Effectiveness of ozonation with zirconium and tin tetrachloride for stabilized anaerobic landfill leachate treatment
Siti Nor Farhana Zakaria
Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia
School of Civil Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Engineering Campus, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Contribution: Data curation (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hamidi Abdul Aziz
School of Civil Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Engineering Campus, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Solid Waste Management Cluster, Science and Technology Research Centre, Universiti Sains Malaysia Engineering Campus, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Correspondence
Hamidi Abdul Aziz, Solid Waste Management Cluster, Science and Technology Research Centre, Universiti Sains Malaysia Engineering Campus, 14300 Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia.
Email: [email protected]
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Funding acquisition (lead), Methodology (lead), Supervision (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorMotasem Y. D. Alazaiza
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, College of Engineering (COE), A'Sharqiyah University (ASU), Ibra, Oman
Contribution: Validation (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorSiti Nor Farhana Zakaria
Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia
School of Civil Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Engineering Campus, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Contribution: Data curation (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hamidi Abdul Aziz
School of Civil Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Engineering Campus, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Solid Waste Management Cluster, Science and Technology Research Centre, Universiti Sains Malaysia Engineering Campus, Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Correspondence
Hamidi Abdul Aziz, Solid Waste Management Cluster, Science and Technology Research Centre, Universiti Sains Malaysia Engineering Campus, 14300 Nibong Tebal, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia.
Email: [email protected]
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Funding acquisition (lead), Methodology (lead), Supervision (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorMotasem Y. D. Alazaiza
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, College of Engineering (COE), A'Sharqiyah University (ASU), Ibra, Oman
Contribution: Validation (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Landfill leachate can threaten the environment and human life. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the efficiency of ozone (O3), O3 with zirconium tetrachloride (O3/ZrCl4), and O3 with tin tetrachloride (O3/SnCl4) in remediating the stabilized anaerobic landfill leachate (SAL) from Alor Pongsu, Perak. Hydroxyl radical (OH•) is an important oxidizing agent in the ozonation process. Its presence was tested using tert-butyl alcohol. Results showed that using ZrCl4 and SnCl4 in ozonation boosted the generation of hydroxyl radical, thereby enhancing the oxidation process and pollutant removal inside the sample. The O3/ZrCl4 mix at chemical oxygen demand (COD) to ZrCl4 ratio of 1:1.5, pH 8–9, and 90-min reaction time resulted in the highest reduction rates of COD and color at 91.9% and 99.6%, respectively. All results demonstrated that the optimum performance occurred at alkaline conditions (pH > 8), proving that OH radicals primarily oxidized the pollutants through an indirect reaction pathway. The biodegradability (biochemical oxygen demand/COD) ratio was also considerably improved from 0.02 (raw) to 0.37 using O3/ZrCl4, compared with using O3 alone and using O3/SnCl4, which only recorded 0.23 and 0.28, respectively, after the treatment. The study demonstrated that O3/ZrCl4 was the most efficient combination.
Practitioner Points
- The O3/ZrCl4 recorded the highest COD and color removals.
- The O3/ZrCl4 combination also recorded higher OH• concentrations.
- The biodegradability of leachate (BOD5/COD ratio) improved from 0.02 to 0.37.
Graphical Abstract
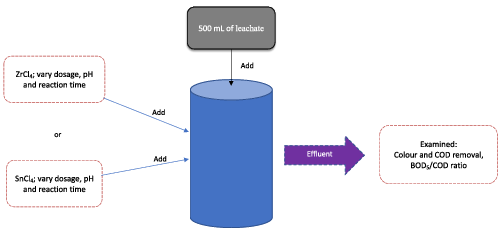
In this study, a combination of O3/ZrCl4 and O3/SnCl4 in SAL treatment was investigated. Three factors were varied; dosage of ZrCl4 and SnCl4, pH of sample and reaction time. The performances were evaluated based on colour, COD and BOD5/COD ratio. O3/ZrCl4 was the best combination that effectively removed COD and colour, up to 91.9% and 99.6%, respectively, and improved the leachate biodegradability in terms of the BOD5/COD ratio.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
REFERENCES
- Aboonajmi, J., Mousavi, M. R., Maghsoodlou, M. T., Hazeri, N., & Masoumnia, A. (2015). ZrCl4 as an efficient catalyst for one-pot synthesis of highly functionalized piperidines via multi-component organic reactions. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 41(4), 1925–1934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-013-1320-z
- Akatova, I. N., Nikulin, S. S., Korystin, S. I., & Kondrat'eva, N. A. (2004). Effect of the type of coagulant on coagulation properties of rubbers, compounds and vulcanisates. International Polymer Science and Technology, 31(8), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1177/0307174X0403100801
10.1177/0307174X0403100801 Google Scholar
- Baird, R. B., Eaton, A. D., & Rice, E. W. (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (Vol. 23). American Public Health Association.
- Amr, S. S. A., & Aziz, H. A. (2012). New treatment of stabilized leachate by ozone/Fenton in the advanced oxidation process. Waste Management, 32(9), 1693–1698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.04.009
- Amr, S. S. A., Aziz, H. A., Adlan, M. N., & Bashir, M. J. (2013). Pretreatment of stabilized leachate using ozone/persulfate oxidation process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 221, 492–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.038
- Amr, S. S. A., Zakaria, S. N. F., & Aziz, H. A. (2016). Performance of combined ozone and zirconium tetrachloride in stabilized landfill leachate treatment. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 19(4), 1384–1390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-016-0524-x
- Aziz, S. Q., Aziz, H. A., Bashir, M. J. K., & Mojiri, A. (2015). Assessment of various tropical municipal landfill leachate characteristics and treatment opportunities. Global NEST Journal, 17(3), 439–450.
- Batakliev, T., Georgiev, V., Anachkov, M., & Rakovsky, S. (2014). Ozone decomposition. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 7(2), 47–59. https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2014-0008
- Beltrán, F. J., Rivas, F. J., & Montero-de-Espinosa, R. (2003). Ozone-enhanced oxidation of oxalic acid in water with cobalt catalysts. 2. Heterogeneous catalytic ozonation. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 42(14), 3218–3224. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie020999u
- Bila, D. M., Montalvao, A. F., Silva, A. C., & Dezotti, M. (2005). Ozonation of a landfill leachate: Evaluation of toxicity removal and biodegradability improvement. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 117(2–3), 235–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.09.022
- Block, P. A., Brown, R. A., & Robinson, D. (2004). Novel activation technologies for sodium persulfate in situ chemical oxidation. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds (pp. 24–27). Battelle Press.
- Brown, T. L., LeMay, H. E. Jr., & Bursten, B. E. (2005). Chemical thermodynamics. In Chemical thermodynamics of zirconium. NEA OECD, Elsevier.
- Chen, C., Chen, Y., Yoza, B. A., Du, Y., Wang, Y., Li, Q. X., Yi, L., Guo, S., & Wang, Q. (2017). Comparison of efficiencies and mechanisms of catalytic ozonation of recalcitrant petroleum refinery wastewater by Ce, Mg, and Ce-Mg oxides loaded Al2O3. Catalysts, 7(3), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7030072
- Chen, D., Wang, D., Wu, W., & Xiao, L. (2015). SnCl4·5H2O: A highly efficient catalyst for hydration of alkyne. Applied Sciences, 5(2), 114–121. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5020114
10.3390/app5020114 Google Scholar
- Dai, Q., Zhang, Z., Zhan, T., Hu, Z. T., & Chen, J. (2018). Catalytic ozonation for the degradation of 5-sulfosalicylic acid with spinel-type ZnAl2O4 prepared by hydrothermal, sol–gel, and coprecipitation methods: A comparison study. ACS Omega, 3(6), 6506–6512. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00263
- Deng, H., & Yu, X. (2015). Fluoride removal from drinking water by zirconium-impregnated fibrous protein. Desalination and Water Treatment, 54(6), 1594–1603. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.887038
- Department of Environment Malaysia (DOE). (1997). Environmental Quality Act 1974. Government of Malaysia, Ministry of Natural Resources and Energy ( 4th ed.). Percetakan Nasional Malaysia Berhad.
- Durai, N. J., Gopalakrishna, G. V. T., Padmanaban, V. C., & Selvaraju, N. (2020). Oxidative removal of stabilized landfill leachate by Fenton's process: Process modeling, optimization & analysis of degraded products. RSC Advances, 10(7), 3916–3925. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra09415frsc.li/rsc-advances
- Ershov, B. G., Morozov, P. A., & Gordeeev, A. V. (2012). Effect of silver and copper ions on the decomposition of ozone in water. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 86(12), 1795–1799. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024412120072
- Fang, H. H. P., Lau, I. W. C., & Wang, P. (2005). Anaerobic treatment of Hong Kong leachate followed by chemical oxidation. Water Science and Technology, 52(10–11), 41–49. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2005.0677
- Fang, Z., & Dixon, D. A. (2013). Hydrolysis of ZrCl4 and HfCl4: The initial steps in the high-temperature oxidation of metal chlorides to produce ZrO2 and HfO2. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117(15), 7459–7474. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp400228d
- Firouzabadi, F. H., & Jafarpour, M. (2008). Some applications of zirconium(IV) tetrachloride (ZrCl4) and zirconium(IV) oxydichloride octahydrate (ZrOCl2·8H2O) as catalysts or reagents in organic synthesis. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 2, 159–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03246012
- Fringuelli, F., Pizzo, F., & Vaccaro, L. (2001). Lewis-acid catalyzed organic reactions in water. The case of AlCl3, TiCl4, and SnCl4 believed to be unusable in aqueous medium. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 66(13), 4719–4722. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo010373
- Frontistis, Z., Xekoukoulotakis, N. P., Diamadopoulos, E., & Mantzavinos, D. (2008). Ozonation of landfill leachates: Treatment optimization by factorial design. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 11(2), 370–377. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2008-0223
- Gardoni, D., Vailati, A., & Canziani, R. (2012). Decay of ozone in water: A review. Ozone Science and Engineering, 34(4), 233–242. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2012.686354
- Garrido-Cardenas, J. A., Esteban-García, B., Agüera, A., Sánchez-Pérez, J. A., & Manzano-Agugliaro, F. (2020). Wastewater treatment by advanced oxidation process and their worldwide research trends. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010170
- Gomes, J., Matos, A., Gmurek, M., Quinta-Ferreira, R. M., & Martins, R. C. (2019). Ozone and photocatalytic processes for pathogens removal from water: A review. Catalysts, 9(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010046
- Hamid, M. A. A., Aziz, H. A., Yusoff, M. S., & Rezan, S. A. (2020). Optimization and analysis of zeolite augmented electrocoagulation process in the reduction of high-strength ammonia in saline landfill leachate. Water, 12(1), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010247
- He, X., Min, X., & Luo, X. (2017). Efficient removal of antimony (III, V) from contaminated water by amino modification of a zirconium metal–organic framework with mechanism study. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 62(4), 1519–1529. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.7b00010
- Hussain, S., van Leeuwen, J., Chow, C. W., Aryal, R., Beecham, S., Duan, J., & Drikas, M. (2014). Comparison of the coagulation performance of tetravalent titanium and zirconium salts with alum. Chemical Engineering Journal, 254, 635–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.014
- Ikhlaq, A., Brown, D. R., & Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. (2012). Mechanisms of catalytic ozonation on alumina and zeolites in water: Formation of hydroxyl radicals. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 123, 94–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.015
- Jarvis, P., Sharp, E., Pidou, M., Molinder, R., Parsons, S. A., & Jefferson, B. (2012). Comparison of coagulation performance and floc properties using a novel zirconium coagulant against traditional ferric and alum coagulants. Water Research, 46(13), 4179–4187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.04.043
- Kamaruddin, M. A., Yusoff, M. S., Aziz, H. A., & Hung, Y. T. (2015). Sustainable treatment of landfill leachate. Applied Water Science, 5(2), 113–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0177-7
- Kishimoto, N., & Nakamura, E. (2012). Bromate formation characteristics of UV irradiation, hydrogen peroxide addition, ozonation, and their combination processes. International Journal of Photoenergy, 114, 45–58. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/107293
10.1155/2012/107293 Google Scholar
- Kow, H., Fahmi, M. R., Abidin, C. Z. A., Ong, S. A., & Sabri, S. N. (2017). Degradation efficiency, kinetic and intermediates of phenol by ozonation. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 11(3), 71–78. http://www.ajbasweb.com/old/ajbas/2017/Special%20issue%20ICCEIB/71-78.pdf
- Lage Filho, F. A. (2010). Ozone application in water sources: Effects of operational parameters and water quality variables on ozone residual profiles and decay rates. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 27(4), 545–554. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322010000400006
- Li, W., Zhou, Q., & Hua, T. (2010). Removal of organic matter from landfill leachate by advanced oxidation processes: A review. International Journal of Chemical Engineering, 17, 33–42. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/270532
10.1155/2010/270532 Google Scholar
- Magallanes, D., Rodríguez, J. L., Poznyak, T., Valenzuela, M. A., Lartundo, L., & Chairez, I. (2015). Efficient mineralization of benzoic and phthalic acids in water by catalytic ozonation using a nickel oxide catalyst. New Journal of Chemistry, 39(10), 7839–7848. https://doi.org/10.1080/00028899908984478
- Multani, M. Y., Shah, M. J., & Student, P. G. (2014). Removal of colour and COD from reactive green–19 dyeing wastewater using ozone. International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology, 3(2), 699–704.
- Naveen, B. P., Mahapatra, D. M., Sitharam, T. G., Sivapullaiah, P. V., & Ramachandra, T. V. (2017). Physico-chemical and biological characterization of urban municipal landfill leachate. Environmental Pollution, 220, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.002
- Patil, M. K., Prasad, A. N., & Reddy, B. M. (2011). Zirconia-based solid acids: Green and heterogeneous catalysts for organic synthesis. Current Organic Chemistry, 15(23), 3961–3985. https://doi.org/10.2174/138527211798072430
- Prasobhan, P. (2014). Comparison of Al, Fe, Zr performance on coagulation (Master's thesis, Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Ås).
- Qi, L., You, H., Zhang, Z., Feng, C., & van Agtmaal, S. (2013). Degradation of 4-chlorophenol by catalytic ozonation using γ-Al2O3/TiO2 supported manganese oxides in aqueous solution. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 8(4), 5457–5468. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2014.846657
- Raghab, S. M., El Meguid, A. M. A., & Hegazi, H. A. (2013). Treatment of leachate from municipal solid waste landfill. HBRC Journal, 9(2), 187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbrcj.2013.05.007
10.1016/j.hbrcj.2013.05.007 Google Scholar
- Rakness, K. L., Hunter, G., Lew, J., Mundy, B., & Wert, E. C. (2018). Design considerations for cost-effective ozone mass transfer in sidestream systems. Ozone: Science & Engineering, 40(3), 159–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2018.1424532
- Rani, S., Aggarwal, M., Kumar, M., Sharma, S., & Kumar, D. (2016). Removal of methylene blue and rhodamine B from water by zirconium oxide/graphene. Water Science, 30(1), 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wsj.2016.04.001
10.1016/j.wsj.2016.04.001 Google Scholar
- Ratnawati, R., Kusumaningtyas, D. A., Suseno, P., & Prasetyaningrum, A. (2018). Mass transfer coefficient of ozone in a bubble column. In MATEC Web of Conferences (Vol. 156) (02015). EDP Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201815602015
10.1051/matecconf/201815602015 Google Scholar
- Sarif, S. M., Alias, S. S., Ridwan, F. M., Salim, K. K., Abidin, C. Z. A., & Ali, U. M. (2018). Ozonation of return activated sludge for disintegration and solubilisation with synthesized titanium oxide as catalyst. In E3S Web of Conferences (Vol. 34) (02009). EDP Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20183402009
- Show, P. L., Pal, P., Leong, H. Y., Juan, J. C., & Ling, T. C. (2019). A review on the advanced leachate treatment technologies and their performance comparison: An opportunity to keep the environment safe. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(4), 227–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7380-9
- Stranic, I., Pang, G. A., Hanson, R. K., Golden, D. M., & Bowman, C. T. (2013). Shock tube measurements of the tert-butanol + OH reaction rate and the tert-C4H8OH radical β-scission branching ratio using isotopic labeling. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 117(23), 4777–4784. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp402176e
- Sun, Q., Li, L., Yan, H., Hong, X., Hui, K. S., & Pan, Z. (2014). Influence of the surface hydroxyl groups of MnOx/SBA-15 on heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of oxalic acid. Chemical Engineering Journal, 242, 348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.12.097
- Tizaoui, C., Bouselmi, L., Mansouri, L., & Ghrabi, A. (2007). Landfill leachate treatment with ozone and ozone/hydrogen peroxide systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 140(1–2), 316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.023
- Wang, J. L., & Xu, L. J. (2012). Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: Formation of hydroxyl radical and application. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 42(3), 251–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2010.507698
- Yang, D. M., Wang, B., Ren, H. Y., & Yuan, J. M. (2012). Effects and mechanism of ozonation for degradation of sodium acetate in aqueous solution. Water Science and Engineering, 5(2), 155–163. https://doi.org/10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2012.02.004
- Yasar, A., Ahmad, N., Chaudhry, M. N., Rehman, M. S. U., & Khan, A. A. A. (2007). Ozone for color and COD removal of raw and anaerobically biotreated combined industrial wastewater. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 16(2), 112–121. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/106d/17777c1385d7ee766c13498e86b3ade23e5a.pdf
- Zainal, S. F. F. S., & Aziz, H. A. (2017). Potential of tin (IV) chloride for treatment in Alor Pongsu as stabilized landfill leachate. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 1892) (040003). AIP Publishing LLC. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5005683
- Zakaria, S. N. F., Aziz, H. A., & Amr, S. S. A. (2015). Performance of ozone/ZrCl4 oxidation in stabilized landfill leachate treatment. In Applied Mechanics and Materials (Vol. 802) (pp. 501–506). Trans Tech Publications Ltd.. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.802.501
- Zakaria, S. N. F., Aziz, H. A., Amr, S. S. A., & Hung, Y. T. (2018). Optimisation of anaerobic stabilised leachate treatment using catalytic ozonation with zirconium tetrachloride. International Journal of Environment and Waste Management, 21(2–3), 102–119. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEWM.2018.092717
- Zhai, X. D., Wang, Q. H., Ma, J., Zhang, H. S., & Deng, J. (2009). Detection of hydroxyl radicals in catalytic ozonation by using ESR spectroscopy. In 2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology (Vol. 3) (pp. 358–361). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESIAT.2009.423
10.1109/ESIAT.2009.423 Google Scholar
- Zhu, S. N., Hui, K. N., Hong, X., & Hui, K. S. (2014). Catalytic ozonation of basic yellow 87 with a reusable catalyst chip. Chemical Engineering Journal, 242, 180–186.