Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Fast Optical Reflectance Measurements during Spin Coating and Annealing of Organic–Inorganic Perovskite Precursor Solutions
- First Published: 05 May 2021

In article number 2000479, Jörg Rappich and co-workers address early stages of film formation and crystallization of organic lead triiodide perovskites by employing in-situ high-speed spectral reflectance measurements. The time scale ranges from 0.2 milliseconds to seconds. Data were taken during spincoating and subsequent low-temperature annealing. The measurements enable the investigation of changes in the solution of the spin-coating process. The evaporation of the solvent during spin-coating results in the spontaneous crystallization of the perovskite layer. During the subsequent annealing process, the diffuse reflectance measured with high sensitivity provides insight into the transformation and crystallization process of the precursor layer to the final perovskite layer.
Masthead
Original Papers
Postirradiation Annealing and Reirradiation Study of High-Dose Proton-Irradiated Fe–Cu Model Alloys by Positron Annihilation and Nanoindentation
- First Published: 26 January 2021
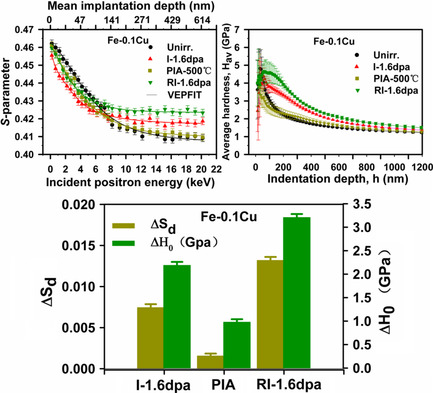
Microstructural evolution and hardening properties of Fe–Cu alloys under initial irradiation, postirradiation annealing, and reirradiation are investigated by positron annihilation spectroscopy and nanoindentation. Vacancy defects and Cu precipitates are the main contributors to Fe–Cu alloy hardening. Hardness measurements show that irradiation effects can be mitigated by annealing.
Influence of Cu-Doping on Linear and Nonlinear Optical Properties of High-Quality ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Spin-Coating Technique
- First Published: 09 February 2021
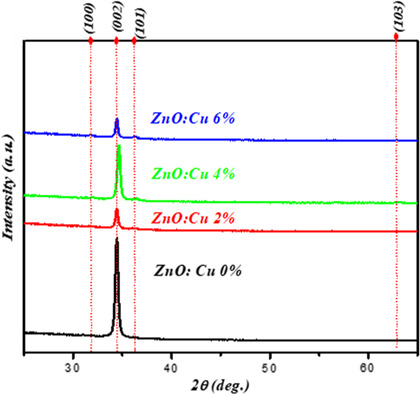
ZnO thin films doped with copper (0–6 mol%) are deposited on glass substrates by sol–gel/spin-coating technique. The effect of Cu on the morphological, structural, and the linear and nonlinear optical properties is studied. It is found that the Cu-doped ZnO films show better nonlinear properties than the pure ZnO film.
Fast Optical Reflectance Measurements during Spin Coating and Annealing of Organic–Inorganic Perovskite Precursor Solutions
- First Published: 11 February 2021
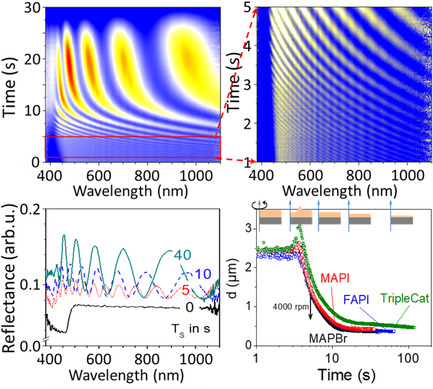
In situ high-speed spectral reflectance measurements of methyl ammonium lead triiodide (MAPI), methyl ammonium lead tribromide (MAPBr), formamidinium lead triiodide (FAPI), and triple cation-based perovskite Cs0.05(FA0.83MA0.17)0.95Pb(I0.83Br0.17)3 (TripleCat) solutions are carried out. The timescale ranges from 0.2 ms to seconds. Data are taken during spin coating and subsequent low-temperature annealing to determine layer thickness, drying kinetics, and phase transitions.
Fabrication and Characterization of Metal-Free Composite Electrodes Based on Few-Layer-Graphene Nanoplatelets for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Applications
- First Published: 30 December 2020
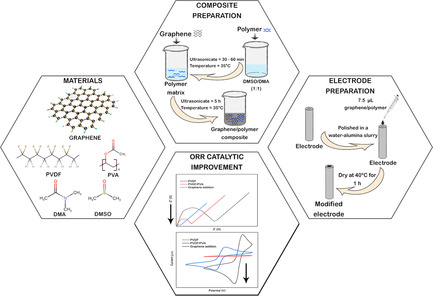
Metal-free few layer graphene-based composite electrodes for oxygen reduction reaction applications are fabricated and characterized. The authors' best formulation shows cathodic peak current density up to –469 μA cm−2, the lowest potential peak separation of 0.17 V, and the lowest charge transfer resistance of 1657 Ω cm−2, which is five times lower than compared to the electrode without graphene.
The Remarkable Anisotropic Compressibility and Metallic CrCr Chains in Topological Semimetal CrP4 under High Pressure
- First Published: 31 December 2020
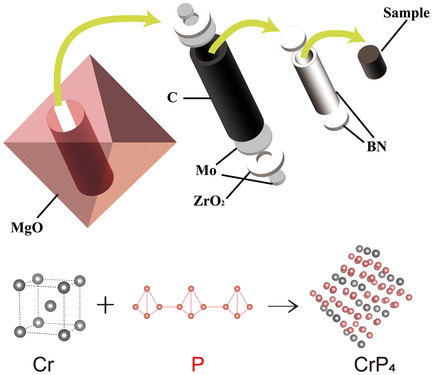
Herein, the phosphorus-rich phosphide CrP4 single crystal is prepared by a multianvil apparatus (SHTech-2000) under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. The synchrotron X-ray diffraction experiment shows that CrP4 exhibits remarkable anisotropic compressibility. The focus is laid on the structural evolution behavior and the variation of chemical bonding in CrP4 under high pressure.
High-Purity Er3N@C80 Films: Morphology, Spectroscopic Characterization, and Thermal Stability
- First Published: 03 February 2021

The low-energy cluster beam deposition (LECBD) technique applying a mass-selected ion beam is successfully used for the fabrication of ultrathin Er3N@C80 films which are characterized by combined analysis of their morphology and electronic and vibronic properties. The film morphology is governed by the conversion of ion energy into surface mobility, the lateral dispersion interaction, and the pinning by surface imperfections.
Determination of the Rashba and Dresselhaus Spin–Orbit Interaction Parameters and g-Factor from the Critical Points of the Spectrum in a 2D Electron Gas in an In-Plane Magnetic Field
- First Published: 04 March 2021

It is shown that the spin–orbit interaction (SOI) parameters and the g-factor of a 2D electron gas with SOI of both Rashba and Dresselhaus type can be determined by defining the energy position of the critical points of the energy spectrum in a parallel magnetic field from measurement of the conductivity tensor.
The Effect of X-Ray Irradiation on Conductivity of C and 2C Polytype TlInS2 Ferroelectrics
- First Published: 15 February 2021
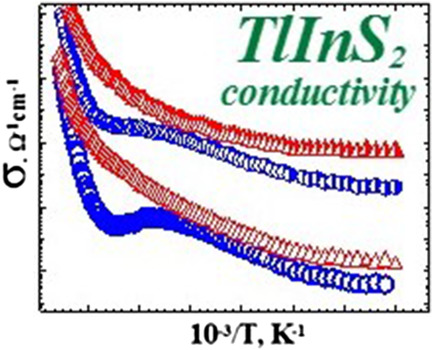
In the TlInS2 crystals of the C polytype, an anomalous temperature dependence of the conductivity is observed at the appearance of the incommensurate phase—the decrease in temperature is accompanied by the increase in the conductivity. The X-ray irradiation “blurs” the anomaly and leads to increase in the conductivity of both C and 2C polytypes of TlInS2 crystals.
Growth of Self-Passivating Oxide Layers on Aluminum—Pressure and Temperature Dependence
- First Published: 16 January 2021
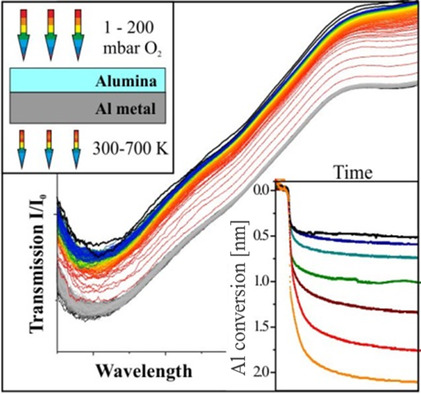
In situ optical spectroscopy is used to probe the oxidation of aluminum as a function of pressure and temperature. Two oxidation regimes are revealed, an initial fast one following the Cabrera–Mott theory and a slower one that is based on thermal Al diffusion through the emerging oxide film and does not lead to self-passivation.
Structure and Magnetic Properties of Pulsed Electrodeposited Nickel–Indium Alloy
- First Published: 16 January 2021
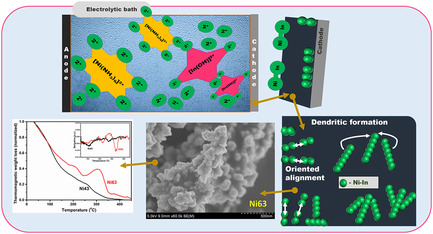
This article describes the structure and magnetic properties of nickel–indium alloy obtained through pulsed electrodeposition. Metastable face centered cubic (fcc) phase could be obtained with 37 at% In, exhibiting better magnetic properties. The binding energy of formation is evaluated from X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Properties of the sample at higher temperatures are studied using magnetic thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry.
Regulation of Magnetic Phase Transition and Magnetocaloric Effect of DyCo2−xCrx Compounds
- First Published: 31 December 2020
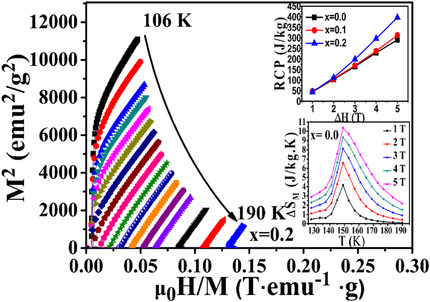
The magnetic phase transformation, magnetism, and magnetocaloric properties of DyCo2−xCrx are studied. The introduction of Cr can regulate the magnetic phase transformation type of DyCo2 from first order to second order. The Cr content can also increase the magnetic refrigeration capacity of DyCo2−xCrx from 290.6 to 396.7 J kg−1. Overall, DyCo2−xCrx compounds are promising magnetic refrigeration materials.
Negative Compressibility in Hexagonal and Trigonal Models Constructed by Hinging Wine-Rack Mechanism
- First Published: 09 February 2021
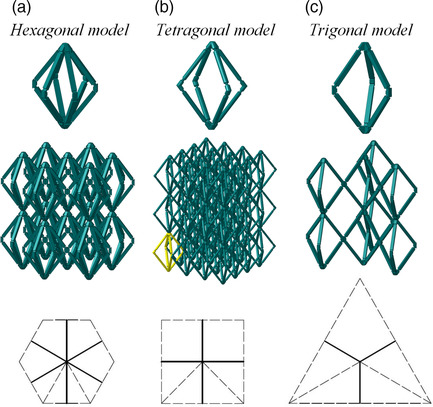
Herein, a hexagonal (image a) and a trigonal (image c) model are proposed and analyzed for negative compressibility property. Comparing with the tetragonal model (image b), it can be found that the three models have strong similarity and can be analyzed uniformly, and the trigonal model has the greatest negative compressibility property among the three models.
Solid-State Synthesis and Characterization of the Stable Nanostructured Ni21Ti2B6 Phase
- First Published: 01 February 2021
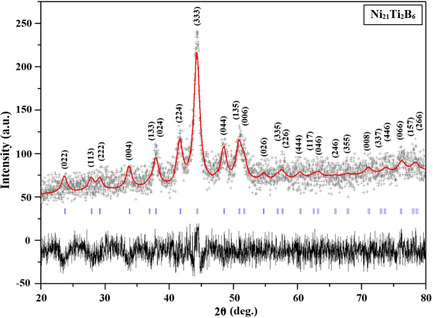
Herein, nanostructured ternary Ni–Ti–B alloy synthesized by mechanical alloying from the elemental Ni, Ti, and B powders by high energy ball milling is described. The synthesized alloy of nominal composition of Ni70Ti10B20 results in the formation of a unique stable phase of Ni21Ti2B6, which happens to be stoichiometrically very close to Ni70Ti10B20 in the cubic symmetry.
Research Articles
The Fabrication of Wrinkle-Free Graphene Patterns on Ge(110) Substrate
- First Published: 16 February 2021
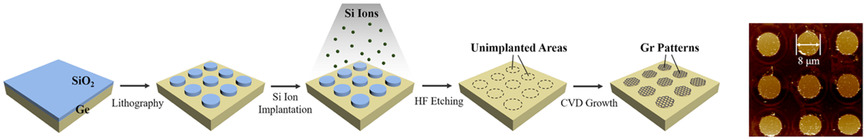
Wrinkle-free graphene patterns are grown on Ge(110) substrate with the assistance of 5 × 1016 cm−2 Si ion implantation. The wrinkle-free graphene only grows on unimplanted areas, whereas no graphene is synthesized on Si ion implanted areas. The formation of wrinkle-free graphene is closely related to the compressive strain distribution in graphene.
Effects of Ag2O Nanosheets on the Structural, Optical, and Dielectric Properties of GeO2 Stacked Layers
- First Published: 19 February 2021
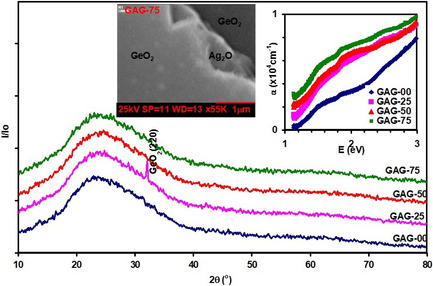
Herein, the structural, optical, and dielectric enhancements that are achieved via insertion of Ag2O nanosheets between stacked layers of GeO2 are reported. An increase in light absorbability, dielectric constant, and optical conductivity by 11 times, 59.6%, and 191.4%, respectively, is reached in the infrared range of light.
Effect of Dopant Concentrations on the Luminescent Properties of LiAl5O8:Fe Phosphors
- First Published: 11 February 2021
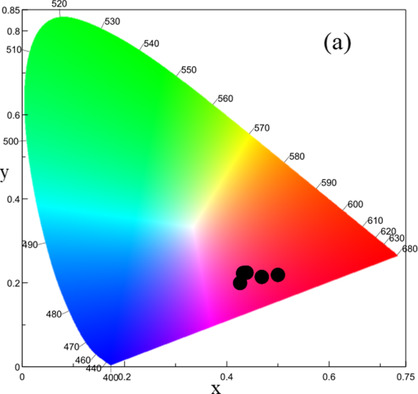
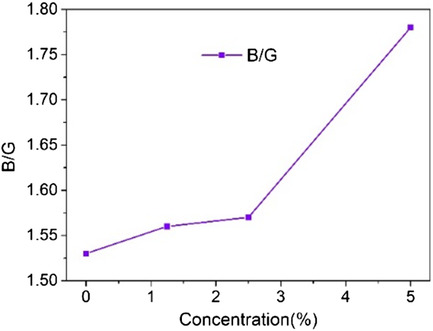
The influence of iron concentration in LiAl5O8 on structural and optical properties is investigated. All samples obtained from present with a single crystalline phase. The luminescent properties indicate the gradual increase in the intensity of the emission until reaching the maximum emission. In addition to the luminescent intensity, the increase in the dopant provided the color change.
Influences of Vacancy Concentration and Al Substitution on Structural, Electronic, and Elastic Properties of Nb5Si3 from First-Principles Calculations
- First Published: 12 February 2021
Herein, the formation energy, elastic modulus, and electronic properties of three different Nb vacancies in Nb5Si3 are discussed in detail. These vacancies result in the transition from brittleness to ductility, and Nb5Si3 with 5% vacancy concentration exhibits ductile behavior. It is predicted that vacancies can improve the ductility behavior of Nb5Si3.
A Universal Model for DX-Center Binding Energy in Cubic III–V Compounds
- First Published: 29 January 2021
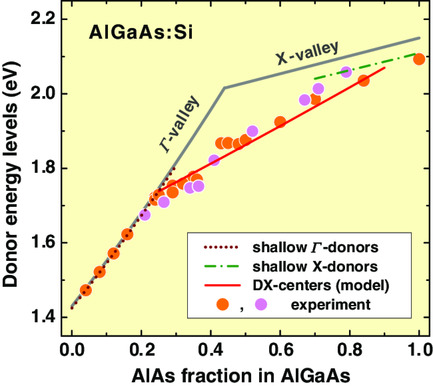
A simple model is suggested to estimate energy levels (binding energies) of DX-centers in zinc-blende ternary and quaternary III–V alloys, using the data on the bandgaps in Γ-, X-, and L-valleys of the conduction band. The model predicts narrowing with the bandgap of the alloy composition range where DX-center formation dominates over that of shallow donors.
Investigation on the Stability, Elastic Properties, and Electronic Structure of Mg2Si Doped with Different Concentrations of Cu: A First-Principles Calculation
- First Published: 09 February 2021

Herein, the effect of Cu doping with different concentrations on the stability, elastic properties, and electronic structure of Mg2Si are investigated by first-principles calculations based on density functional theory. This investigation will provide some theoretical basis for the application of Mg2Si intermetallic compounds in structural materials and thermoelectric materials.
Analysis of Deep Traps in Mist Chemical Vapor Deposition-Grown n-Type α-Ga2O3 by Photocapacitance Method
- First Published: 29 January 2021
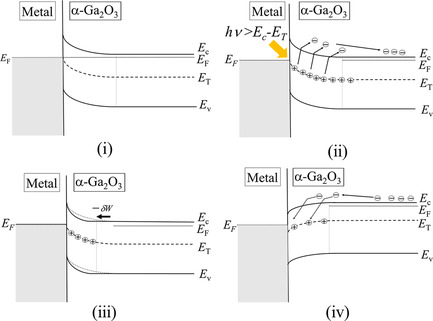
Deep traps in n-type α-Ga2O3 grown by mist chemical vapor deposition are analyzed by the photocapacitance method and deep-level optical spectroscopy. Three trap levels near the midgap are evident. The Frank–Condon shift of all three traps is large as seen for β-Ga2O3, indicating a high degree of lattice coupling in the midgap state in α-Ga2O3.
Magnetoresistance of Nanosized, Granular Sr2FeMoO6–δ–SrMoO4 Core–Shell Structures
- First Published: 16 February 2021
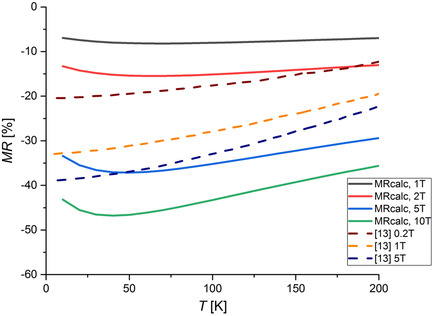
This work presents a model describing the magnetoresistance in nanosized Sr2FeMoO6–δ–SrMoO4 core–shell structures. It is based on the fluctuation-induced tunneling model. Model parameters of the granular Sr2FeMoO6–δ–SrMoO4 structure are calculated. The magnetic field is considered to affect the tunneling barrier height. The linear and quadratic coefficients of this effect are estimated.
Spin Half-Adder
- First Published: 29 January 2021
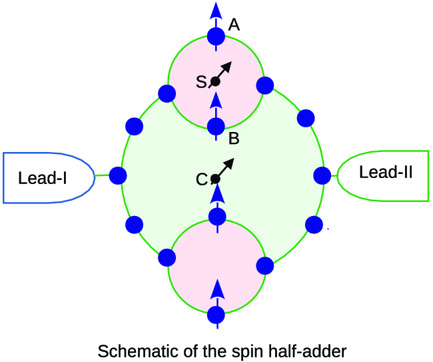
A new proposal is given to design a nanoscale spin half-adder along with memory operation, utilizing voltage-induced circular current and magnetic field. The magnetic field is used to regulate the orientations of the output states of the “sum” (S) and “carry” (C). Using the same geometry, several other logical operations are also discussed.
Broadband Efficient Dual-Polarization Airy Beam Generation with Reflective Metasurface
- First Published: 24 February 2021
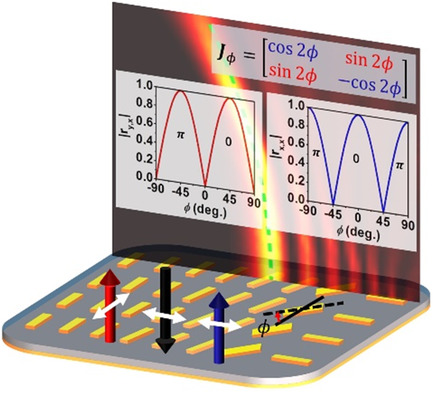
A broadband efficient Airy beam generation strategy is presented. Continuous amplitude and binary phase modulation suitable for encoding Airy beam is obtained for not only cross-polarized but also copolarized scattering field components by rotation of unit cell with reflection symmetry. Near theoretical limit generation efficiency is experimentally verified. The proposed strategy can be generalized to THz, infrared, and optical regime.







