Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Chemotherapy: A partnership with immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 437-441
- First Published: 20 December 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
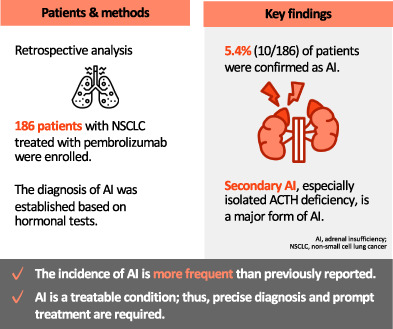
Clinical characteristics of adrenal insufficiency induced by pembrolizumab in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 442-449
- First Published: 15 December 2022
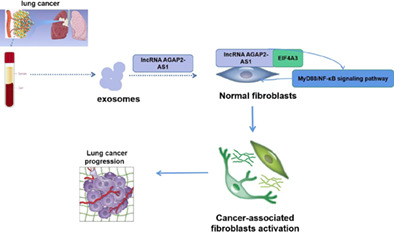
EIF4A3 stabilizes the expression of lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 to activate cancer-associated fibroblasts via MyD88/NF-κb signaling
- Pages: 450-461
- First Published: 21 December 2022
The regularity of anatomical variations of dominant pulmonary segments in the right upper lobe
- Pages: 462-469
- First Published: 13 December 2022
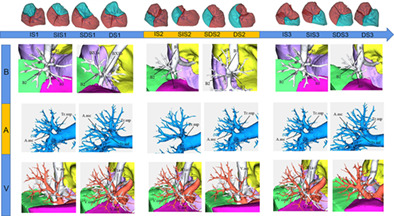
The mean volume ratio of the anterior segment of the right upper lobe (39.6 ± 8.6%) is highest, and that of the posterior segment (28.6 ±7.9%) lowest. Therefore, the dominant-type segment (DS + SDS) was dominant in the anterior segment, accounting for 74.6% (597/800), and the inferior-type segment (SIS + IS) was dominant in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe, accounting for 71.5% of cases (573/800). During the transformation of dominant and inferior lung segments, the corresponding regularity of anatomical variations could be displayed. For example, with an increase in the volume of the anterior segment of the right upper lobe, the occurrence rate of the bifurcated type of bronchus (B1 + 2, B3), the “central vein type” and the involvement of the trunk inferior and ascending artery in the blood supply of anterior segment gradually increased.
Circulating tumor cells PD-L1 expression detection and correlation of therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibition in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 470-478
- First Published: 11 January 2023
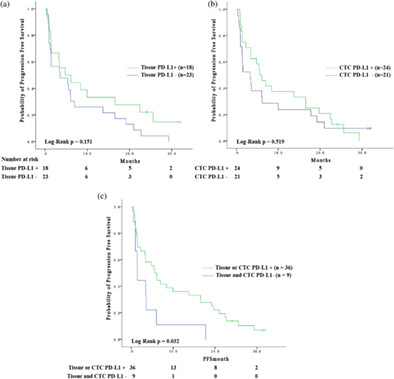
To investigate whether programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) is associated with immunotherapy efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients, we isolated CTCs based on a negative enrichment method and detected their PD-L1 expression status. Patients with PD-L1 + on tissue or CTCs released a significantly prolonged mPFS compared with those without PD-L1 expression (5.6 months vs. 1.4 months; log-rank p = 0.032).
High incidence and reversible bradycardia events following alectinib initiation
- Pages: 479-488
- First Published: 19 December 2022
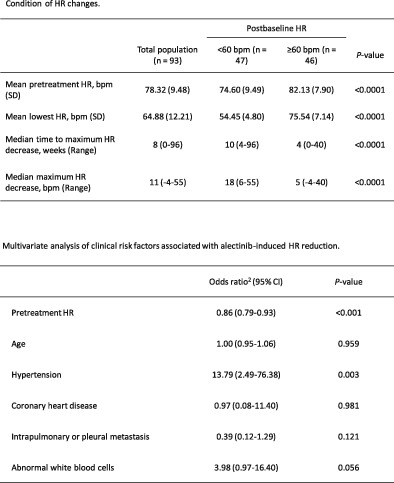
To clarify the bradycardia associated with alectinib, 93 patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer treated with alectinib were enrolled in this retrospective analysis. The results showed that alectinib-induced bradycardia had a high incidence, appeared relatively early, and was reversible by dose reduction or withdrawal. Baseline heart rate and history of hypertension were independent risk factors for alectinib-related bradycardia.
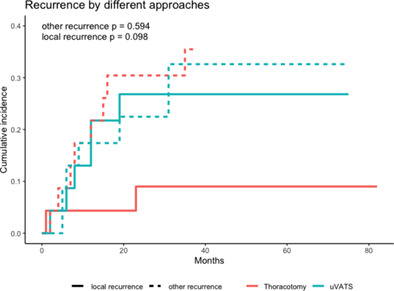
Uniportal VATS lobectomy versus thoracotomy lobectomy for NSCLC larger than 5 cm: A propensity score-matched study
- Pages: 489-496
- First Published: 23 December 2022
The development of a tumor-associated autoantibodies panel to predict clinical outcomes for immune checkpoint inhibitor-based treatment in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 497-505
- First Published: 02 January 2023
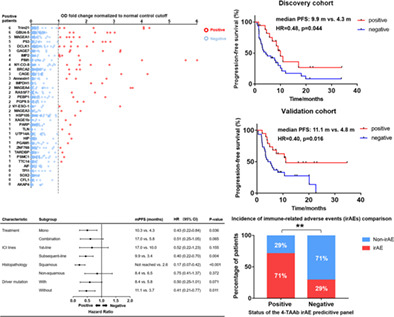
Tumor-associated autoantibodies (TAAbs) have been recognized as potential biomarkers to predict both the efficacy and toxicity of immunotherapy for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Our study enrolled 97 advanced NSCLC patients who received immune checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy, randomly divided into a training cohort (n = 48) and a validation cohort (n = 49), and collected their peripheral blood samples to measure the serum level of 35 TAAbs. In the training cohort, a 7-TAAb panel was derived to predict progression-free survival (PFS). The statistical association between the panel positivity and longer PFS was confirmed in the validation cohort and in different subgroups of patients. Moreover, another 4-TAAb panel was developed to predict the occurrence of irAEs.
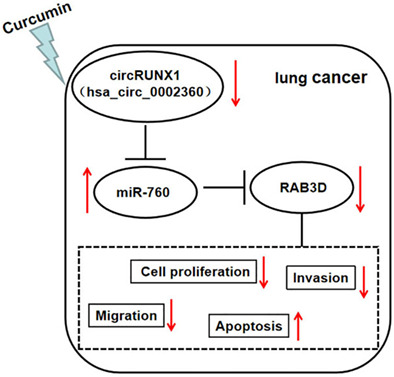
Curcumin suppresses lung cancer progression via circRUNX1 mediated miR-760/RAB3D axis
- Pages: 506-516
- First Published: 15 December 2022
Analysis of influencing factors of postoperative myasthenic crisis in 564 patients with myasthenia gravis in a single center
- Pages: 517-523
- First Published: 03 January 2023
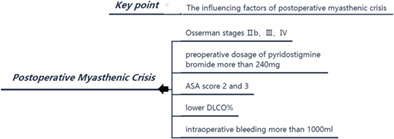
We found that poor Osserman stages, higher preoperative dosage of pyridostigmine bromide, higher American Society of Anesthesiologists score, poor pulmonary function (low diffusion lung capacity for carbon monoxide), and more intraoperative bleeding are relevant to the occurrence of postoperative myasthenic crisis. Patients with these characteristics should be highly vigilant.
CASE REPORTS
Unprecedented long-term survival in a patient with malignant pleural mesothelioma treated with subsequent systemic chemo- and immunotherapeutic regimens
- Pages: 524-527
- First Published: 04 January 2023
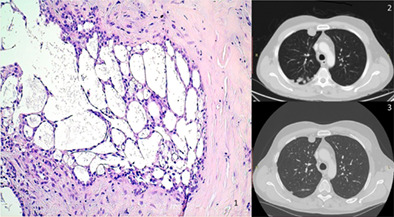
Pleural mesothelioma is a disease with a dismal prognosis. Here, we show an unusual case of a patient with pleural mesothelioma with adenomatoid histology (1), with nonsurgically operable disease. This patient was managed with multiple lines of systemic therapy, achieving long lasting survival from 2012 (2) to date (3). Disease control is still ongoing and the patient is asymptomatic with a good performance status.
Indocyanine green navigation in minimally invasive resection of multiple metachronous pulmonary metastases of hepatoblastoma
- Pages: 528-532
- First Published: 15 January 2023
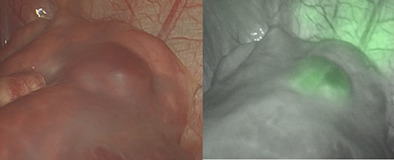
Pulmonary metastatic lesions are easily detected by indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence due to lack of accumulation in normal lung tissue, which results in a clear contrast generated in pulmonary metastases of hepatocyte neoplasic cell such as hepatoblastomas. ICG-guided resection via thoracoscopic approach is particularly useful in patients with multiple and/or metachronous hepatoblastoma metastases requiring multiple surgical interventions.