Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
The immune-enhancing potential of peptide fractions from fermented Spirulina platensis by mixed probiotics
- First Published: 27 May 2020
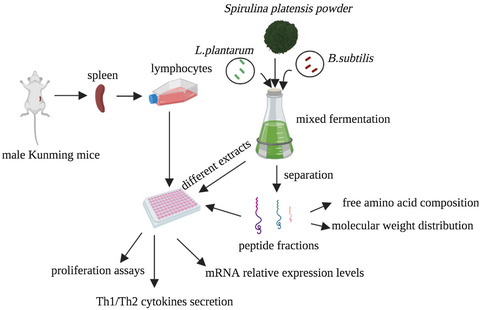
The mixed fermentation by probiotics enhanced the immunomodulatory activity of S. platensis with higher lymphocyte proliferation compared with non-fermented S. platensis. Notably, the low molecular weight (<3 kDa) peptide fraction from fermented S. platensis (L-PFS), especially at 40 μg/ml, presented the strongest activity in promoting lymphocytes proliferation and modulating cytokines (IL-2 and IL-10) secretion and the relative mRNA expression of Th1 cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-2 and TNF-α) and Th2 cytokines (IL-4 and IL-10), thus promoted the Th1/Th2 balance.
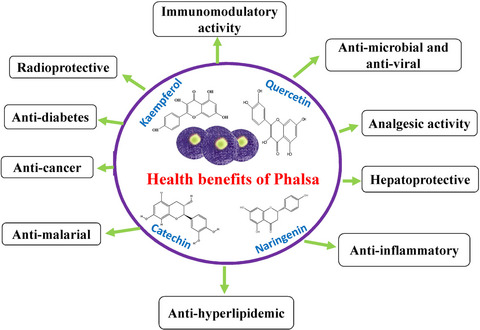
Nutraceutical perspectives and value addition of phalsa (Grewia asiatica L.): A review
- First Published: 22 April 2020
Phytoconstituents and pharmaco-therapeutic benefits of pitaya: A wonder fruit
- First Published: 07 May 2020
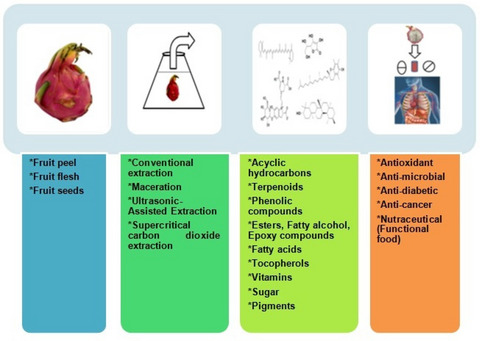
- All the parts of the dragon fruit, namely, flesh, peel and seeds are enriched with several phytoconstituents.
- The phytoconstituents of the dragon fruit are linked with therapeutic properties like antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-diabetic, anticancer, and nutraceutical.
- The review provides a framework for researchers across different fields to establish the mechanistic correlation between the phytoconstituents and therapeutic benefits of this wonder fruit.
Preparation, characterization, and cytokine-stimulating activity of oligosaccharides from Tremella fuciformis Berk
- First Published: 16 April 2020
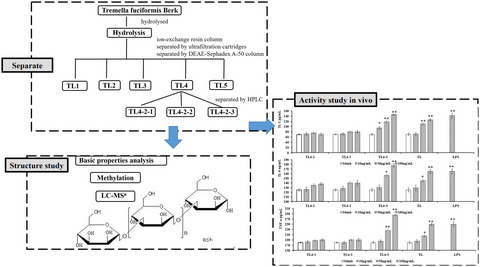
- Different oligosaccharides were prepared by gel-filtration and HPLC chromatography from the hydrolysate of Tremella polysaccharide.
- The structures of the oligosaccharide were identified as (1→3) oligomannans by component sugars, methylation and LC-MS analysis.
- The cell experiment showed the (1→3) hexmannan is the smallest active structure for keeping the cytokine-stimulating activity. The result shall be profitable in further utilization and research for Tremella polysaccharide.
Esculetin and idebenone ameliorate galactose-induced cataract in a rat model
- First Published: 16 April 2020
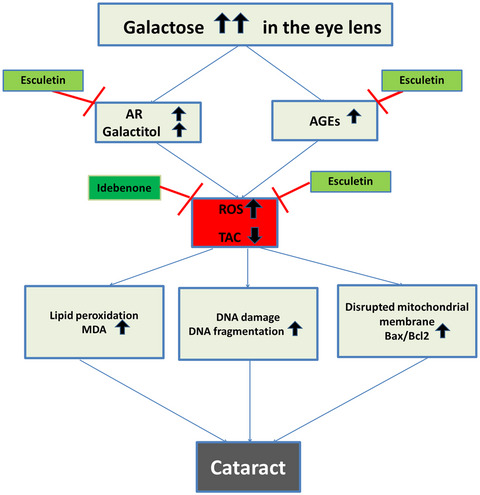
The present study confirms the link between high galactose levels and apoptosis of lens epithelial cells. Esculetin has been found to prevent the accumulation of polyol and AGEs in the lens tissue. Esculetin and idebenone have been found to protect the lens against galactose-induced oxidative stress, DNA damage, and lipid peroxidation. Overall, esculetin and idebenone are potentially useful for delaying galactose-induced cataractogensis through the suppression of apoptotic cell death in the lens epithelium.
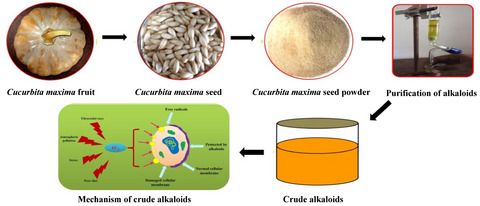
Retracted: Characterization of partially purified alkaloids from Cucurbita maxima seed and evaluation of their antioxidant activity in human erythrocytes and leukocytes
- First Published: 17 April 2020
Persimmon highly galloylated-tannins in vitro mitigated α-amylase and α-glucosidase via statically binding with their catalytic-closed sides and altering their secondary structure elements
- First Published: 17 April 2020
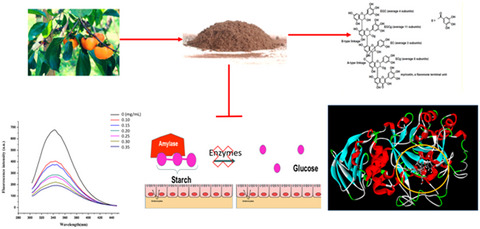
α-Amy and α-Glu are the crucial starch digestive enzymes associated with type II diabetes mellitus in humans. Persimmon is an excellent source of bio-functional tannins which potentially mitigate the type II diabetes. This study showed that PT beneficially decreased the action of the carbohydrate digestion-related enzymes, namely α-Amy and α-Glu via interaction simultaneously, which could be used to formulate a functional food and natural medicine.
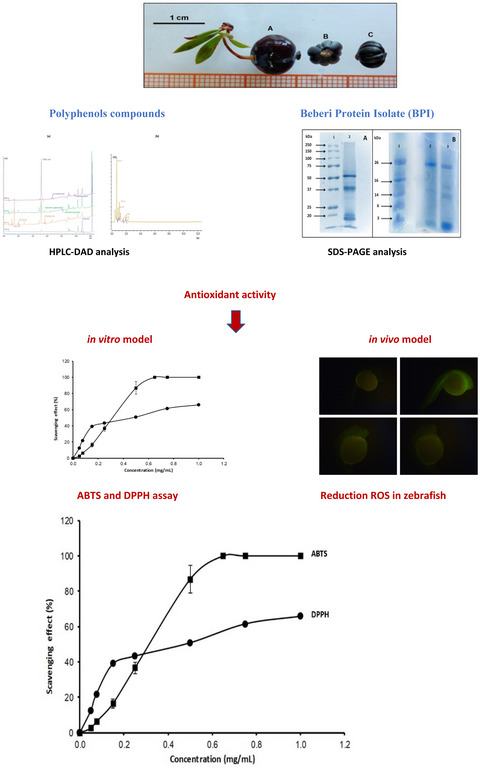
Argentine Patagonia barberry chemical composition and evaluation of its antioxidant capacity
- First Published: 28 April 2020
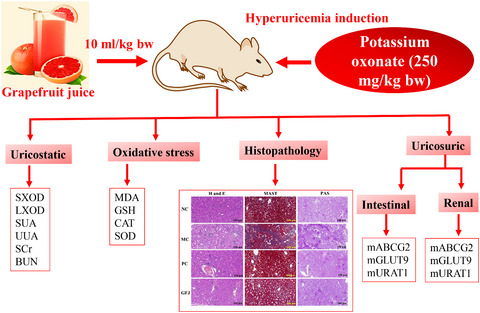
Uricostatic and uricosuric effect of grapefruit juice in potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemic mice
- First Published: 29 April 2020
Biochemical and functional properties of wheat middlings bioprocessed by lactic acid bacteria
- First Published: 03 May 2020
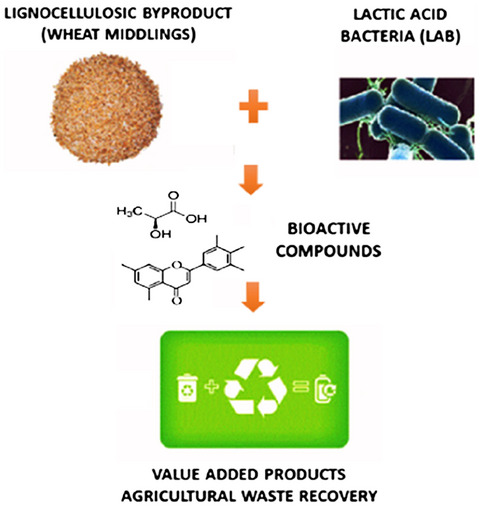
Wheat middlings were bioprocessed with lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Bioprocessed wheat middlings exhibited antioxidant, antibrowning, antibacterial and prebiotic properties, probably associated with the increase of total phenolic content. This can be a valuable approach to improve the availability of health-promoting compounds from byproducts of wheat flour production.
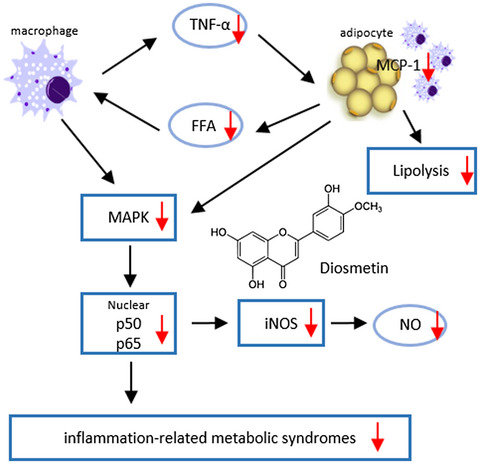
Inhibitory effect of diosmetin on inflammation and lipolysis in coculture of adipocytes and macrophages
- First Published: 04 May 2020
Hepatoprotective homoisoflavonoids from the fruits of Cucumis bisexualis
- First Published: 04 May 2020
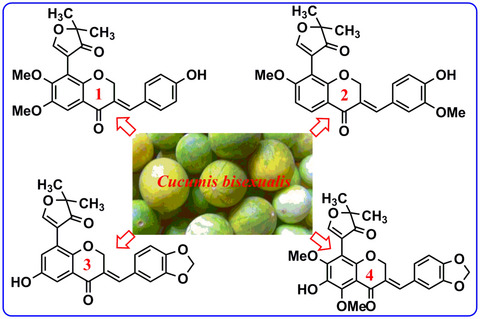
- Cucumis bisexualis is not only a favourite fruit, but also a traditional Chinere medicine.
- Four new homoisoflavonoids (1–4), and eight known homoisoflavonoid derivatives (5–12) were isolated from C. bisexualis for the first time.
- Compounds 3, 4, 8, and 9 exhibited certain hepatoprotective activities.
In vivo and in vitro anti-diabetic activity of ethanolic propolis extract
- First Published: 07 May 2020
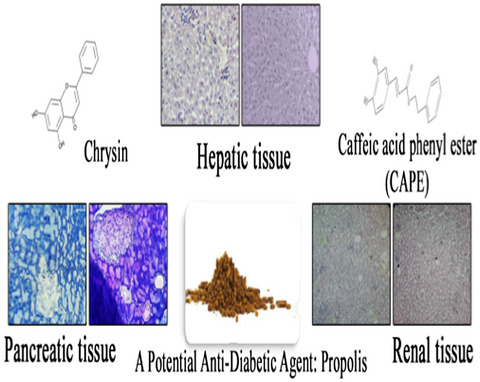
- In the current study, propolis was evaluated as a possible anti-diabetic agent thanks to in vitro and in vivo data.
- It was emphasized that ethanolic propolis extract significantly decreased the blood sugar level in diabetic rats and it showed a promising effect on the tissue of pancreatic, hepatic, and renal.
- As a consequence of the experimental analysis and biochemical evaluations, the studied doses of ethanolic extracts could be consumed as a natural product against diabetes disease.
Neferine inhibits proliferation and migration of human prostate cancer stem cells through p38 MAPK/JNK activation
- First Published: 11 May 2020
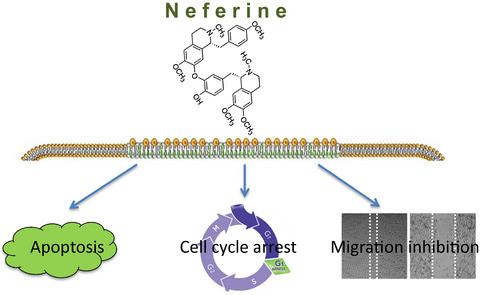
Neferine, a natural alkaloid, significantly inhibits the survival of human prostate cancer cells and cancer stem cells through inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. The molecule also prevents cancer stem cell migration, an important event for cancer metastasis in the body. The results of the study suggest that neferine may have a therapeutic effect on human prostate cancer.
The contribution ratio of various characteristic tea compounds in antioxidant capacity by DPPH assay
- First Published: 11 May 2020
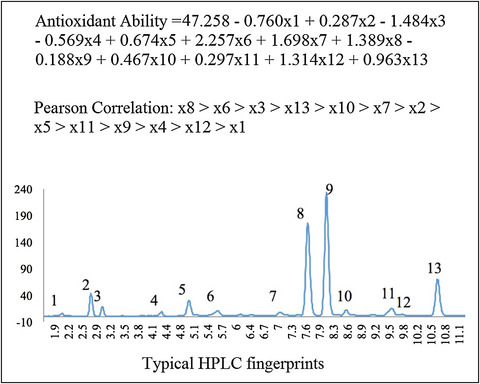
Based on the results of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl and high performance liquid chromatography, the contribution ratio of each tea compound to the antioxidant ability was analyzed by the Pearson correlation analysis and the partial least squares regression. We obtain a better understanding of the antioxidant activity of complex tea polyphenols component.
Characterization of Vicia ervilia (bitter vetch) seed proteins, free amino acids, and polyphenols
- First Published: 11 May 2020
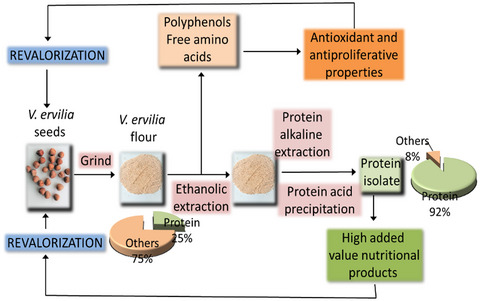
The polyphenol content in V. ervilia seeds average at 0.13%. Luteolin, kaempferol, apigenin, and quercetin were the main aglycones. Total free amino acids ranged from 0.05% to 0.19%, and canavanine represented between 9% and 22% of these. V. ervilia seed extracts inhibited the growth of Caco-2 cells and exhibited antioxidant properties in these cells. The average protein content in V. ervilia seeds was 24.1%. V. ervilia seeds proved a good substrate for the preparation of high-quality protein isolates.
Effects of walnut oil on metabolic profile and transcription factors in rats fed high-carbohydrate-/-fat diets
- First Published: 18 May 2020
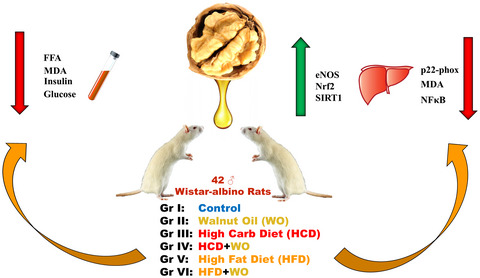
Walnut oil (WO) supplementation improves the metabolic response to rats fed high fat (HFD) and high carbohydrate (HCD) by reducing of hepatic nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and NADPH oxidase subunit p22phox, whereas increasing the endothelial-NO synthase (e-NOS), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2), and sirtuin-1 (SIRT-1).
Tithonia diversifolia-derived orizabin suppresses cell adhesion, differentiation, and oxidized LDL accumulation by Akt signaling suppression via PTEN promotion in THP-1 cells
- First Published: 15 May 2020
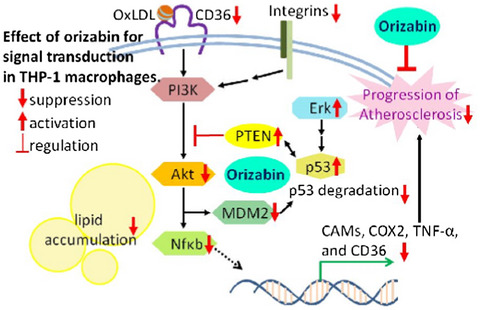
Orizabin suppresses inflammatory and adhesion of THP-1 cells and HUVECs, and inhibits macrophage differentiation and lipid uptake in THP-1 cells. Furthermore, Orizabin significantly promoted PTEN mRNA expression in THP-1 cells. Tithonia diversifolia-derived orizabin suppresses Akt signaling pathway and NFκB transcriptional activity, and it has anti-atherosclerotic function.
Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and impairs migration and invasion in a mouse model of ovarian cancer
- First Published: 15 May 2020
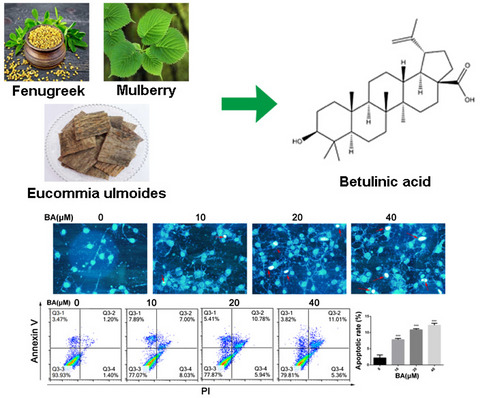
- BA showed a time- and dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on ovarian cancer cell lines in vitro.
- BA could significantly induce cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent and remarkably suppressed the migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process.
- BA significantly retarded tumor growth in the xenograft tumor mouse model by suppressing tumor cells proliferation.
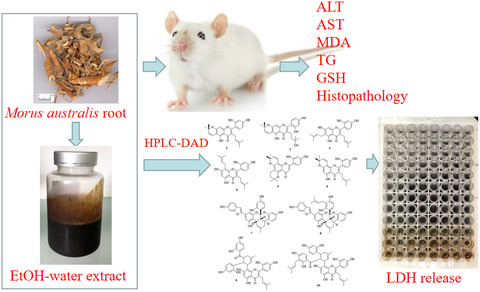
Simultaneous characterization and quantification of flavonoids in Morus australis root as potential hepatoprotective nutraceutical
- First Published: 19 May 2020
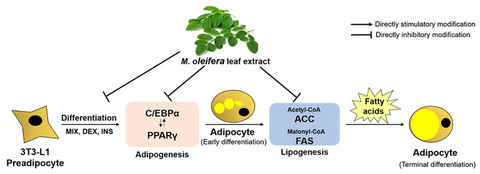
Extracts of Moringa oleifera leaves from different cultivation regions show both antioxidant and antiobesity activities
- First Published: 20 May 2020
Arthrocen, an avocado-soy unsaponifiable agent, improves acetic acid-induced colitis in rat by inhibition of NF-kB signaling pathway
- First Published: 22 May 2020
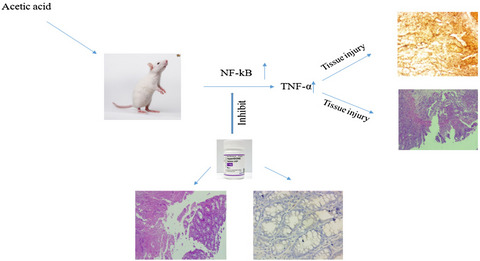
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an immune-mediated chronic relapsing disorder affecting the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) featuring chronic bowel inflammation
- Arthrocen is a plant-based dietary supplement containing avocado and soy unsaponifiable extracts in a ratio of 1:2 that have showed anti-inflammatory properties
- This study shows that Arthrocen reduced acetic acid induced colitis in rats through the inhibition of NF-kB signaling pathway
1-Methylcyclopropene treatment controls ethanol accumulation associated with regulation of mitochondrial energy metabolism in kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) cv. “Bruno” during storage at room temperature
- First Published: 25 May 2020
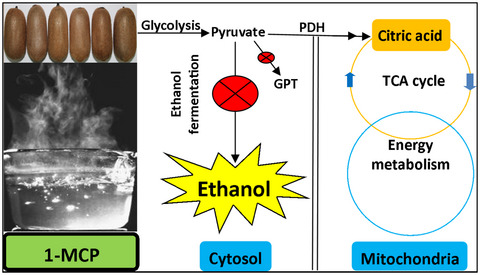
- 1-MCP treatment controlled ethanol accumulation via regulating the higher ATP and EC in kiwifruit cv. ‘Bruno’ during storage.
- 1-MCP treatment regulated the mitochondrial energy metabolism-related enzymatic activities.
- 1-MCP treatment maintained oxidative phosphorylation by regulating TCA and NADH/NAD+ ratio.
Anti-inflammatory effects of Beopje curly dock (Rumex crispus L.) in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells and its active compounds
- First Published: 26 May 2020
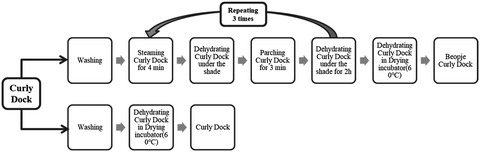
Inflammation is a defense response of the body to stimuli. Curly dock (CD) is an herbal food with anti-inflammatory effects. Beopje is a herbal food processing method that reduces toxicity and enhances beneficial effects. This study investigated the effects of CD and Beopje curly dock (CD-B) extracts on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory damage in RAW 264.7 cells. Our results indicate that CD-B has a more significant inhibitory effect on the LPS-induced inflammatory response in RAW264.7 cells than CD, suggesting that the Beopje process potentially enhances the anti-inflammatory effect of CD.
Study on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Desmodesmus armatus
- First Published: 27 May 2020
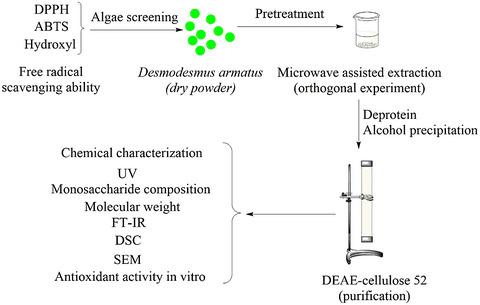
- A method for optimal extraction of Desmodesmus armatus polysaccharide was obtained through orthogonal experiment.
- Four polysaccharides fractions (DAP1, DAP2, DAP3 and DAP4) were obtained and their physicochemical properties were studied.
- DAP2 and DAP3 have strong scavenging effects on ABTS, DPPH and hydroxyl radicals.
Detection and isolation of the typical gut indigenous bacteria from ddY mice fed a casein-beef tallow-based or egg yolk-based diet
- First Published: 27 May 2020
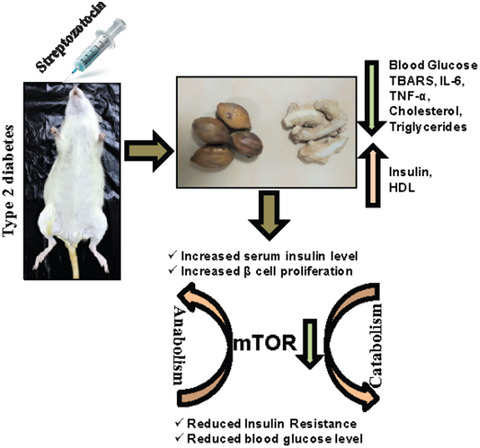
The role of mTOR and oral intervention of combined Zingiber officinale-Terminalia chebula extract in type 2 diabetes rat models
- First Published: 27 May 2020
A novel fibrinolytic enzymes from the Korean traditional fermented food—Jotgal: Purification and characterization
- First Published: 28 May 2020
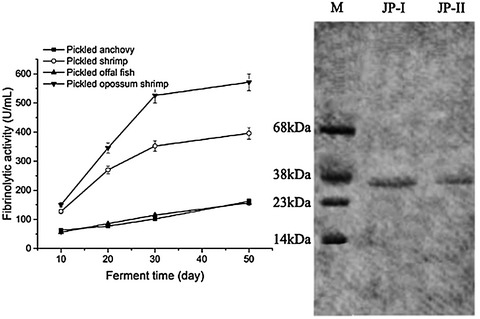
- Two metalloproteases with fibrinolytic activity from Gonjaegijot, a Korean traditional fermented food of pickled opossum shrimp were identified, and named them as JP-I and JP-II, respectively.
- The optimal condition for fibrinolytic activity of JP-I was at 50°C and pH 8.1, while that of JP-II was at 45°C and 9.9.
- The results suggest that the JP-I and JP-II, having direct-acting for fibrin, has enough potential to be novel agents for antithrombotic agents for cardiovascular diseases and possible complications.
Effects of fermented rice bran on DEN-induced oxidative stress in mice: GSTP1, LINE-1 methylation, and telomere length ratio
- First Published: 28 May 2020
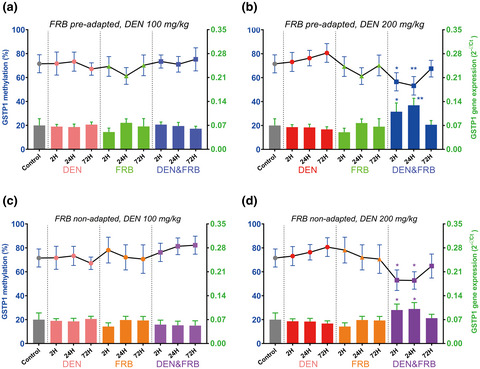
This study aimed to investigate the effect of FRB on N-diethylnitrosamine-induced oxidative stress through DNA methylation and telomere length analysis. The results show that FRB may alleviate DEN-triggered oxidative stress, based on changes in glutathione-S-transferase P1, long interspersed nuclear element-1 methylation and telomere length ratios, thereby revealing the potential of dietary intervention during inflammation.
Supplementation of nanofiltrated deep ocean water ameliorate the progression of osteoporosis in ovariectomized rat via regulating osteoblast differentiation
- First Published: 01 June 2020
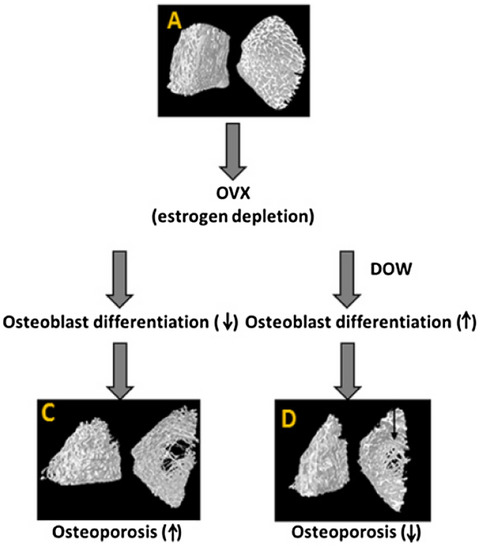
The nanofiltrated deep ocean water (DOW) rich in magnesium possesses a protective effect in ovariectomy (OVX)-caused osteoporosis. Estrogen depletion reduces the rate of osteoblast differentiation, while supplementation of DOW is capable of maintaining the bone structure through upregulating the osteoblast differentiation.
Effect of polysaccharide extract SPSS1 from Apostichopus japonicus spermary on HepG2 cells via iTRAQ-based proteome analysis
- First Published: 06 July 2020