Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Materials and Corrosion. 5/2023
- Page: 653
- First Published: 02 May 2023

Cover:
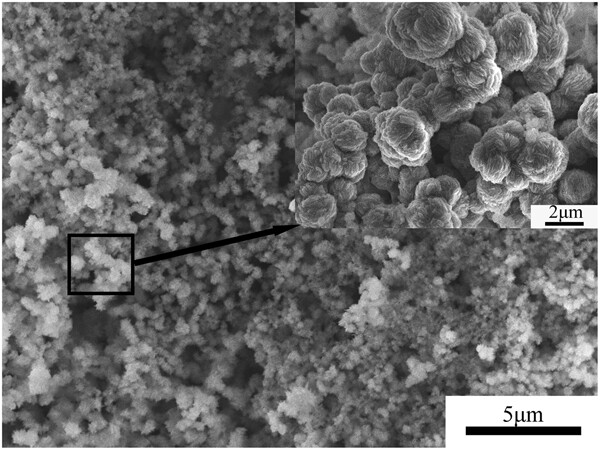
Local SEM morphologies of 304SS with different machined roughness after an immersion test: (a) and (b) Ra3.2, (c) and (d) Ra6.0. Comparing Figures (a) and (c), it shows that the number of small pits decreases with increasing machined surface roughness. Figures (b) and (d) show that the pits initiated mainly on both sides of the peak ribs and rarely in the valleys.
More detailed information can be found in: Xin Tan, Rulei Lan, Qiong Yao, Qiyong Tu, Longlin Lei, Jun Zhang, Yangting Sun, Jin Li, Yiming Jiang, Influence of the Machined Surface Roughness on the Pitting Behavior of 304 Stainless Steel, Materials and Corrosion 2023, 74, 660.
MASTHEAD
CONTENTS
Contents: Materials and Corrosion. 5/2023
- Pages: 656-659
- First Published: 02 May 2023
ARTICLES
Influence of the machined surface roughness on the pitting behavior of 304 stainless steel
- Pages: 660-669
- First Published: 28 November 2022
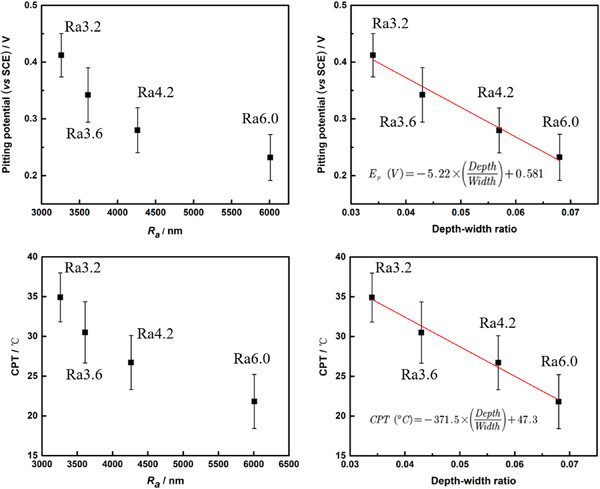
We deal with the surface roughness of specimens from machining, at a different level than what had been studied previously. Compared with the Ra value, the depth–width ratio shows a simpler linear relationship with critical pitting temperature and Ep of machined 304ss. This finding makes it easier to predict and evaluate the pitting resistance of different machined state specimens in the industry.
Corrosion of Hastelloy-N and Hastelloy-G35 from vapors generated from FLiNaK salt with addition of 5% oxygen in argon atmosphere
- Pages: 670-682
- First Published: 23 December 2022
This work brings significantly different approach to the problem of corrosion of special alloys with interaction with FLiNaK salt as can be found in majority of research works. In absolute majority of research papers very clean atmosphere is used, however, in any application one cannot avoid some contamination with the air. Thus, in this study oxygen is added intentionally and mixed with the vapors of FLiNaK salt at elevated temperature.
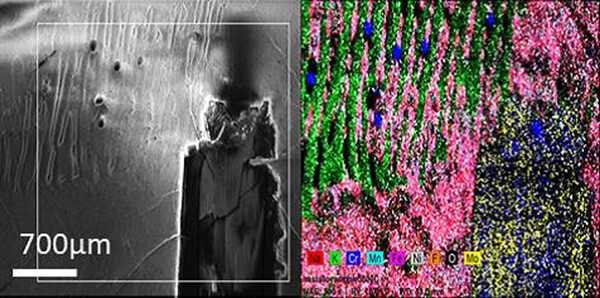
Corrosion characterization of NiTi alloy by femtosecond laser surface processing
- Pages: 683-693
- First Published: 21 December 2022
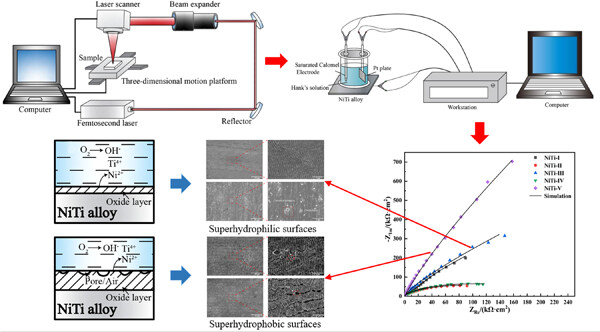
A femtosecond laser was used to process different wettability surfaces on the NiTi alloy and corrosion behavior was investigated. The results show that hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces are more prone to erosion, while the corrosion resistance of superhydrophilic surfaces is enhanced to some degree and superhydrophobic surfaces have excellent corrosion resistance.
Field exposure study under sheltered and open exposure conditions at different test sites in Germany: First-year corrosion rate and atmospheric corrosivity
- Pages: 694-708
- First Published: 08 December 2022

The corrosivity of atmospheres in Europe has changed significantly in recent decades. For this reason, results are presented from a field exposure study in the Berlin metropolitan area and in Helgoland. Using standard specimens, values for the corrosion rate after 1 year of exposure and the atmospheric corrosivity category are determined for open exposure and for a special kind of sheltering.
Corrosion behavior and kinetics model of rare earth low-alloy steel in a soil simulation solution
- Pages: 709-723
- First Published: 27 December 2022
Effect of quenching in aqueous polyvinylpyrrolidone solutions on the microstructure and pitting corrosion resistance of AISI 1045 carbon steel
- Pages: 724-733
- First Published: 21 December 2022

This paper reports the pitting corrosion resistance of four types of microstructures (water-quenched martensite, tempered martensite, bainite and degenerate pearlite, and ferrite–pearlite) in AISI 1045 medium-carbon steel. The pitting corrosion resistances of the microstructures in near-neutral pH solutions containing chloride ions are ordered as follows: (high) water-quenched martensite > bainite and degenerate pearlite > tempered martensite > ferrite–pearlite (low).
Effect of electrified surface casing on the interference characteristics of stray current generated by deep-well anode beds
- Pages: 734-746
- First Published: 22 December 2022
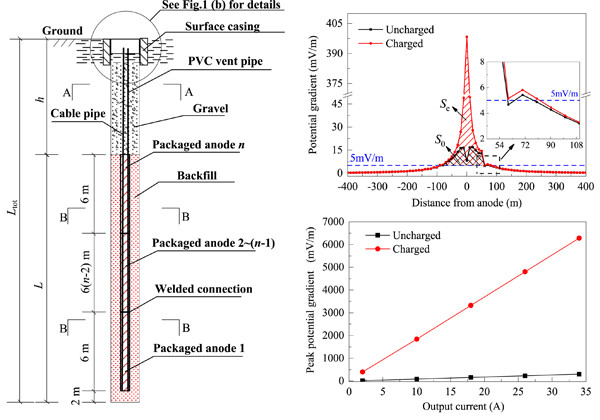
Thirteen deep-well anode beds were selected randomly to investigate whether their surface casings were electrified. The difference in the interference characteristics between situations with charged and uncharged casings was also discussed. It should be noted that 30.7% of the surface casings were charged. The peak potential gradient and comprehensive interference intensity were about 20 times and 3–6 times, respectively, those in situations where the casing was uncharged.
Effect of different structures on corrosion resistance of Mg–Zn–Ca–Cu alloys
- Pages: 747-753
- First Published: 27 January 2023
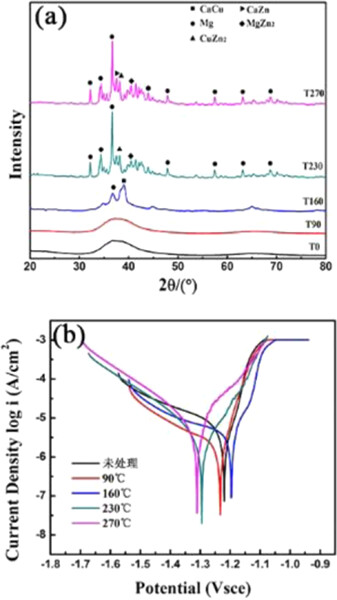
The effects of different structures of magnesium-based metallic glasses (Mg66Zn29.5Ca4Cu0.5) as potential materials for clinical implants were investigated. The phase composition was determined by X-ray diffraction, and electrochemical tests and hydrogen evolution experiments were carried out in a simulated liquid at 37°C. The results show that the corrosion resistance of the alloy is seriously affected by its microstructure.
Double-anticorrosion ability of in-situ superhydrophobic MgAl-LDH coating with excellent stability of the corrosion resistance on magnesium alloy AZ31
- Pages: 754-765
- First Published: 11 January 2023
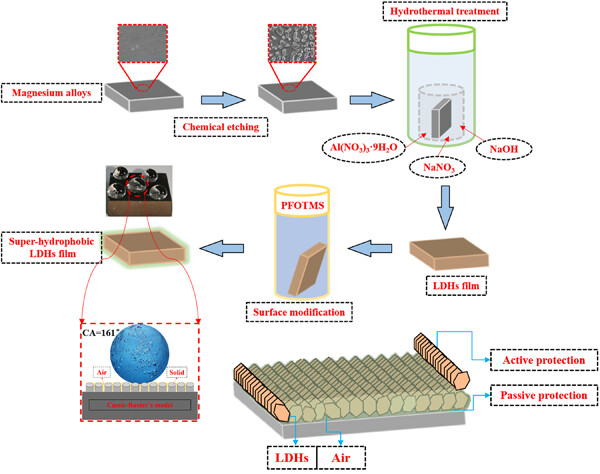
A facile method is used to fabricate the superhydrophobic layered double hydroxide (LDH) coating on the surface of Mg alloy AZ31. The coating is composed of microislands and LDH nanosheets, and exhibits good superhydrophobicity with a contact angle of 161°. The superhydrophobic LDH coatings provide strong protection for the Mg matrix due to the double-anticorrosion mechanism associated with LDH coating and superhydrophobic structure.
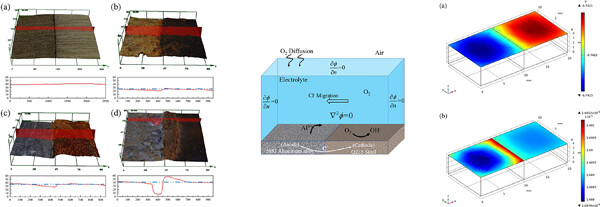
Galvanic corrosion behavior and numerical simulation of 5083 aluminum alloy and Q235 steel in 3.5% NaCl solution
- Pages: 766-776
- First Published: 29 January 2023
Automated detection and quantification of the onset of undercoating corrosion using pulsed thermography
- Pages: 777-792
- First Published: 28 November 2022
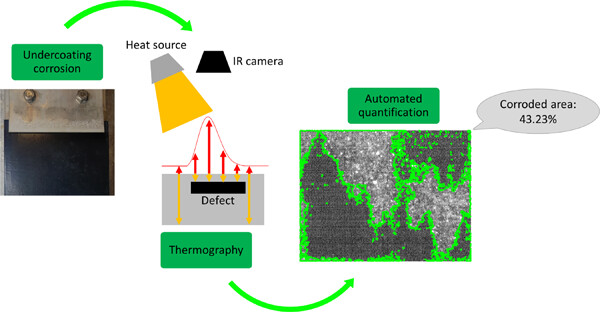
Thermography is a nondestructive evaluation technique to inspect parts for defects. In this paper, it was used to detect undercoating corrosion in mild steel samples. Currently highly trained and costly operators analyze images and determine the extent of damage and whether a part needs to be replaced. In this paper, an algorithm was developed and tested to detect and quantify the corroded area autonomously and reliably with a 3% absolute error.
Molecular dynamics study of corrosion behavior of iron with vacancies exposed to lead-bismuth eutectic
- Pages: 793-802
- First Published: 26 December 2022
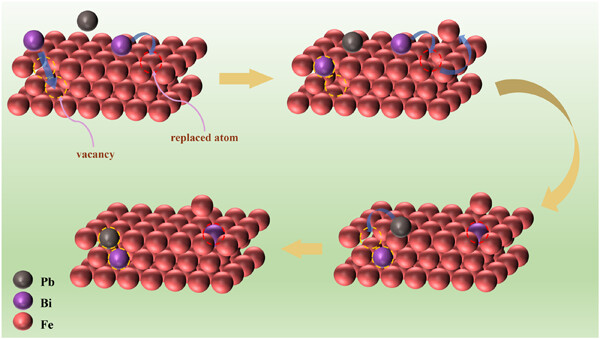
Corrosion simulations have been performed for iron-based materials with or without defects at various temperatures by the molecular dynamics method. The results show that the substitution of vacancy with a Pb/Bi atom is more favorable than that of a Fe atom with a Pb/Bi atom, and Bi atoms have a stronger diffusion ability than Pb atoms. The present study provides new insight into challenges related to the corrosion behavior of iron-based materials with vacancy-type defects.