Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
EDITORIAL BOARD
REVIEW ARTICLES
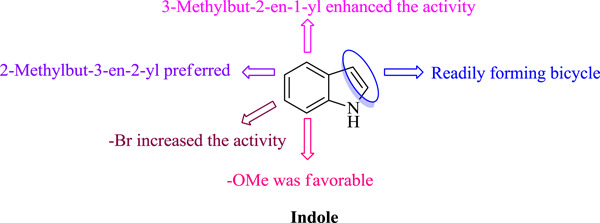
Natural indole-containing alkaloids and their antibacterial activities
- First Published: 18 June 2020
Indole/isatin-containing hybrids as potential antibacterial agents
- First Published: 15 July 2020
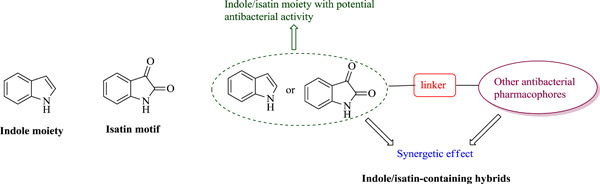
Indole/isatin-containing hybrids show promising activity against many clinically important Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and are thus privileged scaffolds for the discovery of novel antibacterial candidates. This review, covering articles published between January 2015 and May 2020, summarizes the recent advances in the development of indole/isatin-containing hybrids as potential antibacterial agents.
FULL PAPERS
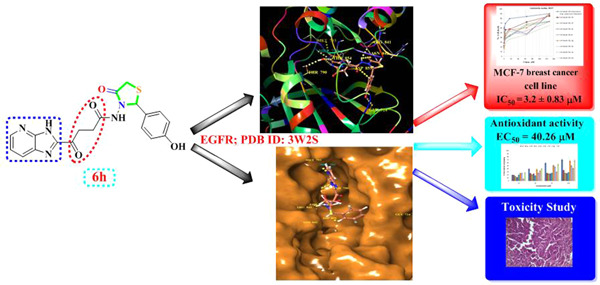
Novel 2-cyanoacrylamido-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene derivatives as potent anticancer agents
- First Published: 13 July 2020
![Novel 2-cyanoacrylamido-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene derivatives as potent anticancer agents](/cms/asset/444688f5-b470-4f62-b9fd-6082d52ba4f7/ardp202000069-gra-0001-m.jpg)
Bis-ethyl 2-(2-cyanoacrylamido)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylate derivatives 5–10 with aliphatic linkers were synthesized and tested in vitro as anticancer agents against HepG2, MCF-7, HCT-116, and BJ1 cells. Compounds 7 and 9 emerged as the most promising compounds, with IC50 values (HepG2) of 13.5 and 32.2 µg/ml, respectively, compared with doxorubicin. The effects of compounds 7 and 9 on gene expression and DNA fragmentation were evaluated.
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of imidazopyridine-linked thiazolidinone as potential anticancer agents
- First Published: 06 July 2020
Novel hybrids of imidazopyridine and thiazolidinone ring compounds were synthesized as potent anticancer agents. The lead molecule was identified as N-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxothiazolidin-3-yl]-4-(3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-2-yl)-4-oxobutanamide, showing an excellent spectrum of anticancer activities against breast, lung, and human prostate cancer cell lines (MCF-7, A549, and DU145).
Discovery of 2,4-diaminopyrimidine derivatives targeting p21-activated kinase 4: Biological evaluation and docking studies
- First Published: 06 July 2020
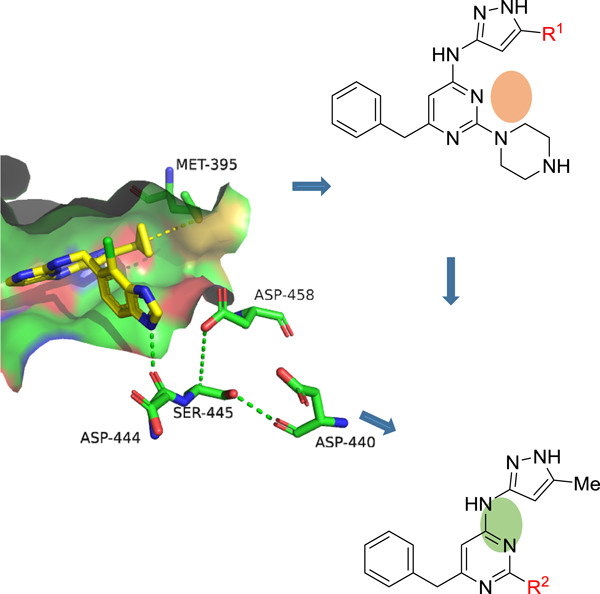
PAK4 (p21-activated kinase 4) is associated with cancer, and the combined application of PAK4 and PD-1 inhibitors provides a new approach to avoid the resistance to PD-1 blockade therapy. In this paper, a structure-based drug design strategy was used to create a novel series of 2,4-diaminopyrimidine skeleton PAK4 inhibitors. Among these new derivatives, compound B6 can serve as a candidate for the development of a PAK4 inhibitor molecule.
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of LD-RT and some novel thiadiazole derivatives through COX-2 inhibition
- First Published: 02 July 2020
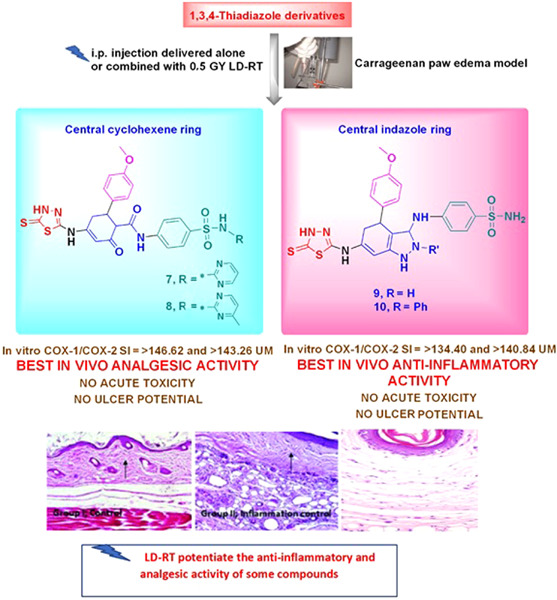
A novel series of 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives was designed and synthesized as possible nontoxic, nonulcerogenic analgesic, and anti-inflammatory agents through COX-2 inhibition. The anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of low-dose radiotherapy, in particular with a single dose of 0.5 Gy, was tested alone and in combination with the most potent compounds.
1,2,3-Triazole-linked 5-benzylidene (thio)barbiturates as novel tyrosinase inhibitors and free-radical scavengers
- First Published: 08 July 2020
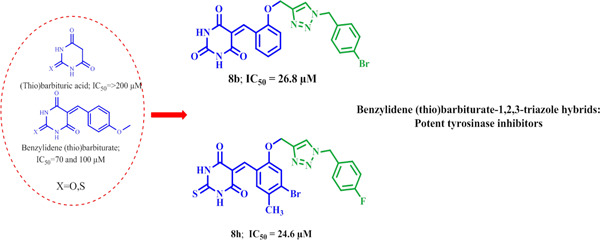
In this study, benzyl-1,2,3-triazole-linked 5-benzylidene (thio)barbiturate derivatives 7a–d and 8a–h were designed as potential tyrosinase inhibitors and free-radical scavengers. The thiobarbiturate derivative 8h and the barbiturate derivative 8b bearing 4-fluoro and 4-bromo groups on the benzyl–triazole moiety are the most potent tyrosinase inhibitors (IC50s = 24.6 ± 0.9 and 26.8 ± 0.8 μM, respectively). Both compounds 8b and 8h are well accommodated in the active site of tyrosinase.
Synthesis, characterization, molecular docking, and biological activities of coumarin–1,2,3-triazole-acetamide hybrid derivatives
- First Published: 09 July 2020
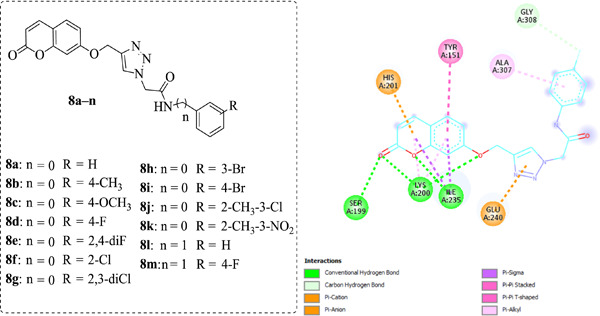
A series of novel coumarin–1,2,3-triazole-acetamide hybrids was tested for their inhibitory activity against metabolic enzymes such as α-glycosidase, α-amylase, acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, and human carbonic anhydrases I and II. The new hybrids represent potential drug candidates to treat diseases such as epilepsy, glaucoma, type-2 diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer's disease, and leukemia.
Thieno[2,3-b]pyridine amines: Synthesis and evaluation of tacrine analogs against biological activities related to Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 13 July 2020
![Thieno[2,3-b]pyridine amines: Synthesis and evaluation of tacrine analogs against biological activities related to Alzheimer's disease](/cms/asset/a41a85f4-ca51-4a6e-97ab-f762ea25f5a9/ardp202000101-gra-0001-m.jpg)
Novel tacrine analogs with lower toxicity were designed and synthesized. They could efficiently inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), with IC50 values of 1.55 and 0.23 µM, respectively. The most potent compounds (5e and 5d) could inhibit AChE-induced and self-induced amyloid-beta aggregation
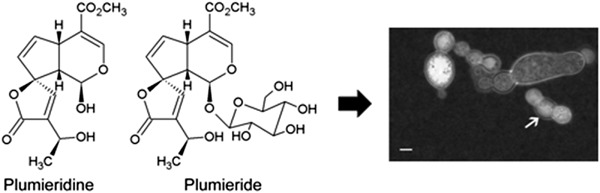
Antifungal activity of Allamanda polyantha seed extract and its iridoids promote morphological alterations in Cryptococcus spp.
- First Published: 08 July 2020
Investigation of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory and antioxidant effects of various hydroxycoumarin derivatives
- First Published: 10 July 2020
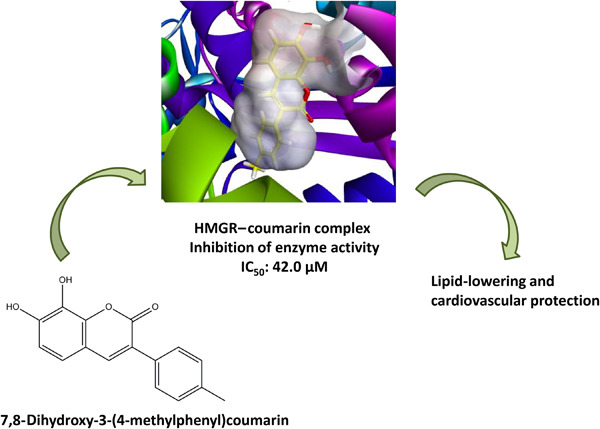
Five dihydroxycoumarins were synthesized and investigated for their antioxidant and in vitro 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitory effects. The quantum-chemical properties of the coumarin derivatives were explored and molecular docking was performed to determine the binding strength of each coumarin derivative. Compound IV displayed the highest HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity, with IC50 = 42.0 µM.
Comparison of extraction efficiency and selectivity between low-temperature pressurized microwave-assisted extraction and prolonged maceration
- First Published: 31 August 2020
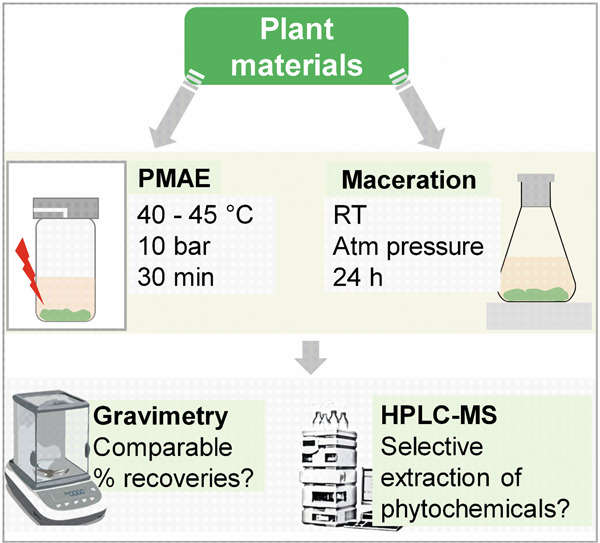
Prolonged maceration was compared with short-time pressurized microwave-assisted extraction (PMAE) at low temperatures. Low-temperature PMAE can attain reasonable extraction efficiencies with the added value of sparing compounds of low thermal stability. The method can also enable the recovery of compounds distinct from those obtained by maceration.
ERRATUM
Erratum: Synthesis of novel 4,5-dihydropyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines, pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin]-2-ones and their antituberculosis and anticancer activity
- First Published: 07 September 2020