Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index has utility as a biomarker of COVID-19 severity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Aim
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are reported to have greater coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity compared with patients without NAFLD. Previous studies have reported that noninvasive liver fibrosis scores, including the Fibrosis-4 index, NAFLD fibrosis score, and aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI), have utility in predicting COVID-19 mortality and disease severity in patients without NAFLD. However, the utility of liver fibrosis scores in predicting COVID-19 mortality and disease severity among patients with NAFLD infected with SARS-CoV-2 has yet to be evaluated.
Methods
This retrospective observational study comprised 126 patients with NAFLD and active SARS-CoV-2 infection. Patients were classified into low COVID-19 severity (mild or moderate I disease) and high COVID-19 severity (moderate II or severe disease) groups based on the therapeutic guideline implemented by the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan.
Results
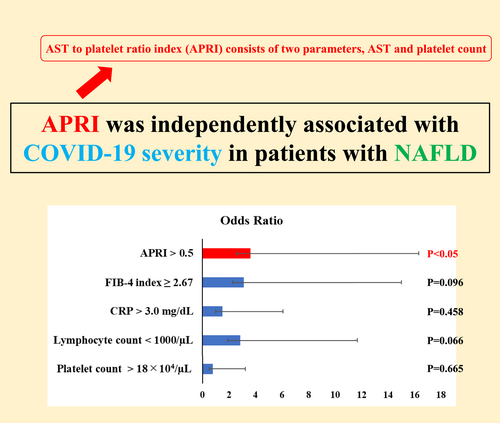
Of the 126 patients, only one had been diagnosed with NAFLD before admission. Age; levels of serum aspartate aminotransferase, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, lactate dehydrogenase, blood urea nitrogen, and serum C-reactive protein; Fibrosis-4 index; NAFLD fibrosis score; and APRI levels on admission were higher in the high COVID-19 severity group compared with the low COVID-19 severity group. Serum albumin levels, platelet counts, and lymphocyte counts on admission were lower in the high COVID-19 severity group compared with the low COVID-19 severity group. Univariate and multivariate analysis revealed that APRI values were significantly associated with COVID-19 severity and hospitalization duration for COVID-19.
Conclusions
APRI was independently associated with COVID-19 severity and hospitalization duration for COVID-19 in patients with NAFLD.
Graphical Abstract
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are reported to have greater COVID-19 severity than those without nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index consists of two parameters, aspartate aminotransferase and platelet count, and is much simpler than other liver fibrosis scores. The aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index was independently associated with COVID-19 severity and hospitalization duration for COVID-19 in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
Hitoshi Yoshiji is Deputy-Editor-in-Chief of the journal and a co-author of this article. They were excluded from the peer-review process and all editorial decisions related to the acceptance and publication of this article. Peer review was handled independently by Yoshiyuki Ueno and Shinya Maekawa, who are in charge of this manuscript to minimize bias.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data are not publicly available due to privacy.