Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Numerical Investigation of the Combined Effect of Reactive Cleaning and Active Filtration on Inclusion Removal in an Induction Crucible Furnace
- First Published: 02 November 2021

The cover image presents the melt flow inside the induction crucible furnace utilized under the frame of the Collaborative Research Centre (CRC 920) to investigate melt filtration and inclusion removal. The results of the numerical simulations indicate the importance of reactive cleaning and formation of carbon monoxide bubbles to remove inclusions from steel melt and enhance steel quality. Further details can be found in the article number 2100122 by Amjad Asad and co-worker.
Masthead
Contents
Research Articles
Numerical Investigation of the Combined Effect of Reactive Cleaning and Active Filtration on Inclusion Removal in an Induction Crucible Furnace
- First Published: 03 June 2021
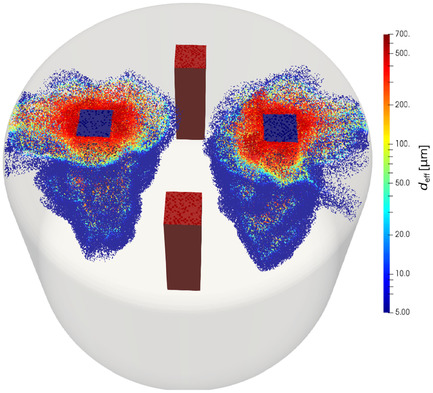
The effect of the combination between active filtration and reactive cleaning on the melt cleanliness is investigated in the article. The main aim of the article is to show the importance of the reactive effect of the filter and of the formation of carbon monoxide bubbles on inclusion removal in steel casting industry.
Tempering and Intercritical Annealing of Air-Hardening 4 wt% Medium Manganese Steels
- First Published: 04 May 2021
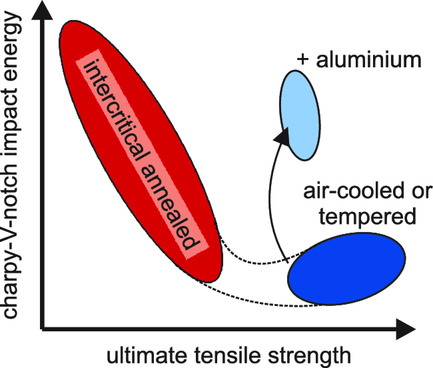
The mechanical properties of 4 wt% medium manganese steels after different heat treatments are investigated. While the air-hardened as well as tempered condition is characterized by high strengths and comparatively low ductilities, this balance is reversed for the intercritically heat-treated samples. This trade-off can be prevented by the alloying of aluminum, leading to a superior property balance.
Research on Nozzle Design and Application of Single-Flow Postcombustion Oxygen Lance in a 120 t Top-Blown Converter
- First Published: 02 June 2021
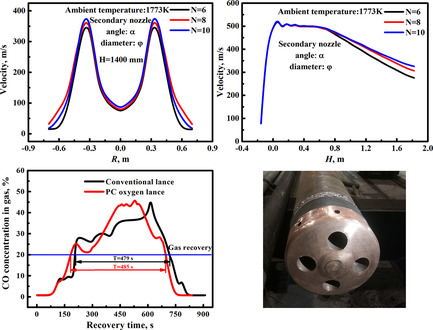
Design criteria of a single-flow postcombustion (PC) oxygen lance are first proposed. Then, the influences of key parameters of the secondary nozzles on the jet characteristics and PC behavior are studied by numerical simulation. Finally, an optimal PC oxygen lance is designed and its smelting effect is compared with that of a conventional lance by industrial tests.
Novel Gradient Alloy Steel with Quasi-Continuous Ratios Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting: Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior
- First Published: 02 June 2021
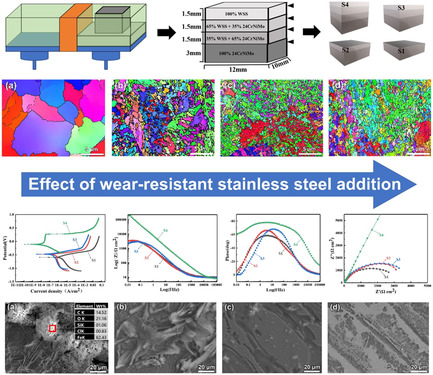
A quasi-continuous ratio gradient alloy steel for external strengthening layer of high-speed railway brake disc is fabricated by selective laser melting for the first time. With the increase in the content of wear-resistant stainless steel, the microstructure refine and the texture intensity decrease, and the corrosion resistance of the material is significantly improved.
Effect of Bonding Area Formation During Sintering on the Reaction Characteristics of Iron Ores
- First Published: 23 June 2021
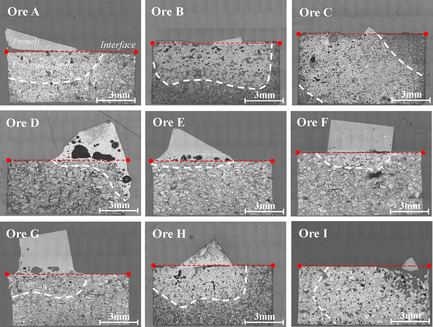
Herein, new findings regarding bonding area formation during the sintering of various iron ores and its implications in reactivity and blending are suggested, which is critical to the iron-making process. A new reactivity index is introduced to clearly distinguish the reaction characteristics of iron ore and investigate the effect on the product yield and size of the sintered ore.
Nitride Dispersion Strengthened Steel Development after Sintering of Nitrided Fe-4.6 at% Al Alloy Powder
- First Published: 05 June 2021
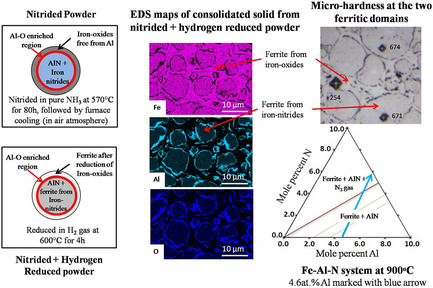
The production of a nitride dispersion strengthened steel is achieved by the spark plasma sintering of nitrided Fe-4.6 at% Al alloy powders. The unique microstructures developed during consolidation of the treated powders are discussed. The final microstructure primarily consists of hard ferritic domains (strengthened by a uniform distribution of nanosized AlN precipitates) embedded/distributed in a soft ferritic phase.
Influence of Cooling Parameters on the Microstructure and Primary Carbide Precipitation in GCr15 Steel
- First Published: 05 June 2021

The solidification behavior of GCr15 steel with different cooling mechanisms is investigated by the high-temperature confocal laser scanning microscope (HT-CLSM). The solidification microstructure forms in the earlier solidification process, while the primary carbide participates in the later cooling stage. The primary carbide size can still be reduced with a higher cooling rate in the subsequent cooling stage.
Effect of Pressure on Second Dendrite Arm Spacing and Columnar to Equiaxed Transition of 30Cr15Mo1N Ingot
- First Published: 30 June 2021

Pressurization decreases the second dendrite arm spacing (SDAS) of 30Cr15Mo1N ingot by enhancing cooling rate. The distance between the center of ingot and columnar to equiaxed transition (CET) position decreases with increasing pressure. The reason is that pressurization increases columnar dendrite tip growth rate and inhibits nucleation and growth of equiaxed dendrite.
Effects of Yttrium on the Microstructure and Properties of 20MnSi Steel
- First Published: 29 June 2021
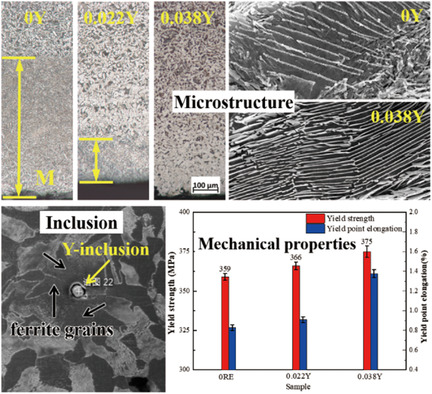
With increasing Y content, the thickness of the martensite layer on the surface of 20MnSi steel decreases gradually which is attributed to Y reducing martensitic transformation temperature. Y refines the size of the pearlitic lamellae, which improves the yield strength. Y-containing composite inclusions assist the nucleation of ferrite, thereby resulting in an increase in the yield point elongation.
Computational Investigation on Effect of Impeller Dimension on Fluid Flow and Interface Behavior for Kanbara Reactor Hot Metal Treatment
- First Published: 29 June 2021
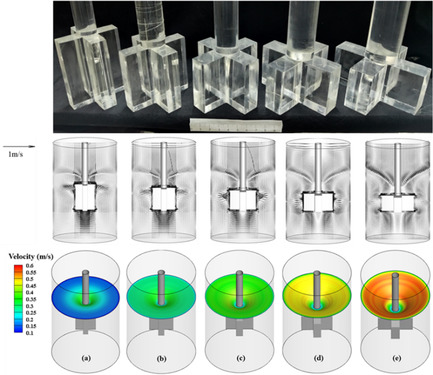
The influences of impeller dimension on bath flow, mixing characteristics, and interface behaviors are investigated through the water model experiments and numerical simulations. As the aspect ratio of the impeller increases, the upper recirculating region is successively strengthened and enlarged. Impeller III is the optimal dimension. Furthermore, a relationship between the vortex core depth and aspect ratio is proposed.
Influence of Interlayer Forced Air Cooling on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Wire Arc Additively Manufactured 304L Austenitic Stainless Steel
- First Published: 11 July 2021
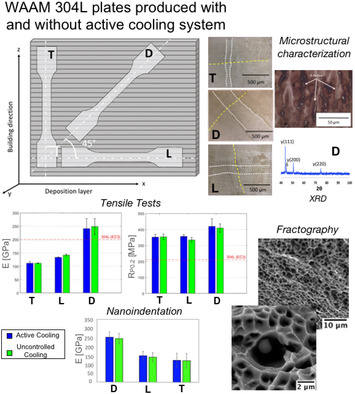
Herein, mechanical properties and microstructural features of 304 L wire-and-arc additively manufactured (WAAM) plates are compared. The focus is on the effect of an interpass air cooling and possible process-induced anisotropy. The results reveal no remarkable influence of the cooling on the microstructure and mechanical behavior, which are instead related to the orientation to the deposited layers.
Experimental Study on Rare Earth and Magnesium Composite Treatment of 49MnVS3 Non-quenched and Tempered Steel
- First Published: 01 July 2021
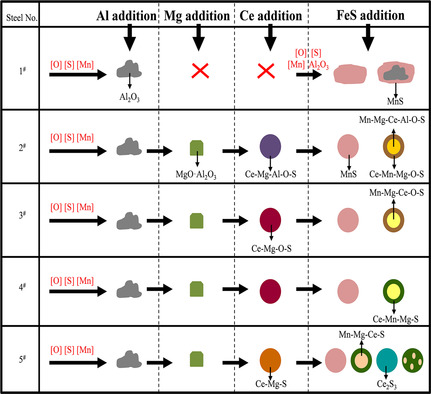
A novel method of combining rare-earth cerium and magnesium to treat the 49MnVS3 steel with low oxygen and fair sulfur was proposed. After Ce and Mg treatment, attributed to modified inclusions and optimized microstructure, the steel achieves the optimum comprehensive mechanical properties with the proper amount of Ce and Mg.
Characterization of Nonmetallic Inclusions in Low-Alloyed Steels Using Pulse Distribution Analysis Optical Emission Spectroscopy and Offline Investigation Methods
- First Published: 06 July 2021
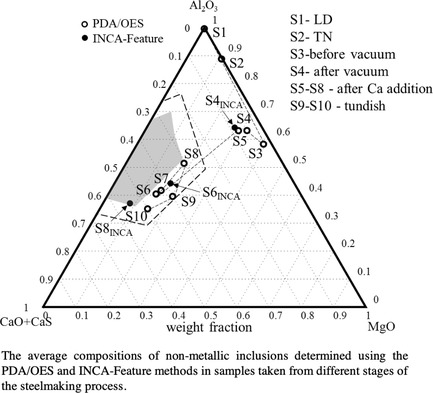
Herein, the characteristics of nonmetallic inclusions (NMIs) in low-alloyed steel samples before and after Ca treatment are evaluated using the pulse distribution analysis optical emission spectroscopy (PDA/OES), INCA-Feature, and electrolytic extraction (EE) methods. The results are compared. Overall, the PDA/OES method enables a fast online evaluation of inclusion compositions during steelmaking, which can be applied to avoid possible clogging problems.
Metallographic, Structural, and Mechanical Characterization of Weld Nuggets in Fe–Mn–Al–C Low-Density Steels Microalloyed with Ti/B and Ce/La by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding Process
- First Published: 06 July 2021
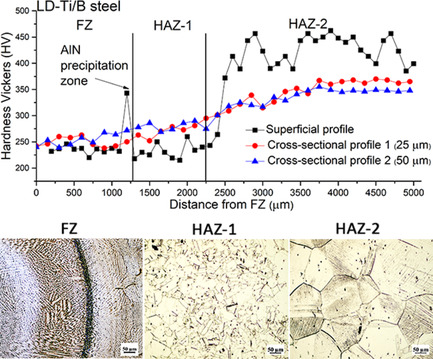
Herein, weld nuggets of Fe–Mn–Al–C low-density steels microalloyed with Ti/B and Ce/La obtained by gas tungsten arc welding process are microstructurally studied. Three well-defined zones are noticed: a fusion zone and two heat-affected zones. A significant decrease in hot-cracking is observed in the microalloyed grades. κ-carbide particles are responsible of the largest hardness values (≈450 Vickers microhardness).
Experimental Study of Mass Transfer Mechanisms for Solute Mixing in a Gas-Stirred Ladle Using the Particle Image Velocimetry and Planar Laser-Induced Fluorescence Techniques
- First Published: 26 July 2021
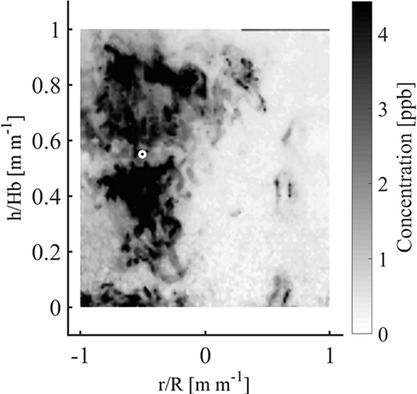
Using particle image velocimetry (PIV) to obtain flow patterns and turbulence together with planar laser-induced fluorescence (PLIF) to measure instantaneous concentration maps during the mixing of tracers injected in a physical model of gas-stirred ladles allows computing the relative importance of convective and turbulent diffusion mass transport mechanisms governing the mixing kinetics for centric and off-centric injection.
3D Growth of Intragranular Pearlite in an Aged 100Mn13 Steel
- First Published: 09 July 2021
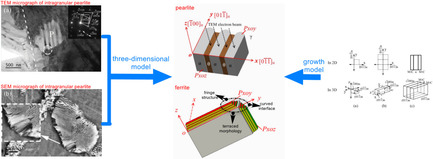
Lamellar pearlite nucleated directly in austenite grain displays a 3D terraced morphology, formed by the layer upon layer of ledges. Ferrite and cementite in intragranular pearlite keep orientation relationship with austenite, especially a new orientation relationship between cementite and austenite. Growth models describing the morphology and growth process of intragranular pearlite in 3D space are proposed.
Slanted Blades Optimizing Grain Texture and Work Hardening of Non-Oriented Electrical Steel in Stress Coverages during Shearing and Blanking Processes
- First Published: 27 July 2021
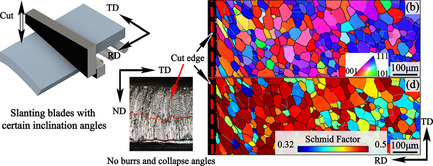
The objective herein is to expound the sheared edges of nonoriented electrical sheets cut by shears with slanted blades. The slanted blades of shears optimize the textures of the edges away from γ (<111>//ND) fiber texture. Particularly, the single blade with a 45°-slanted blade and a flat backing plate show distinct texture optimization with low residual stresses.
Kinetics of Dephosphorization at Different Slag Basicities in the Double Slag Converter Steelmaking Process
- First Published: 04 August 2021
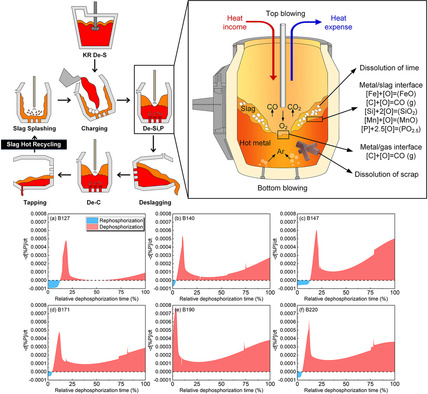
The dephosphorization kinetic model is developed for the double slag converter steelmaking process (DSP) based on the coupled reaction model with consideration of the dissolution of lime and scrap, the heat balance, top and bottom blowing. The predicted P contents are in good agreement with the industry experimental results at the different slag basicities.
Effect of Prior Austenite Grain Size on Crystallographic Characteristics and Low-Temperature Toughness of a Quenched Low-Carbon Low-Alloy Steel
- First Published: 27 July 2021
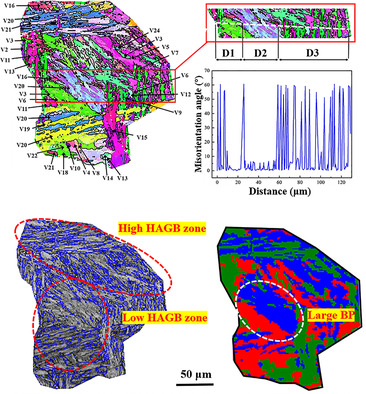
Although there are more variants in larger austenite grains than that in smaller austenite after quenching, the oversized austenite causes coarsened blocks and Bain groups (BPs). Therefore, to improve low-temperature toughness, it is more important to balance the block and BP size refinement and uniformity rather than only consider the fraction of high-angle grain boundaries in quenched low-carbon low-alloy steel.
Characterization of Nonmetallic Inclusions in Different Ferroalloys used in the Steelmaking Processes
- First Published: 27 July 2021
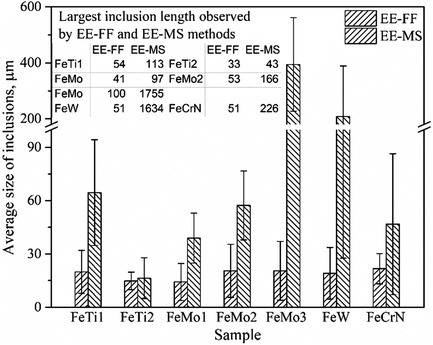
2D investigations on a polished cross section; 3D investigations on a film filter (EE-FF) and a metal surface (EE-MS) after electrolytic extraction are carried out to investigate inclusions in five different types of ferroalloys (FeTi, FeMo, FeW, MnN, and FeCrN). This study helps to better understand the impurities in different ferroalloys and their possible effect on the steel cleanliness.
Use of Bentonite and Organic Binders in the Briquetting of Particulate Residues from the Midrex Process for Improving the Thermal Stability and Reducibility of the Briquettes
- First Published: 05 August 2021
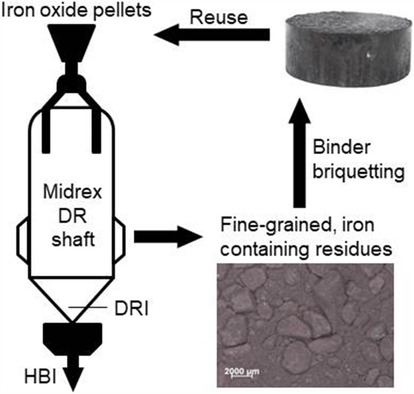
During the production of direct reduced iron using the Midrex process, iron-containing, fine-grained residues are produced. To avoid disposal, a way of briquetting the residues with organic and inorganic binder and returning the briquettes to the Midrex direct reduction process is demonstrated. Laboratory-scale briquetting experiments and reducibility tests are presented.
Enhanced Strength and Toughness of Low-Carbon Bainitic Steel by Refining Prior Austenite Grains and Austempering Below Ms
- First Published: 16 August 2021
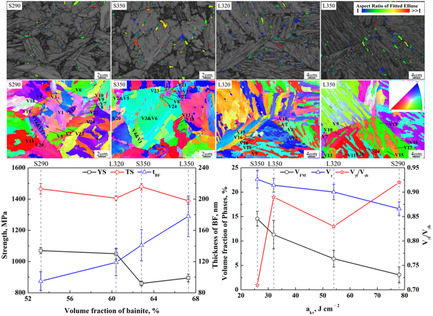
Austempering is conducted below and above Ms at two kinds of prior austenite grain size (PAGS), respectively, in a low-carbon bainitic steel, and the relationship between multiphase microstructure and mechanical properties is investigated. The results indicate that the excellent combination of mechanical properties can be achieved by the coupling effect of finer PAGS and austempering below Ms.
Occurrence State and Behavior of Carbon Brick Brittle in a Large Dissected Blast Furnace Hearth
- First Published: 28 July 2021
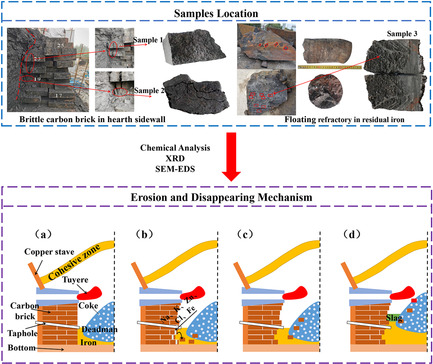
Based on the brittle carbon brick in the hearth sidewall and floating refractory in residual iron during the blast furnace dissection, the occurrence state of the hearth carbon bricks is characterized by chemical analysis, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscope (SEM)–energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The erosion and disappearing mechanism of the carbon bricks are proposed.
Effect of Mo and Tempering Treatment on the Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of M2 High-Speed Steel Prepared by Laser-Directed Energy Deposition
- First Published: 29 July 2021
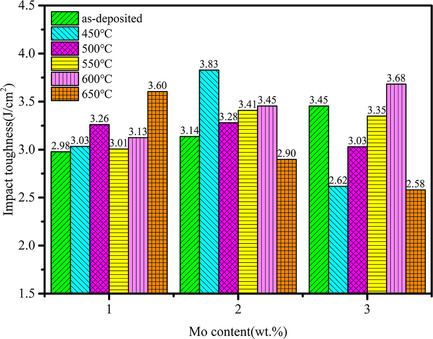
M2 high-speed steel (HSS) with Mo is prepared by laser-directed energy deposition. The addition of an appropriate amount of Mo can promote grain refinement and martensite transformation in M2 HSS, and improve the impact toughness. The hardness of all alloys increases after tempering. The impact toughness of M2+2 wt% Mo after tempering at 450 °C is improved by 126.6%.
Microstructure and Fracture Characteristics of Heat-Affected Zone in Shipbuilding Steel Plates with Mg Deoxidation after High Heat Input Welding
- First Published: 29 July 2021
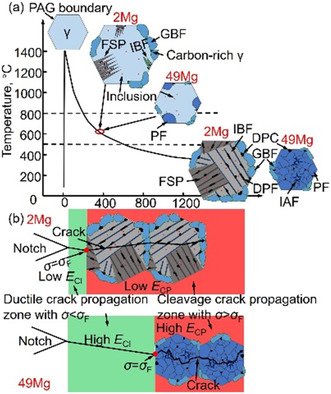
With increasing Mg content in shipbuilding steel plates from 0.0002 to 0.0049 wt%, TiN particles are incrementally refined, and austenite grain size is decreased. The microstructures are changed from coarse ferrite side plates and intragranular bainite ferrites to fine polygonal ferrites with higher crack resistance. So the crack initiation and propagation energies increase, improving the toughness.
A Novel Stacked Rotary Cup Atomizer Toward Efficient Centrifugal Granulation of Molten Blast Furnace Slag
- First Published: 18 August 2021
Atomizer is an important facility in molten slag centrifugal granulation heat recovery system, which concerns the heat recovery rate and the quality of slag particles. A novel stacked rotary cup atomizer is proposed, and the results demonstrate that the novel atomizer has excellent granulation performance in large slag flow rate to produce smaller particles and suppress slagging.
Study on the High-Temperature Evolution and Formation Mechanism of Inclusions in Te-Treated Resulfurized Special Steel
- First Published: 30 July 2021
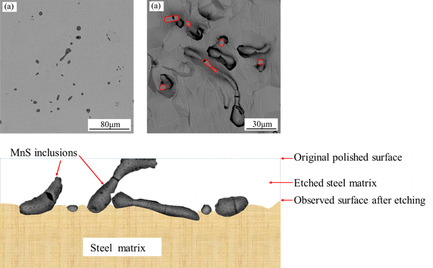
MnS inclusions in steels usually have many kinds of morphology. Inclusions with a circle and ellipse morphology in two dimensions show more complex morphology in three dimensions in high-sulfur steel by using nonaqueous solution electrolytic etching. The difference and relationship between the distribution, size, and shape of sulfides in 2D and 3D state are studied.
Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Wire + Arc Additively Manufactured Mild Steel by Welding with Trailing Hammer Peening
- First Published: 30 July 2021
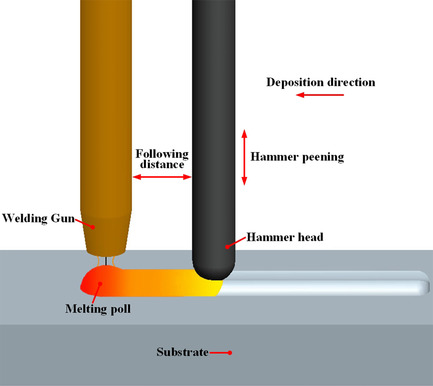
Aiming to improve the microstructure and mechanical properties of Wire Arc Additive Manufacture (WAAM), the welding with trailing hammer peening (WTHP) process is used. The finite element simulation and experiments are conducted, as well as the light microscopy and EBSD are used for microcharacterization. The results show that the WTHP can improve the mechanical properties of the mild steel single layer of WAAM significantly.
Effect of Shot Peening on Microstructures and High-Temperature Tribological Properties of 4Cr9Si2 Valve Steel
- First Published: 07 August 2021
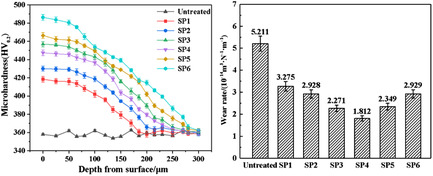
Herein, valve steel 4Cr9Si2 is subjected to shot peening (SP) using different processing parameters. SP yields numerous dislocations, refines the grains, introduces residual stresses, and increases microhardness, which is vital to the tribological behaviors. Under the positive effects of SP, sample SP4 shows the lowest wear rate and the best wear resistance at elevated temperatures.
Comparison of the Impact Wear Performances of Quenching and Partitioning and Quenching and Tempering Steels
- First Published: 06 August 2021
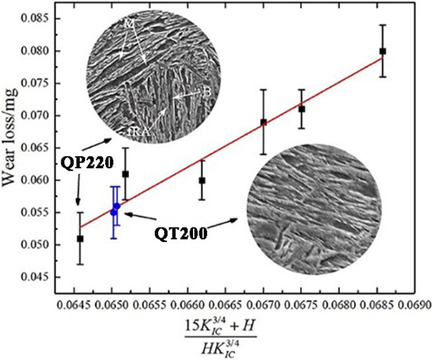
In comparison with the quenching and tempering treatment, the quenching and partitioning processes at quenching temperature of 220 °C and partitioning temperature of 350 °C show finer martensite and better wear performance. The correlation of wear loss, hardness, and fracture toughness is proposed to determine wear performance of samples treated by different routes by conducting only three groups of wearing tests.










