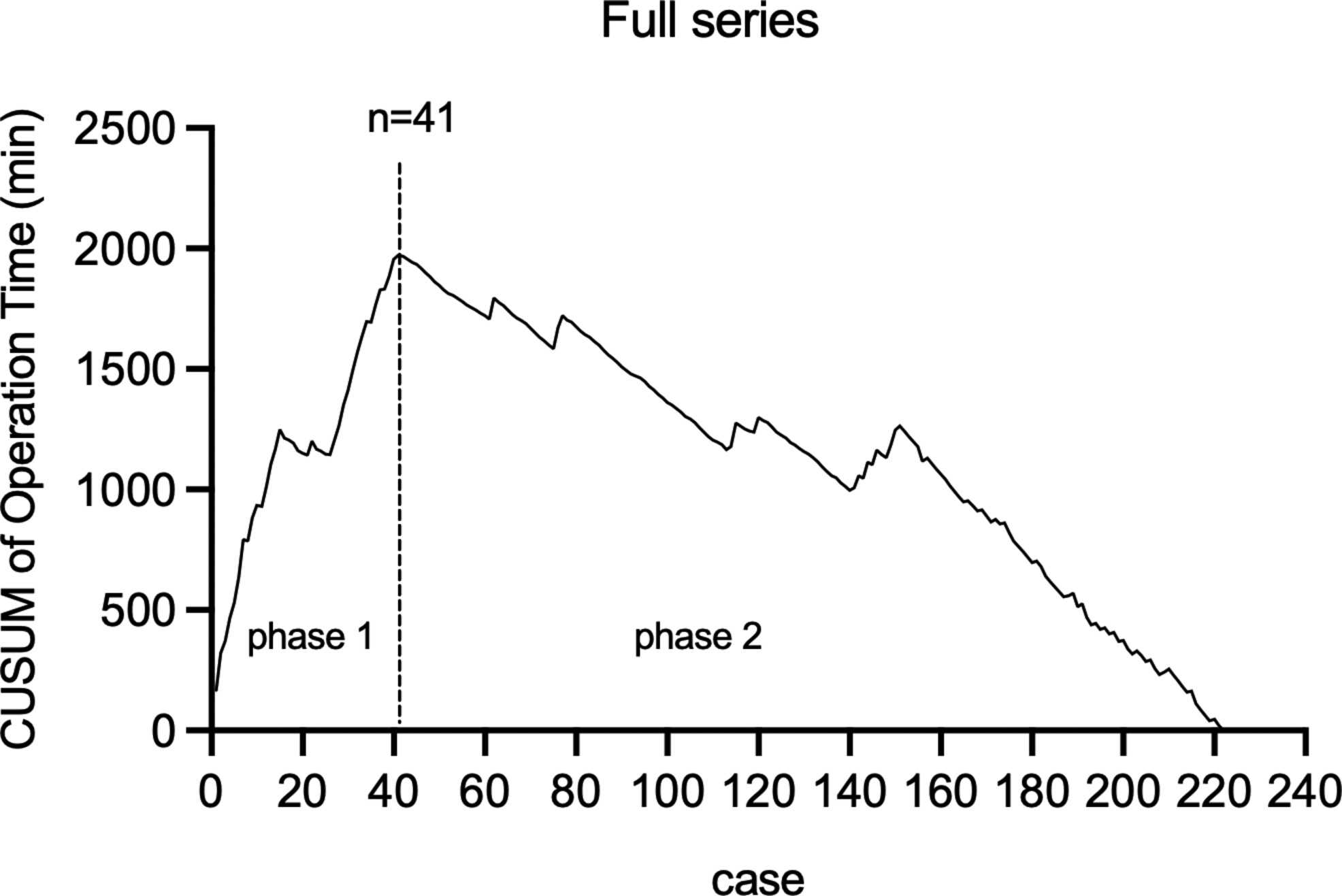
The present study is the first one to evaluate the learning curve of trans-areola single-site endoscopic thyroidectomy (TASSET) in terms of operation time and surgical stress. Experience of 41 cases was required for surgical competence and proficiency in TASSET and benign nodule cases were recommended for the learning stage.
Effect of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibition on cancer events: A pooled, post hoc, competing risk analysis of alirocumab clinical trials
- Pages: 16859-16868
- First Published: 17 July 2023
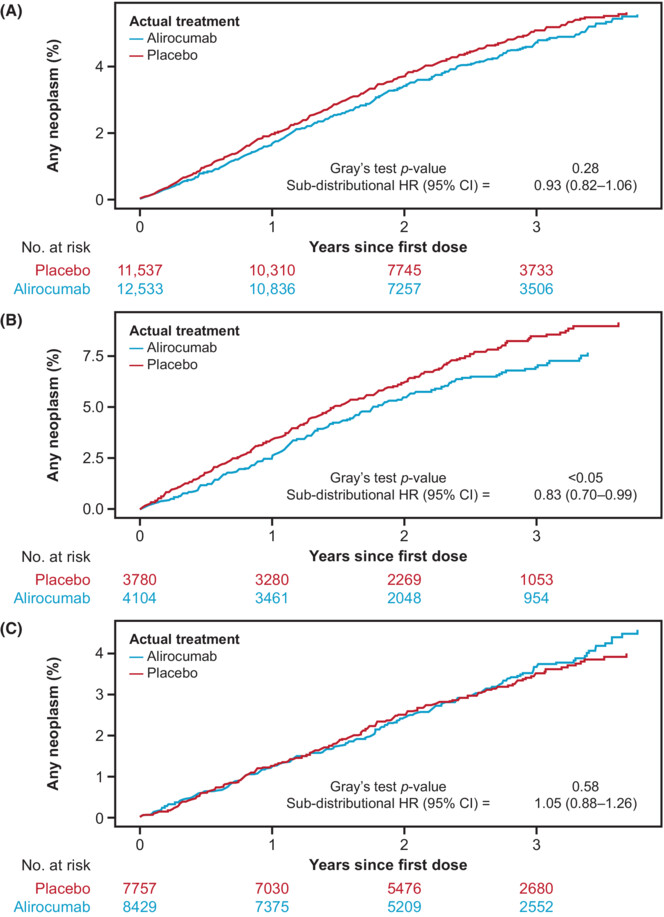
The risk of new and worsening cancer events was assessed among participants who received the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor alirocumab combined with a statin. Our results demonstrated that intensive low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering does not appear to increase the risk of new or worsening cancer events.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
Updated COVID-19 clearance time among patients with cancer in the Delta and Omicron waves
- Pages: 16869-16875
- First Published: 01 July 2023
We conducted a retrospective review of oncology patients with COVID-19 infection at a single tertiary care center during the Delta and Omicron waves and compared clearance strategies. Median clearance as defined by two consecutive negative tests was 32 days, and was prolonged in hematologic malignancy and in patients who received B-cell depletion. Single-negative test clearance showed high recurrence in patients with hematologic malignancy but may be appropriate for patients with solid tumors.
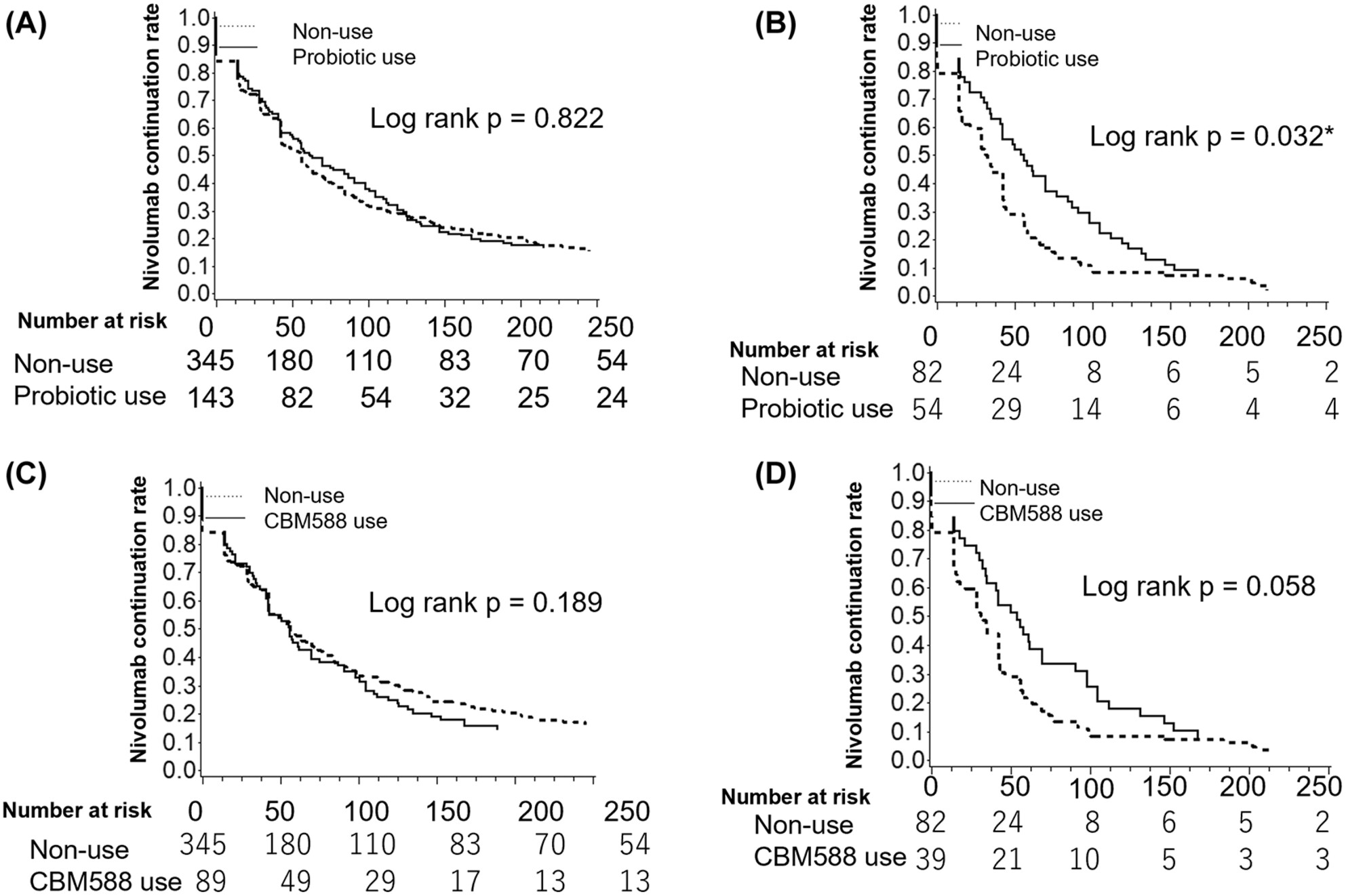
Association of probiotic use with nivolumab effectiveness against various cancers: A multicenter retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 16876-16880
- First Published: 08 July 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
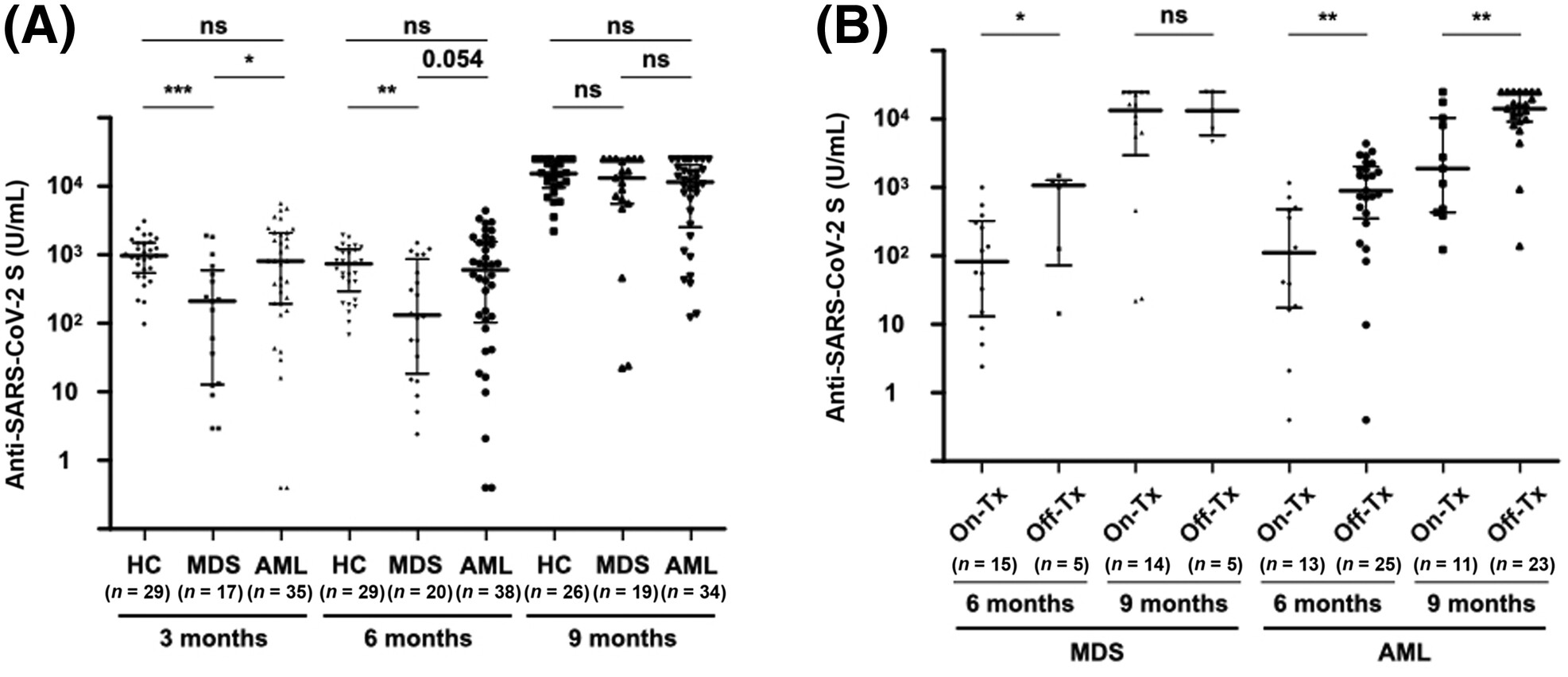
Booster effect of a third mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine dose in patients with myeloid malignancies
- Pages: 16881-16888
- First Published: 06 July 2023
Compliance to genomic test recommendations to guide adjuvant chemotherapy decision-making in the case of hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer, in real-life settings
- Pages: 16889-16895
- First Published: 06 July 2023
Lobe-specific analysis of perioperative chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer patients
- Pages: 16896-16905
- First Published: 05 July 2023
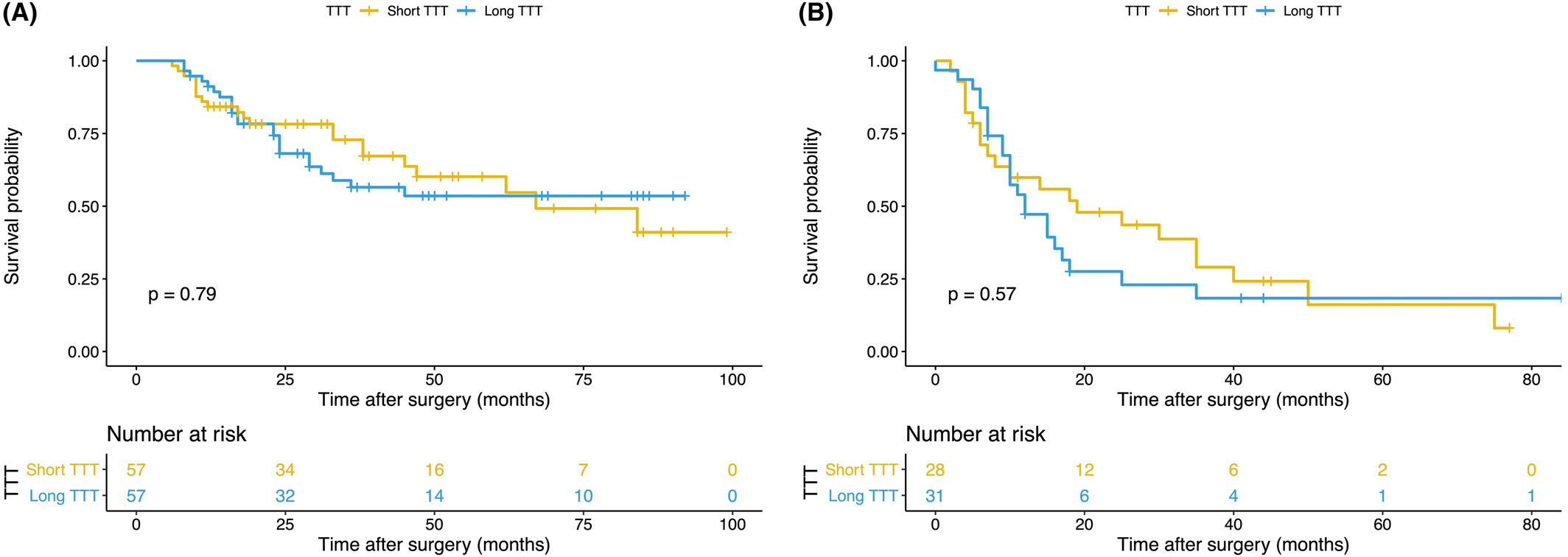
The impact of preoperative waiting time in Stage II–III gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: A population-based cohort study
- Pages: 16906-16917
- First Published: 04 July 2023
The population-based study suggests that preoperative waiting within an acceptable range dose not impact the survival in Stage II–III gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer.
Predictive and prognostic role of early apolipoprotein A-I alteration in recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with anti-PD-1 therapy
- Pages: 16918-16928
- First Published: 06 July 2023
Clinical outcome of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia patients. Real-life experience in a University Hospital and a Cancer Center in France
- Pages: 16929-16944
- First Published: 07 August 2023
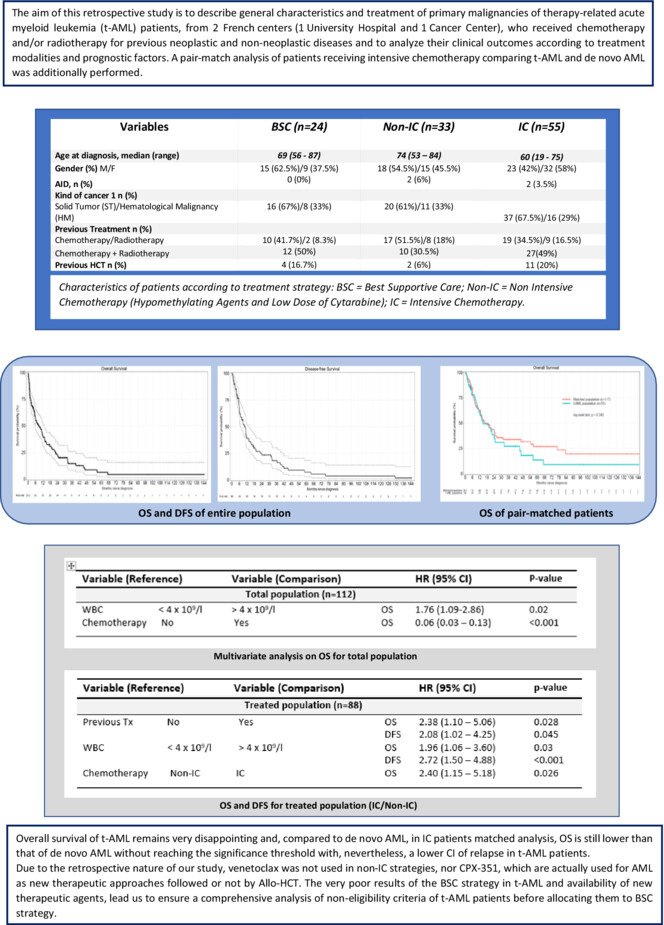
Therapy-related AML patients had for the majority of them unfavorable features. Among whole population of our study 50% of patients received intensive chemotherapy (71% of CR), 30% nonintensive chemotherapy (12% of CR) and the rest, best supportive care. Median OS and Median DFS were 9 months and 6.3 months in the whole population and 13.5 months and 8.2 months in treated population. Best outcomes obtained in patients receiving IC must be balanced by known confounding variables and should be improved by using new innovative agents and therapeutic strategies.
Clinical outcome assessment trends in clinical trials—Contrasting oncology and non-oncology trials
- Pages: 16945-16957
- First Published: 08 July 2023
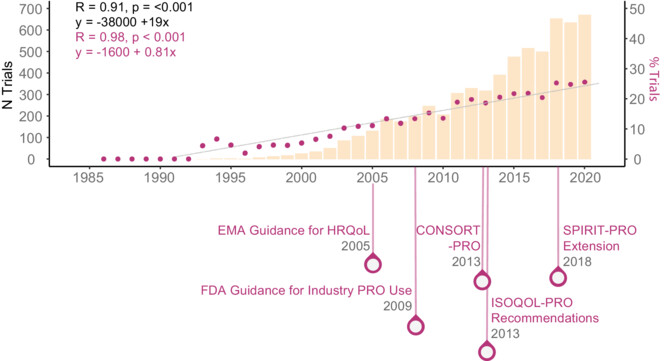
Comprehensive evaluation of interventional clinical trials in the ClinicalTrials.gov registry revealed low but increasing rates of clinical outcome assessment incorporation in oncology trials. While the study revealed a positive impact of regulatory and advocacy efforts on increasing use of clinical outcome assessments, there remains a need to further target early phase and treatment-focused oncology trials.
Prediction of malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: A nomogram based on clinical information and radiological outcomes
- Pages: 16958-16971
- First Published: 11 July 2023
With the hope of improving the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas, we developed a new malignancy-predicted nomogram for IPMN, based on five verified independent predictors of malignant IPMN in our study. We employed Prognostic nutrition index (PNI) to constructed the nomogram for the first time and stratified the diameter of main pancreatic duct and the size of Mural Nodules which were helpful to achieve a more precise risk for malignancy. The nomogram shows excellent capability in predicting malignant IPMN and has a promising application potential.
Utility of cerebrospinal fluid liquid biopsy in distinguishing CNS lymphoma from cerebrospinal infectious/demyelinating diseases
- Pages: 16972-16984
- First Published: 27 July 2023
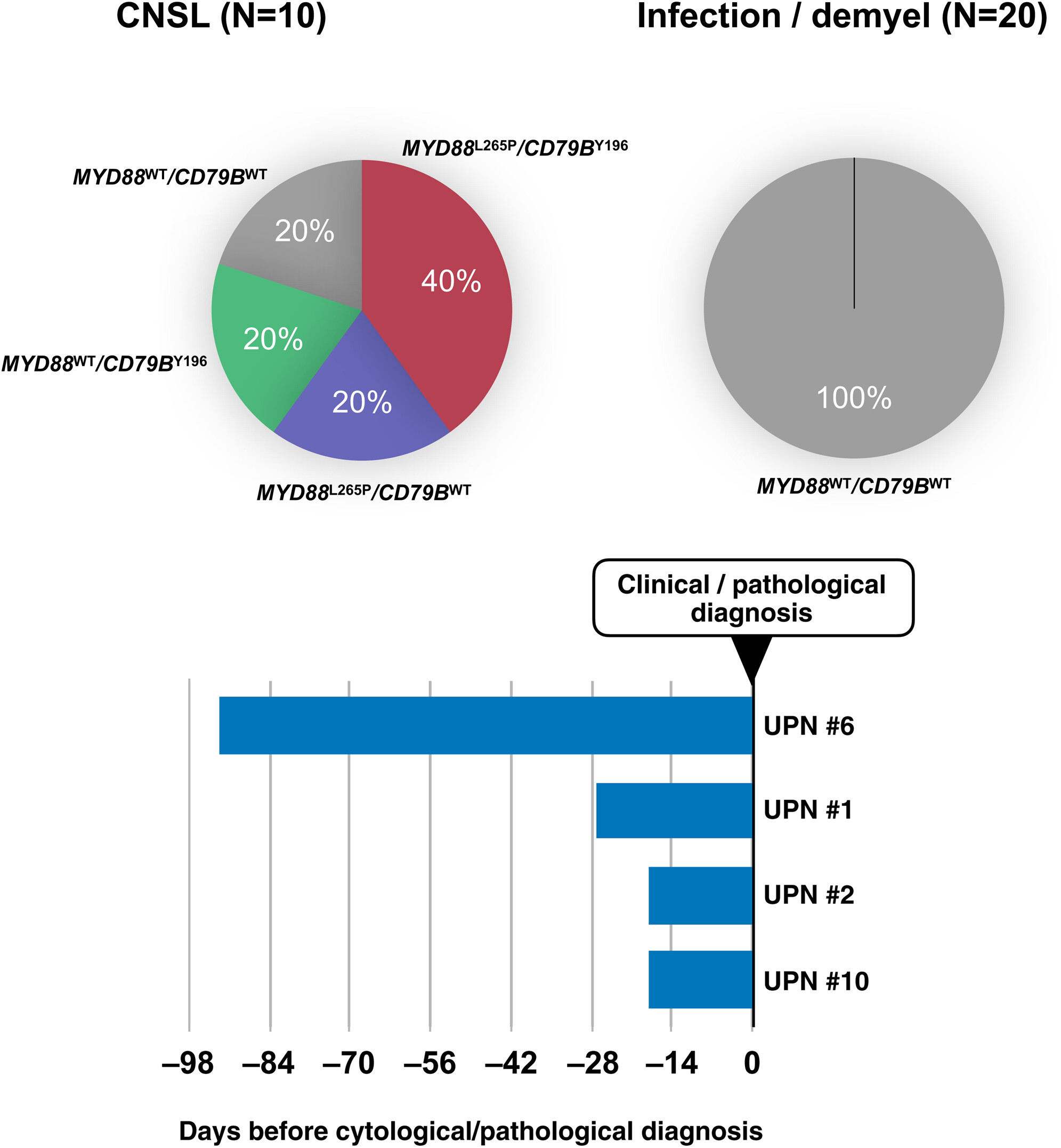
Genetic analyses using cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA (CSF-cfDNA) (liquid biopsy) is a useful strategy for distinguishing central nervous system lymphoma (CNSL) from CNS infectious/demyelinating diseases. Genetic analysis using CSF-cfDNA can be contribute to earlier detection of CNSL than conventional methods.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells exhibit increased mitochondrial respiration after adjuvant chemo- and radiotherapy for early breast cancer
- Pages: 16985-16996
- First Published: 13 July 2023
Comparison of gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin versus gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel as first-line chemotherapy for advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A single-center retrospective analysis
- Pages: 16997-17004
- First Published: 03 August 2023
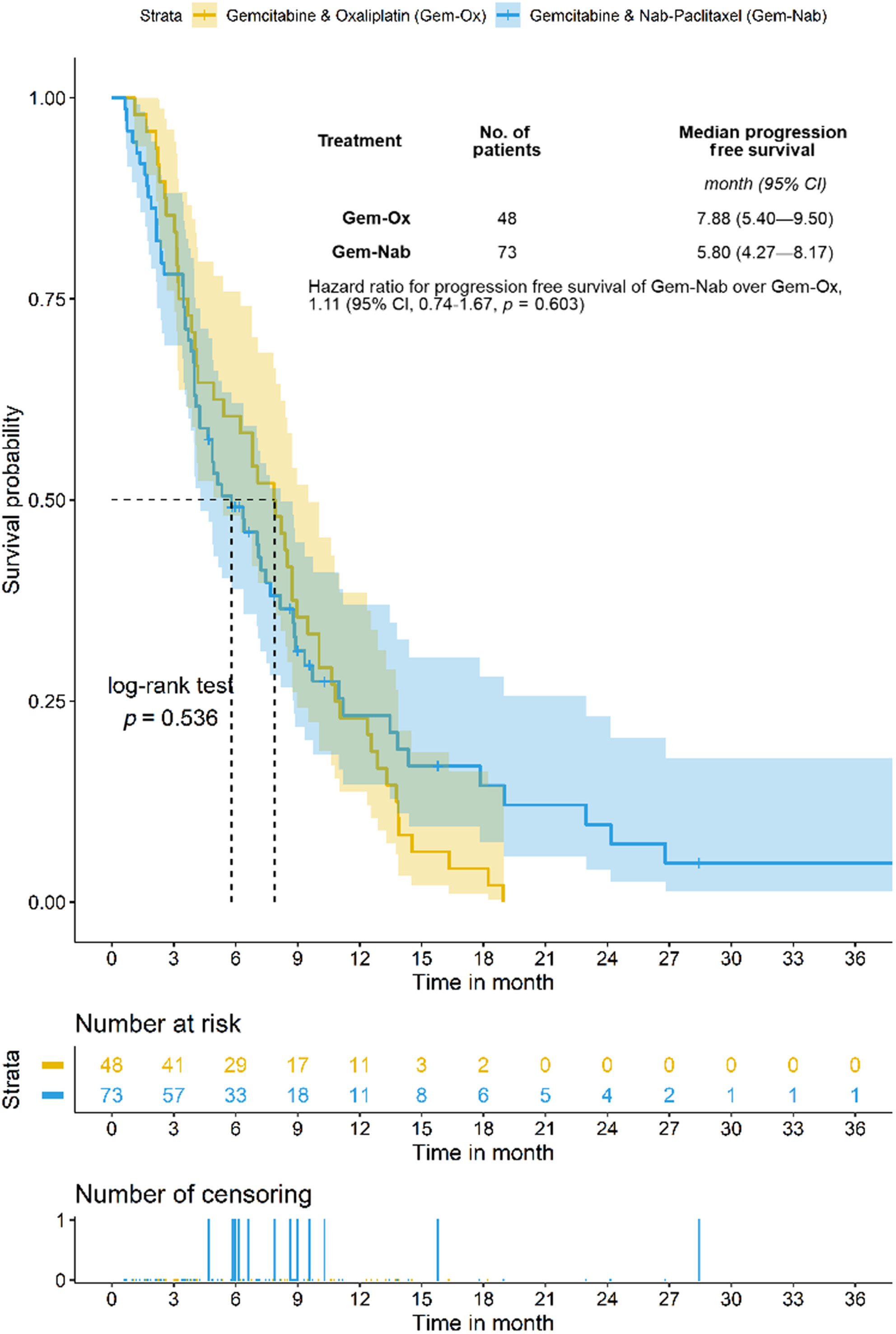
This single-center retrospective real world study includes 121 patients diagnosed with locally advanced or primary metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma who were treated with chemotherapy doublet, with either Gem-Nab or Gem-Ox in palliative first-line. Survival rates were analyzed using the Kaplan–Meier method, and comparisons were made with log-rank tests.
A deep learning model using hyperspectral image for EUS-FNA cytology diagnosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 17005-17017
- First Published: 17 July 2023
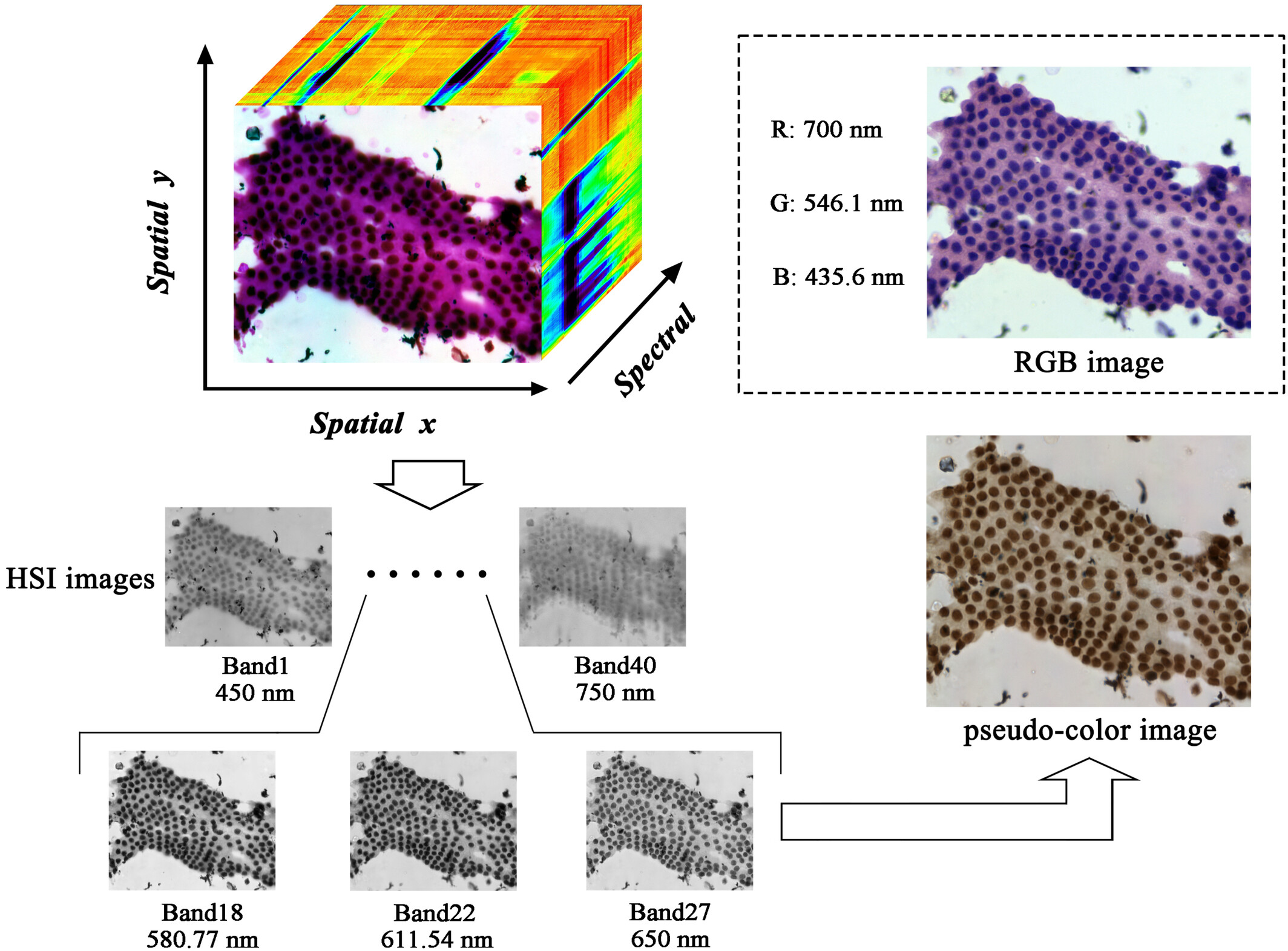
Accurate pathological diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) poses a challenge for cytopathologists. Therefore, we aimed to develop a hyperspectral imaging (HSI)-based convolution neural network (CNN) algorithm to aid in the diagnosis of pancreatic cytology specimens obtained using endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration/biopsy (EUS-FNA/B). A total of 1913 HSI images were obtained from 33 benign pancreatic tissue samples and 39 PDAC specimens, and the model was trained on these images.
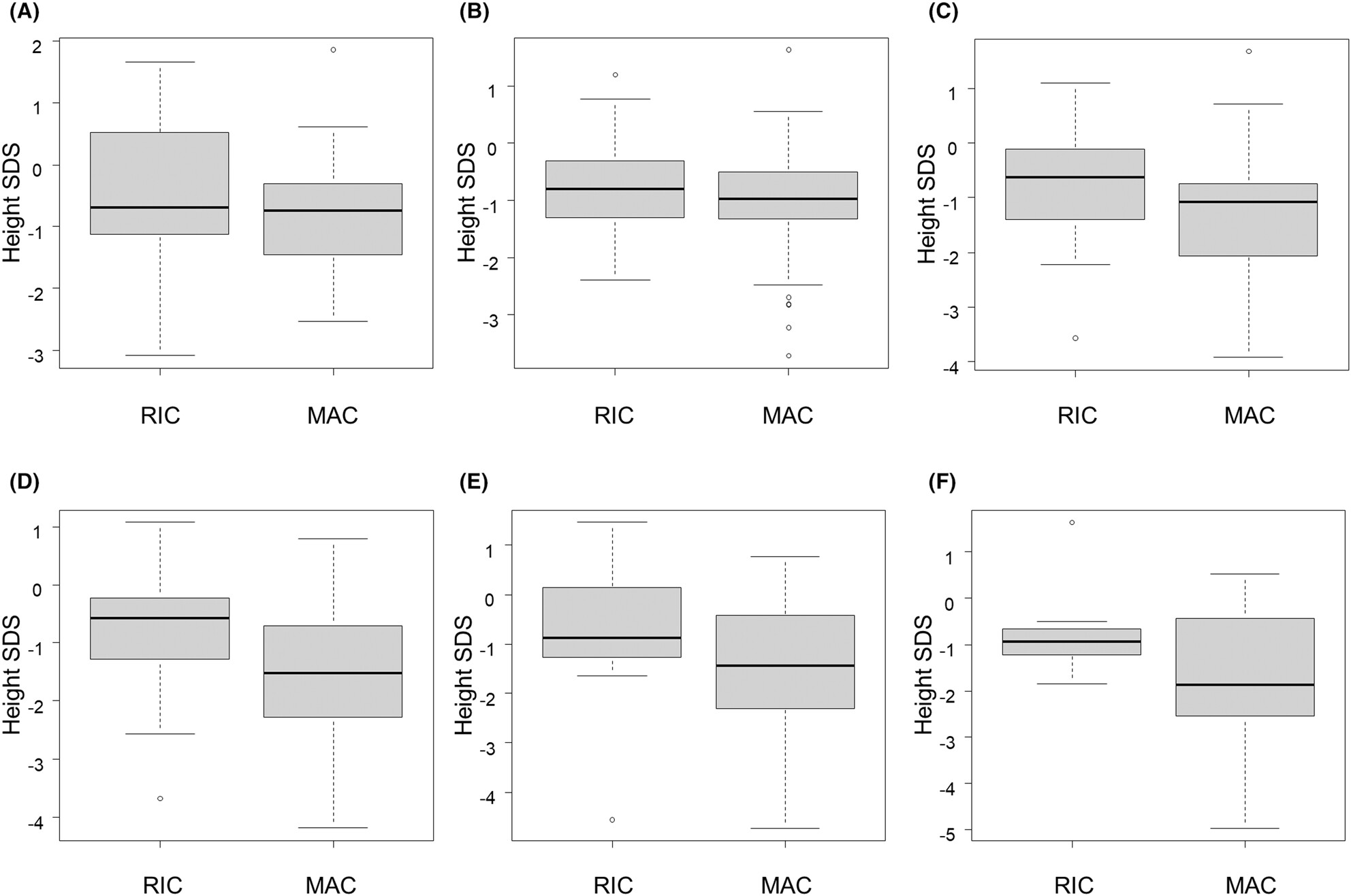
Association between conditioning intensity and height growth after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children
- Pages: 17018-17027
- First Published: 11 July 2023
Micro-histology combined with cytology improves the diagnostic accuracy of endometrial lesions
- Pages: 17028-17036
- First Published: 17 July 2023
Insurance status impacts survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients after liver resection
- Pages: 17037-17046
- First Published: 16 July 2023
The rare entity of gastrointestinal leiomyosarcomas: An Italian multicenter retrospective study in high-volume referral centers
- Pages: 17047-17055
- First Published: 16 July 2023
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
Association between serum uric acid and prostate cancer mortality in androgen deprivation therapy: A population-based cohort study
- Pages: 17056-17060
- First Published: 16 July 2023
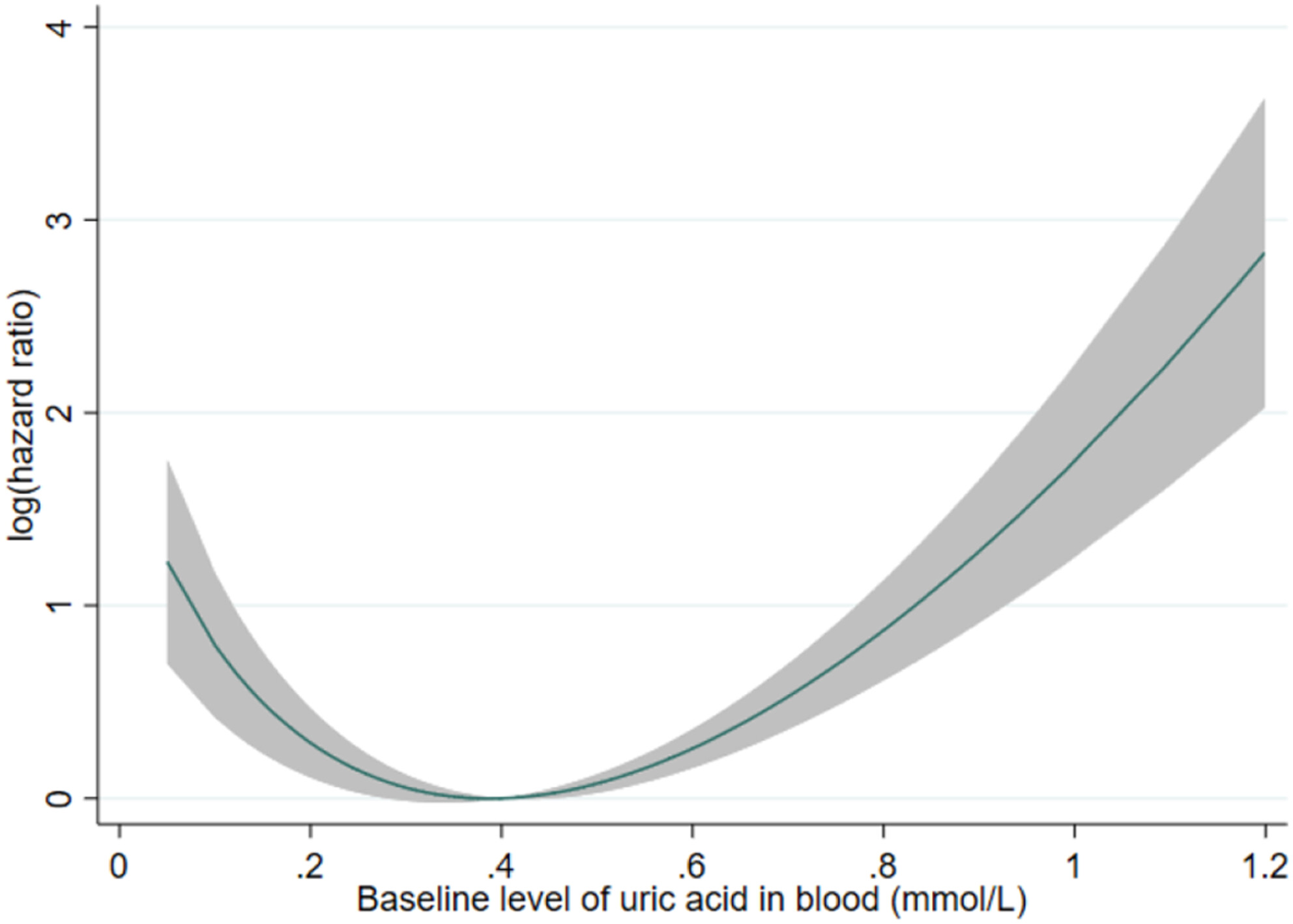
Amongst patients with prostate cancer undergoing androgen deprivation therapy, a J-shape relationship exists between baseline uric acid level and the risk of prostate cancer-related mortality, with both high and low uric acid levels being associated with similarly elevated risks when compared against normal uric acid levels.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
First-line nivolumab, paclitaxel, carboplatin, and bevacizumab for advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: Updated survival analysis of the ONO-4538-52/TASUKI-52 randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 17061-17067
- First Published: 28 August 2023
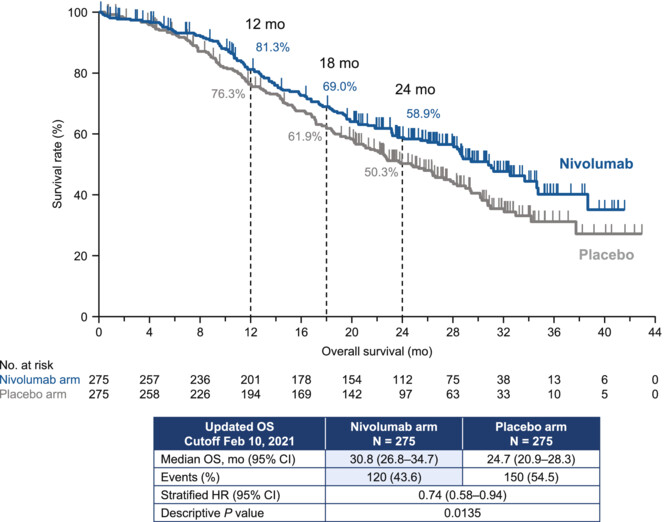
The ONO-4538-52/TASUKI-52 study investigated the efficacy and safety of nivolumab versus placebo, both combined with platinum chemotherapy and bevacizumab, as first-line treatment for advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). After a minimum follow-up of 19.4 months, overall survival significantly favored the nivolumab arm, and this survival benefit was observed regardless of programmed death-ligand 1 expression level. These results indicate that nivolumab plus platinum chemotherapy and bevacizumab is an effective option for treatment-naive patients with advanced non-squamous NSCLC without driver mutations.
FDG uptake reflects an immune-enriched subtype of thyroid cancer: Clinical implications of imaging-based molecular characterization
- Pages: 17068-17077
- First Published: 19 July 2023
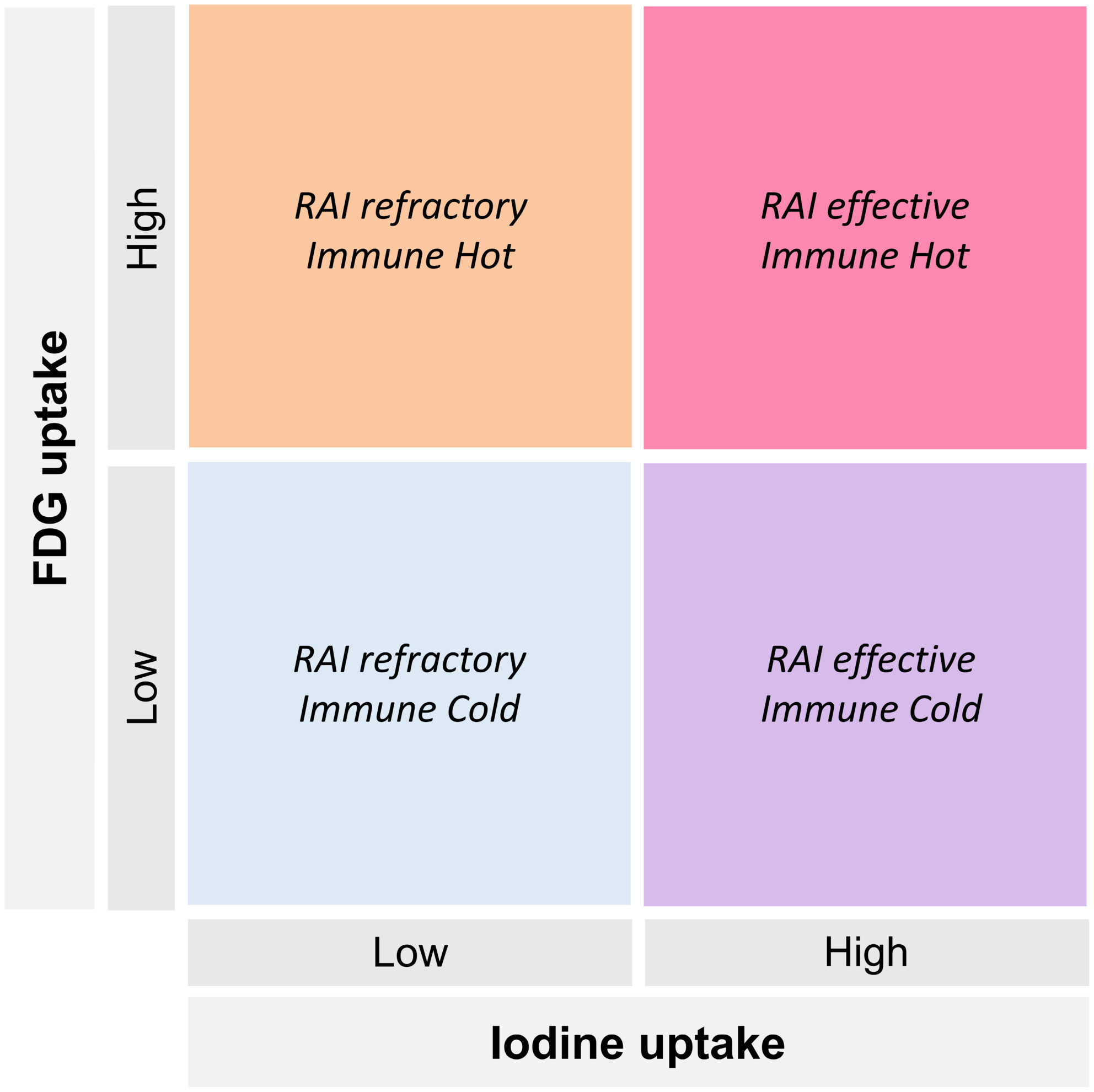
Thyroid cancers can be divided into radioactive iodine (RAI) refractory and RAI effective cancers depending on the degree of iodine uptake. In addition, thyroid cancers are further classified as immune cold and immune hot because FDG uptake represents the immune abundancy of the thyroid cancer microenvironment.
Induction chemotherapy-based organ-preservation protocol improve the function preservation compared with immediate total laryngectomy for locally advanced hypopharyngeal cancer—Results of a matched-pair analysis
- Pages: 17078-17086
- First Published: 19 July 2023
The prognosis of clinical stage IIIa non-small cell lung cancer in Taiwan
- Pages: 17087-17097
- First Published: 26 July 2023
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on paediatric renal tumour presentation and management, a SIOP renal tumour study group study
- Pages: 17098-17111
- First Published: 26 July 2023
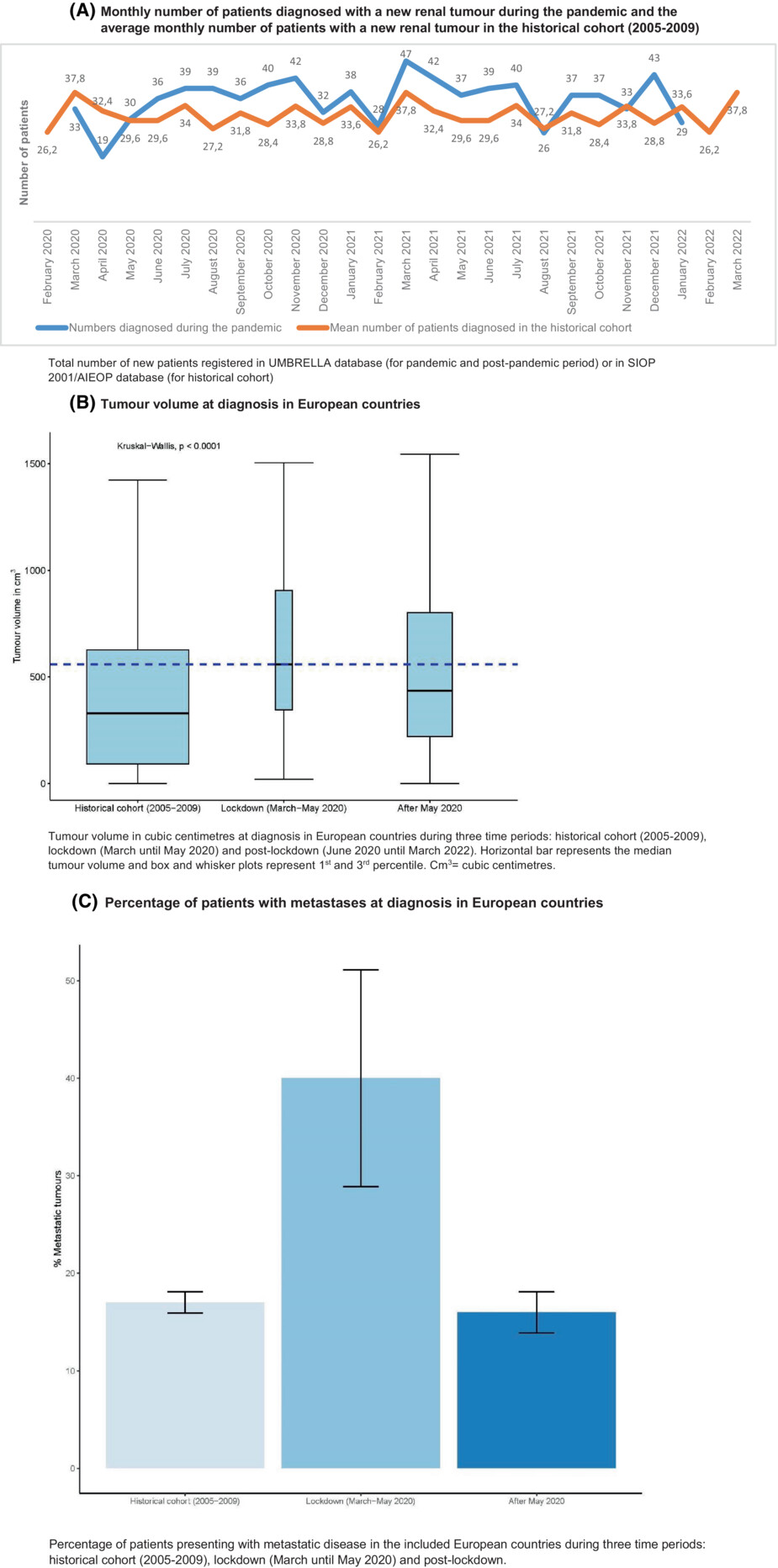
The COVID-19 pandemic briefly changed the tumour characteristics of children presenting with renal tumours. During the first peak of COVID-19, more children presented with metastatic disease and median tumour volume was higher. Further analyses after longer follow-up is needed to study the influence on clinical outcomes.
Real-world treatment outcomes of medicines used in special situations (off-label and compassionate use) in oncology and hematology: A retrospective study from a comprehensive cancer institution
- Pages: 17112-17125
- First Published: 26 July 2023
The study provides a real world data analysis of outcomes of off-label and compassionate uses in a large cohort of oncology and hematology patients from a comprehensive and multicenter cancer institution. Main findings showed that survival outcomes differ between hematology and oncology, and a higher ECOG and advanced disease stage were associated with worse survival. Enhancing our understanding of real-world outcomes associated with off-label and compassionate offers valuable insights that can improve clinical decision-making and contribute to the expanding body of knowledge in this field.
Efficacy of chemotherapy combined with surgical resection for gastric cancer with synchronous ovarian metastasis: A propensity score matching analysis
- Pages: 17126-17138
- First Published: 30 July 2023
Deep learning-based prediction of H3K27M alteration in diffuse midline gliomas based on whole-brain MRI
- Pages: 17139-17148
- First Published: 17 July 2023
Cancer Biology
Selenium-binding protein 1 inhibits malignant progression and induces apoptosis via distinct mechanisms in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 17149-17170
- First Published: 22 August 2023
Genomic alterations of oligodendrogliomas at distant recurrence
- Pages: 17171-17183
- First Published: 02 August 2023
The effects of coagulation factors and their inhibitors on proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 17184-17192
- First Published: 17 July 2023
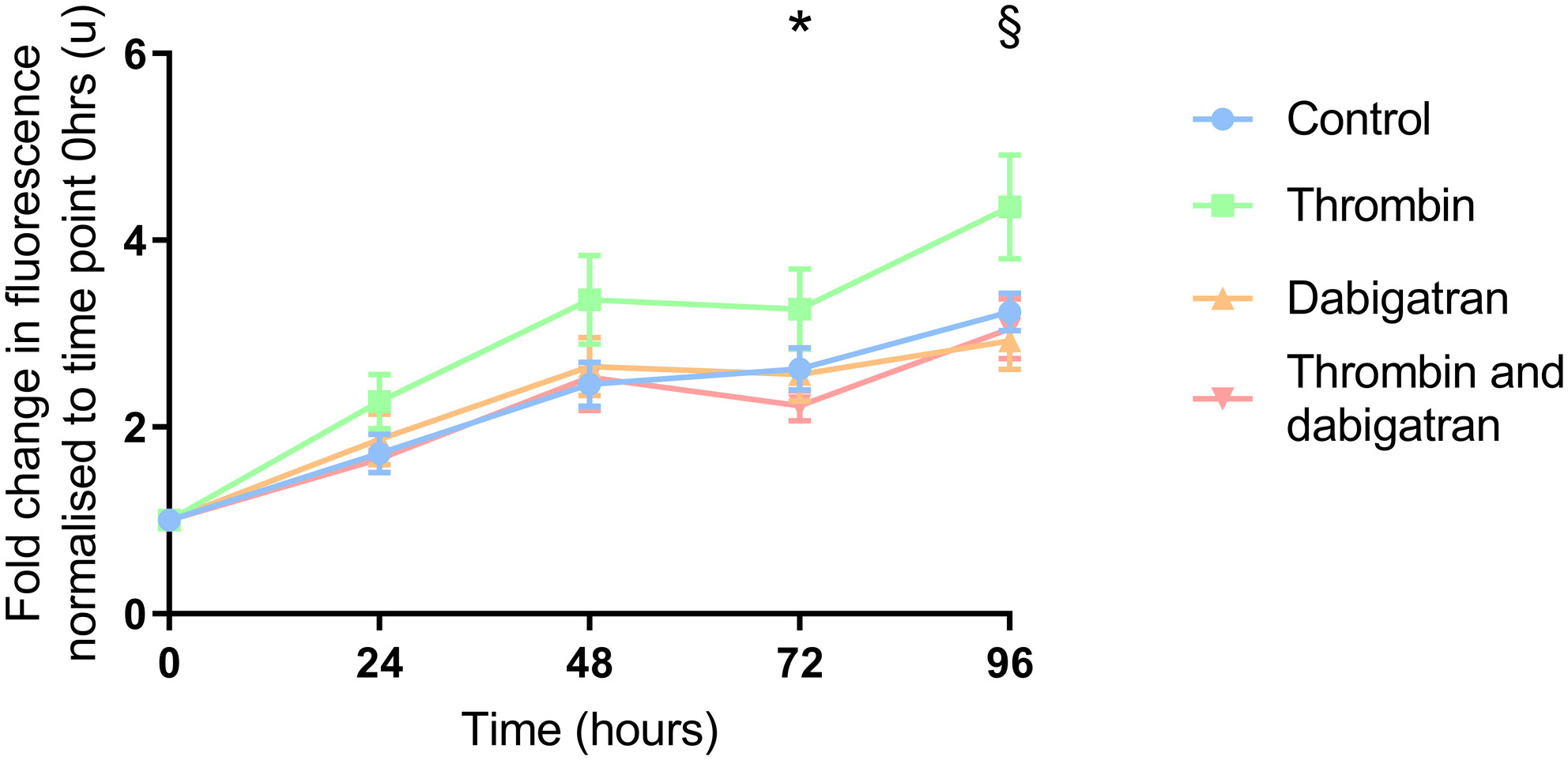
We investigated if coagulation proteins promote proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines, and whether their direct inhibitors can attenuate these effects. Thrombin, factor Xa and tissue factor all increase migration in CRC in vitro. A thrombin-induced increase in proliferation is abrogated by dabigatran.
ADT-OH synergistically enhanced the antitumor activity of celecoxib in human colorectal cancer cells
- Pages: 17193-17211
- First Published: 26 July 2023
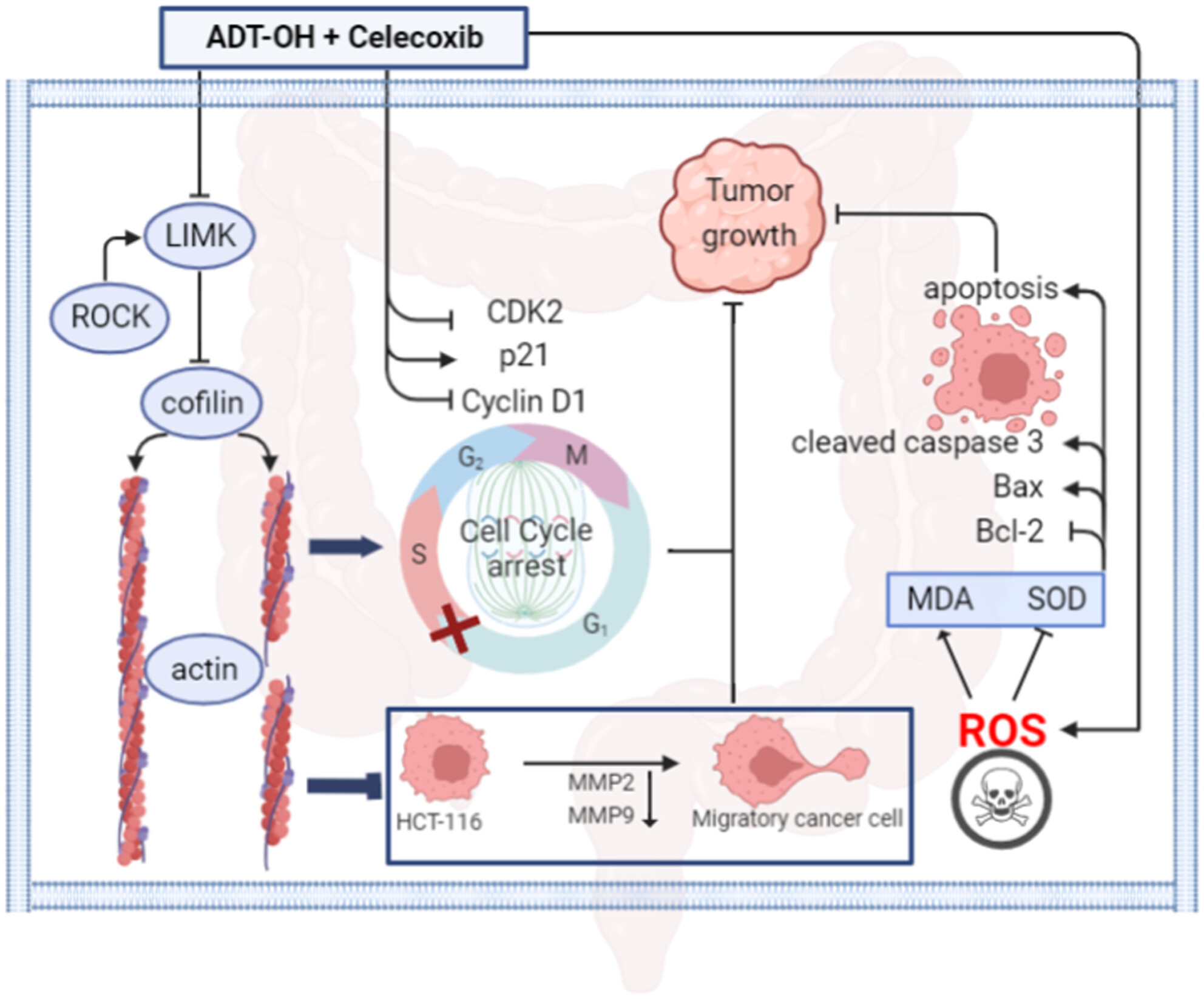
ADT-OH combined with celecoxib synergistically inhibited the proliferation and migration ability of human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells, altered the cell cycle and cytoskeleton, increased intracellular ROS, and promoted cell apoptosis (Figure 8). Furthermore, in vivo, experiments with HCT116 xenografts in nude mice showed that the combination therapy inhibited tumor growth more effectively than ADT-OH and celecoxib alone. In summary, this work elucidates the potential of ADT-OH combined with celecoxib as an effective combination therapy strategy for colorectal cancer patients.
ZDHHC11B is decreased in lung adenocarcinoma and inhibits tumorigenesis via regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Pages: 17212-17222
- First Published: 11 July 2023
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Cancer Prevention
Could B-scan technique compromise a promising clinical study?
- Pages: 17223-17224
- First Published: 23 June 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Prevention
Health status and mental distress in people with cancer and comorbid conditions: The Australian National Health Survey analysis
- Pages: 17225-17238
- First Published: 23 June 2023
Quality-of-life, mental health, and perspective on TKI dose reduction as a prelude to discontinuation in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 17239-17252
- First Published: 06 July 2023
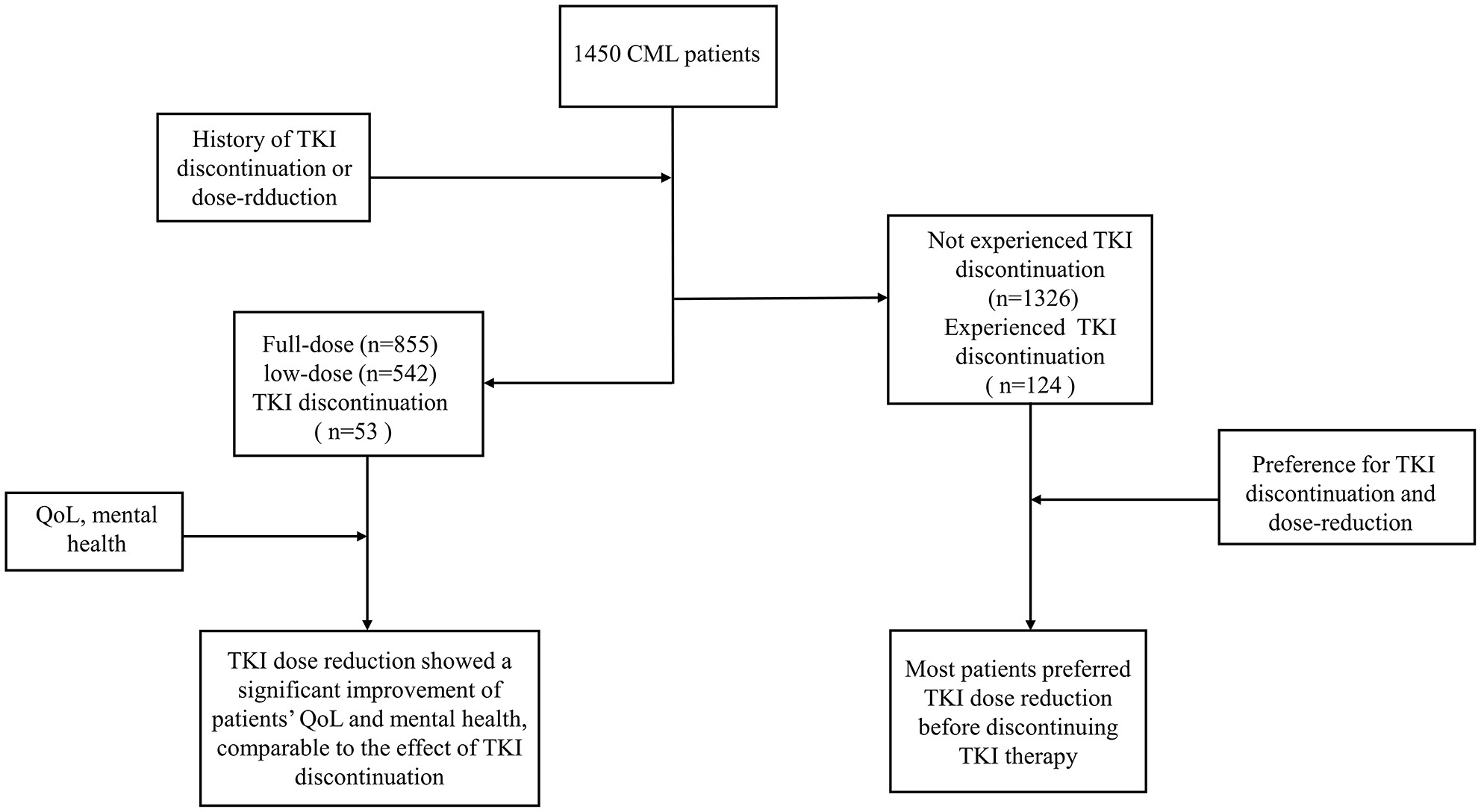
A cross-sectional study was conducted to explore the quality of life (QoL), mental health in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients with diverse tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) dose, and perspective on TKI dose reduction as a prelude to discontinuation. TKI dose reduction showed a significant improvement of patients' QoL and mental health, comparable to the effect of TKI discontinuation. Most patients preferred dose reduction before discontinuing TKI therapy. In clinical practice, TKI dose reduction can be considered as a bridge from full-dose TKI treatment to TKI discontinuation.
Age-specific cardiovascular disease-related mortality among patients with major gastrointestinal cancers: A SEER population-based study
- Pages: 17253-17265
- First Published: 30 June 2023
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Cancer Prevention
Esophageal cancer patients’ need for information and support in making a treatment decision between standard surgery and active surveillance
- Pages: 17266-17272
- First Published: 01 July 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Prevention
The role of a discussion forum within a web-based psychoeducational intervention focusing on sex and fertility—What do young adults communicate?
- Pages: 17273-17283
- First Published: 04 July 2023
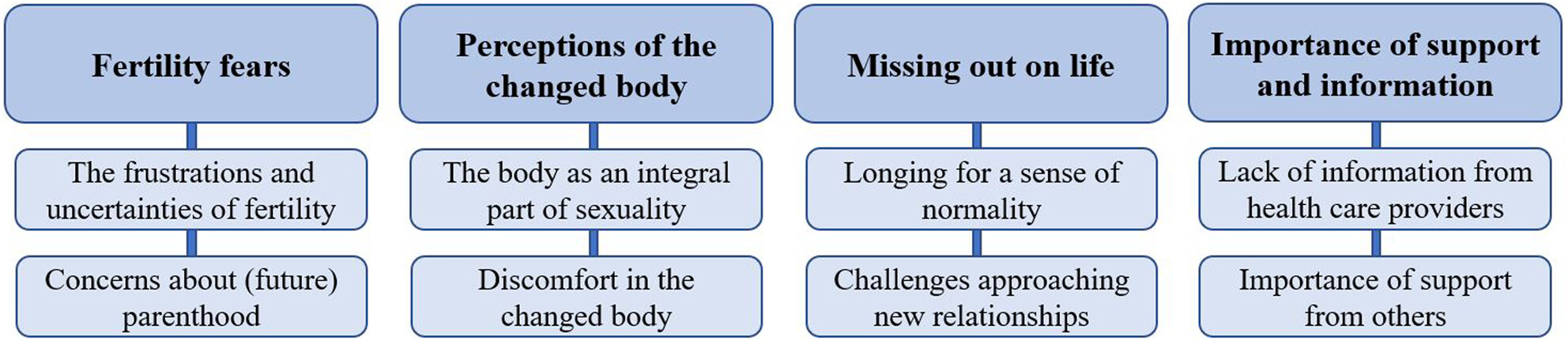
This study aimed to investigate interactive participation and content of a moderated discussion forum within a web-based intervention for young adult cancer survivors experiencing fertility distress and sexual dysfunction. The discussion forum was utilized by a majority of intervention participants, and provided appreciated support for those who posted in the forum. We recommend similar interventions to include this opportunity for interaction and communication among young adult cancer survivors.
Epidemiology of cervical cancer in elderly women: Analysis of incidence, treatment, and survival using German registry data
- Pages: 17284-17295
- First Published: 05 July 2023
Conventional and assisted suicide in Switzerland: Insights into a divergent development based on cancer-associated self-initiated deaths
- Pages: 17296-17307
- First Published: 09 August 2023
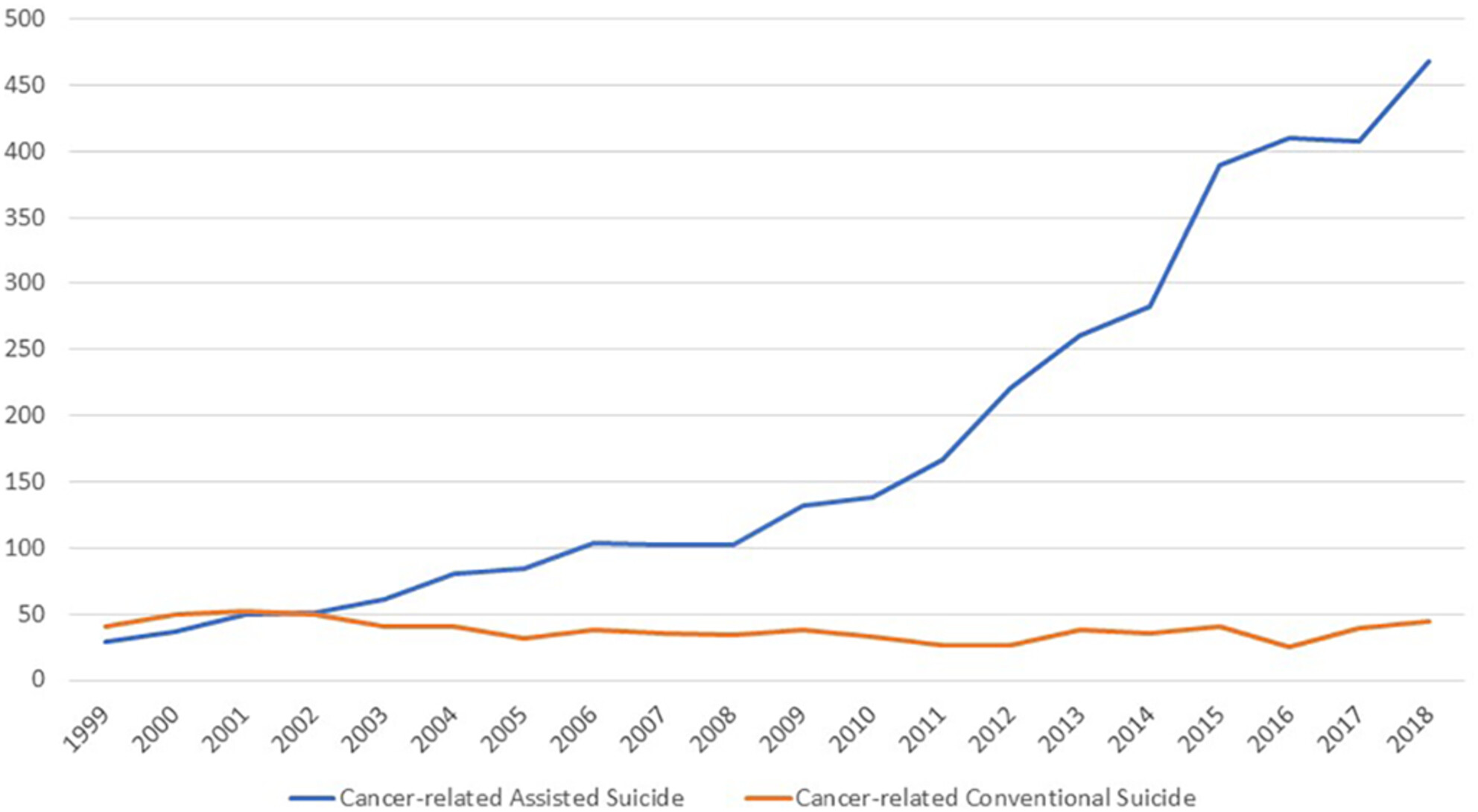
In order to test the hypothesis of supporters of assisted suicide (AS) that legalization of this procedure might be able to prevent cases of conventional suicide (CS), we tested the long-term development of 30,756 self-initiated deaths in Switzerland over a 20-year period (1999–2018; CS: n = 22,018, AS: n = 8738), focusing on people suffering from cancer who died from AS or CS. While cancer was the most often listed principal disease for AS (n = 3580, 41.0% of AS cases), cancer was listed in only a small minority of CS cases (n = 832, 3.8% of CS cases). There was a significant increase in the absolute number of cancer-associated AS cases in that there was approximately a doubling of cases every 5 years (1999–2003: n = 228, 2004–2008: n = 474, 2009–2013: n = 920, 2014–2018: n = 1958). In parallel, the numbers of cancer-associated CS remained comparatively stable (1999–2003: n = 240, 2004–2008: n = 199, 2009–2013: n = 187, 2014–2018, n = 206). The assumption that, with the increasingly accessible option of AS for patients with cancer, CS suicide will become “superfluous” cannot be confirmed. There are strong reasons indicating that situations and circumstances of cancer-associated CS are different from those for cancer-associated AS.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Cancer Prevention
Telehealth use and perceptions among prostate cancer survivors
- Pages: 17308-17312
- First Published: 16 July 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Prevention
A short screening tool identifying systemic barriers to distress screening in cancer care
- Pages: 17313-17321
- First Published: 12 July 2023
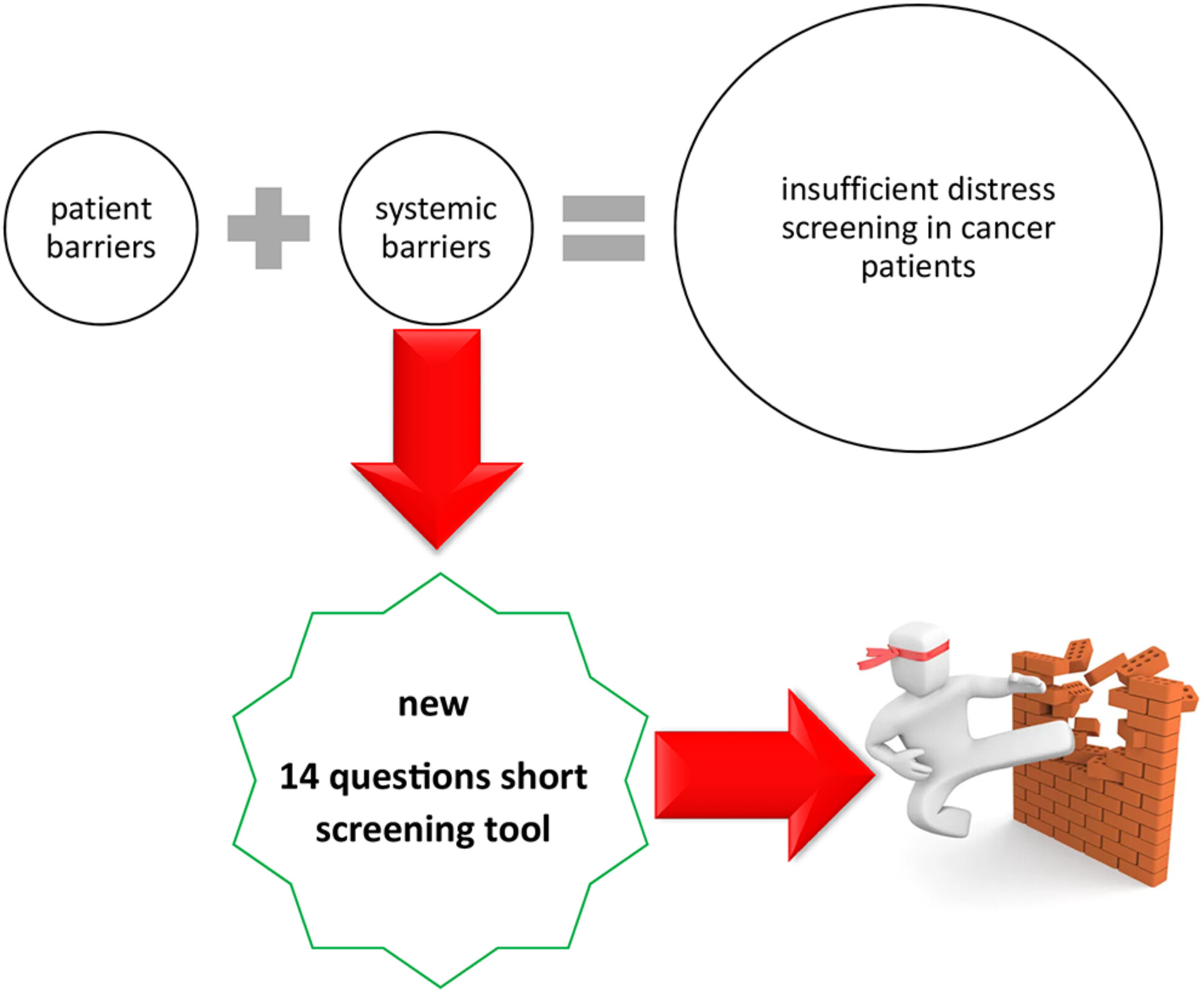
In this study we developed a new ultra short survey (14 questions) to identify (and possibly resolve) barriers to screening for distress in patients with cancer. Despite international guidelines recommending screening for distress in all cancer patients, screening rates are low internationally. The survey presented should be a tool for hospital administrators to rapidly identify reasons for low screening rates and implement remedies. The study also presents results from surveying a total of 248 nurses in Switzerland responsible for distress screening on their perceived barriers. Across several hospitals in Switzerland, the timing of the first distress screening, lack of capacity, patient and staff overload, and refusal of distressed patients to be referred to support services emerged as major problems.
Availability of cancer care services and the organization of care delivery at critical access hospitals
- Pages: 17322-17330
- First Published: 12 July 2023
Associations between health insurance status, neighborhood deprivation, and treatment delays in women with breast cancer living in Georgia
- Pages: 17331-17339
- First Published: 12 July 2023
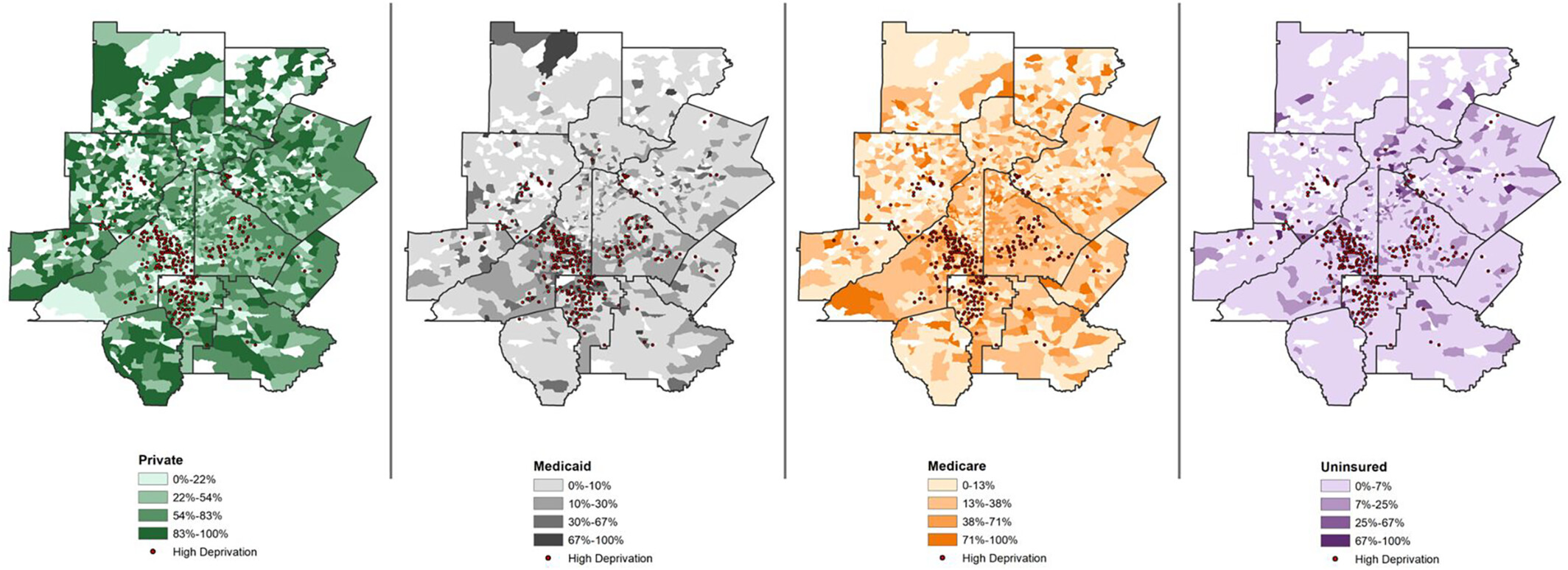
This study of women with breast cancer living in Georgia showed that patients who were Medicare enrollees, Medicaid enrollees, and uninsured had significantly higher odds of treatment delays compared to privately insured patients. Significant differences in odds of treatment delays by insurance coverage were observed for patients living in neighborhoods of low deprivation but not for those living in areas of high deprivation. Policy and interventions should target equity in insurance coverage to improve timely treatment initiation.
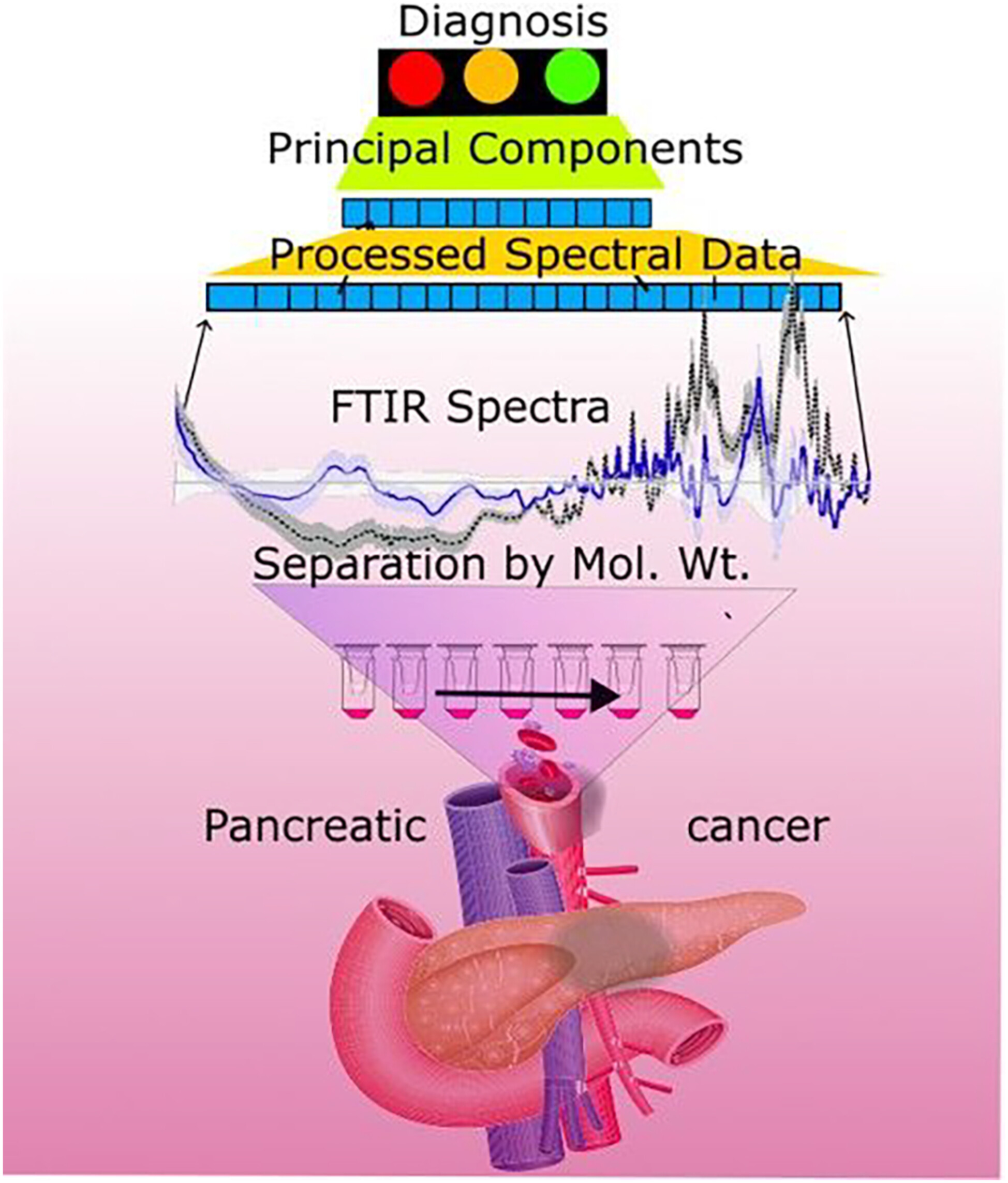
Frontline clinical diagnosis—FTIR on pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 17340-17345
- First Published: 19 July 2023
Health care delivery system contributions to management of newly diagnosed prostate cancer
- Pages: 17346-17355
- First Published: 20 July 2023
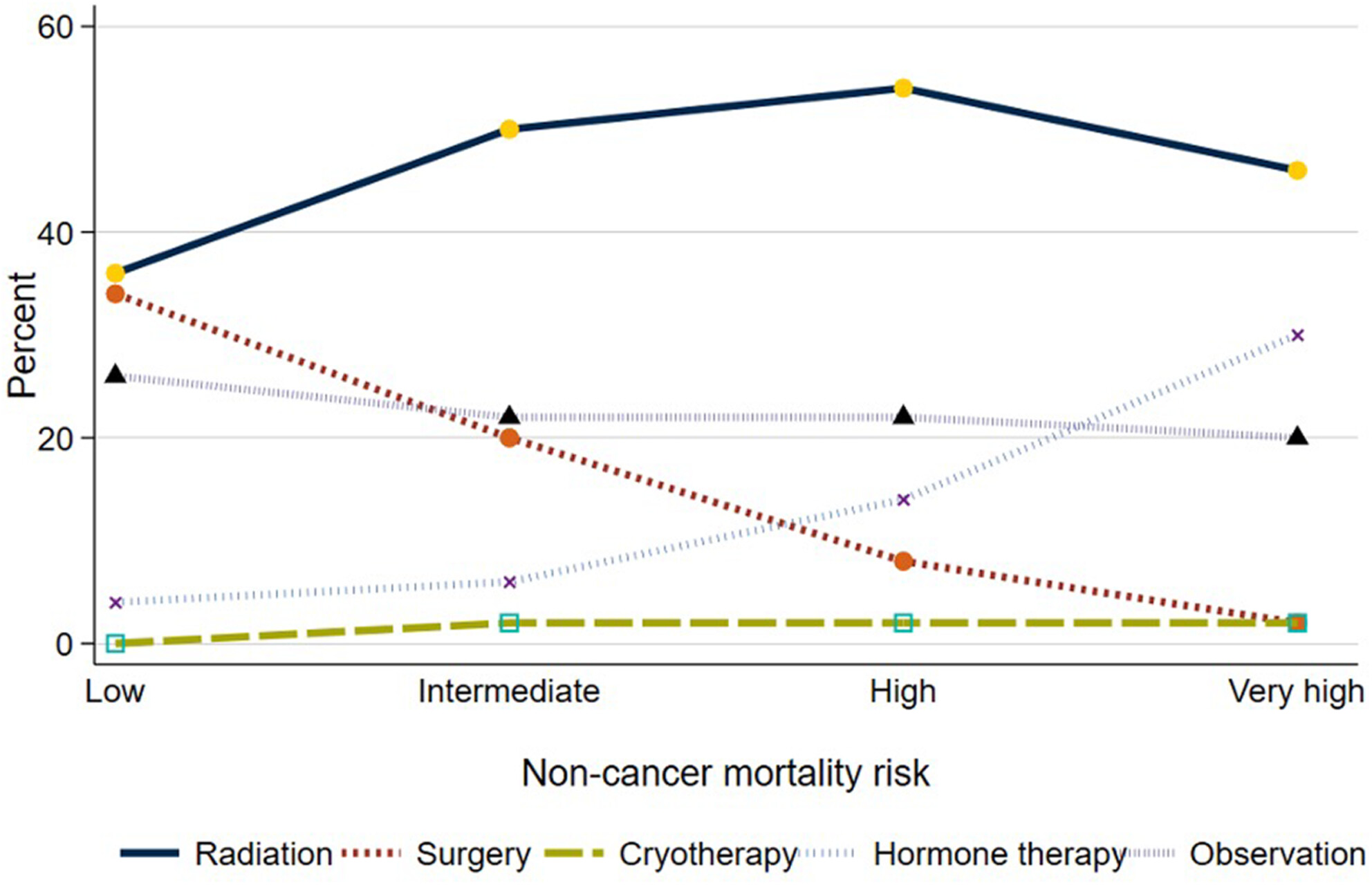
Despite increasing use of conservative management for men with prostate cancer, there is tremendous variation in its uptake. This variation may be amplified by features of the delivery system, particularly among men with competing health risks, for whom treatment decisions are challenging. In this study, we find that variation in use of treatment was highest for men with high and very high-risk noncancer mortality. Characteristics of the delivery system, measured at the level of the practice explained a large share of this variation.
The many “costs” of transportation: Examining what cancer caregivers experience as transportation obstacles
- Pages: 17356-17364
- First Published: 23 July 2023
The impact of COVID-19 on mortality, length of stay, and cost of care among patients with gastrointestinal malignancies: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Pages: 17365-17376
- First Published: 31 July 2023
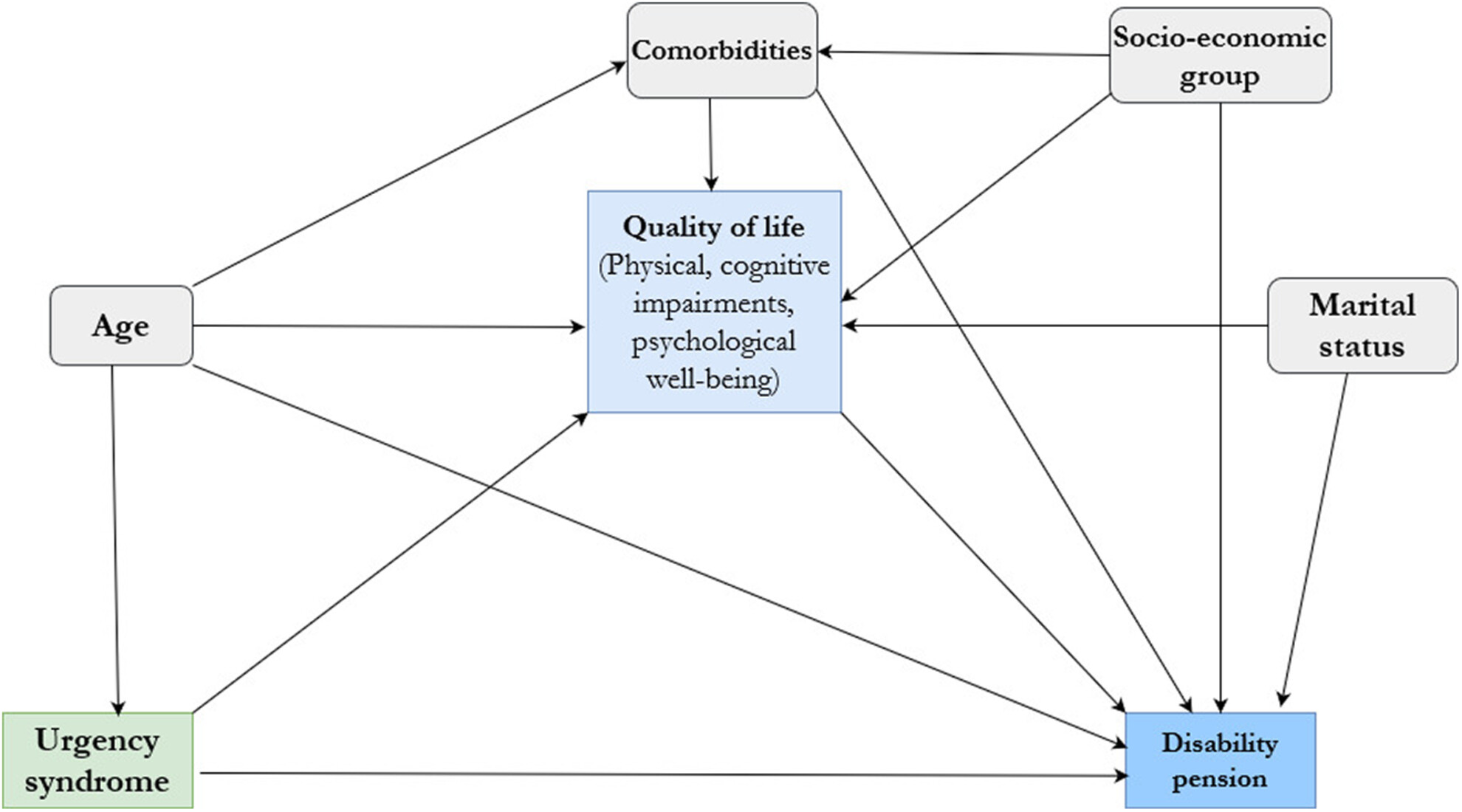
The physical and psychological aspects of quality of life mediates the effect of radiation-induced urgency syndrome on disability pension in gynecological cancer survivors
- Pages: 17377-17388
- First Published: 24 July 2023
Individual and joint effect of socioeconomic status and lifestyle factors on cancer in Korea
- Pages: 17389-17402
- First Published: 25 July 2023
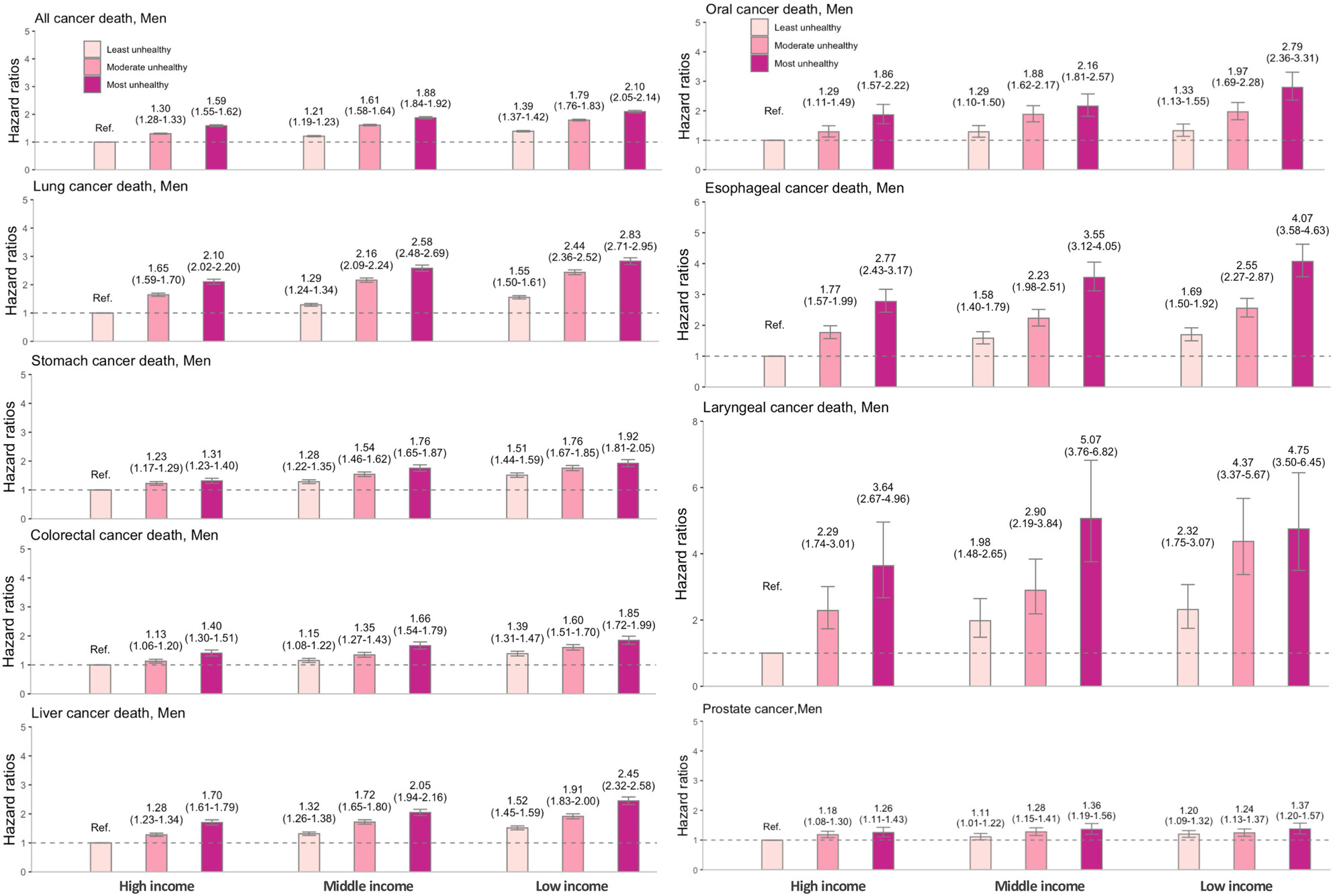
Using large population-based data, this study shows the individual and joint effect of SES and lifestyle factors on cancer incidence and mortality, varied by cancer type and sex. Individuals of the lowest income and unhealthiest lifestyle experience the highest risk for cancer incidence and mortality. The effect appeared to be stronger with cancer-specific mortality than with cancer incidence among both sexes, with men showing a more substantial effect than women.
The effects of tislelizumab treatment on the health-related quality of life of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 17403-17412
- First Published: 17 August 2023
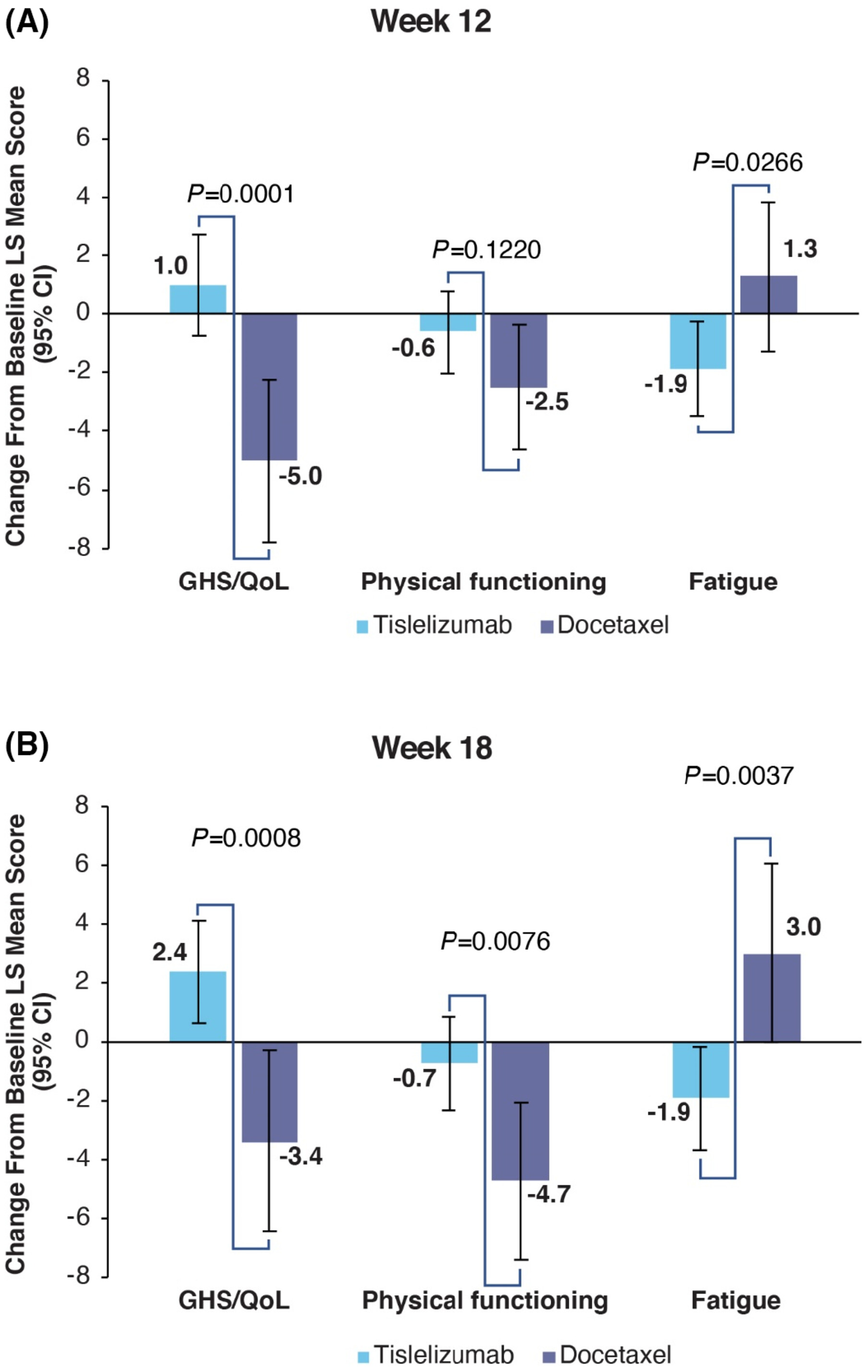
Patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have a poor prognosis and poor health-related quality of life (HRQoL). This study found that patients treated with tislelizumab had greater improvements in the HRQoL measures of the EORTC QLQ-C30 and EORTC lung cancer module (QLQ-LC13) scales and scores compared with patients treated with docetaxel. These results support the favorable risk-benefit ratio of tislelizumab as a second-line therapy in patients with NSCLC who previously failed treatment with a platinum-containing chemotherapy.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Cancer Prevention
Quantifying mortality burden in patients with cancer due to COVID-19 in the US: A national cross-sectional analysis
- Pages: 17413-17417
- First Published: 03 August 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Prevention
Changes in spatial clusters of cancer incidence and mortality over 15 years in South Korea: Implication to cancer control
- Pages: 17418-17427
- First Published: 25 July 2023
Bioinformatics
Pan-cancer analyses reveal multi-omic signatures and clinical implementations of the forkhead-box gene family
- Pages: 17428-17444
- First Published: 04 July 2023
Identification of angiogenesis-related genes signature for predicting survival and its regulatory network in glioblastoma
- Pages: 17445-17467
- First Published: 11 July 2023

In this study, we have constructed a regulatory network based on angiogenesis-related gene signature and identified a signaling pathway, WWTR1 (TAZ)-ANXA1, COL6A1, and PDPN-EMT, which may provide new therapeutic strategies by utilizing the signaling axis in tumor angiogenesis we proposed for GBM patients.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Bioinformatics
Large-scale pathogenicity prediction analysis of cancer-associated kinase mutations reveals variability in sensitivity and specificity of computational methods
- Pages: 17468-17474
- First Published: 06 July 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Bioinformatics
Identification of age- and immune-related gene signatures for clinical outcome prediction in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 17475-17490
- First Published: 11 July 2023
FAM60A promotes osteosarcoma development and progression
- Pages: 17491-17503
- First Published: 12 July 2023
Guanylate-binding proteins signature predicts favorable prognosis, immune-hot microenvironment, and immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 17504-17521
- First Published: 07 August 2023