Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 10 October 2021
The cover image is based on the Research Article Exosomal TUBB3 mRNA expression of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients: Association with patient outcome under abiraterone by Hao Zeng et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.4168.
ISSUE INFORMATION
CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH
REVIEW
EGFR-mutated stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: What is the role of radiotherapy combined with TKI?
- Pages: 6167-6188
- First Published: 10 August 2021
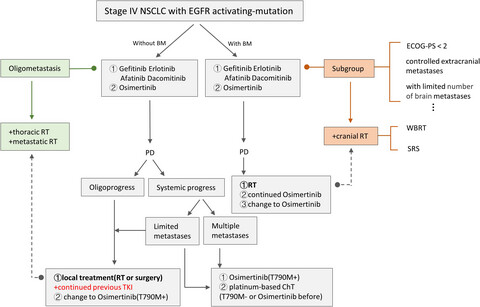
For the oligometastatic setting, radiotherapy (RT) to both primary and metastatic lesions might prolong both progression-free survival and OS. Reduced-dose thoracic RT and critical restriction of the mean lung dose before tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) resistance onset hold some promise. Although epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) TKIs can exert synergistic effects with RT, this regimen should be applied with caution owing to the risk of adverse effects, especially lung damage. In the first- or second-generation EGFR TKI era, upfront brain RT showed better efficacy; however, this is expected to change with the advent of next-generation TKIs with increased central nervous system efficacy. The likely beneficiaries of upfront brain RT, especially stereotactic radiosurgery, with the arrival of the new drugs should be identified through clinical trials.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Late metastatic presentation is associated with improved survival and delayed wide-spread progression after ablative stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastasis
- Pages: 6189-6198
- First Published: 25 August 2021
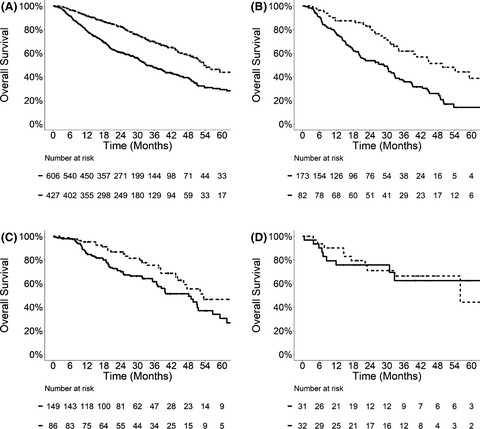
Despite the increasing utilization of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for patients with oligometastasic disease (OMD), prognostic and predictive factors for this treatment modality are not well understood. In this analysis of a large, multi-institutional database of SBRT for OMD, the timing of metastatic presentation is a significant prognostic factor, as patients with late metastasis (>24 months from cancer diagnosis) have lower risk of widespread progression and death after SBRT.
Thirty-day hospital readmission rate, reasons, and risk factors after acute inpatient cancer rehabilitation
- Pages: 6199-6206
- First Published: 27 July 2021
Research is needed to determine the rates of and risk factors for 30-day hospital readmission after acute inpatient cancer rehabilitation to understand the nature of this problem and to decrease costs associated with readmissions. Among adult patients with cancer discharged to a home setting after acute inpatient rehabilitation, the 30-day readmission rate of 21% was higher than that reported for other rehabilitation populations but within the range reported for patients with cancer who did not undergo acute inpatient rehabilitation. Cancer rehabilitation patients may have unique risk factors for readmission.
Prevalence of frailty and prediction of mortality in Chinese cancer patients using a frailty index-based clinical algorithm—A multicentre study
- Pages: 6207-6217
- First Published: 28 July 2021
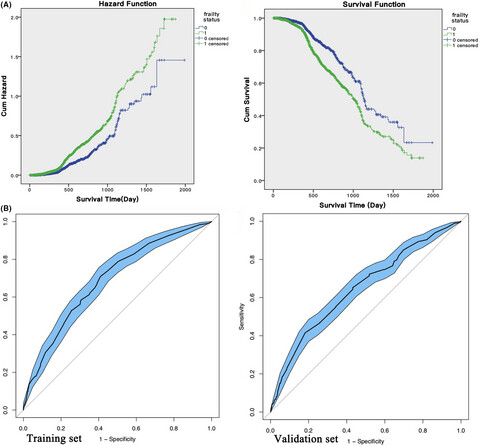
To investigate the frailty status in Chinese cancer patients through establishing a novel prediction algorithm. Frailty as defined by FI-LAB (frailty index composing of routine laboratory data) was common and indicated a significant death risk in cancer patients. Our novel developed algorithm mortality of cancer patients had a passable prediction capacity on 5-year mortality of cancer patients.
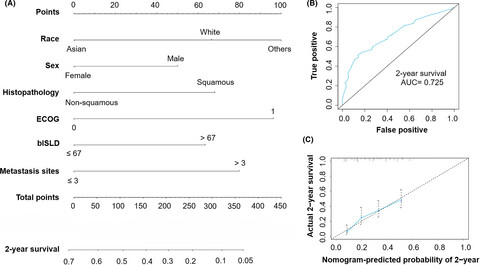
A clinical variable-based nomogram could predict the survival for advanced NSCLC patients receiving second-line atezolizumab
- Pages: 6218-6226
- First Published: 31 July 2021
Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma: From clinical features to cancer genome
- Pages: 6227-6238
- First Published: 31 July 2021
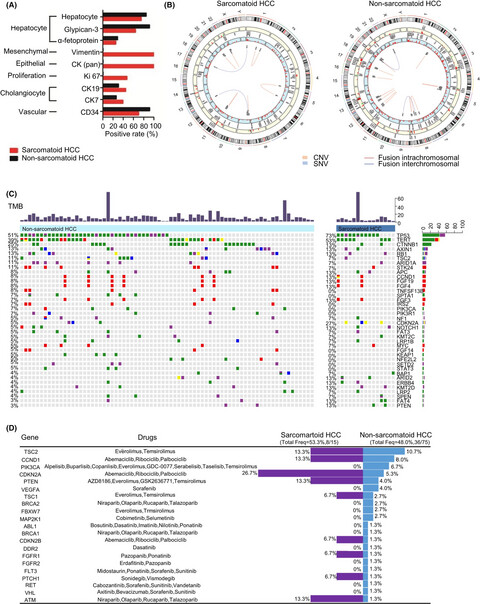
In summary, there is no specific and effective therapies for sarcomatoid HCC. Our cancer genome analysis showed a specific genomic profile of sarcomatoid HCC, which were characterized by a high mutation rate in cell cycle genes particularly CDKN2A. The results indicate CDK4/6 inhibitors including abemaciclib, ribociclib and palbociclib as potential therapeutic targets and may help for therapeutic decision making.
Identifying metrics of success for transitional care practices in childhood cancer survivorship: A qualitative interview study of parents
- Pages: 6239-6248
- First Published: 06 August 2021
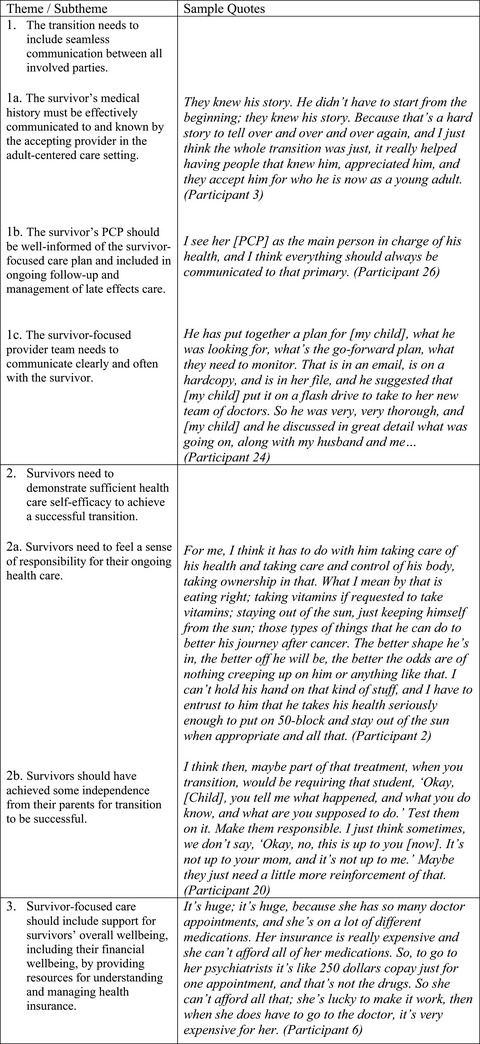
Survivor-focused care for adolescent and young adult (AYA) childhood cancer survivors (CCS) often involves their parents. To parents, adolescent and young adult (AYA) childhood cancer survivors (CCS), the optimal pediatric to adult care transition model should include mechanisms that facilitate communication between parents, CCS, and survivor-focused providers while also supporting self-efficacy and financial literacy as it relates to health insurance.
Cognitive changes and brain connectomes, endocrine status, and risk genotypes in testicular cancer patients–A prospective controlled study
- Pages: 6249-6260
- First Published: 13 August 2021
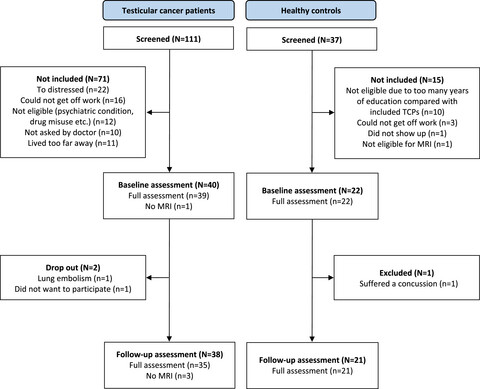
The present study confirms previous findings of domain-specific cognitive decline in testicular cancer patients following orchiectomy, but also points to domain-specific improvements. The results do not indicate changes in brain connectomes or endocrine status to be the main drivers of cognitive changes.
Inflammatory breast cancer appearance at presentation is associated with overall survival
- Pages: 6261-6272
- First Published: 30 July 2021
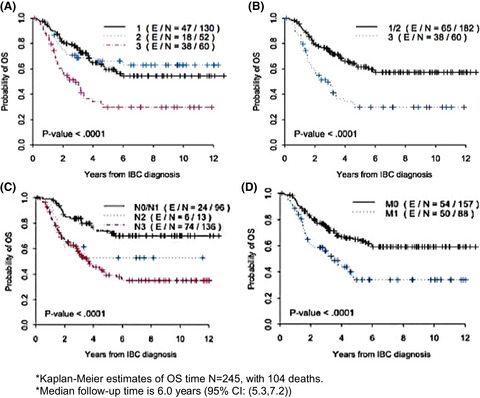
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a clinical diagnosis. Here, we examined the association of a “classic” triad of clinical signs, swollen involved breast, nipple change, and diffuse skin change, with overall survival (OS). Our study concluded for the first time that a triad of classic IBC signs independently predicted OS in patients diagnosed with IBC.
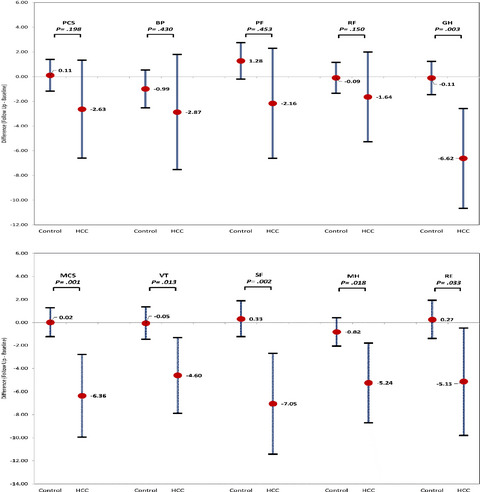
The impact of hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis on patients' health-related quality of life
- Pages: 6273-6281
- First Published: 18 August 2021
Exosomal TUBB3 mRNA expression of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients: Association with patient outcome under abiraterone
- Pages: 6282-6290
- First Published: 28 July 2021
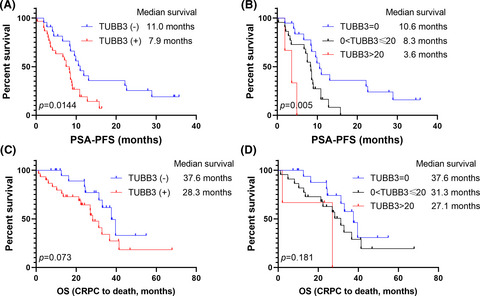
In this study, we presented this novel, non-invasive biomarker for abiraterone resistance in mCRPC patients using a ddPCR approach to quantificationally measure the exosomal TUBB3 mRNA expression. We found that a higher TUBB3 level is correlated with shorter progression time after first-line abiraterone treatment in mCRPC patients.
Three models that predict the efficacy of immunotherapy in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 6291-6303
- First Published: 13 August 2021
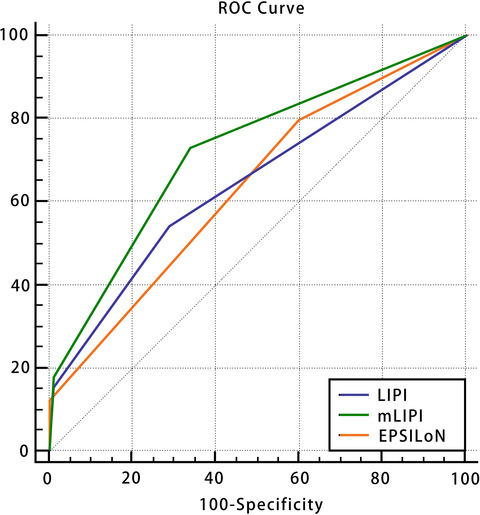
Many tools have been developed to predict the efficacy of immunotherapy, such as lung immune prognostic index (LIPI), EPSILoN [Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS), smoking, liver metastases, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR)], and modified lung immune predictive index (mLIPI) scores. The aim of this study was to determine the ability of to predict outcomes in Chinese aNSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
Cabazitaxel multiple rechallenges in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
- Pages: 6304-6309
- First Published: 12 August 2021
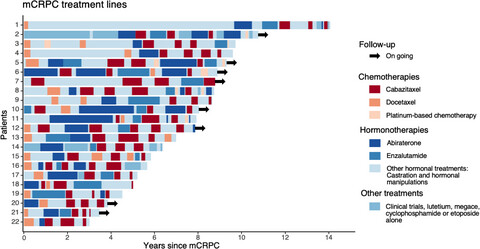
We assessed the efficacy and toxicity of multiple rechallenges with cabazitaxel for 22 patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Median overall survival was 50.9 months from the first cabazitaxel dose, 114.9 months from first life-extending therapy initiation in mCRPC, and 105 months from mCRPC diagnosis. Cabazitaxel rechallenge may be an effective option in heavily pretreated mCRPC patients with a good initial response to cabazitaxel and still fit to receive it, without cumulative grade ≥3 toxicity.
The serological prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia is similar to that in the general population
- Pages: 6310-6316
- First Published: 31 August 2021
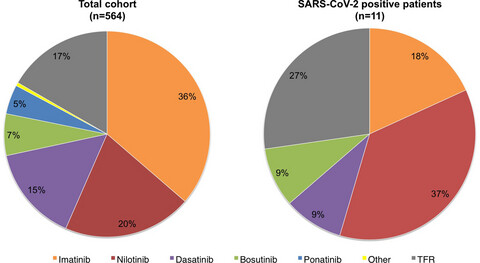
The estimated serological prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with CML after the first pandemic wave was similar to that of the general population (about 2% in Italy). Our data reassure about the safety of continuing TKI treatment during the ongoing pandemic and suggest that patients with CML succeed to mount an antibody response against SARS-CoV-2 whether on TKI treatment or not.
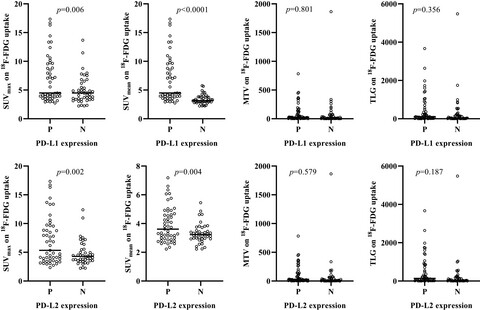
Tumor immunity is related to 18F-FDG uptake in thymic epithelial tumor
- Pages: 6317-6326
- First Published: 07 August 2021
Trends in cancer imaging by indication, care setting, and hospital type during the COVID-19 pandemic and recovery at four hospitals in Massachusetts
- Pages: 6327-6335
- First Published: 06 August 2021
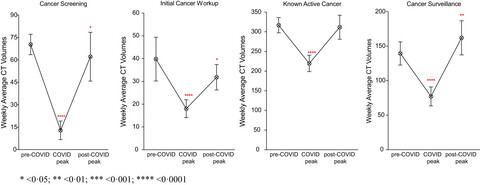
Between March and November 2020, the use of CTs for cancer screening and initial cancer workup was significantly lower than in pre-COVID-19 times. Also, during this time, more cancer-related imaging was performed at community hospitals, in the ED and in the inpatient setting, than at the large academic center and outpatient. The findings are concerning for inappropriate healthcare resource utilization, and the chance that more patients with advanced cancer may present post-pandemic.
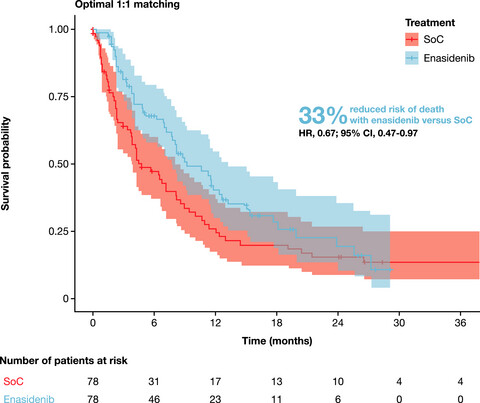
Improved survival with enasidenib versus standard of care in relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia associated with IDH2 mutations using historical data and propensity score matching analysis
- Pages: 6336-6343
- First Published: 24 August 2021
Determining the optimal PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for the first-line treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer with high-level PD-L1 expression in China
- Pages: 6344-6353
- First Published: 12 August 2021
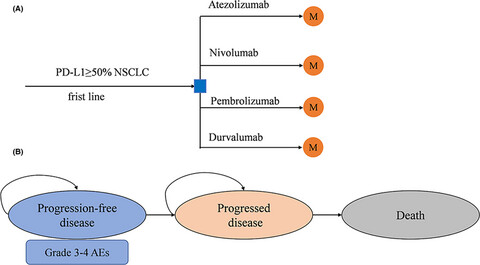
A network meta-analysis was performed to indirectly consider the efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and the Markov model was established to compare their economic.The efficacy and safety of the four PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors analyzed in this study are similar.From the perspective of the Chinese healthcare system, nivolumab therapy is a cost-effective alternative to other drugs as first-line treatments for advanced NSCLC with high-level PD-L1 expression.
A real-world comparison of docetaxel versus abiraterone acetate for metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer
- Pages: 6354-6364
- First Published: 10 August 2021
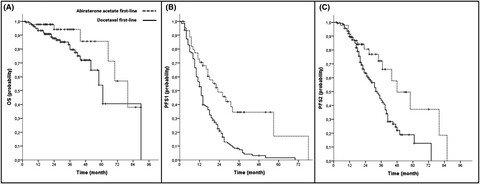
Abiratreone acetate outperforms docetaxel in terms of PFS and PFS2, while the impact on OS as well as the rate of side effects is similar between both groups in real-life utilization. Prospective randomized trials of available agents in mHSPC are required to generate high-level evidence to facilitate sensible drug selection
CANCER BIOLOGY
REVIEWS
The antitumor mechanisms of aerobic exercise: A review of recent preclinical studies
- Pages: 6365-6373
- First Published: 13 August 2021
Metabolic reprogramming of immune cells: Shaping the tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 6374-6383
- First Published: 13 August 2021
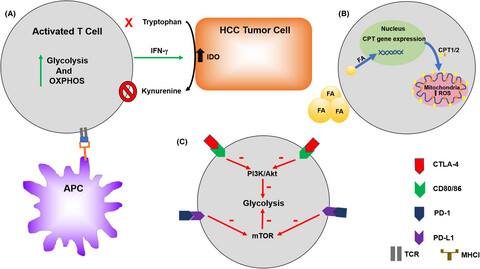
Immune cells in the Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) microenvironment play both pro-and anti-tumoral roles in HCC progression. An increasing number of findings indicate that metabolic reprogramming is essential for immune cell differentiation and function. In this review, we discuss the metabolic changes of different immune cells and correlate these findings to HCC progression.
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors-based treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Mechanisms affecting efficacy and combination therapies
- Pages: 6384-6401
- First Published: 12 August 2021
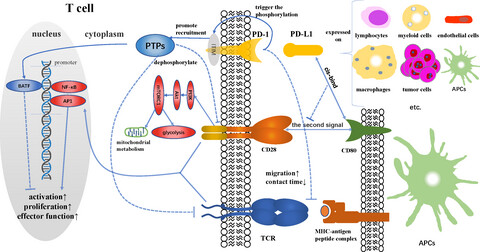
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been gradually applied in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma, but the efficacy is limited. Alternations in PD-L1 expression and cellular immunity can directly or indirectly affect the efficacy of PD-L1 inhibitors. Antiangiogenic drugs and CTLA-4 inhibitors have been shown to significantly improve the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein regulates tumorigenesis of arecoline-promoted human oral carcinoma
- Pages: 6402-6415
- First Published: 11 August 2021
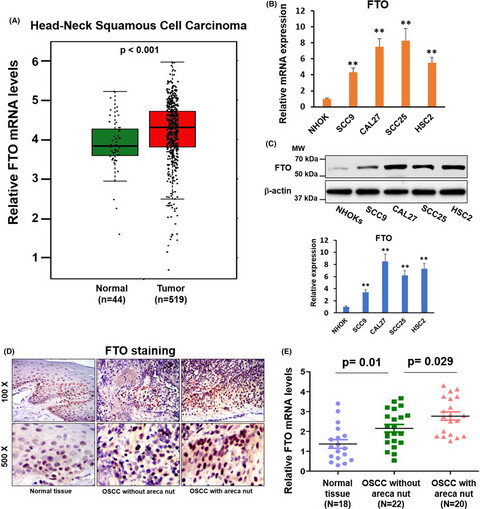
We identified that FTO was significantly upregulated in OSCC tissues from patients with areca nut chewing habits and chronic arecoline-treated OSCC cell lines. Depletion of FTO attenuated the arecoline-promoted stemness, chemoresistance, and oncogenicity of OSCC cells. Therapeutic agents targeting FTO may serve as a promising method to treat OSCC patients, especially those with areca nut chewing habits.
DYRK1A activates NFATC1 to increase glioblastoma migration
- Pages: 6416-6427
- First Published: 26 July 2021
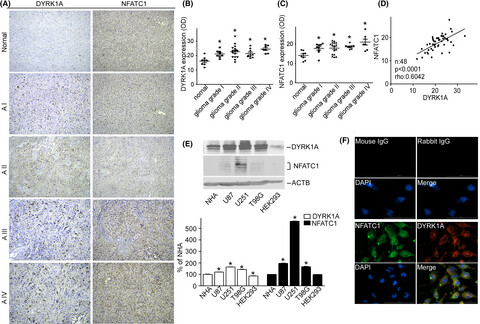
We found that DYRK1A protein was positively correlated with that of NFATc1 through affecting NFATc1 degradation and transactivation in GBM cells. DYRK1A inhibition or polypeptide derived from DYRK1A-targeted motif of NFATc1, clearly destabilized NFATc1 protein and impaired glioblastoma migration. We propose that the recovery of NFATc1 stability is a key oncogenic event in a large proportion of gliomas and polypeptide pharmacological inhibition of DYRK1A could represent a promising therapeutic intervention for NFATc1-dependent GBM.
Integrated pan-cancer of AURKA expression and drug sensitivity analysis reveals increased expression of AURKA is responsible for drug resistance
- Pages: 6428-6441
- First Published: 01 August 2021
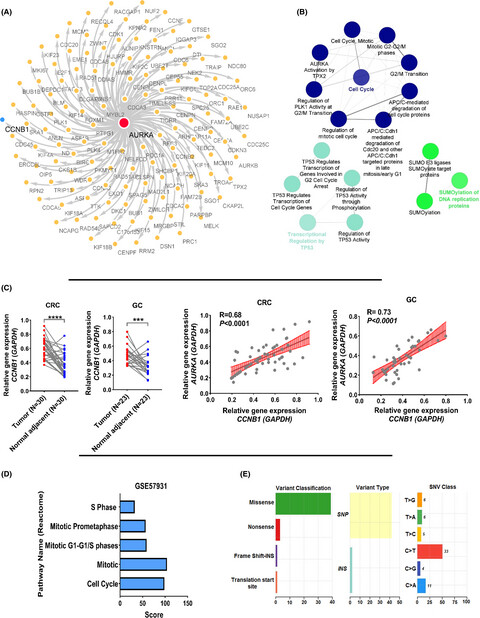
The expression level of AURKA gene in 13 common cancers increased significantly compared to normal. The level of AURKA was significantly associated with resistance to SB 505124, NU-7441, and irinotecan drugs (p < 0.01). Actinomycin D1 and camptothecin could reduce the expression of AURKA gene in different cancer cell lines based on GEO data.
Inhibition of lipid metabolism exerts antitumor effects on rhabdomyosarcoma
- Pages: 6442-6455
- First Published: 02 September 2021
CANCER PREVENTION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Relationship of established risk factors with breast cancer subtypes
- Pages: 6456-6467
- First Published: 31 August 2021

Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease, with subtypes that may have different etiologies. This study evaluated traditional breast cancer risk factors across tumor subtypes, finding distinct sets of risk factors for each subtype. We additionally discuss implications for screening and risk assessment.
Gastric adenocarcinoma burden and late-stage diagnosis in Latino and non-Latino populations in the United States and Texas, during 2004–2016: A multilevel analysis
- Pages: 6468-6479
- First Published: 19 August 2021
Latinos had higher gastric adenocarcinoma incidence than non-Latinos in the U.S., Texas and South Texas from 2004 to 2016. Younger age and social deprivation increased risk of late-stage diagnosis, while Latino ethnicity and female gender increased risk of late-stage gastric adenocarcinoma of the cardia specifically.
Clinical impact of follow-up imaging on mortality in Korean breast cancer patients: A national cohort study
- Pages: 6480-6491
- First Published: 01 September 2021
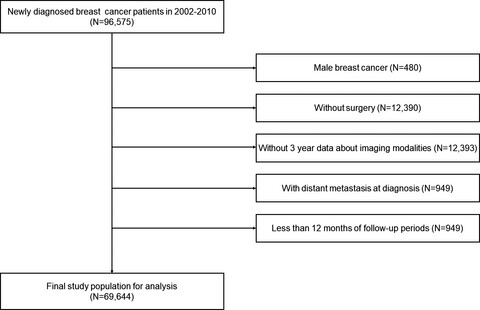
This study aimed to evaluate follow-up imaging usage and the clinical implications after breast cancer surgery using Korea national cohort. We found that only frequent mammography reduced mortality and other imaging modalities did not. Therefore, clinicians need to adhere to the current guidelines for surveillance after breast cancer surgery.
BIOINFORMATICS
RESEARCH ARTICLES
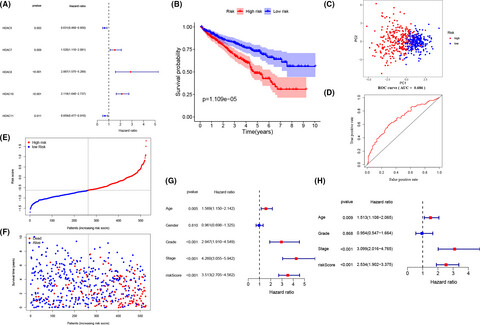
Gene signatures predict biochemical recurrence-free survival in primary prostate cancer patients after radical therapy
- Pages: 6492-6502
- First Published: 28 August 2021
In this work, we established the risk score consisting of six gene signatures, which can predict biochemical recurrence in primary prostate cancer. Clinically, the nomogram model, which incorporates the Gleason score and the risk score, could effectively predict BCRFS and potentially be utilized as a useful tool for the screening of BCRFS in PCa.
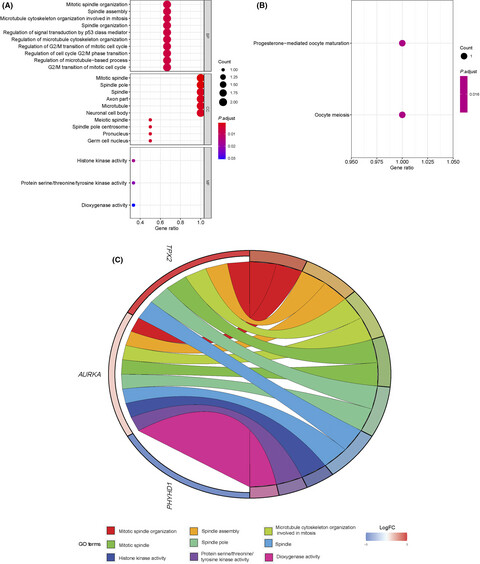
Comprehensive analysis of a new prognosis signature based on histone deacetylases in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 6503-6514
- First Published: 26 July 2021
Risk model consisting of HDAC8, HDAC10, and HDAC11 have a favorable role of risk prediction in ccRCC. Immune-associated functions and pathways were enriched in HDACs, and most of HDACs are related to tumor stemness, stromal cell, and immune cells. Several clinical characteristics are associated with HDACs expression and the activity of some commonly used drugs (such as oxaliplatin, vorinostat, temsirolimus) are also influenced by HDACs.
Expression and prognostic potential of PLEK2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Pages: 6515-6533
- First Published: 30 July 2021
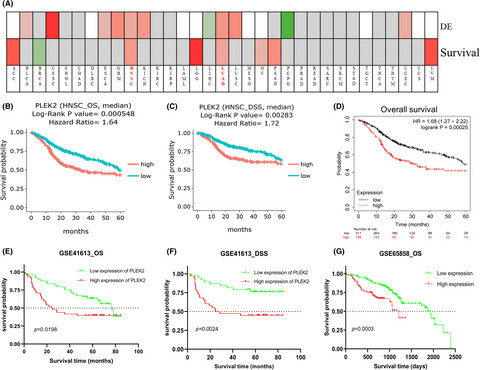
In our study, elevated expression of PLEK2 was observed in HNSCC and was found to portend a poor prognosis. PLEK2 and its co-expressed gene ITGA3 might work in concert to promote HNSCC metastasis. In general, PLEK2 might serve as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of HNSCC and guide the development of targeted therapies for HNSCC.
A robust signature of immune-related long non-coding RNA to predict the prognosis of bladder cancer
- Pages: 6534-6545
- First Published: 10 August 2021
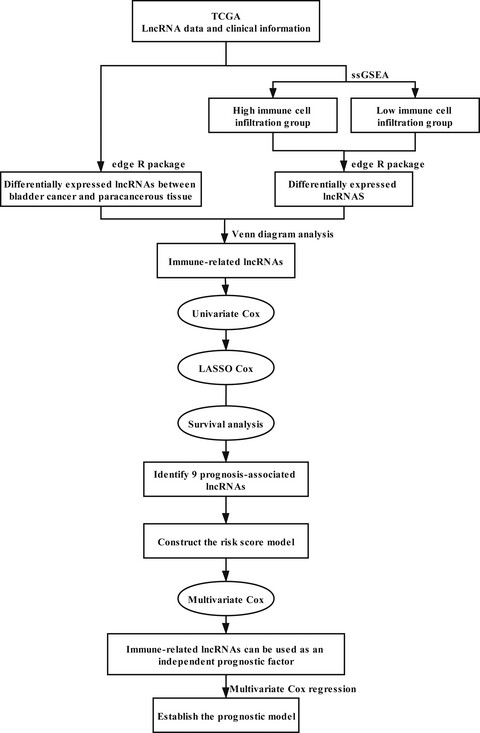
The present study identified nine immune-related long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and the 9-lncRNAs signature possessed prognostic value for patients with bladder cancer. Bioinformatics analysis suggested that immune-related lncRNAs may regulate tumor pathogenesis through the modulation of various immune responses, antigen processing and presentation, and T cell receptor signaling pathway.
Identification of a novel 10 immune-related genes signature as a prognostic biomarker panel for gastric cancer
- Pages: 6546-6560
- First Published: 12 August 2021
Predicting the immune landscape of invasive breast carcinoma based on the novel signature of immune-related lncRNA
- Pages: 6561-6575
- First Published: 11 August 2021