Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Which person with diabetes should receive cardioprotective glucose-lowering medicines?
哪些糖尿病患者应该服用具有心血管保护作用的降糖药?
- Pages: 352-353
- First Published: 02 March 2020
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATIONS
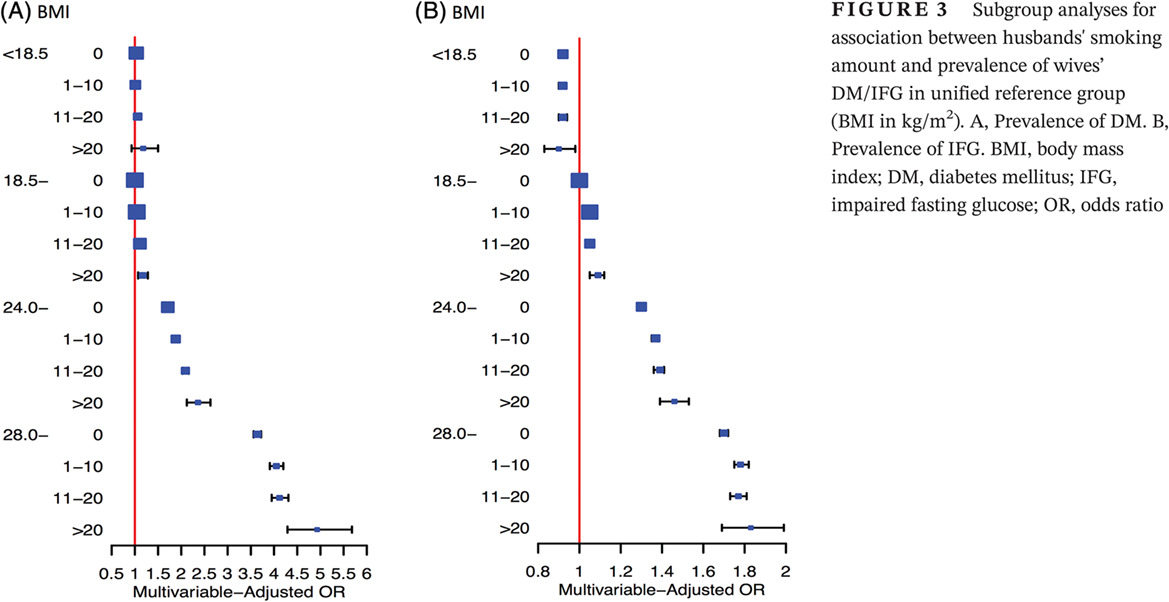
The association of husbands’ smoking with wives' dysglycemia status: A cross-sectional study among over 10 million Chinese women aged 20-49
丈夫吸烟与妻子血糖异常状态的关联:一项基于1000万名20-49岁中国妇女的横断面研究
- Pages: 354-364
- First Published: 20 November 2019
Highlights
- Women whose husbands are smokers are at an increased risk of having impaired fasting glucose or diabetes, and this association exists in both a categorical and dose-response manner.
- We found an interaction effect of body mass index and husbands’ smoking on the risk of dysglycemia in their wives.
- Husbands' smoking cessation or reduced amount of smoking is beneficial for prevention of dysglycemia in their wives.
- Practical family-oriented approaches for smoking cessation and smoking restriction are warranted.
REVIEW ARTICLE
The Jiangnan diet, a healthy diet pattern for Chinese
江南饮食——一种健康的中国传统饮食模式
- Pages: 365-371
- First Published: 17 December 2019
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
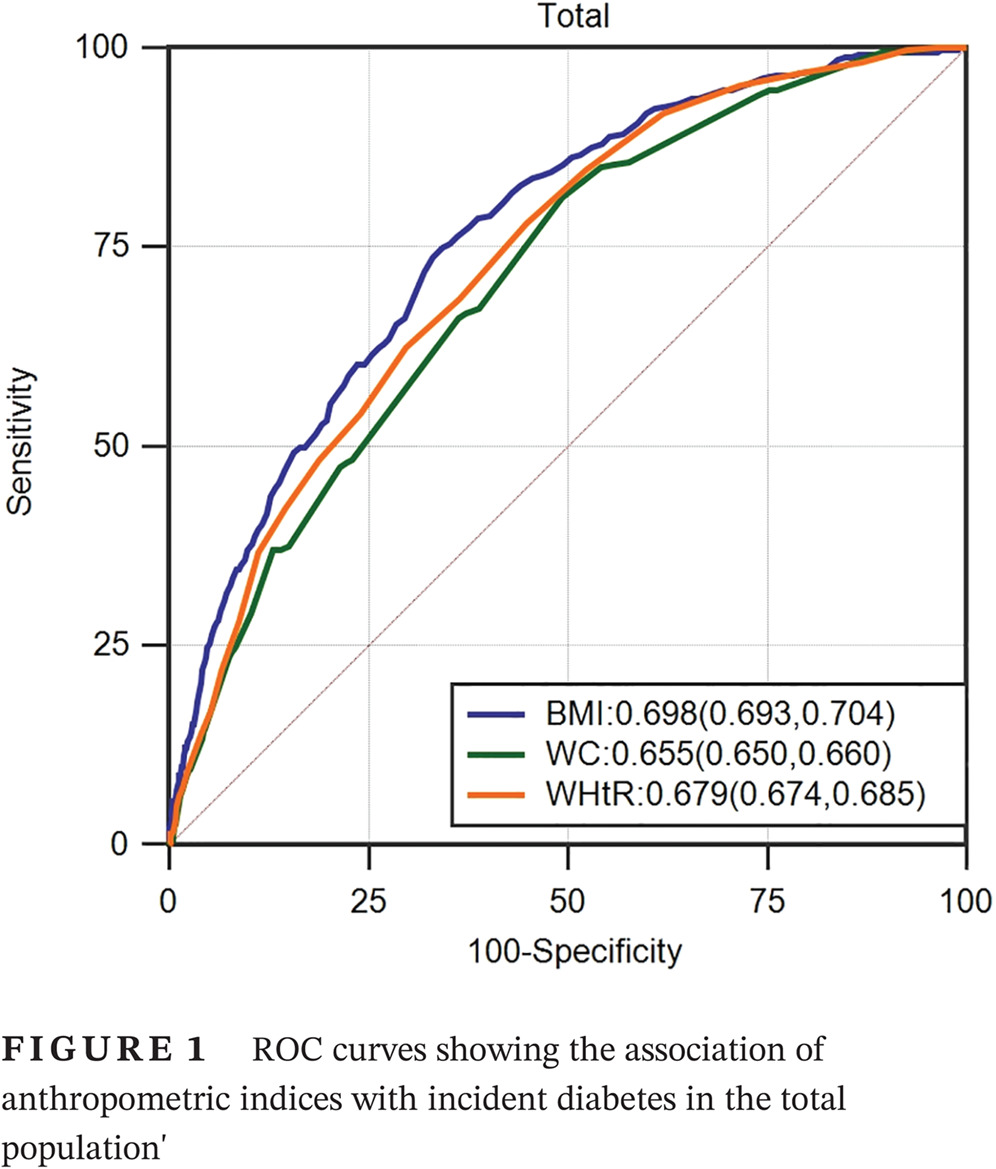
Assessing different anthropometric indices and their optimal cutoffs for prediction of type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Asians: The Jinchang Cohort Study
评估不同人体测量指标预测亚洲人2型糖尿病和空腹血糖受损的状况及其最佳截断值:金昌队列研究
- Pages: 372-384
- First Published: 23 October 2019
Highlights
- We observed significant and positive associations of the risk of type 2 diabetes with BMI, WC and WHtR, and we identified BMI as the best obesity predictor for diabetes.
- Our derived cutoff points were lower than the values specified in the most current Asian diabetes guidelines, and we recommend a cutoff point for BMI in Asians of 23 kg/m2 and a cutoff point for WC of 89 cm in men and 77 cm in women to define high-risk groups for type 2 diabetes; screening should be considered for these populations.
Antidiabetic drug use trends in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
2型糖尿病合并慢性肾病患者抗糖尿病药物使用趋势:国家健康与营养调查的横断面分析
- Pages: 385-395
- First Published: 25 October 2019
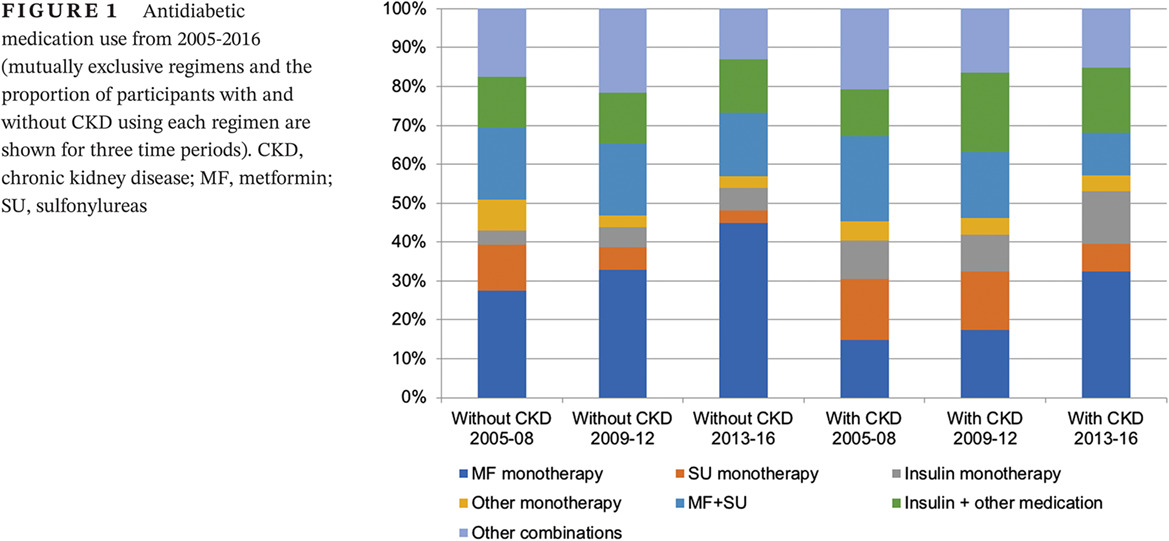
Highlights
- In a cross-sectional analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD), we observed an increased use of metformin (59%-68%) and a decreased use of sulfonylureas (55%-37%) and thiazolidinediones (25%-5%) in 2013-2016 compared to 2006-2008.
- Guideline-discordant use of metformin (8% of CKD stage 4/5) and glyburide (3% of CKD stages 3-5) observed in 2013-2016 warrants stronger policy implementations regarding inappropriate drug use.
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion reduces the risk of postoperative infection
持续皮下胰岛素输注降低术后感染风险
- Pages: 396-405
- First Published: 07 November 2019
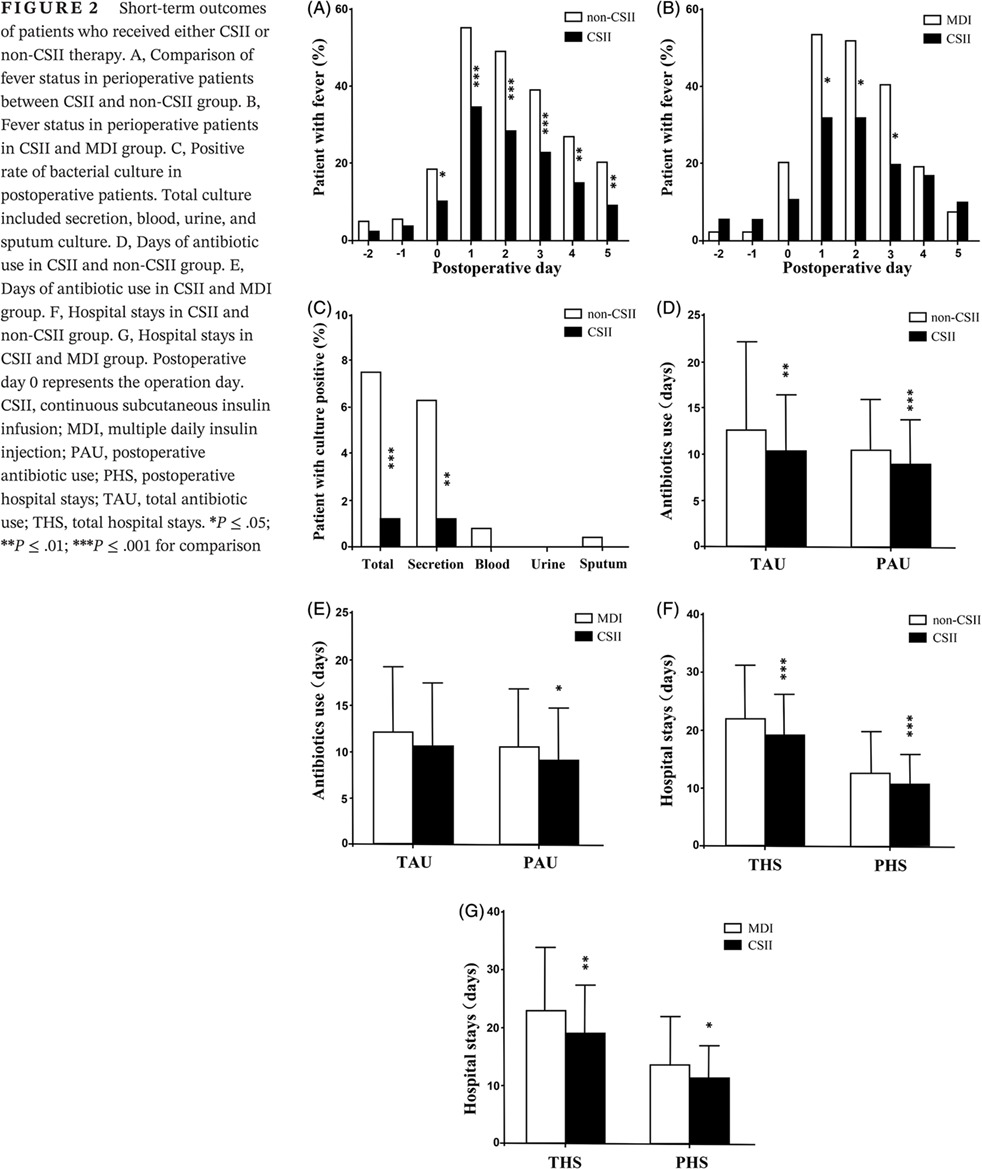
Highlights
- In our study, we adopted propensity matching, which included 1015 patients and 30 types of surgeries.
- The results show that patients who receive continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) therapy have a lower incidence of perioperative fever, a lower positive rate of postoperative secretion culture, and a shorter duration of antibiotic use.
- These results indicate that CSII therapy reduces the risk of postoperative infection and improves the prognosis of patients.
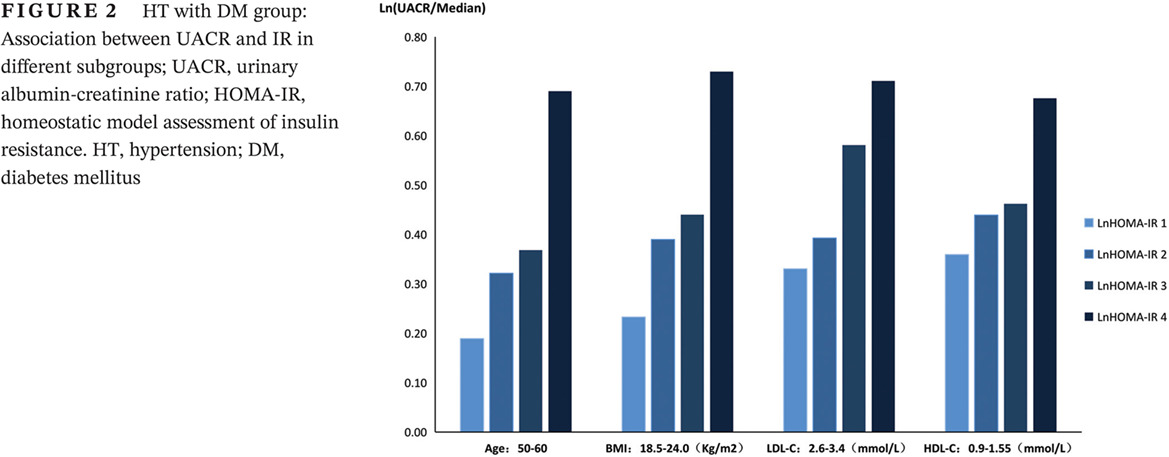
Insulin resistance is associated with urinary albumin-creatinine ratio in normal weight individuals with hypertension and diabetes: The REACTION study
胰岛素抵抗与尿白蛋白肌酐比值在体重指数正常的高血压合并糖尿病人群中相关:中国REACTION研究
- Pages: 406-416
- First Published: 26 November 2019
COMMENTARY
Care for diabetes with COVID-19: Advice from China
糖尿病合并COVID-19的管理:来自中国的建议
- Pages: 417-419
- First Published: 13 April 2020