Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
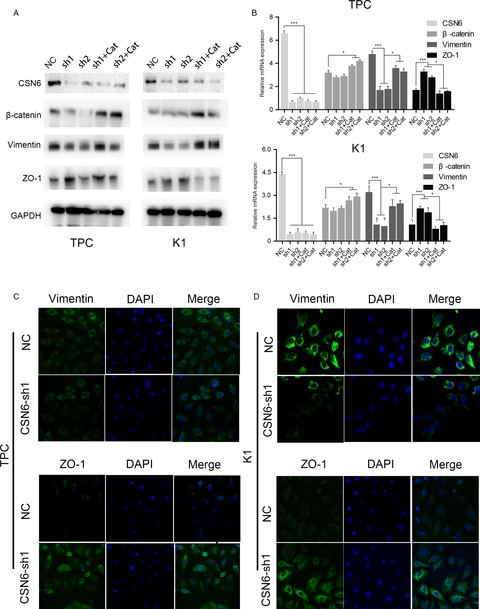
Downregulation of CSN6 attenuates papillary thyroid carcinoma progression by reducing Wnt/β-catenin signaling and sensitizes cancer cells to FH535 therapy
- Pages: 285-296
- First Published: 17 January 2018
Effects of Th17 cells and IL-17 in the progression of cervical carcinogenesis with high-risk human papillomavirus infection
- Pages: 297-306
- First Published: 26 December 2017
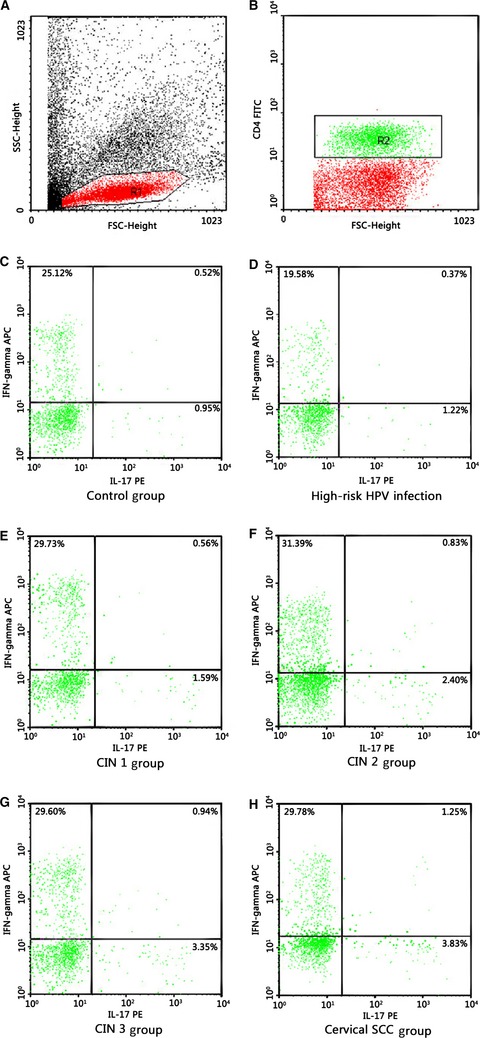
In this work, we evaluated the frequency of Th17 cells in peripheral blood samples obtained from cervical squamous cell carcinoma patients, CIN1 patients, CIN2 patients, CIN3 patients, high-risk HPV-infected women with normal cervical cytology, and healthy controls,as well as the levels of IL-17 in peripheral blood samples and in supernatant of cervical tissue homogenate. So we had come to the conclusion that Th17 cells and IL-17 may play a role of immune enhancement in the infection of high-risk HPV, which contribute to the disease progression of its associated cervical lesions.
Analysis of long-term survival in multiple myeloma after first-line autologous stem cell transplantation: impact of clinical risk factors and sustained response
- Pages: 307-316
- First Published: 28 December 2017
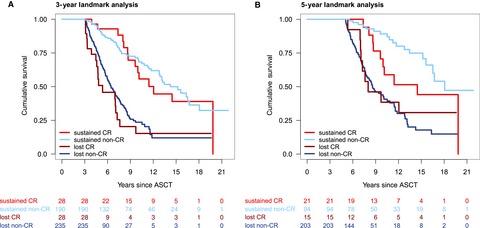
Long-term analysis of 865 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma treated with first-line autologous stem cell transplantation reveals sustained response after transplantation as a major prognostic factor for survival. Administration of maintenance therapy independently improves outcome, supporting the hypothesis that interventions to prolong responses achieved may be essential to reach long-term survival.
Can therapeutic drug monitoring increase the safety of Imatinib in GIST patients?
- Pages: 317-324
- First Published: 07 January 2018
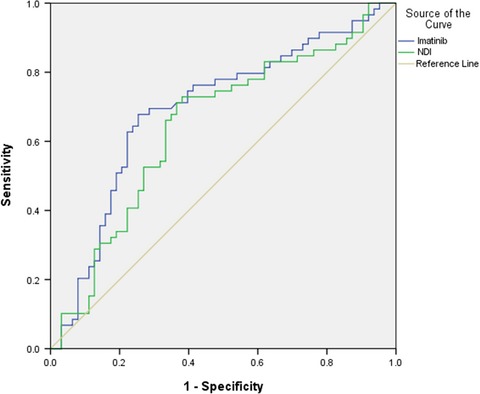
Since Imatinib is usually administered for a prolonged period, rational management of its side effects is of great importance. Few studies have been conducted to investigate the association between plasma concentration and side effects. In this study, Imatinib-induced myelosuppression was found to be correlated significantly with Imatinib concentration, and the estimated exposure threshold for myelosuppression was 1451.6 ng/mL with ROCAUC (95% CI) of 0.693 (0.597–0.789).
CTAPIII/CXCL7: a novel biomarker for early diagnosis of lung cancer
- Pages: 325-335
- First Published: 22 January 2018
Mechanism underlying the negative effect of prostate volume on the outcome of extensive transperineal ultrasound-guided template prostate biopsy
- Pages: 336-343
- First Published: 17 January 2018
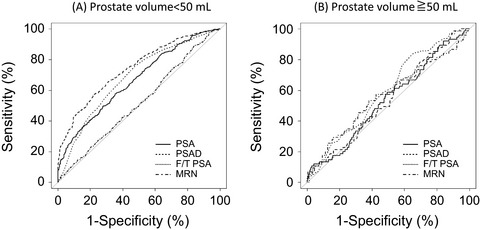
The currents study indicates that the diameters of maximum cancer lesions in patients with prostate volume ≥ 50 mL were significantly smaller than those in patients with prostate volume <50 mL. Loss of diagnostic accuracy of markers in patients with prostate volume ≥ 50mL indicates a decrease in serum levels of PSA produced by prostate cancer, which suggests growth inhibition of the cancer.
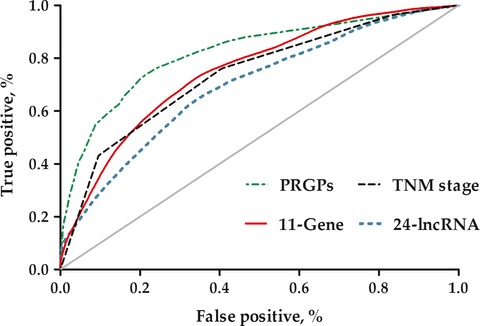
Identification of a novel gene pairs signature in the prognosis of gastric cancer
- Pages: 344-350
- First Published: 28 December 2017
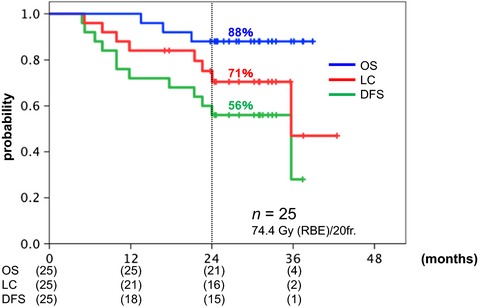
Clinical outcomes of carbon ion radiotherapy with concurrent chemotherapy for locally advanced uterine cervical adenocarcinoma in a phase 1/2 clinical trial (Protocol 1001)
- Pages: 351-359
- First Published: 17 January 2018
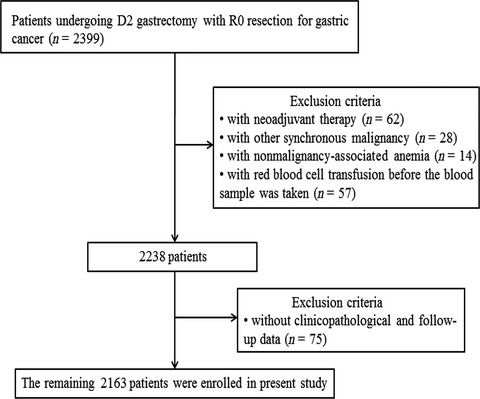
Impact of preoperative anemia on outcomes in patients undergoing curative resection for gastric cancer: a single-institution retrospective analysis of 2163 Chinese patients
- Pages: 360-369
- First Published: 17 January 2018
Spatial barriers impact upon appropriate delivery of radiotherapy in breast cancer patients
- Pages: 370-379
- First Published: 22 January 2018
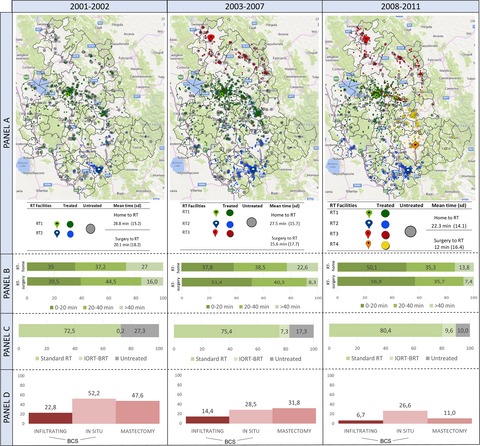
This is the first European study to investigate the impact of spatial barriers upon appropriate radiotherapy (RT) in breast cancer patients. In Umbria, central Italy, journey times >40 min significantly decreased the probability of receiving RT and were consequently associated with poor outcome. New RT centers provided more patients with appropriate treatment, raising the issue of a “hub and spoke” approach. Spatial barriers to RT in Europe deserve investigation.
Cancer Biology
Original Research
Induction of autophagy and autophagy-dependent apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by a new antimalarial artemisinin derivative, SM1044
- Pages: 380-396
- First Published: 26 December 2017
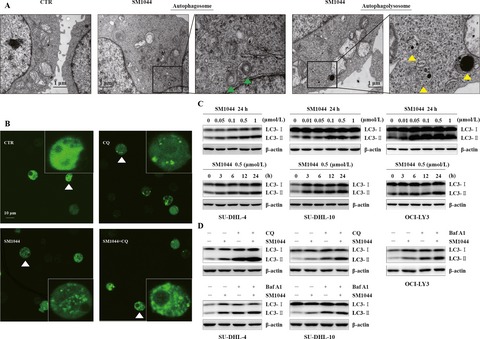
Our research reported an artemisinin derivative, SM1044, induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis which is triggered by an increased acetylation of Survivin, a modification which induces its interaction with LC3-II and its degradation. We also unraveled that the activation of CaMKK2–AMPK–ULK1 axis was molecular basis of SM1044-dependent stimulation of autophagy. These investigations not only point to SM1044 as a promising molecule in fighting diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but also unravel important information of the molecular pathways involved in the oncogenesis of DLBCL.
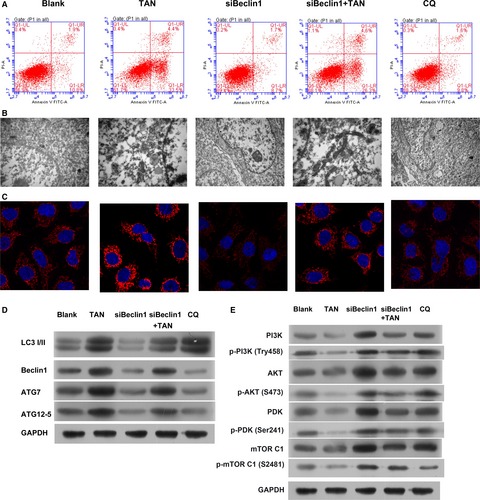
Tanshinone IIA induces cell death via Beclin-1-dependent autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-9 cell line
- Pages: 397-407
- First Published: 06 January 2018
The synergistic role of ATP-dependent drug efflux pump and focal adhesion signaling pathways in vinorelbine resistance in lung cancer
- Pages: 408-419
- First Published: 10 January 2018
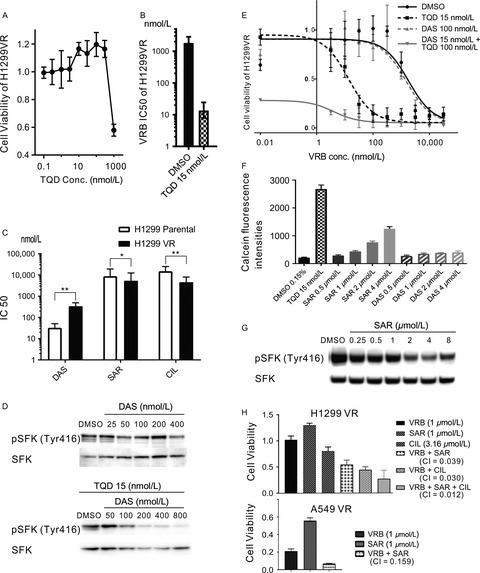
We established vinorelbine-resistant lung cancer cells and examined its transcriptional changes, protein expressions, and activations. On the basis of these results, we focused on the focal adhesion (FA) pathway and tested the effects of gene silencing and inhibitors. In conclusion, FA pathway, particularly integrin and SFK, are promising targets for vinorelbine-resistant lung cancer.
Nuclear division cycle 80 promotes malignant progression and predicts clinical outcome in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 420-432
- First Published: 17 January 2018
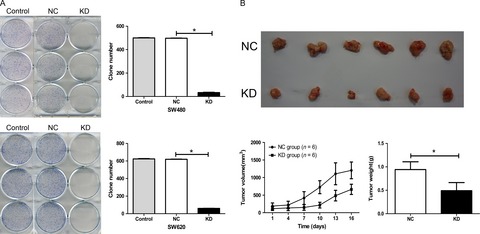
In summary, our results indicate that high NDC80 expression is correlated with advanced tumor stage and unfavorable prognosis in CRC patients. In addition, we also find NDC80 drives malignant progression of CRC cells partly by inactivating DUSP5 and FOXO1. Taken together, these evidences suggest NDC80 is not only a promising clinical biomarker for patient management, but also a potential therapeutical target for CRC diagnosis and treatment.
Contribution of MLH1 constitutional methylation for Lynch syndrome diagnosis in patients with tumor MLH1 downregulation
- Pages: 433-444
- First Published: 17 January 2018
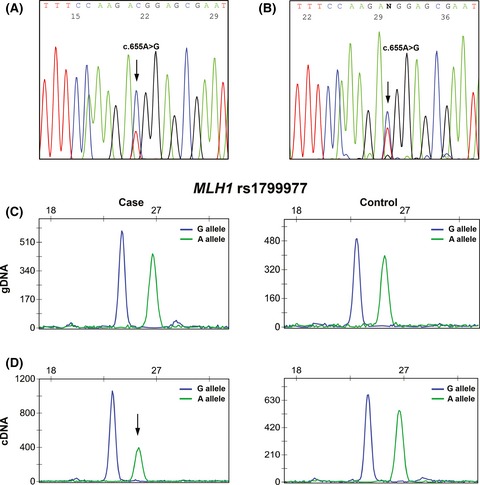
This work aimed to investigate the prevalence of MLH1 constitutional methylation in colorectal cancer patients with abnormal expression of the MLH1 protein in their tumors and without germline mutations. We provide evidence that MLH1 constitutional hypermethylation is the molecular mechanism behind about 3% of Lynch syndrome families, most likely in patients with early onset or multiple primary tumors without significant family history.
AKT3 drives adenoid cystic carcinoma development in salivary glands
- Pages: 445-453
- First Published: 28 December 2017
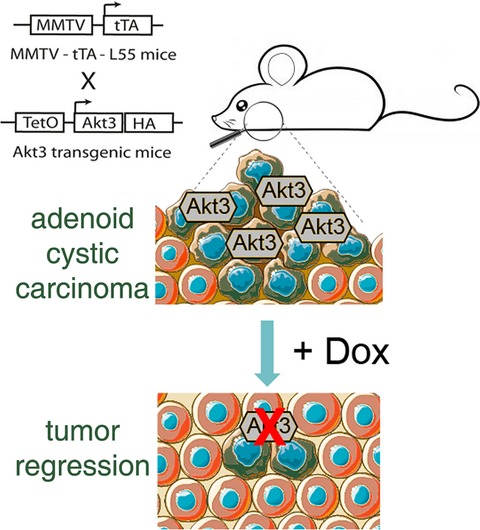
AKT3 expression is associated with bad prognosis in head and neck cancer. Taking advantage of a novel mouse model, we report that conditional Akt3 overexpression triggers adenoid cystic carcinomas in the salivary glands of mice with 100% penetrance. We further show that these adenoid cystic carcinomas are completely dependent on expression of the oncogene.
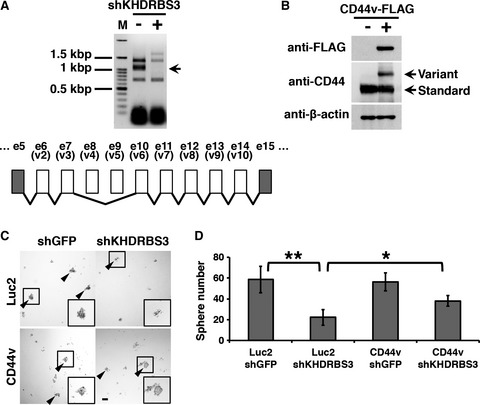
SALL4 - KHDRBS3 network enhances stemness by modulating CD44 splicing in basal-like breast cancer
- Pages: 454-462
- First Published: 22 January 2018
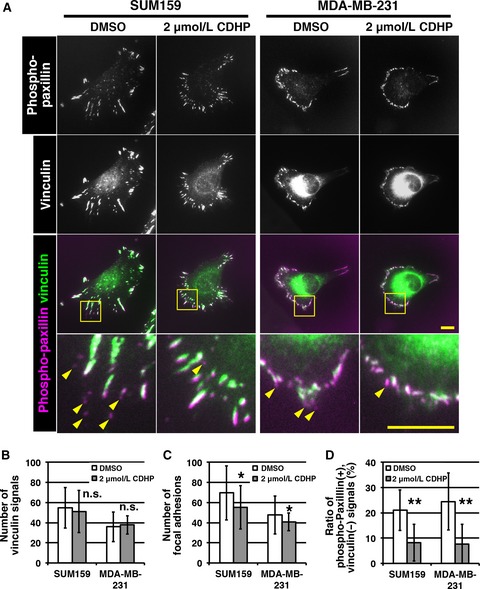
5-Chloro-2,4-dihydroxypyridine, CDHP, prevents lung metastasis of basal-like breast cancer cells by reducing nascent adhesion formation
- Pages: 463-470
- First Published: 22 January 2018
Reviews
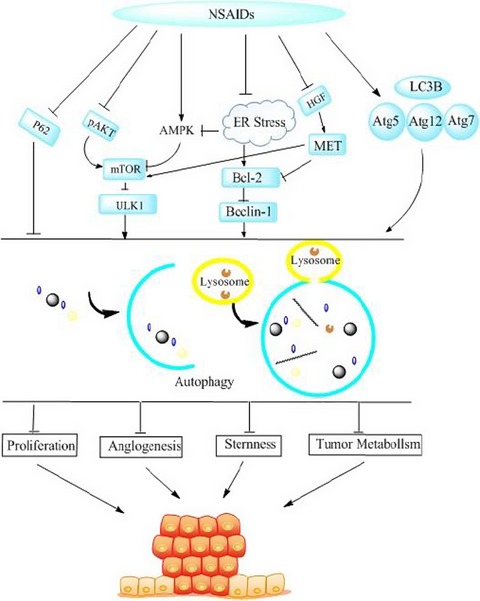
Autophagy: novel applications of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for primary cancer:
- Pages: 471-484
- First Published: 28 December 2017
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
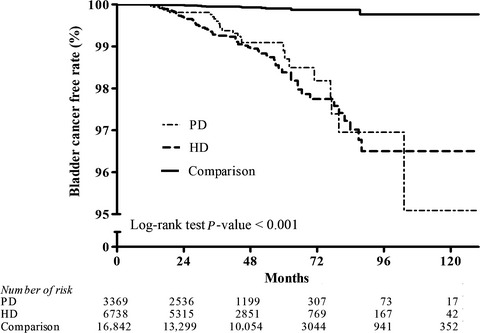
Is there different risk of cancer among end-stage renal disease patients undergoing hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis?
- Pages: 485-498
- First Published: 22 January 2018
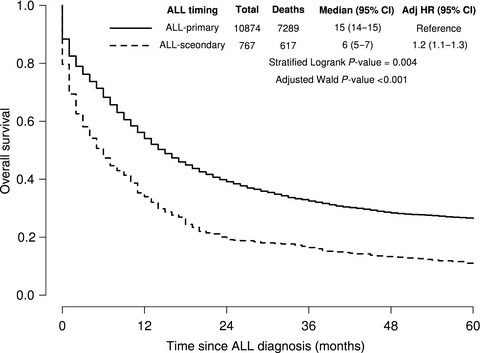
Second primary acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: a SEER analysis of incidence and outcomes
- Pages: 499-507
- First Published: 28 December 2017
Risk stratification for febrile neutropenia in patients with testicular germ cell tumors
- Pages: 508-514
- First Published: 19 January 2018
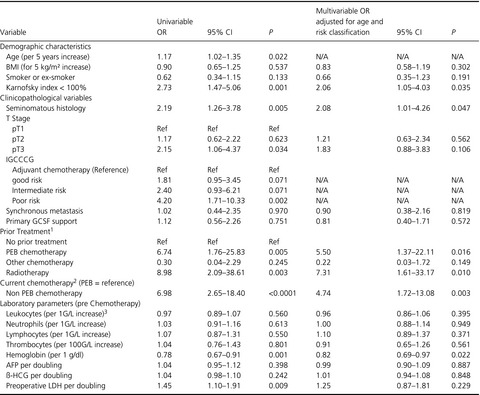
The aim of this study was to detect prognostic factors for febrile neutropenia (FN) in patients with testicular germ cell tumors. We identified (1) higher age, (2) poor performance status, (3) poor IGCCCG risk classification, and (4) prior radiotherapy in the seminoma subpopulation as risk factors for FN in patients with testicular cancer.
Personality and breast cancer screening in women of the GAZEL cohort study
- Pages: 515-524
- First Published: 26 December 2017
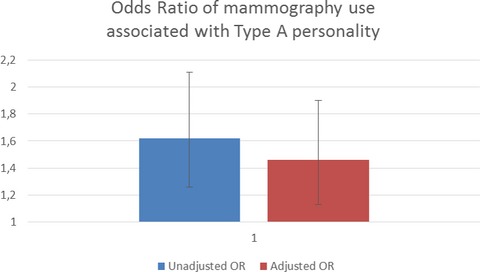
Type A personality traits (i.e., sense of time urgency, high job involvement, competitiveness) independently predicted mammography use among 2691 postmenopausal women of the GAZEL Cohort Study (adjusted Odds Ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.46: [1.13–1.90], P < 0.01). While paying more attention to the adherence of women with low levels of these traits, clinicians may help those with higher levels to better consider the risks of false positives and overdiagnosis.
Disparities in cancer outcomes across age, sex, and race/ethnicity among patients with pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 525-535
- First Published: 11 January 2018
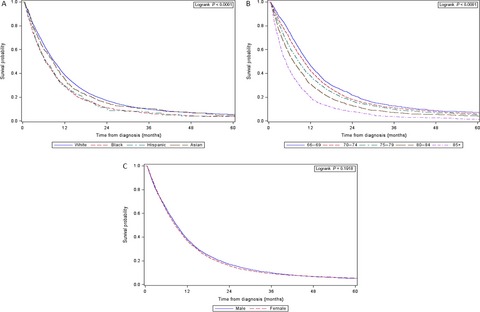
Disparities in pancreatic cancer outcomes exists, but are not fully understood. Our research uses SEER–Medicare data to determine which factors contribute to the differences in treatment receipt and survival outcomes among age, sex, and racial/ethnic subgroups. Our conclusion that disparities continue to persist after adjusting for various covariates highlights the need for additional research in this area.