Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH
REVIEW
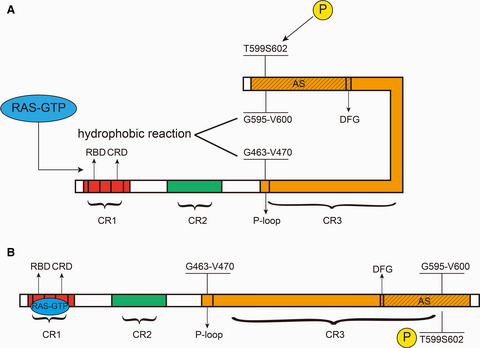
BRAF mutation and its inhibitors in sarcoma treatment
- Pages: 4881-4896
- First Published: 31 May 2020
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Prognostic values of the clinicopathological characteristics and survival outcomes in micropapillary urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: A SEER database analysis
- Pages: 4897-4906
- First Published: 11 June 2020
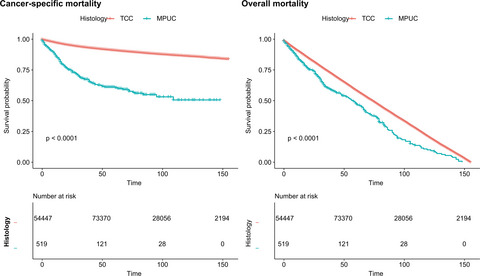
The prognosis of micropapillary urothelial carcinoma (MPUC) is poorer than transitional cell carcinoma. Micropapillary urothelial carcinoma is an independent prognostic factor for overall mortality to patients with urinary bladder cancer. In subgroup analysis, only none distal metastasis MPUC patients faced higher risk of cancer-specific mortality.
Effects of adaptive immune cell therapy on the immune cell profile in patients with advanced gastric cancer
- Pages: 4907-4917
- First Published: 11 June 2020
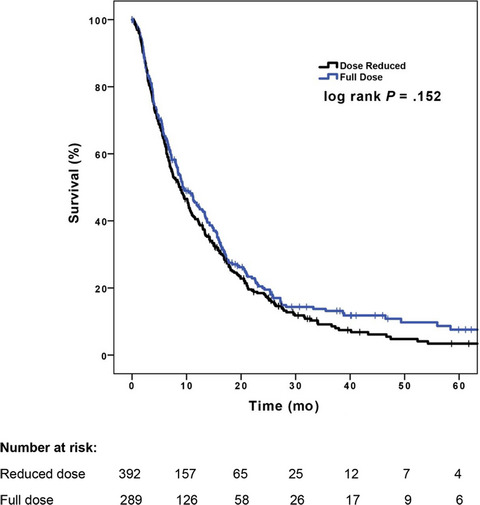
Effect of sorafenib starting dose and dose intensity on survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from a Canadian Multicenter Database
- Pages: 4918-4928
- First Published: 11 June 2020
Palbociclib-letrozole as first-line treatment for advanced breast cancer: Updated results from a Japanese phase 2 study
- Pages: 4929-4940
- First Published: 18 May 2020
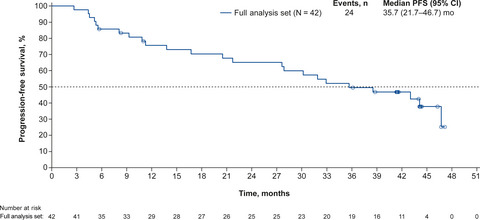
With longer follow-up of an open-label, single-arm, Japanese phase 2 study conducted to investigate the efficacy and safety of palbociclib plus letrozole as first-line treatment in postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer, median progression-free survival was 35.7 months (95% CI, 21.7-46.7). Palbociclib plus letrozole remained effective and tolerable in Japanese postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer.
Clinical and immunological features of platelet transfusion refractoriness in young patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 4941-4948
- First Published: 18 May 2020
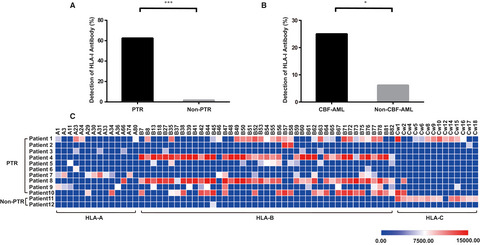
Platelet transfusion refractoriness (PTR) is an intractable clinical issue with increasing risks of bleeding and mortality in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) after receiving platelet transfusion. In the present manuscript, patients with CBF-AML and patients who further had better minimal residual disease (MRD) reduction (≥3-log) after induction chemotherapy had higher tendency to develop HLA-I antibodies and PTR. Moreover, HLA-B was the most frequently identified serum epitope in PTR patients.
A systematic review of evidence for and against routine surveillance imaging after completing treatment for childhood extracranial solid tumors
- Pages: 4949-4961
- First Published: 19 May 2020
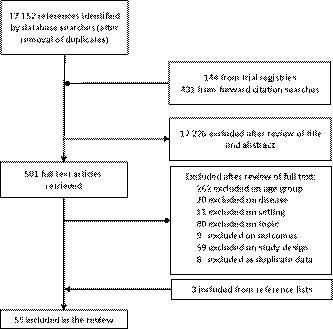
This systematic review examines the impact of routine surveillance imaging after treatment of pediatric extracranial solid tumors on overall survival, psychological distress indicators, number of imaging tests, cost-effectiveness, and qualitative data regarding experiences of surveillance programs. At present, there is insufficient evidence to evaluate the effects of routine surveillance imaging on survival in most pediatric extracranial solid tumors.
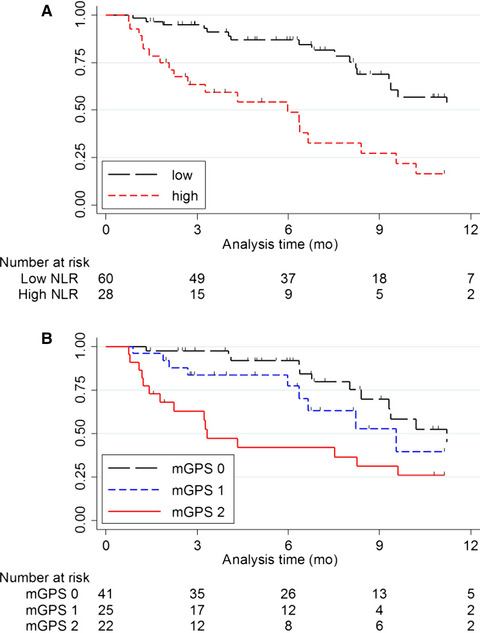
Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with anti–PD-1 therapy
- Pages: 4962-4970
- First Published: 18 May 2020
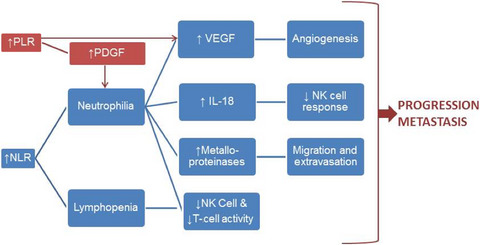
In this study evaluating 103 patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, lower neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were both strongly predictive of improved survival after three cycles of nivolumab. Baseline NLR was not associated with survival. An elevated NLR and PLR in the posttreatment setting may be an early sign of treatment failure and may warrant consideration for early change in therapy.
HIF-1α interacts with Kindlin-2 and influences breast cancer elasticity: A study based on shear wave elastography imaging
- Pages: 4971-4979
- First Published: 21 May 2020
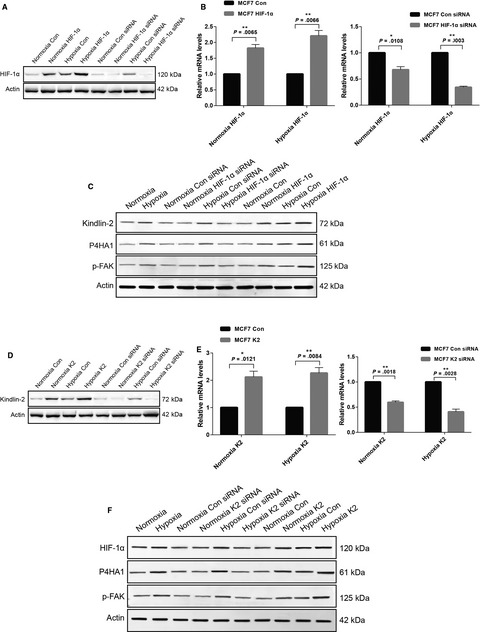
The expression levels of HIF-1α and Kindlin-2 and Emax were correlated with each other. HIF-1α and Kindlin-2 influence the progress of collagen biogenesis through integrin/FAK pathway. Emax could be a physical biomarker for early, noninvasive diagnosis, and HIF-1α and Kindlin-2 could be pathological markers for early diagnosis and targeted therapy.
Stromal score as a prognostic factor in primary gastric cancer and close association with tumor immune microenvironment
- Pages: 4980-4990
- First Published: 20 May 2020
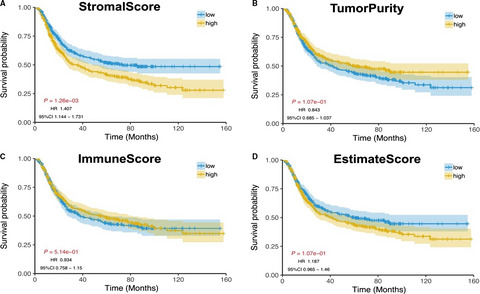
Our study had shown that Stromal score could serve as a biological biomarker for primary gastric cancer and an independent prognostic factor. The prognosis mechanism of stromal score was associate with gene mutation, TMB, MATH, immunity and multiple signaling pathways. These findings may prompt the clinical diagnosis and treatment of primary gastric cancer.
Sorafenib and everolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors and KRAS-mutated NSCLC: A phase I trial with early pharmacodynamic FDG-PET assessment
- Pages: 4991-5007
- First Published: 21 May 2020
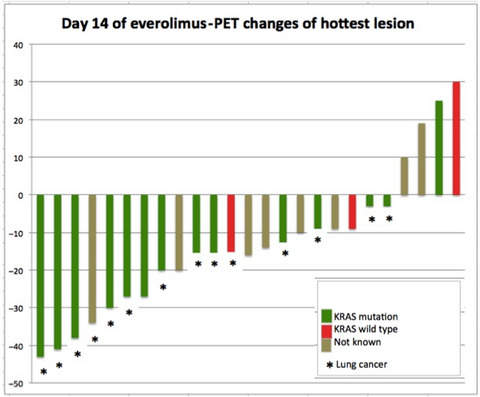
The study investigated the combination of sorafenib and everolimus in patients with solid tumors (dose escalation part) and KRAS mutated NSCLC (expansion part). Although the trial showed manageable safety profile of sorafenib and everolimus, it failed in providing long terms responses for patients with solid tumors and KRAS mutated NSCLC. The novelty of the study was the early pharmacodynamics assessment using FDG-PET implemented in a phase-I.
Effectiveness and safety of low-dose apatinib in advanced gastric cancer: A real-world study
- Pages: 5008-5014
- First Published: 22 May 2020

Apatinib has been demonstrated to be effective and safe among patients with gastric cancer failing after at least two lines chemotherapy. The present study aimed to evaluate its effectiveness and safety of low-dose apatinib for the treatment of gastric cancer in real-world practice. The prospective study suggested that low-dose apatinib was an effective regimen for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer with tolerable or controlled toxicity in real world.
Hematological predictive markers for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck treated with nivolumab: A multicenter study of 88 patients
- Pages: 5015-5024
- First Published: 22 May 2020
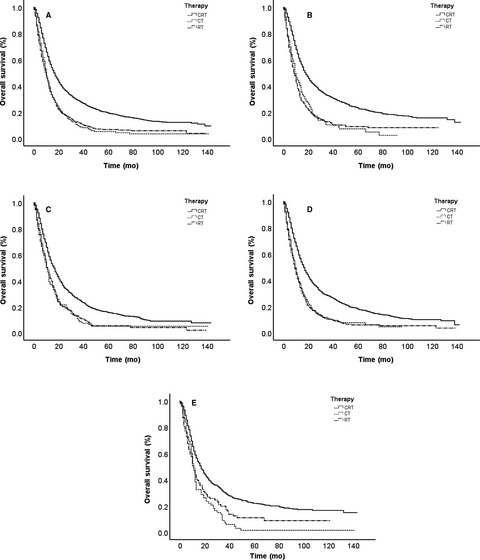
Chemoradiotherapy vs radiotherapy for nonoperative early stage esophageal cancer: A seer data analysis
- Pages: 5025-5034
- First Published: 22 May 2020
Quality of adverse event reporting in phase III randomized controlled trials of breast and colorectal cancer: A systematic review
- Pages: 5035-5050
- First Published: 26 May 2020
Clinical trial reports often emphasize efficacy rather than toxicities of investigational agents, leading to misinterpretation of the risk-to-benefit ratio of new therapies. Here, we evaluated the quality of adverse event reporting in phase III randomized controlled trials of systemic therapies in breast and colorectal cancer. Our results show that most studies inadequately report adverse event data.
Clinical and radiological characteristics of patients with pulmonary marginal zone lymphoma: A single center analysis
- Pages: 5051-5064
- First Published: 26 May 2020
Elevated LDH, B symptoms, advanced stage and failure to achieve complete response after initial treatment are clinical variables associated with shorter progression-free survival (PFS) in pulmonary marginal zone lymphoma (PMZL). Multifocal lung disease, extrapulmonary MZL and cavitary lesions on computed tomography scans have been identified as radiologic features associated with shorter PFS. Radiation therapy and surgery are potentially curative strategies in PMZL.
Radiotranscriptomics signature-based predictive nomograms for radiotherapy response in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer: Combination and association of CT features and serum miRNAs levels
- Pages: 5065-5074
- First Published: 27 May 2020
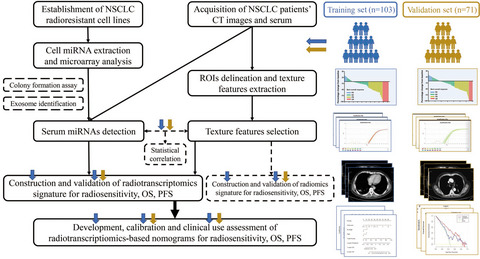
Serum miRNAs expression levels and CT texture features could be combined to develop radiotranscriptomics signature for independently predicting radiotherapy response. Radiotranscriptomics signature-based nomogram was constructed for objective response rates. The statistical significance between serum miRNAs levels and CT texture features was preliminarily explored.
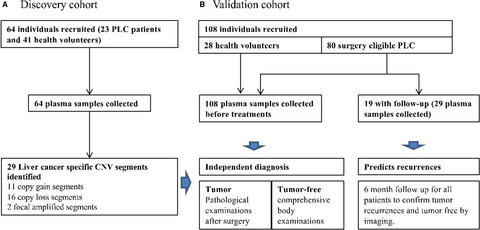
Investigation of Plasma cell-free cancer genome chromosomal instability as a tool for targeted minimally invasive biomarkers for primary liver cancer diagnoses
- Pages: 5075-5085
- First Published: 27 May 2020
Circulating activated lymphocyte subsets as potential blood biomarkers of cancer progression
- Pages: 5086-5094
- First Published: 27 May 2020
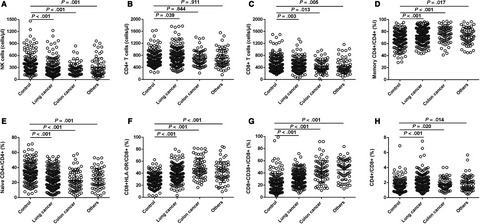
Abnormal levels of NK cell, CD8+ T cells, memory CD4+/CD4+, naïve CD4+/CD4+, CD8+ HLA-DR/CD8+, CD8+CD38+/CD8+, and CD4+/CD8+ can be a potential blood biomarkers of cancer disease progression. Lymphocyte subsets levels were related to gender, age, stage, tumor stage, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, and differentiation.
Risk factors and predictors of lymph nodes metastasis and distant metastasis in newly diagnosed T1 colorectal cancer
- Pages: 5095-5113
- First Published: 29 May 2020
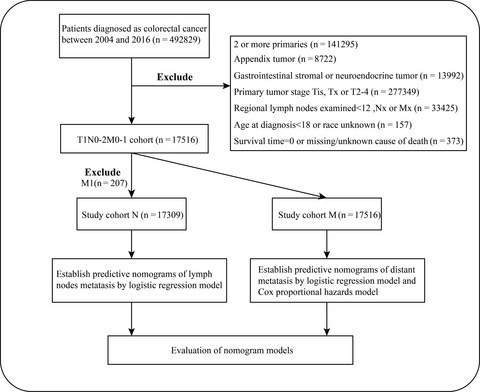
In this study, we analyzed 17 516 participants collected from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. Then, we construct the nomograms to predict the probability of lymph nodes metastasis in colorectal cancer with T1N0-2M0 stage, and to estimate the probability of distant metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer.
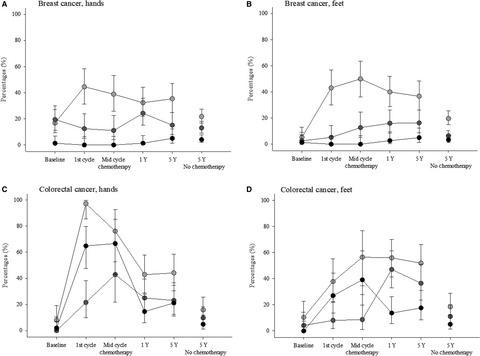
Long-term symptoms of polyneuropathy in breast and colorectal cancer patients treated with and without adjuvant chemotherapy
- Pages: 5114-5123
- First Published: 29 May 2020
Adherence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients to tumor board recommendations
- Pages: 5124-5133
- First Published: 30 May 2020
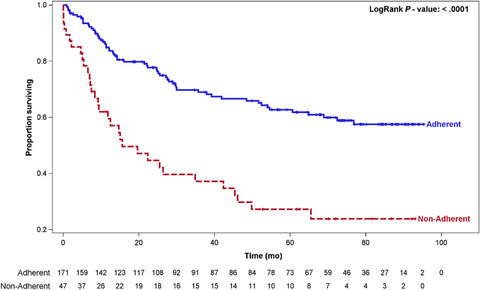
Despite the pivotal role that MDT TBs play in oncology care, the implementation of this science remains nebulous and has scope to improve. The need for standardising TB data reporting will enable to better understand HNC trends globally/regionally. Last but not the least, outcomes in HNC patients discussed at TBs and adherence of HNC patients to TB treatment plan is underreported, and analysis of this key area will be an essential cog in HNC patient management.
Efficacy of NEPA, a fixed antiemetic combination of netupitant and palonosetron, vs a 3-day aprepitant regimen for prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) in Chinese patients receiving highly emetogenic chemotherapy (HEC) in a randomized Phase 3 study
- Pages: 5134-5142
- First Published: 30 May 2020
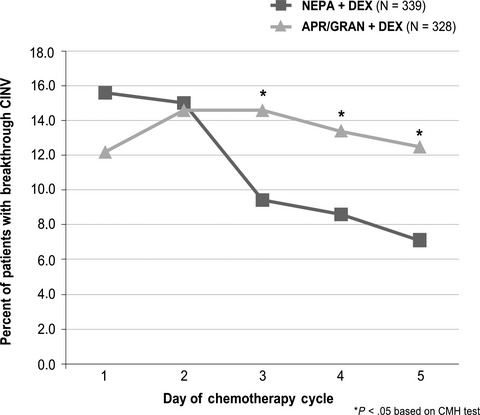
NEPA is a novel fixed combination antiemetic comprised of the NK1RA, netupitant, and the 5-HT3RA, palonosetron. The simultaneous targeting of two critical antiemetic pathways, in unison with single-dose administration, offers a simplified and convenient antiemetic with 5-day CINV prevention. The authors report significantly better protection from CINV during Days 3-5 post-chemotherapy for NEPA vs a 3-day regimen of aprepitant/granisetron in Chinese patients, and in those receiving high-dose cisplatin, in the first head-to-head study comparing NK1RA-containing regimens.
A measure of case complexity for streamlining workflow in multidisciplinary tumor boards: Mixed methods development and early validation of the MeDiC tool
- Pages: 5143-5154
- First Published: 31 May 2020
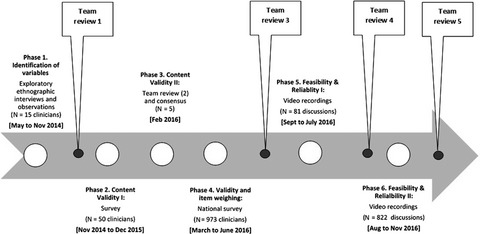
There is increasing emphasis in cancer care globally for care to be reviewed and managed by multidisciplinary teams (ie, in tumor boards). Evidence and recommendations suggest that the complexity of each patient case needs to be considered as care is planned, however no tool currently exists for cancer teams to do so. We report the development and early validation of such a tool. We used a mixed-methods approach involving psychometric evaluation and expert review to develop the Measure of case-Discussion Complexity (MeDiC).
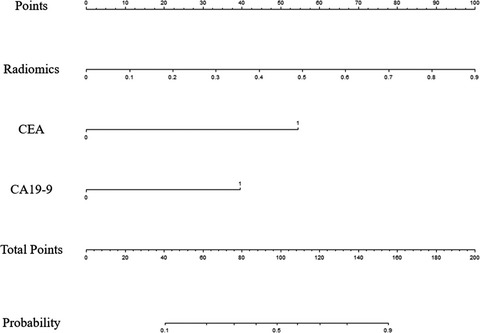
MRI-based radiomics nomogram to predict synchronous liver metastasis in primary rectal cancer patients
- Pages: 5155-5163
- First Published: 31 May 2020
L-Dex, arm volume, and symptom trajectories 24 months after breast cancer surgery
- Pages: 5164-5173
- First Published: 01 June 2020
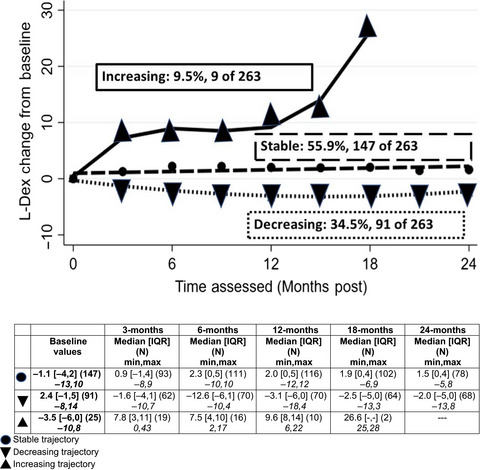
Long-term (24 months) lymphedema prospective surveillance with frequent assessments (every 3 months) at least through 15-months post-surgery is indicated. Convergence of symptom cluster scores with L-Dex unit change supports Bioelectric Impedance Spectroscopy as beneficial in the early identification of sub-clinical lymphedema.
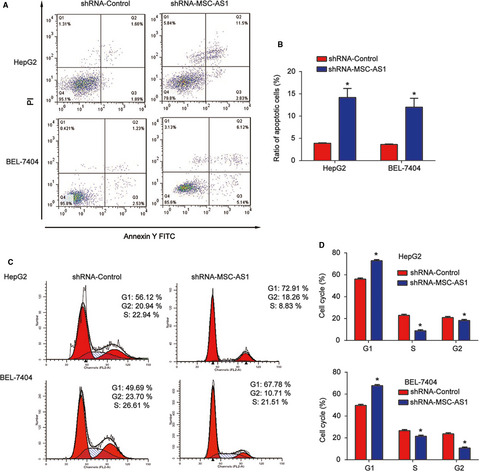
Long noncoding RNA MSC-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma oncogenesis via inducing the expression of phosphoglycerate kinase 1
- Pages: 5174-5184
- First Published: 02 June 2020
CANCER BIOLOGY
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Serine-227 in the N-terminal kinase domain of RSK2 is a potential therapeutic target for mantle cell lymphoma
- Pages: 5185-5199
- First Published: 18 May 2020
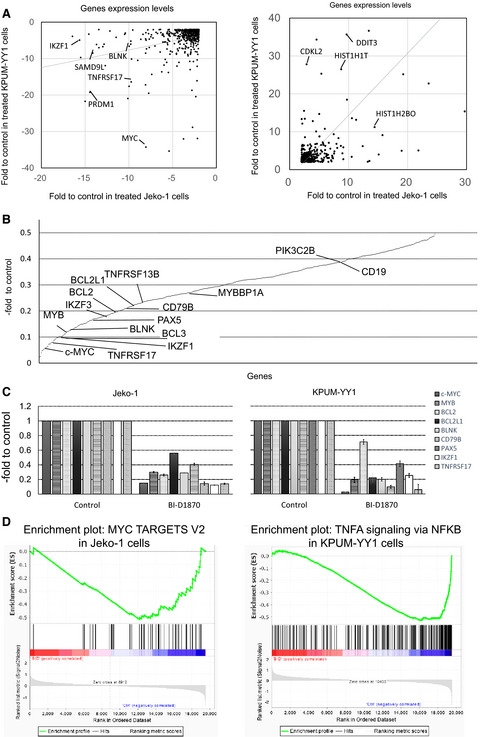
RSK2Ser227 in the N-terminal kinase domain (NTKD) of RSK2 was found to be ubiquitously active in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). RSK2 concomitantly regulates series of genes involved in oncogenesis, apoptosis, B cell development, and B cell receptor signaling. RSK2Ser227 in the NTKD is a potential therapeutic target in MCL.
Identification of the key genes associated with chemotherapy sensitivity in ovarian cancer patients
- Pages: 5200-5209
- First Published: 22 May 2020
Novel recombinant coxsackievirus B3 with genetically inserted basic peptide elicits robust antitumor activity against lung cancer
- Pages: 5210-5220
- First Published: 27 May 2020
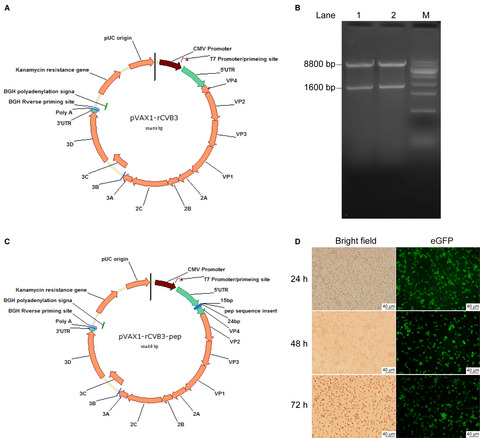
The findings in this study indicate that recombinant CVB3, especially with fused basic peptides, is a potent oncolytic agents, and thus hold promise as oncolytic virus therapy for lung cancer. The elimination of excessive cytokine and immune responses would significantly improve the safety and minimize the adverse effects associated with oncolytic virus therapy in the treatment of lung cancer.
Plasma protein expression differs between colorectal cancer patients depending on primary tumor location
- Pages: 5221-5234
- First Published: 26 May 2020
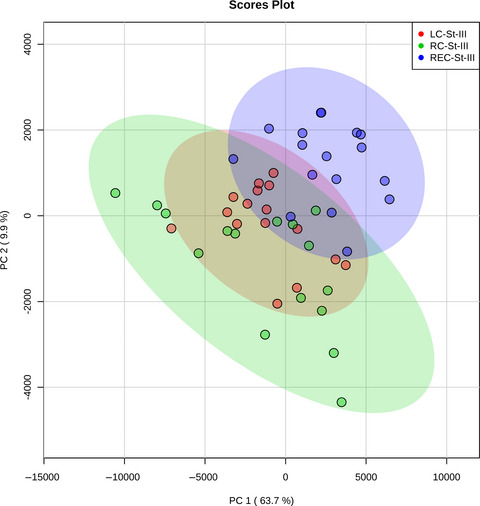
Colorectal cancer (CRC) includes tumors in the right colon, left colon, and rectum, although they differ significantly from each other in aspects such as prognosis and treatment. In this study, we have used mass spectrometry-based proteomics to analyze plasma samples from 83 CRC patients. We subsequently show that plasma protein expression differs significantly between patients with cancer in the colon and rectum.
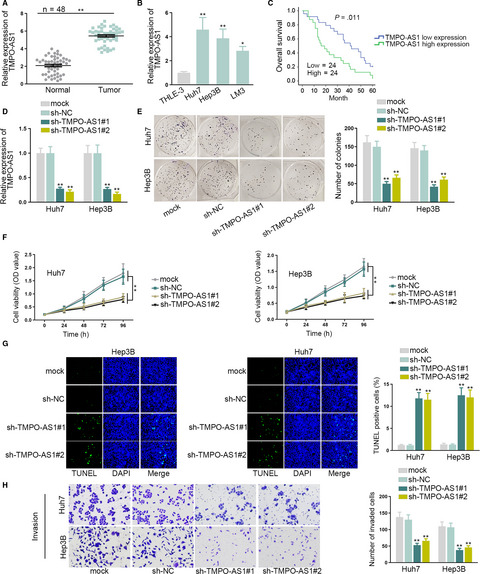
LncRNA TMPO-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion through sponging miR-329-3p to stimulate FOXK1-mediated AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Pages: 5235-5246
- First Published: 27 May 2020
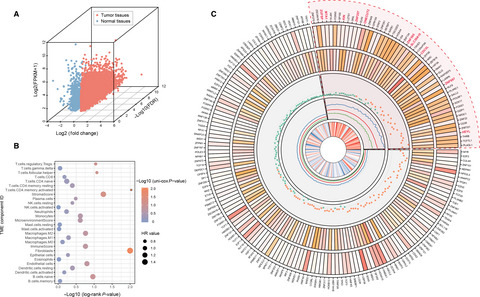
Charactering tumor microenvironment reveals stromal-related transcription factors promote tumor carcinogenesis in gastric cancer
- Pages: 5247-5257
- First Published: 28 May 2020
Noncoding RNA 886 alleviates tumor cellular immunological rejection in host C57BL/C mice
- Pages: 5258-5271
- First Published: 31 May 2020
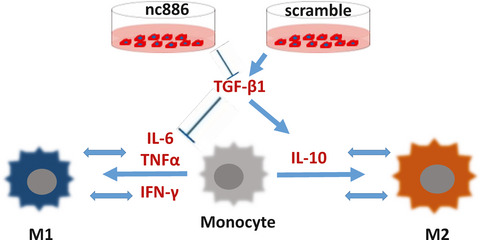
Nc886 broadly decreases the expression of some human leukocyte antigen molecules and antigen transporters, establishing the interesting role in regulating tumor cell antigens. Nc886 alleviates the inflammatory response of acute rejection caused by human-derived prostate cancer cellular xenografts in immunocompetent mouse models. Nc886 reduces the polarization of macrophages through TGF-β1 inhibition.
CANCER PREVENTION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
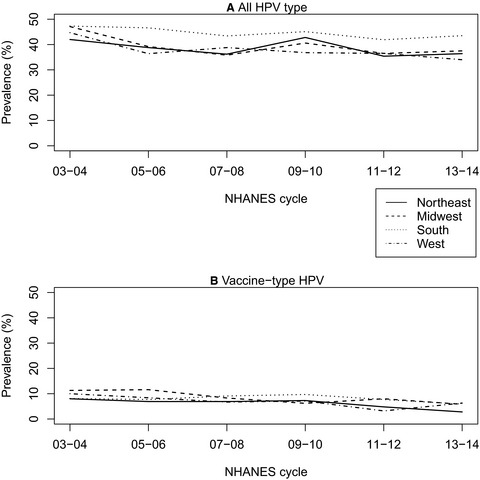
Geographical disparities in human papillomavirus herd protection
- Pages: 5272-5280
- First Published: 01 June 2020
Reasons for not receiving the HPV vaccine among eligible adults: Lack of knowledge and of provider recommendations contribute more than safety and insurance concerns
- Pages: 5281-5290
- First Published: 01 June 2020
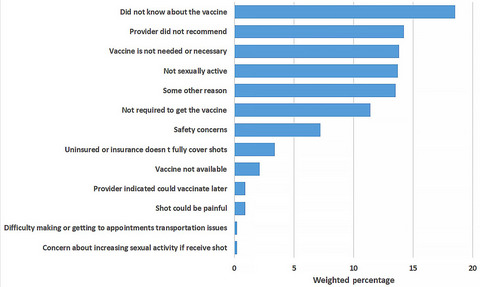
Among HPV-vaccine eligible adults, lack of knowledge about the vaccine and lack of provider recommendations are the most commonly reported reasons for not receiving the HPV vaccine. In this population, educational interventions should focus on enhancing HPV vaccine's knowledge and provider recommendations of the necessity and awareness of HPV vaccination.