Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Rice protein stimulates endogenous antioxidant response attributed to methionine availability in growing rats
- First Published: 12 March 2020
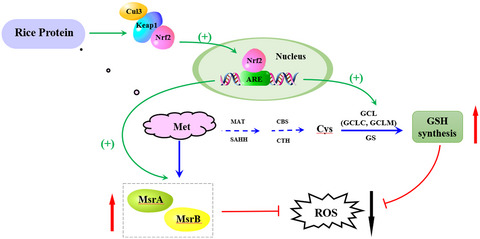
Rice protein is a major plant protein, which is rich in sulfur-containing amino acids and widely consumed throughout the world. This paper emphasizes that methionine plays a key role in inducing the antioxidant activity of rice protein. The present study demonstrates that rice protein stimulates endogenous antioxidant response dependent on methionine availability via activating Nrf2-ARE antioxidant pathway.
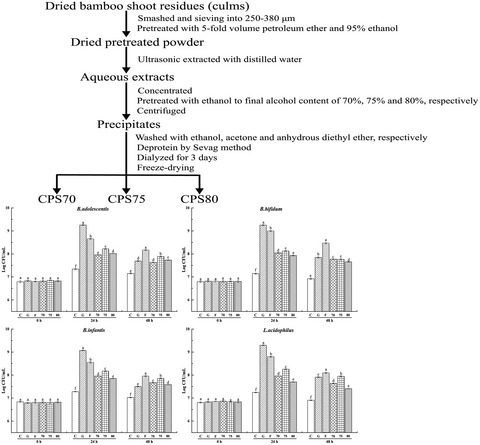
Comparisons of prebiotic activity of polysaccharides from shoot residues of bamboo (Chimonobambusa quadrangularis) via different ethanol concentrations
- First Published: 09 March 2020
Chlorogenic acid improves lipid membrane peroxidation and morphological changes in nitrite-induced erythrocyte model of methemoglobinemia
- First Published: 09 March 2020
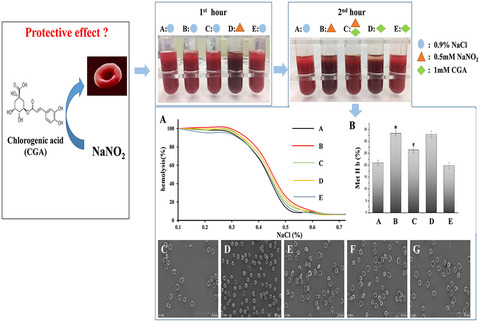
In this study, we evaluated the protective capacity of chlorogenic acid (CGA) against NaNO2 induced damage to rat erythrocytes. We infer that the reaction of CGA and NaNO2 may suppress the cytotoxicity of nitrite on erythrocytes and avoid the generation of oxidative stress induced by NaNO2. Our results suggest a novel diet strategy for preventing the adverse effects of nitrite in those people with exposure to nitrite.
Optimizing the DO-stat protocol for enhanced production of thermostable pullulanase in Escherichia coli by using oxygen control strategies
- First Published: 09 March 2020
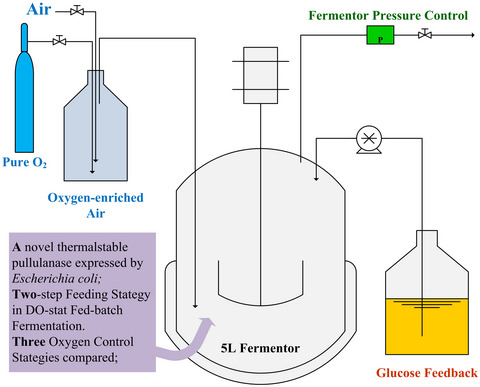
- Production of a thermostable pullulanase by DO-stat fed-batch fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli BL 21 was investigated in a 5 L fermentor.
- The effect of three oxygen control strategies, glucose feedback, shifting fermentor pressure and adding oxygen-enriched air, on cell growth and pullulanase expression were examined.
- Adding oxygen-enriched air strategy was suggested as an effective approach to enhance both cell growth and pullulanase production.
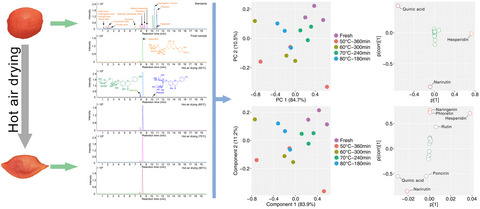
Effect of hot air drying on the polyphenol profile of Hongjv (Citrus reticulata Blanco, CV. Hongjv) peel: A multivariate analysis
- First Published: 09 March 2020
Extraction and characterization of novel multifunctional peptides from Trachinus Draco (greater weever) myofibrillar proteins with ACE/DPP4 inhibitory, antioxidant, and metal chelating activities
- First Published: 09 March 2020
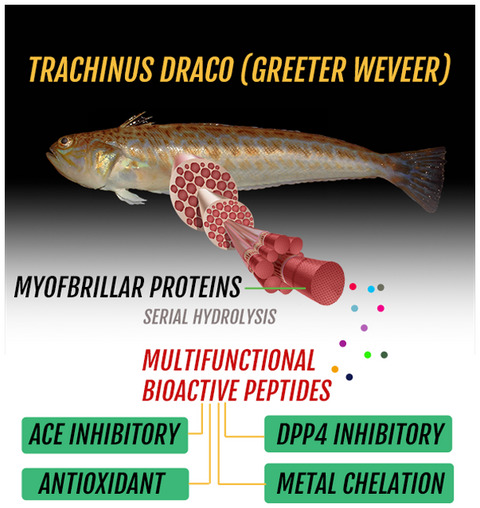
Bioactive peptides are of utmost importance for new drug discovery while marine organisms, particularly fish, represent a great reservoir for novel biomolecules identification. The current work was able to describe 2 multifunctional bioactive peptides from Trachinus Draco (Greeter weveer) myofibrillar proteins after sequential hydrolysis and HPLC fractionation. The de novo sequenced peptides showed ACE inhibitory, DPP4 inhibitory, antioxidant, and metal chelation activities that have a great potential for aging-related pathologies such as diabetes and hypertension.
Digestive abilities, amino acid transporter expression, and metabolism in the intestines of piglets fed with spermine
- First Published: 10 March 2020
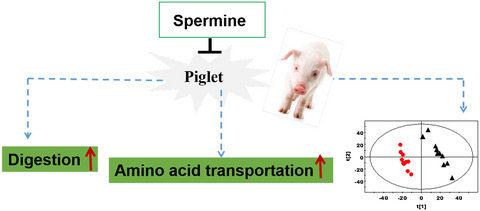
Dietary spermine supplementation and its extended duration may improve digestion by increasing the levels of digestive enzymes and their gene expression levels; spermine intake can result in the high expression of amino acid transporters in the jejuna of piglets; and spermine supplementation can modulate lipid and amino acid metabolisms in the jejuna of piglets.
Dietary fats promote inflammation in Wistar rats as well as induce proliferation, invasion of SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells
- First Published: 10 March 2020
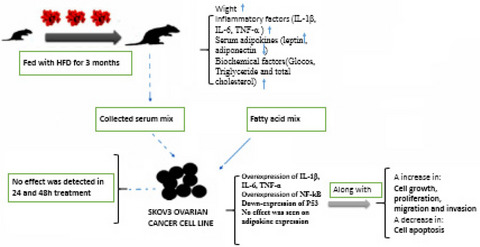
- HFD increases the body weight, biochemical factors, serum adipokine and inflammatory levels in Wistar rats.
- FA mix promotes cell growth, proliferation, migration and invasion in the SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line.
- FA mix enhances the expression of inflammatory factors in SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line.
Antioxidant and protective effect of Stachys pilifera Benth against nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats
- First Published: 10 March 2020
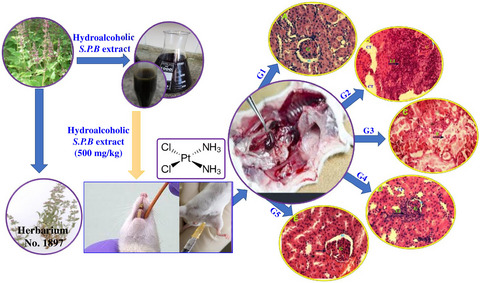
The aim of the current study was to assess the antioxidant and renoprotective effects of Stachys pilifera Benth (S.P.B) hydroalcoholic extract on nephrotoxicity induced with cisplatin (CP). The results showed that S.P.B hydroalcoholic extract improved the biochemical parameters and kidney function as well as restored antioxidant activity in CP-induced nephrotoxicity.
Effect of polysaccharide extract SPSS1 from Apostichopus japonicus spermary on HepG2 cells via iTRAQ-based proteome analysis
- First Published: 11 March 2020
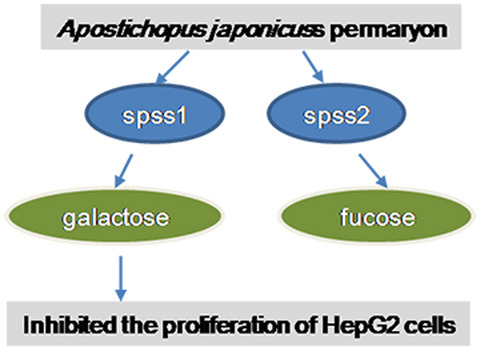
Two main fractions named SPSS1 and SPSS2 were obtained and analyzed from apostichopus japonicuss permary. In addition to the high content of lactose in both kinds of polysaccharides, the highest content of monosaccharide in SPSS1 was galactose, while in SPSS2 it was fucose. Further, the antitumor study of SPSS1 was carried, and the results showed SPSS1 treatment inhibited the proliferation of HepG2 cells.
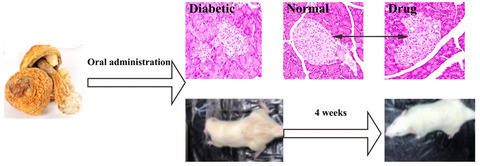
The beneficial effects of Agaricus blazei Murrill on hepatic antioxidant enzymes and the pancreatic tissue recovery in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- First Published: 11 March 2020
Evaluation of the in vitro ⍺-amylase inhibitory, antiglycation, and antioxidant properties of Punica granatum L. (pomegranate) fruit peel acetone extract and its effect on glucose uptake and oxidative stress in hepatocytes
- First Published: 11 March 2020
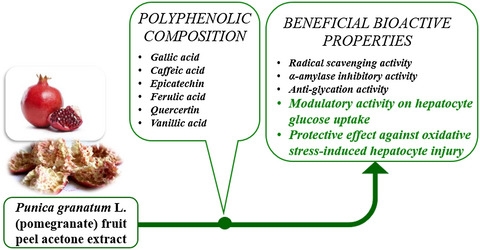
Punica granatum L. (pomegranate) fruit peel acetone extract demonstrated potent radical scavenging activity, inhibitory effects against glycation and α-amylase activity, modulatory effect on hepatocyte glucose uptake, as well as protective capacity against oxidative-stress induced hepatocyte cell injury, which may be influenced by its rich polyphenol and flavonoid content and the presence of some bioactive phenolic acid.
Reused palm oil from frying pork or potato induced expression of cytochrome P450s and the SLCO1B1 transporter in HepG2 cells
- First Published: 11 March 2020
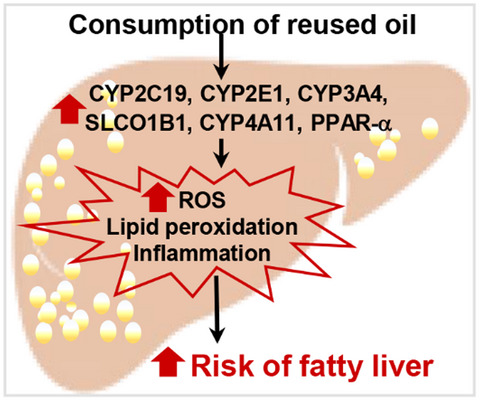
Deep frying degrades cooking oil and generates harmful products. The reused palm oils from frying pork or potato induced mRNA profiles of CYPs and SLCO1B1 while the new oil up-regulated CYP2E1, CYP3A4, and CYP4A11. Both of the reused oils induced PPAR-α but suppressed SREBP-1a and SREBP-1c mRNA. The induction of CYPs, PPAR-α, and SLCO1B1 might contribute to an increased risk of fatty acid accumulation. Hence, consumption of palm oil or reused cooking oil should be of concern.
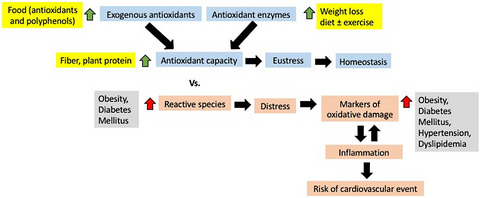
The effect of diet on oxidative stress and metabolic diseases—Clinically controlled trials
- First Published: 11 March 2020
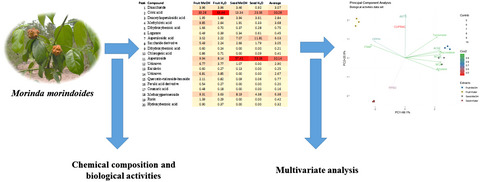
Novel insights into the fruit and seed extracts of Morinda morindoides (Baker) Milne-Redh: HPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS profiling, antioxidant, and enzyme inhibitory propensities
- First Published: 12 March 2020
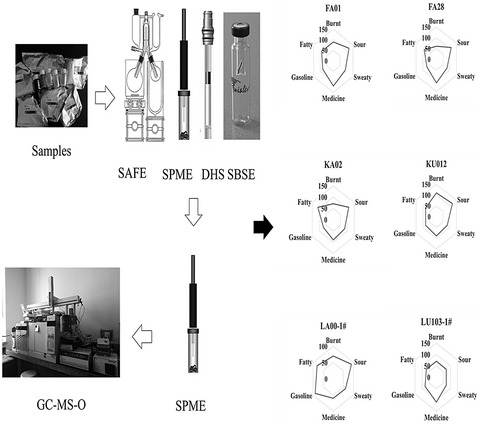
Investigating characteristics and possible origins of off-odor substances in various yeast extract products
- First Published: 12 March 2020
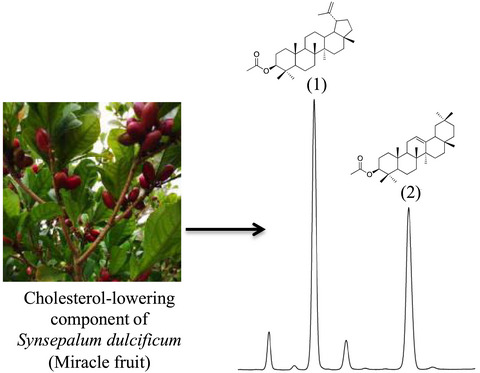
The cholesterol-lowering activity of miracle fruit (Synsepalum dulcificum)
- First Published: 12 March 2020
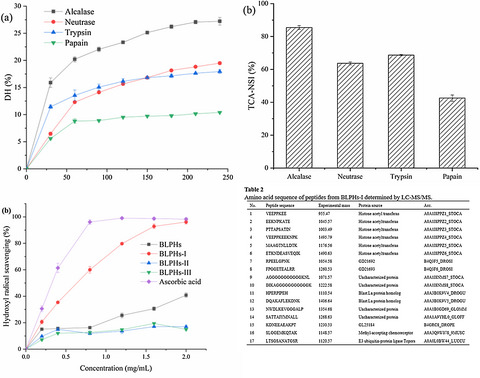
Preparation, antioxidant activity evaluation, and identification of antioxidant peptide from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae
- First Published: 12 March 2020
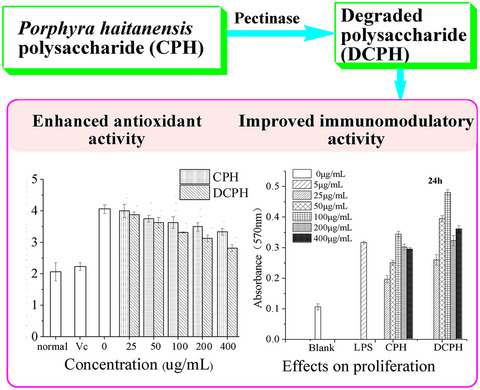
Improved antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of enzymatically degraded Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides
- First Published: 12 March 2020
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Lilium lancifolium bulbs extract
- First Published: 15 March 2020
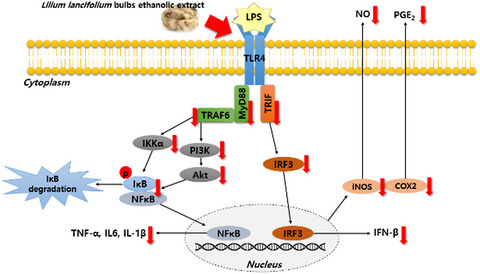
- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Lilium lancifolium bulbs extract
- Wan-Sup Sim, Sun-Il Choi, Tae-Dong Jung, Bong-Yeon Cho, Seung-Hyun Choi, Sung-Min Park, Ok-Hwan Lee
- p-Coumaric acid and ferulic acid contents of Korean L. lancifolium extract were higher than Japanese extract. Korean L. lancifolium bulbs extract exhibited significant antioxidant effects, compared to Japanese extract. Korean L. lancifolium bulbs extract significantly inhibited pro-inflammatory protein expressions through MyD88 dependent pathway, compared to Japanese extract.
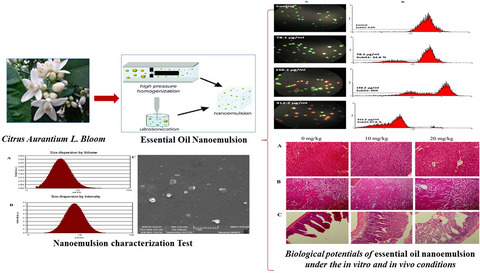
Citrus aurantium L. bloom essential oil nanoemulsion: Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity, and its potential health impacts on mice
- First Published: 15 March 2020
Effects of hydrophobicity and molecular weight on the transport permeability of oligopeptides across Caco-2 cell monolayers
- First Published: 15 March 2020
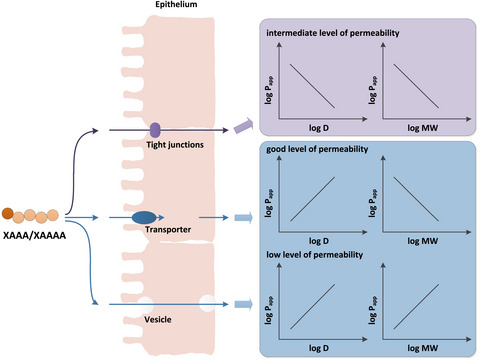
In this paper, results showed that oligopeptides with different N-terminal amino acids had a wide range of permeability values and could be divided into three levels with different correlations to log D and MW. It was found for the first time that the transport permeabilities of oligopeptides across Caco-2 cell monolayers might be closely related to log D and MW. In addition, the transcellular and paracellular pathways may be coexisted for the transport of oligopeptides.
Improved effect of palatinose syrup bioconverted from sucrose on hyperglycemia and regulation of hepatic lipogenesis in male C57BL/6J mice
- First Published: 15 March 2020
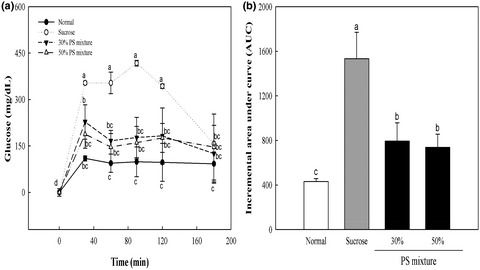
We prepared palatinose–sucrose (PS) mixtures (namely, 30% PS mixture and 50% PS mixture) from sucrose by enzymatic bioconversion to improve low sweetness and low solubility of palatinose and to develop a sugar substitute that can lower blood sugar levels. The results of animal experiments indicated that PS mixtures could prevent metabolic syndrome resulting from excessive sugar levels by regulating hepatic lipogenesis and cholesterol homeostasis. Thus, PS mixtures could be a good alternative to sucrose as a healthy sweetener.
Rubusoside alleviates the ovalbumin-induced mice allergic asthma by modulating the NF-κB activation
- First Published: 17 March 2020
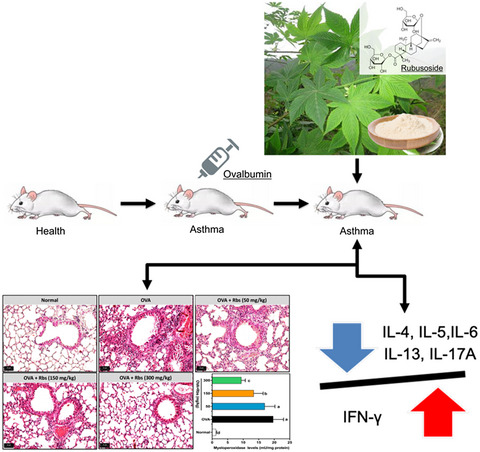
Rubusoside (Rbs) effectively attenuated ovalbumin (OVA)-induced inflammatory reactions in a mouse model of asthma. The 300 mg/kg dose of Rbs decreased the OVA-induced total-IgE and anti-IgG1 generation, and regulated the balance between Th2 and Th1 cytokines in mice with asthma. The anti-inflammatory activity of Rbs was associated with modulating activation of the NF-κB pathway and regulating the Th1 and Th2 cytokine imbalance.
The synergistic effect of cell wall extracted from probiotic biomass containing Lactobacillus acidophilus CL1285, L. casei LBC80R, and L. rhamnosus CLR2 on the anticancer activity of cranberry juice—HPLC fractions
- First Published: 17 March 2020
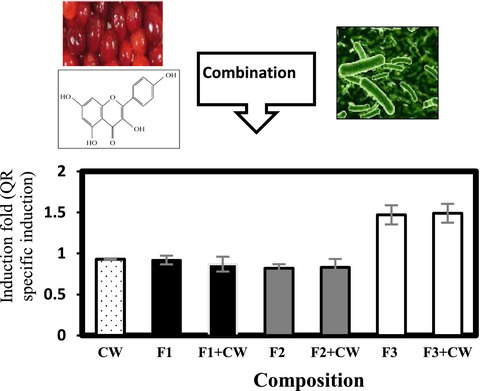
- Cranberry juice fractions and cell wall constituents extracted from probiotic biomass were more effective in inhibiting the growth of HT-29 as compared to the cranberry fractions tested alone, indicating a possible synergy effect between these biofunctional compounds.
- Cranberry juice fraction composes of phenolic acids inhibited the growth of the HT-29 cells' line.
- Cranberry juice fraction containing flavonols had potency as QR inducer.