Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Open Access
oa
Diabetes epidemiology: Analysis of trends over time
- Pages: 790-791
- First Published: 09 December 2022
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
Open Access
oa
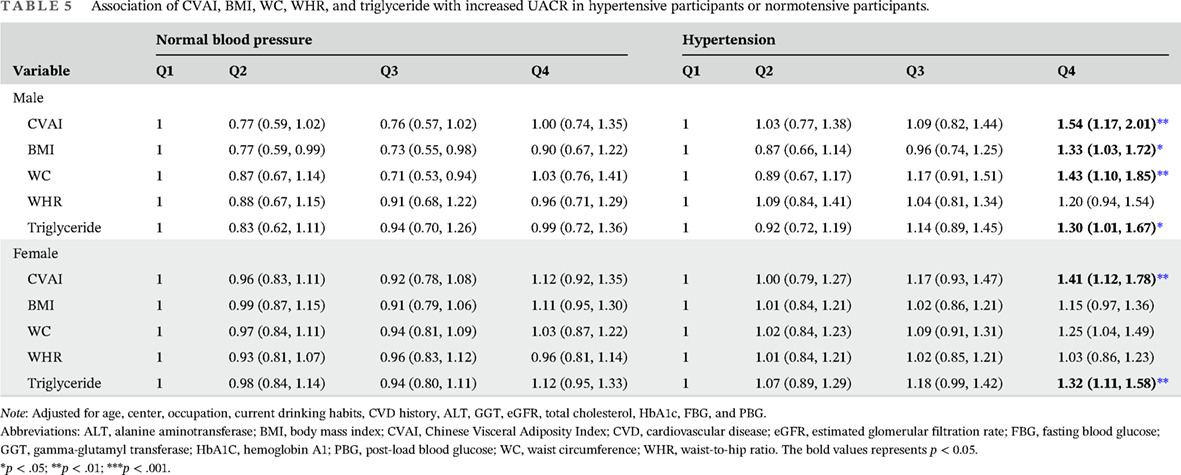
A novel index, Chinese visceral adiposity index is closely associated with urinary albumin-creatinine ratio in Chinese community adults, especially in hypertensive or hyperglycemic population: Results from the REACTION study
一个新的指标, 中国人内脏脂肪指数与中国社区成年人(特别是高血压或高血糖人群)尿白蛋白-肌酐比值密切相关:来自REACTION研究的结果
- Pages: 792-805
- First Published: 29 November 2022
Highlights
- This is the first large-sample, multicenter study of the relationship between Chinese Visceral Adiposity Index (CVAI) and urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) in Chinese community adults.
- CVAI and UACR were significantly associated in both genders.
- At higher CVAI levels, the population with prediabetes, diabetes, and hypertension has a more significant correlation between CVAI and UACR.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Open Access
oa
Metformin and growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A hidden treasure
二甲双胍和生长分化因子15 (GDF15)在2型糖尿病中的作用:一个隐藏的宝藏
- Pages: 806-814
- First Published: 28 November 2022
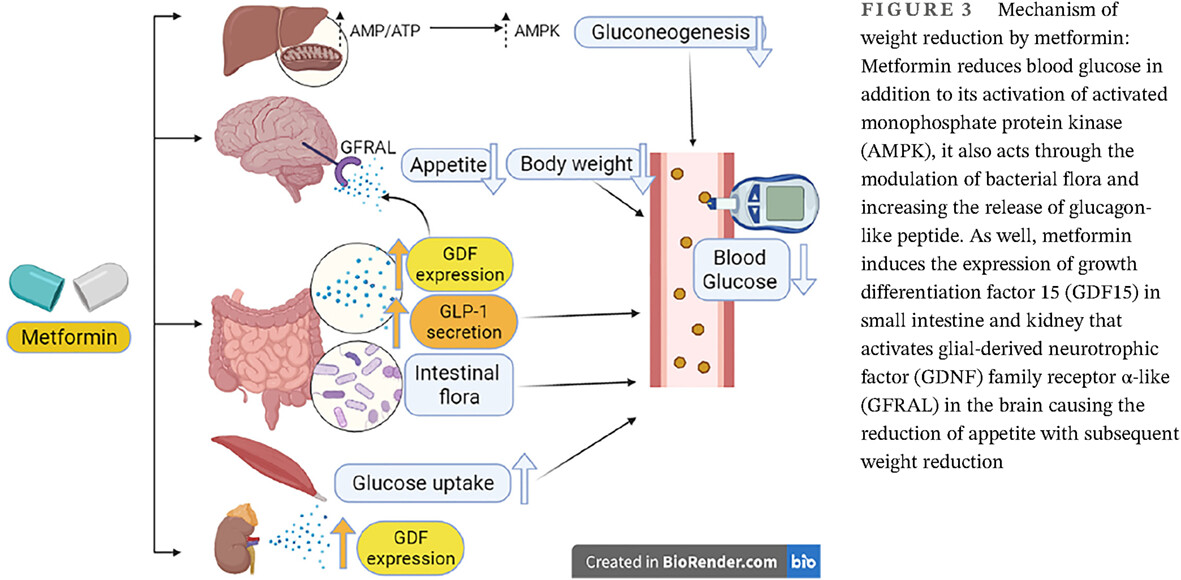
Highlights
- Metformin activates GDF15 expression, which reduces appetite with induction of weight loss in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients.
- GDF15 level is linked and correlated with the progression of diabetic complications including thrombosis, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic neuropathy, and diabetic retinopathy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
Are U-shaped relationships between risk factors and outcomes artifactual?
风险因素与结果之间的U或J型关系以及分布偏倚的作用
- Pages: 815-821
- First Published: 08 December 2022
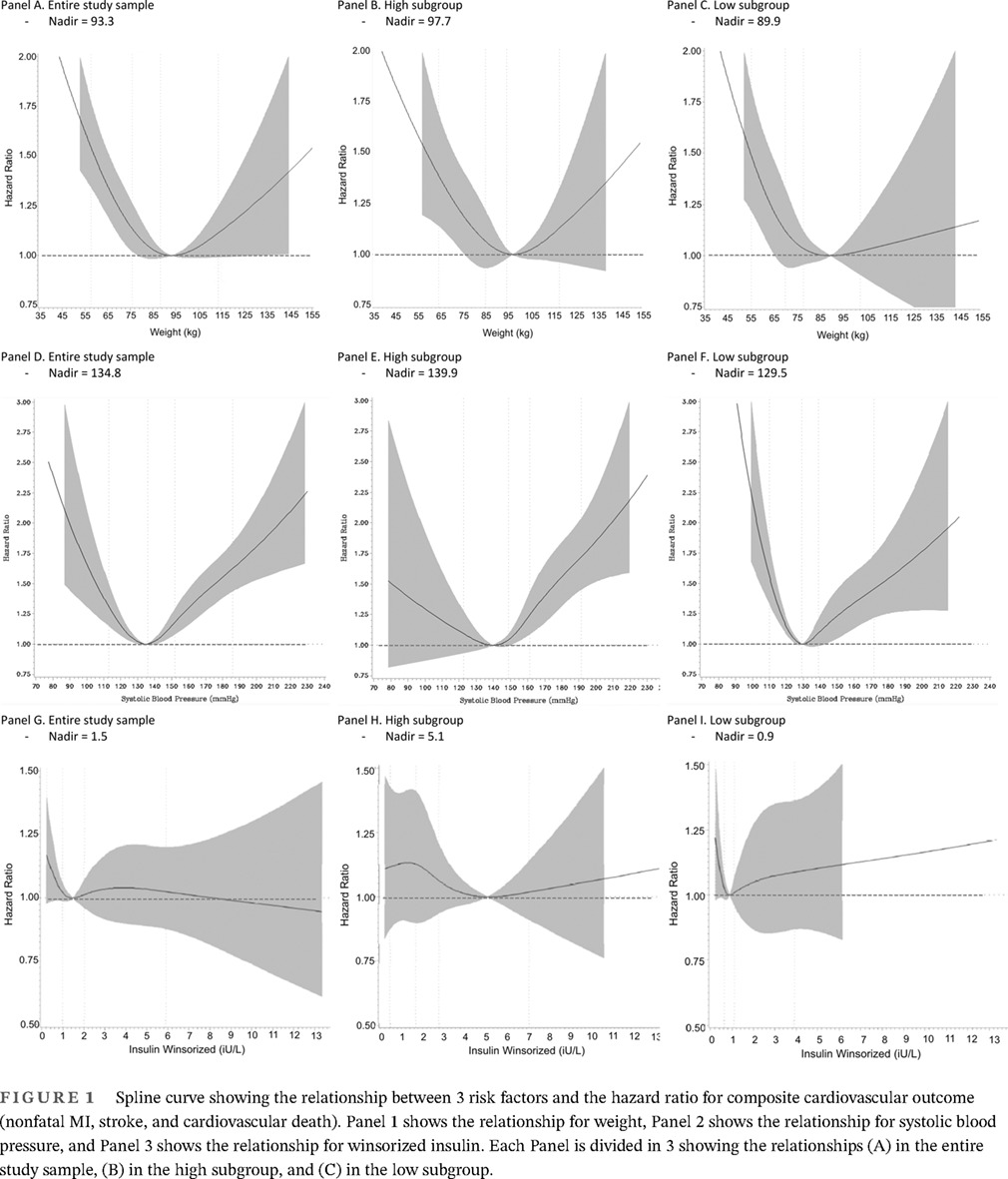
Highlights
- U-shaped relationships between three common cardiovascular risk factors (weight, systolic blood pressure, and insulin) and hazards of composite cardiovascular outcomes were analyzed in three study samples: entire sample, “high” subgroup, and “low” subgroup.
- Nadir values for all three risk factors were shifted left in the low-subgroup population and shifted right in the high-subgroup population when compared to the nadir value in the original population.
- Recommendations that risk factor levels below or above some specific nadir should not be therapeutically targeted in the underlying population based on U- or J- shape relationships observed in epidemiologic studies should be supported by randomized controlled trials.
Open Access
oa
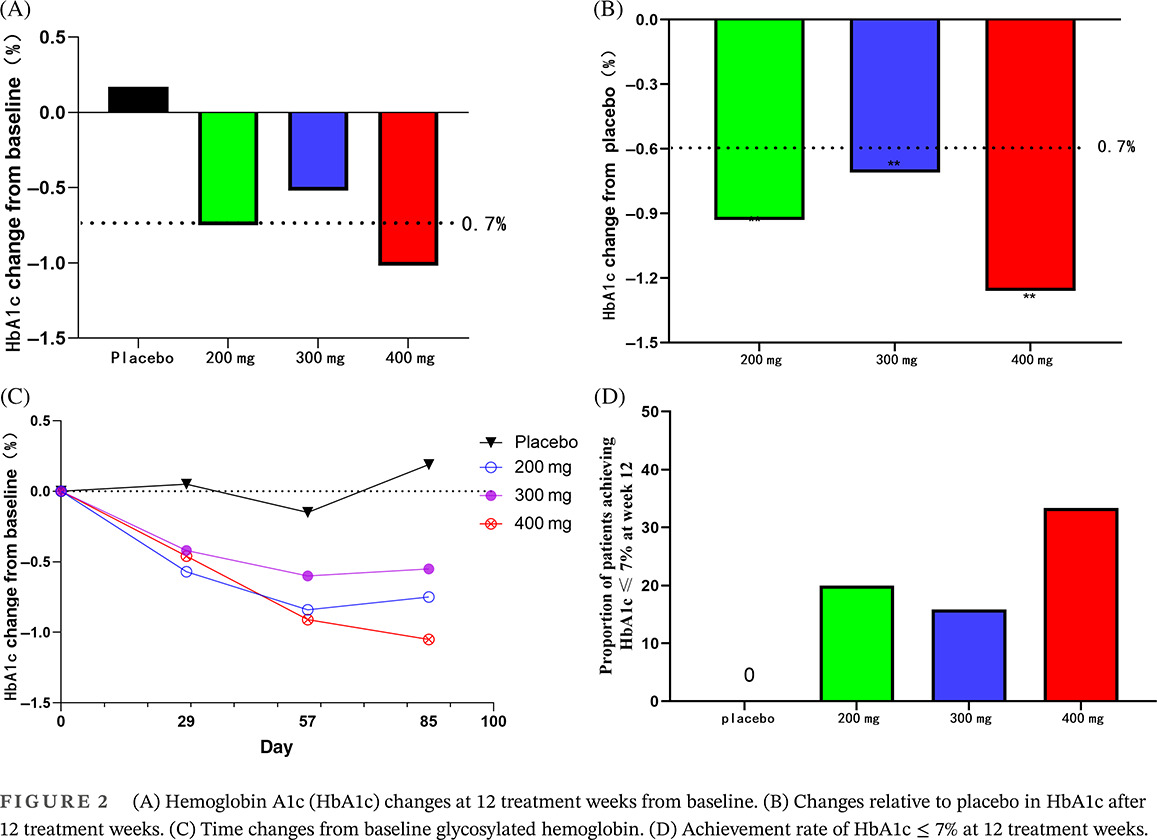
Yogliptin monotherapy in type 2 diabetes: A 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II study
优格列汀单药治疗2型糖尿病:一项12周随机、双盲、安慰剂对照的II期研究
- Pages: 822-830
- First Published: 14 December 2022
Open Access
oa
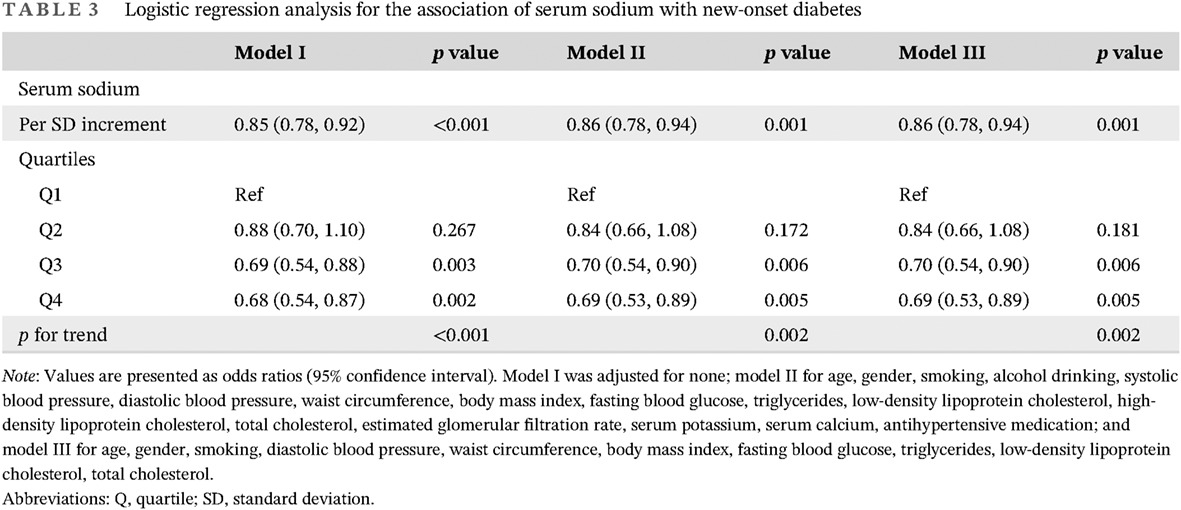
Serum sodium level is inversely associated with new-onset diabetes in hypertensive patients
血清钠水平与高血压患者新发糖尿病呈负相关
- Pages: 831-839
- First Published: 05 December 2022
Open Access
oa
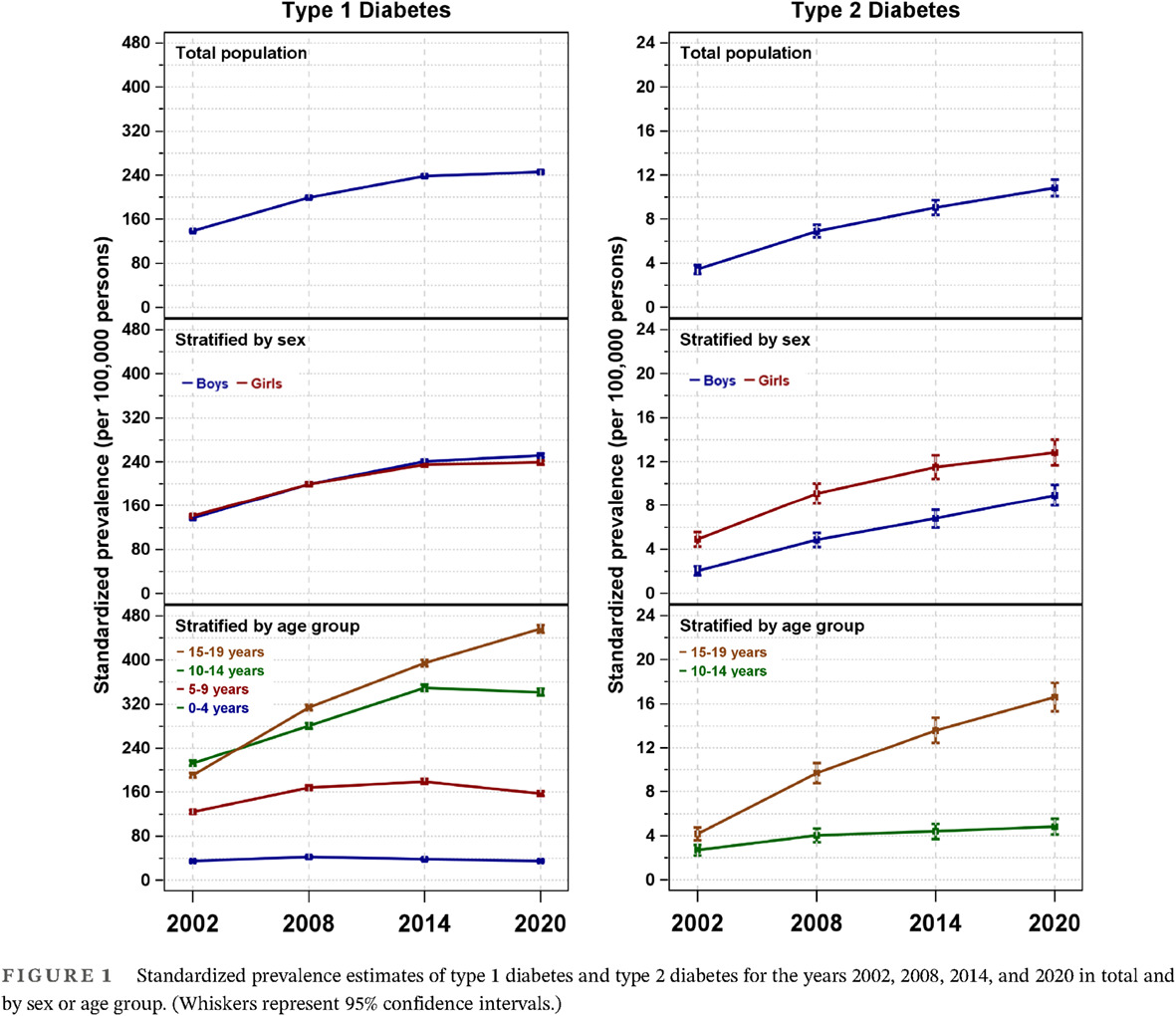
Prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in Germany from 2002 to 2020: A study based on electronic health record data from the DPV registry
2002~2020年德国儿童和青少年1型和2型糖尿病的患病率:一项基于来自DPV登记系统的电子健康记录数据的研究
- Pages: 840-850
- First Published: 14 December 2022