Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
INVITED REVIEWS
Relevance of corona virus in food industry: A literature review on risks, challenges, and potential preventive measures
- First Published: 18 October 2022

Food industry is highly affected by COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, the preventive measures and precautions to be taken to reduce the risk of transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and incidence of infection are necessary. This review integrate and analyze the available information and data on precautions of corona virus in food industry in pursuance of informing the public and the scientific community, as well as creating collective knowledge among food industry establishment and raising awareness of preventive measures during COVID-19 pandemic.
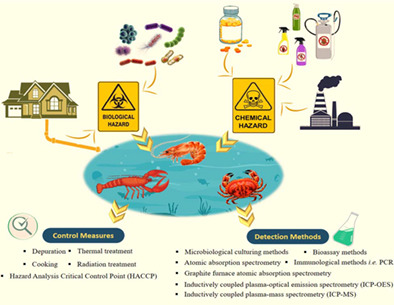
Crustaceans (shrimp, crab, and lobster): A comprehensive review of their potential health hazards and detection methods to assure their biosafety
- First Published: 14 November 2022
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of salmonella Enteritidis isolated from two consecutive Food-Poisoning outbreaks in Sichuan, China
- First Published: 12 October 2022

Four methods, namely PFGE.wgMLST, cgMLST, and wgSNP were appropriate for bacterial typing in Salmonella entrica serotype Enteritidis (SE)-related outbreak investigation. However, wgSNP can assign 12 SE strains from the first outbreak to one cluster and assign two strains from the second outbreak to another cluster, while PFGE, wgMLST, cgMLST did not successfully distinguish the SE strains from different outbreaks. Thus, the SNP-based phylogenetic analysis might be a viable method for differentiating SE strains at the outbreak level.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Antifungal action of quaternary ammonium compounds against environmental molds isolated from food industries
- First Published: 18 October 2022
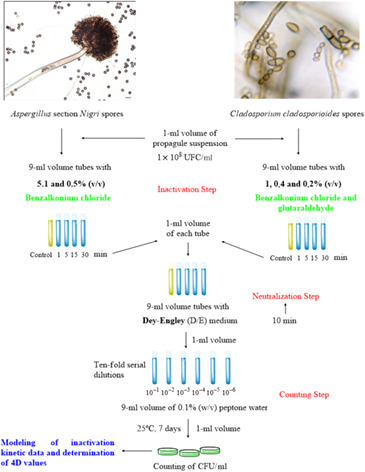
In order to evaluate the antifungal capacity of two commercial preparations made both with benzalkonium chloride alone and with the addition of glutaraldehyde at different concentrations and contact times, it was performed the suspension-neutralization test employing spores of five strains of both Aspergillus section Nigri and Cladosporium cladosporioides, all isolated from food industries environments.Modelling of inactivation kinetic data and determination of 4D values was performed by counting of CFU/ml.
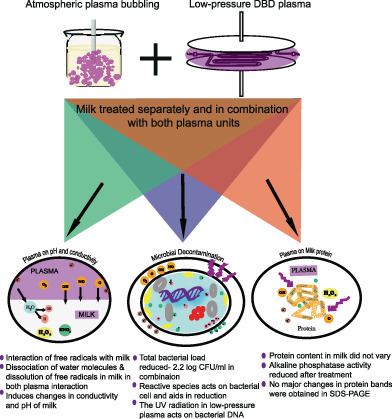
Study on the effect of atmospheric and low-pressure plasma and its combination on the microbial reduction and quality of milk
- First Published: 17 October 2022
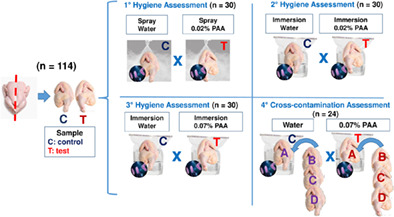
Application of peracetic acid by spray or immersion in chicken carcasses to reduce cross-contamination in the slaughter process
- First Published: 21 October 2022
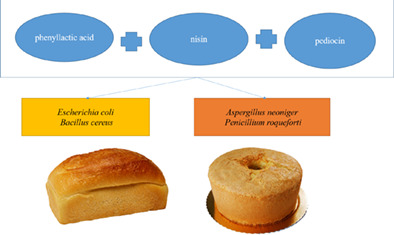
Inhibition of individual and combination of cell free supernatants of phenyllactic acid, pediocin- and nisin-producing lactic acid bacteria against food pathogens and bread spoilage molds
- First Published: 28 October 2022
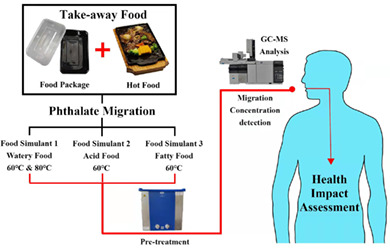
Migration analysis and health impact assessment of phthalates in takeaway food packaging materials
- First Published: 08 November 2022
Microbiological and physicochemical properties of farm bulk tank milk and antimicrobial resistance of its dominant bacteria
- First Published: 29 October 2022
Sheep and goats are reservoirs of colistin resistant Escherichia coli that co-resist critically important antimicrobials: First study from Jordan
- First Published: 06 November 2022
Soluble soybean polysaccharide/TiO2 nanocomposites: Biological activity, release behavior, biodegradability, and biosafety
- First Published: 07 November 2022
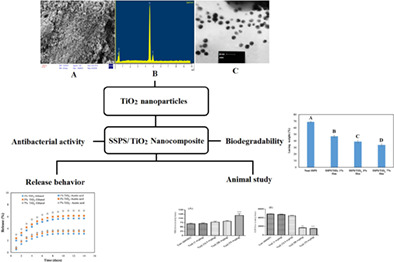
The developed nanocomposite exhibited great antimicrobial activity against Salmonella typhi PTCC 1609. The release profiles for TiO2 in two simulants of ethanol and acetic acid indicated a non-Fickian release. SSPS/TiO2 nanocomposites degraded easily. Oral administration of TiO2 increased malondialdehyde (p < .001) concentration in the liver tissue.
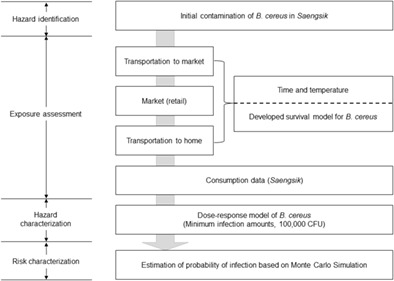
Mathematical modeling of Bacillus cereus in Saengsik, a powdered ready-to-eat food and its application in quantitative microbial risk assessment
- First Published: 11 November 2022