Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Open Access
oa
Obstructive sleep apnea and diabetes
- Pages: 916-919
- First Published: 05 November 2023
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATIONS
Open Access
oa
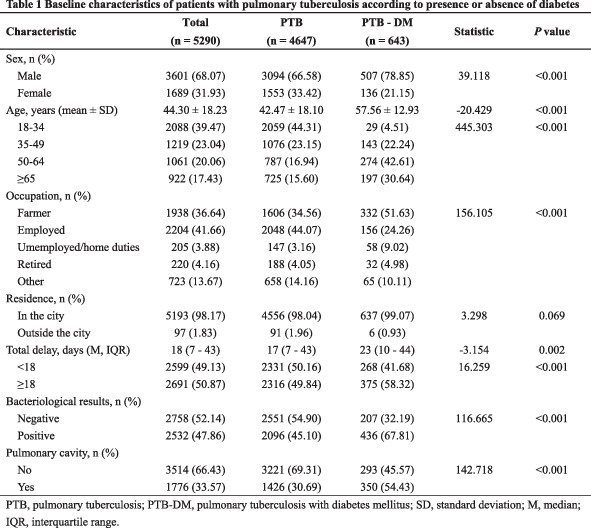
The effect of diabetes mellitus on tuberculosis in eastern China: A decision-tree analysis based on a real-world study
中国东部地区糖尿病对肺结核的影响:基于真实世界研究的决策树分析
- Pages: 920-930
- First Published: 11 July 2023
Open Access
oa
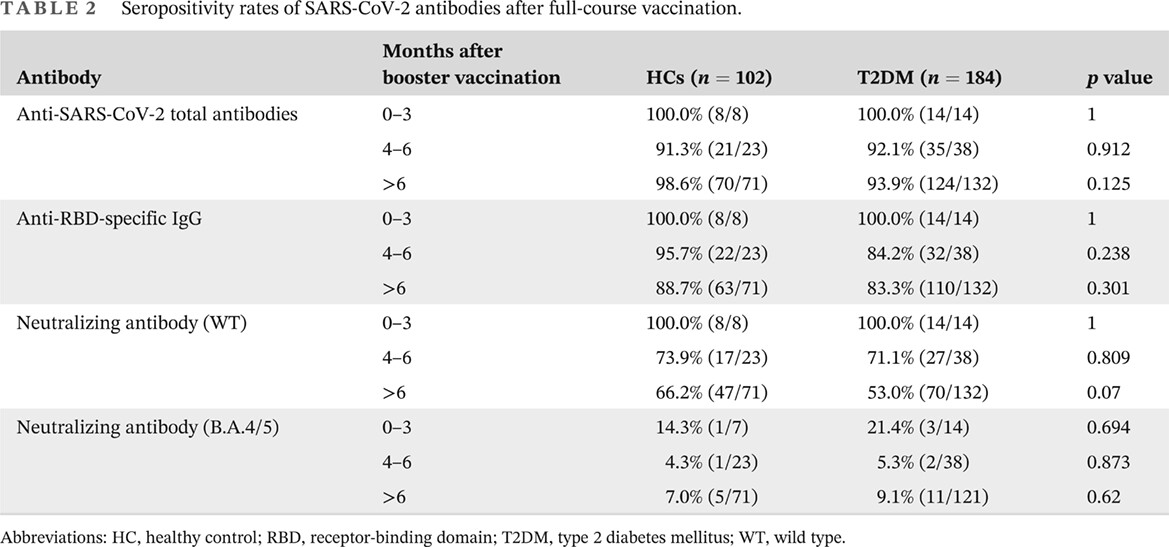
Antibody response to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after the booster immunization
2型糖尿病患者接种增强剂次灭活COVID-19疫苗后的抗体反应
- Pages: 931-943
- First Published: 30 July 2023
Highlights
- Similar antibody response to COVID-19 inactivated vaccine between healthy controls (HCs) and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) after a booster shot vaccine within 6 months.
- Patients with T2DM have reduced antibody response after receiving the third dose of the COVID-19 vaccine for more than 6 months.
- Both HCs and T2DM showed poor resistance against BA.4/5 due to the detected inhibition rates being lower than the positive threshold.
Open Access
oa
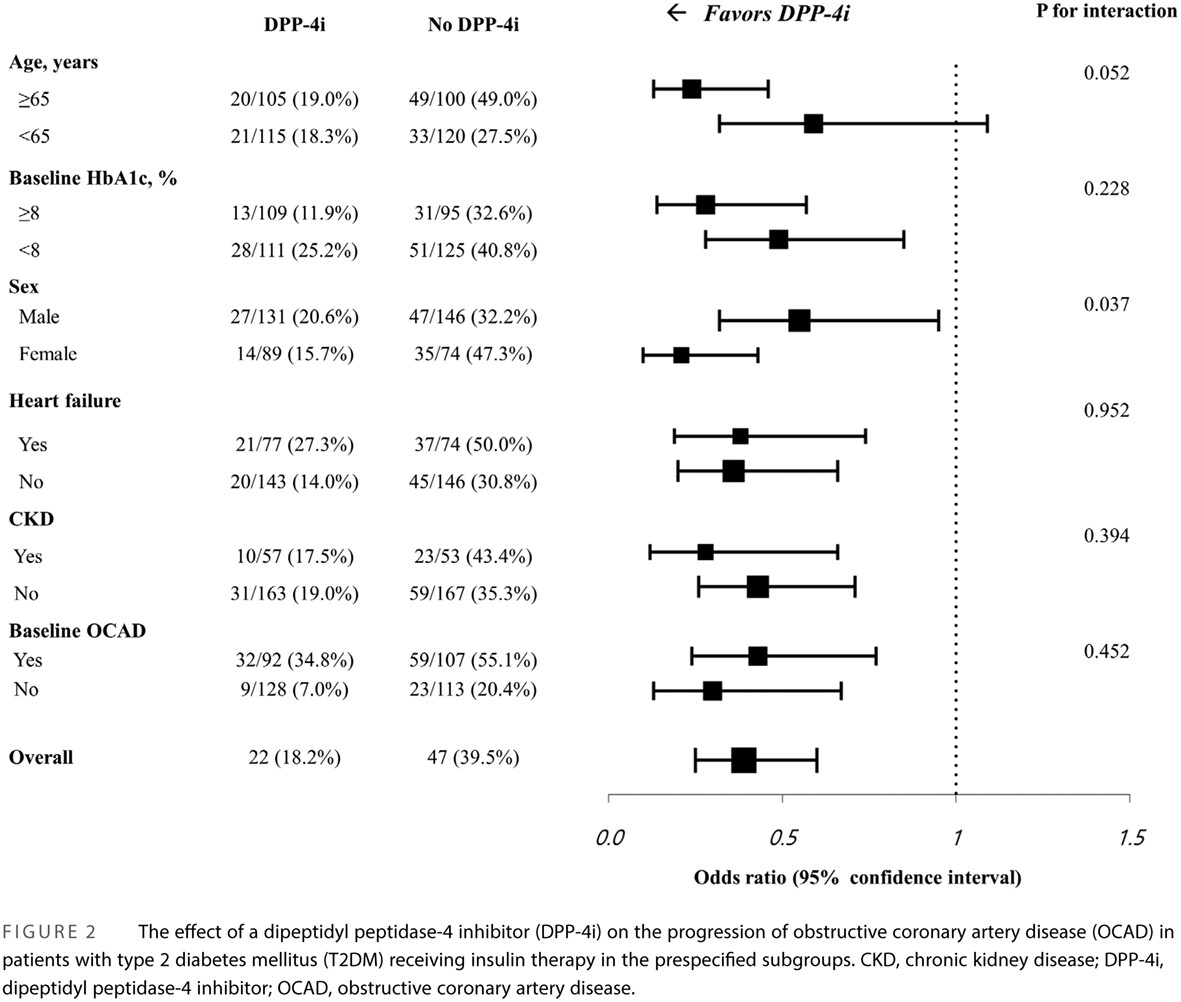
Effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor on the progression of coronary artery disease evaluated by computed tomography in patients receiving insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus
DPP-4抑制剂对接受胰岛素治疗的2型糖尿病患者冠状动脉疾病进展的影响
- Pages: 944-954
- First Published: 01 August 2023
Highlights
- Preclinical data showed that dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4is) may prevent insulin-induced atherosclerosis.
- In patients treated with insulin for type 2 diabetes who underwent ≥2 serial coronary computed tomography angiographies(CCTA), a new obstructive coronary artery disease (OCAD) was less developed on the follow-up CCTA in those who received concomitant DPP-4is.
- A composite outcome of new OCAD, new implantation of coronary stent, or coronary bypass graft surgery was also lower in patients who received DPP-4is.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Open Access
oa
Effect and mechanism of microRNAs on various diabetic wound local cells
microRNA对各种糖尿病创面局部细胞的作用及机制
- Pages: 955-967
- First Published: 07 September 2023
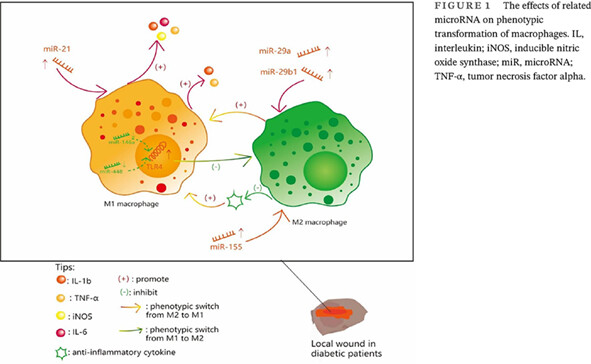
Highlights
- For the first time, we have examined the impact of microRNA on diabetic wounds at a cellular level.
- We have analyzed how a particular microRNA influences different types of cells, uncovering its function and mechanism.
- This study furthers the discovery of the clinical potential of diverse microRNAs by evaluating their distinct effects and mechanisms on multiple cell types.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
A network meta-analysis of association between cardiometabolic risk factors and COVID-19 outcome severity
心血管代谢危险因素与COVID-19严重程度关联的网络荟萃分析
- Pages: 968-977
- First Published: 30 August 2023
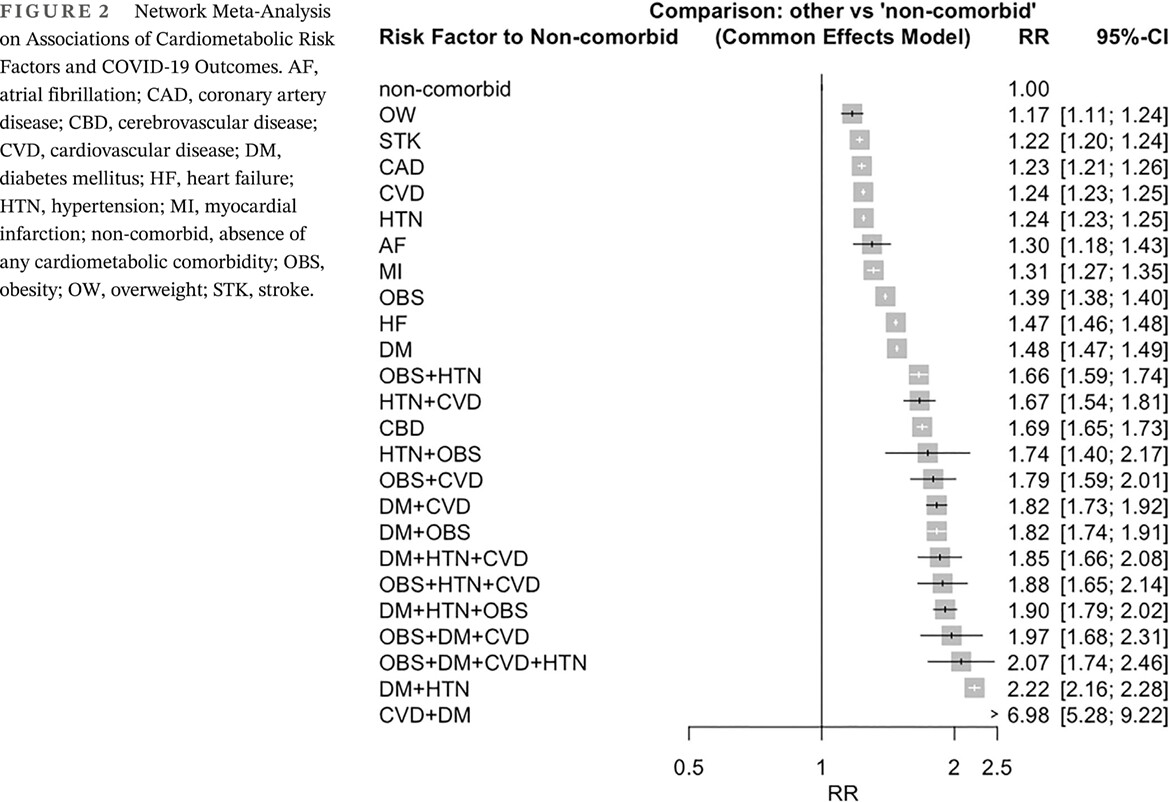
Highlights
- Among 301 studies, diabetes mellitus was the most studied cardiometabolic risk factor.
- In the network meta-analysis, cerebrovascular disease had the highest impact (relative risk [RR] 1.69; 95% CI, 1.65–1.73) on COVID-19 outcomes compared to other cardiometabolic risk factors.
- For different combinations of risk factors, cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus combined (RR 6.98; 95% CI, 5.28–9.22) was more detrimental than others.
Open Access
oa
Exosomal miR-let-7c-5p is involved in the cognitive function of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients by interleukin 10: A cross-sectional study
外泌体miR-let-7c-5p通过白细胞介素10参与2型糖尿病患者的认知功能:一项横断面研究
- Pages: 978-986
- First Published: 02 August 2023
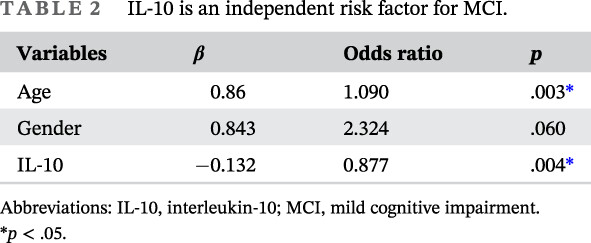
Highlights
- Both interleukin-10 levels and exosomal miR-let-7c-5p levels are correlated with cognitive function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- There is a negative association between interleukin-10 levels and exosomal miR-let-7c-5p levels in the plasma of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Open Access
oa
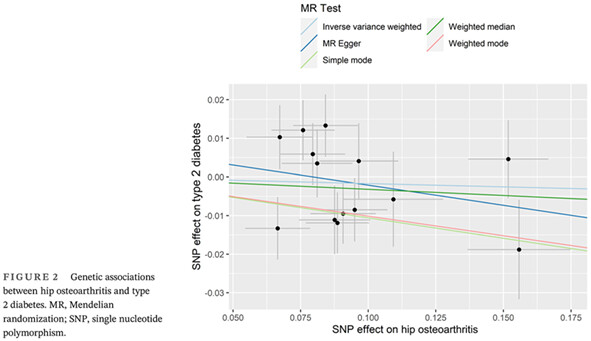
Osteoarthritis and risk of type 2 diabetes: A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
骨关节炎与2型糖尿病的风险:一项双样本孟德尔随机化分析
- Pages: 987-993
- First Published: 31 July 2023
Open Access
oa
Association between depression and risk of type 2 diabetes and its sociodemographic factors modifications: A prospective cohort study in southwest China
抑郁症与2型糖尿病风险及其社会人口学因素的关联:中国西南贵州省的一项前瞻性队列研究
- Pages: 994-1004
- First Published: 15 August 2023
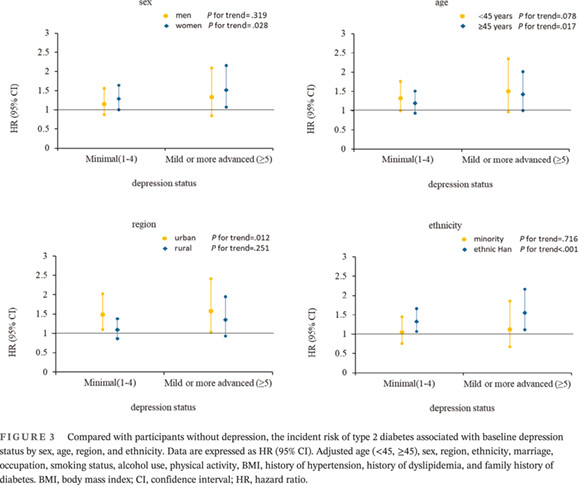
Highlights
- In this study, depression significantly increased the risk of incident type 2 diabetes and the risk increases as the degree of depression increases for a 5.2-year median follow-up.
- The results of this study suggest an age, sex, region and ethnicity difference in the relationship between depression and type 2 diabetes mellitus for Chinese populations.