Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
EDITORIAL BOARD
REVIEW ARTICLES
Reprogramming of antibiotics to combat antimicrobial resistance
- First Published: 10 August 2020
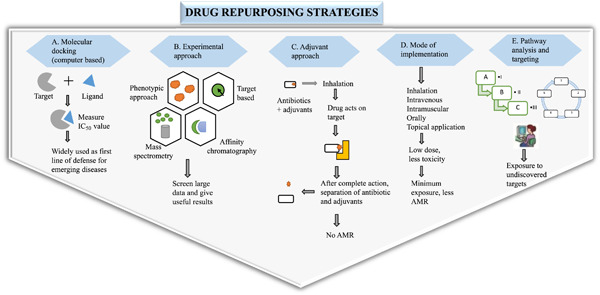
This review provides illustrative examples of drug repurposing (one molecule, multiple targets), which will be useful in tackling the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) problem. Repurposing increases the potency of a drug and reduces its toxicity level. This will be further explored to highlight the application in AMR.
The antimalarial activity of indole alkaloids and hybrids
- First Published: 12 August 2020
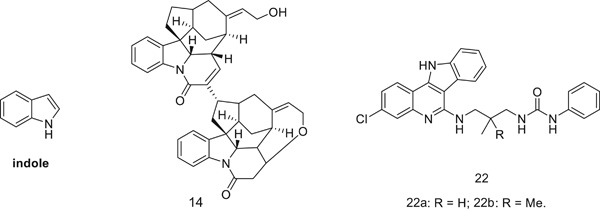
Many indole derivatives exhibited potential in vitro and in vivo activity against both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant malaria, suggesting that the indole moiety is a useful template for the development of novel antimalarial agents. This review outlines the current scenario of indole alkaloids and hybrids with potential therapeutic applications in the fight against malaria.
FULL PAPERS
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new pyrazoloquinazoline derivatives as dual COX-2/5-LOX inhibitors
- First Published: 21 July 2020
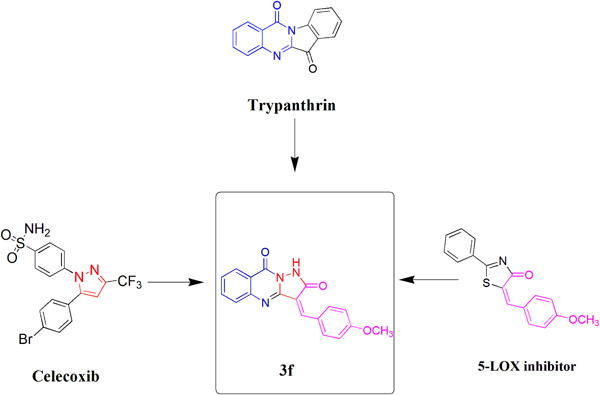
The design of 3-(4-methoxybenzylidene)pyrazolo[5,1-b]quinazoline-2,9(1H,3H)-dione (3f) as a new scaffold for the synthesis of potent, effective, and safe anti-inflammatory agents was based upon hybridization of pharmacophores previously reported to exhibit COX-2 and 5-LOX inhibitory activity. Accordingly, compound 3f was observed to be an excellent dual inhibitor of COX-2/5-LOX, with high selectivity.
Novel VEGFR-2 inhibitors with an N-acylhydrazone scaffold
- First Published: 15 July 2020
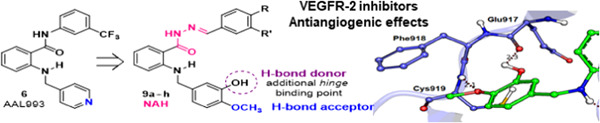
VEGFR-2 is a tyrosine kinase that mediates cell responses associated with angiogenesis, and its modulation is considered a promising strategy in the prevention and control of solid tumor growth. The design, synthesis, and enzyme inhibitory and antiangiogenic activities of a novel series of VEGFR-2 inhibitors with an N-acylhydrazone scaffold are reported in this study. Compounds 9b–f effectively inhibited neovascularization induced by VEGF.
Design, synthesis, and cytotoxicity screening of new synthesized imidazolidine-2-thiones as VEGFR-2 enzyme inhibitors
- First Published: 05 August 2020
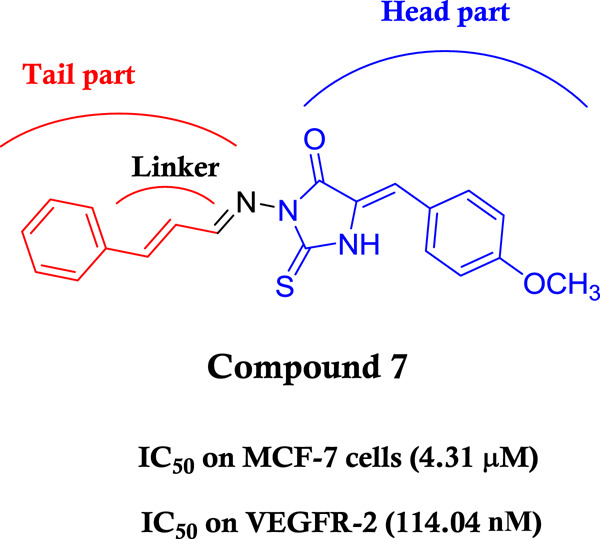
A series of imidazolin-2-thione derivatives was synthesized and evaluated for their cytotoxic activity against the breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Compounds 3 and 7 with the best cytotoxic activity also displayed a good inhibition of the VEGFR-2 kinase and upregulated the activation of the effector caspase-3/7.
In vitro inhibitory effects of some acetophenone derivatives on some metabolic enzymes and molecular docking
- First Published: 02 September 2020
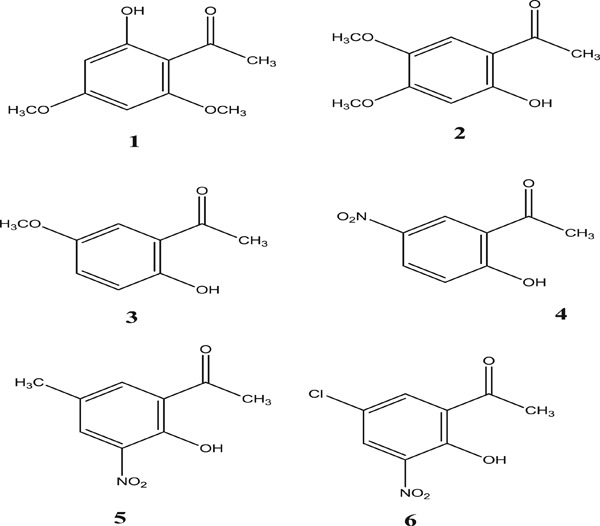
Six acetophenone derivatives were found to be effective inhibitor molecules for α-glycosidase, human carbonic anhydrases I and II, and acetylcholinesterase. The biological activities of compounds 1–6 were compared with their docking scores in those enzymes. The ADME/T (adsorption, distribution, metabolism, and discharge) analysis was then performed for the future use of these molecules as drugs.
Probing simple structural modification of α-mangostin on its cholinesterase inhibition and cytotoxicity
- First Published: 27 July 2020
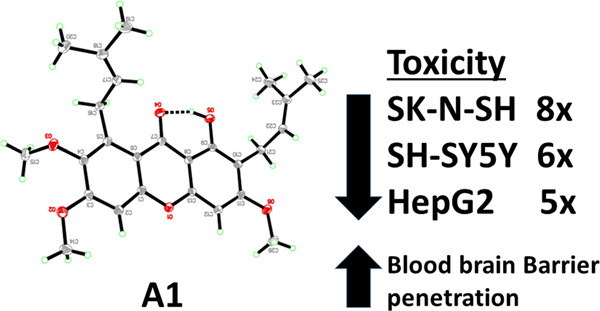
Simple structural modifications of α-mangostin were made and their effects on its acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitory activities and toxicity toward neuroblastoma and liver cancer cells were studied. The derivatives, dialkylated at positions C-3 and C-6 retained good AChE but not BChE inhibitory activities. These AChE selective inhibitors forming hydrophobic interactions at the AChE active site are viable candidates for further structural modification and refinement.
Antiretroviral and cytotoxic activities of Tityus obscurus synthetic peptide
- First Published: 19 July 2020
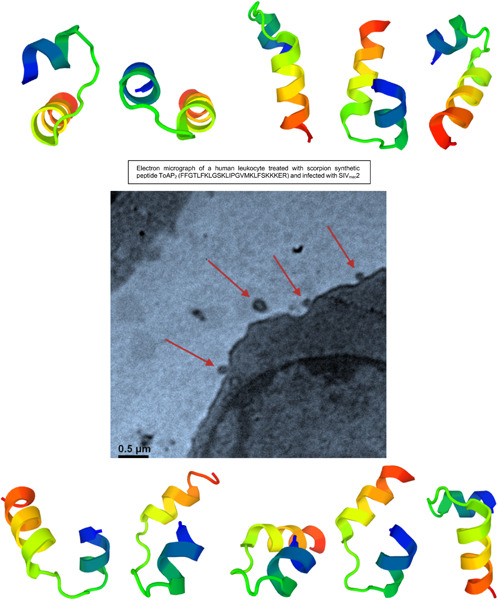
Synthetic peptides based on the transcriptome analysis of diverse scorpion venoms were assayed for their cytotoxicity and antiretroviral activity, based on the reduction of simian immunodeficiency virus replication and quantification of cytokine production after human leukocytes were treated with the scorpion peptides and challenged with virus infection. The Tityus obscurus synthetic peptide showed the best performance.
Evaluation of isoindole derivatives: Antioxidant potential and cytotoxicity in the HT-29 colon cancer cells
- First Published: 10 August 2020
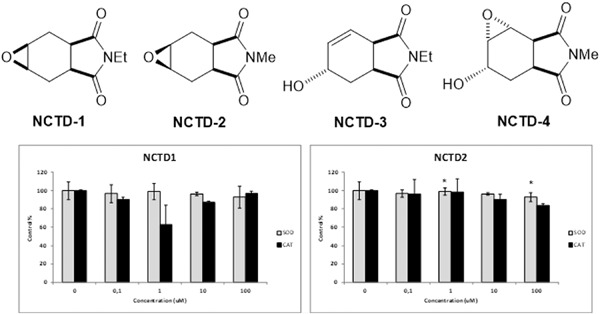
Four isoindoline (norcantharimide) derivatives (NCTD1–4) were synthesized and evaluated in vitro for their antioxidant and cytotoxic potential on HT-29 colon cancer cells. NCTD4 inhibited the growth of HT-29 cells due to membrane damage and exhibited a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect, suggesting that NDTD4 has potential for colon cancer treatment.
Cell death-inducing properties of selected dendrimers against different breast cancer and leukemia cell lines
- First Published: 11 August 2020
Dendrimers are used for drug delivery. However, knowledge of their cell death-inducing properties is essential. Therefore, a series of three poly(amido amine)-derived and one poly(propylene imine) dendrimers was investigated for their cell-growth inhibition of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells and for their antimetabolic effects against the LAMA-84, K562, SD-1, and SUP-B15 leukemia cell lines. The cytotoxic representatives induced necrosis rather than apoptosis.
New nanodrug design for cancer therapy: Its synthesis, formulation, in vitro and in silico evaluations
- First Published: 05 August 2020
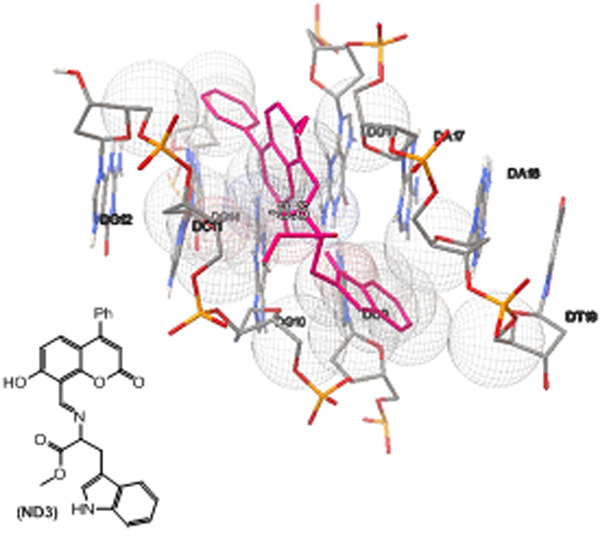
A novel nanosize drug candidate for cancer therapy was developed. A controlled release formulation of (S)-methyl 2-[(7-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-8-yl)methyleneamino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoate was prepared and evaluated against MCF-7 and A549 cancer cells, revealing toxic effects. DNA binding of the coumarin compound was demonstrated and the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity parameters, drug-likeness and toxicity properties were calculated.
New N-phenylacetamide-linked 1,2,3-triazole-tethered coumarin conjugates: Synthesis, bioevaluation, and molecular docking study
- First Published: 09 August 2020
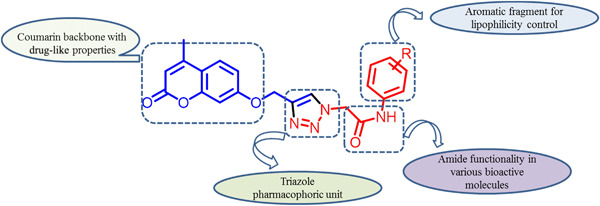
New 1,2,3-triazole-tethered coumarin conjugates linked by N-phenylacetamide were synthesized via click chemistry and evaluated for their in vitro antifungal and antioxidant activities. Compounds 7b, 7d, 7e, 8b and 8e displayed higher potency than the standard drug miconazole. Molecular docking studies showed good binding at the active site of fungal (Candida albicans) P450 cytochrome lanosterol 14α-demethylase.





