Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Research Reviews
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and volatile organic compounds in biochar and biochar-amended soil: a review
- Pages: 990-1004
- First Published: 31 March 2016
Socioeconomic indicators for sustainable design and commercial development of algal biofuel systems
- Pages: 1005-1023
- First Published: 29 March 2016
Original Research
A realistic meteorological assessment of perennial biofuel crop deployment: a Southern Great Plains perspective
- Pages: 1024-1041
- First Published: 06 October 2016
The expansion of short rotation forestry: characterization of determinants with an agent-based land use model
- Pages: 1042-1056
- First Published: 01 September 2016
Microbial communities and diazotrophic activity differ in the root-zone of Alamo and Dacotah switchgrass feedstocks
- Pages: 1057-1070
- First Published: 29 July 2016
Estimating product and energy substitution benefits in national-scale mitigation analyses for Canada
- Pages: 1071-1084
- First Published: 20 July 2016
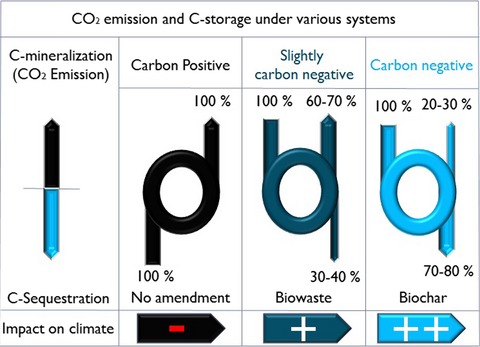
Investigating the biochar effects on C-mineralization and sequestration of carbon in soil compared with conventional amendments using the stable isotope (δ13C) approach
- Pages: 1085-1099
- First Published: 03 September 2016
Field-grown transgenic switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) with altered lignin does not affect soil chemistry, microbiology, and carbon storage potential
- Pages: 1100-1109
- First Published: 01 October 2016
Biochar stimulates the decomposition of simple organic matter and suppresses the decomposition of complex organic matter in a sandy loam soil
- Pages: 1110-1121
- First Published: 10 September 2016
Could Miscanthus replace maize as the preferred substrate for anaerobic digestion in the United Kingdom? Future breeding strategies
- Pages: 1122-1139
- First Published: 10 December 2016

The abundance of non-structural carbohydrates (NSC) was analysed in diverse genotypes of green-cut Miscanthus with a view to replacing maize as the preferred substrate for anaerobic digestion. The maximum yield of NSC was 5-fold lower than maize but there was wide diversity in this trait to target for breeding.
Carbon accrual rates, vegetation and nutrient dynamics in a regularly burned coppice woodland in Germany
- Pages: 1140-1150
- First Published: 03 October 2016
Can the agricultural AquaCrop model simulate water use and yield of a poplar short-rotation coppice?
- Pages: 1151-1164
- First Published: 16 December 2016
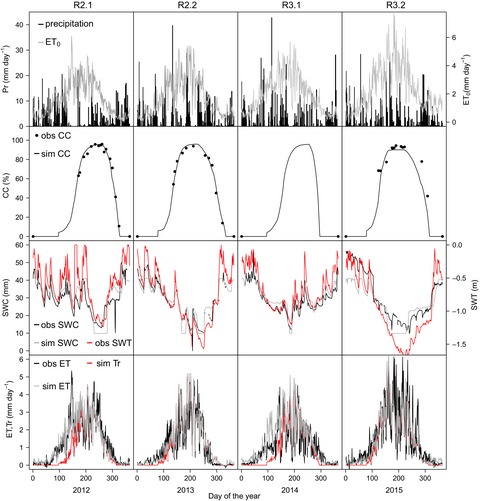
User-friendly and reliable models are needed to accurately estimate water use, biomass production, and the generated energy of short-rotation coppice plantations under different environmental conditions. This study focuses on water use and biomass production of poplars in bioenergy plantations and shows that the agricultural model AquaCrop can be used as a complement for the more complex process-based forest models that have been used so far. AquaCrop can reliably simulate evapotranspiration (calibrated with eddy covariance data) and potential yield of a poplar short-rotation coppice plantation. It can also detect yield gaps caused by the management or by environmental problems.