Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Research Reviews
Transport biofuels in global energy–economy modelling – a review of comprehensive energy systems assessment approaches
- Pages: 1168-1180
- First Published: 06 February 2017
This paper is based upon a structured selection of global energy modelling studies addressing the future, potential role of transport biofuels. The paper is finding that the reviewed papers depict highly varying levels of future biofuel use. This can be attributed to model differences and to different assumptions with regards to the amount of available biomass, the climate targets, the deployment of new technologies and the time perspectives applied.
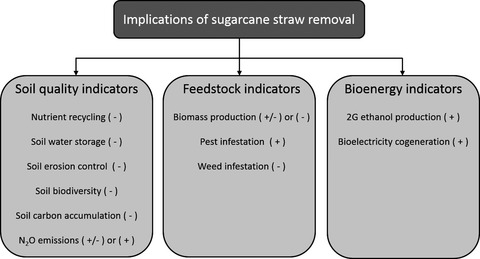
Agronomic and environmental implications of sugarcane straw removal: a major review
- Pages: 1181-1195
- First Published: 15 December 2016
Original Research
Aged biochar affects gross nitrogen mineralization and recovery: a 15N study in two contrasting soils
- Pages: 1196-1206
- First Published: 06 February 2017
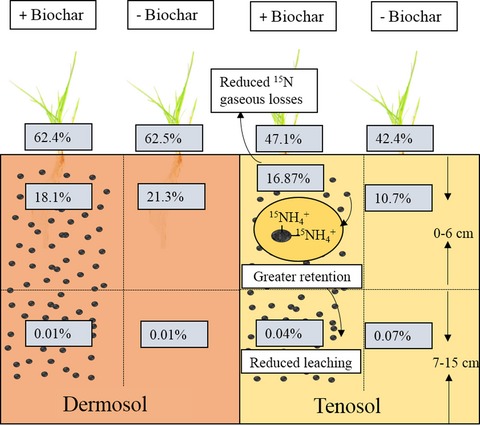
Biochar is rich in pyrogenic carbon with large surface area and variable charge that contribute to nutrient cycling. The change in biochar properties with time in the soil, that is ageing, may be dynamic and can affect nutrient cycling. Here, we examined the effects of a biochar (20 t ha−1), that has aged in two soil types, that is a Tenosol and a Dermosol, on gross nitrogen (N) mineralization (GNM) and 15N recovery using a 15N tracer. The field experiment also included a phosphorus (P) addition treatment (1 kg ha−1). Effects of biochar on GNM and 15N recovery were soil specific. Biochar application significantly reduced GNM in the clayey Dermosol, possibly due to formation of organo-mineral complexes, while it significantly increased 15N recovery in the sandy Tenosol. Retention of 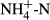 at biochar-derived cation exchange sites may have reduced leaching and gaseous loss of 15N, resulting in increased 15N recovery.
at biochar-derived cation exchange sites may have reduced leaching and gaseous loss of 15N, resulting in increased 15N recovery.
Environmental impacts of bioenergy wood production from poplar short-rotation coppice grown at a marginal agricultural site in Germany
- Pages: 1207-1221
- First Published: 16 December 2016
Transcriptomic characterization of candidate genes responsive to salt tolerance of Miscanthus energy crops
- Pages: 1222-1237
- First Published: 07 December 2016

Miscanthus lutarioriparius, an endemic species in central China, is considered to be a promising candidate of second-generation energy crops. Seeds of the five populations of M. lutarioriparius were collected in natural habitats and planted in the experimental field (natural saline soil) in Dongying, Shandong province of China. After one year long-term salt stress, the growth status of Suaeda salsa that originally derived from the experimental field and one of the five populations of M. lutarioriparius are as the picture showed. Compared with S. salsa, the better growth status of M. lutarioriparius indicated that it has the capability of producing high biomass on the saline marginal land.
Carbon balances of bioenergy systems using biomass from forests managed with long rotations: bridging the gap between stand and landscape assessments
- Pages: 1238-1251
- First Published: 29 December 2016
Cover crop root contributions to soil carbon in a no-till corn bioenergy cropping system
- Pages: 1252-1263
- First Published: 30 January 2017
Predicting future biomass yield in Miscanthus using the carbohydrate metabolic profile as a biomarker
- Pages: 1264-1278
- First Published: 10 December 2016

The carbohydrate metabolic profile was used as a biomarker to predict yields in Miscanthus. The modelled vs. actual yields had a correlation of R = 0.67, demonstrating that yield could be predicted to a high degree of accuracy. Yield was linked to the partitioning of carbohydrates between cellulose and starch.
Impact of six lignocellulosic biochars on C and N dynamics of two contrasting soils
- Pages: 1279-1291
- First Published: 07 December 2016