Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Laser Reduction of Graphene Oxide/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Nanocomposites as a One-Step Process for Supercapacitor Fabrication
- First Published: 05 June 2020
Laser Reduction
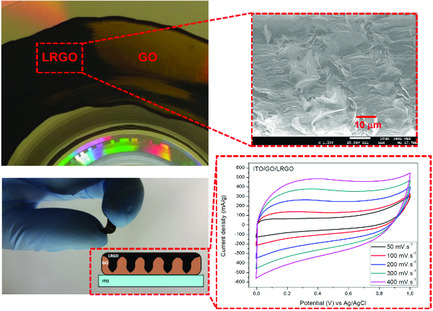
In article number 1901046, Artemis Marti Ceschin and co-workers propose laser scribing of insulator-conductor graphene oxide/laser-reduced graphene oxide micro-heterojunctions and the current collector to produce at low-cost and in a single step a flexible supercapacitor device.
Masthead
Original Papers
Conceptual Implementation of a Photonic–Plasmonic Transistor onto a Structured Nano-Guided Hybrid System
- First Published: 28 April 2020
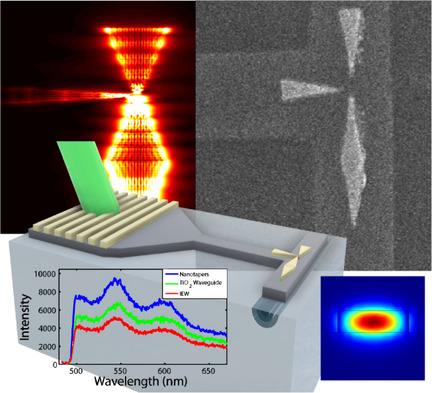
In the conceptual design of an integrated photonic–plasmonic transistor, quantum emitters and plasmonic nanostructures unlock unprecedented functionalities, potentially useful for novel–concept photonics. A mixed nanofabrication approach allows realizing a prototype where a nano–guided hybrid system enables plasmon–exciton exchanges. The numerical study of the system confirms the possibility to efficiently route and modulate high–frequency optical signals.
Cost-Effective Green Synthesis of Boron-Rich Carbide Coatings for Infrared Windows and Night-Vision Optics
- First Published: 29 April 2020
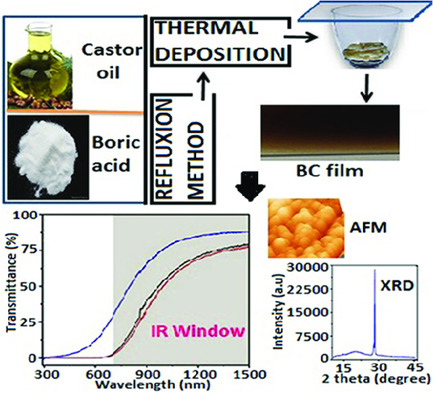
The morphological, structural, and optical properties of the boron-rich boron carbide films, prepared by a cost-effective low-temperature green synthesis, are studied. The absorption coefficient, extinction coefficient, refractive index, dissipation factor, optical conductivity, and the excellent transmittance of the film in the infrared region suggest its potential for infrared window applications.
Laser Reduction of Graphene Oxide/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Nanocomposites as a One-Step Process for Supercapacitor Fabrication
- First Published: 24 April 2020
Anti-Counterfeiting Microstructures Induced by Ultrashort Laser Pulses
- First Published: 21 April 2020
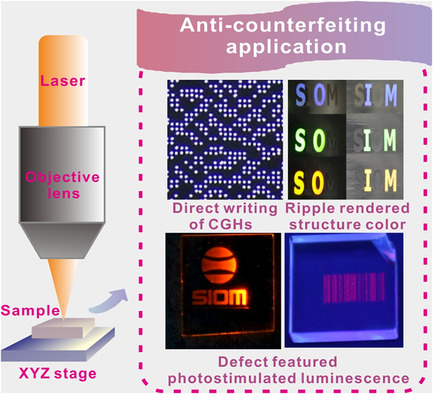
Ultrashort-pulsed laser enables selective ablation of metal films on glass substrates, ripple formation on metal surface, and defect generation inside functional glass. Correspondingly, direct writing of computer-generated holograms (CGHs), ripple rendered structure color, and defect featured photostimulated luminescence can be realized. Due to the feature of small size or invisibility, these induced microstructures can be used for anti-counterfeiting.
Inorganic Functionalization of CdSexS1–x/ZnS Core–Shell Quantum Dots and Their Photoelectric Properties
- First Published: 22 April 2020
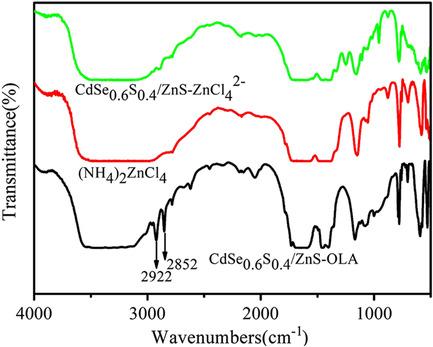
The ligand exchange of CdSe0.6S0.4-St core quantum dots (QDs) with (NH4)2ZnCl4 destroys its surface structure and deteriorates the photoelectric properties. The photocurrent density of CdSe0.6S0.4/ZnS-OLA core–shell QDs after ZnCl42− ligand exchange reaches 7.23 mA cm−2, which is about 11 times higher than the photocurrent density before ligand exchange.
Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties in p-Type Double Half-Heusler Ti2−yHfyFeNiSb2−xSnx Compounds
- First Published: 28 April 2020
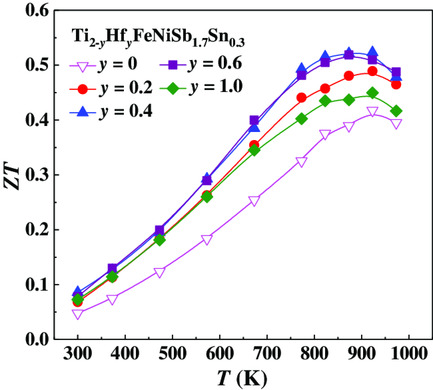
Double half-Heusler Ti2FeNiSb2-based compounds have a lower intrinsic thermal conductivity due to the smaller group velocity phonons and the disordered scattering. A peak thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT) of ≈0.52 at 923 K is obtained in Ti1.6Hf0.4FeNiSb1.7Sn0.3 through enhancing carrier concentration by Sn doping and decreasing lattice thermal conductivity by Hf alloying, indicating the promising applications of double half-Heusler compounds.
Influence of Interface Layer on the Properties of Exploding Foil Flyer Generator by Integrating Al/Ni Multilayers
- First Published: 28 April 2020

The interface layer of Al/Ni reactive multilayer films (RMFs) is controlled by adjusting annealing temperatures. The effects of interface layer on the properties for an exploding foil flyer generator (EFFG) are systematically investigated by synchronously recording current, voltage, and flyer velocity. The results show that the EFFG integrated Al/Ni RMFs with larger interface layer decreases the electrical plasma performances.
Development of High-Efficiency n-Type Front and Back Contact Passivated Emitter and Rear Locally Diffused Solar Cells Using Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition of Phosphosilicate Glass and Laser Processing
- First Published: 28 April 2020
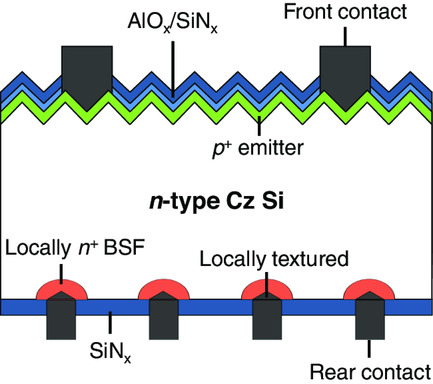
This work studies two industry-feasible approaches for fabricating n-type passivated emitter and rear locally diffused (nPERL) solar cells: via 1) laser doping, and 2) laser ablation. Atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (APCVD) and laser processes are adopted to form locally back surface field (BSF). The champion nPERL cell shows an efficiency of 21.3% with a high fill factor of 81.1%.