Journal list menu
 Issue
IssueWater Environment Research: Volume 94, Issue 1
January 2022
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
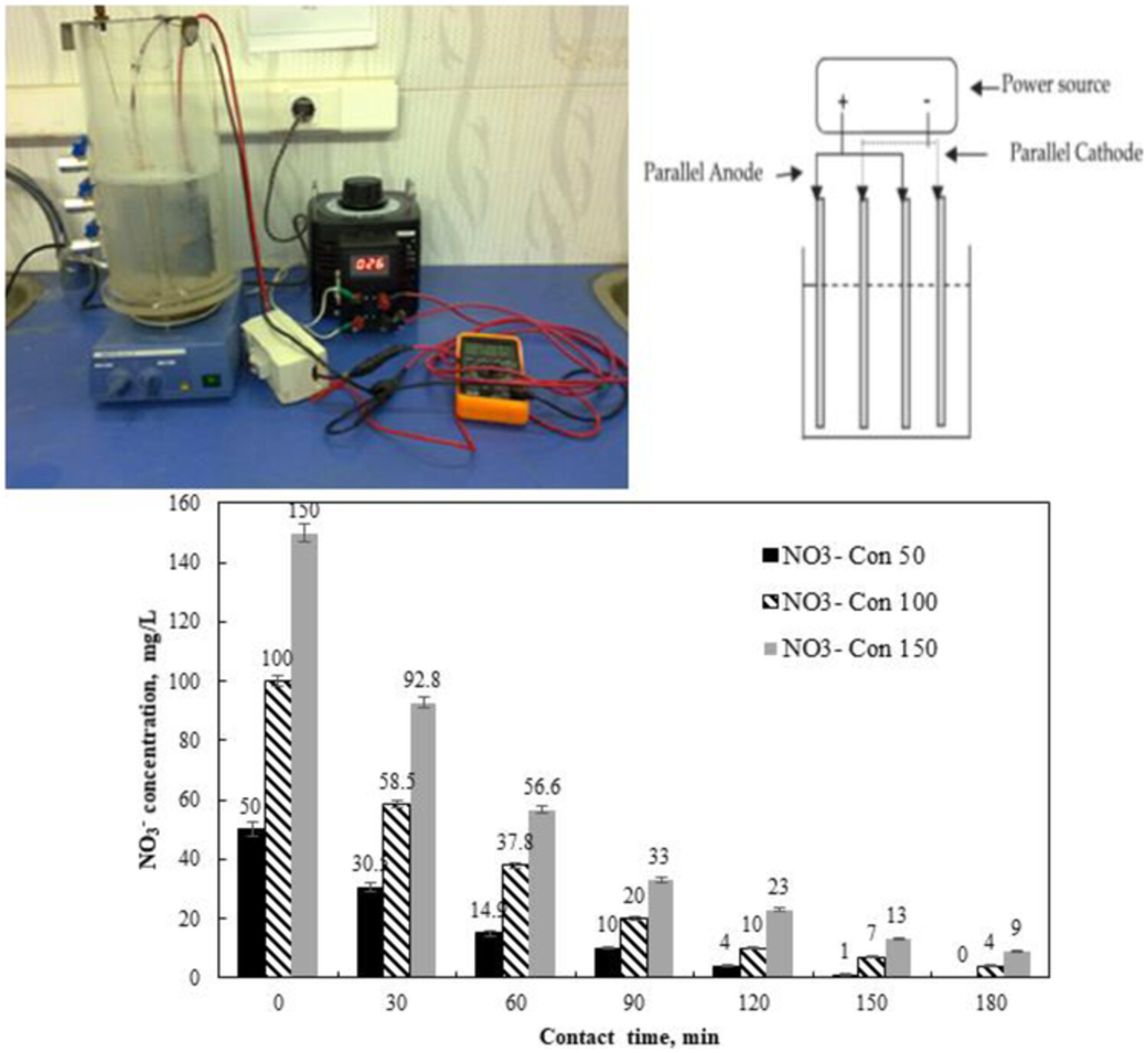
Optimization of the electrochemical reduction process and ORP effects in nitrate removal
- First Published: 15 November 2021
REVIEWS
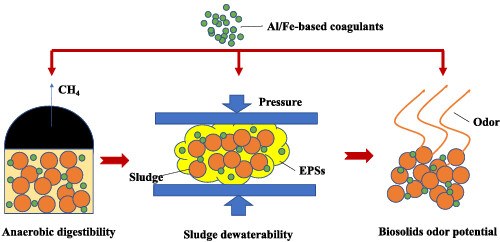
Impacts of aluminum- and iron-based coagulants on municipal sludge anaerobic digestibility, dewaterability, and odor emission
- First Published: 29 December 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Decolorization of textile wastewater by electrooxidation process using different anode materials: Statistical optimization
- First Published: 29 December 2021
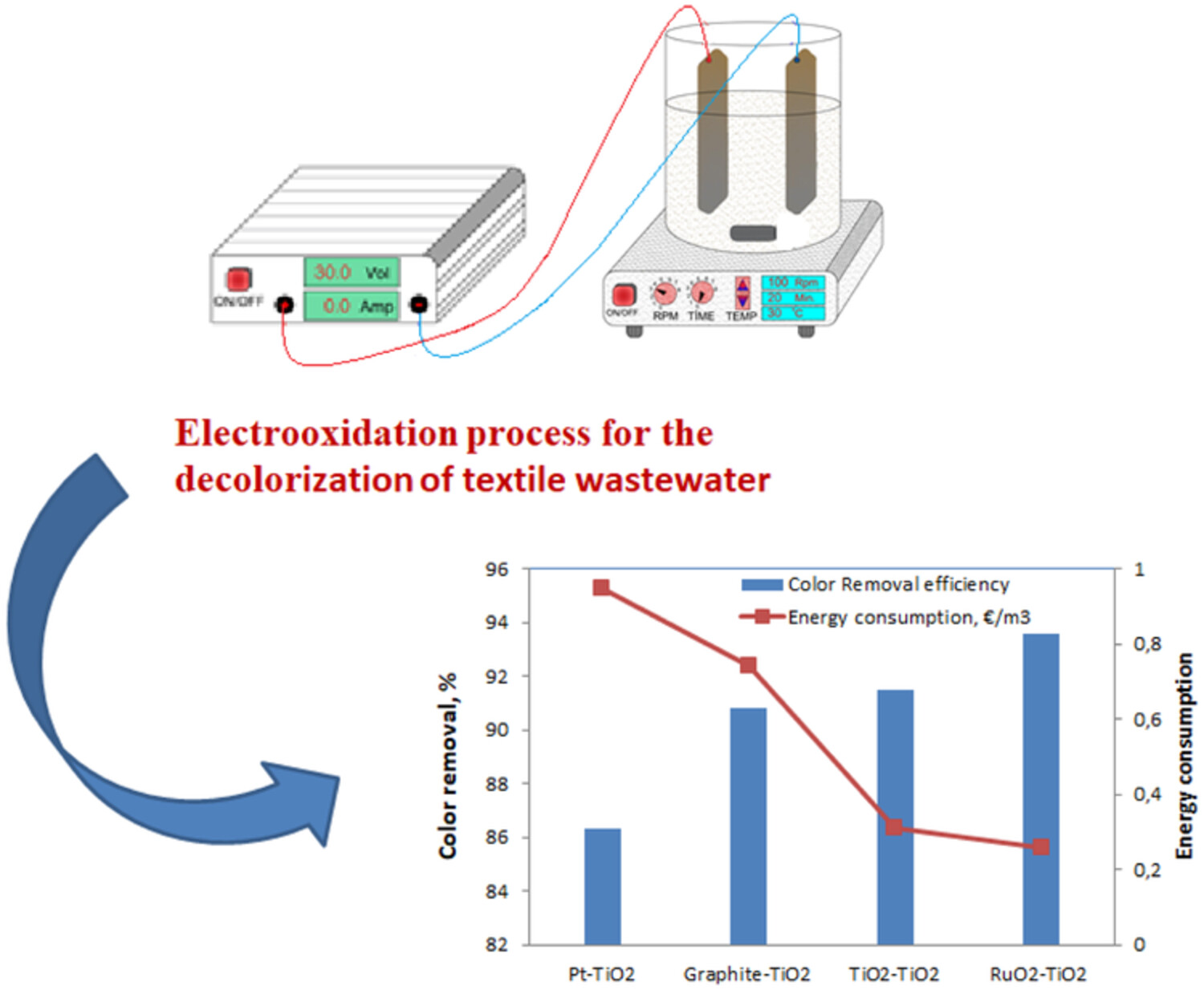
In this study, it is aimed to investigate the applicability of the electrooxidation process on the decolorization of real textile wastewater using four different anodic materials. Platinized titanium (abbreviated as platine; in fact, it consists of a titanium electrode covered with a nano-layer of platinum), ruthenium dioxide (RuO2), titanium dioxide (TiO2), and graphite was tested for their anodic contribution, noting that TiO2 electrode was used as a cathode. Operating parameters such as pH, applied current, and electrolysis time were systematically optimized using the response surface methodology (RSM) with the Box–Behnken experimental design (BBD) to obtain the highest color removal efficiency.
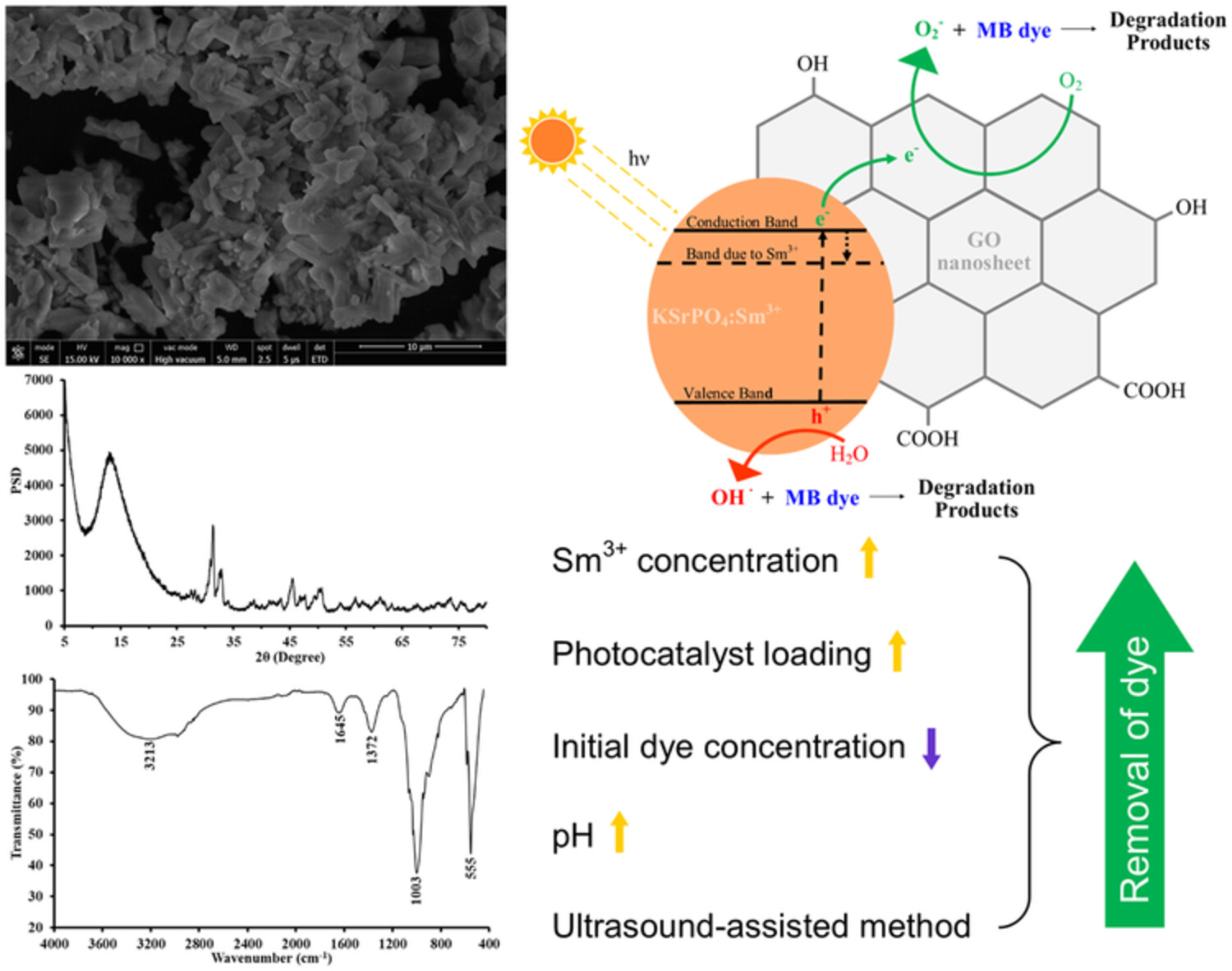
Sonochemical preparation and characterization of Sm-doped GO/KSrPO4 nanocomposite photocatalyst for degradation of methylene blue dye
- First Published: 29 December 2021
Water recovery from yarn fabric dyeing wastewater using electrochemical oxidation and membrane processes
- First Published: 26 December 2021
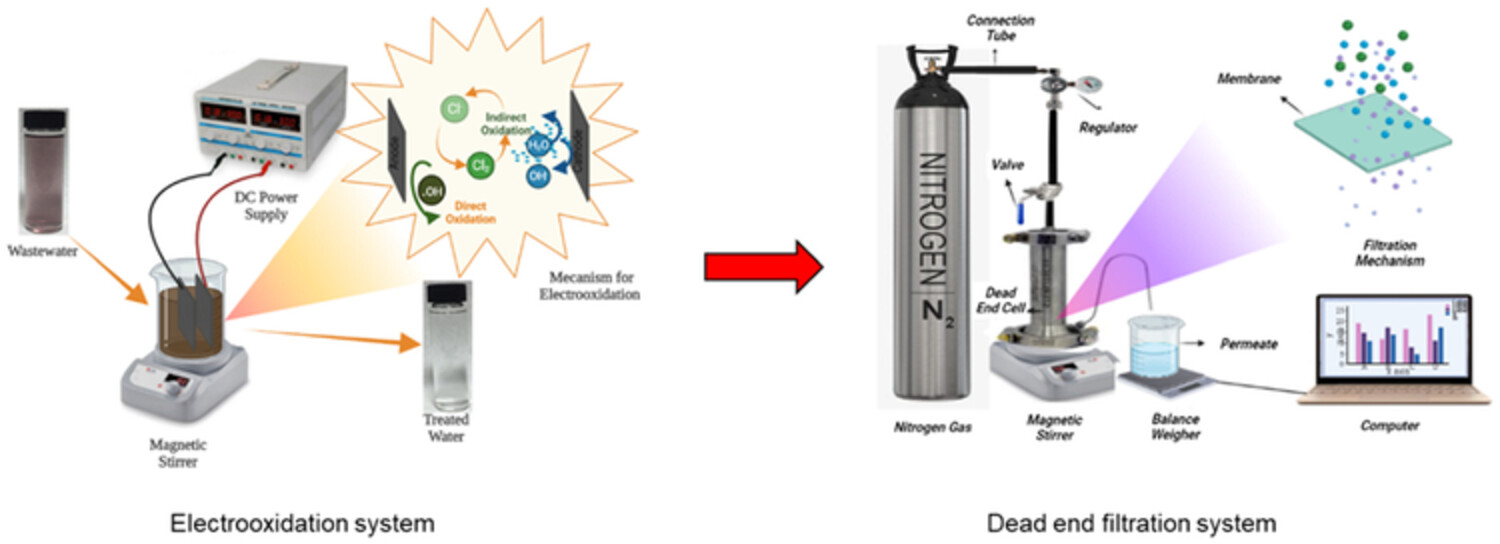
Effective electrochemical oxidation and different membrane filtration systems were applied for the treatment of yarn fabric dyeing wastewater in terms of COD, color, salinity and conductivity removals. The Use of reverse osmosis membrane demonstrated relatively complete removal of color concentration and 98% of COD elimination. The obtained water could be recycled back to the process in that way offering economic profits by decreasing water consumption and wastewater treatment cost.
Ecotoxicological and human health risk assessment of selected pesticides in Kurose River, Higashi-Hiroshima City (Japan)
- First Published: 07 December 2021
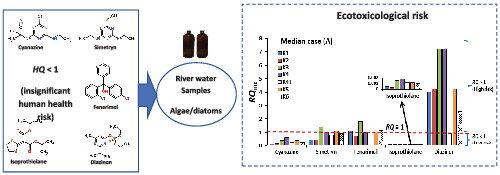
To assess the impact of the some pesticides on the Kurose River, Japan, an integrated approach combining monitoring, assessment of environmental toxicity and human risk was used. Cyanazine was the most commonly detected, followed by simetryn and diazinon. Average concentrations of the selected pesticides were generally higher in spring followed by summer, autumn and winter. The study showed that there were unacceptable environmental toxicity risks for diazinon, cyanazine, simetryn and fenarimol, while the environmental risks for isoprothiolane were low. For adults and children, the risk was highest for diazinon, while isoprothiolane showed the lowest risk to humans.
Bio-purification of domestic wastewater through constructed wetland planted with Paspalidium flavidum
- First Published: 02 January 2022
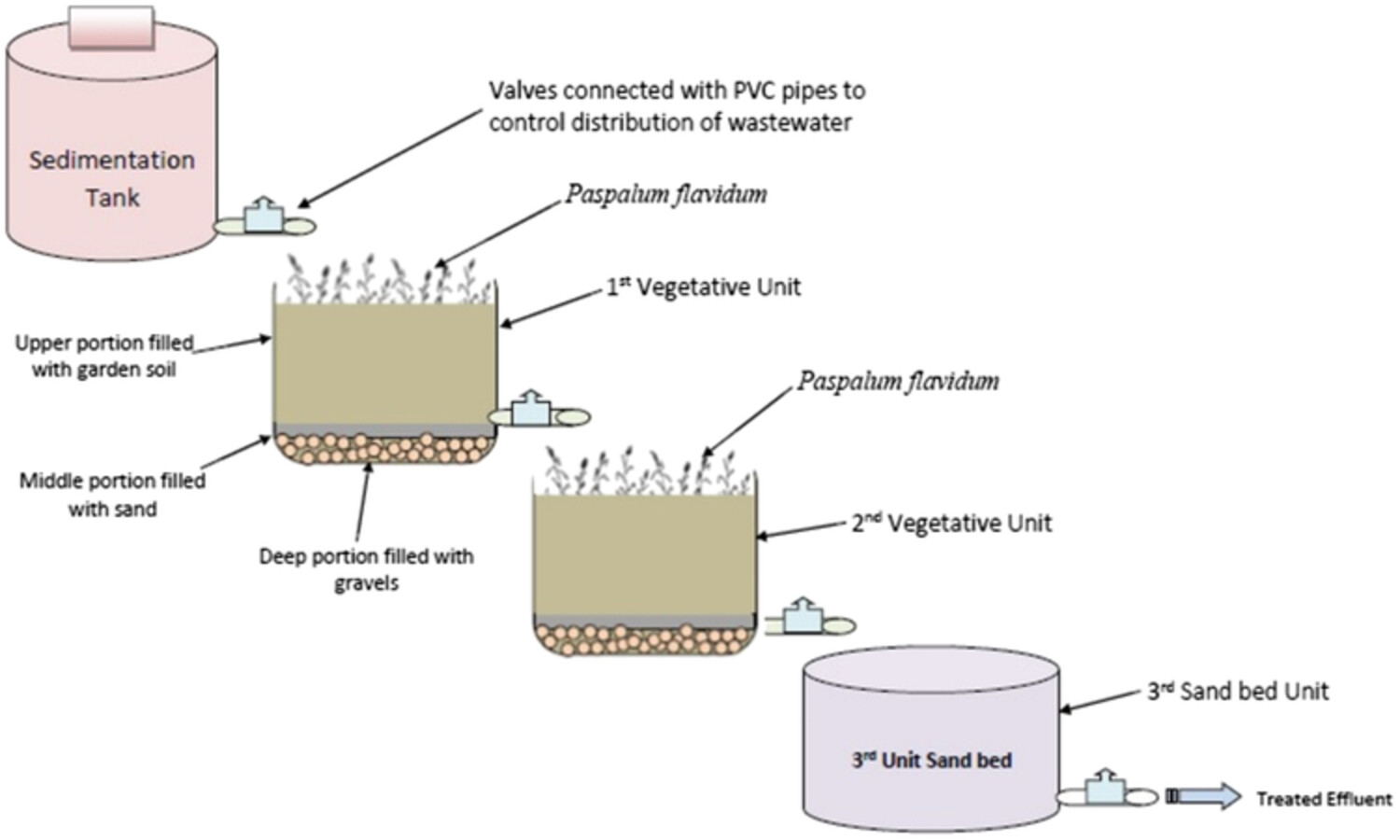
In this work, laboratory scale constructed wetland (CW) was designed for the treatment of domestic waste water. The performance evaluation of CW planted with Paspalidium flavidum was recorded at different temperatures and retention times. Various physico-chemical parameters were analyzed and the treatment efficiencies were recorded as COD (59.7–65.6%), TDS (59.6–76.8%), TSS (64.9–76.7%), and turbidity (72.7–91.6%), respectively.
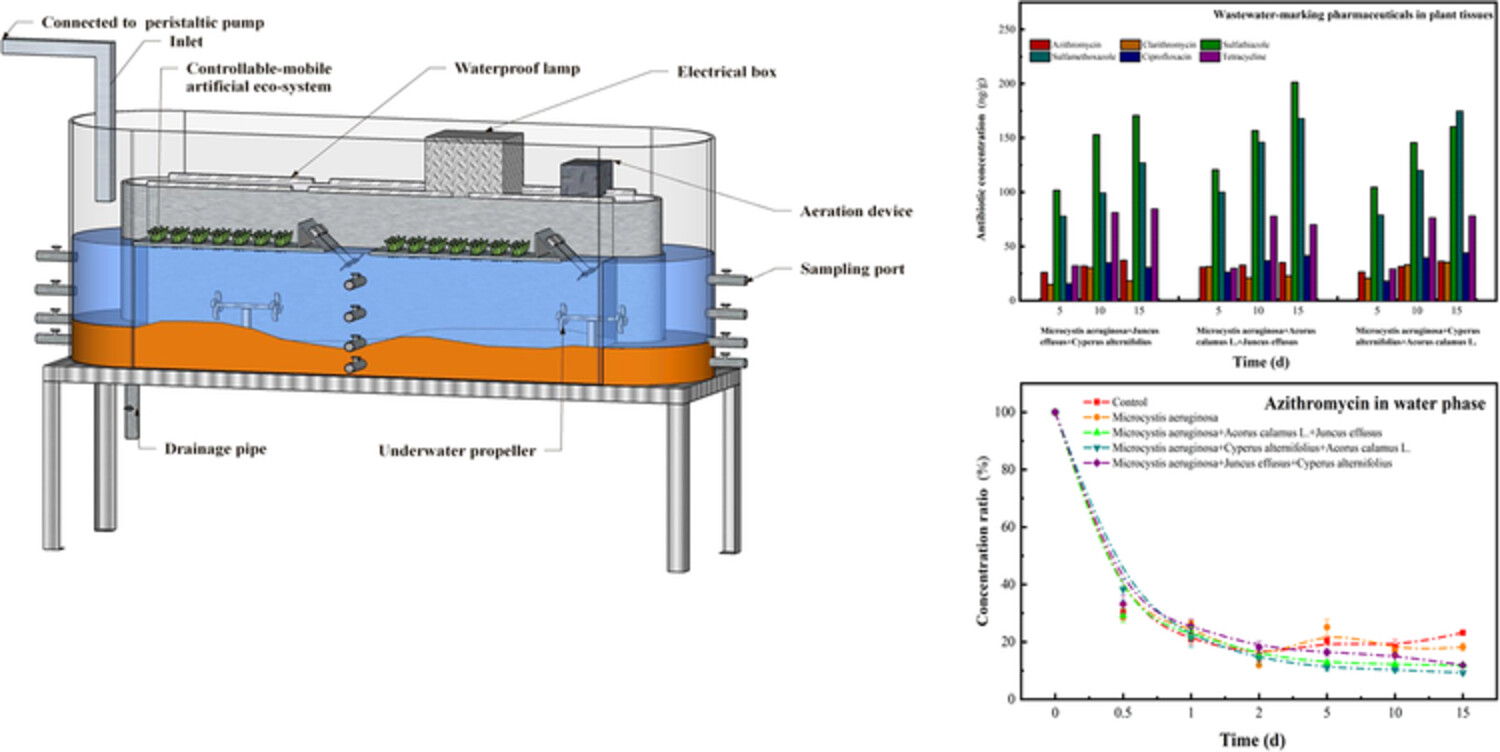
Antibiotic fate in an artificial-constructed urban river planted with the algae Microcystis aeruginosa and emergent hydrophyte
- First Published: 02 December 2021
Life-cycle assessment of full-scale membrane bioreactor and tertiary treatment technologies in the fruit processing industry
- First Published: 15 November 2021
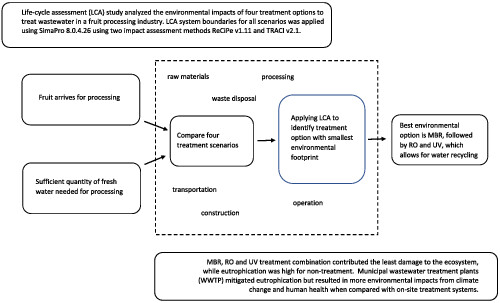
Life-cycle assessment (LCA) study was completed to analyze the environmental impacts of four treatment options to treat wastewater in a fruit processing industry. The best environmental option was MBR, followed by RO and UV, which allows for water recycling. Treating water at a municipal wastewater treatment plant mitigated eutrophication but resulted in more environmental impacts with on-site treatment systems.
Optimization of fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution over mesoporous titania-alumina composites using Taguchi method
- First Published: 20 November 2021
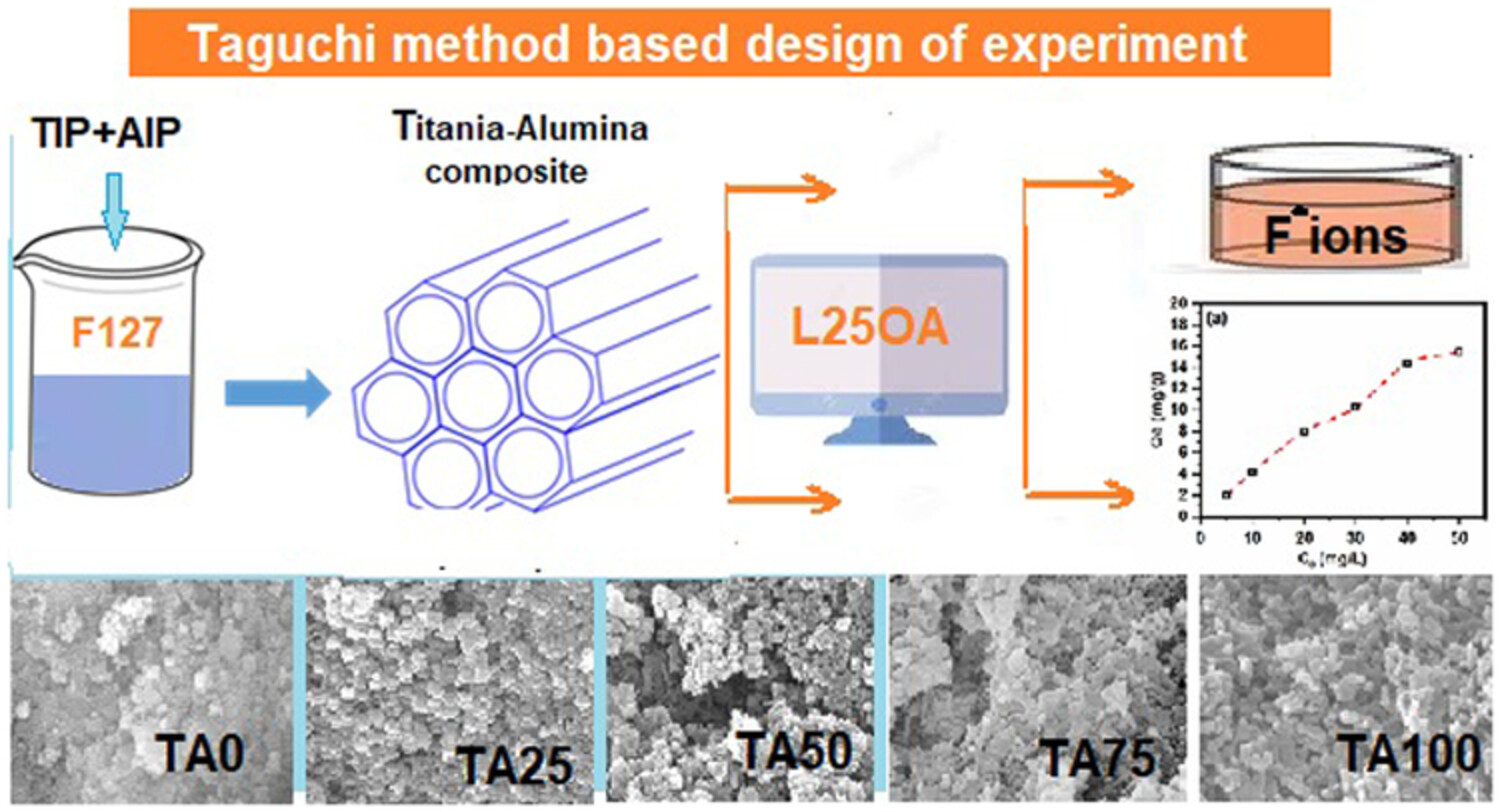
The synthesis of mesoporous Ti-Al mixed oxide from TIP and AIP and its application in flouride removal from waste water wherein the optimization is done using a L25 Taguchi design. Due to the mopholoical variation in Ti-Al mixed oxide depending on the composition of oxide, a variation in adsorption capacity is expected.
CASE STUDIES
Biological process architecture in continuous-flow activated sludge by gravimetry: Controlling densified biomass form and function in a hybrid granule–floc process at Dijon WRRF, France
- First Published: 21 November 2021
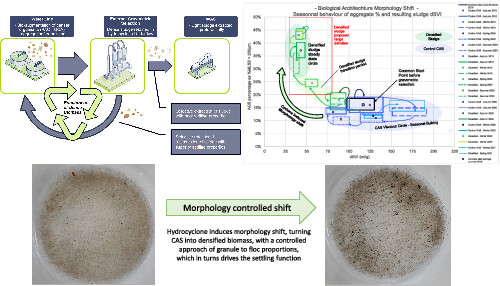
Conventional activated sludge was converted into a hybrid granule-floc process by external gravimetric selection. Wasting excess sludge through hydrocyclone overflow enabled a controlled shift of biomass morphology and progressively enriched granulated proportions, eventually leading to breaking the interannual bulking cycle and stabilizing year-round SVI low values.
SHORT COMMUNICATIONS
Preliminary study on the toxicological response of red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) on landfill leachate treated with Tin(IV) chloride and Jatropha curcas
- First Published: 29 November 2021
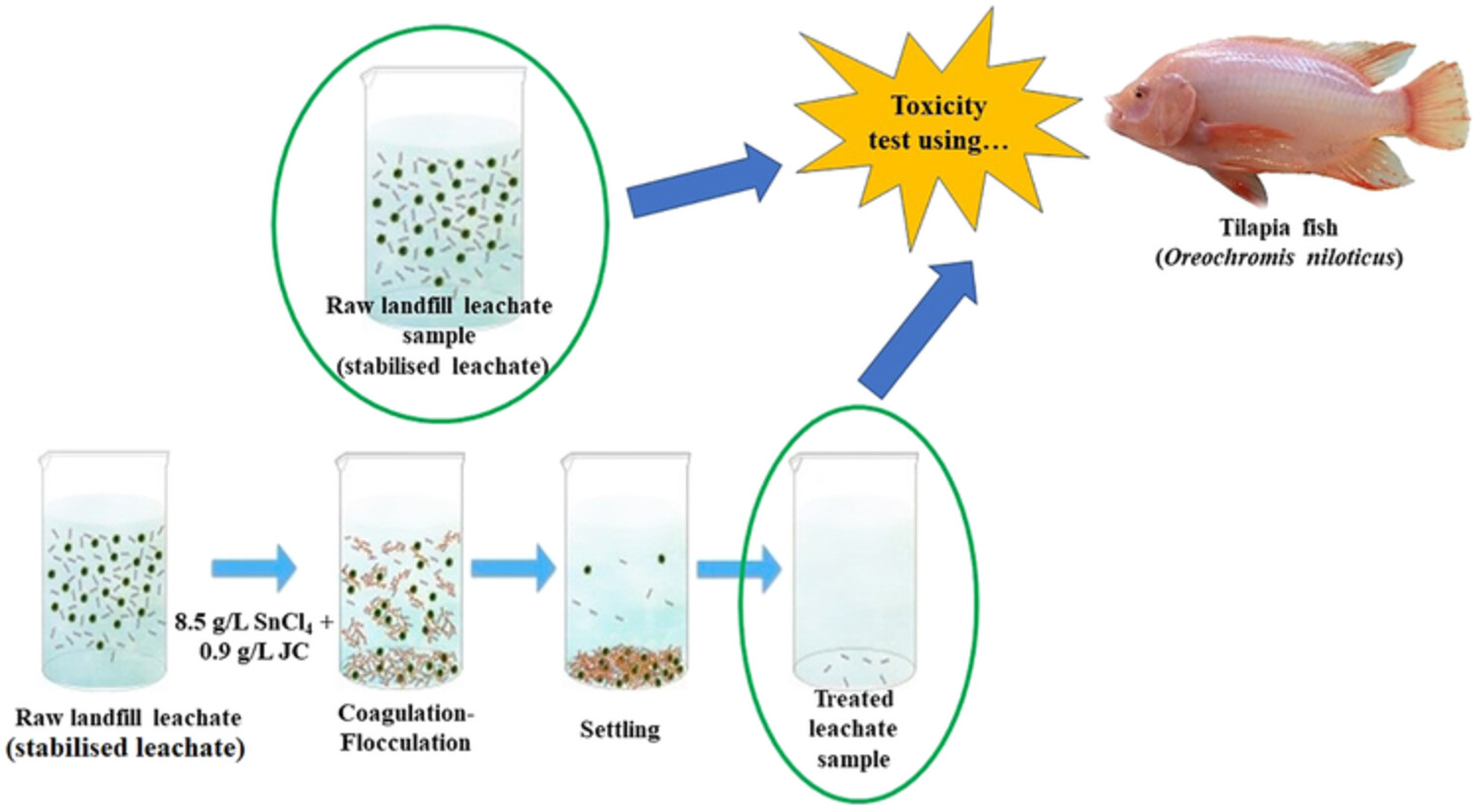
The acute toxicity level test using Tilapia fish was done to determine the toxicity effect of treated effluent after the coagulation-flocculation process by SnCl4 as a coagulant and JC seed as a flocculant. The results revealed that the fish tested with treated leachate using SnCl4 as a coagulant and JC as a flocculant were more viable and resistant compared to fish tested with raw leachate.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
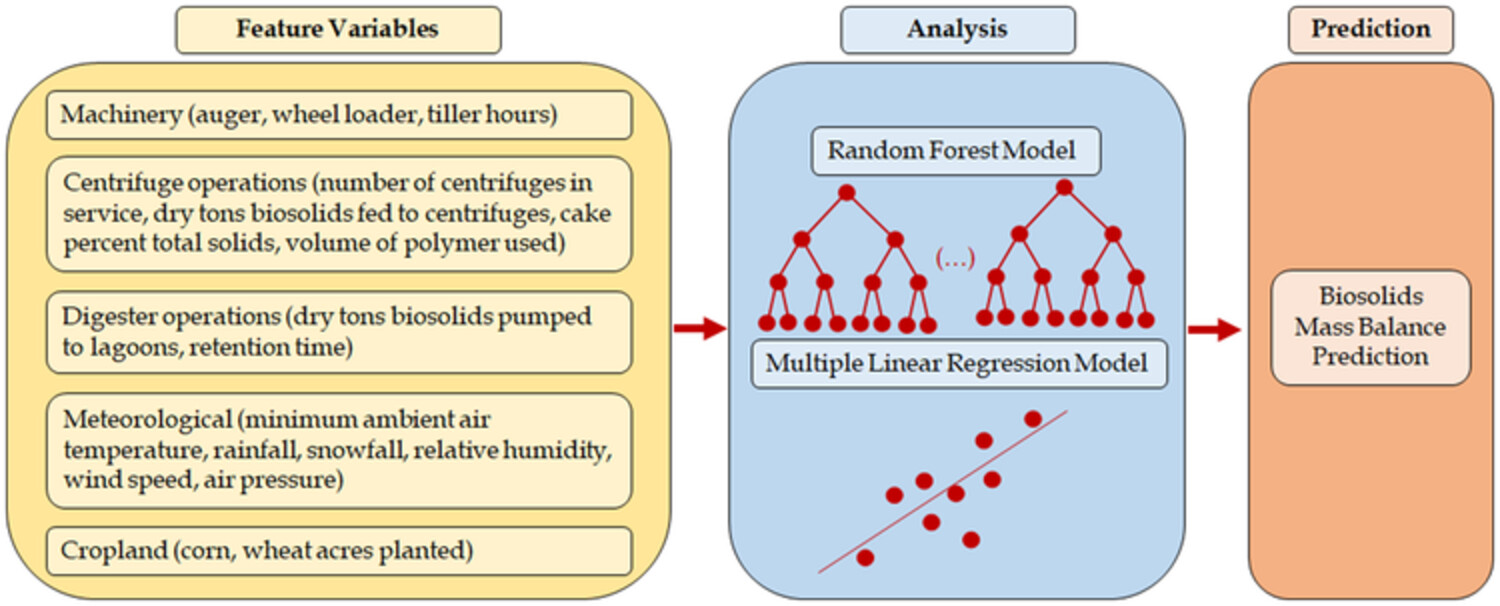
Comparison of random forest and multiple linear regression to model the mass balance of biosolids from a complex biosolids management area
- First Published: 30 November 2021
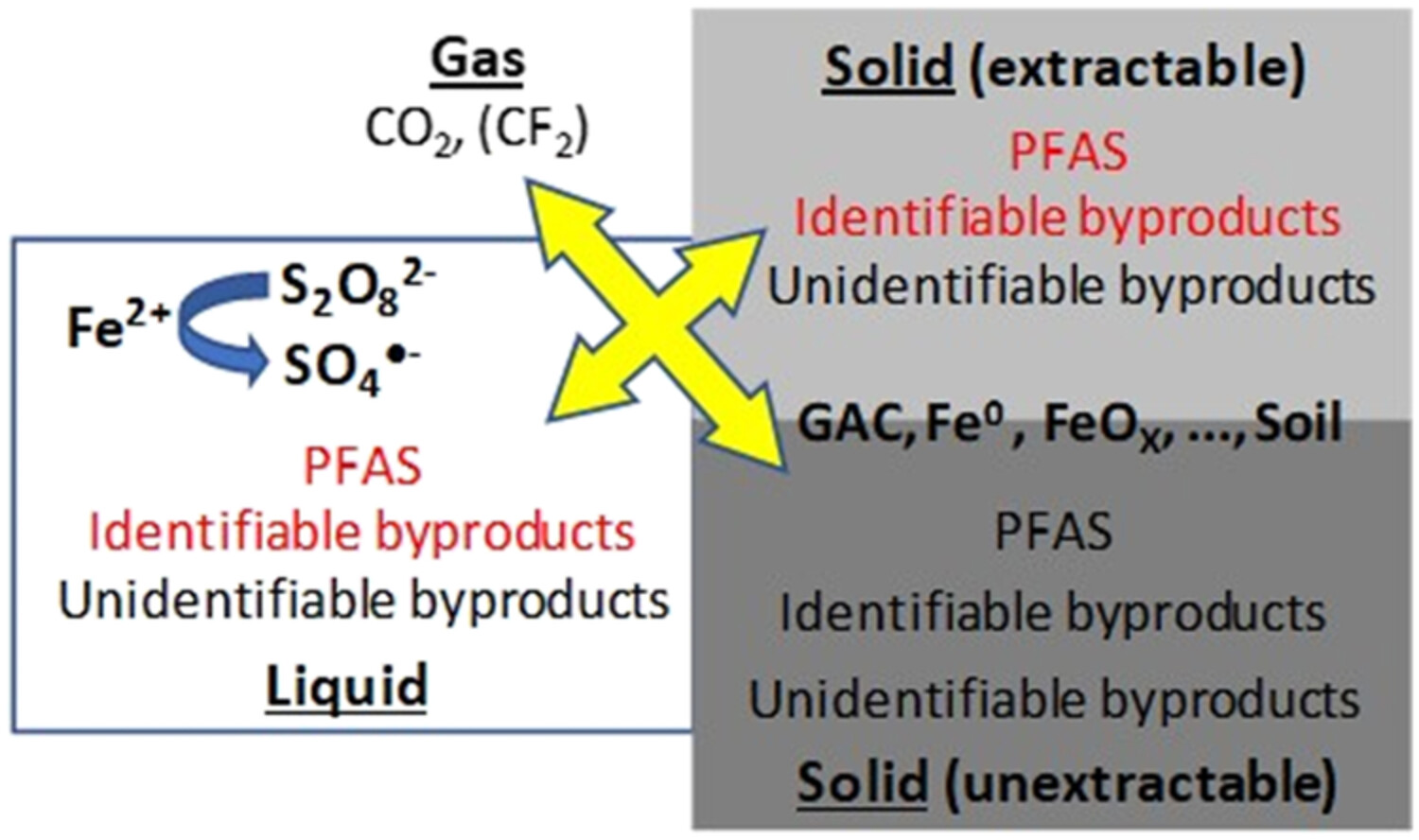
Removal of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and water/soil slurry using Fe0-modified reactive activated carbon conjugated with persulfate
- First Published: 01 December 2021
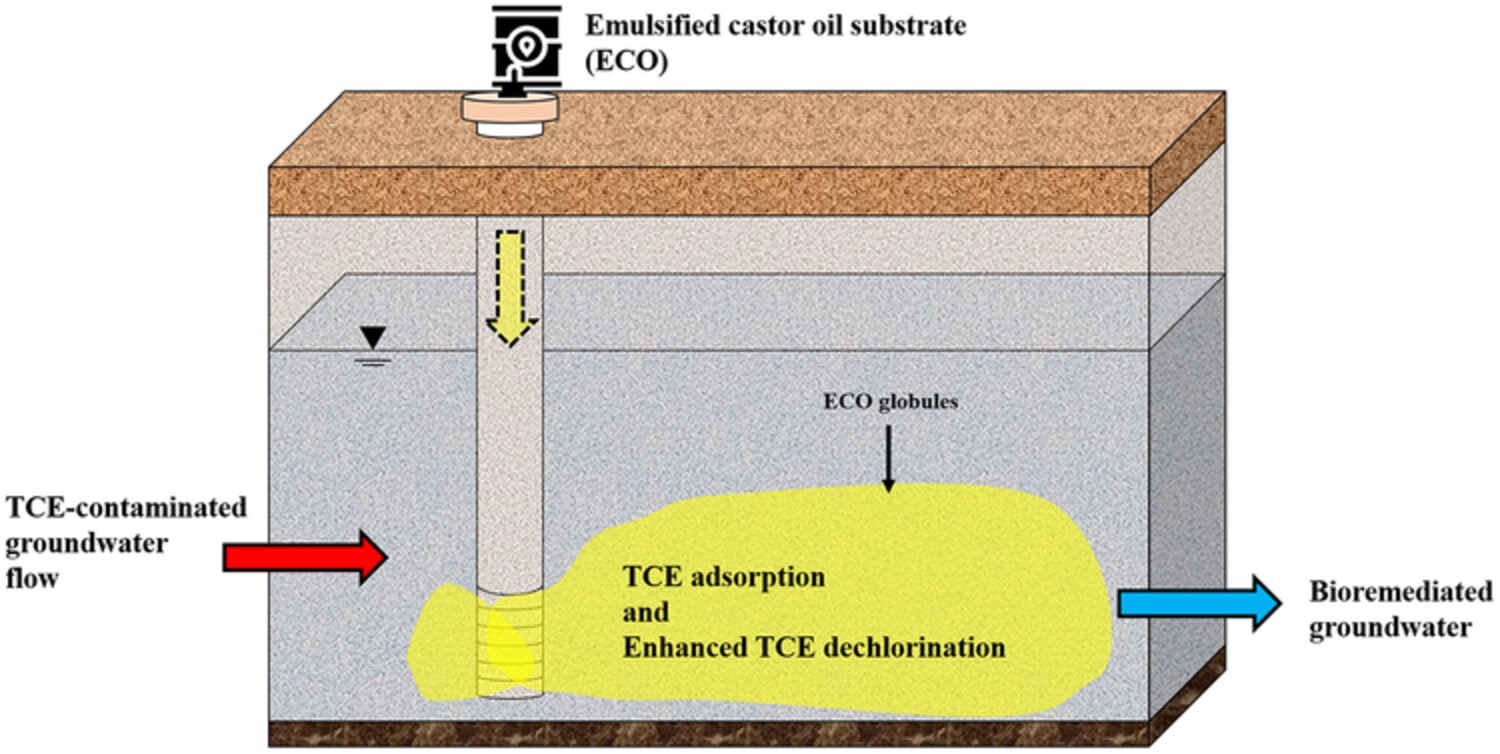
Bioremediation of trichloroethylene-polluted groundwater using emulsified castor oil for slow carbon release and acidification control
- First Published: 03 December 2021
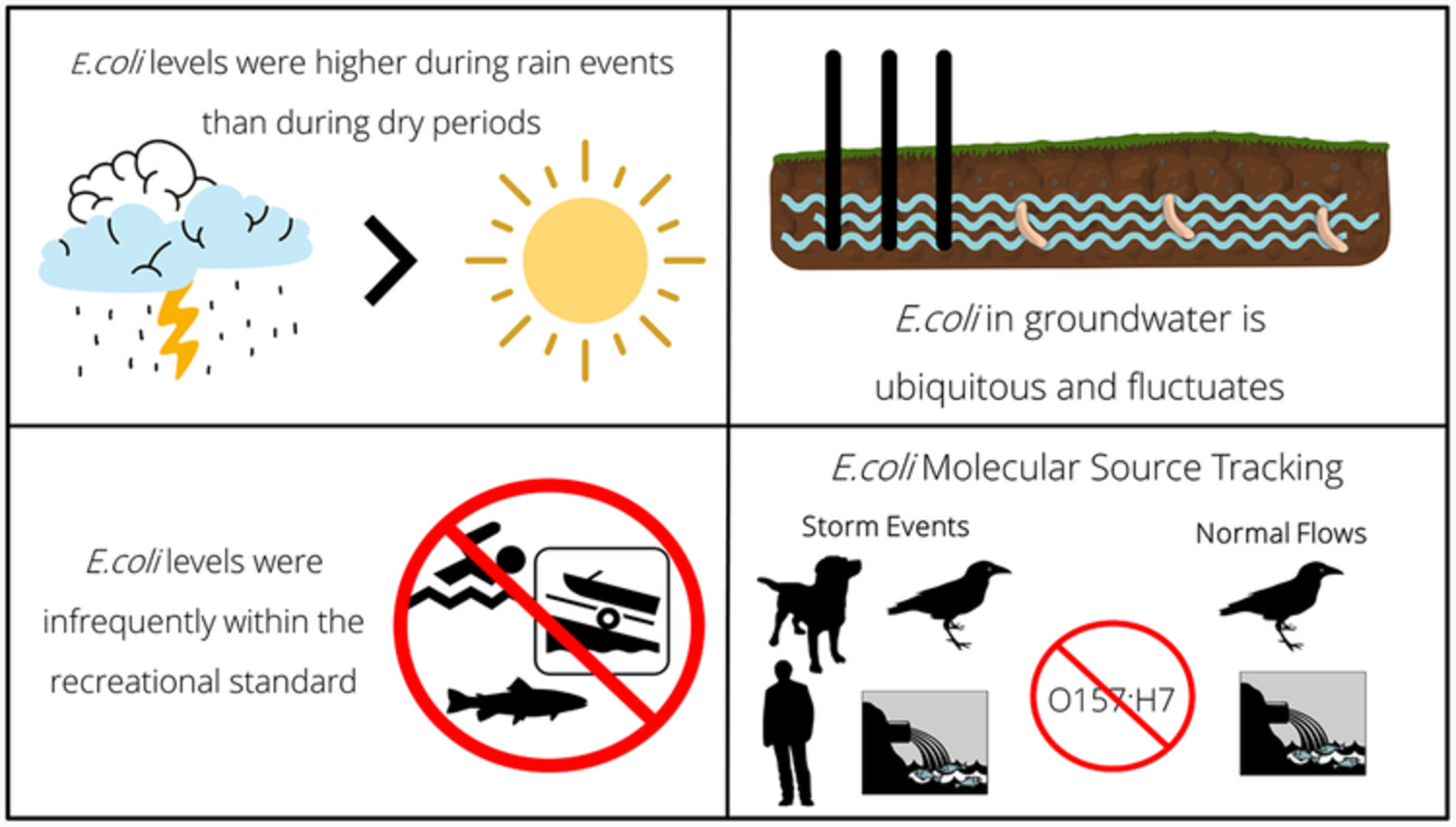
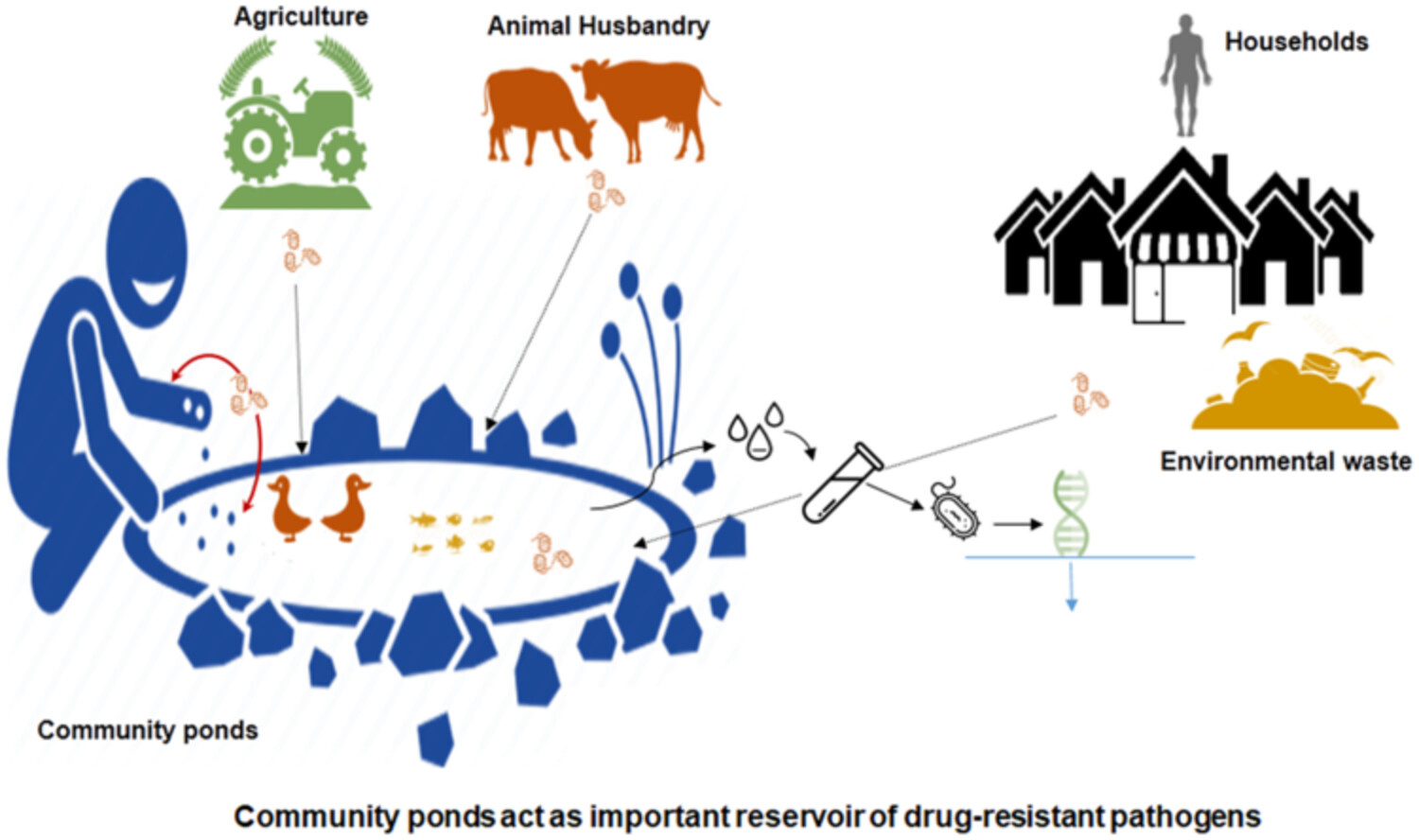
Escherichia coli levels and microbial source tracking in stormwater retention ponds and detention basins
- First Published: 06 December 2021
REVIEWS
A review on upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor: Factors affecting performance, modification of configuration and its derivatives
- First Published: 26 November 2021
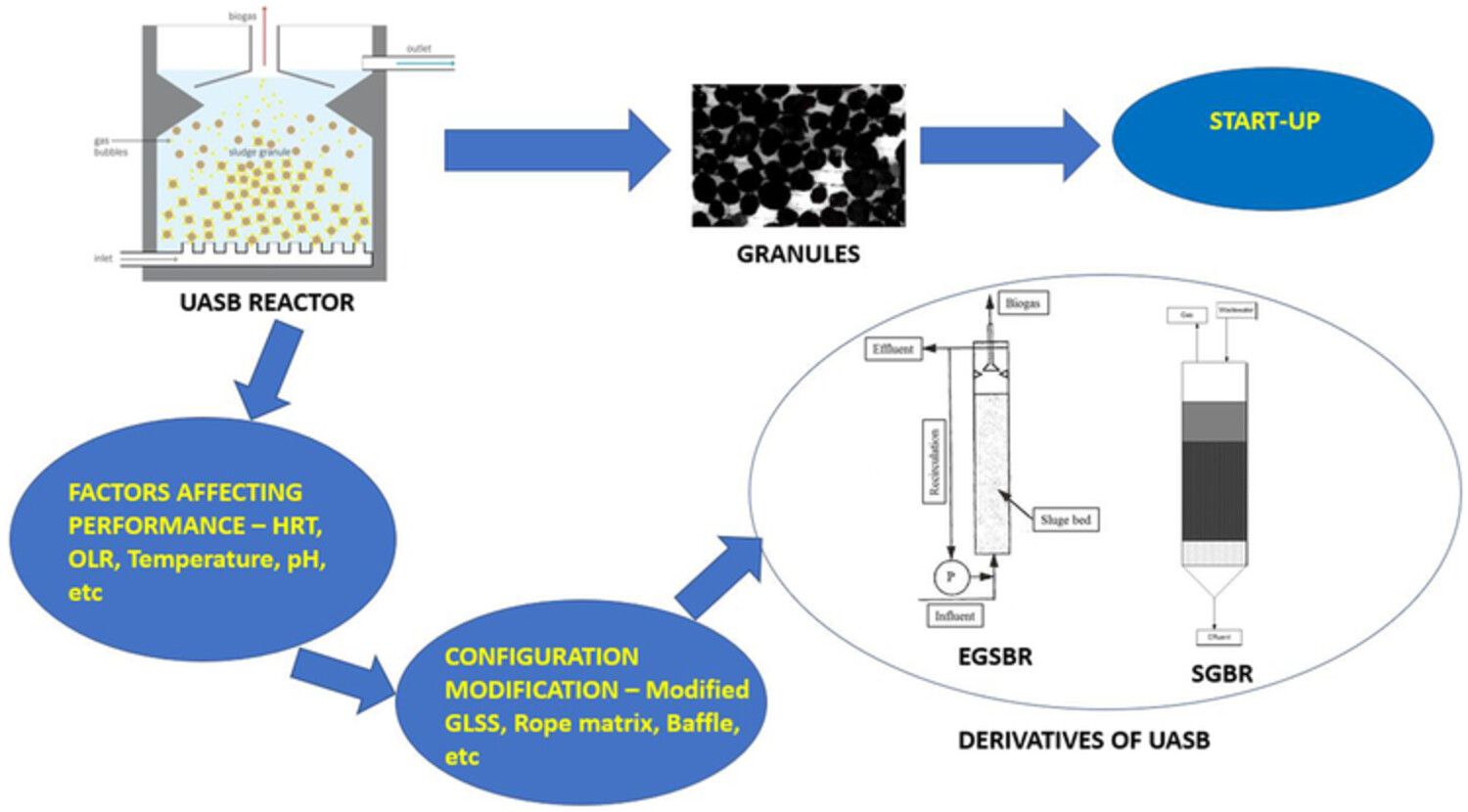
The figure shows a schematic view of the conventional UASB reactor, and to improve the performance of the reactor, development of granules should be given more importance. To make the granules suitable for the reactor, start-up has to be initiated. Furthermore, factors affecting performance of the reactor were also discussed. To improve the performance furthermore, various modifications of UASB by imposing variations in configuration were tried. It also shows schematic view of EGSBR and SGBR (derivatives of UASB).
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Influence of oxygen on the vinyl acetate elimination pathway and microbial community structure of methanogenic sludge
- First Published: 26 November 2021
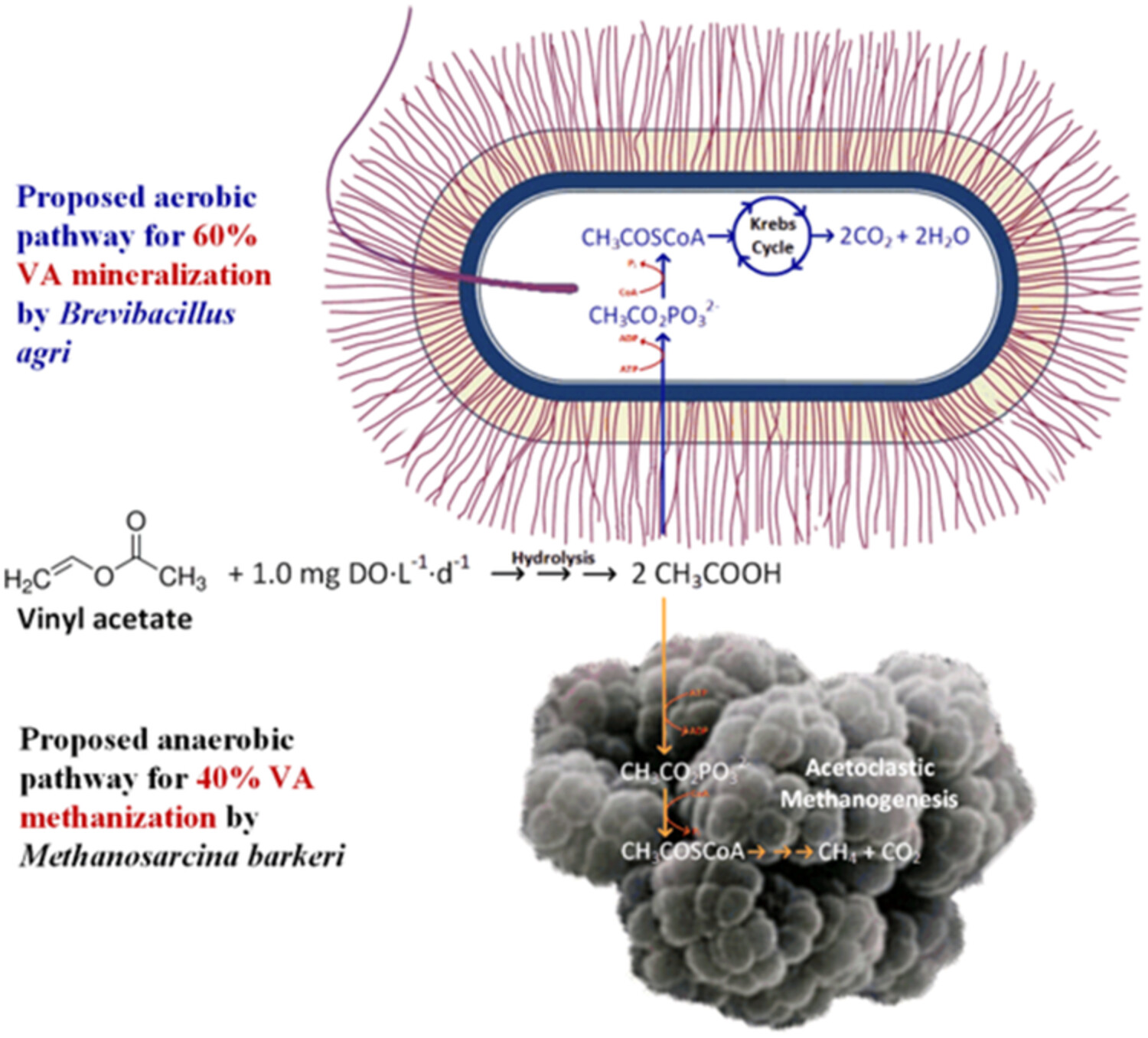
The presence of an aerobic bacterium could be relevant for accelerating VA hydrolysis, and archaea of the Methanosarcina genus are an important player on VA elimination. This evidence proposes the following route of elimination of VA with methanogenic sludge fed with oxygen, which arises from the mass balance of both batch and continuous assays.
Effectiveness of ozonation with zirconium and tin tetrachloride for stabilized anaerobic landfill leachate treatment
- First Published: 03 December 2021
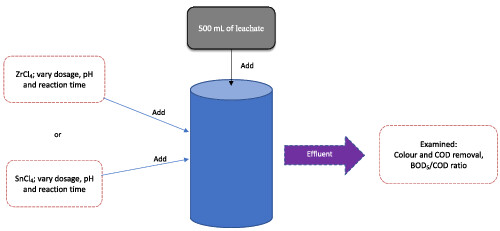
In this study, a combination of O3/ZrCl4 and O3/SnCl4 in SAL treatment was investigated. Three factors were varied; dosage of ZrCl4 and SnCl4, pH of sample and reaction time. The performances were evaluated based on colour, COD and BOD5/COD ratio. O3/ZrCl4 was the best combination that effectively removed COD and colour, up to 91.9% and 99.6%, respectively, and improved the leachate biodegradability in terms of the BOD5/COD ratio.
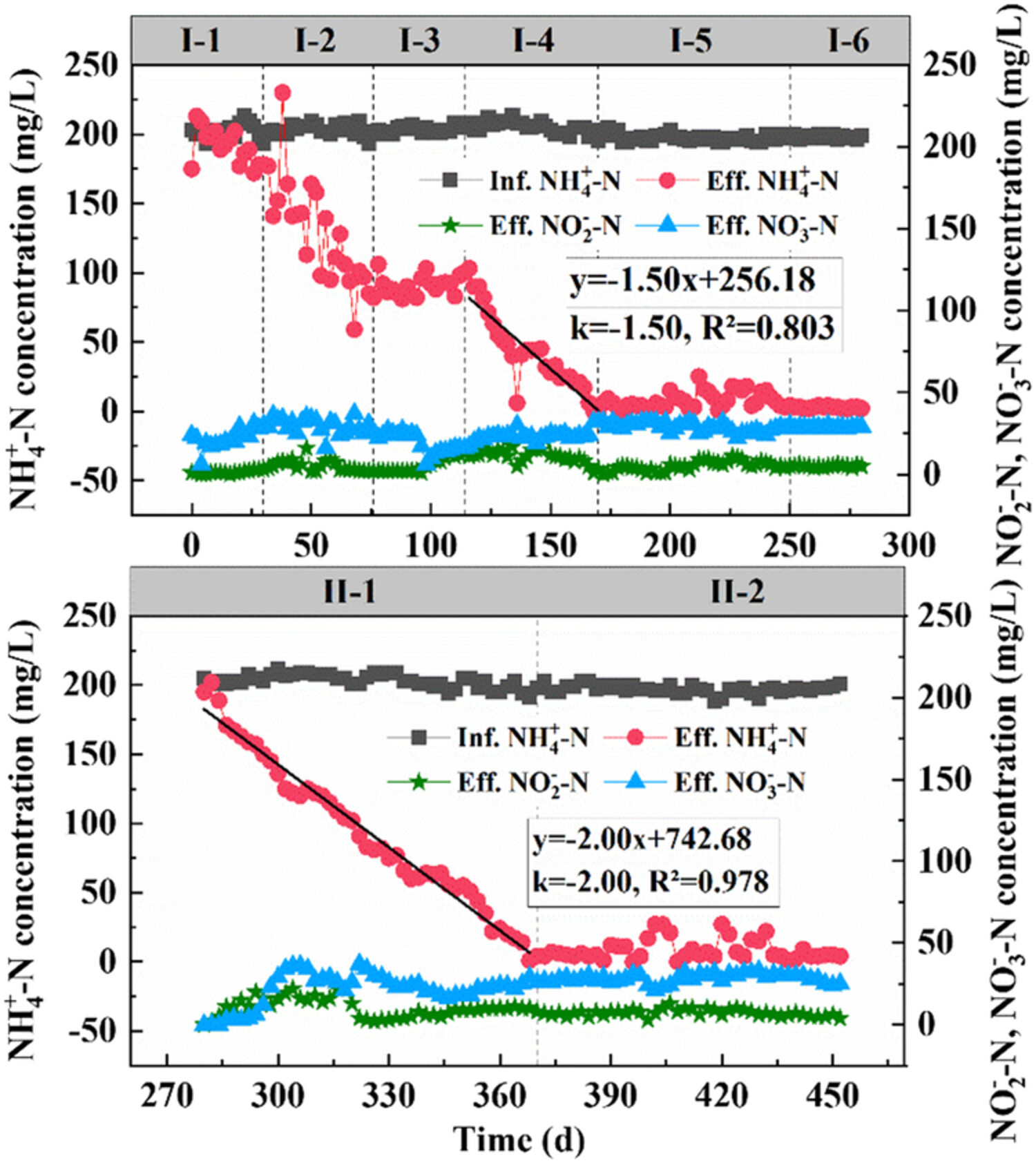
Effects of alkalinity addition with different strategies on CANON process: Start-up, performance, and microbial community
- First Published: 06 December 2021
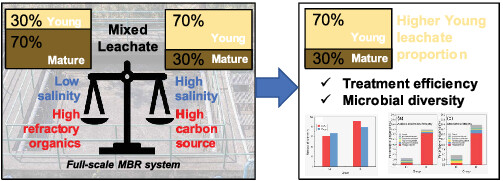
Microbial community response of the full-scale MBR system for mixed leachates treatment
- First Published: 12 December 2021
CASE STUDIES
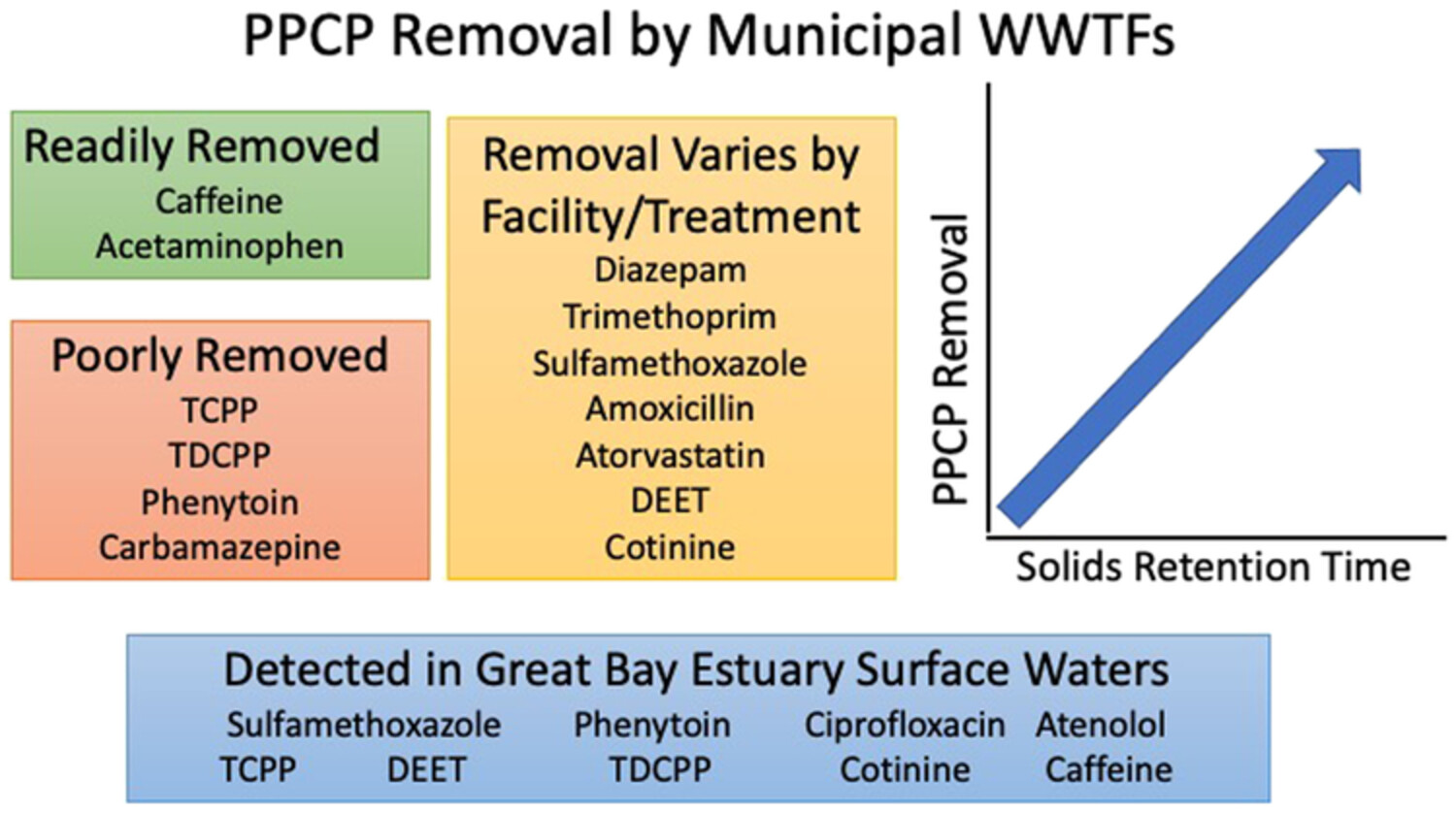
The fate and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products within wastewater treatment facilities discharging to the Great Bay Estuary
- First Published: 22 December 2021