Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
EDITORIAL BOARD
REVIEW ARTICLES
Resveratrol isoforms and conjugates: A review from biosynthesis in plants to elimination from the human body
- First Published: 04 September 2020
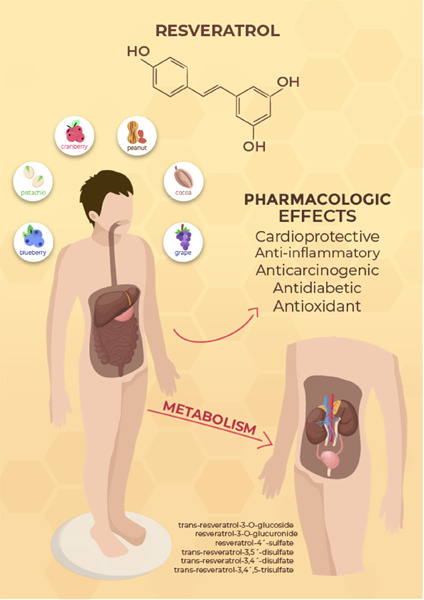
Resveratrol is a natural substance found in many plant species. Its main function is to protect these plants against infections and harmful stimuli. To humans, it represents an essential nutrient, as it can only be obtained through eating and digestion. The aim of this review is to study its pathways of synthesis in plants and its dietary sources, and to consider the biochemical processes and transformations during digestion, focusing on the pharmacologic effects of its two isomers: cis- and trans-resveratrol.
Structure–activity relationship studies of indolin-2-one derivatives as vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitors and anticancer agents
- First Published: 03 September 2020
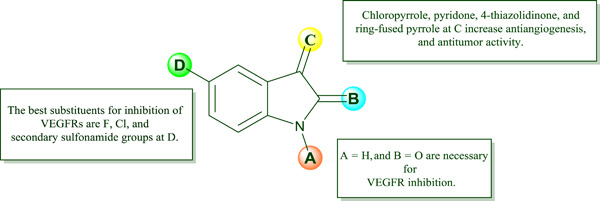
Sunitinib is the first oral indolin-2-one derivative marketed as a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitor in the treatment of certain cancers. Novel compounds possessing the sunitinib scaffold were designed by different researchers to improve the anticancer activity. This review summarizes the structure–activity relationship of indolin-2-one analogs as VEGFR inhibitors, illustrating that substitutions at C-3 of the oxindole ring play an important role in their antiangiogenic and anticancer activities.
FULL PAPERS
Antiproliferative and apoptotic activity of new indazole derivatives as potential anticancer agents
- First Published: 18 August 2020
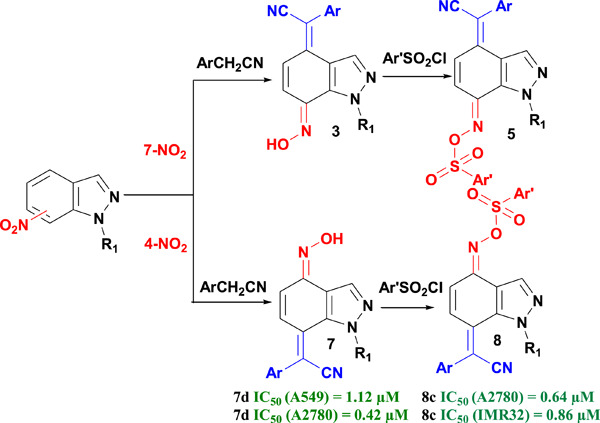
A new series of 2-(aryl)-2-(7(4)-(arylsulfonyl)oxime-1-alkyl-1H-indazol-7(4)-ylidenes) was synthesized and screened for their antiproliferative and apoptotic activities. Also, 95% of these compounds showed a quite interesting antiproliferative activity, with IC50 values ranging from 0.42 to 17 µM against both cell lines. In particular, compounds 5a, 5c, 5f, 7d, and 8c showed an excellent anticancer activity. Notably, compound 8c was found as potently arresting the cell cycle at the S phase.
Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted pyrrolidines and pyrroles as potential anticancer agents
- First Published: 09 August 2020
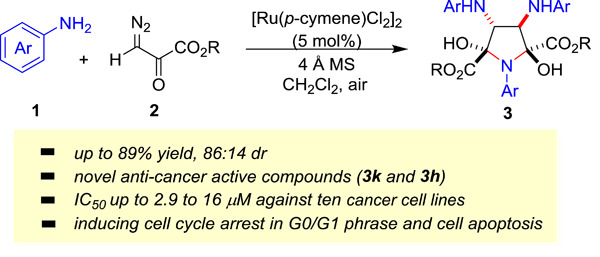
A series of polysubstituted pyrrolidines (3a–k) and pyrroles (4a–c) were synthesized from ruthenium-catalyzed cascade cyclization reaction of diazo pyruvates and anilines. Of these compounds, 3k and 3h showed the most potent antiproliferation activities in cancer cells, with IC50 values from 2.9 to 16 μM against 10 cancer cell lines. Compound 3k induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HCT116 and HL60 cells.
Novel 1,2,4-triazole derivatives: Design, synthesis, anticancer evaluation, molecular docking, and pharmacokinetic profiling studies
- First Published: 06 September 2020
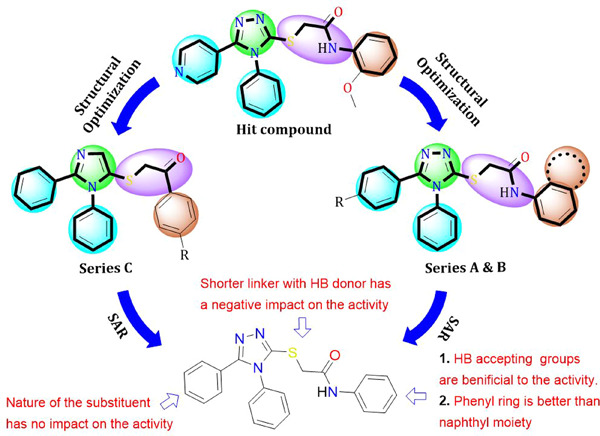
Three novel series of 1,2,4-triazole derivatives were designed as potential adenosine A2B receptor antagonists, based on a virtual screening of a previously constructed library of compounds targeting human adenosine A2B. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluation was carried out against MDA-MB-231 cells (human breast adenocarcinoma), with four of the designed derivatives showing promising cytotoxic effects against the selected cancer cell line, compared with doxorubicin.
Synthesis of novel 4,5-dihydropyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines, pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin]-2-ones and their antituberculosis and anticancer activity
- First Published: 12 August 2020
![Synthesis of novel 4,5-dihydropyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines, pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin]-2-ones and their antituberculosis and anticancer activity](/cms/asset/b0ee8f68-3efa-4e61-a53c-bffc6c59ee9f/ardp202000192-gra-0001-m.jpg)
A facile strategy was developed for the synthesis of biologically important 4,5-dihydropyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines and pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin]-2-ones, which were then evaluated for their antituberculosis, antibacterial, and anticancer activities. Compounds 3d and 3e demonstrated good activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, whereas compounds 3d, 3g, 5d, 5e, and 5i showed remarkable inhibition of A549, DU145, HeLa, HepG2, MCF-7, and B16-F10 cells. Staphylococcus aureus was inhibited by compounds 5b, 5e, 5d, 5g, and 5l.
Determination of the inhibition profiles of pyrazolyl–thiazole derivatives against aldose reductase and α-glycosidase and molecular docking studies
- First Published: 06 August 2020
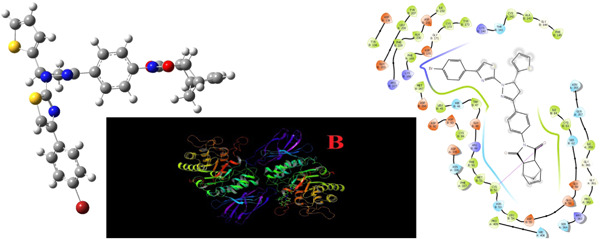
The inhibitory effects of pyrazolyl–thiazoles ((3aR,4S,7R,7aS)-2-(4-{1-[4-(4-bromophenyl)thiazol-2-yl]-5-(aryl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl}phenyl)-3a,4,7,7a-tetrahydro-1H-4,7-methanoisoindole-1,3(2H)-dione derivatives; 3a–i) on aldose reductase and α-glycosidase were investigated. All compounds showed a good inhibitory action against the two enzymes. Molecular modeling was performed to predict the binding affinities of the compounds with aldose reductase and α-glycosidase.
Novel thiazole–pyrazolone hybrids as potent ACE inhibitors and their cardioprotective effect on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction
- First Published: 25 August 2020
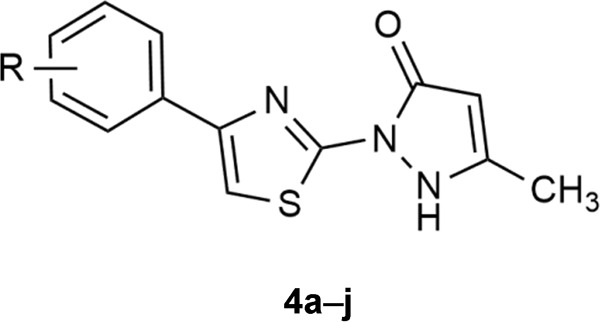
This study reports the synthesis of a novel series of thiazole-bearing pyrazolones, which were identified as potent angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Particularly, the most potent compound 4i was shown to protect against cardiac injury induced by isoproterenol in Sprague Dawley rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.
Novel pyrazole-clubbed thiophene derivatives via Gewald synthesis as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents
- First Published: 07 September 2020
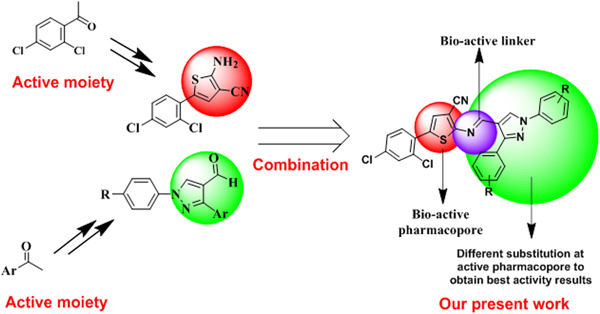
Newer potent Schiff bases were synthesized via Gewald synthesis and screened for their in vitro antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities. Compounds 8b, 8c, 8f, 8g, 8k, 8n, and 8o showed promising antibacterial activity. The interactions between the substituted pyrazoles and bovine protein revealed promising anti-inflammatory activity. In summary, the pyrazole ring and the substitution pattern on the heterocyclic moiety have an effect on the bioactivity.
Synthesis and radioligand-binding assay of 2,5-disubstituted thiadiazoles and evaluation of their anticonvulsant activities
- First Published: 27 August 2020
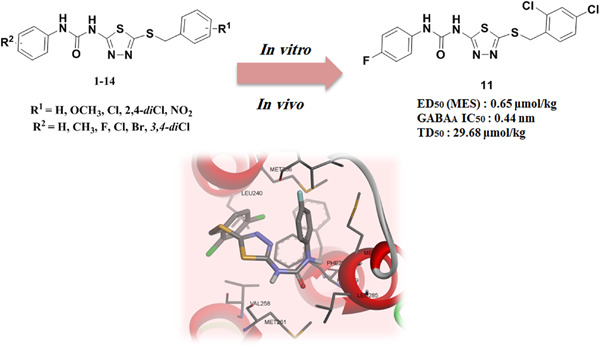
In this study, 2,5-disubstituted 1,3,4-thiadiazoles were synthesized as anticonvulsant agents. Compound 11 showed a good anticonvulsant activity in the maximal electroshock seizure test. The anticonvulsant effect of compound 11 was completely blocked by flumazenil and the involvement of benzodiazepine receptors was confirmed by the radioligand-binding assay.
Effect of substituents in the A and B rings of chalcones on antiparasite activity
- First Published: 17 August 2020
Many chalcones have already been synthetized and assayed against parasites; however, the structural features involved in this biological property are largely unknown. Thus, in this study, 21 chalcones were synthesized to determine the effect of substituents in the A and B rings on the activity against Leishmania braziliensis, Trypanosoma cruzi, and Plasmodium falciparum, revealing that the electron-donating substituents in ring B and the hydrogen bonds at C-2′ with carbonyl affect the antiparasitic activity.
Synthesis, characterization, and biological studies of chalcone derivatives containing Schiff bases: Synthetic derivatives for the treatment of epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 20 August 2020
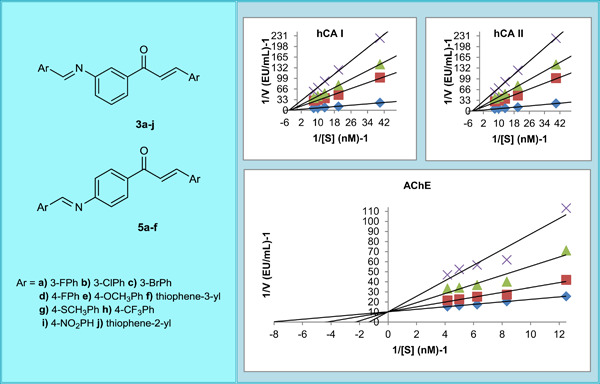
Schiff base-containing chalcone derivatives were synthesized and their inhibitory effects on the activities of human carbonic anhydrases (hCA I/II) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) were investigated. Compound 5e with p-OCH3 substituent showed the best inhibition of hCA I, compound 3b with m-Cl substituent showed the best inhibitory activity against hCA II, and compound 5c with m-Br substituent was most active against AChE.





