Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
“Path of the Heart” (The BPROAD Study) Addresses Optimal Systolic Blood Pressure for Patients With Diabetes
- First Published: 23 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
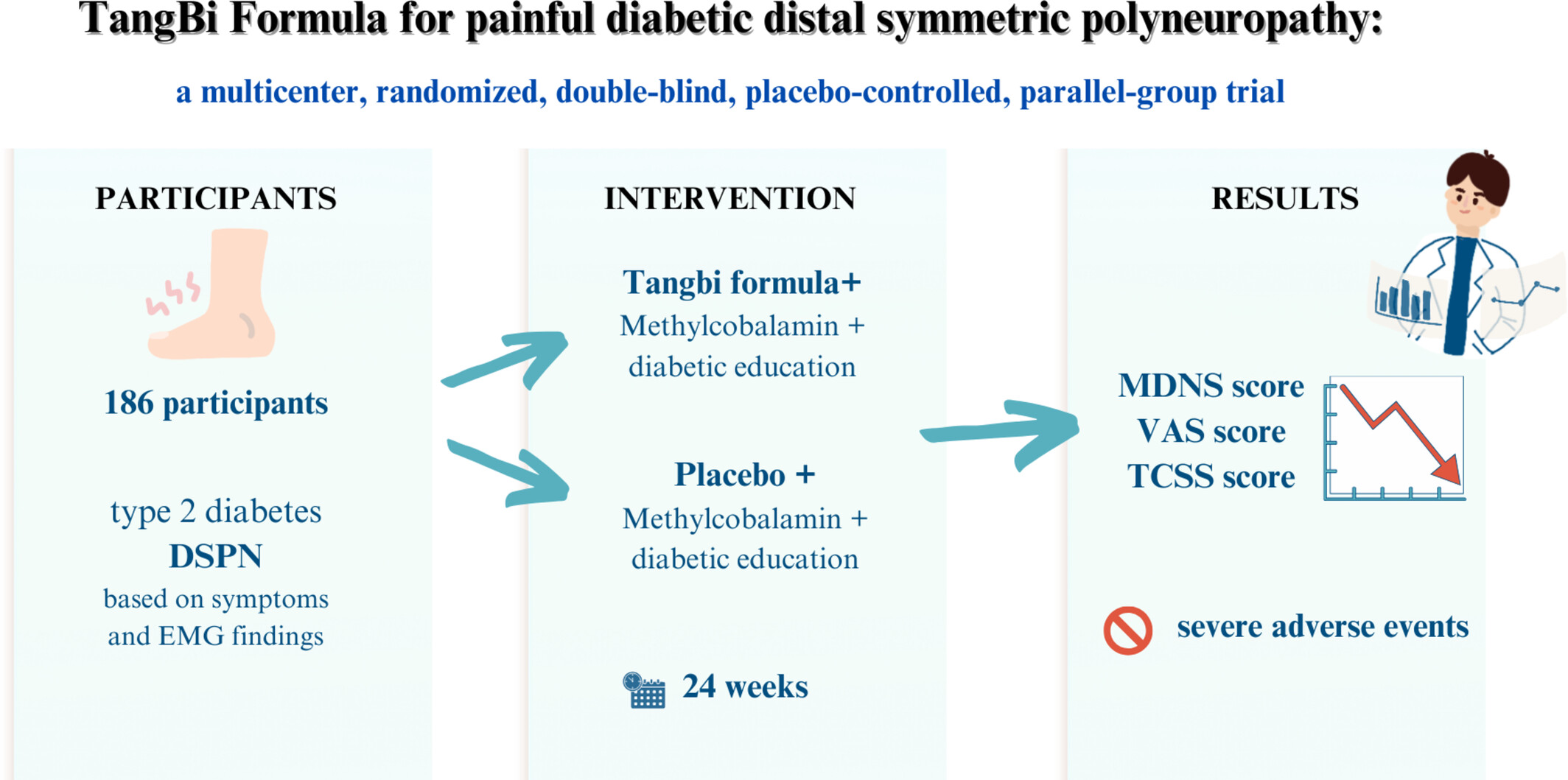
TangBi Formula for Painful Diabetic Distal Symmetric Polyneuropathy: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled and Parallel-Group Trial
- First Published: 05 January 2025
Global and Regional Burden of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attributable to Low Physical Activity From 1990 to 2021
- First Published: 06 January 2025
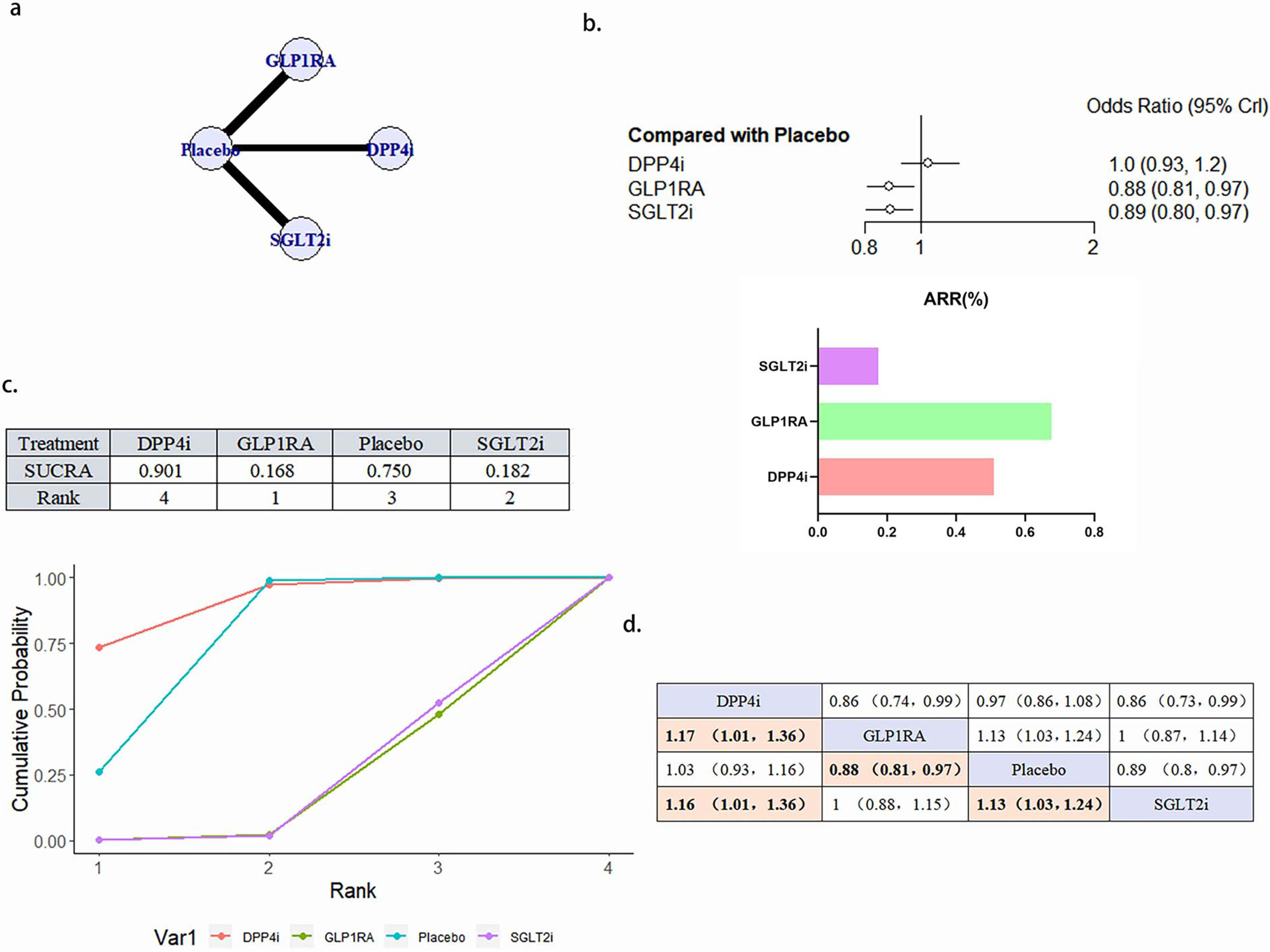
Cardiovascular Therapy Benefits of Novel Antidiabetic Drugs in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Complicated With Cardiovascular Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 09 January 2025
B Lymphocyte—A Prognostic Indicator in Post-Acute Pancreatitis Diabetes Mellitus
- First Published: 12 January 2025
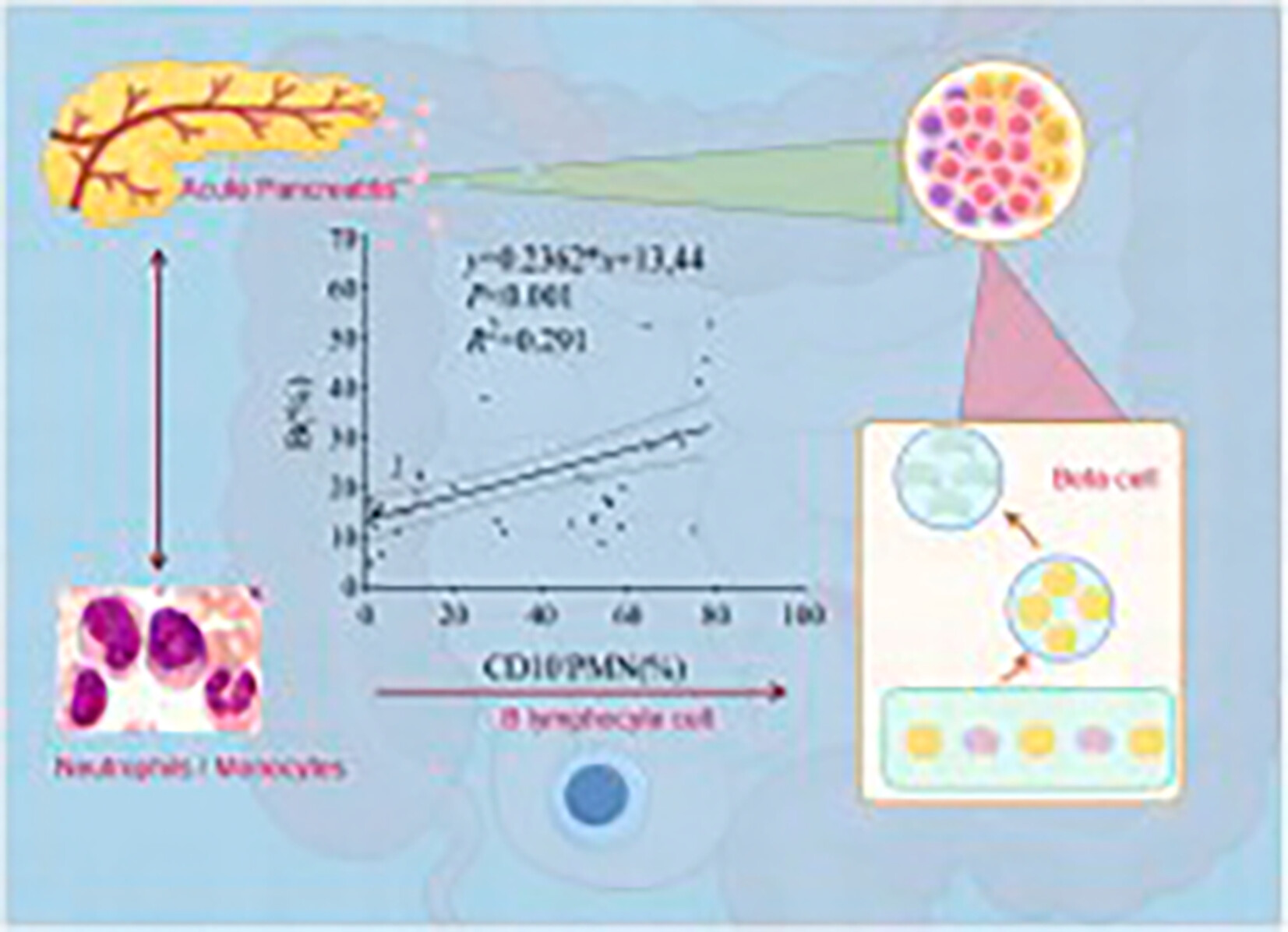
In this study, we aimed to determine the value of lymphocyte subsets and granulocyte/monocyte markers in predicting the risk of post-acute pancreatitis diabetes mellitus (PPDM-A). Our study is the first to confirm the correlation between PPDM-A and lymphocyte subsets and indicated that age, fatty liver, serous effusion, recurrent AP, and B% were independent risk factors for PPDM-A. The interaction mechanism of granulocyte and monocyte surface markers and B lymphocytes on glucose metabolism disorder after AP is worthy of further study.
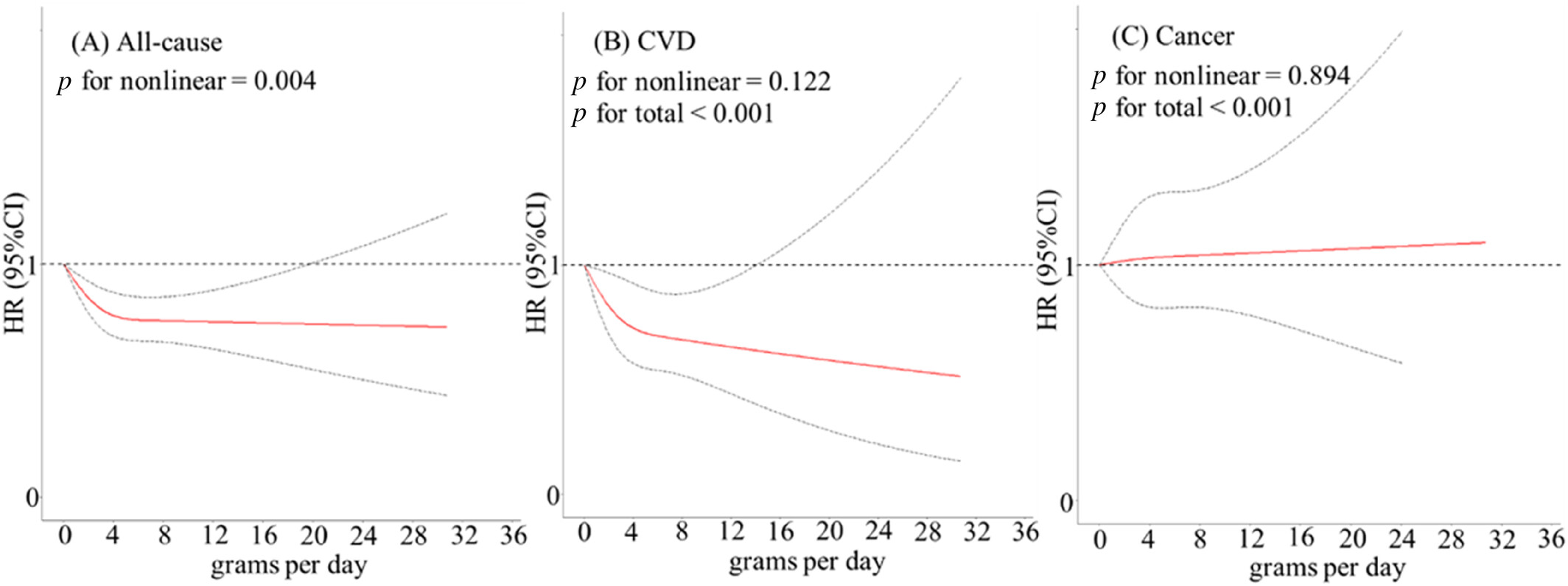
Associations of Tea Consumption With the Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality Among Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study in China
- First Published: 20 January 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
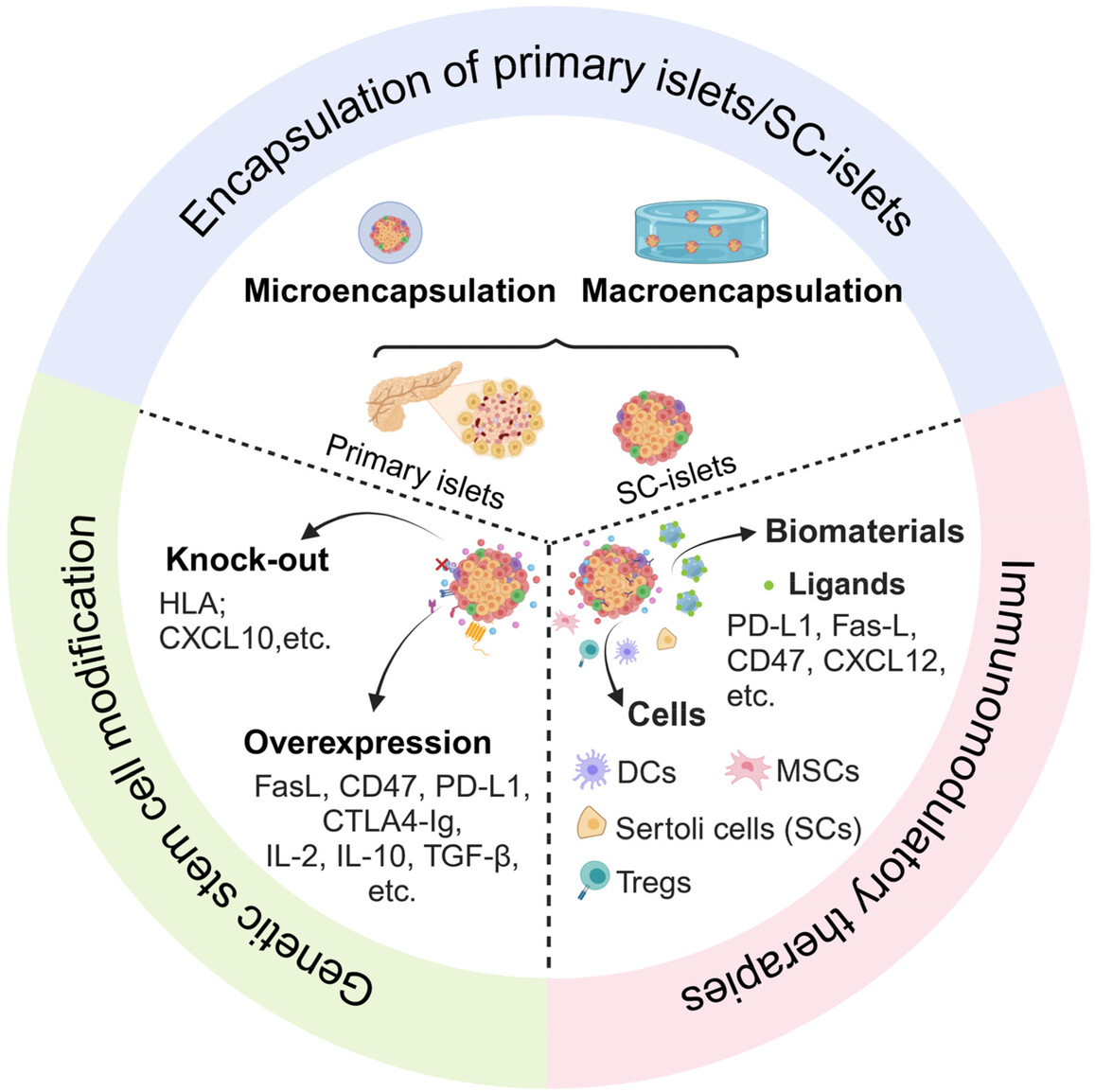
Advancements and Challenges in Immune Protection Strategies for Islet Transplantation
- First Published: 20 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
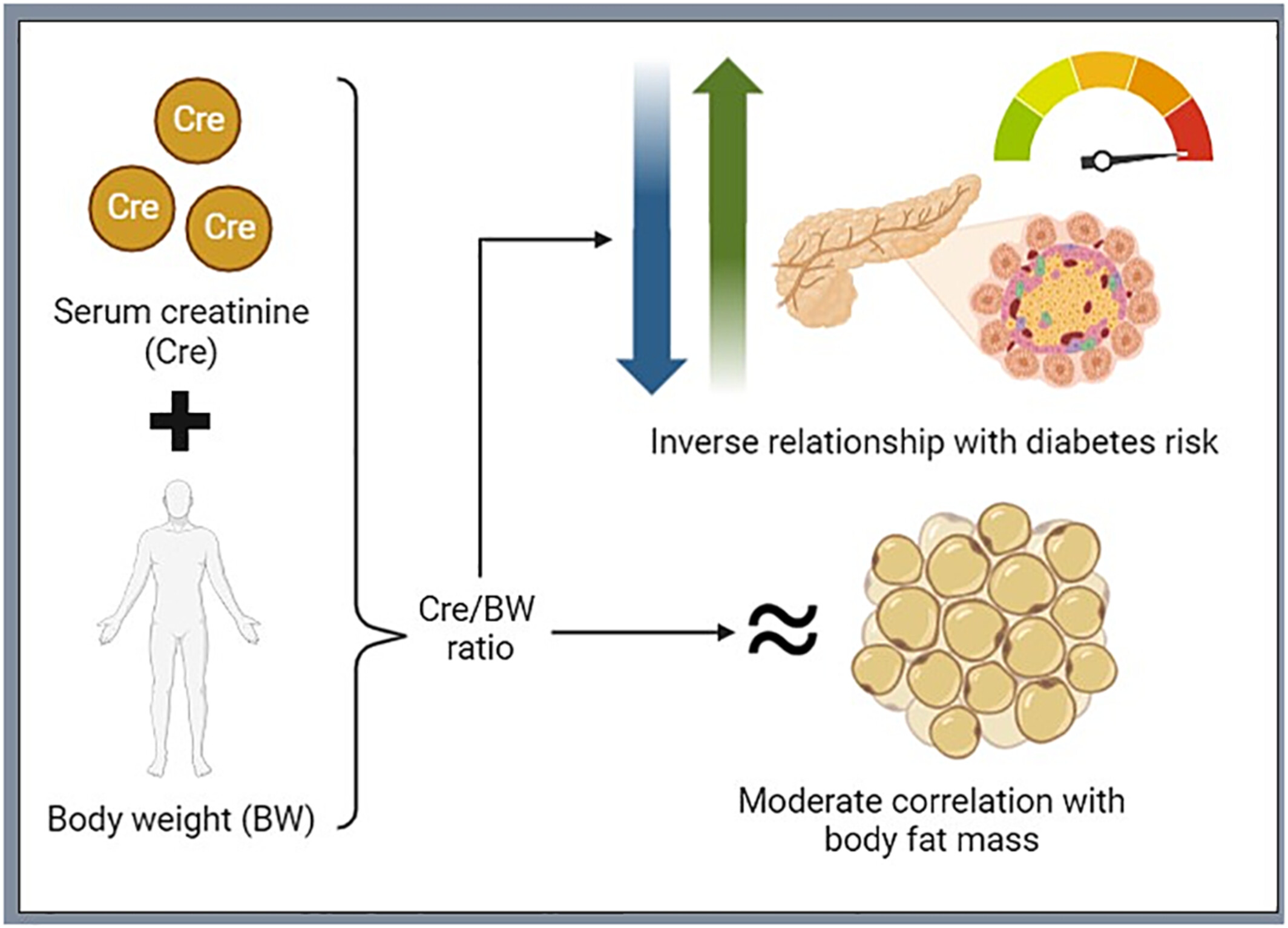
Linking Creatinine-to-Body Weight Ratio With Diabetes Incidence: A Multiethnic Malaysian Cohort Study
- First Published: 22 January 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
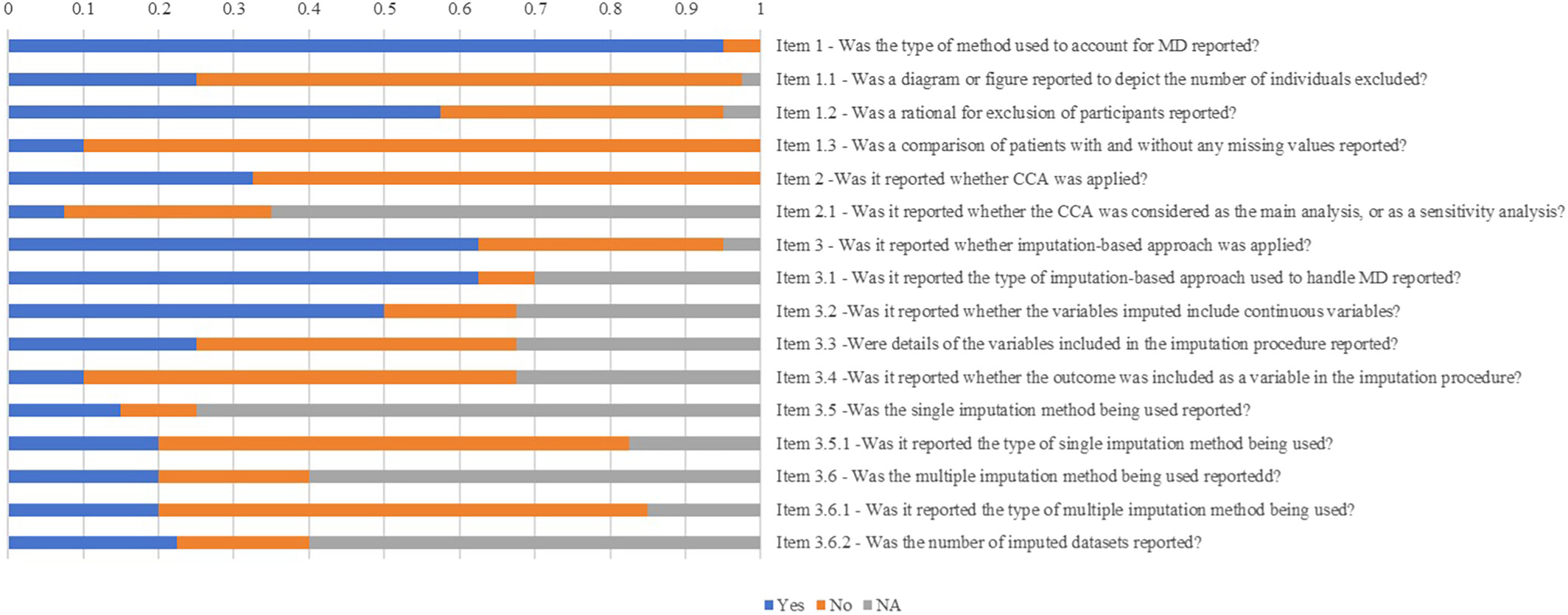
Overcoming Missing Data: Accurately Predicting Cardiovascular Risk in Type 2 Diabetes, A Systematic Review
- First Published: 22 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
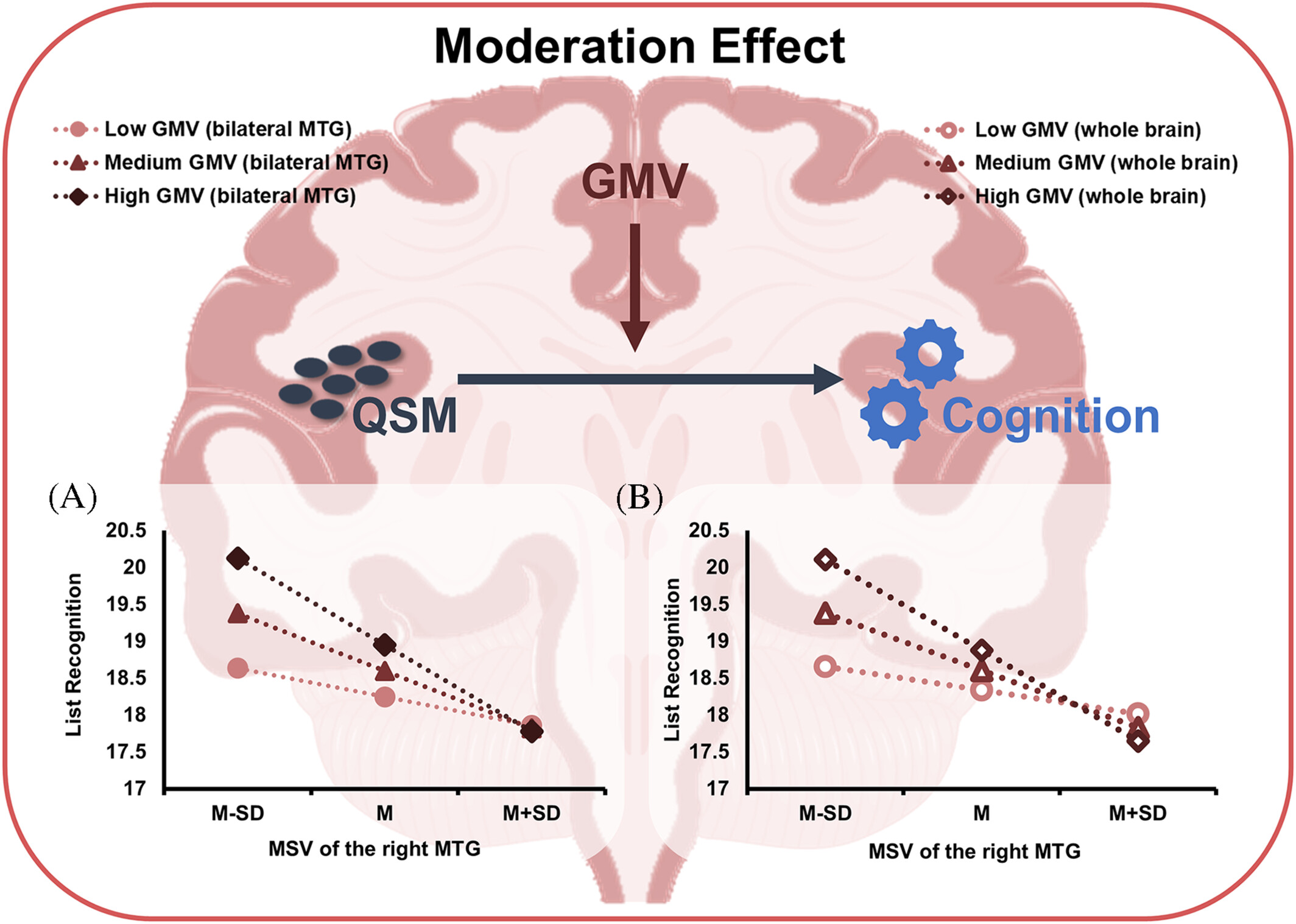
Brain Iron Deposition Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment Based on Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping
- First Published: 22 January 2025
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Commentary on “Protective Effect of Regular Physical Activity Against Diabetes-Related Lower Extremity Amputation”
- First Published: 22 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Is Weight Loss the Main Driver for A1C Improvement by Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists? A 2.5-Year Analysis in Real-World Clinical Practice
- First Published: 23 January 2025
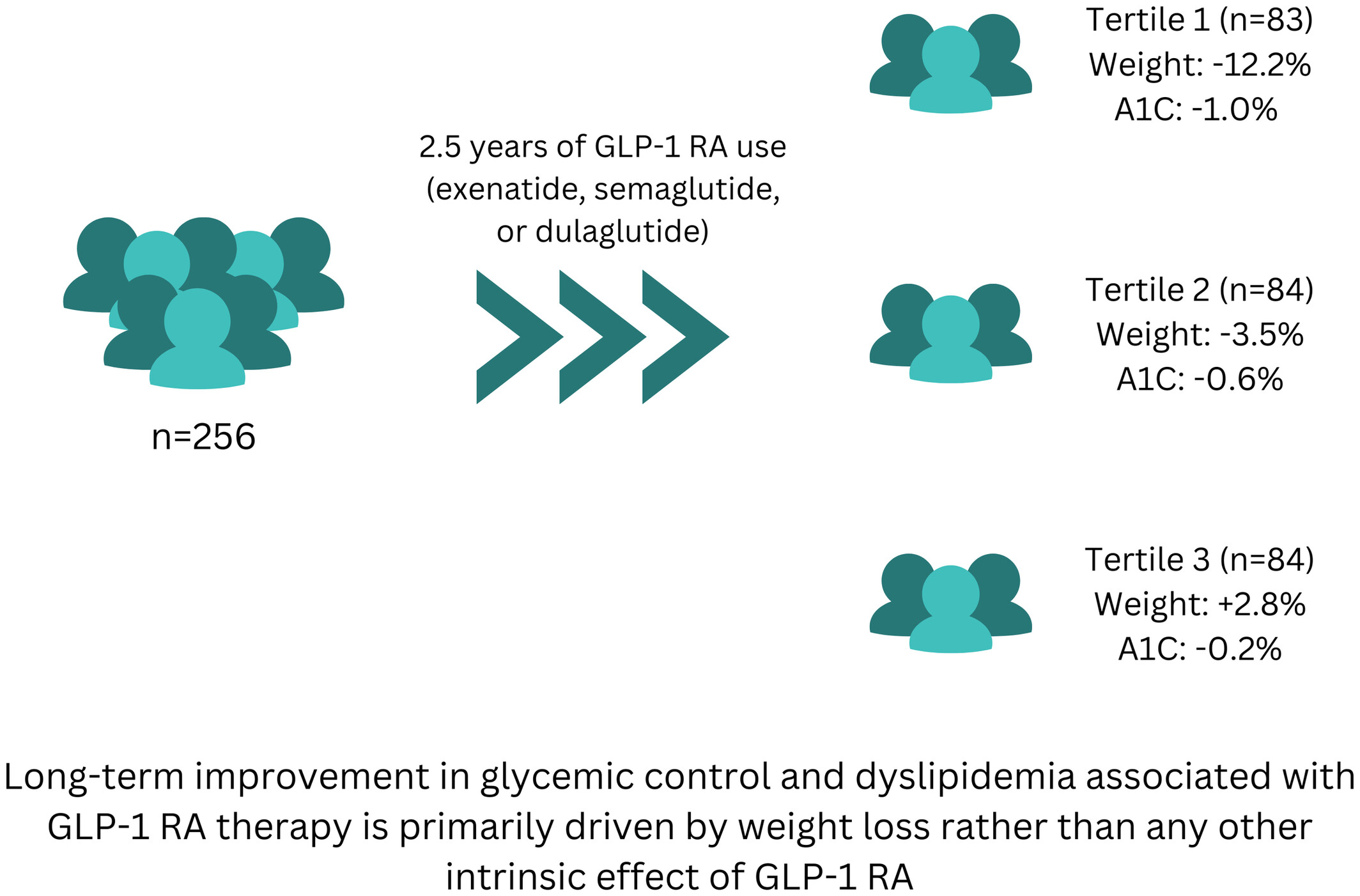
This retrospective study of 256 patients reveals a strong correlation between percentage weight change and A1C reduction in patients on long-term GLP-1 RA use. Additionally, patients who lost more weight had significant improvements in dyslipidemia. These findings emphasize weight reduction as a crucial therapeutic target to enhance metabolic outcomes in real-world clinical practice.