Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
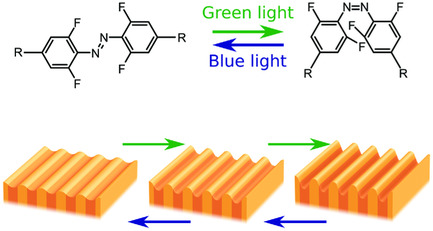
Configurable Multi-Stable Surface Topographies: Re- and Preconfigurable Multistable Visible Light Responsive Surface Topographies (Small 50/2018)
- First Published: 13 December 2018

In article number 1803274, Dirk J. Broer, Albertus P. H. J. Schenning, and co-workers fabricate multi-stable, re- and pre-configurable visible light responsive surface topographies by using low illumination doses. Preliminary studies reveal that these light responsive polymers are suitable as adaptive biological surfaces. The authors would like to thank Karel Haesevoets for the cover design and the ICMS for the creation of the image.
Inside Front Cover
Thermoelectric Performance: Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in CuSbSe2 Nanoplate-Based Pellets by Texture Engineering and Carrier Concentration Optimization (Small 50/2018)
- First Published: 13 December 2018

In article number 1803092, Qingyu Yan, Mercouri G. Kanatzidis, and co-workers develop a bottom-up self-assembly process to prepare CuSbSe2-PtTe2 based pellets with highly oriented single-crystalline nanoplates, which results in an orientation factor of ≈0.8 for (00l) facets. The texture engineering and carrier concentration optimization enable an ≈500% enhanced ZT value (0.50 at 673 K) for CuSbSe2-2.0 mol% PtTe2 compared to pure CuSbSe2.
Inside Back Cover
Analytical Ultracentrifugation: Nanoparticle Gradient Materials by Centrifugation (Small 50/2018)
- First Published: 13 December 2018

In article number 1803518, Helmut Cölfen and co-workers use analytical ultracentrifugation to fabricate tailored nanoparticle gradient materials. Gradients of gold spheres, gold rods, and spherical iron oxide nanoparticles are generated by sedimentation of the nanoparticles in a thermoreversible gelatin matrix. The materials can be simulated in advance and the gradients are detected online by the optical systems of the centrifuge to produce desired property gradients.
Back Cover
Tumor Margin Demarcation and Therapy: A NanoFlare-Based Strategy for In Situ Tumor Margin Demarcation and Neoadjuvant Gene/Photothermal Therapy (Small 50/2018)
- First Published: 13 December 2018
In article number 1802745, Yong-Qiang Li and co-workers report a robust tumor microenvironment-responsive theranostic nanoprobe (NanoFlare). By virtue of its anisotropic oligonucleotides-spike nanostructure, the NanoFlare can enter tumor cells universally regardless of cell type and produce a redox-activated fluorescence signal. The NanoFlare enables accurate intraoperative margin demarcation of different tumors and efficient gene/photothermal neoadjuvant therapy in vivo.
Masthead
Correction
SERS-Active-Charged Microgels for Size- and Charge-Selective Molecular Analysis of Complex Biological Samples
- First Published: 13 December 2018
Reviews
Single-Nanostructured Electrochemical Detection for Intrinsic Mechanism of Energy Storage: Progress and Prospect
- First Published: 30 October 2018
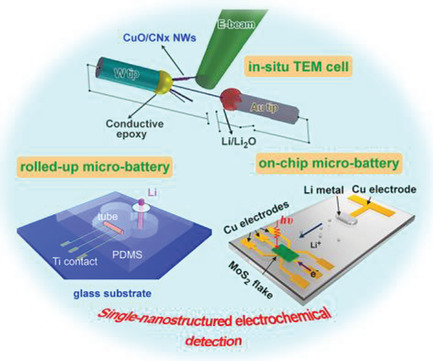
Single-nanostructured electrochemical detection to understand the intrinsic mechanisms of energy storage is reviewed in detail, with a focus on the in situ investigation and real-time observation of electrode evolution, phase transition, interface formation, and electron conductivity during battery operation, by using custom-made single-nanostructured microbatteries and in situ transmission electron microscopy cells.
Communications
Nanoparticle Gradient Materials by Centrifugation
- First Published: 06 November 2018
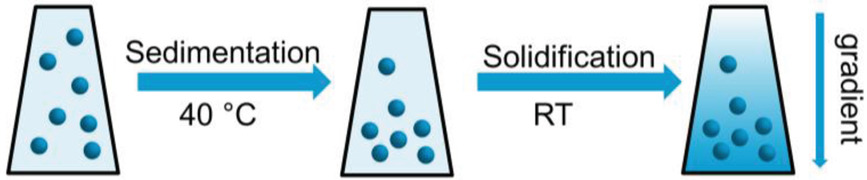
Analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) meets material chemistry. AUC is used as a new method to fabricate nanoparticle gradient materials. The materials are designed at the computer in advance and are able to be detected anytime during centrifugation with the optical systems of the centrifuge. A variety of gradients of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and shapes in gelatin is presented.
Frontispiece
Nanoelectrode Gaps: Parallel Fabrication of Self-Assembled Nanogaps for Molecular Electronic Devices (Small 50/2018)
- First Published: 13 December 2018

In article number 1803471, Johnas Eklöf-Österberg, Kasper Moth-Poulsen, and co-workers make isolation, positioning, and electronic measurements on single molecules possible using a combined top-down and bottom-up strategy. Proto-devices, which are self-assembled nanogaps composed of two gold nanoparticles linked by a single or a few molecules, are guided onto top-down prefabricated nanosized electrodes by surface charge interactions. The assembly process enables electrical measurements through particle–molecule–particle devices.
Communications
Parallel Fabrication of Self-Assembled Nanogaps for Molecular Electronic Devices
- First Published: 25 October 2018
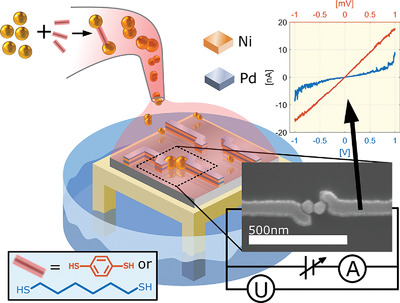
A colloidal dispersion of dimer particles are formed by linking gold nanoparticles with benzene 1,4-dithiol or 1,6-hexanedithiol. The dimers are subsequently deposited and guided towards prefabricated nickel/palladium nanoelectrode gaps. Electrical measurements, performed as a proof of concept, shows that it is possible to conduct current through this system and that there is a difference in conductance between the molecules.
π-Conjugated Molecule Boosts Metal–Organic Frameworks as Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction Catalysts
- First Published: 16 October 2018
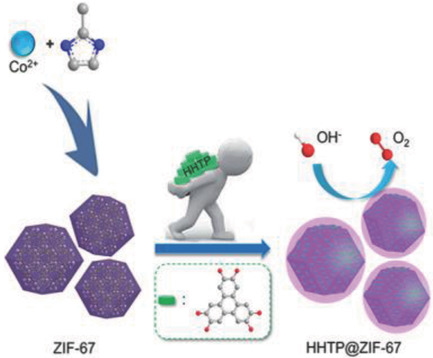
A novel metal–organic framework (MOF) composite 2,3,6,7,10,11-hexahydroxytriphenylene@ZIF-67 is obtained via a direct coating strategy under solvothermal conditions. The conductivity of the obtained composite is extremely ameliorated due to the improved electron transfer resulting from the π-conjugated skeleton. Together with the high specific surface area preserved from the pristine MOFs, the synthesized composite displays efficient electrocatalytic activity in the oxygen evolution reaction performance.
Designable 3D Microshapes Fabricated at the Intersection of Structured Flow and Optical Fields
- First Published: 21 October 2018
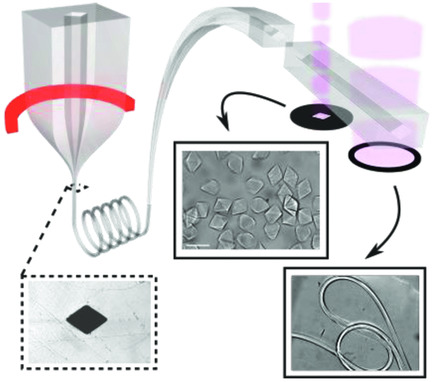
A microshape fabrication method is presented that combines a thermally drawn transparent fiber template with a masked UV-photopolymerization approach to enable biaxial control of a microshape design. High-resolution production of complex microshapes not producible using alternative methods is demonstrated, such as octahedrons, dreidels, and axially asymmetric fibers, at throughputs as high as 825 structures min−1.
Acoustic Actuation of Integrin-Bound Microbubbles for Mechanical Phenotyping during Differentiation and Morphogenesis of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
- First Published: 14 November 2018
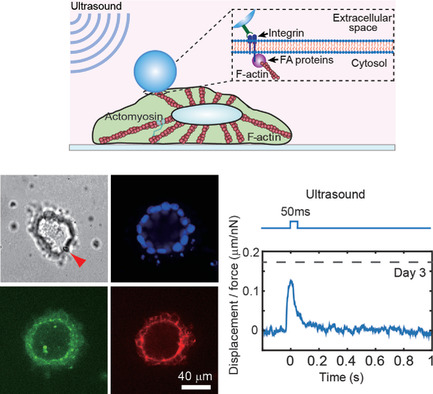
Ultrasound actuation of functionalized microbubbles targeted to integrin (acoustic tweezing cytometry) is employed for in situ measurement of cell stiffness during human embryonic stem cell neural differentiation and morphogenesis in 3D embryogenesis model. The results suggest that cell stiffness changes not only due to 3D spatial organization, but also with cell fate change.
Full Papers
Re- and Preconfigurable Multistable Visible Light Responsive Surface Topographies
- First Published: 24 October 2018
Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in CuSbSe2 Nanoplate-Based Pellets by Texture Engineering and Carrier Concentration Optimization
- First Published: 21 October 2018
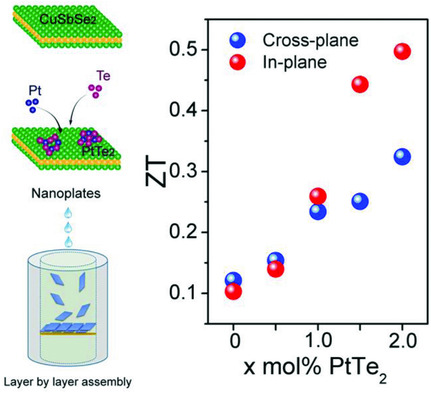
Enhanced thermoelectric performance of CuSbSe2 based pellets with highly oriented single crystalline nanoplates are achieved by texture engineering and carrier concentration optimization, an orientation factor of ≈0.8 for (00l) facets and a high ZT value of 0.50 at 673 K are reported for CuSbSe2-2.0 mol% PtTe2 sample along the primary surface of the pellets (in-plane direction).
A NanoFlare-Based Strategy for In Situ Tumor Margin Demarcation and Neoadjuvant Gene/Photothermal Therapy
- First Published: 07 October 2018
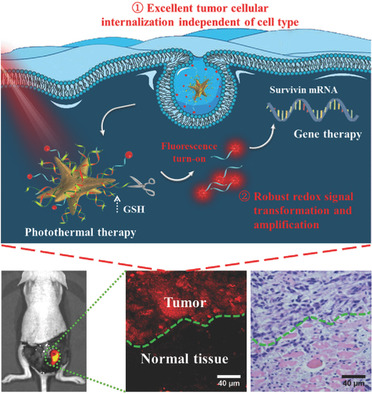
A NanoFlare-based strategy for in situ tumor margin demarcation and neoadjuvant gene/photothemal therapy is reported. In virtue of anisotropic antisense oligonucleotides-spike nanostructure, the NanoFlare can enter tumor cells universally regardless of cell types and produce redox-activated fluorescence signals. The NanoFlare enables accurate intraoperative margin demarcation of differetn tumors and efficient gene/photothermal neoadjuvant therapy in vivo.
Charge Density Waves Driven by Peierls Instability at the Interface of Two-Dimensional Lateral Heterostructures
- First Published: 29 October 2018
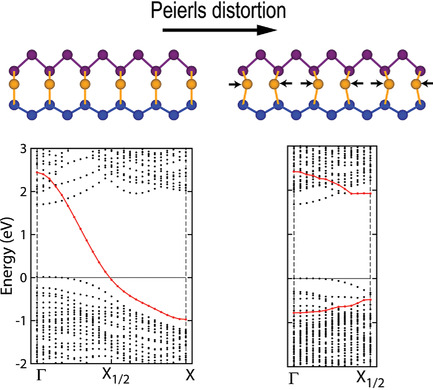
Charge density wave (CDW) formation at the one-dimensional interface embedded in a lateral two-dimensional (2D) heterostructure comprising blue and black phosphorene is found. The CDW formation is driven by the Peierls instability and substantially modifies the band alignment of the heterostructure. These findings are applicable to other 2D lateral heterostructures and have important implications for their application.
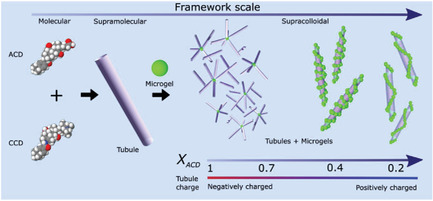
Sphere–Tubule Superstructures through Supramolecular and Supracolloidal Assembly Pathways
- First Published: 29 October 2018
Intracameral Delivery of Layer-by-Layer Coated siRNA Nanoparticles for Glaucoma Therapy
- First Published: 23 October 2018
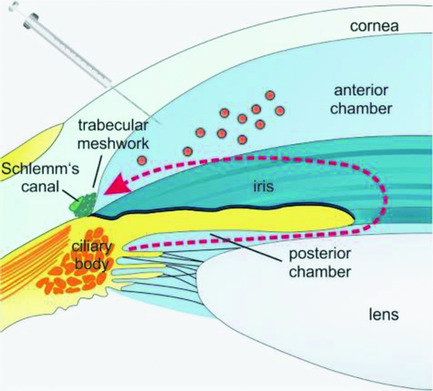
Nanoparticles loaded with siRNA against connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and coated with a final layer of hyaluronan (HA) are proposed as a novel and causative approach for glaucoma treatment. HA-coated nanoparticles deeply penetrate into the outflow region of porcine, murine, and human eyes ex vivo and have the capability of silencing CTGF in cultures of human trabecular meshwork cells.
Flexible Fire-Resistant Photothermal Paper Comprising Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires and Carbon Nanotubes for Solar Energy-Driven Water Purification
- First Published: 29 October 2018
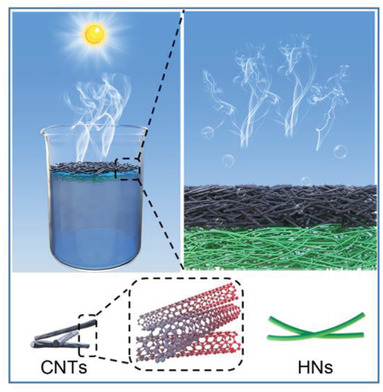
Highly flexible fire-resistant photothermal paper is fabricated using ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires and carbon nanotubes for highly efficient solar energy-driven seawater desalination and wastewater purification, it has a high performance in recycling and long-time usage, and it has promising application in the production of clean drinkable water from seawater and wastewater to mitigate the water scarcity crisis.
Tumor Starvation Induced Spatiotemporal Control over Chemotherapy for Synergistic Therapy
- First Published: 29 October 2018
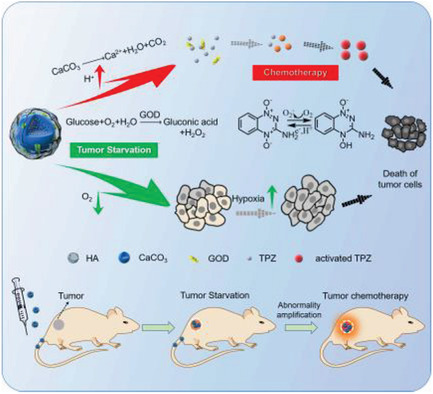
This study reports a multitherapy modality of tumor starvation triggered synergism with sensitized chemotherapy. Tumor starvation confers not only spatial control over the chemotherapeutic exposure just to tumors but also the temporal control over timely chemotherapy initiation to match the occurrence of hypoxia amplification needed for chemotherapy reinforcement, thus benefiting perfect synergism between starvation therapy and chemotherapy.
In Situ Fabrication of Heterostructure on Nickel Foam with Tuned Composition for Enhancing Water-Splitting Performance
- First Published: 11 October 2018
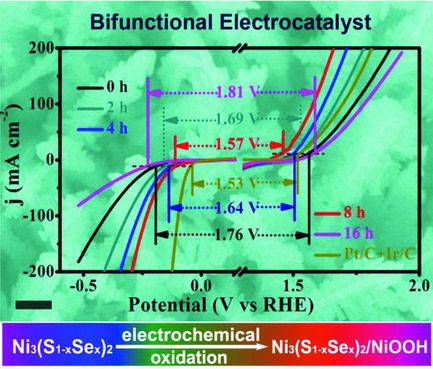
A novel core–shell Ni3(S1−xSex)2@NiOOH heterostructure hybrid is in situ fabricated on nickel foam via a facile and stepwise controllable strategy, presenting superior hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions bifunctional and water-splitting performance owing to the vertical standing architecture, effective electron transfer, exposed abundant active sites, and synergistically interfacial enhancement from two components.
Phosphate Species up to 70% Mass Ratio for Enhanced Pseudocapacitive Properties
- First Published: 05 November 2018
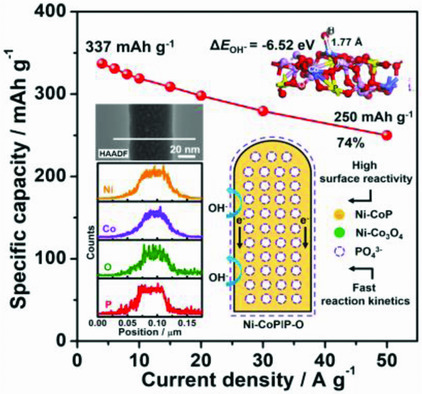
Highly proportioned and well-dispersed phosphate species with superwettability and strong affinity for OH− in the electrolyte are leveraged to comprehensively enhance the redox reaction kinetics and capacitive contribution of the highly conductive mesoporous Ni-doped CoP nanowire matrix. The nanohybrids can deliver an ultrahigh specific capacity of 250 mAh g−1 at the high current density of 50 A g−1.
A Nonpresodiate Sodium-Ion Capacitor with High Performance
- First Published: 30 October 2018
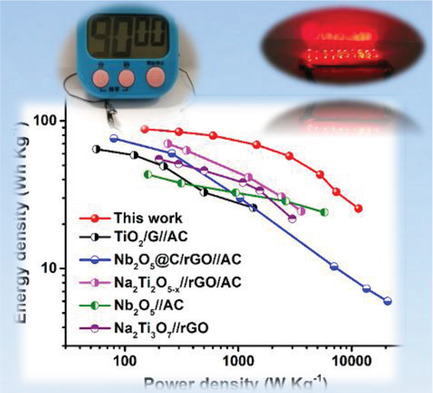
A high-performance sodium-ion capacitor is fabricated using Fe1−xS nanoplates as the anode material and an ether-based electrolyte. Due to the lower bonding energy between sodium ions and the solvent and the smaller sodium diffusion barriers in ether-based electrolytes, the hybrid device exhibits a high energy and power density as well as excellent cycling stability, without the presodiation process.
General Nondestructive Passivation by 4-Fluoroaniline for Perovskite Solar Cells with Improved Performance and Stability
- First Published: 12 November 2018
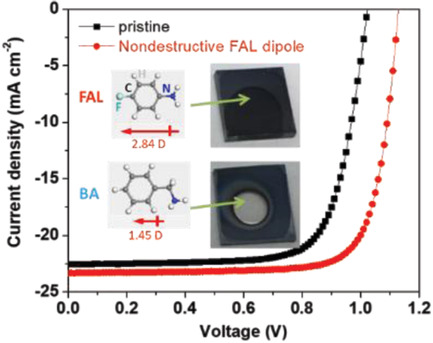
A general nondestructive passivation approach is developed for perovskite solar cells by using 4-fluoroaniline (FAL). FAL is not only an antisolvent surface modifier, but also a large dipole molecule with a directional field to separate charge at the interface, thus delivering a 20.48% power conversion efficiency with improved stability. Micro/time-resolved photoluminescence reveals the impact picture of boundary on the local carriers after passivation.
Quinic Acid-Conjugated Nanoparticles Enhance Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors via Interactions with Endothelial Selectins
- First Published: 09 November 2018
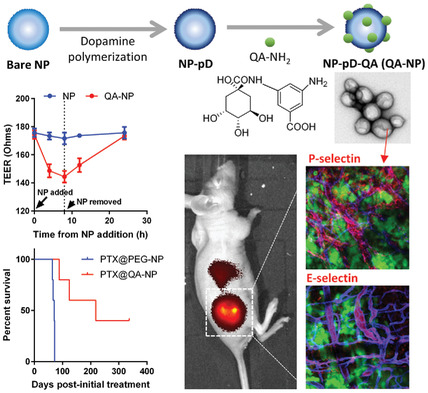
To overcome the endothelial barrier when accessing tumors, polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) are modified with a quinic acid (QA) derivative, synthetic mimic of selectin ligands, via polydopamine. The QA-decorated NPs interact with selectin-overexpressing endothelial cells and induce a transient increase in endothelial permeability to translocate across the endothelial layer. The QA-NPs reach selectin-upregulated tumors, achieving greater tumor accumulation and paclitaxel delivery than polyethylene glycol-decorated NPs.