Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 20/2016
- Page: 2201
- First Published: 18 October 2016

Front Cover: This work represents the RAFT copolymerization of the phosphine-functional styrenic monomer, 4-(diphenylphosphino)styrene, with styrene. Copolymerization behaviour is explored to establish the statistical distribution of the phosphine functionality within the copolymer. There is a strong tendency for the phosphine-bearing monomer to homopolymerize whilst styrene prefers to copolymerize. This results in the polymer possessing gradient-microstructure from preferential incorporation of phosphine-based functionality. Further details can be found in the article by Kyle J. Sykes, Simon Harrisson, and Daniel J. Keddie* on page 2310.
Masthead
Contents
Contents: Macromol. Chem. Phys. 20/2016
- Pages: 2203-2206
- First Published: 18 October 2016
Editorial
Australian European Self-Assembly through Macromolecular Interactions
- Pages: 2207-2208
- First Published: 18 October 2016
Talent
Molecular Polymer Brushes in Nanomedicine
- Pages: 2209-2222
- First Published: 06 May 2016
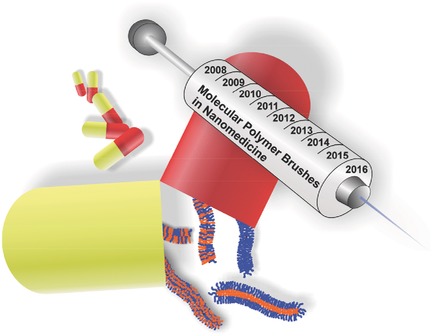
Molecular polymer brushes present an emerging class of polymer nanostructures with the potential to address persevering problems in nanomedicine. Recent improvements in the synthesis of these polymeric architectures allowed the tailoring of sophisticated nanomaterials for applications in drug and gene delivery, as well as the design of new imaging probes and prototype nanomaterials.
Trend
Polymeric Drift Control Adjuvants for Agricultural Spraying
- Pages: 2223-2242
- First Published: 04 July 2016

Polymeric drift control adjuvants (DCAs) increase the droplet size produced during agricultural spraying which minimizes drift of agrichemicals. Current DCAs are reviewed, highlighting key weaknesses and the mechanism through which they increase droplet size. A discussion on the applicability of new polymer chemistries and architectures to drift control then follows.
Full Papers
Temperature-Controlled Antimicrobial Release from Poly(diethylene glycol methylether methacrylate)-Functionalized Bottleneck-Structured Porous Silicon for the Inhibition of Bacterial Growth
- Pages: 2243-2251
- First Published: 17 May 2016
Synthesis and Conjugation of Alkyne-Functional Hyperbranched Polyglycerols
- Pages: 2252-2261
- First Published: 07 March 2016
Fluorinated POSS-Star Polymers for 19F MRI
- Pages: 2262-2274
- First Published: 06 May 2016
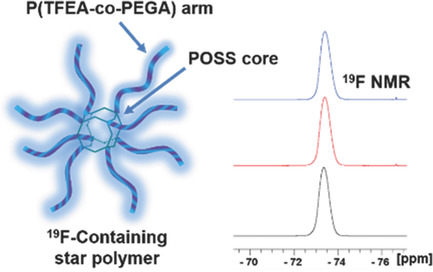
Novel hybrid star polymers with a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane core and eight partly fluorinated copolymer arms are synthesized through R-group approach by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. The 19F magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) capability is preliminarily confirmed by a single and strong 19F resonance in 19F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and the imaging intensity is also calculated for a spin-echo pulse sequence.
A Journey into the Microstructure of PVDF Made by RAFT
- Pages: 2275-2285
- First Published: 06 June 2016
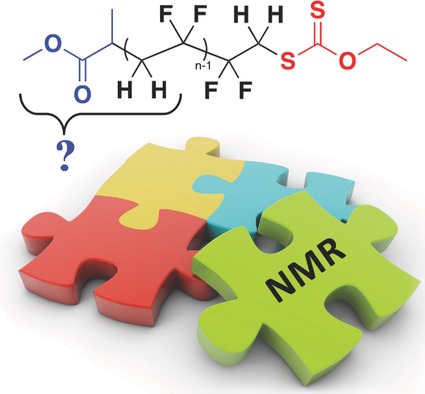
This article presents the results obtained from advanced 1H, 13C, and 19F NMR spectroscopy experiments using decoupling strategies, to ascertain unequivocally the microstructure of PVDF synthesized via RAFT polymerization. An uncommon NMR heteronuclear coupling between the proton of the stereocenter of the CTA R-group and the fluorine atoms of the CF2 moiety of the first added VDF unit is highlighted.
1H DOSY NMR Determination of the Molecular Weight and the Solution Properties of Poly(N-acryloylmorpholine) in Various Solvents
- Pages: 2286-2293
- First Published: 15 June 2016
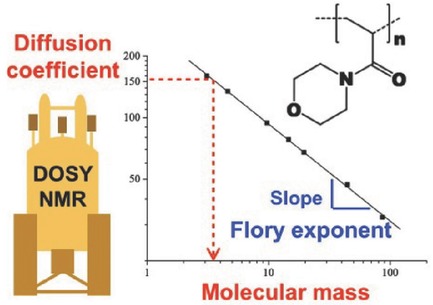
1H DOSY NMR provides a simple and convenient way to determine both the weight-average molecular weight Mw and the Flory exponent of poly(N-acryloylmorpholine) (PNAM) in various organic and aqueous solvents. Determination of the average diffusion coefficients DPNAM of PNAM samples synthesized by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization with various molecular weights leads to highly linear relationship between Log DPNAM and Log Mw.
Improved Particle Size Control for the Dispersion Polymerization of Methyl methacrylate in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
- Pages: 2294-2301
- First Published: 09 June 2016
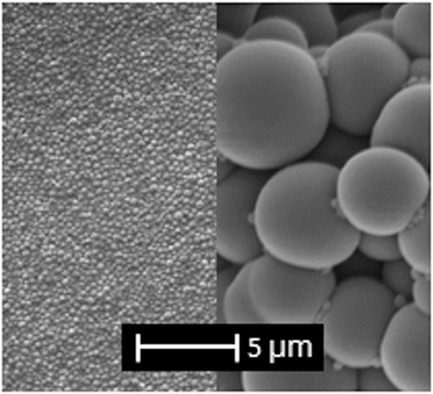
This study presents control of PMMA particle size over an unprecedented range (0.3–5.3 μm) using only a single stabilizer by free radical dispersion polymerization in scCO2. This study explores also delayed monomer addition to considerably reduce batch-to-batch variability and reduced agglomeration between particles.
Direct Correlation Between Zeta Potential and Cellular Uptake of Poly(methacrylic acid) Post-Modified with Guanidinium Functionalities
- Pages: 2302-2309
- First Published: 20 July 2016
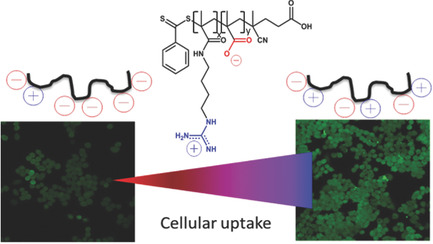
Conjugation of agmatine to poly(methacrylic acid) can enhance the cellular uptake of the polymer by cancer cells. It is observed that only small amounts of guanidinium are required to achieve a visibly increased cellular uptake. These nontoxic polymers with zwitterionic structure can be useful for polymer–drug conjugates to assist the efficient delivery of drugs into cells.
Phosphorus-Containing Gradient (Block) Copolymers via RAFT Polymerization and Postpolymerization Modification
- Pages: 2310-2320
- First Published: 15 June 2016
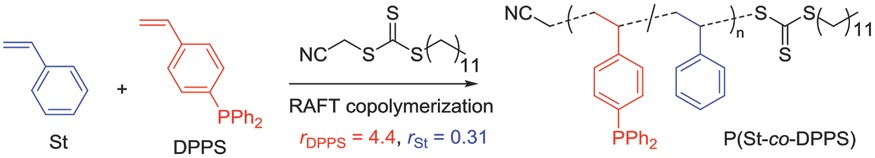
RAFT copolymerization of styrene and 4-(diphenylphosphino)styrene is explored to establish the statistical distribution of the phosphine-functional monomer within the copolymer. RAFT copolymerization provides phosphine-functional copolymers of low dispersity. Estimation of reactivity ratios indicates DPPS has a strong tendency to homopolymerize while St preferentially copolymerizes with DPPS. Block copolymers as well as polymeric phosphine oxides and phosphonium salts are also prepared.
Colloidal and Supported TiO2: Toward Nonextractable and Recyclable Photocatalysts for Radical Polymerizations in Aqueous Dispersed Media
- Pages: 2321-2329
- First Published: 20 July 2016
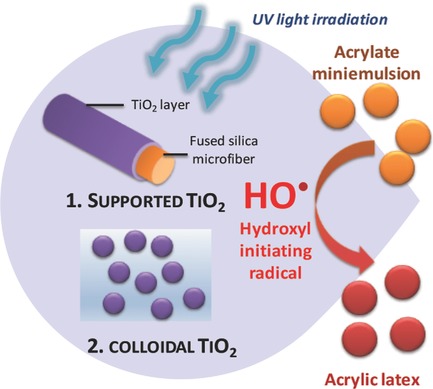
Intensively investigated as photocatalysts for the photodegradation of persistent organic contaminants, TiO2 nanomaterials can be tamed to enable miniemulsion photopolymerization. In particular, colloidal and supported titania offer many advantages compared to conventional molecular photoinitiator: facile addition to the monomer dispersion, high surface-to-volume ratio, nonmigrating, no byproducts, simple and low cost process, and possible recovery/reuse.
Development of a Redox-Responsive Polymeric Profluorescent Probe
- Pages: 2330-2340
- First Published: 31 August 2016
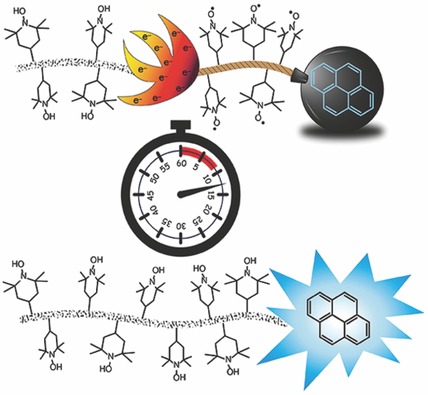
Profluorescent nitroxides (PFNs) are an important class of imaging agents for monitoring intracellular redox status and oxidative stress levels. The preparation of nitroxide-containing polymers of different chain length coupled to a fluorophore and their reduction with pentafluorophenylhydrazine are reported. The fluorescence switch-on kinetics and radical concentrations are monitored by fluorescence and EPR spectroscopy and compared to a conventional single-nitroxide PFN.