Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front Cover
- First Published: 01 April 2025

Cover image: The cover image is based on the article High-Frequency rTMS Improves Visual Working Memory in Patients With aMCI: A Cognitive Neural Mechanism Study by Yun-Xia Li et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.70301.
Additional Cover
- First Published: 06 April 2025

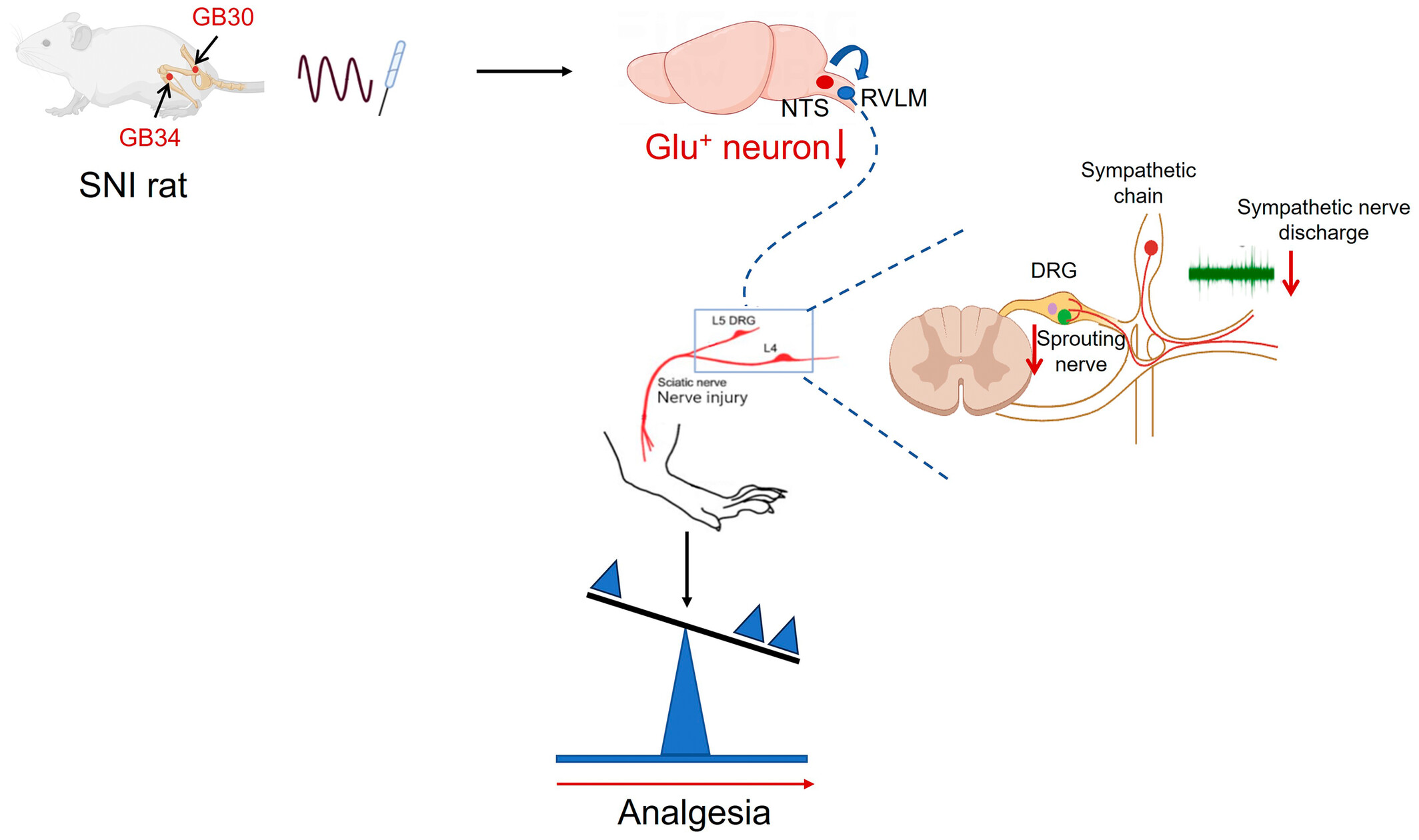
Cover image: The cover image is based on the article Electroacupuncture Regulates Sympathetic Nerve Through the NTSGlu–RVLM Circuit to Relieve Spontaneous Pain in SNI Rats by Wen Chen et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.70327.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Allopregnanolone as an Adjunct Therapy to Midazolam is More Effective Than Midazolam Alone in Suppressing Soman-Induced Status Epilepticus in Male Rats
- First Published: 28 February 2025
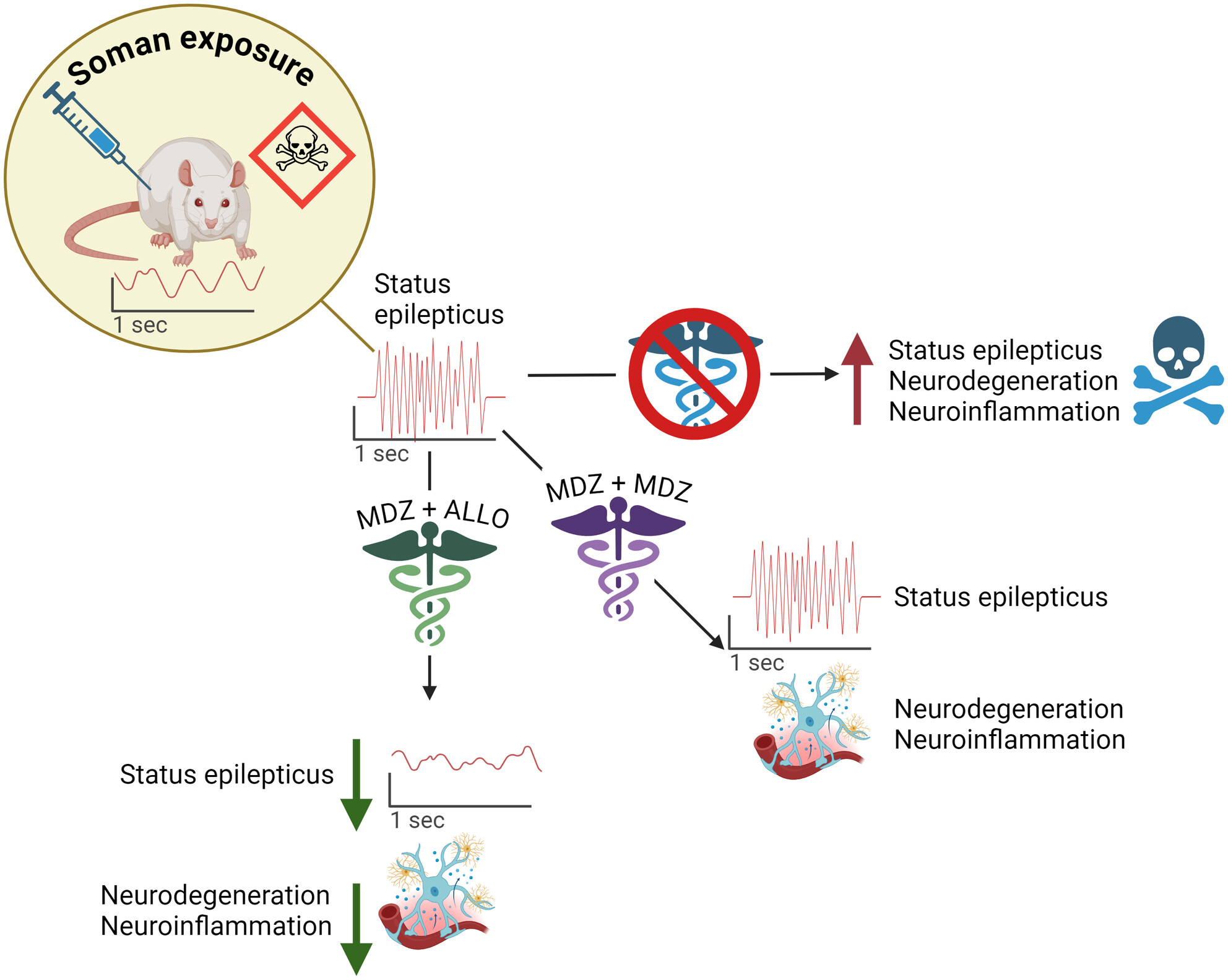
Acute poisoning with the organophosphate, soman, triggers status epilepticus that rapidly becomes refractory to standard of care treatment with midazolam (MDZ). Combined treatment with MDZ and allopregnanolone (ALLO) significantly suppresses seizure activity, which is associated with attenuated neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation.
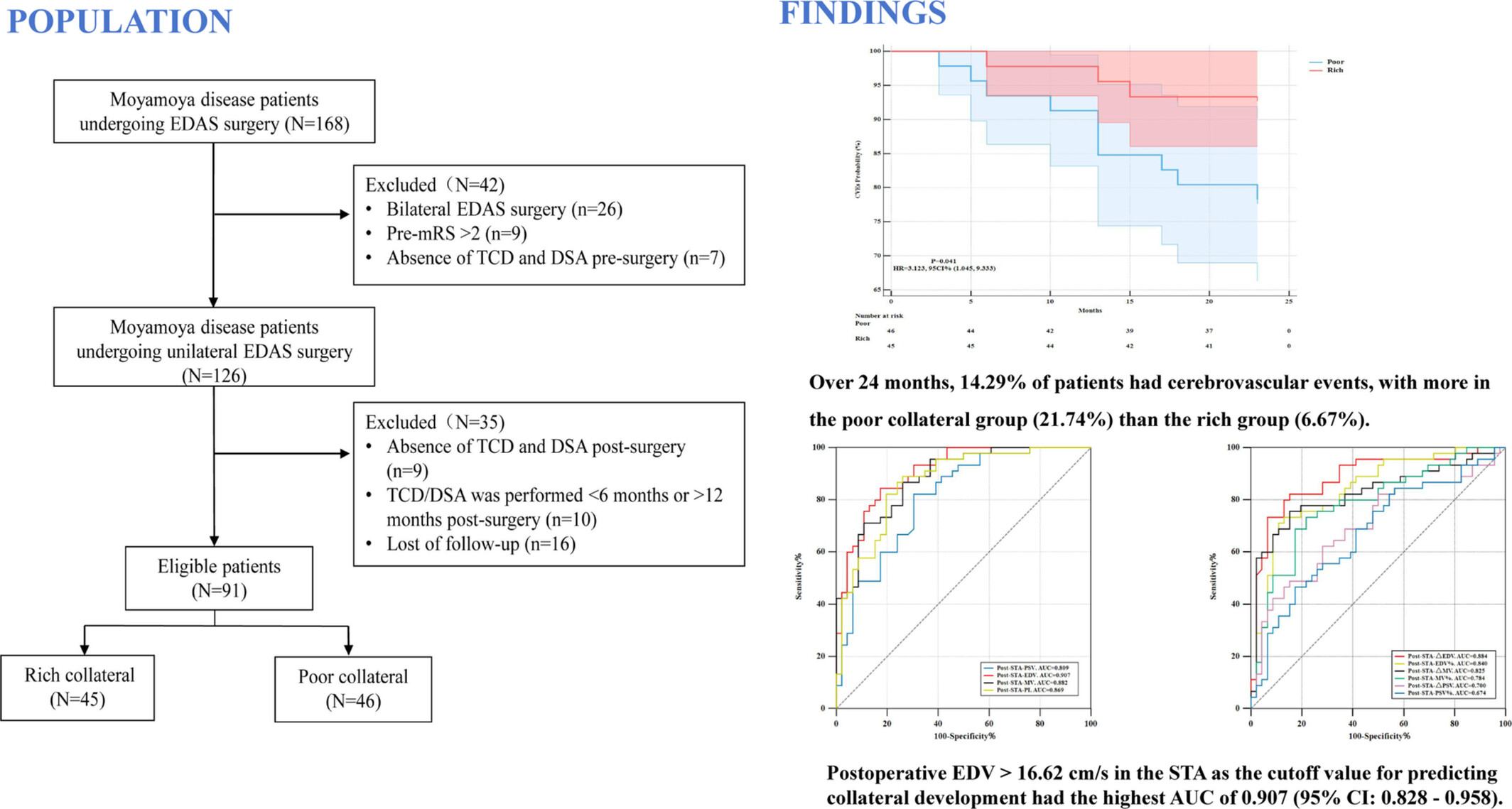
The Role of TCD in Assessing Postoperative Collateral Development and Long-Term Clinical Outcome in Moyamoya Disease
- First Published: 18 March 2025
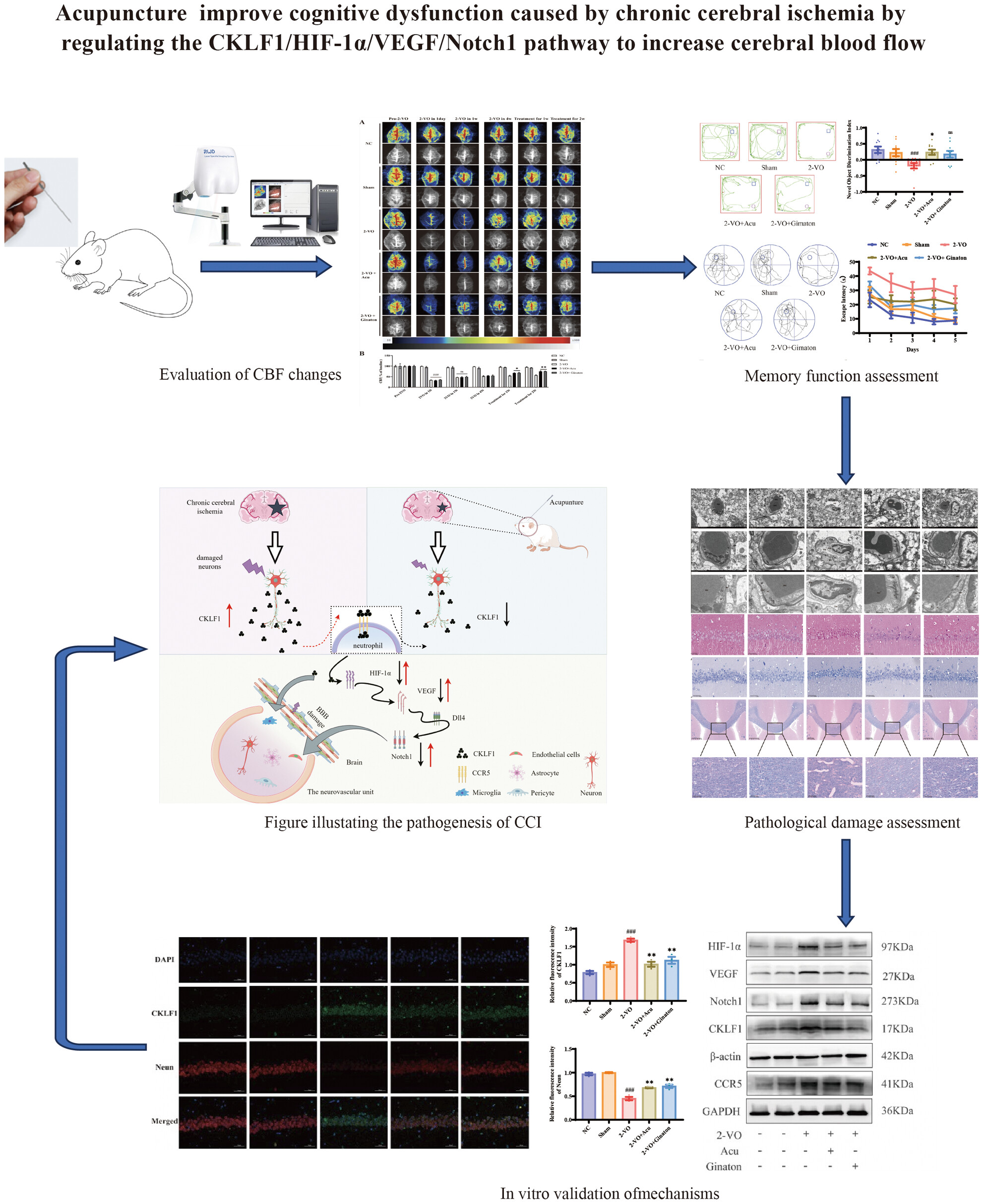
Acupuncture Improves Chronic Cerebral Ischemia by Inhibiting the CKLF1/HIF-1α/VEGF/Notch1 Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 28 February 2025
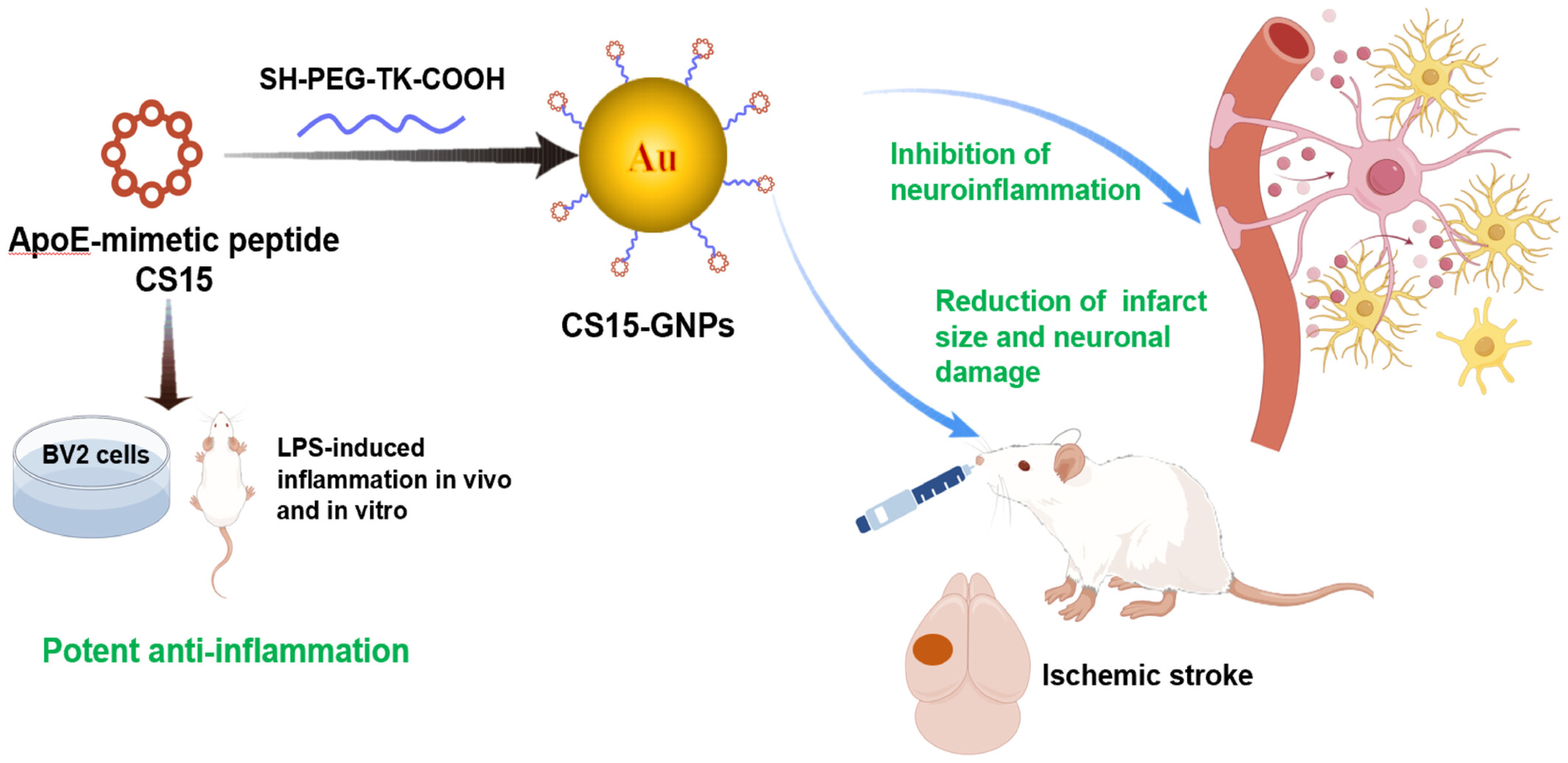
Intranasal Administration of a Novel ApoE-Mimetic Peptide-Coated Gold Nanoparticles as Therapy for Ischemic Stroke
- First Published: 18 March 2025
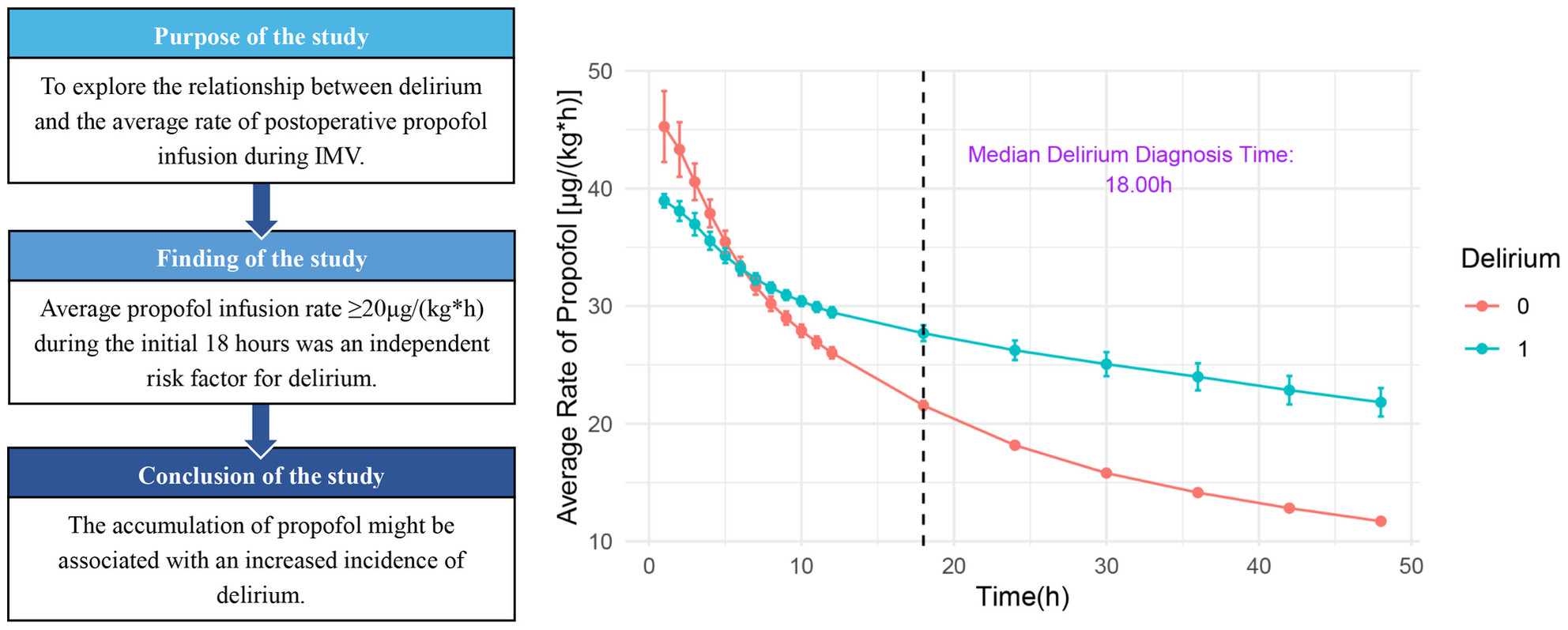
The Relationship Between the Average Infusion Rate of Propofol and the Incidence of Delirium During Invasive Mechanical Ventilation: A Retrospective Study Based on the MIMIC IV Database
- First Published: 28 February 2025
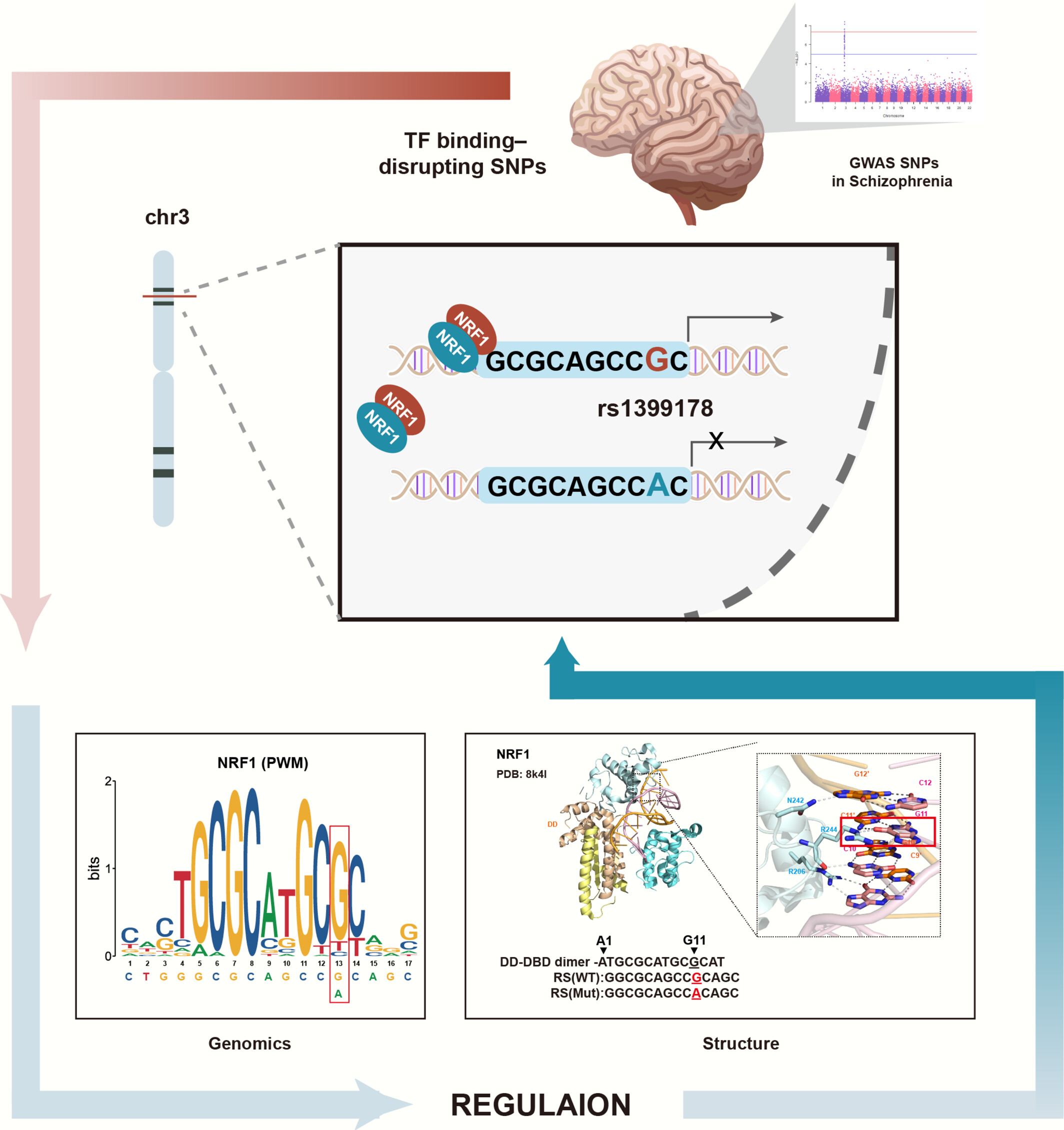
Identification of Schizophrenia-Risk Regulatory Variant rs1399178 in the Non-coding Region With Its Impact on NRF1 Binding
- First Published: 28 February 2025
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Clarifying the Specificity of Transcranial Pulse Stimulation in Neuromodulatory-Based Therapeutic Applications
- First Published: 28 February 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Nonmotor Symptom Changes and Their Association With Falls Among Parkinson's Disease Patients Undergoing Deep Brain Stimulation: A 1-Year Cohort Study
- First Published: 28 February 2025
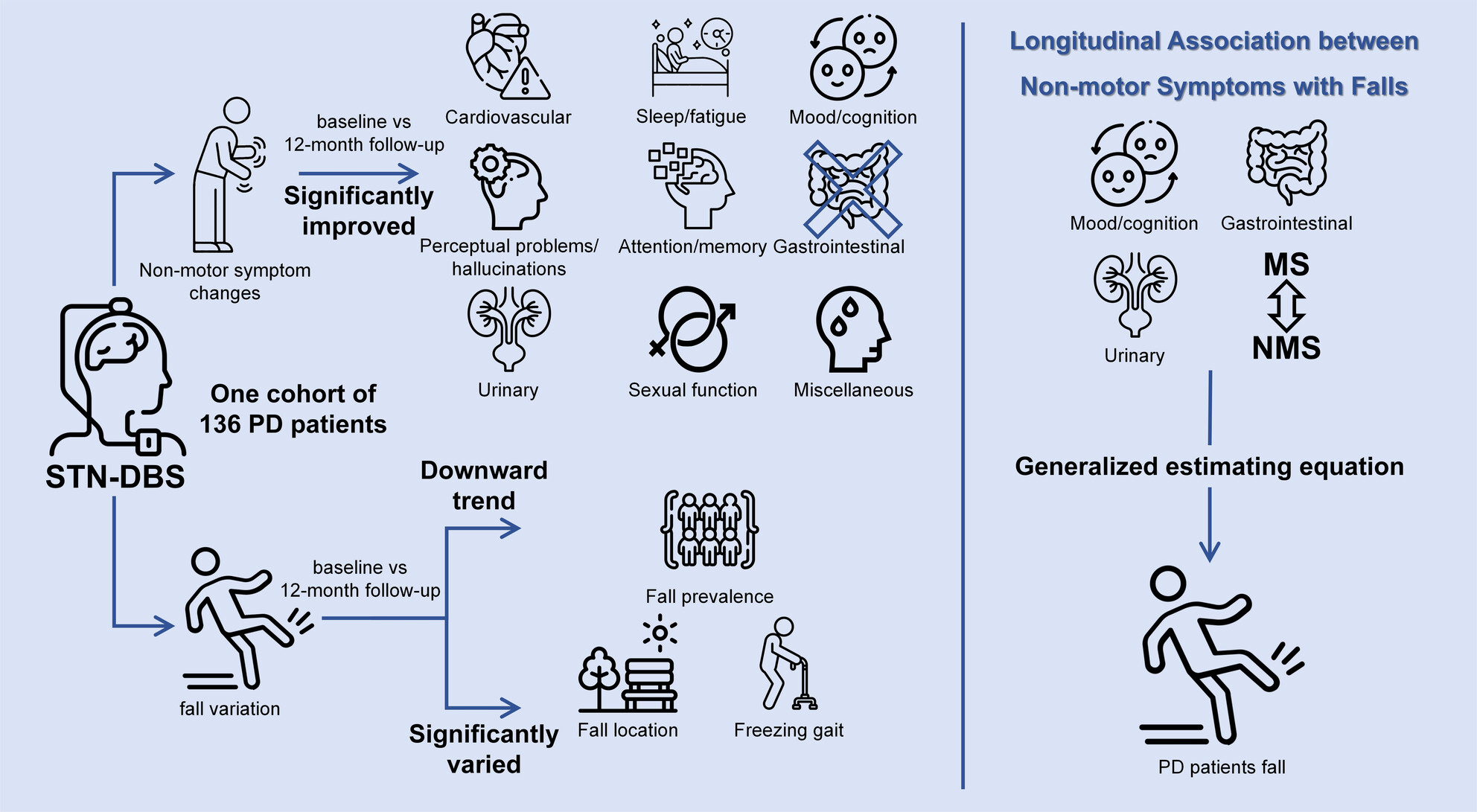
It is the first study to link nonmotor symptoms with falls in Parkinson's patients post-DBS. Generalized estimating equations were used to assess the longitudinal impact of NMS with falls in 136 patients, finding that mood/cognition, gastrointestinal, and urinary symptoms, as well as their interactions with motor symptoms, were related to fall risk.
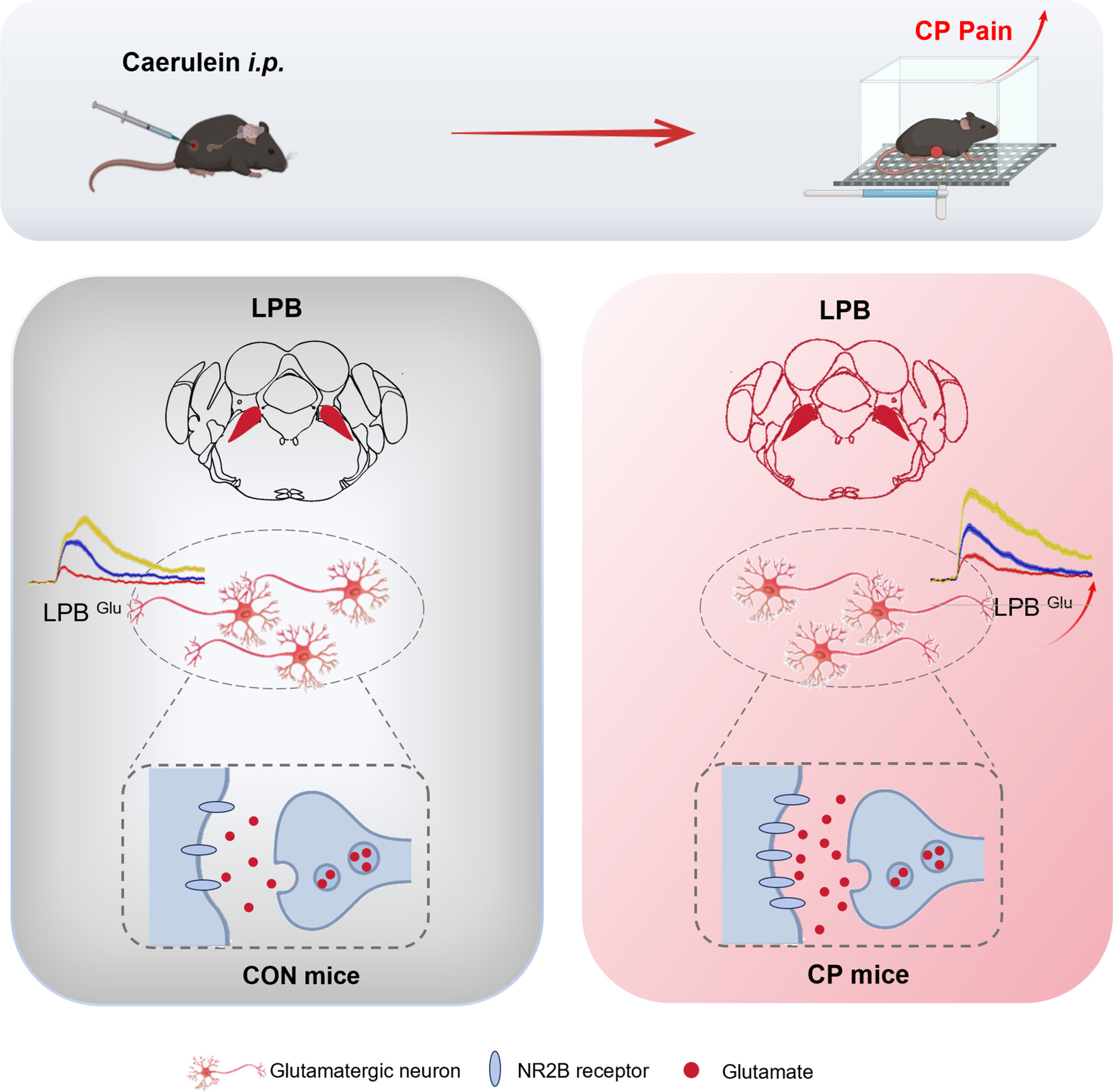
Upregulation of NR2B Subunits of NMDA Receptors in the Lateral Parabrachial Nucleus Contributes to Chronic Pancreatitis Pain
- First Published: 28 February 2025
Quantitative EEG Insights Into A Hundred Adult ADHD Patients: A Deep Dive Into Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA) Correlations and Attention Dynamics
- First Published: 18 March 2025
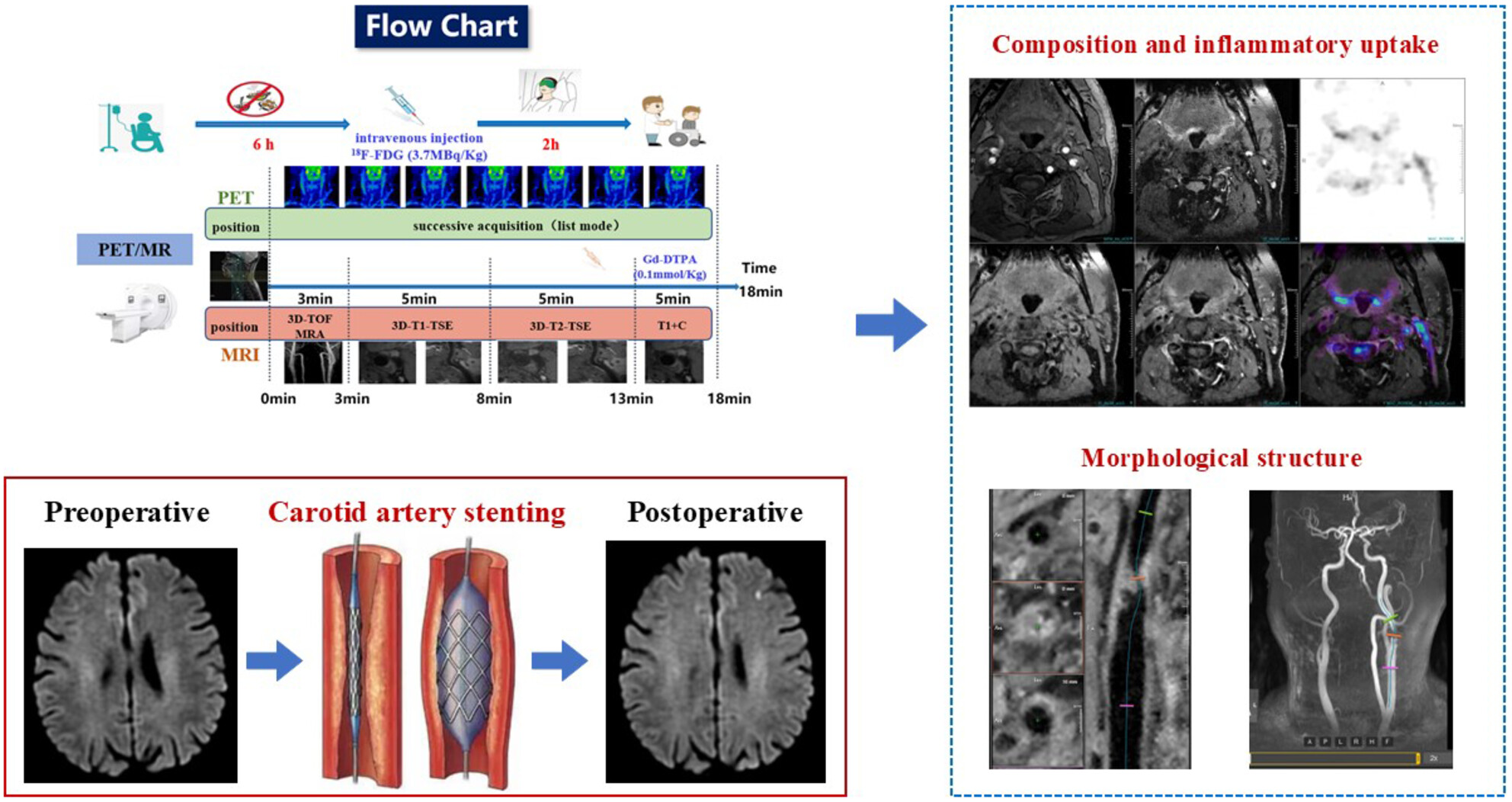
Association of Plaque Characteristics With New Ischemic Lesions After Carotid Artery Stenting
- First Published: 03 March 2025
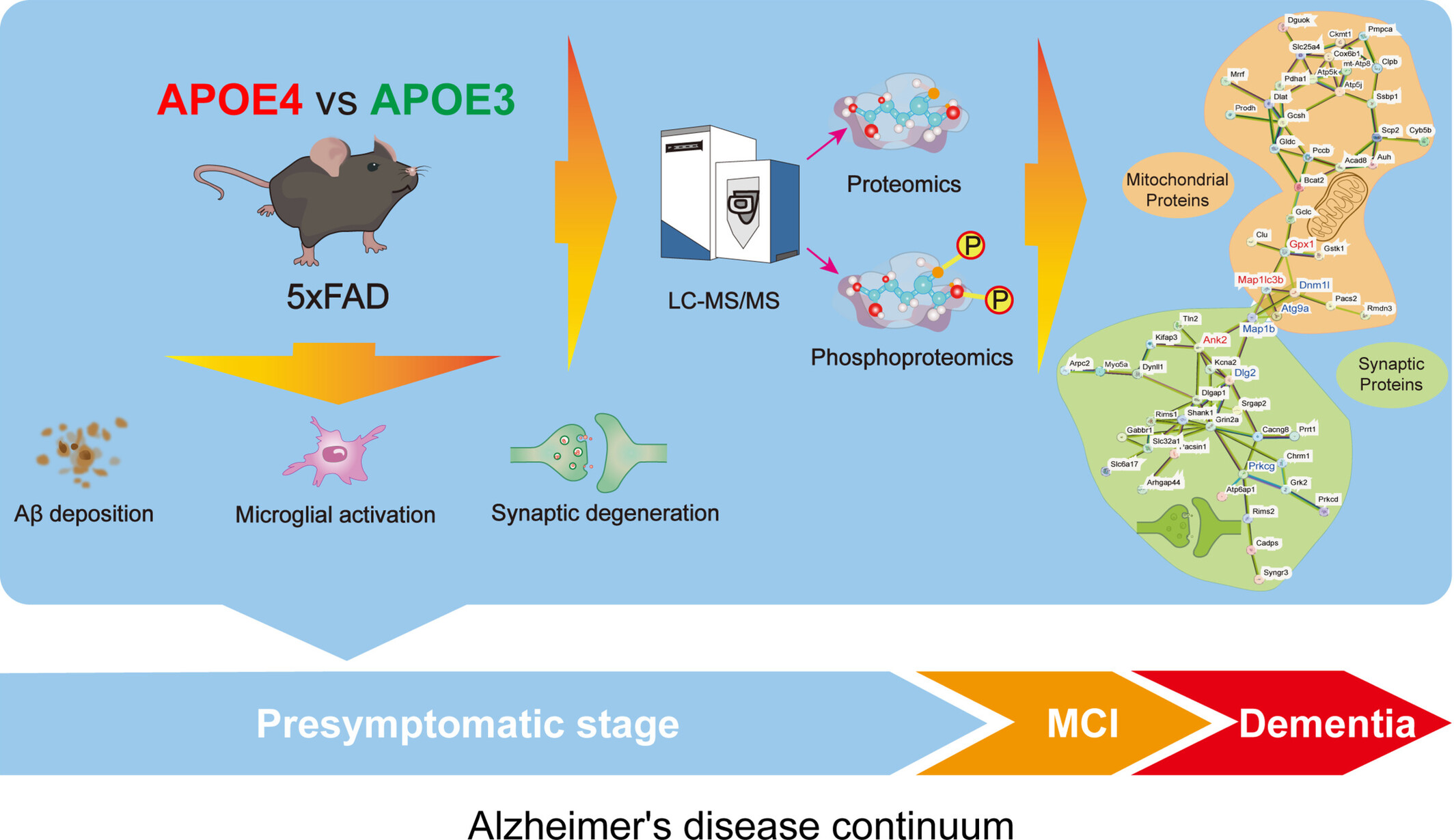
Sequential Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Key APOE4-Induced Pathological and Molecular Features at the Presymptomatic Stage in Alzheimer's Disease Mice
- First Published: 12 March 2025
The Effect of Electroconvulsive and Magnetic Seizure Therapy (MST) on Cortical Thickness in Schizophrenia
- First Published: 03 March 2025

Does magnetic shock have an impact on the brain? No, it is effective and safe! Magnetic shock therapy (MST) has significant advantages in treatment. After the patient was admitted, the doctor recommended more advanced magnetic shock therapy to her, which caused less damage to the brain's cognition and memory. The focus of this project is to explore the effect of magnetic shock on the thickness of the cerebral cortex.
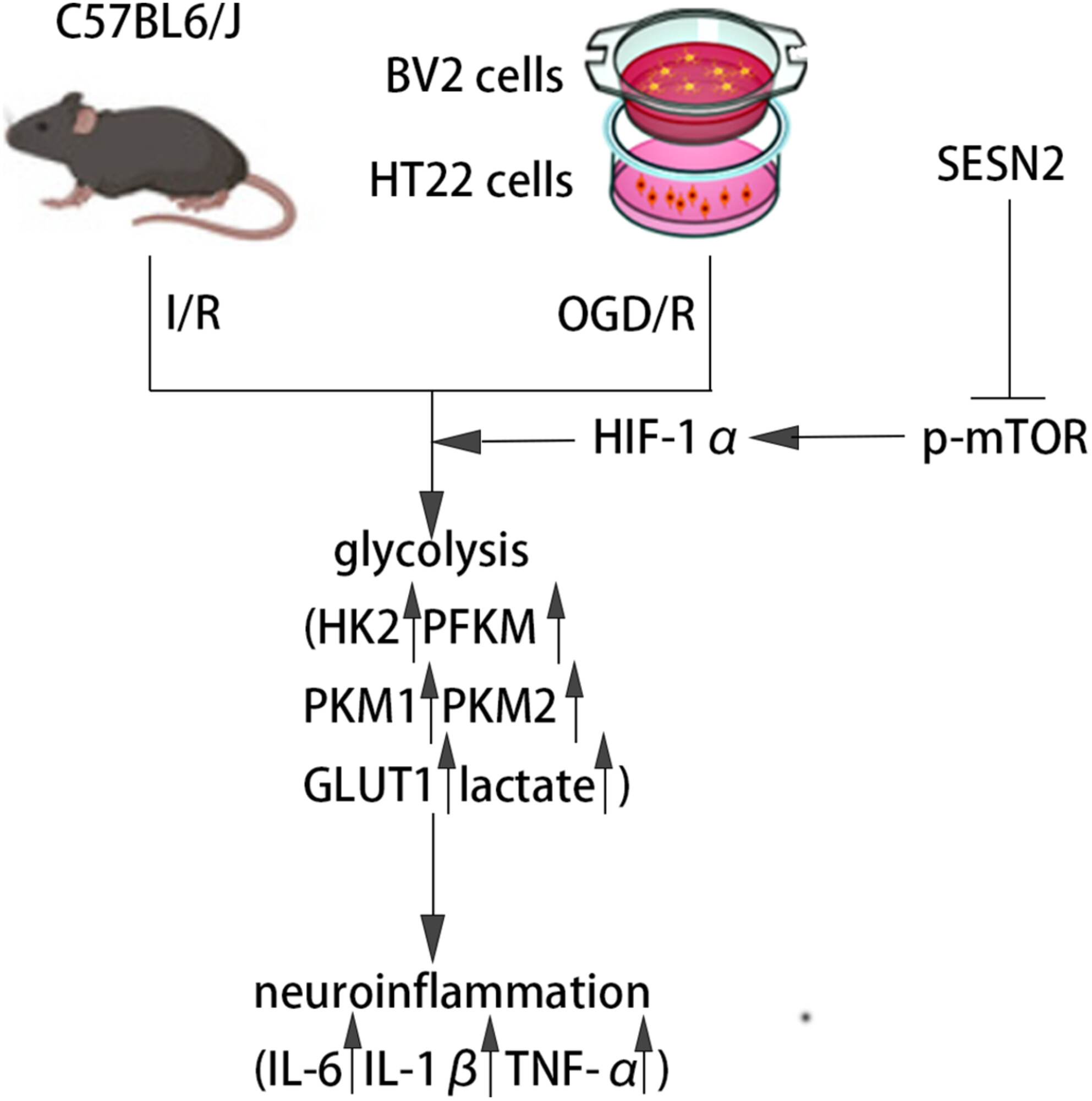
Knockdown of SESN2 Exacerbates Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury Through Enhancing Glycolysis via the mTOR/HIF-1α Pathway
- First Published: 03 March 2025
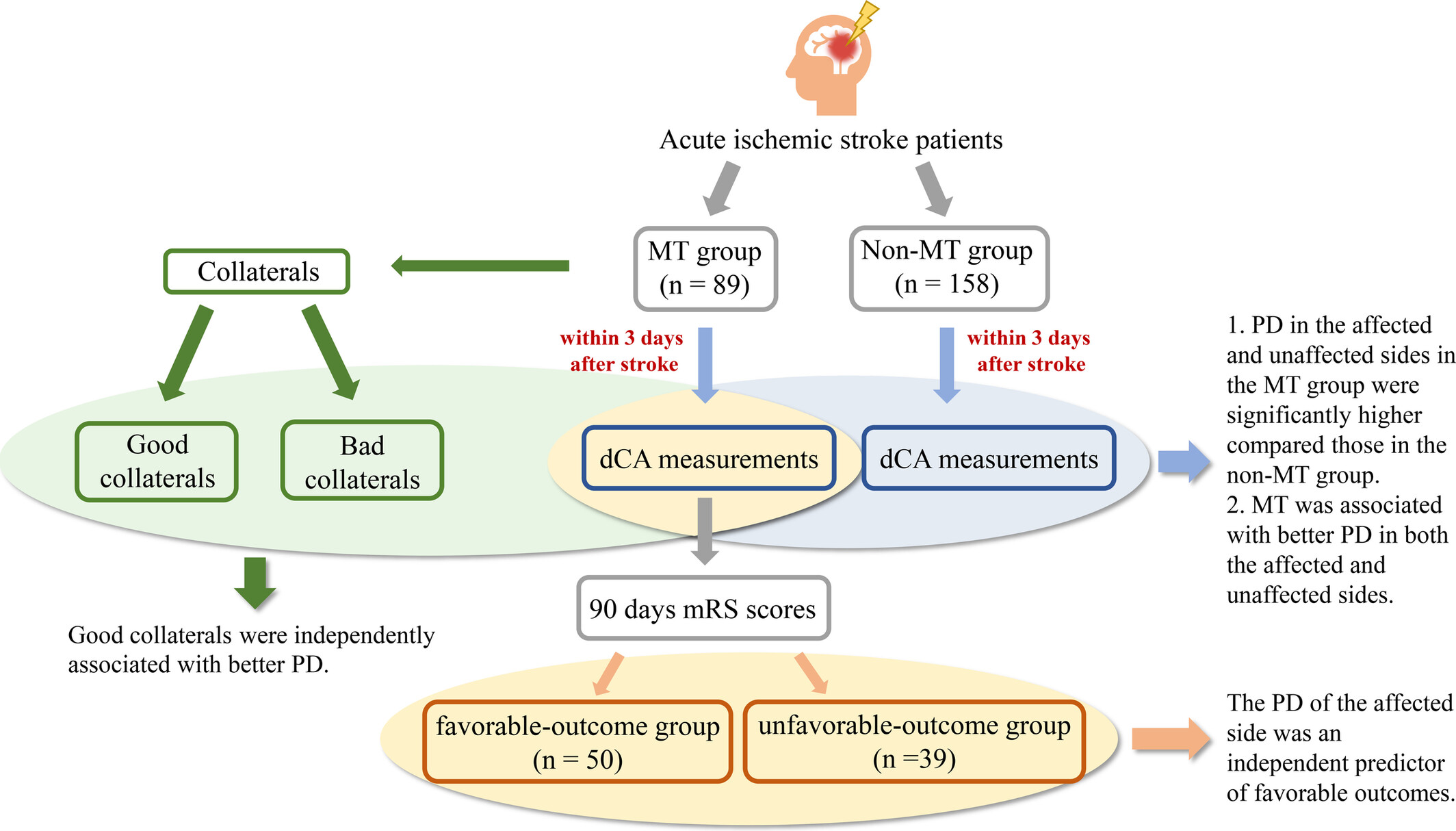
Characteristics of Cerebral Autoregulation After Mechanical Thrombectomy and Its Relationship With Prognosis
- First Published: 04 March 2025
Exploring the Therapeutic Mechanism of Xinbao Pill in Brain Injury After Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Based on Network Pharmacology, Metabolomics, and Experimental Verification
- First Published: 04 March 2025
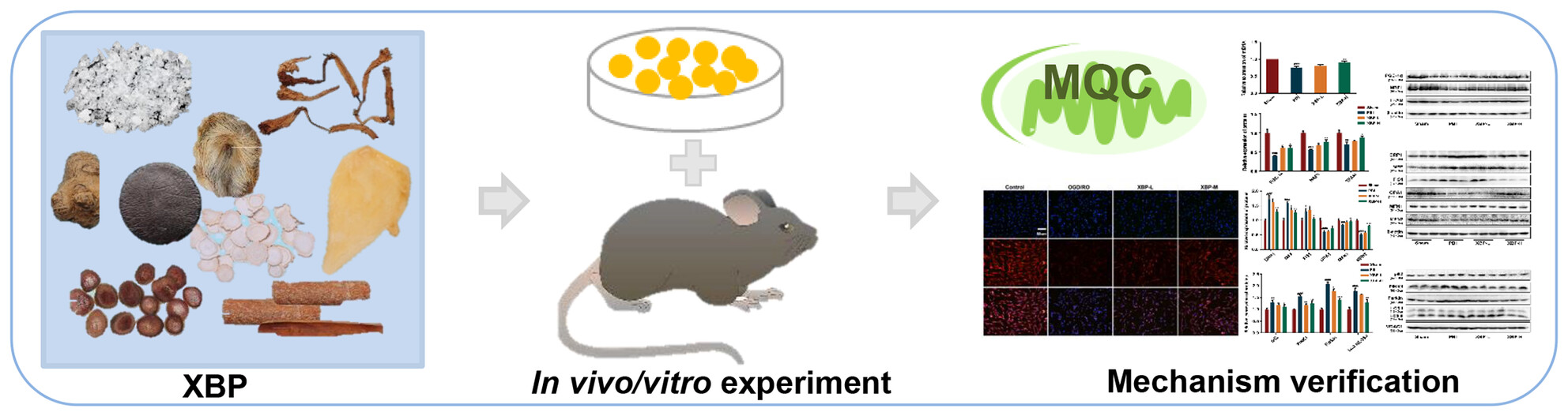
A diagram illustrating a network-based mechanism exploration framework for XBP against brain injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. (A) In vivo and in vitro pharmacodynamic confirmation of XBP against PBI. (B) Network pharmacology approach as well as metabolomics analysis to explore the potential mechanisms. (C) Mechanism verification of XBP against PBI.
DNLA Delayed the Appearance of Learning and Memory Impairment of APP/PS1 Mice: Involvement of mTOR/TFEB/v-ATPase Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 06 March 2025
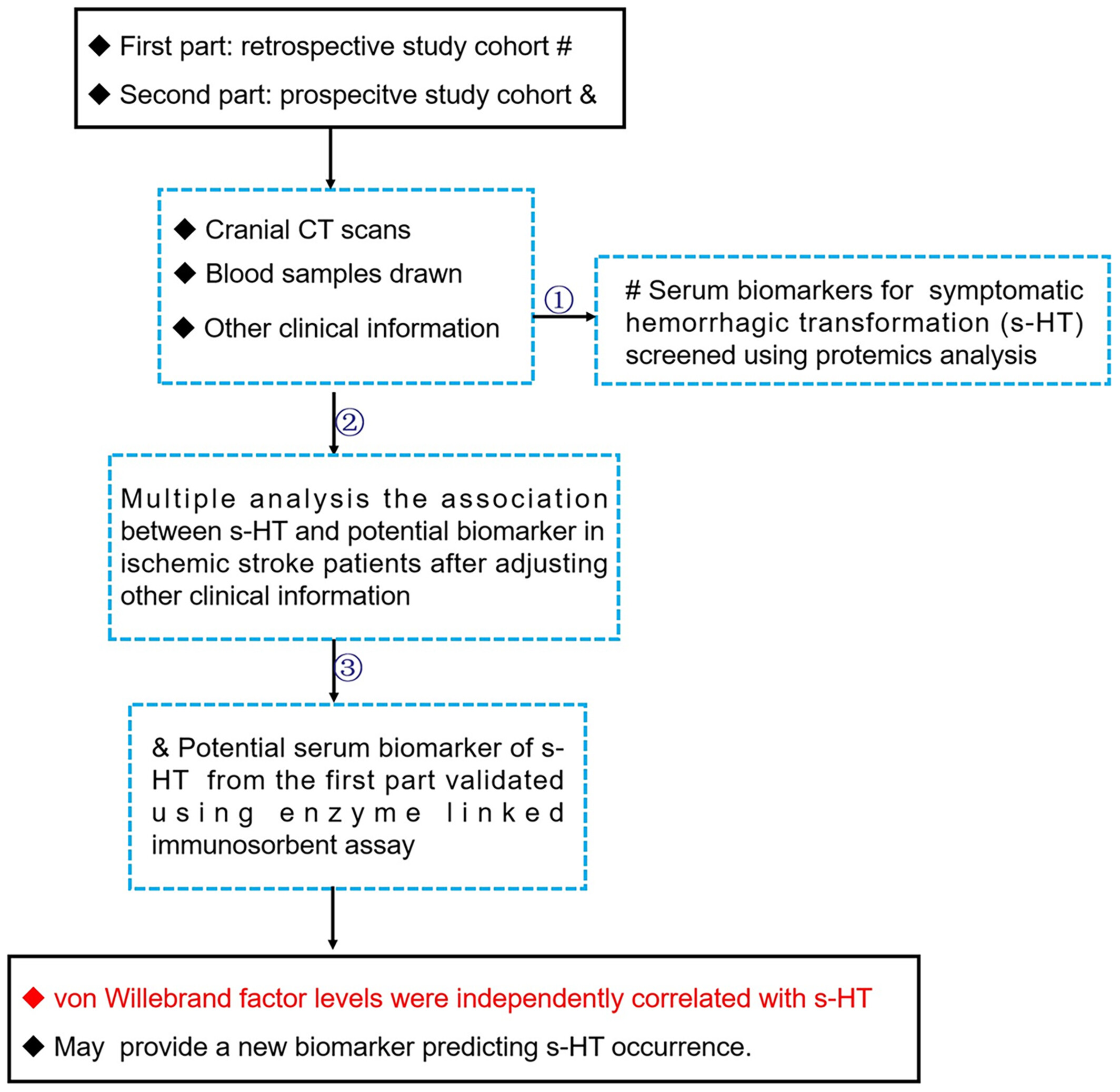
The Association of Serum Biomarkers With Symptomatic Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Combined Retrospective and Prospective Study
- First Published: 26 March 2025
CORRECTION
Correction to “RNF122 Promotes Glioblastoma Growth via the JAK2/STAT3/c-Myc Signaling Axis”
- First Published: 12 March 2025
REVIEW
Linking Circadian Rhythms to Gut-Brain Axis Lipid Metabolism Associated With Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Alzheimer's Disease
- First Published: 09 March 2025
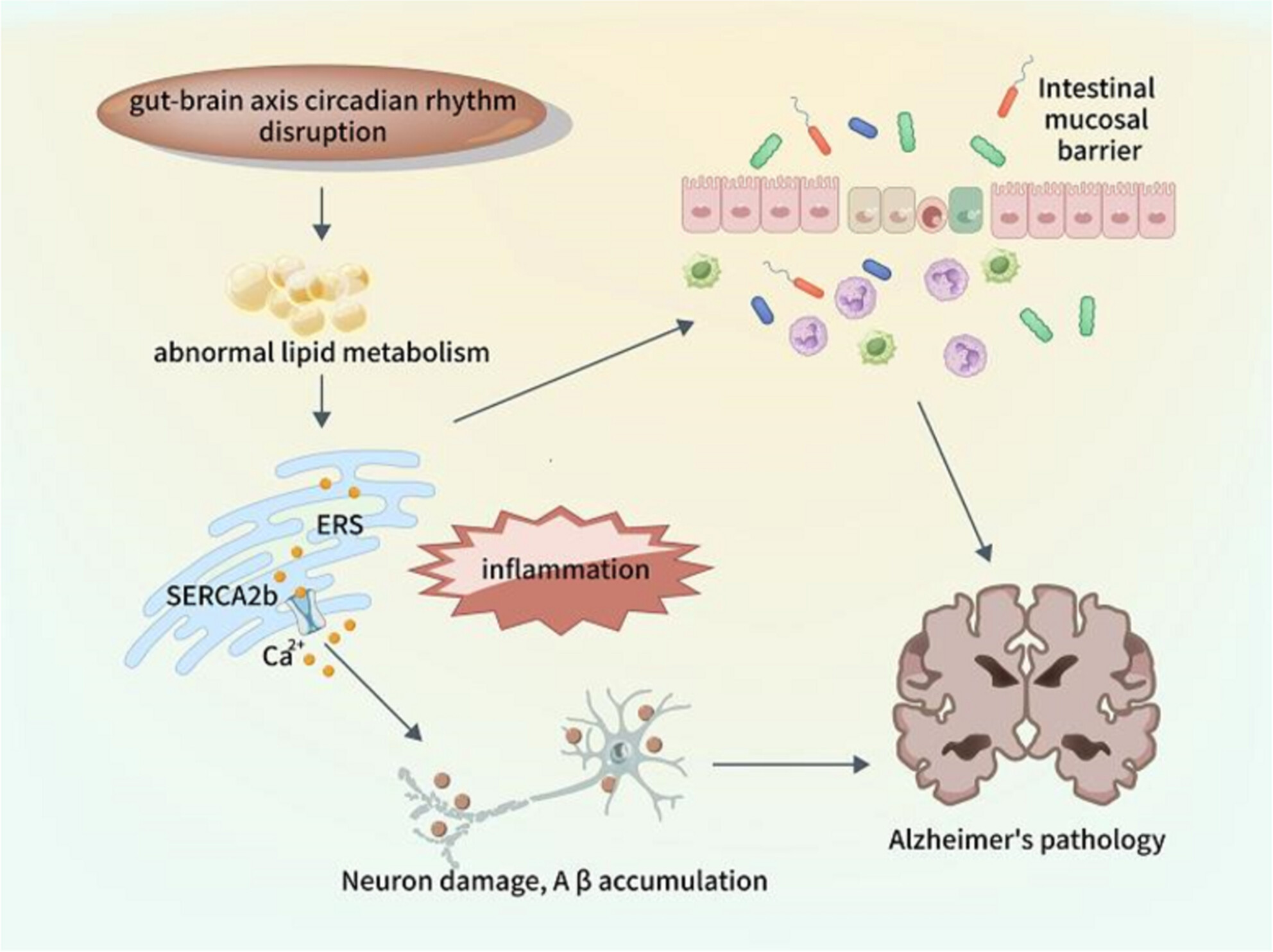
The effect of gut-brain axis lipid abnormalities metabolism mediated by circadian rhythm disruption on AD were discussed. The membrane lipids abnormalities surrounding sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ -ATPase (SERCA) influencing SERCA to release Ca2+ mediate ERS and inflammation, which contribute to neuron damage Aβ accumulation in AD. In addition, Intestinal mucosal ERS leads to increased permeability, and accelerate AD progression by the increase of Lipopolysaccharide and proinflammatory factor.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
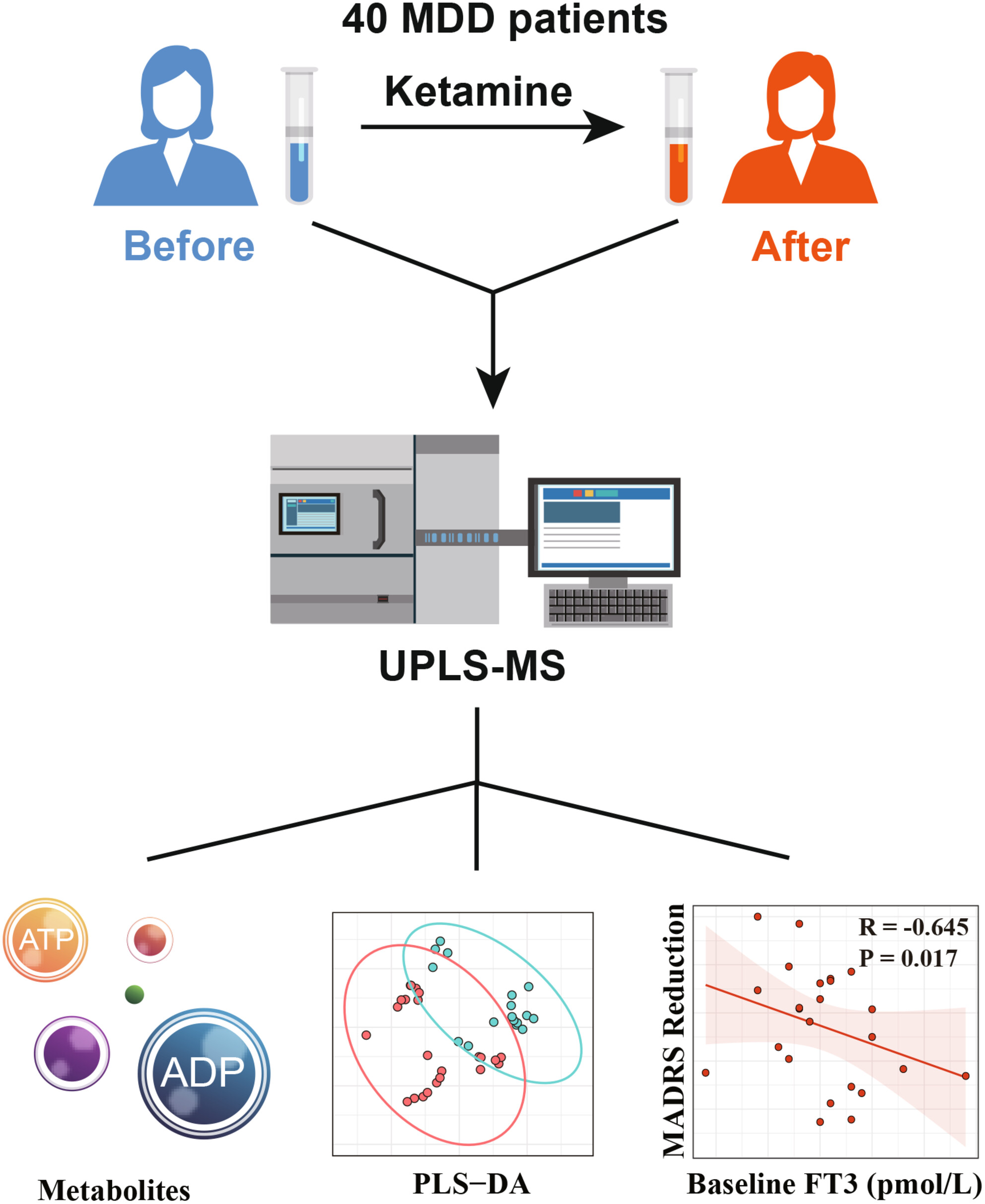
The Restoration of Energy Pathways Indicates the Efficacy of Ketamine Treatment in Depression: A Metabolomic Analysis
- First Published: 09 March 2025
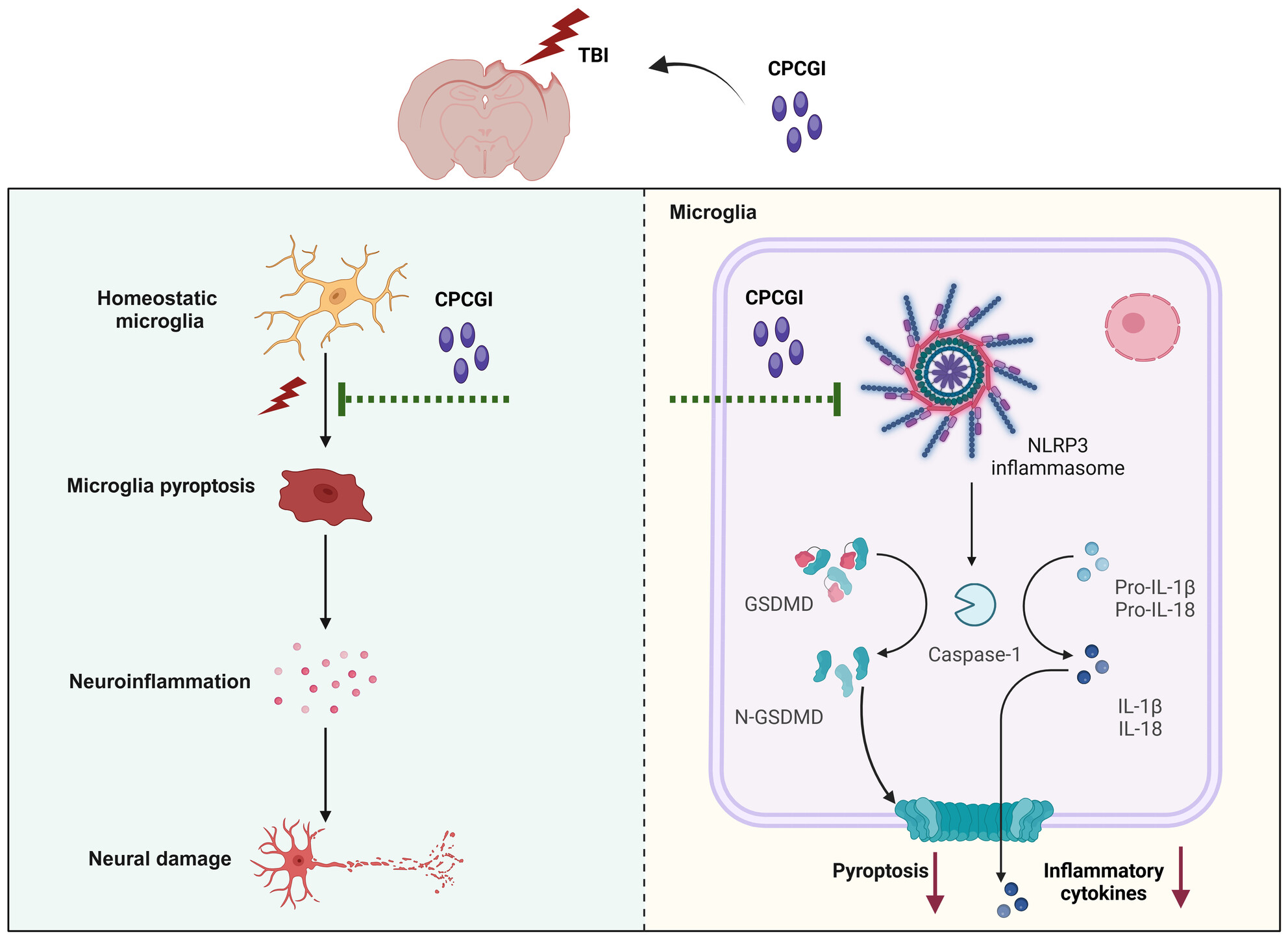
CPCGI Alleviates Neural Damage by Modulating Microglial Pyroptosis After Traumatic Brain Injury
- First Published: 09 March 2025
Central Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation Modulates Autonomic Nervous System Responsiveness in Disorders of Consciousness
- First Published: 06 March 2025
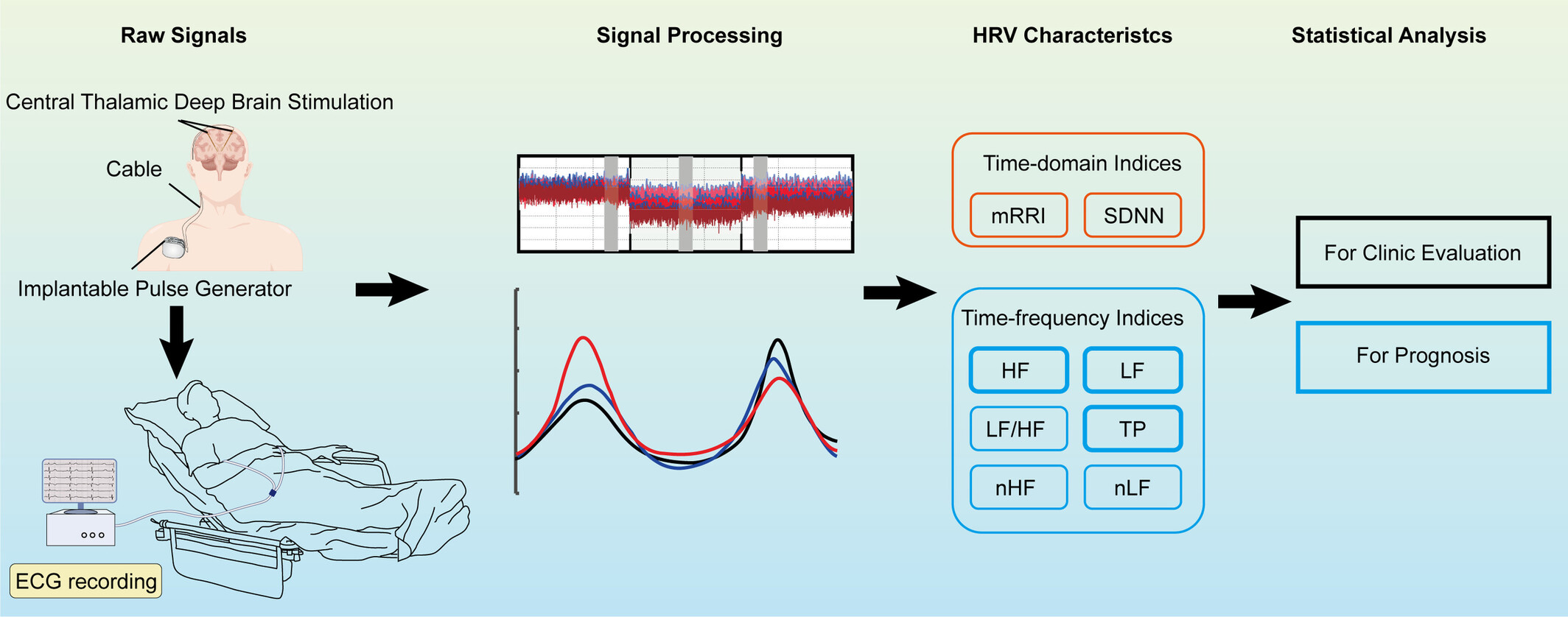
Central thalamus deep brain stimulation (DBS) exerts a regulatory effect on the autonomic nervous system in patients with disorders of consciousness (DOC). We analyzed the HRV indices, including time-domain and frequency-domain parameters across various time points for all patients. The HRV exhibited a consistent trend across the three groups with different parameters. Notably, the most pronounced HRV changes were induced by the 100 Hz. Long-term follow-up indicates that high-frequency (HF), low-frequency (LF), and total power (TP) of HRV may serve as predictive indicators in the prognosis of patients.
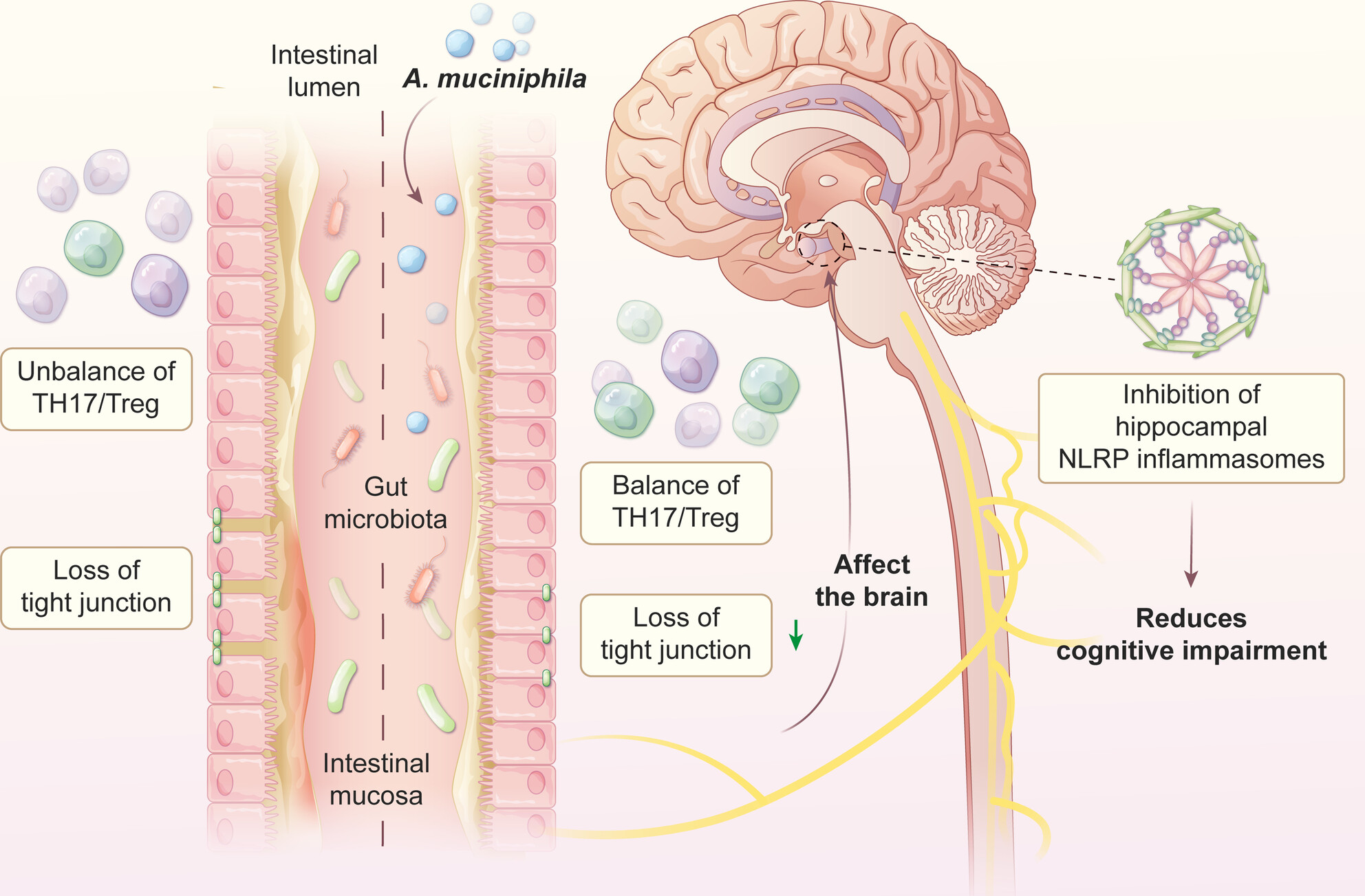
Akkermansia muciniphila Modulates Central Nervous System Autoimmune Response and Cognitive Impairment by Inhibiting Hippocampal NLRP3-Mediated Neuroinflammation
- First Published: 06 March 2025
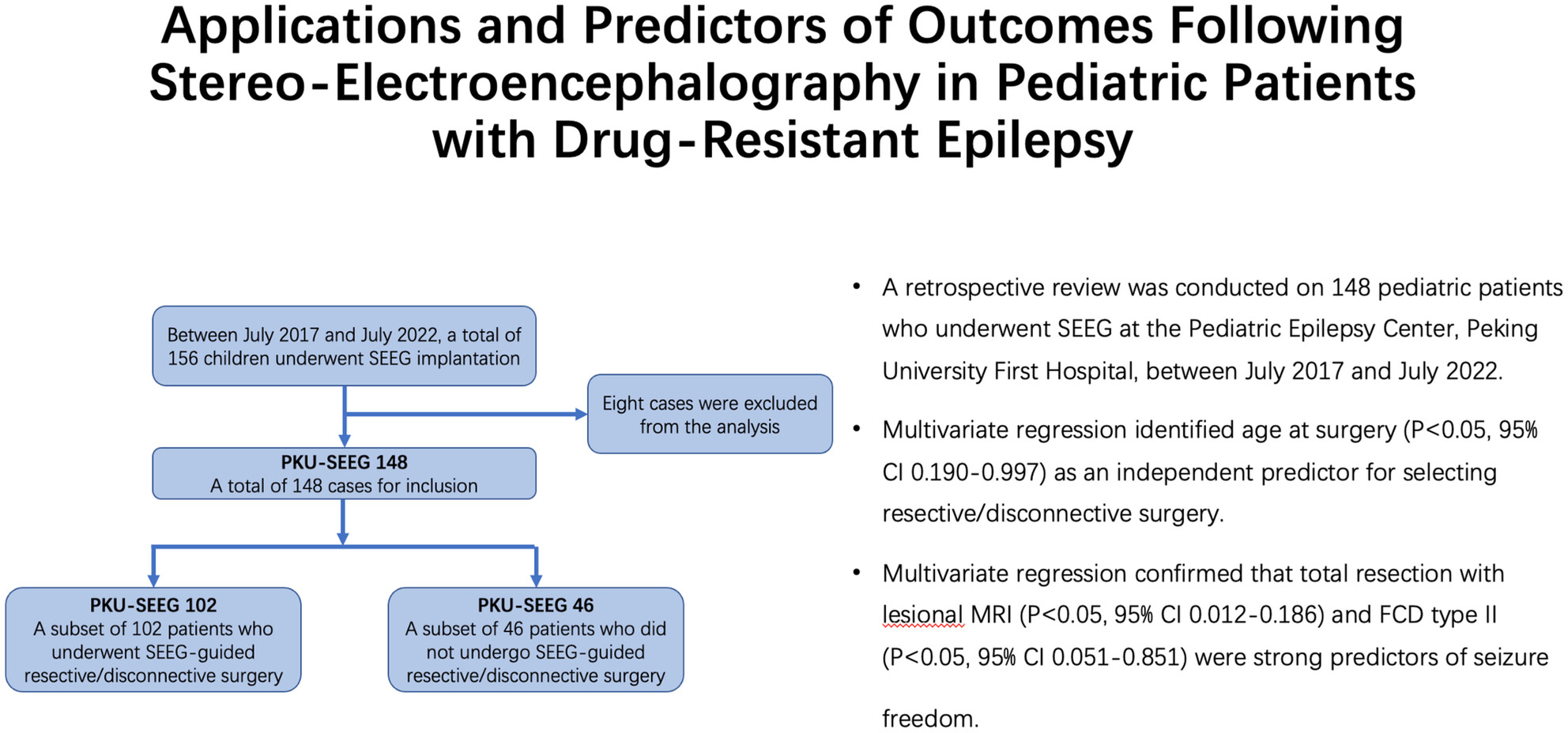
Applications and Predictors of Outcomes Following Stereo-Electroencephalography in Pediatric Patients With Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
- First Published: 12 March 2025
Neural Correlates and Adaptive Mechanisms in Vascular Cognitive Impairment: Exploration of a Structure–Function Coupling Network
- First Published: 09 March 2025
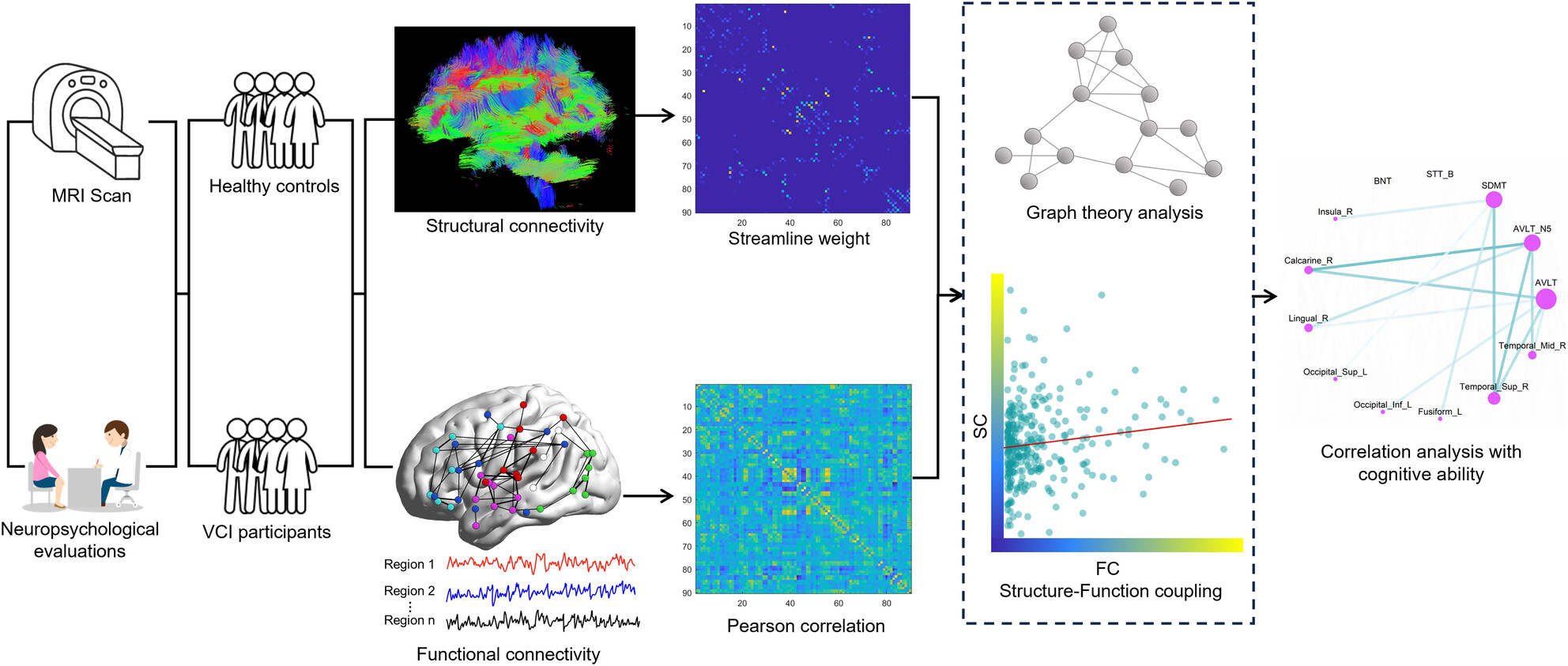
Our study revealed significant disruptions in brain structural networks in vascular cognitive impairment participants, including reduced fractional anisotropy and altered network properties. Despite no significant functional topology differences, enhanced structure–function coupling in key regions correlated with cognitive performance, suggesting compensatory neuroplasticity and offering insights for cognitive disorders prevention.
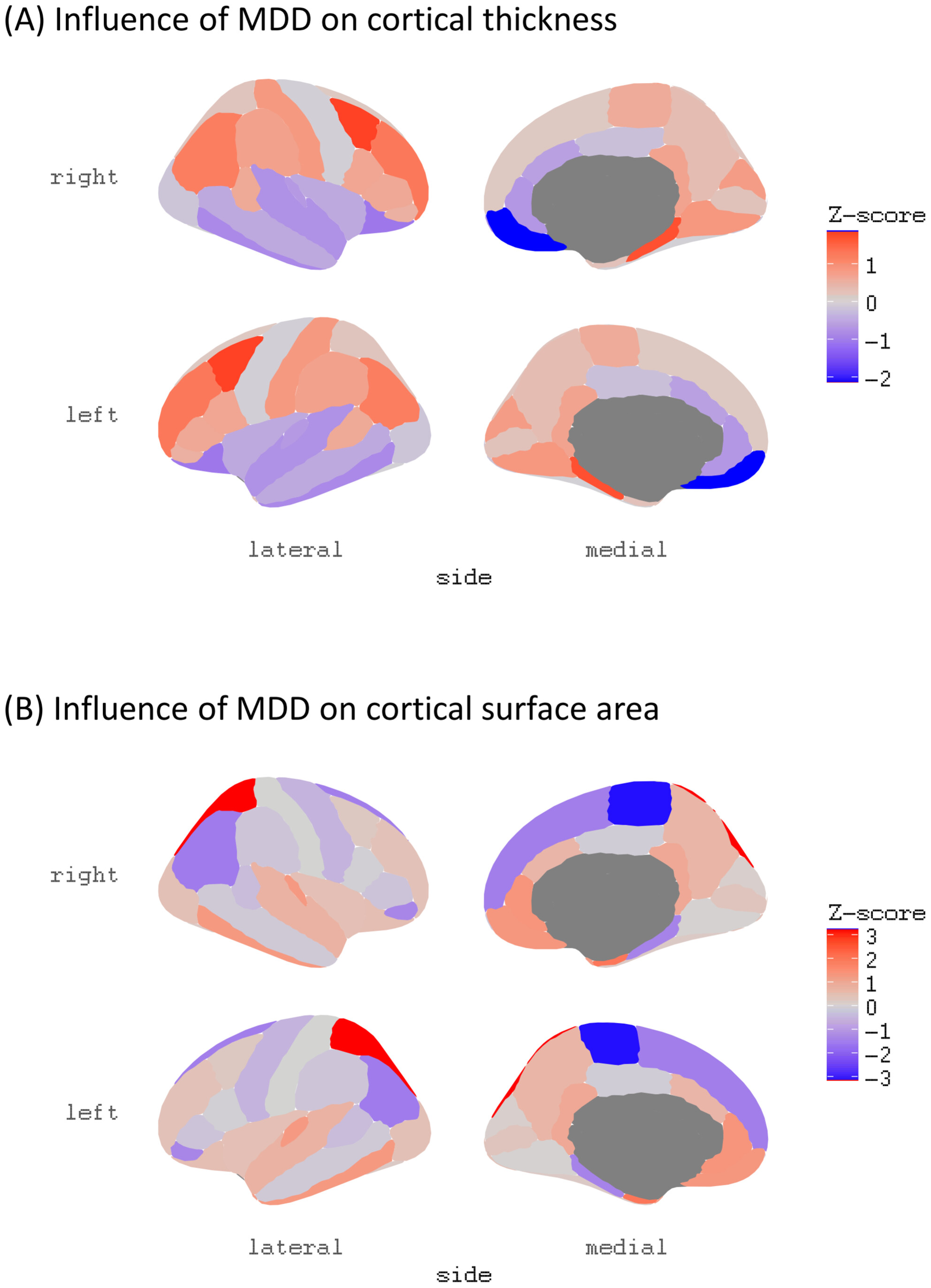
Causal Association Between Major Depressive Disorder and Cortical Structure: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study and Mediation Analysis
- First Published: 09 March 2025
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Comments on “H4K12 Lactylation-Activated Spp1 in Reprogrammed Microglia Improves Functional Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury”
- First Published: 12 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Anwulignan Alleviates Bone Cancer Pain by Modulating the PPARα/CXCR2 Signaling Pathway in the Rat Spinal Cord
- First Published: 13 March 2025
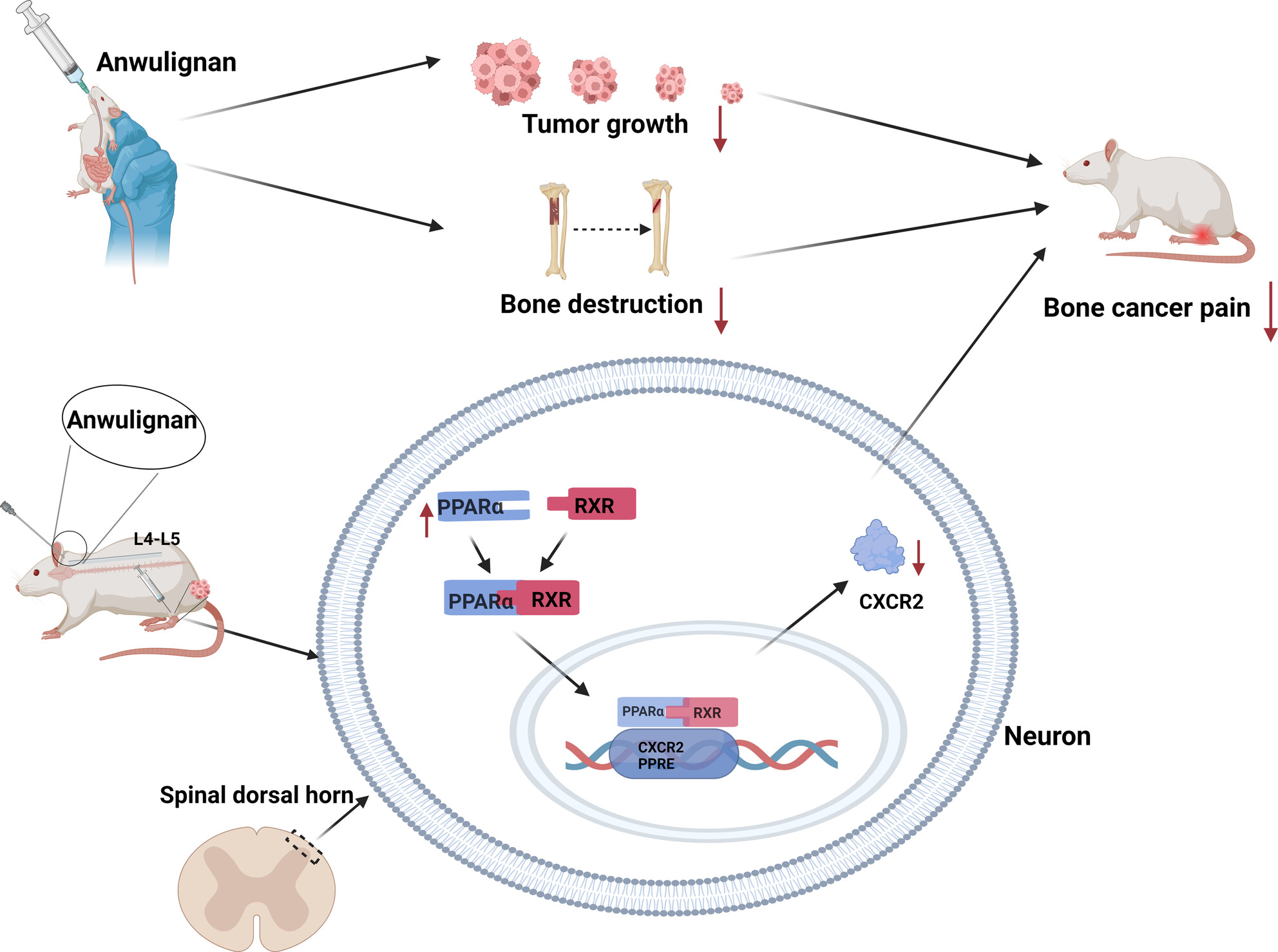
Anwulignan enhances PPARα expression in the spinal dorsal horn of rats, facilitating its binding to RXR and forming an active PPARα/RXR complex. This complex translocates to the nucleus, inhibits CXCR2 expression, and alleviates bone cancer pain (BCP) while reducing tumor-induced bone destruction and burden.
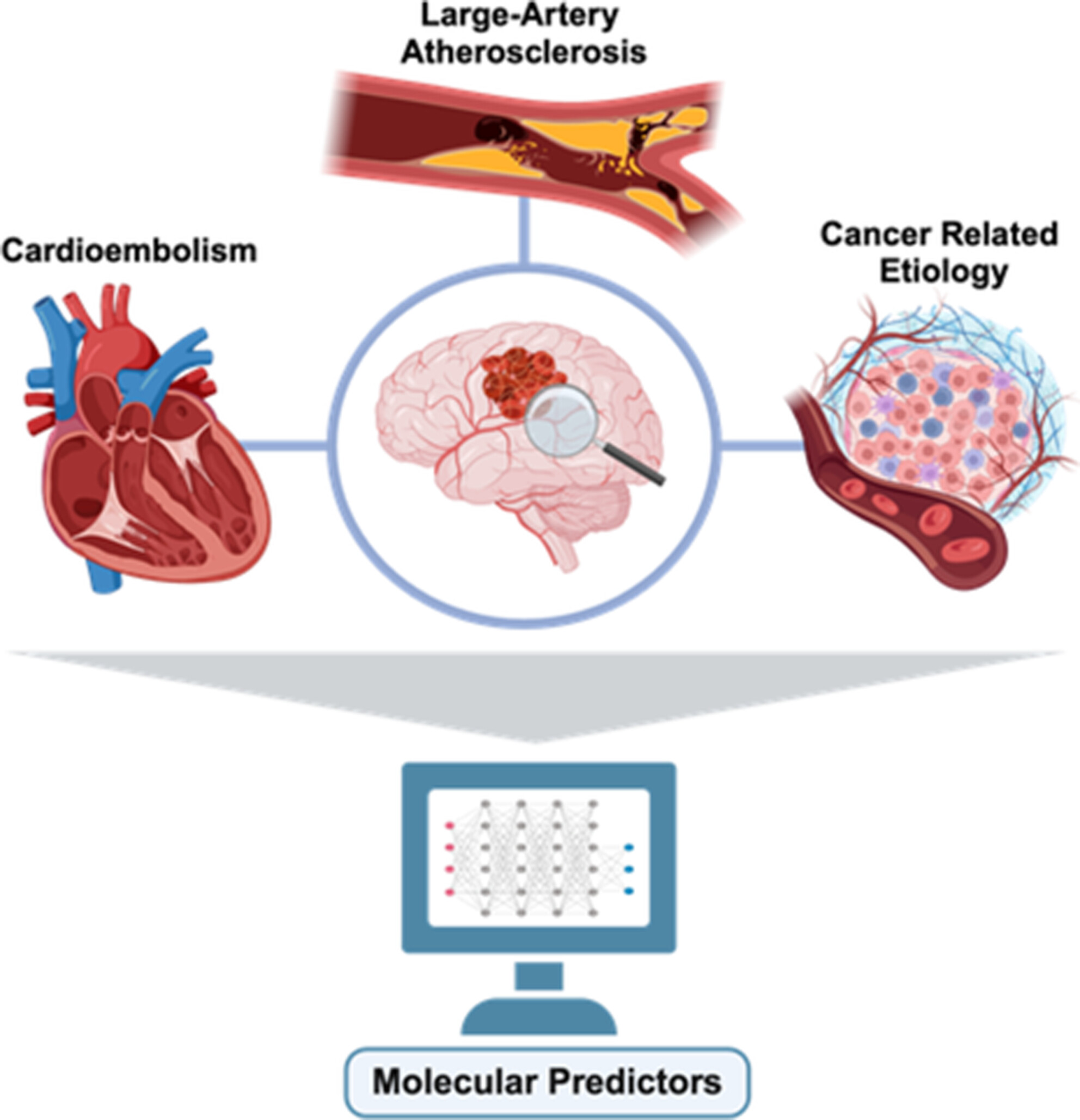
Proteomic Analyses of Clots Identify Stroke Etiologies in Patients Undergoing Endovascular Therapy
- First Published: 13 March 2025
Electroacupuncture Regulates Sympathetic Nerve Through the NTSGlu-RVLM Circuit to Relieve Spontaneous Pain in SNI Rats
- First Published: 27 March 2025
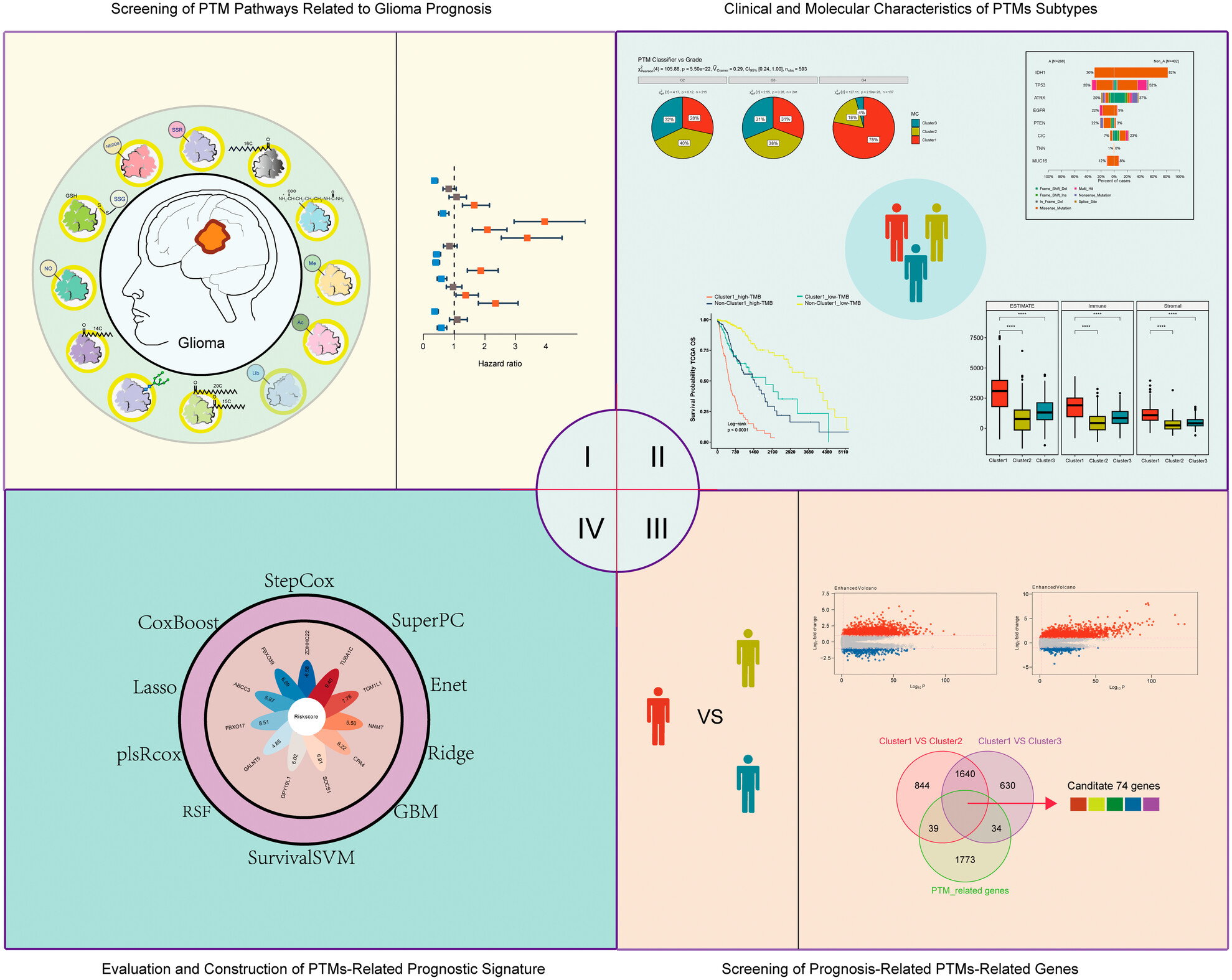
Unveiling the Role of Protein Posttranslational Modifications in Glioma Prognosis
- First Published: 16 March 2025
Inhibition of Salt-Inducible Kinase 2 Protects Motor Neurons From Degeneration in ALS by Activating Autophagic Flux and Enhancing mTORC1 Activity
- First Published: 26 March 2025
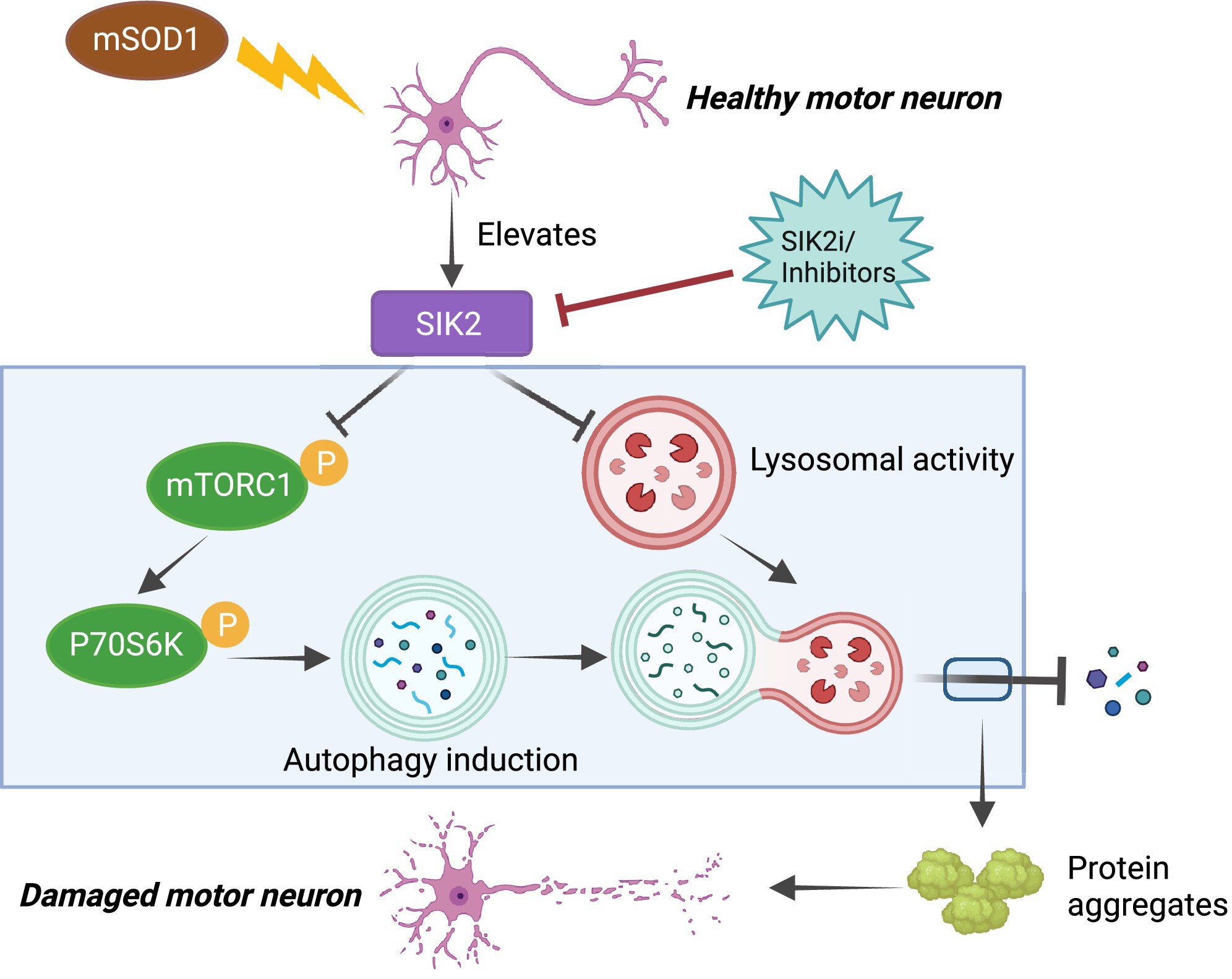
Schematic diagram of potential mechanisms by which SIK2 regulates autophagy in ALS. SIK2 contributes to the induction of autophagy by inhibiting mTORC1 signaling. However, SIK2 disrupts lysosomal dysfunction, ultimately resulting in defective autophagy flux. Inhibition of SIK2 promotes mSOD1 accumulation removal by activating autophagy flux and restores mTORC1 activity, thus playing a neuroprotective role on motor neurons in ALS.
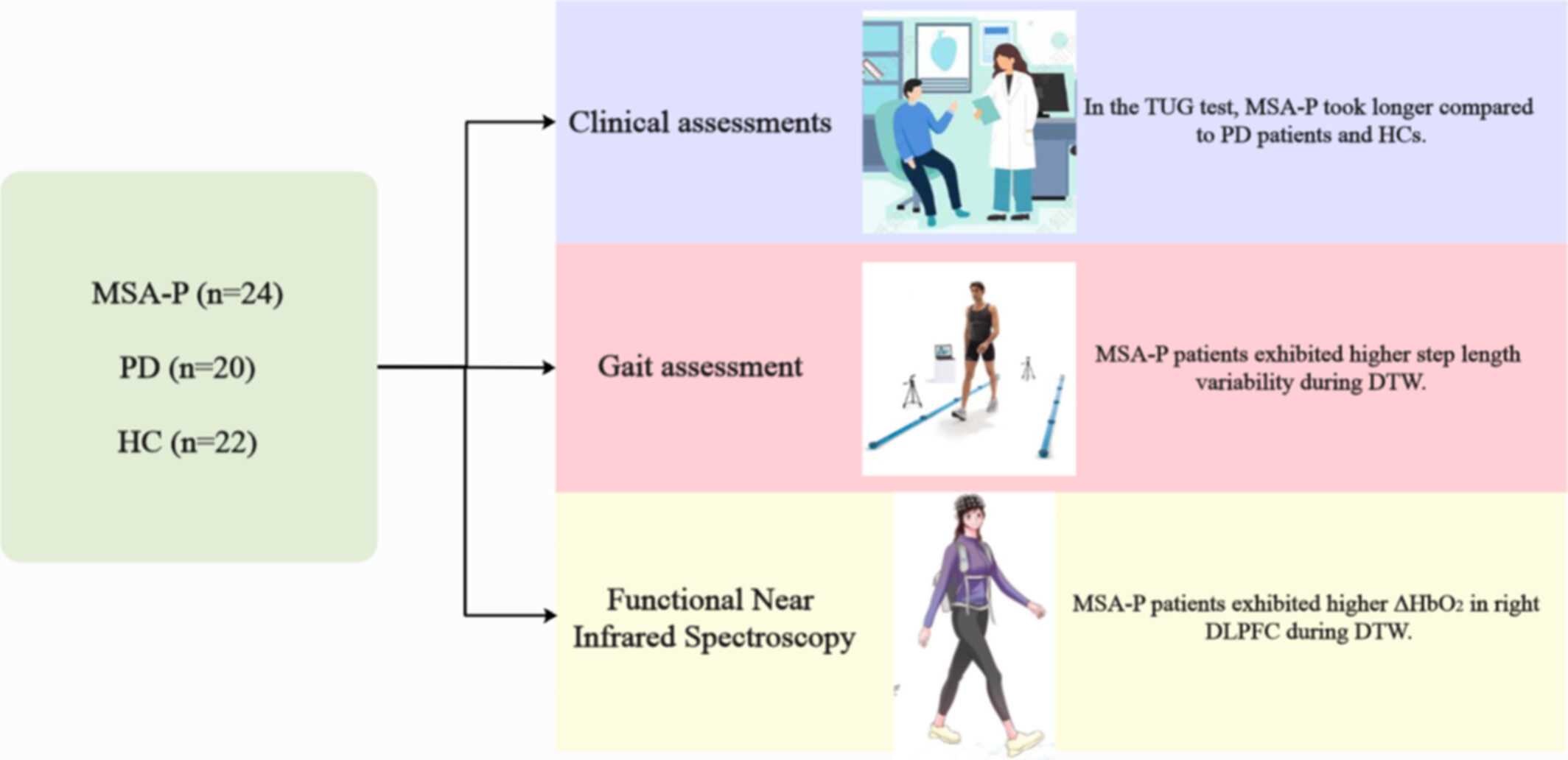
Differences Between Patients With Multiple System Atrophy With Predominant Parkinsonism and Parkinson's Disease Based on fNIRS and Gait Analysis
- First Published: 26 March 2025
Early Prediction of the Evolution of Self-Limited Epilepsy With Centrotemporal Spikes to Epileptic Encephalopathy With Spike-and-Wave Activation in Sleep: A Prediction Model Construction Based on Quantitative Electroencephalography Characteristics
- First Published: 18 March 2025
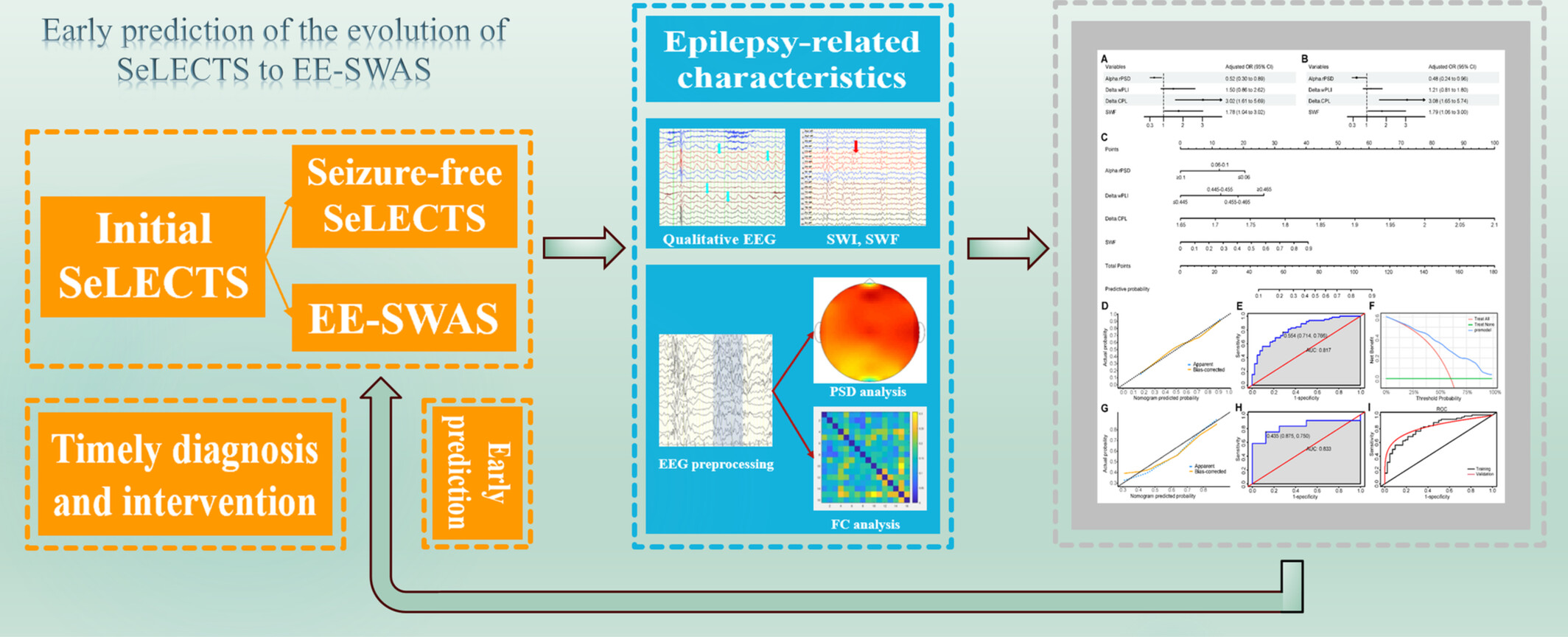
In children with SeLECTS, early EEG features such as SWF, relative PSD, wPLI, and CPL are significantly associated with the presence of EE-SWAS during the disease course. We successfully construct a model to predict the evolution of EE-SWAS in SeLECTS, thereby aiding early clinical diagnosis and timely intervention for EE-SWAS.
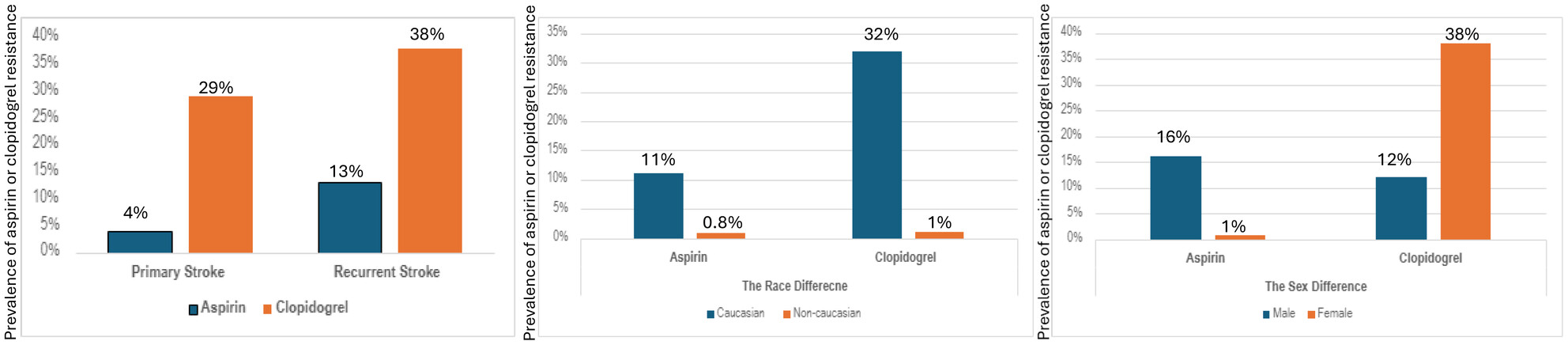
Prevalence of Aspirin or Clopidogrel Pharmacological Resistance in Ischemic Stroke: A Step Toward Precision Medicine
- First Published: 18 March 2025
The Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex on the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients With Cognitive Impairment: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, and Sham Control Trial
- First Published: 18 March 2025
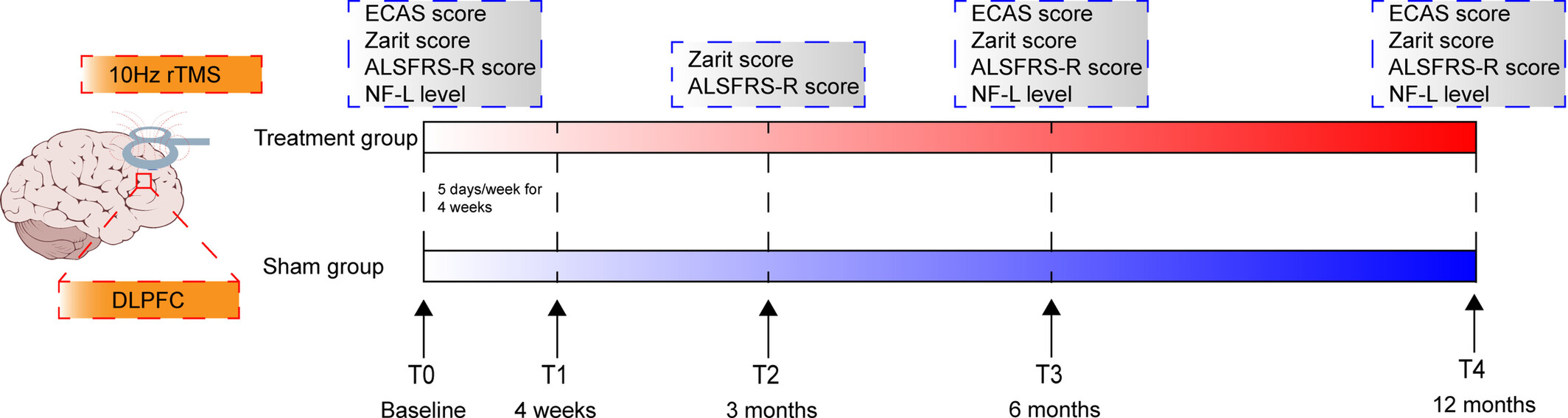
Study design comparing the treatment and sham groups. The treatment group received 4 weeks of rTMS on the DLPFC (5 days per week), while the sham group underwent sham stimulation. Assessments were conducted at baseline (T0), 4 weeks (T1), 3 months (T2), 6 months (T3), and 12 months (T4), measuring ECAS, Zarit, ALSFRS-R scores, and NF-L levels to evaluate group differences.
Incidence, Characteristics, and Risk Factors of Post-Radiosurgery Headaches: A Prospective Observational Study
- First Published: 18 March 2025
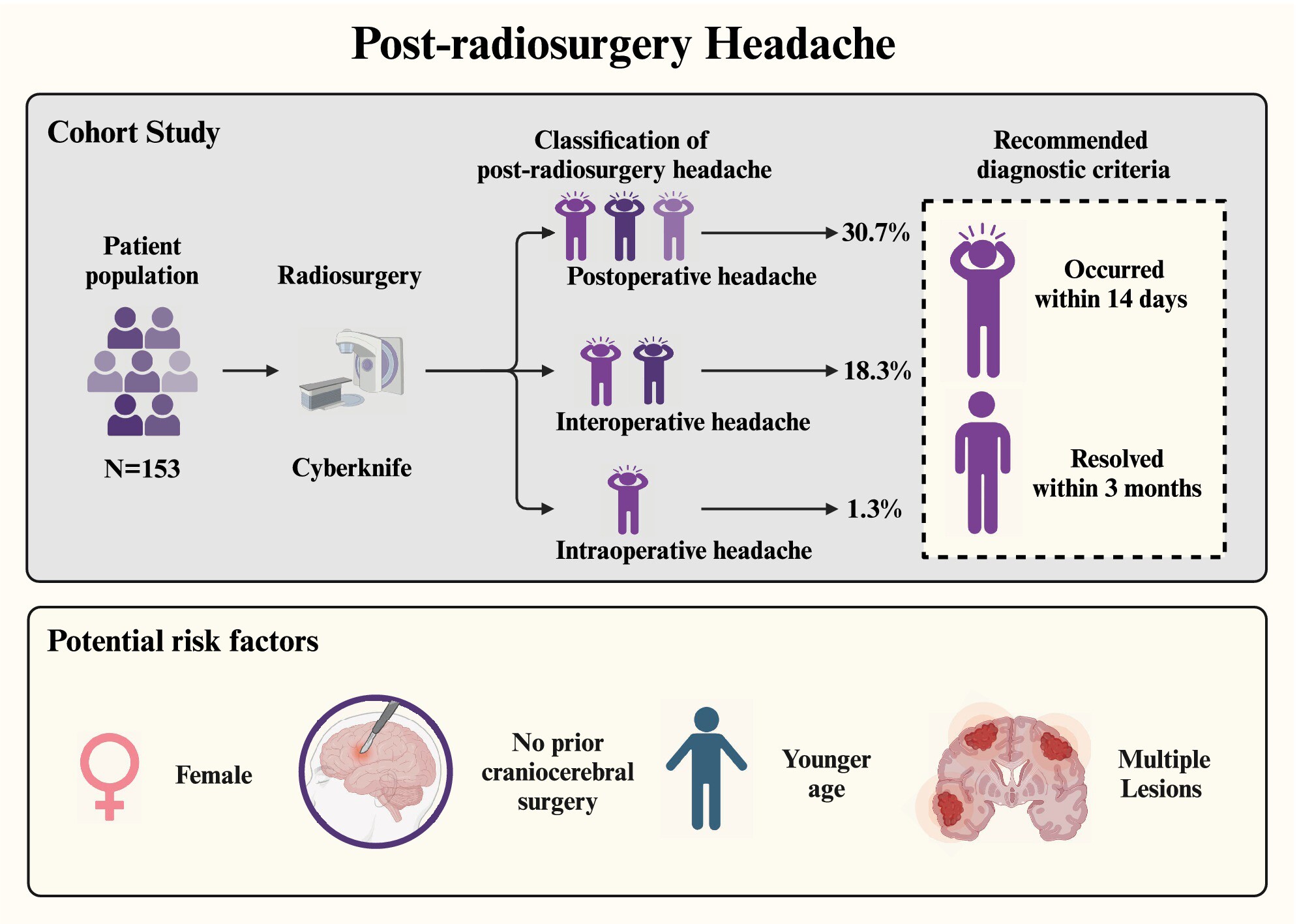
Based on prospective observations of the characteristics of post-radiosurgery headache, supplementary diagnostic criteria have been proposed. Female gender, younger age, no prior craniocerebral surgery, and multiple lesions are identified as risk factors for the occurrence of post-radiosurgery headache.
Acute Restraint Stress Induces Long-Lasting Synaptic Enhancement by Inhibiting AMPK Activation in AD Model Mice
- First Published: 18 March 2025
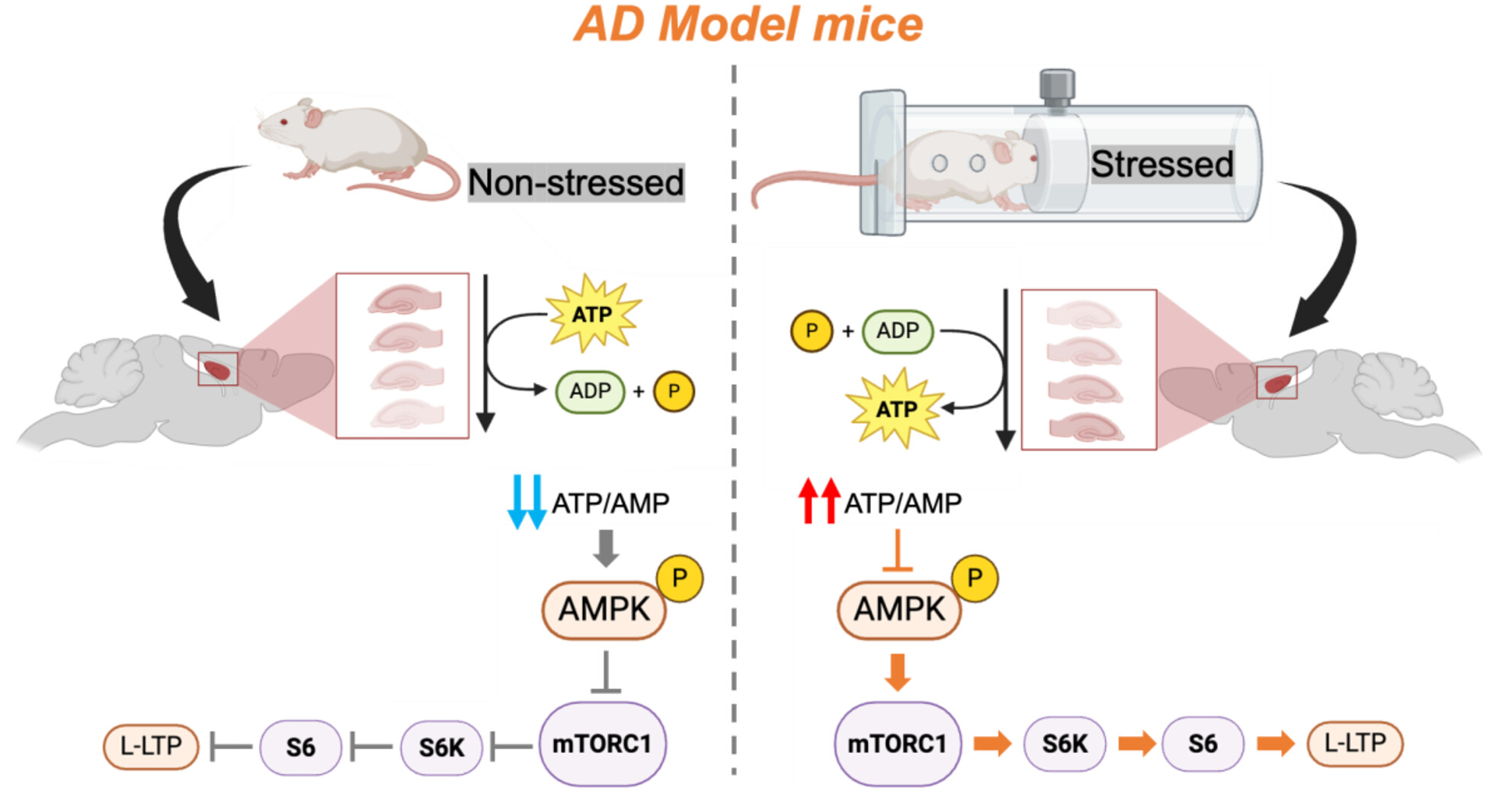
Acute restraint stress regulates ATP production in the hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease model mice and inhibits abnormal activation of AMPK under the pathologic condition, resulting in the removal of the suppression of the mTOR pathway, which is involved in the enhancement and maintenance of L-LTP.
REVIEW
Malignant Cells Beyond the Tumor Core: The Non-Negligible Factor to Overcome the Refractory of Glioblastoma
- First Published: 19 March 2025
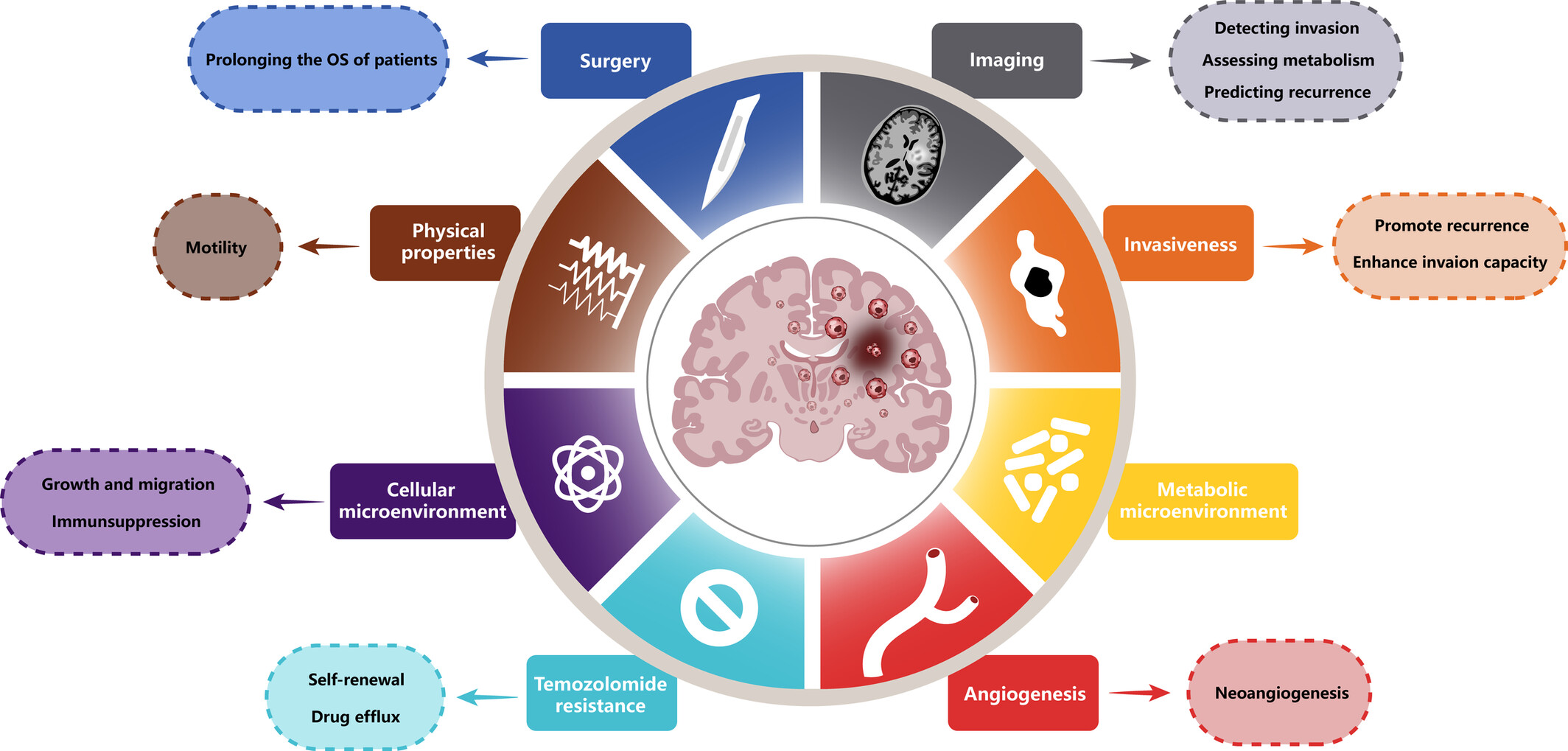
Located beyond the tumor core, questiona cells (Q cells) exhibit high invasiveness, metabolic adaptations, and drug resistance, driving tumor recurrence despite aggressive treatment. Their physical properties, such as low solid stress and soft tissue stiffness, further enhance their migratory and invasive capabilities. Advanced imaging techniques (e.g., DTI, MRS, DWI, PET) enable their detection, while interactions with the tumor microenvironment (e.g., TAMs, Tregs, fibroblasts) present new therapeutic challenges and opportunities.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Gastrodin Alleviates Tau Pathology by Targeting the Alzheimer's Risk Gene FERMT2, Reversing the Reduction in Brain Viscoelasticity
- First Published: 22 March 2025
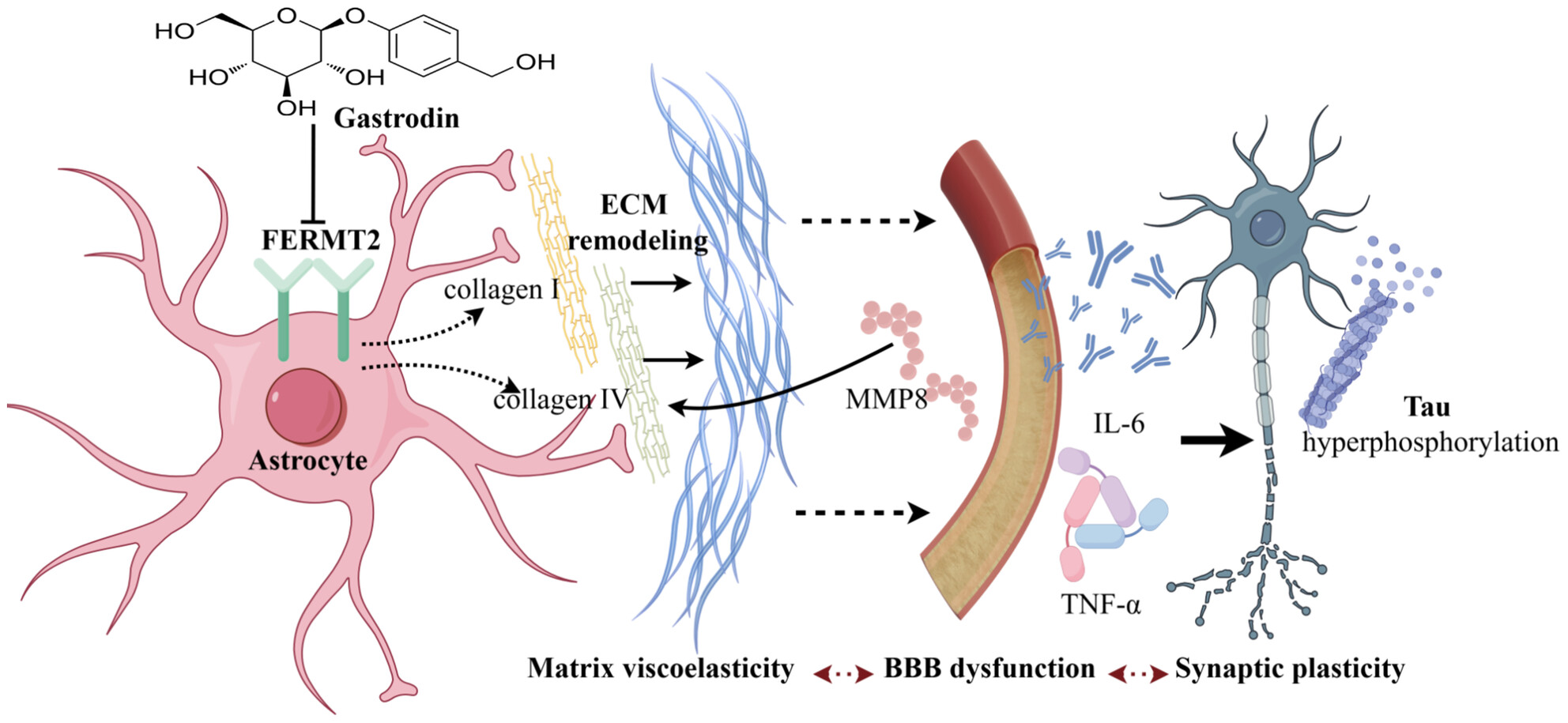
Gastrodin reduces tau hyperphosphorylation in 3xTg-AD mice, reverses decreased brain matrix viscoelasticity, and remodels ECM components by targeting the Alzheimer's risk gene FERMT2, primarily in astrocytes. It binds to FERMT2, inhibiting its expression, which leads to ECM remodeling, restored matrix viscoelasticity, and blood–brain barrier recovery. Gastrodin also modifies neuroinflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6, and MMP8.
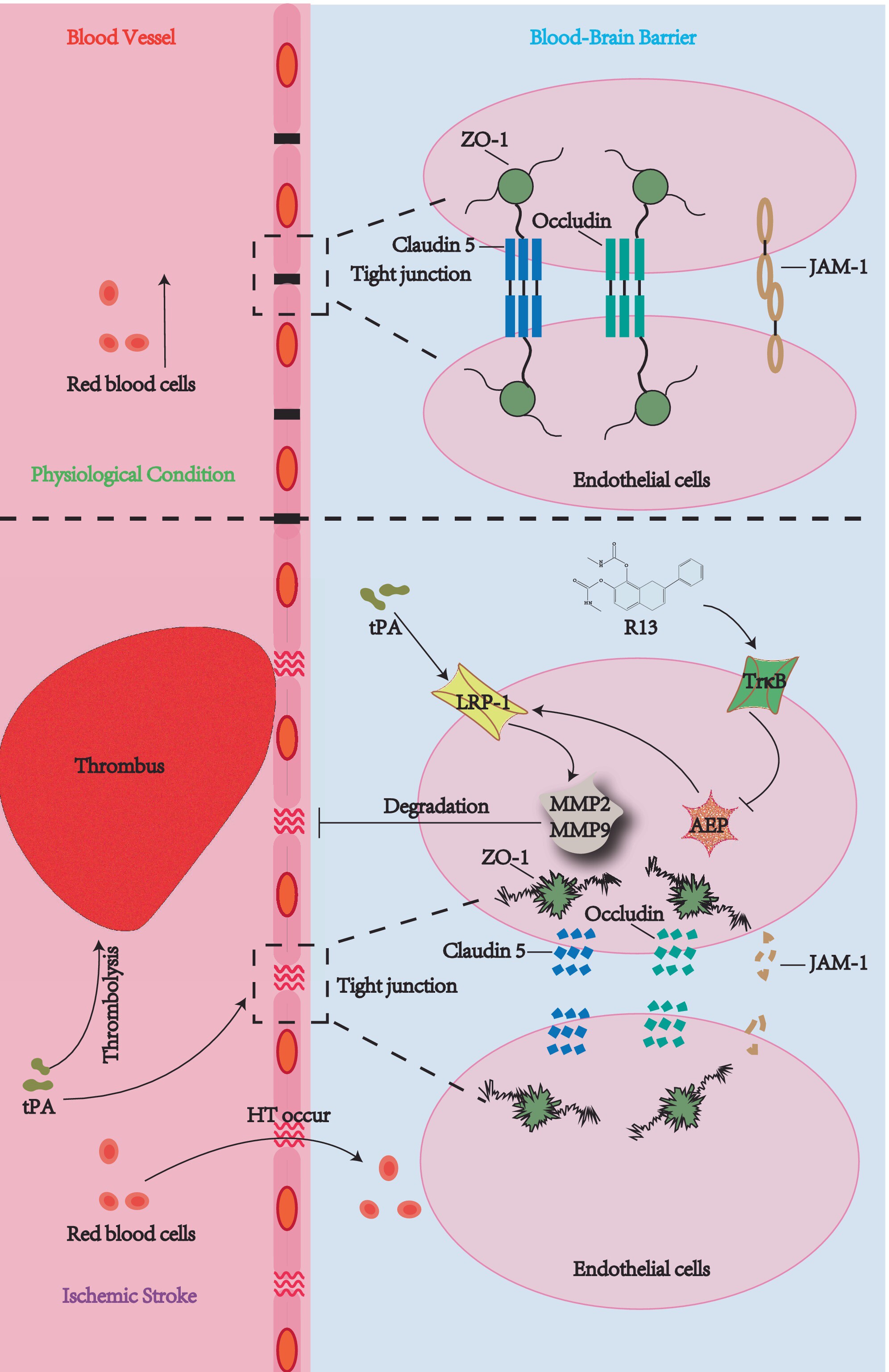
Asparagine Endopeptidase Inhibition Attenuates Tissue Plasminogen Activator-Induced Brain Hemorrhagic Transformation After Ischemic Stroke
- First Published: 21 March 2025
Possible GABAkine-Mediated Sedative-Like Antidepressant Effects of Phytol: Molecular Interventions Through In Vitro, In Vivo and In Silico Approaches
- First Published: 21 March 2025
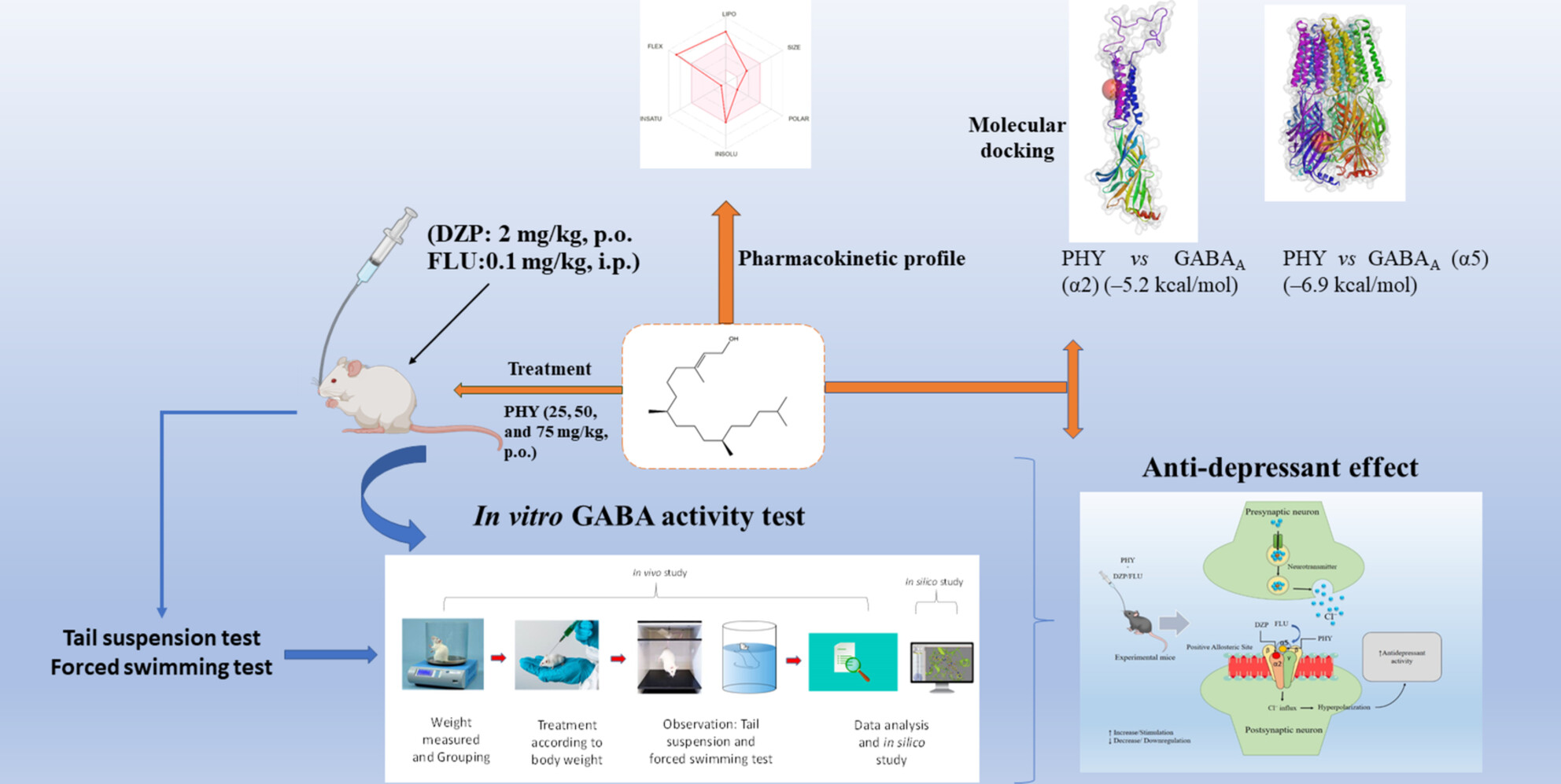
Phytol (PHY) concentration-dependently inhibited GABA activity and dose-dependently reduced immobility time (IMT) in Swiss mice. It also modulated the GABA activity and IMT values of diazepam and flumazenil. It showed a slight sex-dependent antidepressant effect on mice, possibly through the GABAA receptor interaction pathway.
A Novel Compound QO-83 Alleviates Acute and Chronic Epileptic Seizures in Rodents by Modulating KV7 Channel Activity
- First Published: 24 March 2025
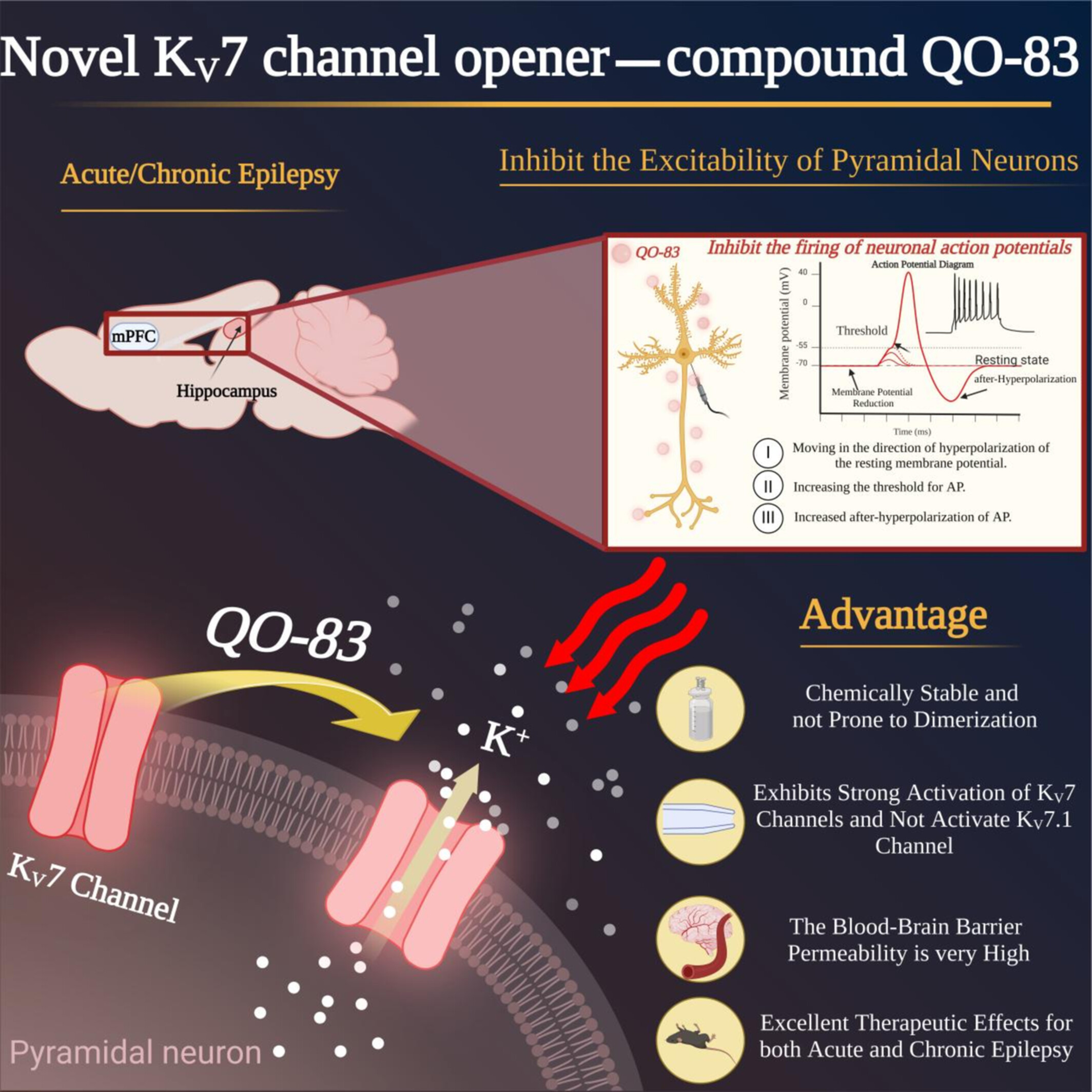
QO-83 has better opening effects on KV7.2 and KV7.2/7.3 channels, with W236 as the key site for its high binding free energy to KV7.2. By opening KV7 channels, regulating sIPSC and sEPSC amplitudes, and inhibiting epileptiform discharges, QO-83 outperforms RTG in both acute and chronic epilepsy models.
Aloe-Emodin Improves Mitophagy in Alzheimer's Disease via Activating the AMPK/PGC-1α/SIRT3 Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 24 March 2025
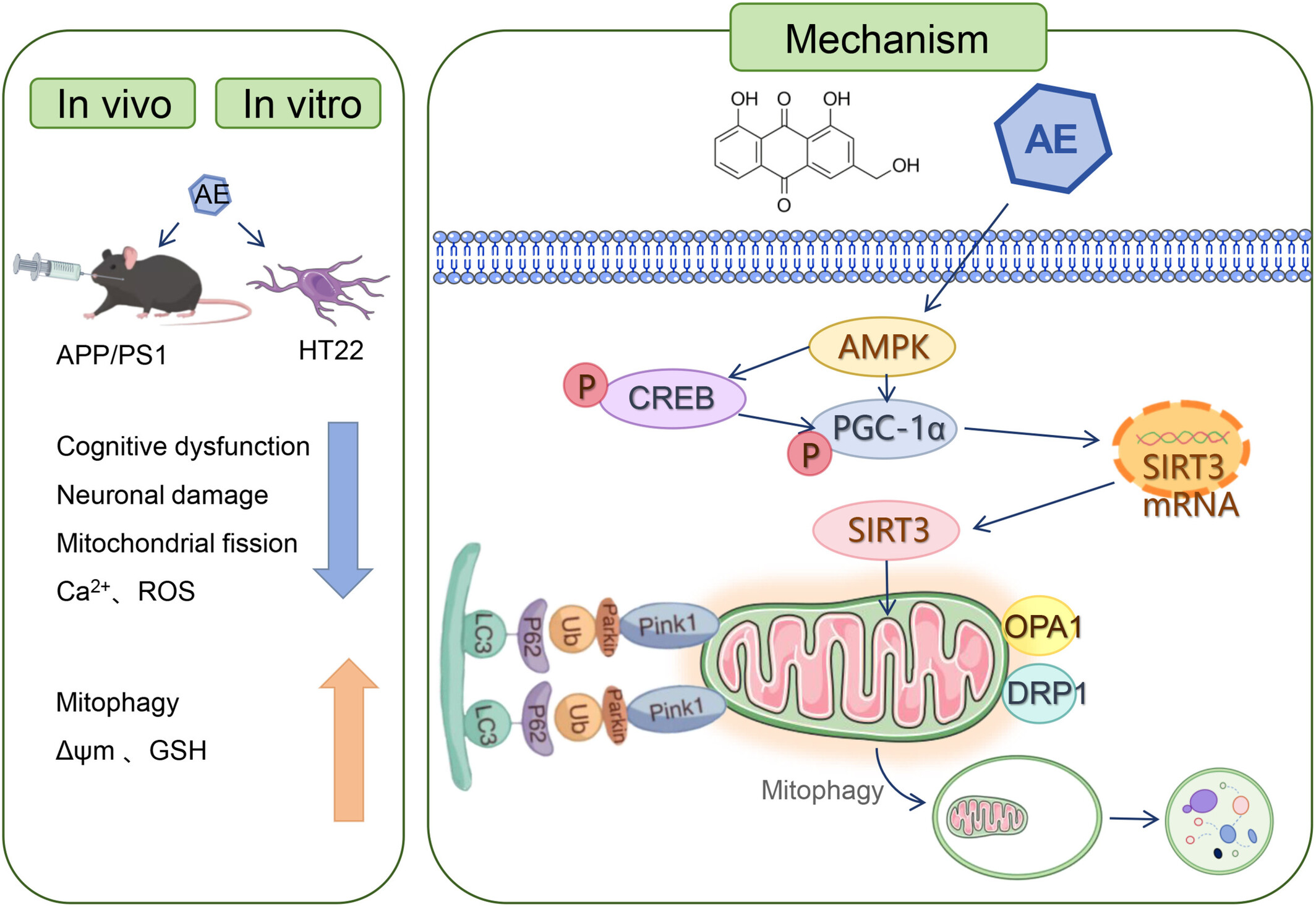
AE activates the AMPK/PGC-1α/SIRT3 pathway. Increased expression of SIRT3 in mitochondria promotes mitophagy and regulates the function of mitochondrial proteins. Consequently, the mitochondrial membrane potential, GSH, ROS, and Ca2+ levels gradually recover, alleviating the pathological manifestations of ad.
Melatonin Alleviates Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental Abnormalities in Offspring Caused by Prenatal Stress
- First Published: 25 March 2025
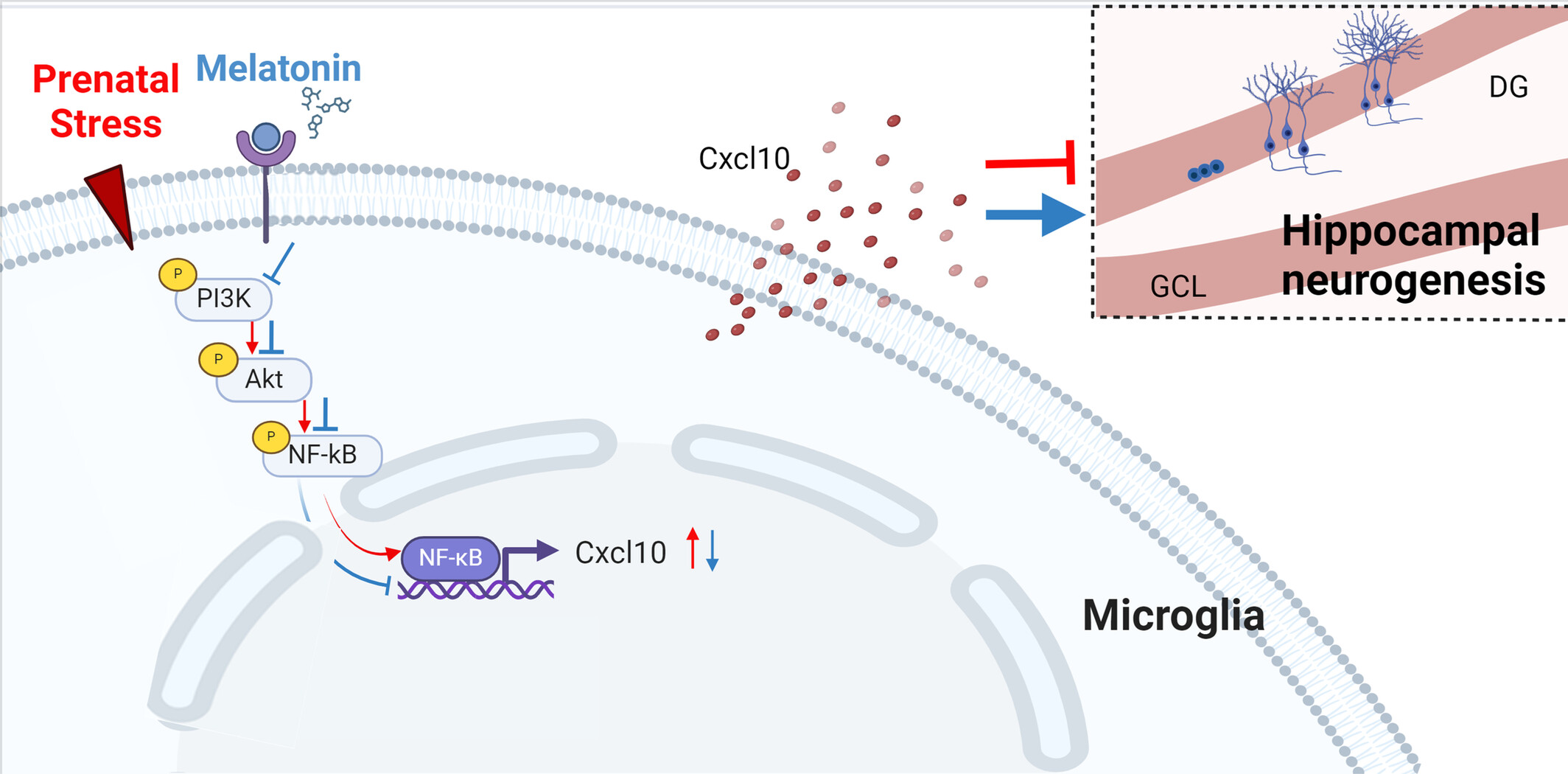
Prenatal stress increases the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders and psychiatric illnesses in offspring. This study demonstrates that melatonin alleviates emotional and cognitive deficits in offspring exposed to prenatal stress. By modulating the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway in microglia and reducing the elevated expression of CXCL10 in the dentate gyrus, melatonin promotes neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity.
Noradrenergic Locus Coeruleus-CA3 Activation Alleviates Neuropathic Pain and Anxiety- and Depression-Like Behaviors by Suppressing Microglial Neuroinflammation in SNI Mice
- First Published: 25 March 2025
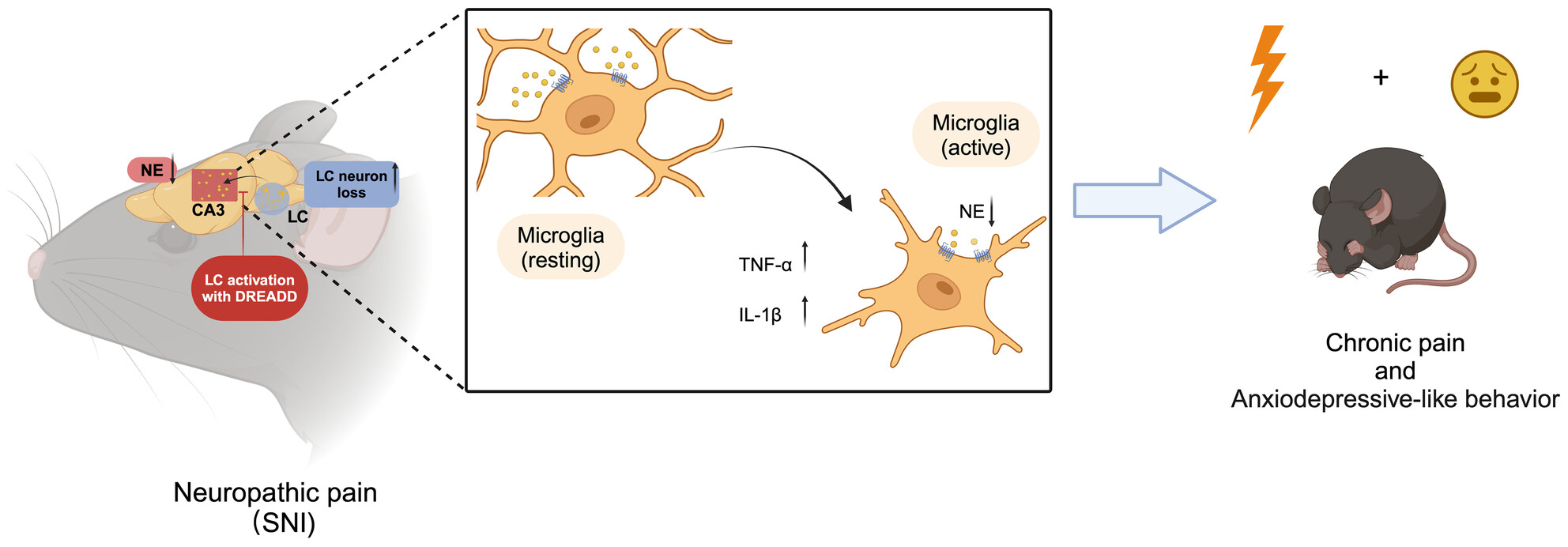
NP induces LC neuron loss; it also diminishes norepinephrine (NE) release and increases inflammatory activation of microglia and neuroinflammation in CA3 of the hippocampus. Selective activation of the LC-CA3 noradrenergic neurons with Gq-DREADD efficiently alleviates NP and anxiety- and depression-like behaviors, and reduces microglial neuroinflammation in CA3 of mice 12 weeks post-SNI.
TSG-6 Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury via Upregulating Hsp70-1B in Astrocytes
- First Published: 25 March 2025
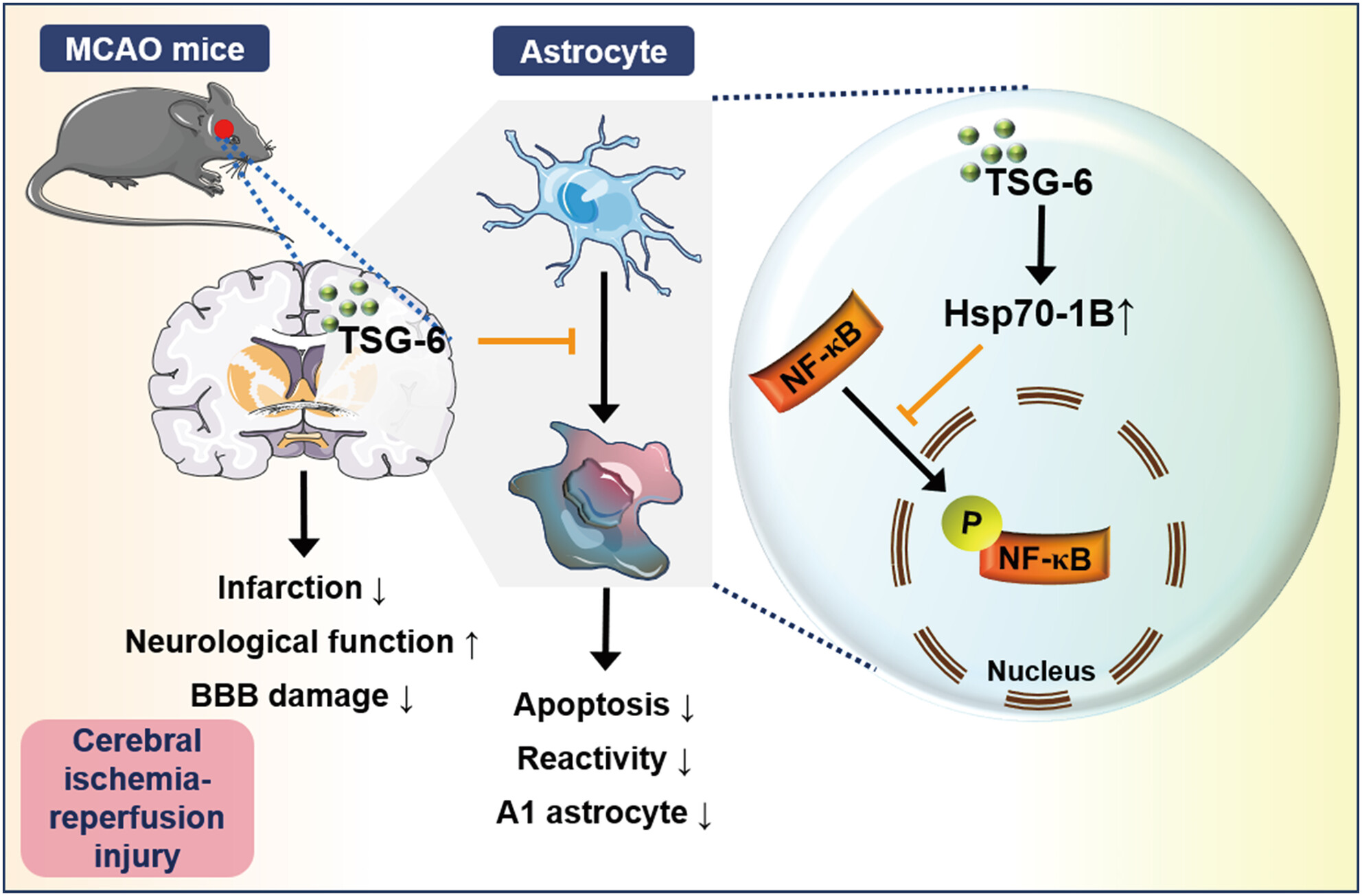
TSG-6 diminishes infarct volume, enhances neurological function, and mitigates blood–brain barrier damage following acute cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury. Furthermore, TSG-6 exerts neuroprotective effects by upregulating Hsp70-1B to inhibit NF-κB phosphorylation in oxygen–glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced astrocytes, thereby suppressing apoptosis, astrocyte reactivity, and A1 phenotype transformation.
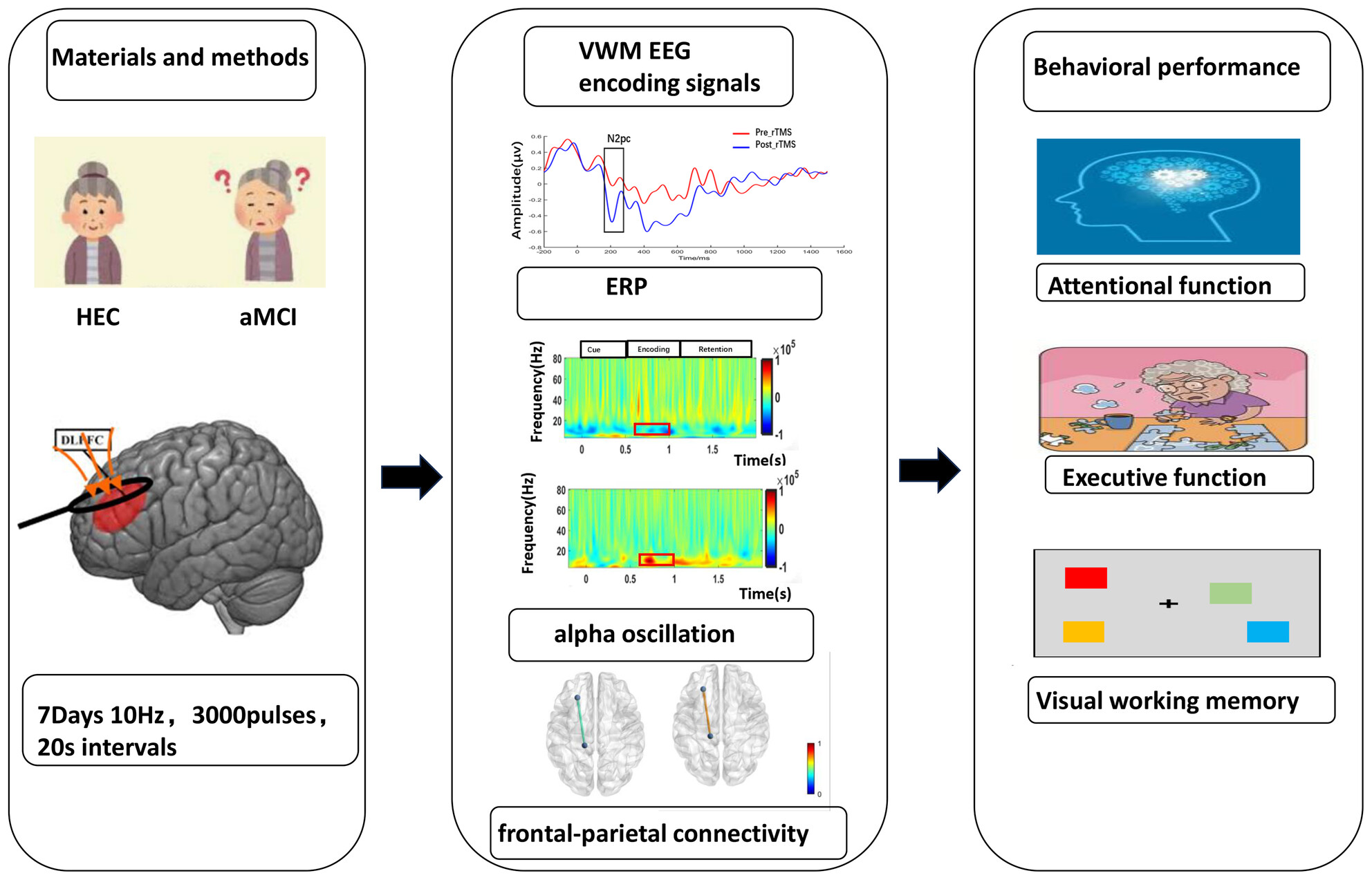
High-Frequency rTMS Improves Visual Working Memory in Patients With aMCI: A Cognitive Neural Mechanism Study
- First Published: 24 March 2025
A Novel Nomogram Integrating Retinal Microvasculature and Clinical Indicators for Individualized Prediction of Early Neurological Deterioration in Single Subcortical Infarction
- First Published: 12 March 2025
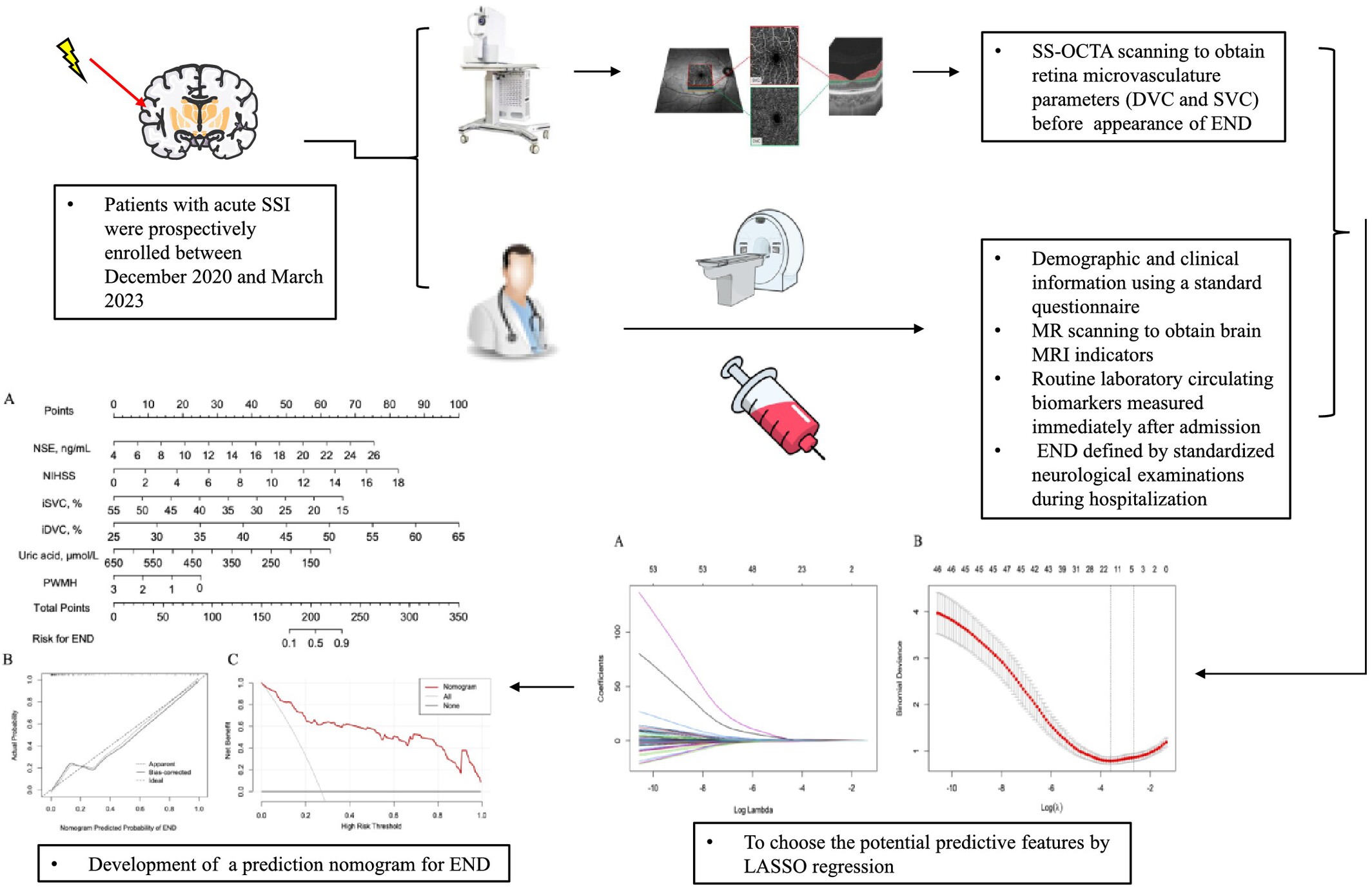
We developed a novel nomogram that incorporated four routine clinical variables with two OCTA-derived retinal microvascular metrics in predicting END in SSI patients, which exhibits high accuracy in predicting END in SSI patients. It could help identify SSI patients with a high risk of END at an early stage and benefit a better prognosis.
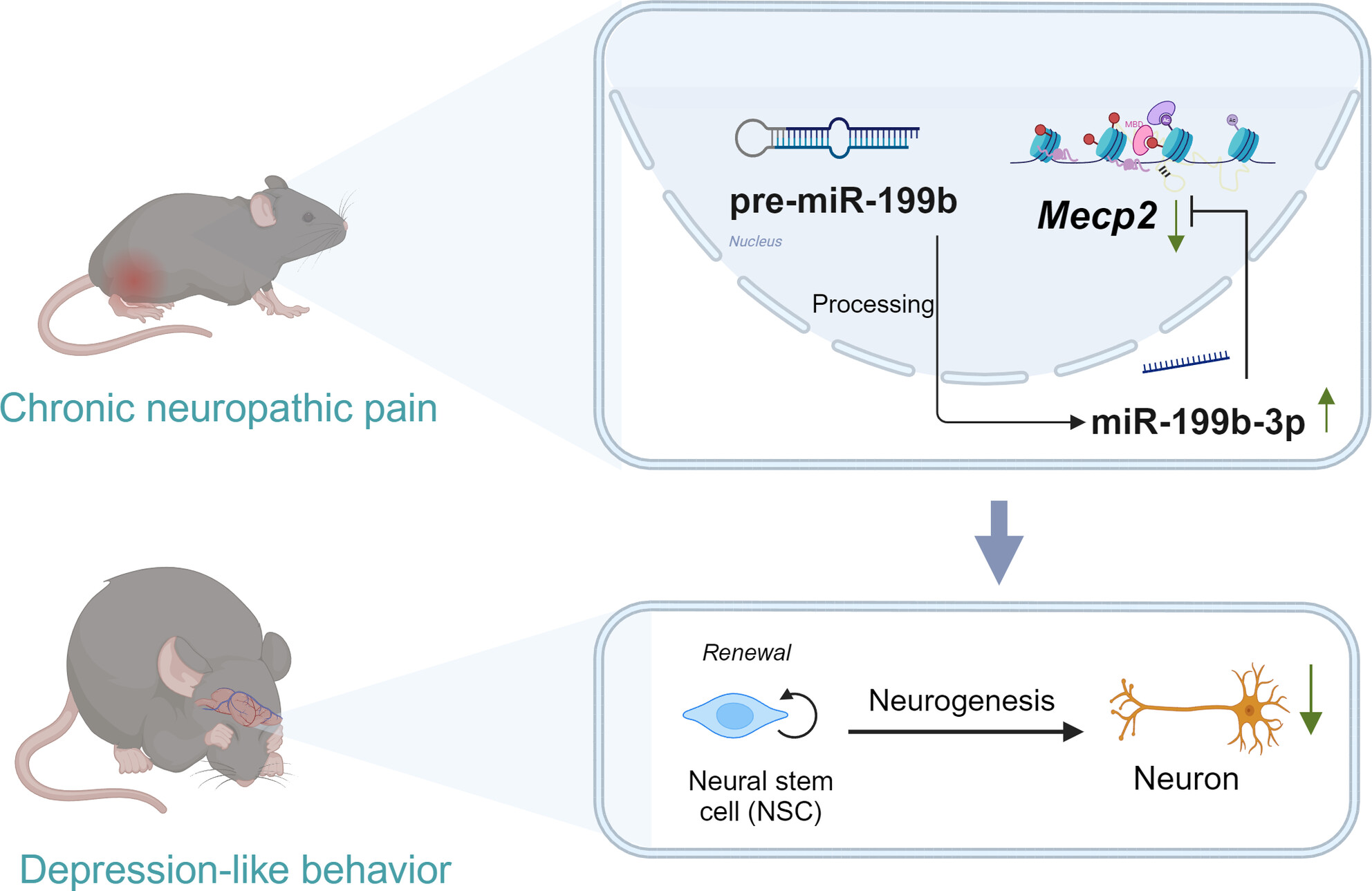
MeCP2 Modulates Depression-Like Behaviors Comorbid to Chronic Pain by Regulating Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis
- First Published: 07 April 2025
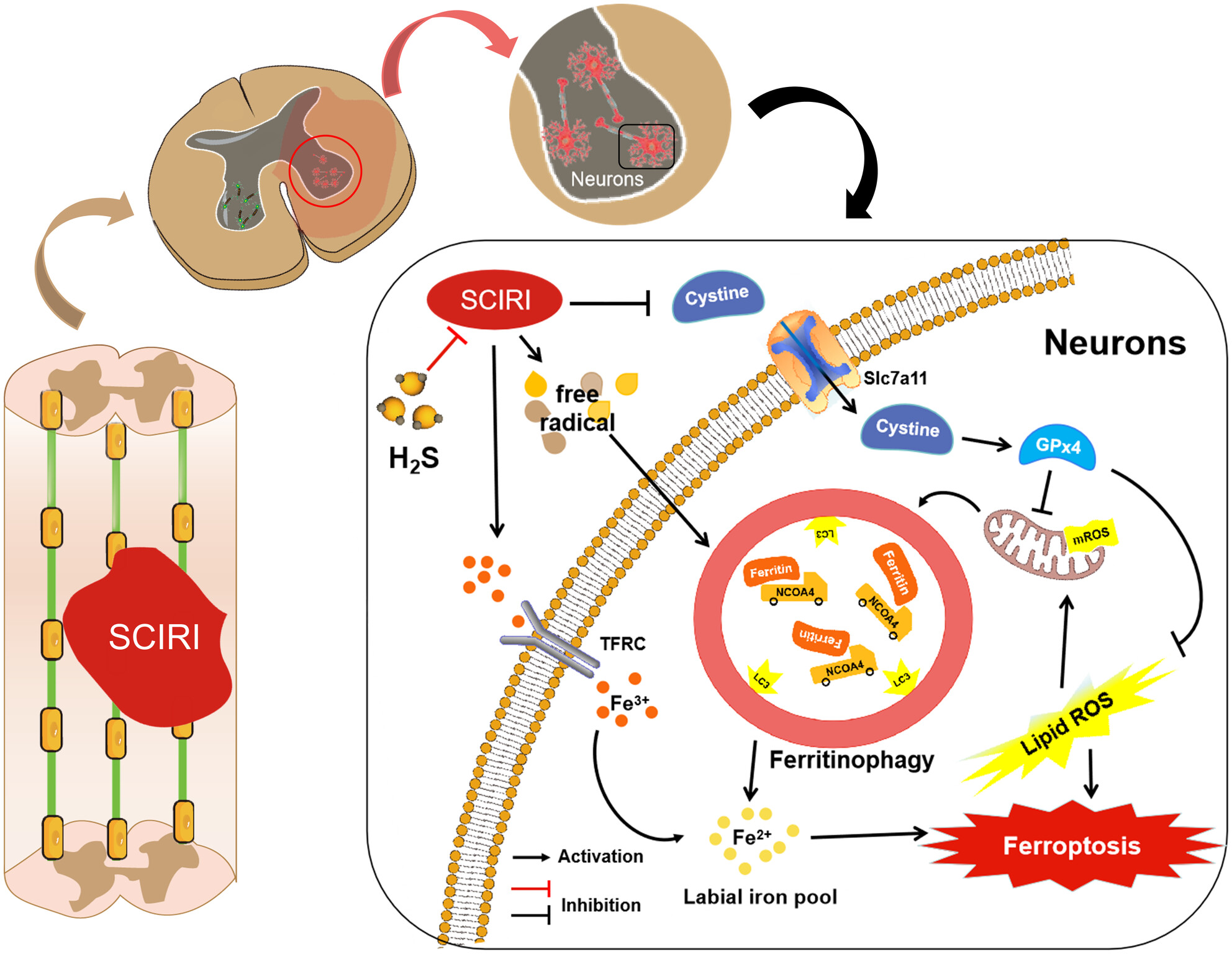
Hydrogen Sulfide Sustained Release Donor Alleviates Spinal Cord Ischemia–Reperfusion-Induced Neuron Death by Inhibiting Ferritinophagy-Mediated Ferroptosis
- First Published: 01 April 2025
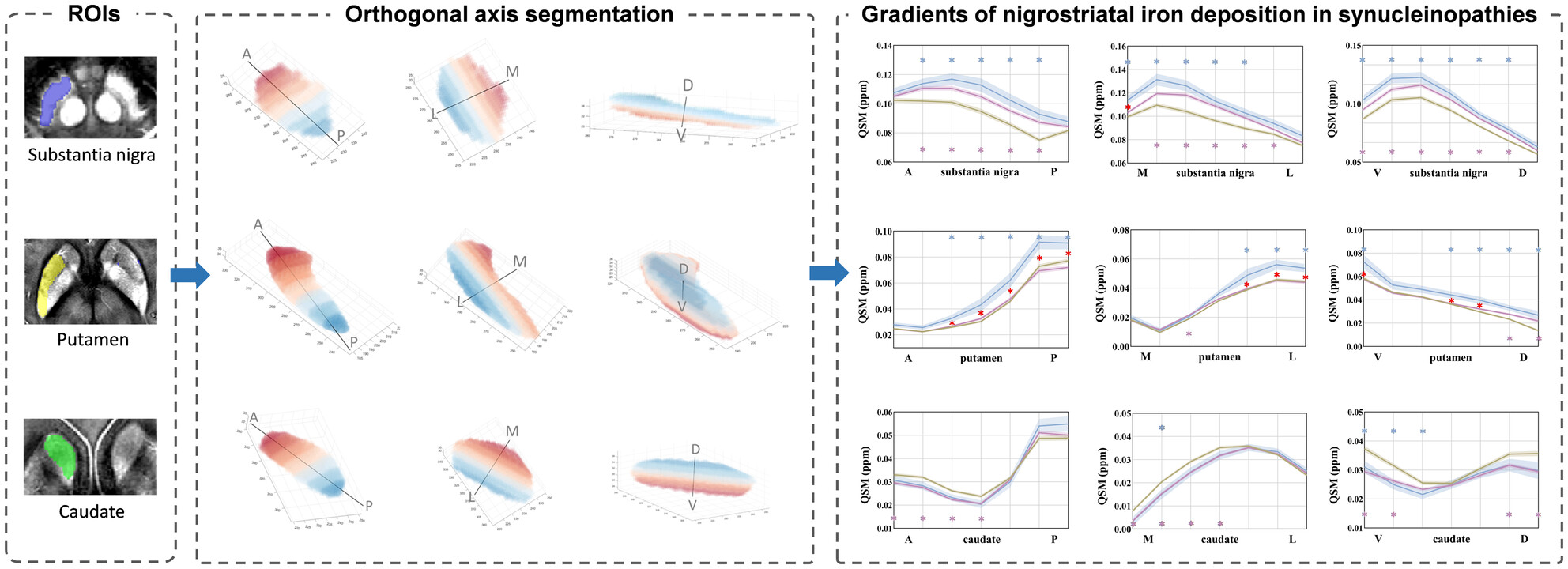
Gradients of Nigrostriatal Iron Deposition in Healthy Aging and Synucleinopathies
- First Published: 25 March 2025
Association of Increased Brain Iron Levels With Anxiety and Motor Dysfunction in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
- First Published: 25 March 2025
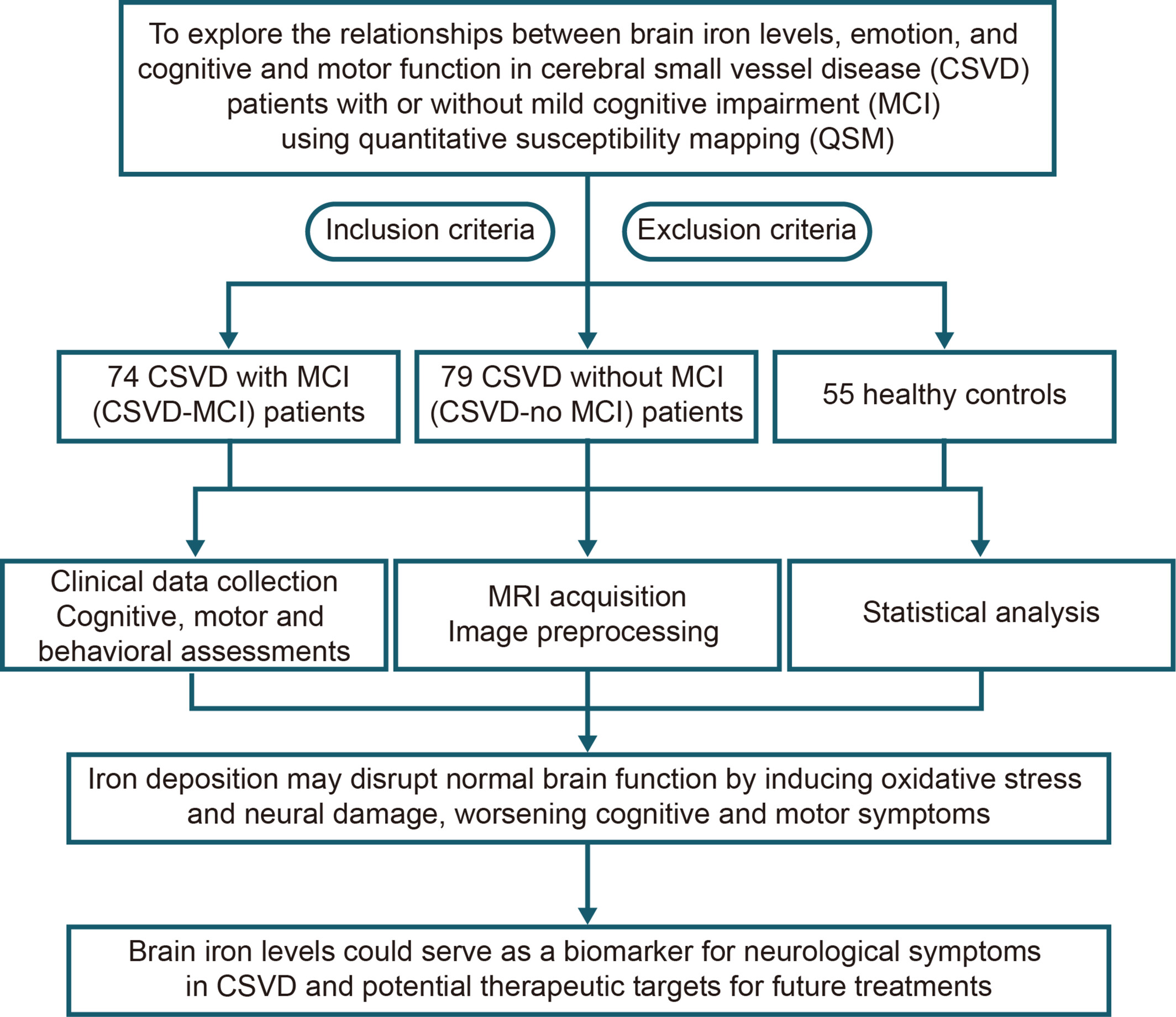
We investigated the relationship between brain iron levels, emotion, and cognitive and motor function in cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) patients using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM). Our findings showed that increased brain iron levels were significantly associated with anxiety and motor dysfunction in CSVD patients. Iron deposition may disrupt normal brain function by inducing oxidative stress and neural damage, worsening cognitive and motor symptoms. These results suggest that brain iron levels could serve as a biomarker for neurological symptoms in CSVD and potential therapeutic targets for future treatments.
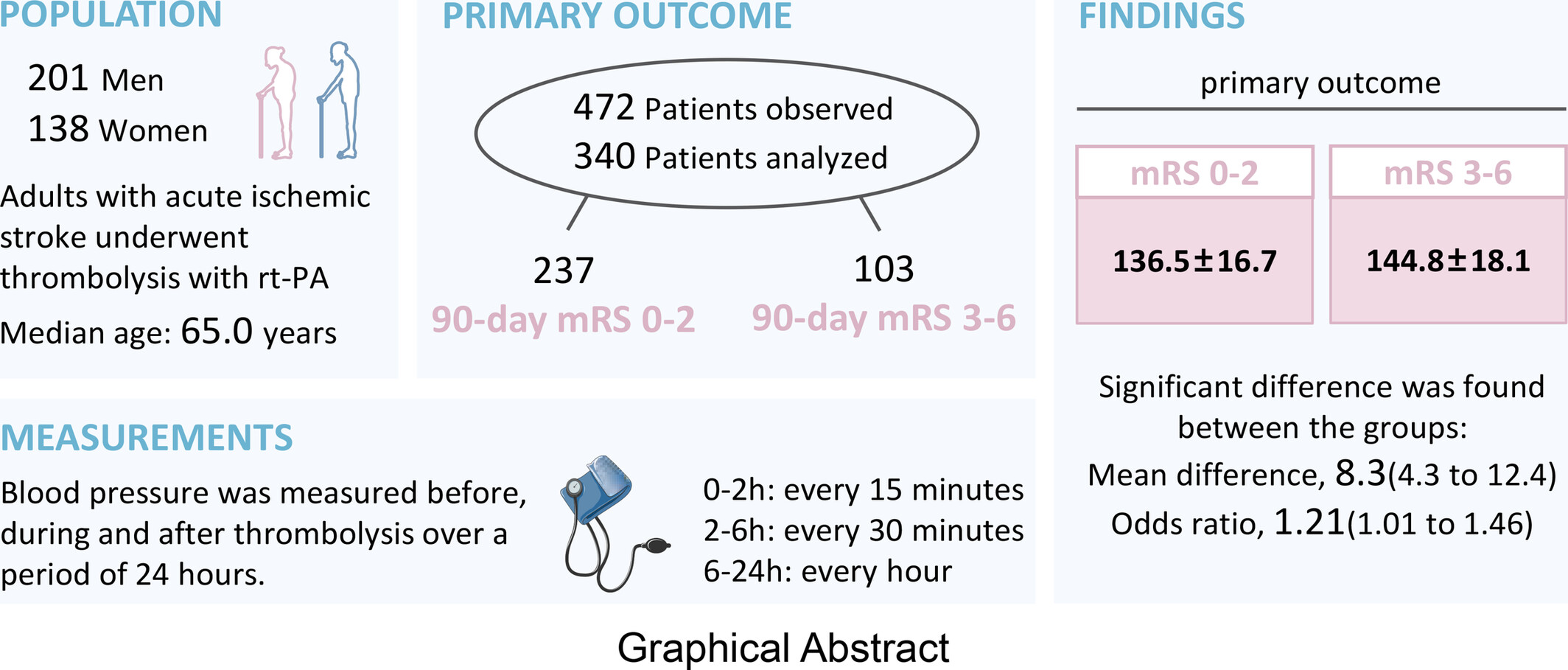
Association of Early Blood Pressure Levels and Outcomes in Ischemic Stroke Treated With Intravenous Thrombolysis: A Prospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 12 March 2025
Long-Term Minocycline Treatment Exhibits Enhanced Therapeutic Effects on Ischemic Stroke by Suppressing Inflammatory Phenotype of Microglia Through the EMB/MCT4/STING Pathway
- First Published: 26 March 2025
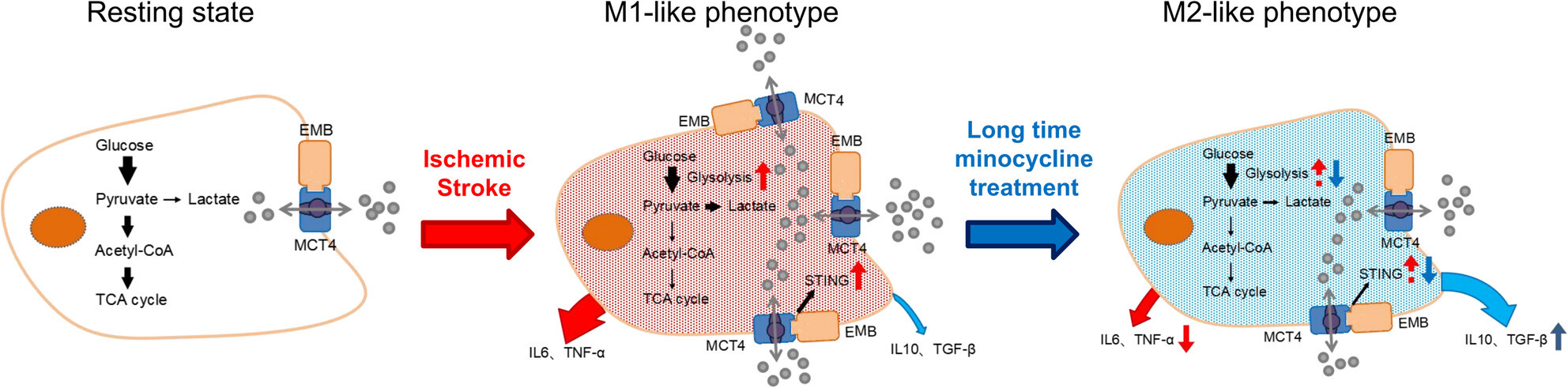
Extending the treatment duration of minocycline appropriately can more effectively inhibit neuroinflammatory injury caused by microglial activation in stroke. In the process, glycolysis levels were downregulated through the EMB/MCT4/STING axis, thereby suppressing neuroinflammatory responses induced by microglia.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
GAD65 Antibody-Associated Neurologic Syndrome Overlapping Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
- First Published: 28 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Comprehensive Analysis of Uric Acid and Myasthenia Gravis: IGF1R as a Protective Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target
- First Published: 28 March 2025
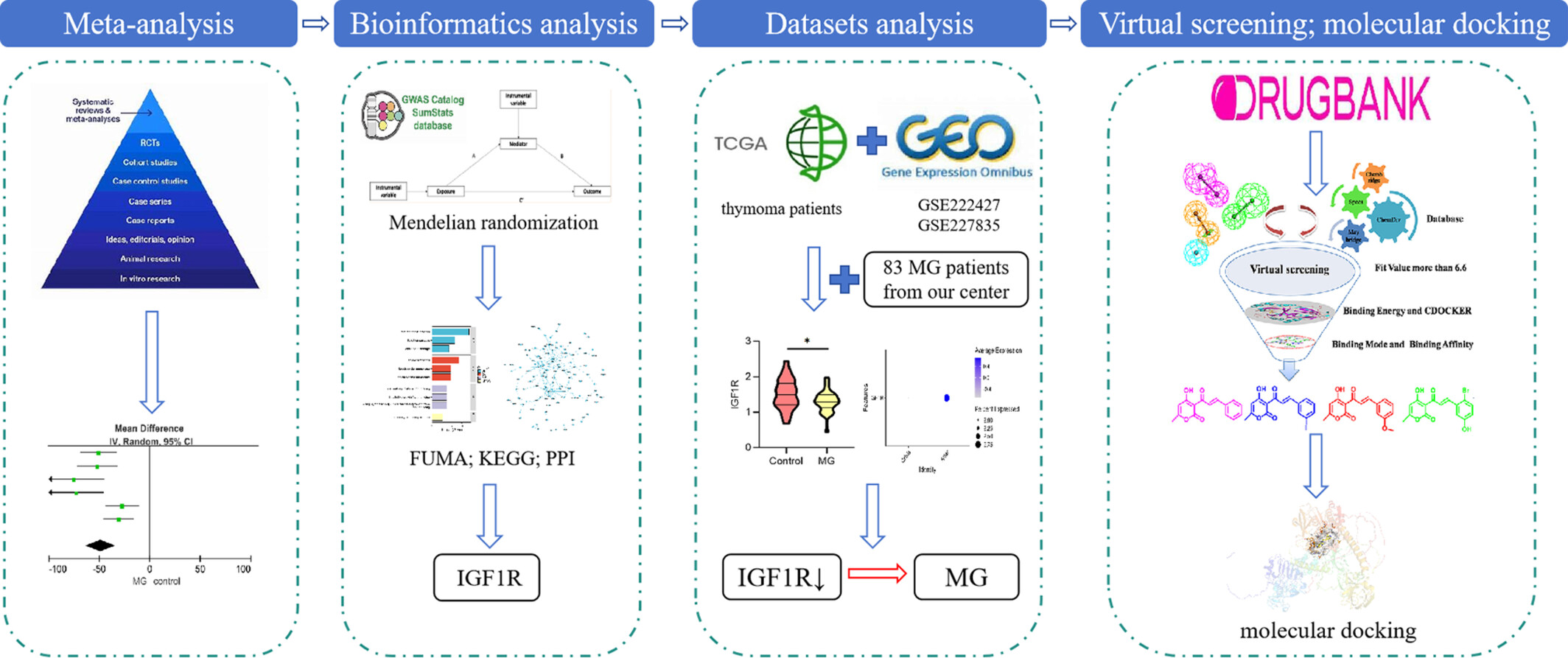
This study used meta-analysis to establish a correlation between low UA levels and MG. Furthermore, MR and bioinformatics analyses identified IGF1R as a key protein in this relationship. The correlation between IGF1R and MG was further validated using the TCGA dataset, GEO single-cell RNA sequencing datasets, and clinical data from MG patients, which indicated that low IGF1R expression is associated with MG. Finally, several small-molecule drugs targeting IGF1R were identified, offering potential therapeutic options for MG.
REVIEW
Cognitive Sequelae of COVID-19: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Approaches
- First Published: 28 March 2025
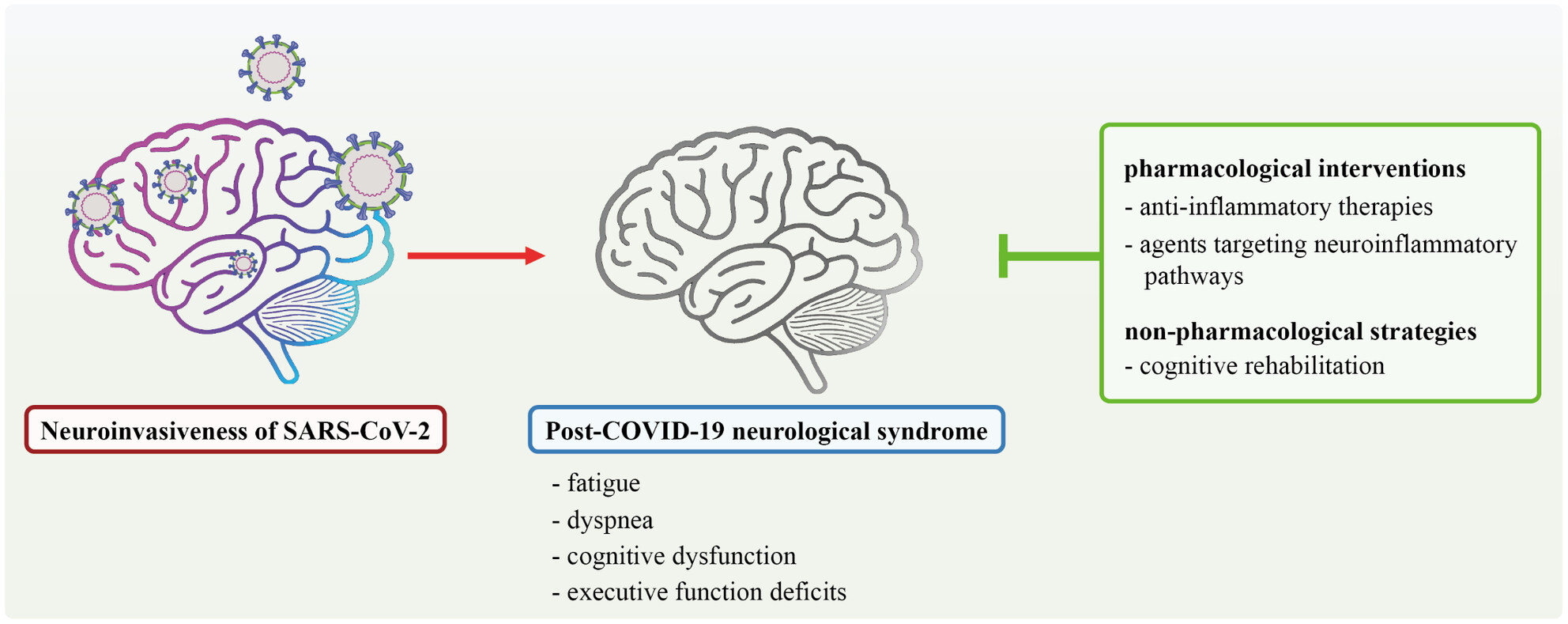
Post-COVID-19 neurological syndrome, marked by cognitive dysfunction, stems from mechanisms like neuroinflammation, cerebrovascular injury, and psychological stress. This review highlights pharmacological treatments and cognitive rehabilitation as promising strategies to address cognitive impairment from acute COVID-19 to long-COVID phases.