Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Titelbild Chem. Ing. Tech. 6/2019
- Page: 681
- First Published: 23 May 2019

Elektrochemische Prozesse werden im Zuge der Energiewende immer bedeutender, da regenerative elektrische Energie zunehmend zur Primärenergie wird, in andere Energieformen umgewandelt und wegen des fluktuierenden Anfalls der erneuerbaren Energien auch gespeichert werden muss. Für die erforderliche Entwicklung von elektrochemischen Prozessen sind Reaktionstechnik und Verfahrenstechnik essentielle Disziplinen, die den Schritt von der Elektrochemie zu technischen Zellen und Systemen erst ermöglichen. Nur durch quantitative Beschreibung des Zusammenwirkens von elektrochemischen Reaktionen mit Stoff- und Wärmetransportvorgängen können Verluste minimiert und Verfahren effizient gestaltet werden. Ein technisch relevantes Beispiel hierfür sind Gasdiffusionselektroden:
F. Kubannek, T. Turek, U. Krewer*, Chem. Ing. Tech. 2019, 91 (6), 720 – 733. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cite.201800181
Editorial
Reaktions- und Verfahrenstechnik als Enabler elektrochemischer Technologien
- Page: 683
- First Published: 23 May 2019
Inhalt
Aus den Gesellschaften
Forum
Lehre – Forschung – Wissenschaft
50 Jahre Chemietechnik und BCI in Dortmund – ein kurzer Abriss aus Lehre und Forschung
- Pages: 695-698
- First Published: 23 May 2019
Essays
The Role of Electrochemistry in Future Dynamic Bio-Refineries: A Focus on (Non-)Kolbe Electrolysis
- Pages: 699-706
- First Published: 25 March 2019
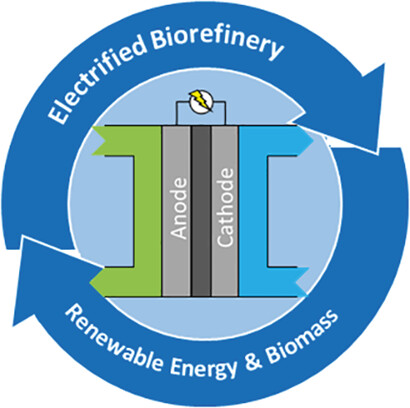
A circular economy with closed carbon dioxide cycles is connected to a change of feedstocks. Considering the role of natural carboxylic acids, (non-)Kolbe electrolysis attracts interest to valorize renewable feedstocks providing access to both biofuels and chemicals. The role of Kolbe chemistry in an electrified biorefinery is discussed.
Übersichtsbeiträge
Die Rolle der Gasdiffusionselektroden in der Zink-Luft- und Lithium-Luft-Batterie
The Role of Gas Diffusion Electrodes in the Zinc-Air and Lithium-Air Battery
- Pages: 707-719
- First Published: 08 May 2019

Der Bedarf an Hochenergiespeichersystemen ist für die zukünftige mobile und stationäre Energieversorgung groß. Das Interesse an wiederaufladbaren Zink-Luft- und Lithium-Luft-Batterien ist daher nach wie vor ungebrochen. Warum sich diese Technologien noch nicht nachhaltig durchgesetzt haben, wird durch Einblicke in die grundlegenden Mechanismen und Herausforderungen deutlich.
Reviews
Modeling Oxygen Gas Diffusion Electrodes for Various Technical Applications
- Pages: 720-733
- First Published: 07 May 2019
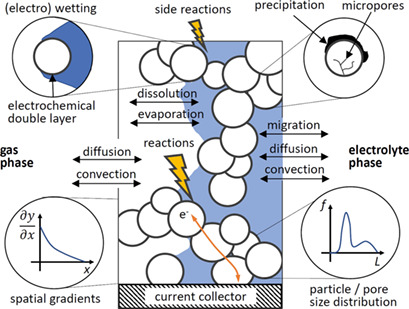
Gas diffusion electrodes (GDEs) are used for important technical applications in energy transformation and chemical synthesis. An overview of existing models for GDEs and their specific purpose, with an emphasis on oxygen reduction electrodes, is given. Various modeling approaches are described and perspectives for future research are discussed.
Übersichtsbeiträge
Strategien zur gezielten Verbesserung des anodenseitigen Elektronentransfers in mikrobiellen Brennstoffzellen
Strategies for Targeted Improvement of Anodic Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells
- Pages: 744-757
- First Published: 30 April 2019
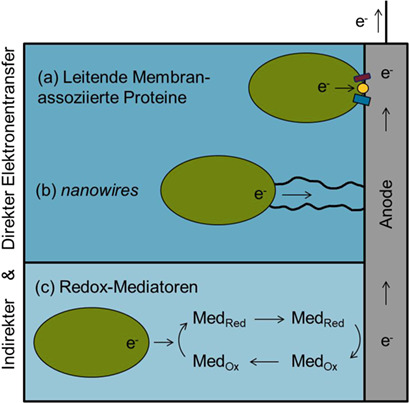
Mikrobielle Brennstoffzellen (MFCs) wurden im letzten Jahrzehnt als praktische Anwendung in der Abwasseraufbereitung auch in Maßstäben bis 1000 L realisiert. Hier werden verfügbare Strategien vorgestellt, um den bislang noch limitierenden extrazellulären Elektronentransfer im Anodenraum von MFCs zu erhöhen.
Reviews
Microstructure- and Theory-Based Modeling and Simulation of Batteries and Fuel Cells
- Pages: 758-768
- First Published: 17 April 2019
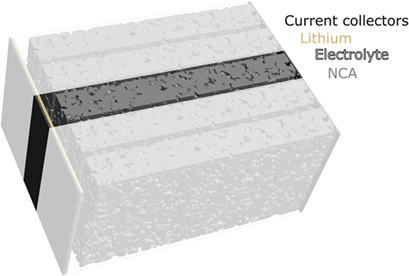
An overview over new predictive modeling and simulation techniques for batteries and fuel cells will be given. A special focus is on microstructure resolved simulations for Li-ion batteries, advanced modeling techniques for new electrolytes and metal air batteries and spatially resolved simulations of low temperature (PEM) fuel cells.
Übersichtsbeiträge
Elektrochemische Reaktoren für die Wasserbehandlung
Electrochemical Reactors for Wastewater Treatment
- Pages: 769-785
- First Published: 01 April 2019
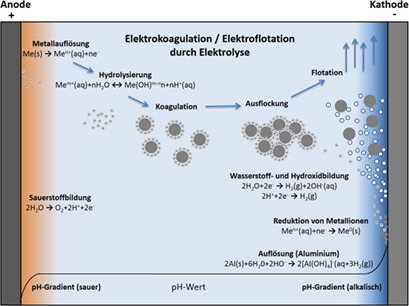
Dieser Beitrag gibt eine Übersicht zu den in der Aufbereitung von Wasser, Prozesswasser und Abwasser eingesetzten elektrochemischen Reaktoren. Es werden die Grundlagen der elektrochemischen Verfahren zur Behandlung von Wasser vorgestellt, Beispiele für Anwendungen gegeben und die verwendeten Reaktoren beschrieben.
Reviews
Which Parameter is Governing for Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries with Organic Active Material?
- Pages: 786-794
- First Published: 26 March 2019
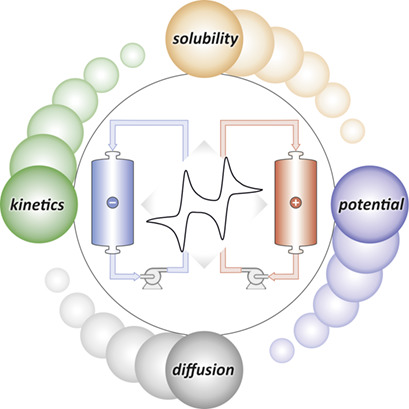
Due to their high efficiency and promising cycle life, redox flow batteries are one of the future energy storage technologies. Their performance is influenced by a multitude of factors, which are often difficult to determine independently from each other – a task that requires the joint input of chemists, materials scientists, and reaction and process engineers.
Energy-Efficient Gas-Phase Electrolysis of Hydrogen Chloride
- Pages: 795-808
- First Published: 25 April 2019
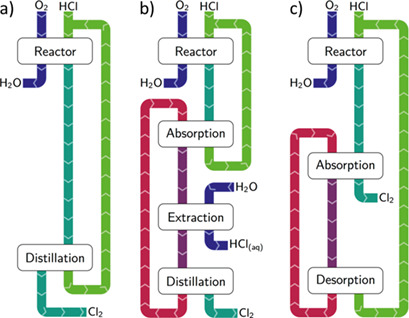
The electrochemical oxidation of HCl to Cl2 plays a significant role in the production of polycarbonates and polyurethanes. While the currently industrially implemented electrolysis processes all rely on a liquid-phase reactor, recent investigations have shown that employing a gas-phase reactor leads to enormous exergetic savings. This article outlines the concept of the energy efficient electrolysis of gaseous HCl on the reactor and overall process level.
Research Articles
Electrochemical Ceramic Membrane Reactors in Future Energy and Chemical Process Engineering
- Pages: 809-820
- First Published: 25 April 2019
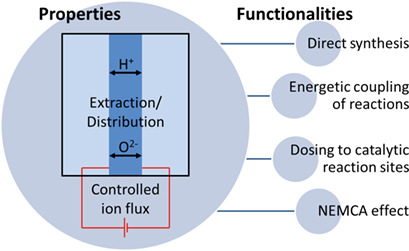
Electrochemical ceramic membrane reactors (ECMRs) can be used to efficiently couple electrical, chemical, and thermal energy sectors. An overview of ECMR functionalities and their benefits for future energy and chemical process systems is given. The suitability of reactions for bulk chemical production is examined with a simple thermodynamic method.
Design of a Zero-Gap Laboratory-Scale Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Alkaline Water Electrolysis Stack
- Pages: 821-832
- First Published: 24 April 2019
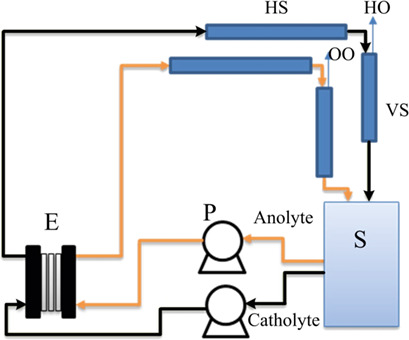
A laboratory-scale alkaline water electrolysis stack utilizing a polymer electrolyte membrane was developed and constructed showing the importance of the hydraulic circuit design with regard to the purity of the produced gases and the stability of the cell components. A simple mathematical model proposed has proven to be an efficient tool in the scale-up and optimization of the electrolyzer stack.
Dynamic Modeling of Reversible Solid Oxide Cells
- Pages: 833-842
- First Published: 07 May 2019
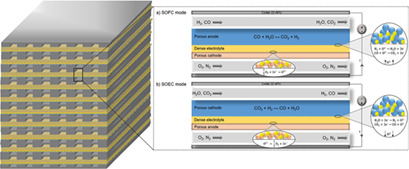
Reversible solid oxide cells (rSOCs) are a promising technology for a future distributed clean energy supply, being able to switch between storage (SOEC) and release (SOFC) modes. Highly detailed modeling is crucial for a thorough understanding of the cells' dynamic behavior and for visualizing time-dependent distributed variables within the stack.
Microkinetic Modeling of Nickel Oxidation in Solid Oxide Cells: Prediction of Safe Operating Conditions
- Pages: 843-855
- First Published: 17 April 2019
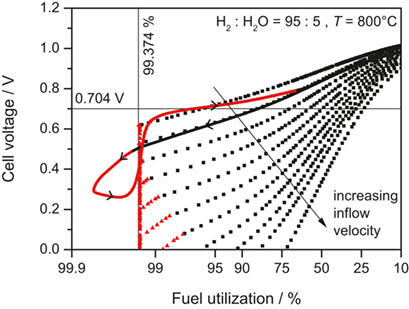
Nickel oxidation is a severe degradation mechanism in solid oxide cells. A microkinetic model allows to analyze spatiotemporal oxidation behavior in the cell, to assess the relative importance of thermochemical (concentration-driven) and electrochemical (potential-driven) mechanisms, and to identify operation conditions avoiding nickel oxidation.
Modeling and Parameter Identification for a Biofilm in a Microbial Fuel Cell
- Pages: 856-864
- First Published: 22 March 2019
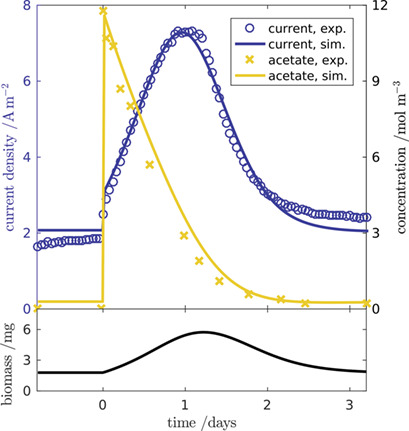
A dynamic physical model of a microbial fuel cell (MFC) anode is presented that is particularly useful for process monitoring or control purposes. Theoretical and practical parameter identifiability is evaluated, and parameter confidence intervals are determined using data from the MFC's response to a substrate concentration pulse.
Forschungsarbeiten
Statistische Analyse des lokalen Wassertransportes einer Polymer-Elektrolyt-Brennstoffzelle
Statistical Analysis of the Local Water Transport of a Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell
- Pages: 865-871
- First Published: 12 March 2019
Der Wassertransport in der Gasdiffusionsschicht (GDL) einer Polymer-Elektrolyt-Brennstoffzelle wurde auf Basis eines stochastischen Geometriemodells simuliert. Die aus der GDL austretenden Wassertropfen wurden an der Grenzfläche zum Luftkanal analysiert. Neben der Form der Tropfen wurde der dynamische Verlauf betrachtet.
Research Articles
Utilizing Formate as an Energy Carrier by Coupling CO2 Electrolysis with Fuel Cell Devices
- Pages: 872-882
- First Published: 07 May 2019
Electrolyzing CO2 with renewable energy to formate is a promising process to utilize CO2 as feedstock. While the lack of market volume and applications for formate reduces the economic attractiveness of this process, its use as an energy carrier by re-electrification via fuel cells adds economic value to the formate solution obtained from CO2 electrolysis.
Simulation of Electrolyte Imbibition in Gas Diffusion Electrodes
- Pages: 883-888
- First Published: 29 March 2019
An optimal design of gas diffusion electrodes ensures intimate contact between gaseous reactants, catalyst, and electrolyte in technical processes like chlor-alkali electrolysis. The physically based contact line force model is employed to simulate the electrolyte imbibition into solid microstructures using the SPH method.
Simulative Approach for Linking Electrode and Electrolyte Properties to Supercapacitor Performance
- Pages: 889-899
- First Published: 18 April 2019

A simulative approach to link the influence of the electrode thickness, electrolyte conductivity, and ionic conductivity to the performance of supercapacitors is presented. The approach can be employed to identify bottlenecks in the supercapacitor electrode design depending on the charging/discharging time aimed for.
Exploring Flow Characteristics in Vanadium Redox-Flow Batteries: Optical Measurements and CFD Simulations
- Pages: 900-906
- First Published: 24 April 2019
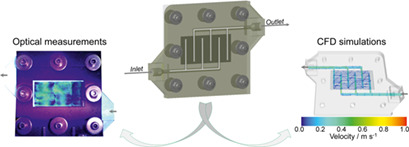
The flow of a vanadium redox-flow battery is investigated by a combined approach using optical measurements and CFD simulations. Thereby, a fluorescing tracer visualizes the actual flow distribution during the optical measurements. Additionally, a pseudo-homogeneous CFD model allows analyzing the fluid velocity in all three dimensions.
Forschungsarbeiten
Ortsaufgelöste Stromdichtemessung in PEM-Elektrolyse-Zellen
Spatially Resolved Current Density Mapping in PEM-Water Electrolysis Cells
- Pages: 907-918
- First Published: 02 April 2019
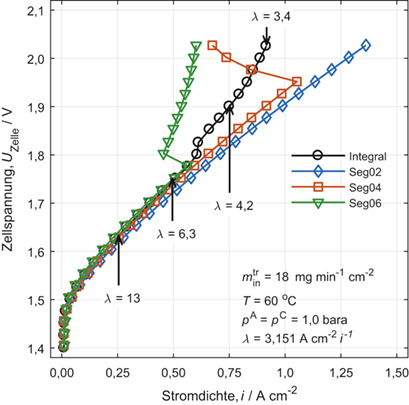
Die lokale Stromdichte- und EIS-Messung entlang einer 50 cm langen PEMWE-Zelle mit unterschiedlichen stöchiometrischen Wasserverhältnissen (λ) zeigt, dass λ ≤ 5 zu einer inhomogen verteilten Erhöhung von ionischer Leitfähigkeit in der Membran, aber auch zu großen Transportverlusten im Katalysator führt.
Buchbesprechung
Chemische Verfahrenstechnik – Berechnung, Auslegung und Betrieb chemischer Reaktoren, 3. Auflage. Von K. Hertwig, L. Martens, C. Hamel.
- Page: 919
- First Published: 23 May 2019
Vorschau
Überblick
Überblick Inhalt: Chem. Eng. Technol. 6/2019
- Page: 923
- First Published: 23 May 2019