Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
STEATOHEPATITIS
Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index has utility as a biomarker of COVID-19 severity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Pages: 1047-1058
- First Published: 19 July 2023
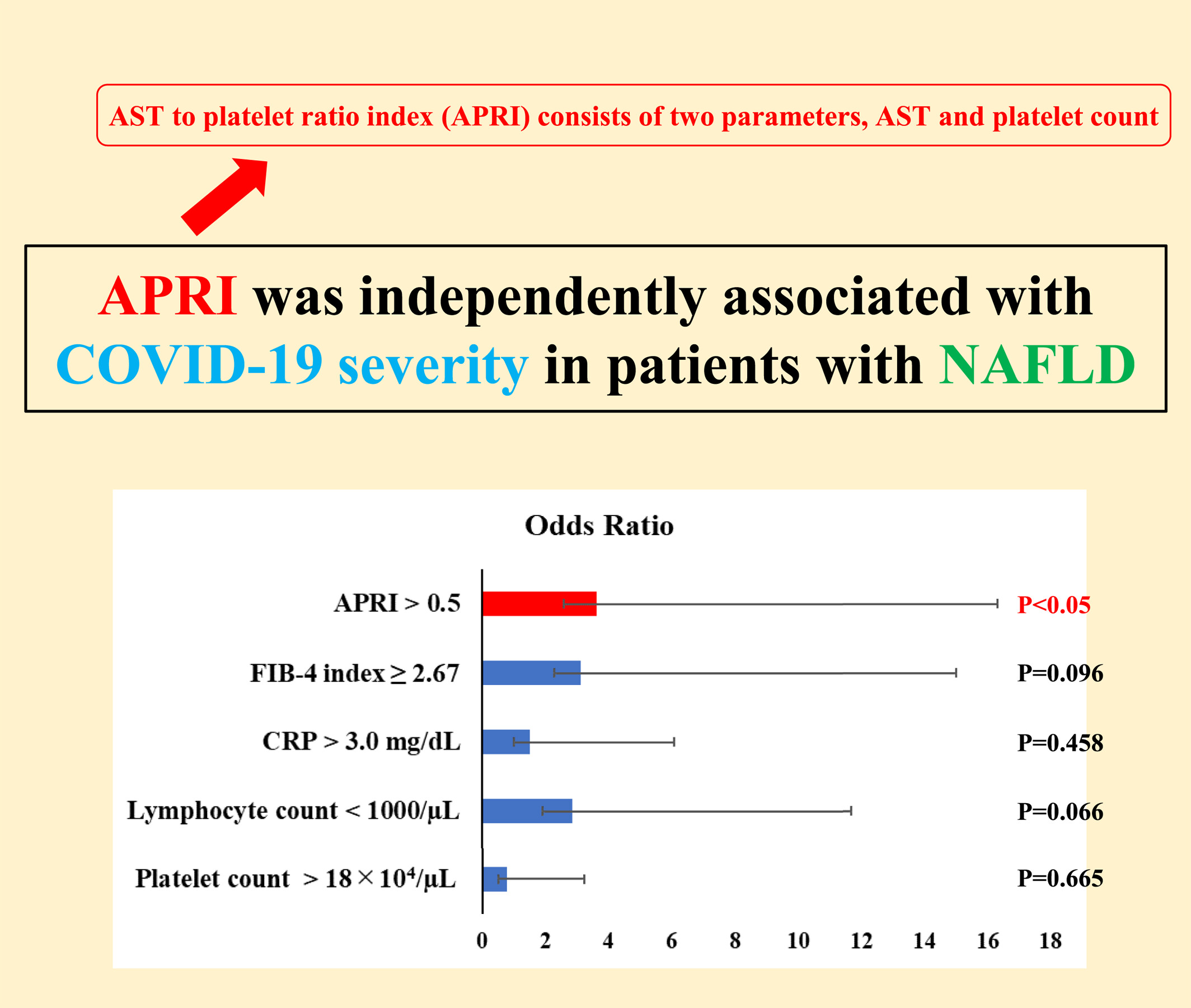
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are reported to have greater COVID-19 severity than those without nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index consists of two parameters, aspartate aminotransferase and platelet count, and is much simpler than other liver fibrosis scores. The aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index was independently associated with COVID-19 severity and hospitalization duration for COVID-19 in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
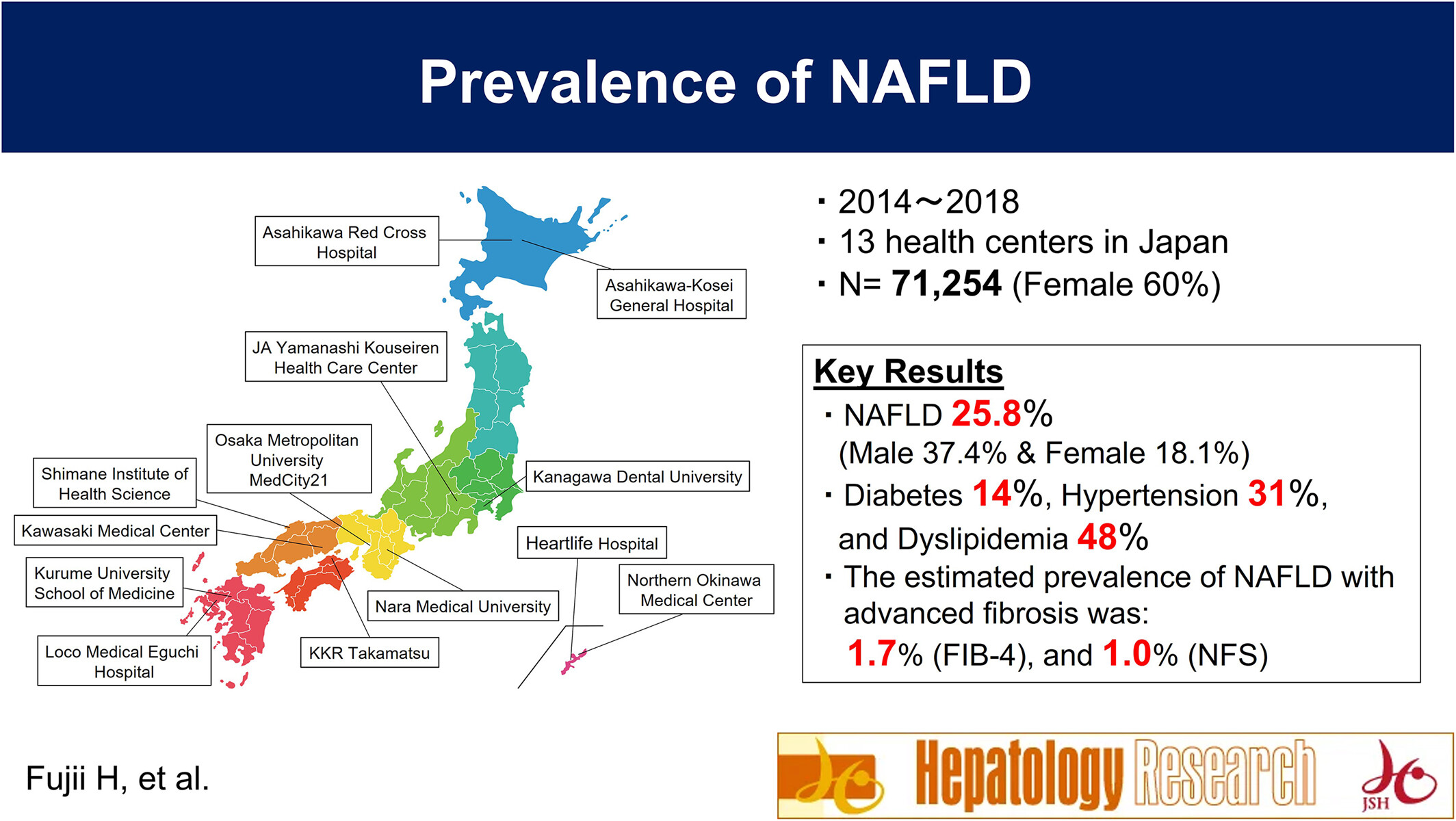
Prevalence and associated metabolic factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the general population from 2014 to 2018 in Japan: A large-scale multicenter retrospective study
- Pages: 1059-1072
- First Published: 03 August 2023
AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASE
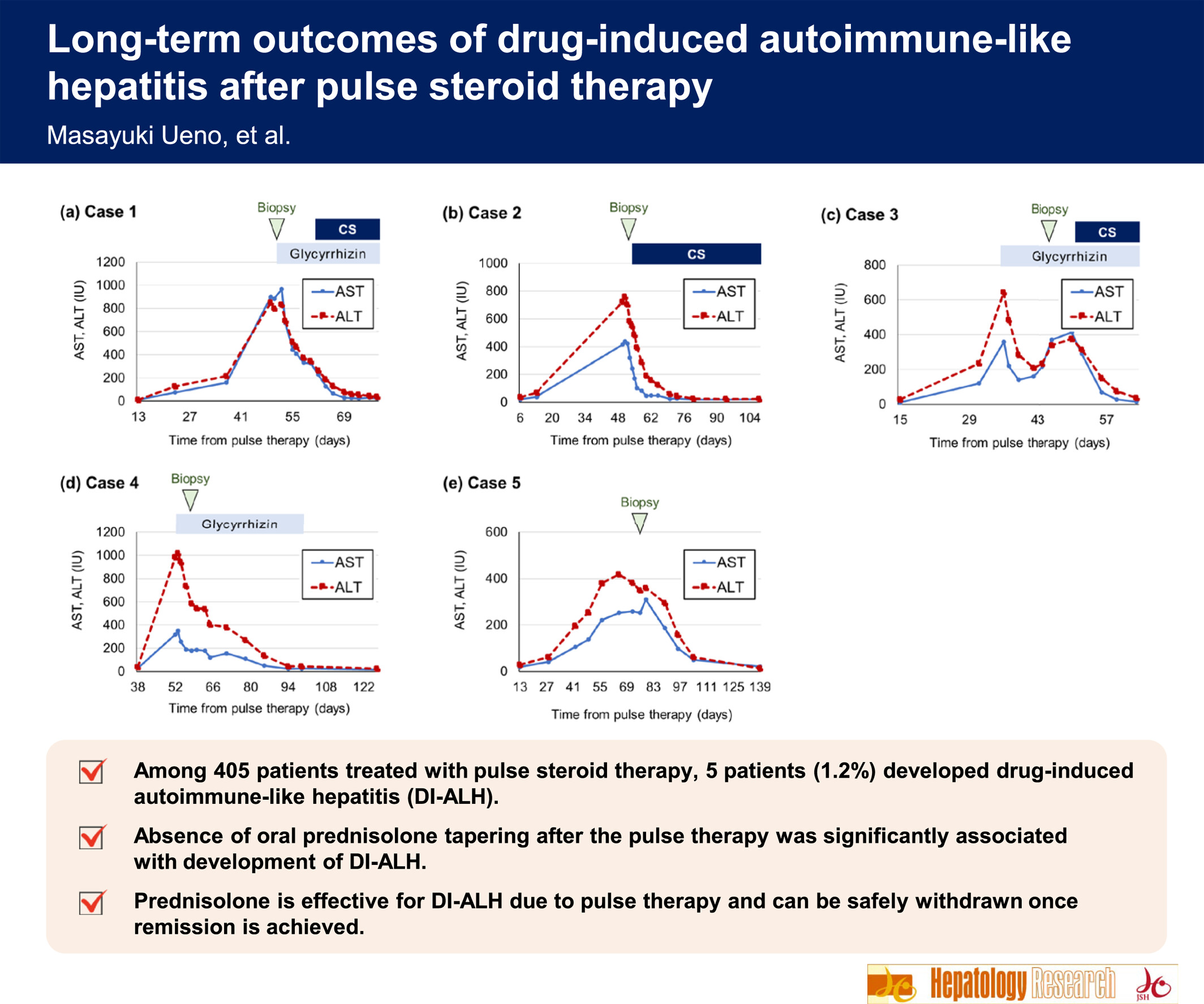
Long-term outcomes of drug-induced autoimmune-like hepatitis after pulse steroid therapy
- Pages: 1073-1083
- First Published: 22 June 2023
CIRRHOSIS
Correlation between hepatic venous pressure gradient and portal pressure gradient in patients with autoimmune cirrhotic portal hypertension and collateral branches of the hepatic vein
- Pages: 1084-1095
- First Published: 23 June 2023
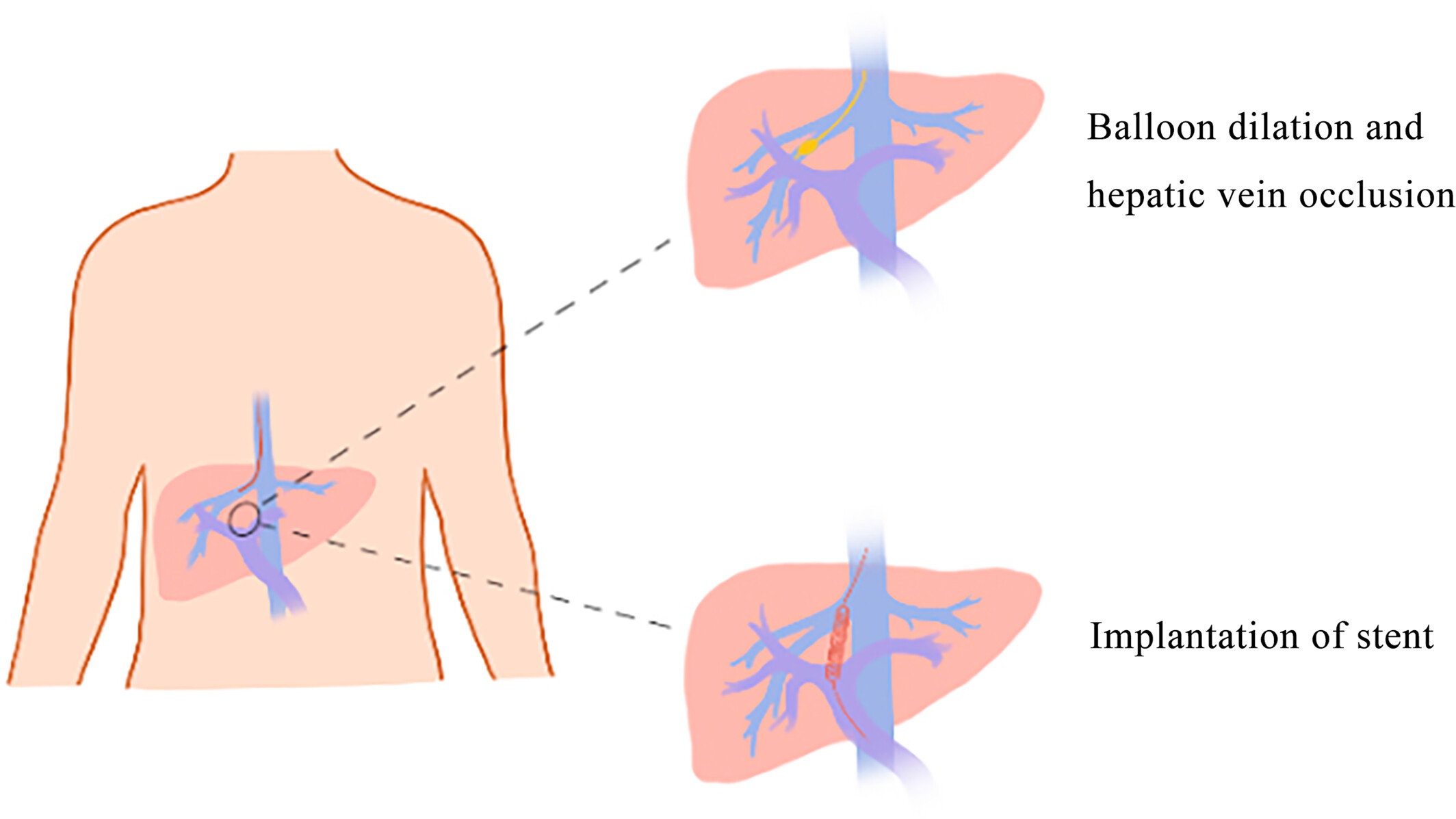
Our study confirmed that the correlation between the wedged hepatic venous pressure (WHVP) and portal venous pressure groups and between the hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) and portal pressure gradient groups was better in both triphasic shunting and portal vein visualization by innovative angiography, with the best agreement in the portal vein visualization group. Hepatic vein collateral branches were an important factor in underestimating WHVP and HVPG; the earlier the appearance of collateral branches, the more pronounced the underestimation. The absence of hepatic vein collateral veins is a crucial factor in the overestimation of the WHVP and HVPG.
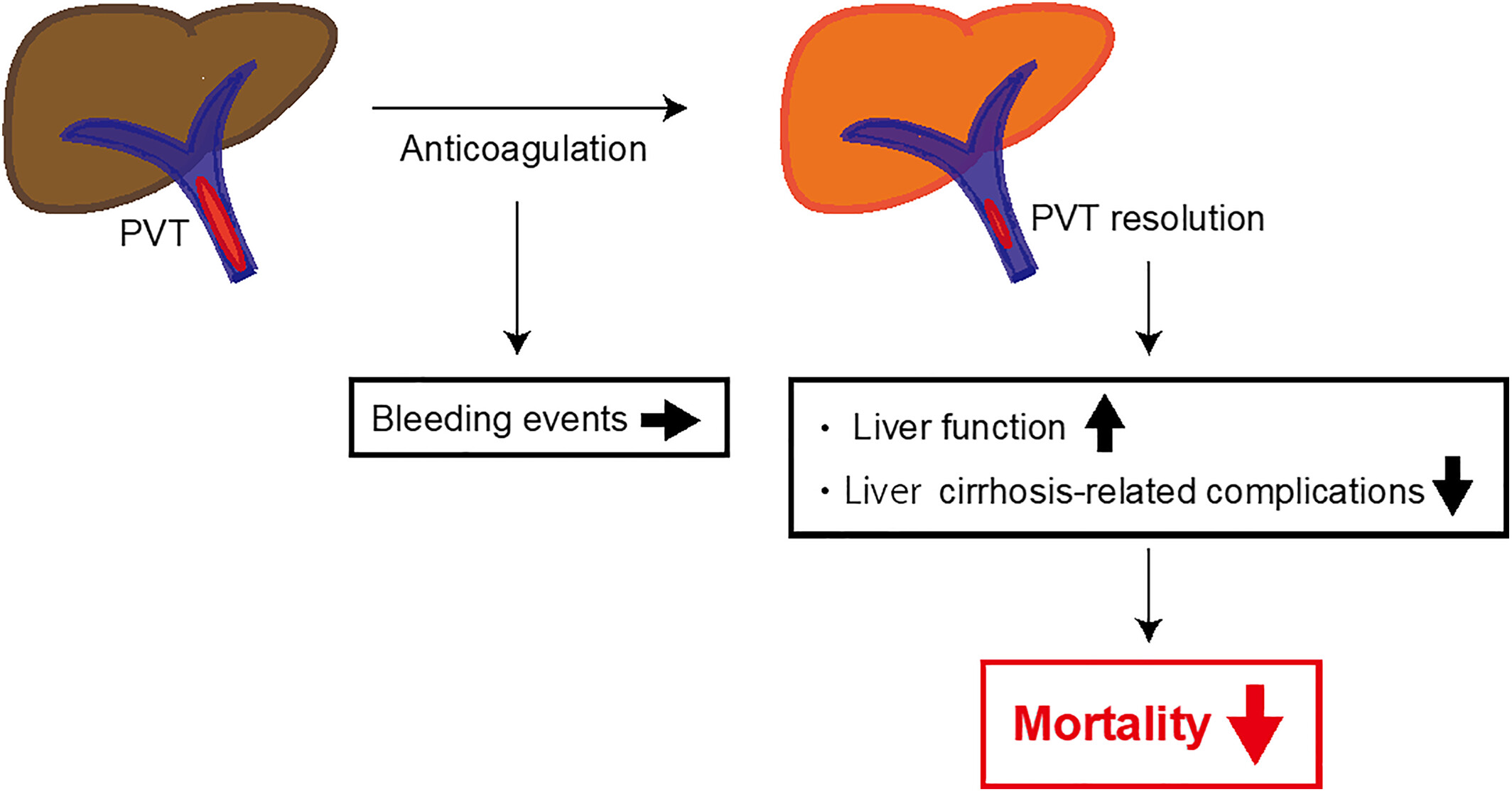
Anticoagulation against portal vein thrombosis reduces mortality and liver cirrhosis-related complications: A propensity score-matched study
- Pages: 1096-1104
- First Published: 12 July 2023
Safety and effectiveness of lusutrombopag in patients who have chronic liver disease with thrombocytopenia and undergoing invasive procedures: Real-world post-marketing surveillance in Japan
- Pages: 1105-1116
- First Published: 27 July 2023
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA AND OTHER MALIGNACY
Clinical utility of postablation liver tumor biopsy and possibility of gene mutation analysis
- Pages: 1117-1125
- First Published: 24 July 2023
SURGERY
Predictive model containing gene signature and shear wave elastography to predict patient outcomes after Kasai surgery in biliary atresia
- Pages: 1126-1133
- First Published: 31 July 2023
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Rare sequence variants associated with the risk of non-syndromic biliary atresia
- Pages: 1134-1141
- First Published: 25 July 2023
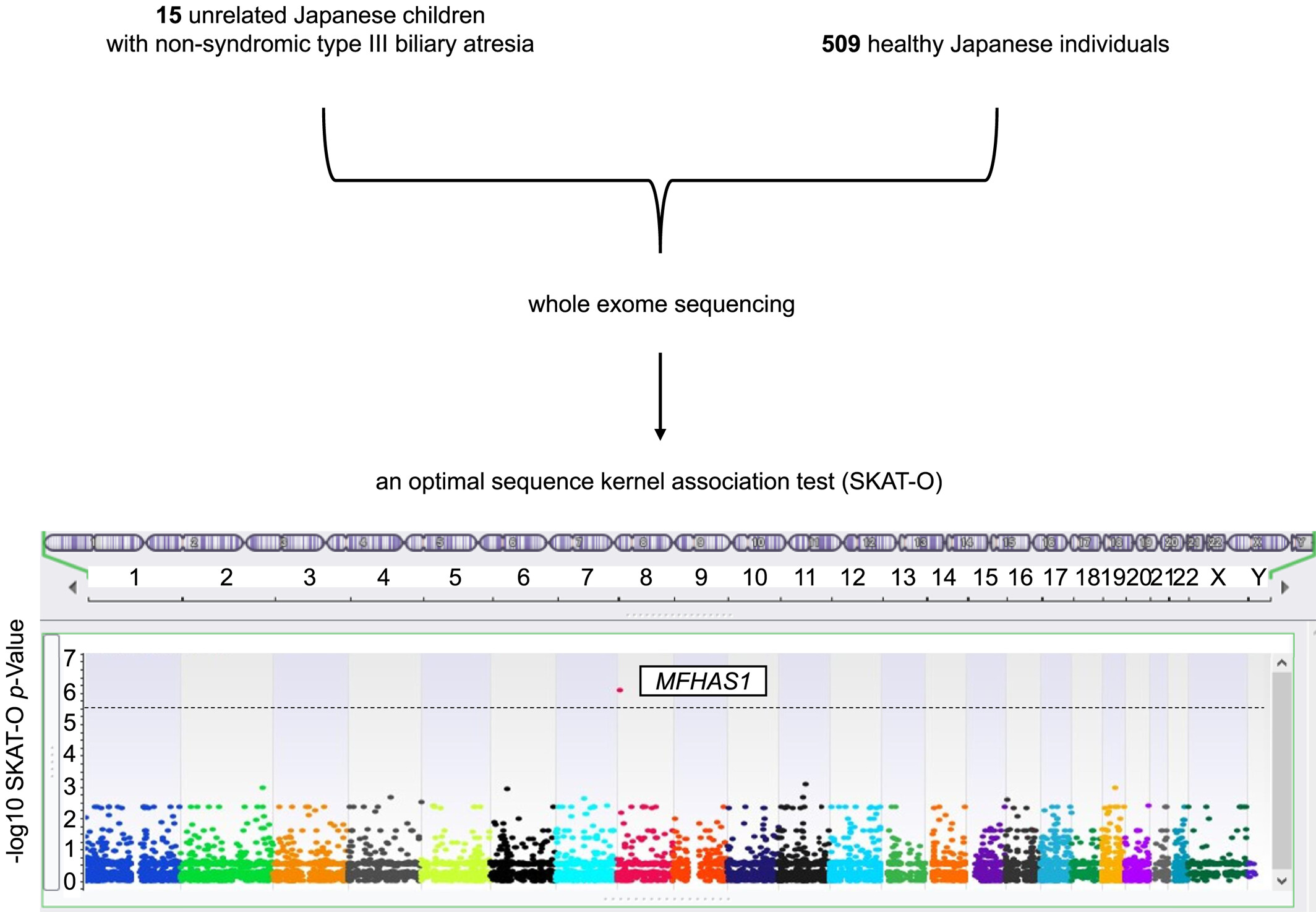
We conducted an optimal sequence kernel association test using exome data of 15 Japanese patients with non-syndromic type III biliary atresia and 509 control individuals. The results indicate that rare damaging variants in MFHAS1 may constitute a risk factor for non-syndromic biliary atresia; however, the overall contribution of monogenic variants to the disease predisposition is small.